|
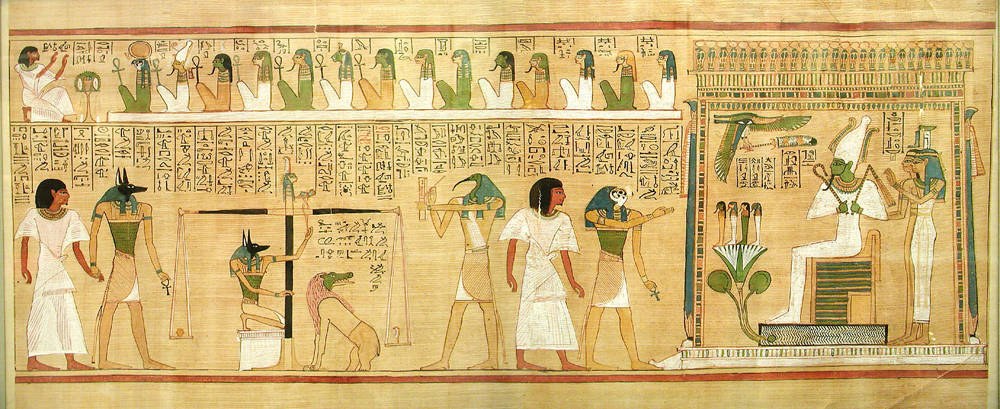
Maat
Maat or Maʽat ( Egyptian: mꜣꜥt /ˈmuʀʕat/, Coptic: ⲙⲉⲓ) refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Ma'at was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and regulated the stars, seasons, and the actions of mortals and the deities who had brought order from chaos at the moment of creation. Her ideological opposite was Isfet (Egyptian '' jzft''), meaning injustice, chaos, violence or to do evil. Pronunciation Cuneiform texts indicate that the word ''m3ˤt'' was pronounced /múʔʕa/ during the New Kingdom of Egypt, having lost the feminine ending ''t''. Vowel assimilation of ''u'' to ''e'' later produced the Coptic word "truth, justice". History The earliest surviving records indicating that Maat is the norm for nature and society, in this world and the next, were recorded during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, the earliest substantial surviving examples being found in the Pyramid Texts of Unas (ca. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are the oldest ancient Egyptian funerary texts, dating to the late Old Kingdom. They are the earliest known corpus of ancient Egyptian religious texts. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved onto the subterranean walls and sarcophagi of pyramids at Saqqara from the end of the Fifth Dynasty, and throughout the Sixth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, and into the Eighth Dynasty of the First Intermediate Period. The oldest of the texts have been dated to c. 2400–2300 BCE. Unlike the later Coffin Texts and Book of the Dead, the Pyramid Texts were reserved only for the pharaoh and were not illustrated. The use and occurrence of Pyramid Texts changed between the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms of Ancient Egypt. During the Old Kingdom (2686 BCE – 2181 BCE), Pyramid Texts could be found in the pyramids of kings as well as three queens, named Wedjebten, Neith, and Iput. During the Middle Kingdom (2055 BCE – 1650 BCE), Pyramid Texts were not written in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV ( egy, jmn-ḥtp, links=no, meaning "Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning Egypt's traditional polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheistic, or whether it was monolatry, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name excluded from lists of rulers compiled by later pharaohs. Traditional religious practice was gradually restored, not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with many deities believed to be present in, and in control of the world. Rituals such as prayer and offerings were provided to the gods to gain their favor. Formal religious practice centered on the pharaohs, the rulers of Egypt, believed to possess divine powers by virtue of their positions. They acted as intermediaries between their people and the gods, and were obligated to sustain the gods through rituals and offerings so that they could maintain Ma'at, the order of the cosmos, and repel Isfet, which was chaos. The state dedicated enormous resources to religious rituals and to the construction of temples. Individuals could interact with the gods for their own purposes, appealing for help through prayer or compelling the gods to act through magic. These practices were distinct from, but closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radiocarbon dating places the beginning of the New Kingdom between 1570 BC and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period. It was Egypt's most prosperous time and marked the peak of its power. The concept of a "New Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The later part of this period, under the Nineteenth and Twentieth dynasties (1292–1069 BC), is also known as the ''Ramesside period''. It is named after the eleven pharaohs who took the name Ramesses, after Ramesses I, the founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty. Possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut (; also Hatchepsut; Egyptian: '' ḥꜣt- špswt'' "Foremost of Noble Ladies"; or Hatasu c. 1507–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the second historically confirmed female pharaoh, after Sobekneferu. (Various other women may have also ruled as pharaohs or at least regents before Hatshepsut, as early as Neithhotep around 1,600 years prior.) Hatshepsut came to the throne of Egypt in 1478 BC. As the principal wife of Thutmose II, Hatshepsut initially ruled as regent to Thutmose III, a son of Thutmose II by another wife and the first male heir. While Thutmose III had inherited the throne at about two years old, Hatshepsut continued to rule by asserting her lineage as the daughter and only child of Thutmose I and his primary wife, Ahmose. Her husband Thutmose II was the son of Thutmose I and a secondary wife named Mutnofret, who carried the title 'King's daughter' and was probably a child of Ahmose I. Hatshepsut and Thutmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald B
Donald is a masculine given name derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers, and partly associated with the spelling of similar-sounding Germanic names, such as '' Ronald''. A short form of ''Donald'' is ''Don''. Pet forms of ''Donald'' include ''Donnie'' and ''Donny''. The feminine given name ''Donella'' is derived from ''Donald''. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name ''Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and the 20th centuries. Not only was the last king of the Early Dynastic Period related to the first two kings of the Old Kingdom, but the "capital", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu (Egyptian Deity)
Shu (Egyptian ''šw'', "emptiness" or "he who rises up", cop, Ϣⲟⲩ) was one of the primordial Egyptian gods, spouse and brother to the goddess Tefnut, and one of the nine deities of the Ennead of the Heliopolis cosmogony. He was the god of peace, lions, air, and wind. Family In Heliopolitan theology, Atum created the first couple of the Ennead, Shu and Tefnut by masturbating or by spitting. Shu was the father of Nut and Geb and grandfather of Osiris, Isis, Set, and Nephthys. His great-grandsons are Horus and Anubis. Myths As the air, Shu was considered to be a cooling, and thus calming, influence, and pacifier. Due to the association with dry air, calm, and thus Ma'at (truth, justice, order, and balance), Shu was depicted as the dry air/atmosphere between the earth and sky, separating the two realms after the event of the First Occasion. Shu was also portrayed in art as wearing an ostrich feather. Shu was seen with between one and four feathers. The ostrich feather was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
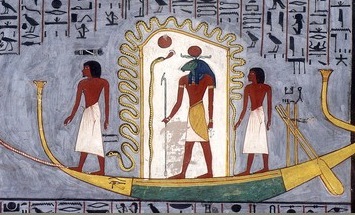
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duat
The Duat ( egy, dwꜣt, Egyptological pronunciation "do-aht", cop, ⲧⲏ, also appearing as ''Tuat'', ''Tuaut'' or ''Akert'', ''Amenthes'', ''Amenti'', or ''Neter-khertet'') is the realm of the dead in ancient Egyptian mythology. It has been represented in hieroglyphs as a star-in-circle: 𓇽. The god Osiris was believed to be the lord of the underworld. He was the first mummy as depicted in the Osiris myth and he personified rebirth and life after death. The underworld was also the residence of various other gods along with Osiris. The geography of the ''Duat'' is similar in outline to the world the Egyptians knew: There are realistic features like rivers, islands, fields, lakes, mounds and caverns, but there were also fantastic lakes of fire, walls of iron, and trees of turquoise. In the ''Book of Two Ways'' (a Coffin Text) there is even a map-like image of the ''Duat''. Resident souls, gods, and demons The ''Duat'' was also a residence for various gods, including Osiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)