|
Pallasite
The pallasites are a class of stony–iron meteorite. Structure and composition It consists of centimetre-sized olivine crystals of peridot quality in an iron-nickel matrix. Coarser metal areas develop Widmanstätten patterns upon etching. Minor constituents are schreibersite, troilite, chromite, pyroxenes, and phosphates ( whitlockite, stanfieldite, farringtonite, and merrillite). Classification and subgroups Using the oxygen isotopic composition, meteoric iron composition and silicate composition pallasites are divided into 4 subgroups:O. Richard Norton. ''The Cambridge encyclopedia of meteorites''. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2002. . * Main group pallasites (PMG): Almost all pallasites * Eagle Station group (PES): 5 specimens known. They are related to IIF irons. * Pyroxene Pallasite grouplet (PPX): Counts only Vermillion and Yamato 8451. They take their name from the high orthopyroxene content (about 5%). Metal matrix shows a fine octahedrite Widmanst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridot
Peridot ( /ˈpɛr.ɪˌdɒt, -ˌdoʊ/ ''PERR-ih-dot, -doh''), sometimes called chrysolite, is a deep yellowish-green transparent variety of olivine. Peridot is one of the few gemstones that only occurs in one color. Peridot can be found in mafic and ultramafic rocks occurring in lava and peridotite xenoliths of the mantle. The gem occurs in silica-deficient rocks such as volcanic basalt and pallasitic meteorites. Peridot is one of only two gems observed to be formed not in the Earth’s crust, but in the molten rock of the upper mantle. Gem-quality peridot is rare on Earth's surface due to its susceptibility to weathering during its movement from deep within the mantle to the surface. Peridot has the formula of (Mg, Fe)2SiO4. Peridot is one of the birthstones for the month of August. Etymology The origin of the name ''peridot'' is uncertain. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' suggests an alteration of Anglo– Norman (classical Latin -), a kind of opal, rather than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
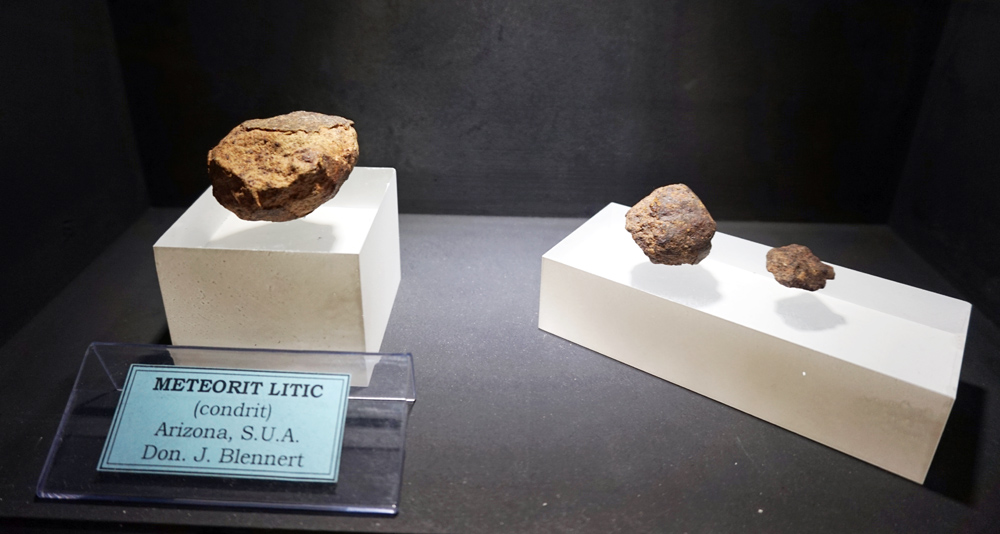
Stony–iron Meteorite
Stony-iron meteorites or siderolites are meteorites that consist of nearly equal parts of meteoric iron and silicates. This distinguishes them from the stony meteorites, that are mostly silicates, and the iron meteorites, that are mostly meteoric iron. Stony-iron meteorites are all differentiated, meaning that they show signs of alteration. They are therefore achondrites. The stony-irons are divided into mesosiderites and pallasites. Pallasites have a matrix of meteoric iron with embedded silicates (most of it olivine). Mesosiderites are breccias which show signs of metamorphism. The meteoric iron occurs in clasts instead of a matrix.Karl K. Turekian. ''Meteorites, comets, and planets'112/ref> They are in the top rank of all Meteorite classification schemes, usually called "Type". Mineralogy The meteoric iron of stony-irons is similar to that of iron meteorites, consisting mostly of kamacite and taenite in different proportions. The silicates are dominated by olivine. Accessory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermillion Meteorite
The Vermillion meteorite is a pallasite ( stony-iron) meteorite and one of two members of the pyroxene pallasite grouplet. Discovery The meteorite was found near and was named after Vermillion, Marshall County, Kansas. It was found by two farmers while planting on a grain field in 1991. It was recognized as a meteorite and first described in 1995. Mineralogy Vermillion meteorite consists of around 86volume-% meteoric iron and 14% silicate minerals. The silicates include olivine (93% of silicates), orthopyroxene (5%), chromite (1.5%) and merrillite (0.5%). Other accessory minerals include troilite, whitlockite, and cohenite. Classification The Vermillion meteorite is classified as a pyroxene pallasite because it contains pyroxene as an accessory mineral and shares a distinct oxygen isotope signature with Yamato 8451. Some studies also object to this grouping, referring to the differences in siderophile trace elements and the occurrence of cohenite in the Vermillion meteorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallasite Main Group
Almost all pallasite meteorite A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object ...s are part of the pallasite main group. References Meteorite groups {{Meteorite-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eagle Station Group
The Eagle Station group (abbreviated PES - Pallasite Eagle Station) is a set of pallasite meteorite specimen that don't fit into any of the other defined pallasite groups. In meteorite classification five meteorites have to be found, so they can be defined as their own group. Currently only five Eagle Station type meteorites have been found, which is just enough for a separate group. Naming and history The Eagle Station group is named after the Eagle Station meteorite, the type specimen of the group. It is in turned named after Eagle Station, Carroll County Kentucky where it was found. Description The Eagle Station group has a composition similar to Main group pallasites. Diagnostic differences are that the olivine is richer in iron and calcium. The group also has a distinct oxygen isotope signature. The meteoric iron is similar to the IIF iron meteorites. This might indicate that Eagle station group and IIF formed close to each other in the solar nebula. Parent body The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Netherlands and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new system of animal classification was praised by Georges Cuvier. Pallas wrote ''Miscellanea Zoologica'' (1766), which included descriptions of several vertebrates new to science which he had discovered in the Dutch museum collections. A planned voyage to southern Africa and the East Indies fell through when his father recalled him to Berlin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorite Classification
In meteoritics, a meteorite classification system attempts to group similar meteorites and allows scientists to communicate with a standardized terminology when discussing them. Meteorites are classified according to a variety of characteristics, especially mineralogical, petrological, chemical, and isotopic properties. Terminology There is no single, standardized terminology used in meteorite classification; however, commonly used terms for categories include ''types'', ''classes'', ''clans'', ''groups'', and ''subgroups''. Some researchers hierarchize these terms, but there is no consensus as to which hierarchy is most appropriate. Meteorites that do not fit any known group (though they may fit somewhere within a higher level of classification) are ''ungrouped''. Genetic relationships Meteorite classification may indicate that a "genetic" relationship exists between similar meteorite specimens. Similarly classified meteorites may share a common origin, and therefore may come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. For this reason, olivine has been proposed as a good candidate for accelerated weathering to sequester carbon dioxide from the Earth's oceans and atmosphere, as part of climate change mitigation. Olivine also has many other historical uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians Russian conquest of Siberia, conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western Siberia, Western and Eastern Siberia, Eastern. Siberia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk ( ; rus, Красноя́рск, a=Ru-Красноярск2.ogg, p=krəsnɐˈjarsk) (in semantic translation - Red Ravine City) is the largest city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yenisey River, and is the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk, with a population of over 1.1 million. Krasnoyarsk is an important junction of the renowned Trans-Siberian Railway, and is one of the largest producers of aluminium in the country. The city is known for its natural landscape; author Anton Chekhov judged Krasnoyarsk to be the most beautiful city in Siberia. The Stolby Nature Sanctuary is located 10 km south of the city. Krasnoyarsk is a major educational centre in Siberia, and hosts the Siberian Federal University. In 2019, Krasnoyarsk was the host city of the 2019 Winter Universiade, the third hosted in Russia. Geography The total area of the city, including suburbs and the river, is .Poexaly.ru. Krasno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pood
''Pood'' ( rus, пуд, r=pud, p=put, plural: or ) is a unit of mass equal to 40 ''funt'' (, Russian pound). Since 1899 it is set to approximately 16.38 kilograms (36.11 pounds). It was used in Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine. ''Pood'' was first mentioned in a number of 12th-century documents. Unlike '' funt'', which came at least in the 14th century from gmh, phunt, orv, пудъ (formerly written * ) is a much older borrowing from Late Latin "pondo", from Classical "pondus". Use in the past and present Together with other units of weight of the Imperial Russian weight measurement system, the USSR officially abolished the ''pood'' in 1924. But the term remained in widespread use at least until the 1940s. In his 1953 short story "Matryona's Place", Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn presents the ''pood'' as still in use amongst the Khrushchev-era Soviet peasants. Its usage is preserved in modern Russian in certain specific cases, e.g., in reference to sports weights, such as tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
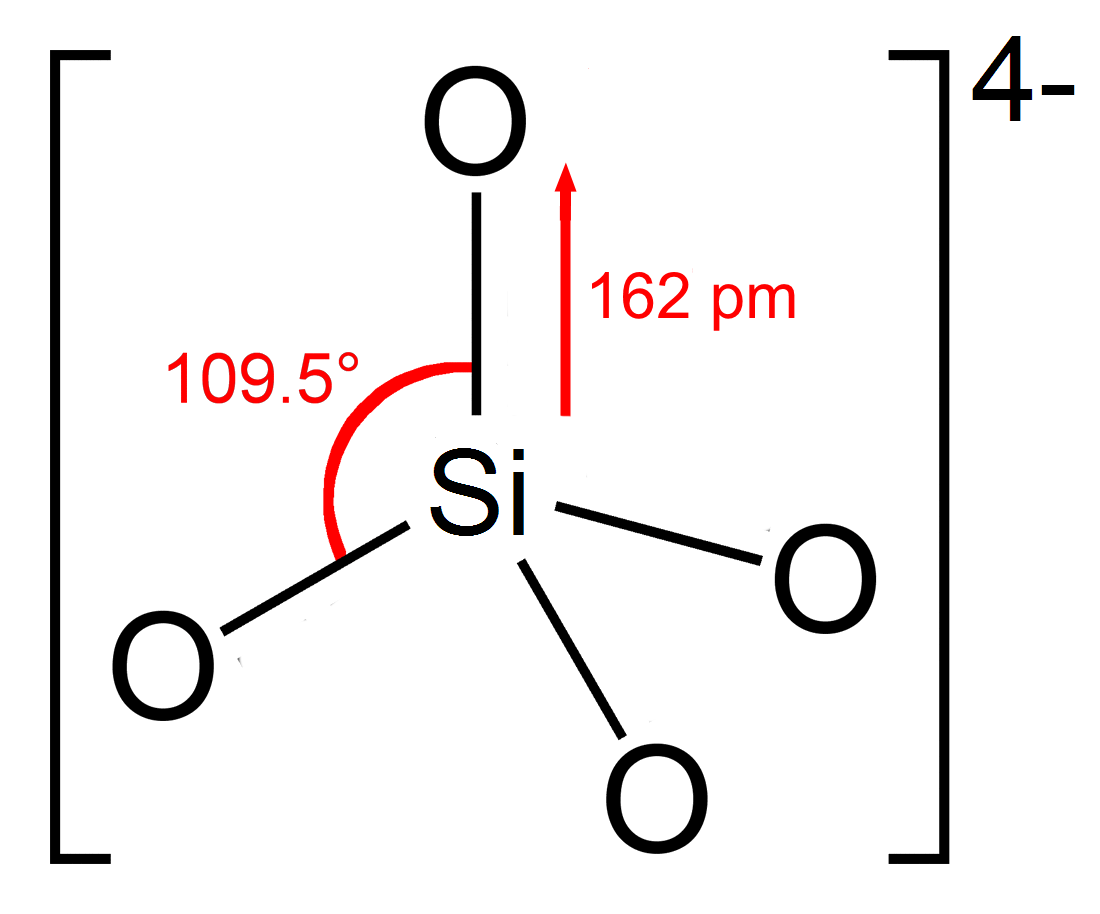
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |