|
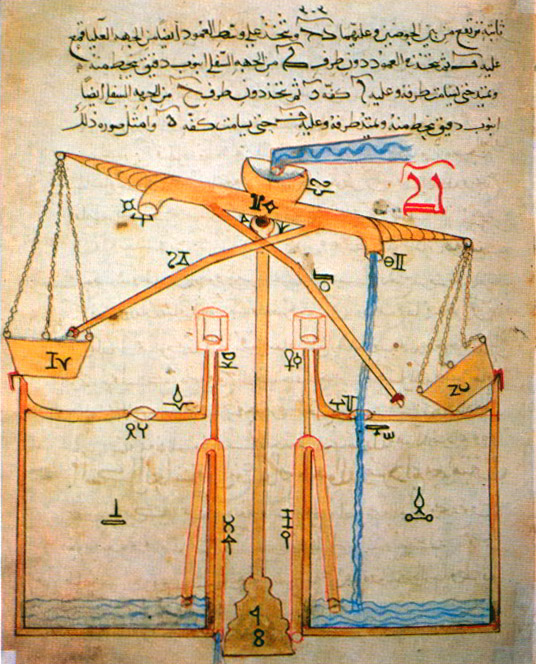
Al-Jazari
Badīʿ az-Zaman Abu l-ʿIzz ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ar-Razāz al-Jazarī (1136–1206, , ) was a Muslim polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan and artist from the Artuqid Dynasty of Jazira in Mesopotamia. He is best known for writing ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' (, also known as ''Automata'') in 1206, where he described 50 mechanical devices, along with instructions on how to construct them. One of his more famous inventions is the elephant clock. He has been described as the "father of robotics" and modern day engineering. Biography Al-Jazari was born in the area of Upper Mesopotamia in 1136. Sources state his exact location is unknown, but they speculate he could have been born in Jazirat ibn Umar, where he got the name Jazari from or Al-Jazira which was used to denote Upper Mesopotamia. The only biographical information known about him is contained in his ''Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices''. Like his father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Inventions In The Medieval Islamic World
The following is a list of inventions, discoveries and scientific advancements made in the medieval Islamic world, especially during the Islamic Golden Age, George Saliba (1994), ''A History of Arabic Astronomy: Planetary Theories During the Golden Age of Islam'', pp. 245, 250, 256–57. New York University Press, . as well as in later states of the Age of the Islamic Gunpowders such as the Ottoman and Mughal empires. The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the eighth century to the fourteenth century, with several contemporary scholars dating the end of the era to the fifteenth or sixteenth century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid (786 to 809) with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, where scholars from various parts of the world with different cultural backgrounds were mandated to gather a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artuklu Palace
The Artuklu Palace or Artukid Palace or Artuqid Palace () was the seat of the Diyarbakır branch of the Artuqid dynasty, a Turkish Beylik that ruled eastern Anatolia and Al-Jazira in the 12th and 13th centuries. It was located in the İçkale (citadel) of the historic walled district of Diyarbakır. Partially excavated in the 1960s, the main body of the palace is today still buried under a mound. History The palace was situated in the present-day İçkale neighborhood, inside the Diyarbakır City Walls. It was built during the reign of Nasir al-Din Mahmud () (1200–1222). There are further Artukid palatial residences in Mardin, Hasankeyf and Palu whose remains stand, but this one in Diyarbakır is usually referred to as the "Palace" of the sons of Artuk. This palace was also where, as his father before him, the groundbreaking Muslim scholar, inventor, and mechanical engineer Al-Jazari had worked for 30 years and was the place, inspiration and context of many of this inven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artuqid
The Artuqid dynasty (alternatively Artukid, Ortoqid, or Ortokid; Old Anatolian Turkish: , , pl. ; ; ) was established in 1102 as a Turkish Anatolian Beylik (Principality) of the Seljuk Empire. It formed a Turkoman dynasty rooted in the Oghuz tribe, and followed the Sunni Muslim faith. It ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Artuqid dynasty took its name from its founder, Artuk Bey, who was a member of Döger branch of the Oghuz Turks and ruled one of the Turkmen beyliks of the Seljuk Empire. Artuk's sons and descendants ruled the three branches in the region: Sökmen's descendants ruled the region around Hasankeyf between 1102 and 1231; Ilghazi's branch ruled from Mardin and Mayyafariqin between 1106 and 1186 (until 1409 as vassals) and Aleppo from 1117–1128; and the Harput line starting in 1112 under the Sökmen branch, and was independent between 1185 and 1233. History The dynasty was founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Donald Hill
Donald Routledge Hill (6 August 1922 – 30 May 1994)D. A. King, “In Memoriam: Donald Routledge Hill (1922-1994)”, ''Arabic Sciences and Philosophy,'' Volume 5 / Issue 02 / September 1995, pp 297-302 was a British engineer and historian of science and technology best known for his translation of ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' of the Muslim engineer Ismail al-Jazari.Hill Donald(1993) Life and work Born in London, after secondary school Hill served in the British army, in the Royal Engineers from 1941 to 1946. Two years he served in the Eighth Army in North Africa until he was wounded in action in Italy. Back in England he studied Engineering at the London University, obtaining his engineering degree in 1949. In 1964 he obtained his M.Litt in Islamic History at the University of Durham, and in 1970 his PhD from the University of London. Late 1940s Hill started his career working for the Iraq Petroleum Company in Lebanon, Syria and Qatar. Back in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artuqids
The Artuqid dynasty (alternatively Artukid, Ortoqid, or Ortokid; Old Anatolian Turkish: , , plural, pl. ; ; ) was established in 1102 as a Turkish people, Turkish Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian Beylik (Principality) of the Seljuk Empire. It formed a Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman dynasty rooted in the Oghuz Turks, Oghuz tribe, and followed the Sunni Muslim faith. It ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria (region), Syria and Northern Lower Mesopotamia, Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Artuqid dynasty took its name from its founder, Artuk Bey, who was a member of Döger branch of the Oghuz Turks and ruled one of the Turkmen Anatolian beyliks, beyliks of the Seljuk Empire. Artuk's sons and descendants ruled the three branches in the region: Sökmen of Artukids, Sökmen's descendants ruled the region around Hasankeyf between 1102 and 1231; Ilghazi, Ilghazi's branch ruled from Mardin and Mayyafariqin between 1106 and 1186 (until 1409 as vassals) and Aleppo from 111 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer science, robotics focuses on robotic automation algorithms. Other disciplines contributing to robotics include electrical engineering, electrical, control engineering, control, software engineering, software, Information engineering (field), information, electronics, electronic, telecommunications engineering, telecommunication, computer engineering, computer, mechatronic, and materials engineering, materials engineering. The goal of most robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Many robots are built to do jobs that are hazardous to people, such as finding survivors in unstable ruins, and exploring space, mines and shipwrecks. Others replace people in jobs that are boring, repetitive, or unpleasant, such as cleaning, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cengage
Cengage Group is an American educational content, technology, and services company for higher education, K–12, professional, and library markets. It operates in more than 20 countries around the world.(June 27, 2014Global Publishing Leaders 2014: Cengage publishersweekly.comCompany Info – Wall Street JournalCengage LearningCompany Overview of Cengage Learning, Inc. BloombergBusiness Company information The company is headquartered in , Massachusetts, and has some 5,000 employees worldwide across nearly 38 countries. It was headquartered at its |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Prize-winners being featured since its inception. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large-format New York City newspaper was released on August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saladin
Salah ad-Din Yusuf ibn Ayyub ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known as Saladin, was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from a Kurdish family, he was the first sultan of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, he spearheaded the Muslim military effort against the Crusader states in the Levant. At the height of his power, the Ayyubid realm spanned Egypt, Syria, Upper Mesopotamia, the Hejaz, Yemen, and Nubia. Alongside his uncle Shirkuh, a Kurdish mercenary commander in service of the Zengid dynasty, Saladin was sent to Fatimid Egypt in 1164, on the orders of the Zengid ruler Nur ad-Din. With their original purpose being to help restore Shawar as the vizier to the teenage Fatimid caliph al-Adid, a power struggle ensued between Shirkuh and Shawar after the latter was reinstated. Saladin, meanwhile, climbed the ranks of the Fatimid government by virtue of his military successes against Crusader assaults and his personal closeness to al-Adid. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |