|
Fuzhou Tanka
Fuzhou Tanka ( Fuzhou dialect: 曲蹄; Foochow Romanized: Kuóh-dà̤ ; Simplified Chinese: 福州疍民 Hók-ciŭ Dáng-mìng; 江妹仔 Gĕ̤ng-muói-giāng; 曲蹄婆 Kuóh-dà̤-bò̤), or Boat People, are from Fujian, China. A branch of the Tanka people, they traditionally lived on sampans in the lower course of Min River and the coast of Fuzhou in Fujian Province most of their lives and have been officially recognized as Han Chinese since 1955.Jian-min Li (李健民)Origin and Migration of Mindong's Fishermen (闽东疍民的由来及历史变迁), Journal of Ningde Teachers' College, 2009 Vol. 2, pp.38–44 (in Chinese) Origin and etymology There are several different views on the origin of Fuzhou Tanka. The mainstream theory believes that Fuzhou Tanka are descendants of the Baiyue of ancient times. As a branch of the Tanka people, Fuzhou Tanka has been in South China for more than 2000 years.刘传�闽江流域疍民的文化习俗形态(in Chinese) Their Fuzhounes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hockchew Kuoh-da
Fuzhou people (; Foochow Romanized: ''Hók-ciŭ-nè̤ng''), also known as, Foochowese, Hokchew, Hokchia, Hokchiu, Fuzhou Shiyi people (), Eastern Min or Mindong refer to Chinese who originate from the Fuzhou and Mindong regions and the Gutian and Pingnan counties of Fujian province and Matsu Islands in Taiwan. Fuzhou people are a part of the Min Chinese-speaking group that speaks Eastern Min or specifically Fuzhou dialect. There is also a significant overseas Fuzhou population, particularly distributed in Malaysia, Indonesia, Japan, United States (Fuzhou Americans), Singapore and the United Kingdom. Language Fuzhou dialect is a tonal language that has extensive sandhi rules in the initials, rimes, and tones. These complicated rules make Fuzhou dialect one of the most difficult Chinese varieties. Fuzhou dialects List of dialects of the Fuzhou language (): * Min county dialect 福州閩縣話 (prestige) - Fuzhou city and Minhou county. *Gutian dialect 福州� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner River Of Fuzhou
Interior may refer to: Arts and media * ''Interior'' (Degas) (also known as ''The Rape''), painting by Edgar Degas * ''Interior'' (play), 1895 play by Belgian playwright Maurice Maeterlinck * ''The Interior'' (novel), by Lisa See * Interior design, the trade of designing an architectural interior Places * Interior, South Dakota * Interior, Washington * Interior Township, Michigan * British Columbia Interior, commonly known as "The Interior" Government agencies * Interior ministry, sometimes called the ministry of home affairs * United States Department of the Interior Other uses * Interior (topology), mathematical concept that includes, for example, the inside of a shape * Interior FC, a football team in Gambia See also * * * List of geographic interiors * Interiors (other) * Inter (other) Inter may refer to: Association football clubs * Inter Milan, an Italian club * SC Internacional, a Brazilian club * Inter Miami CF, an American club * FC I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has been defined in several ways: as music transmitted orally, music with unknown composers, music that is played on traditional instruments, music about cultural or national identity, music that changes between generations (folk process), music associated with a people's folklore, or music performed by custom over a long period of time. It has been contrasted with commercial and classical styles. The term originated in the 19th century, but folk music extends beyond that. Starting in the mid-20th century, a new form of popular folk music evolved from traditional folk music. This process and period is called the (second) folk revival and reached a zenith in the 1960s. This form of music is sometimes called contemporary folk music or folk r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques include gathering seafood by hand, hand-gathering, spearfishing, spearing, fish net, netting, angling, bowfishing, shooting and fish trap, trapping, as well as destructive fishing practices, more destructive and often illegal fishing, illegal techniques such as electrofishing, electrocution, blast fishing, blasting and cyanide fishing, poisoning. The term fishing broadly includes catching aquatic animals other than fish, such as crustaceans (shrimp/lobsters/crabs), shellfish, cephalopods (octopus/squid) and echinoderms (starfish/sea urchins). The term is not normally applied to harvesting fish raised in aquaculture, controlled cultivations (fish farming). Nor is it normally applied to hunting aquatic mammals, where term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hockchew Tanka Distribution
Fuzhou people (; Foochow Romanized: ''Hók-ciŭ-nè̤ng''), also known as, Foochowese, Hokchew, Hokchia, Hokchiu, Fuzhou Shiyi people (), Eastern Min or Mindong refer to Chinese who originate from the Fuzhou and Mindong regions and the Gutian and Pingnan counties of Fujian province and Matsu Islands in Taiwan. Fuzhou people are a part of the Min Chinese-speaking group that speaks Eastern Min or specifically Fuzhou dialect. There is also a significant overseas Fuzhou population, particularly distributed in Malaysia, Indonesia, Japan, United States (Fuzhou Americans), Singapore and the United Kingdom. Language Fuzhou dialect is a tonal language that has extensive sandhi rules in the initials, rimes, and tones. These complicated rules make Fuzhou dialect one of the most difficult Chinese varieties. Fuzhou dialects List of dialects of the Fuzhou language (): * Min county dialect 福州閩縣話 (prestige) - Fuzhou city and Minhou county. *Gutian dialect 福州� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Min Language
Eastern Min or Min Dong (, Foochow Romanized: Mìng-dĕ̤ng-ngṳ̄), is a branch of the Min group of Sinitic languages of China. The prestige form and most-cited representative form is the Fuzhou dialect, the speech of the capital of Fujian. Geographic distribution Fujian and vicinity Eastern Min varieties are mainly spoken in the eastern part of Fujian Province (闽东) of the People's Republic of China, in and near the cities of Fuzhou and Ningde. They are also widely encountered as the mother tongue on the Matsu Islands controlled by the Republic of China. Additionally, the inhabitants of Taishun and Cangnan to the north of Fujian in Zhejiang also speak Eastern Min varieties. Eastern Min generally coexists with the official standard Chinese in all these areas. United States As the coastal area of Fujian has been the historical homeland of a large worldwide diaspora of overseas Chinese, varieties of Eastern Min can also be found across the world, especially in their res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compulsory Education
Compulsory education refers to a period of education that is required of all people and is imposed by the government. This education may take place at a registered school or at other places. Compulsory school attendance or compulsory schooling means that parents are obliged to send their children to a certain school. The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights requires, within a reasonable number of years, the principle of compulsory education free of charge for all. All countries except Bhutan, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Vatican City have compulsory education. Purpose At the start of the 20th century, compulsory education was to master physical skills which are necessary and can be contributed to the nation. It also instilled values of ethics and social communications abilities in teenagers, it would allow immigrants to fit in the unacquainted society of a new country. Nowadays, compulsory education has been considered as a right of ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Race
The concept of a Malay race was originally proposed by the German physician Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840), and classified as a brown race. ''Malay'' is a loose term used in the late 19th century and early 20th century to describe the Austronesian peoples. Since Blumenbach, many anthropologists have rejected his theory of five races, citing the enormous complexity of classifying races. The concept of a "Malay race" differs with that of the ethnic Malays centered on Malaya and parts of the Malay Archipelago's islands of Sumatra and Borneo. History The linguistic connections between Madagascar, Polynesia and Southeast Asia were recognized early in the colonial era by European authors, particularly the remarkable similarities between Malagasy, Malay, and Polynesian numerals. The first formal publications on these relationships was in 1708 by the Dutch Orientalist Adriaan Reland, who recognized a "common language" from Madagascar to western Polynesia; althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) across a total area of about , Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world (after Uttar Pradesh in India). Its economy is larger than that of any other province in the nation and the fifth largest sub-national economy in the world with a GDP (nominal) of 1.95 trillion USD (12.4 trillion CNY) in 2021. The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, a Chinese megalopolis, is a core for high technology, manufacturing and foreign trade. Located in this zone are two of the four top Chinese cities and the top two Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP; Guangzhou, the capital of the province, and Shenzhen, the first special economic zone in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiamen University
Xiamen University (; Southern Min: ''Ē-mn̂g-toā-o̍h''), colloquially known as Xia Da (; Southern Min: ''Hā-tāi''), is a national public research university in Xiamen, Fujian, China. Founded in 1921 by Tan Kah Kee, a Chinese patriotic expatriate businessman in Singapore, the university has been perennially regarded as one of the top academic institutions in Southern China, with strengths in mathematics, chemistry, oceanography, economics, management, law, communication and political science. Xiamen University is designated as a Class A Double First Class University of the national Double First Class University Plan, also a part of the former Project 985 and Project 211. As of 2020, the university hosts over 40,000 students on its 4 campuses and 6 academic divisions. History Private period In 1919, Tan Kah Kee, a Chinese expatriate in Singapore, businessman, investor, and philanthropist, donated then 4 million dollars to endow Amoy University in the city of Amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
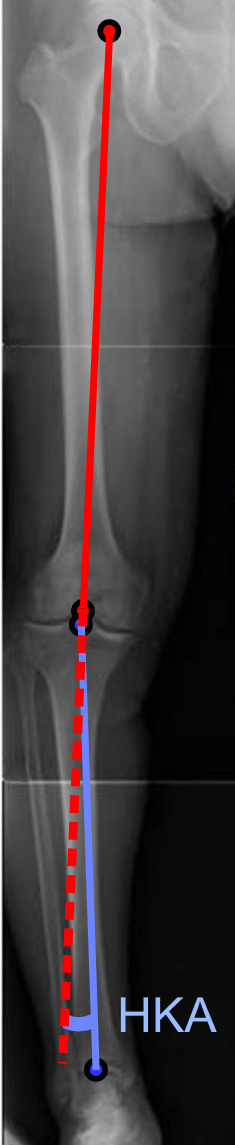
Bowlegged
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving the limb overall the appearance of an archer's bow. Usually medial angulation of both lower limb bones (femur and tibia) is involved. Causes If a child is sickly, either with rickets or any other ailment that prevents ossification of the bones or is improperly fed, the bowed condition may persist. Thus the chief cause of this deformity is rickets. Skeletal problems, infection, and tumors can also affect the growth of the leg, sometimes giving rise to a one-sided bow-leggedness. The remaining causes are occupational, especially among jockeys, and from physical trauma, the condition being very likely to supervene after accidents involving the condyles of the femur. Childhood Children until the age of 3 to 4 have a degree of genu varum. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14763995591).jpg)