|
Continuum Fingerboard
The Continuum Fingerboard or Haken Continuum is a music performance controller and synthesizer developed by Lippold Haken, a professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Illinois, and sold by Haken Audio, located in Champaign, Illinois. The Continuum Fingerboard was initially developed from 1983 to 1998 at the CERL Sound Group at the University of Illinois, to control sound-producing algorithms on the Platypus audio signal processor and the Kyma/Capybara workstation. In 1999, the first Continuum Fingerboard was commercially sold. Until 2008, the Continuum Fingerboard provided IEEE-1394 (FireWire) connections to control a Kyma sound design workstation, as well as MIDI connections to control a MIDI synthesizer module. More recently, the Continuum Fingerboard generates audio directly in addition to providing MIDI connections for MIDI modules, software synthesizers, and Kyma (the IEEE-1394 connection that was present on earlier models has been removed). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Harmony Central
Gibson, Inc. (formerly Gibson Guitar Corporation and Gibson Brands Inc.) is an American manufacturer of guitars, other musical instruments, and professional audio equipment from Kalamazoo, Michigan, and now based in Nashville, Tennessee. Orville Gibson started making instruments in 1894 and founded the company in 1902 as the Gibson Mandolin-Guitar Mfg. Co. Ltd. in Kalamazoo, Michigan, to make mandolin-family instruments. Gibson invented archtop guitars by constructing the same type of carved, arched tops used on violins. By the 1930s, the company was also making flattop acoustic guitars, as well as one of the first commercially available hollow-body electric guitars, used and popularized by Charlie Christian. In 1944, Gibson was bought by Chicago Musical Instruments (CMI), which was acquired in 1969 by Panama-based conglomerate Ecuadorian Company Limited (ECL), that changed its name in the same year to Norlin Corporation. Gibson was owned by Norlin Corporation from 1969 to 1986 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second or 1000 microseconds. A millisecond is to one second, as one second is to approximately 16.67 minutes. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond – time taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
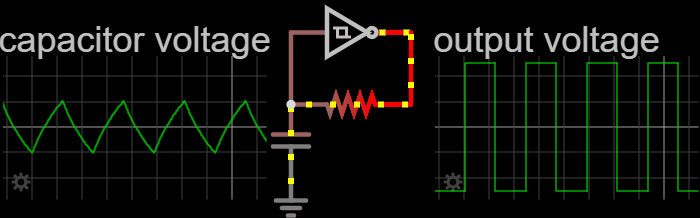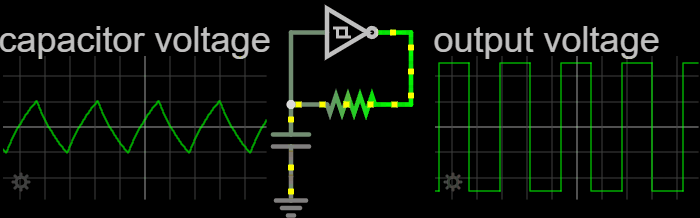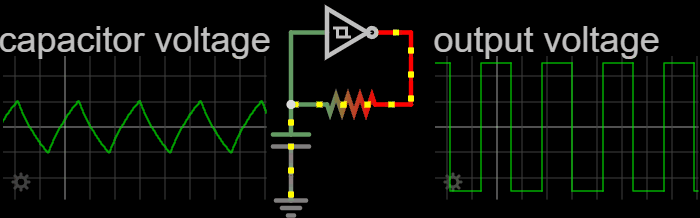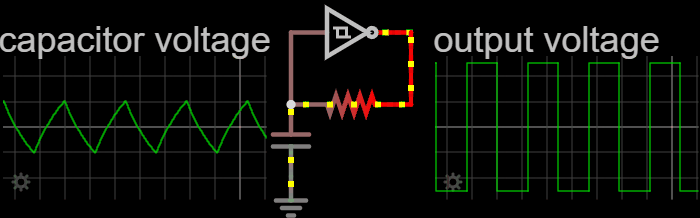
Electronic Oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices. Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal: *A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesizers, to distinguish it from an audio frequency oscillator. *An audio oscillator produces frequencies in the audio range, 20 Hz to 20 kHz. *A radio frequency (RF) oscillator produces signals above the audio range, more generally in the range of 100 kHz to 100 GHz. There are two ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in San Bruno, California, it is the second-most-visited website in the world, after Google Search. In January 2024, YouTube had more than 2.7billion monthly active users, who collectively watched more than one billion hours of videos every day. , videos were being uploaded to the platform at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute, and , there were approximately 14.8billion videos in total. On November 13, 2006, YouTube was purchased by Google for $1.65 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ). Google expanded YouTube's business model of generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by and for YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Digital Synthesizer
A digital synthesizer is a synthesizer that uses digital signal processing (DSP) techniques to make musical sounds, in contrast to older analog synthesizers, which produce music using analog electronics, and samplers, which play back digital recordings of acoustic, electric, or electronic instruments. Some digital synthesizers emulate analog synthesizers, while others include sampling capability in addition to digital synthesis. History The very earliest digital synthesis experiments were made with computers, as part of academic research into sound generation. In 1957, the first programming language for computer music, MUSIC, was developed by Max Mathews on an IBM 704 at Bell Labs in 1957. It generates digital audio waveforms through direct synthesis. , EMS MUSYS 3 system was developed by Peter Grogono (software), David Cockerell (hardware and interfacing) and Peter Zinovieff (system design and operation) at their London (Putney) Studio. The system ran on two mini-co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Modular Synthesizer
Modular synthesizers are synthesizers composed of separate modules for different functions. The modules can be connected together by the user to create a patch. The outputs from the modules may include audio signals, analog control voltages, or digital signals for logic or timing conditions. Typical modules are voltage-controlled oscillators, voltage-controlled filters, voltage-controlled amplifiers and envelope generators. History The first modular synthesizer was developed by German engineer Harald Bode in the late 1950s. The 1960s saw the introduction of the Moog synthesizer and the Buchla Modular Electronic Music System, created around the same period. The Moog was composed of separate modules which created and shaped sounds, such as envelopes, noise generators, filters, and sequencers, connected by patch cords. The Japanese company Roland released the Roland System 100 in 1975, followed by the System 700 in 1976 and the System 100m in 1979. In the late 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Loudness
In acoustics, loudness is the subjectivity, subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relation of physical attributes of sound to perceived loudness consists of physical, physiological and psychological components. The study of apparent loudness is included in the topic of psychoacoustics and employs methods of psychophysics. In different industries, loudness may have different meanings and different measurement standards. Some definitions, such as ITU-R BS.1770 refer to the relative loudness of different segments of electronically reproduced sounds, such as for broadcasting and cinema. Others, such as ISO 532A (Stevens loudness, measured in sones), ISO 532B (Eberhard Zwicker, Zwicker loudness), DIN 45631 and ASA/ANSI S3.4, have a more general scope and are often used to characterize loudness of environmental noise. More modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe and a clarinet, both woodwinds). In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctive with its own unique tone color. Musicians distinguish instruments based on their varied timbres, even instruments playing notes at the same pitch and volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
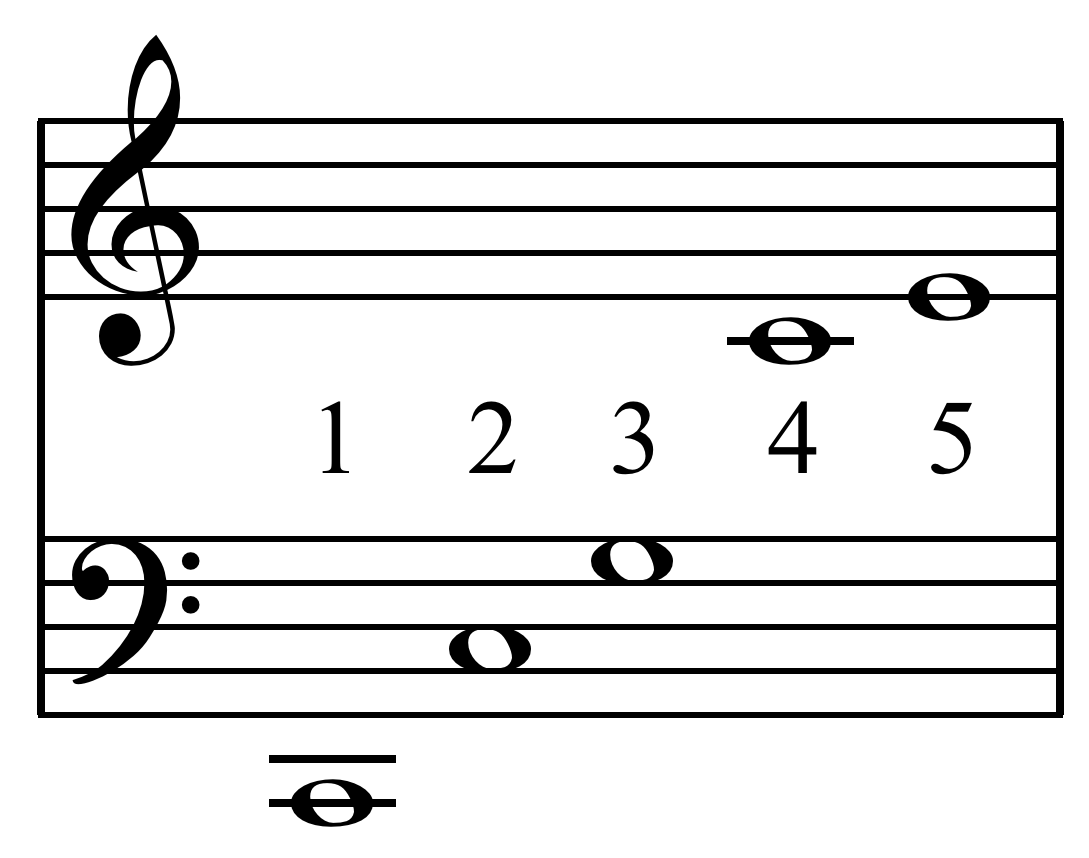
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in this way are said to be pure, and are called just intervals. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice, bowed instruments such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses are tuned using pure fifths or fourths. In contrast, keyboard instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same. This system yields Pitch (music), pitch steps perceived as equal in size, due to the logarithmic changes in pitch frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been 12 equal temperament (also known as ''12 tone equal temperament'', ' or ', informally abbreviated as ''12 equal''), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2, (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western world, Western countries the term ''equal temperamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pitch Bend
In electronic music, a pitch wheel, pitch bend or bender is a control on a synthesizer to vary the pitch in a continuously variable manner (portamento). The first synthesizer with a pitch wheel was the Minimoog, in 1970. Alternatively, pitch bend controllers on synthesizers may be implemented as a joystick, knob, or touch-sensitive ribbon. MIDI represents pitch bend as a 14-bit integer, allowing for 16,384 possible values. General MIDI implementations default to a range of ±2 semitones. See also *Glissando In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a wikt:glide, glide from one pitch (music), pitch to another (). It is an Italianized Musical terminology, musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In ... References External linksPitch Bend Wheel at Dailyanalog Synthesizers Continuous pitch instruments {{electronic-musical-instrument-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. Vibrato is typically characterized in terms of two factors: the amount of pitch variation ("extent of vibrato") and the speed with which the pitch is varied ("rate of vibrato"). In singing, it can occur spontaneously through variations in the larynx. The vibrato of a string instrument and wind instrument is an imitation of that vocal function. Vibrato can also be reproduced mechanically (Leslie speaker) or electronically as an Audio signal processing, audio effect close to Chorus (audio effect), chorus. Terminology History Descriptions of what would now be characterised as vibrato go back to the 16th century. However, no evidence exists of authors using the term vibrato before the 19th century. Instead, authors used various descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |