wire bond on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wire bonding is a method of making interconnections between an
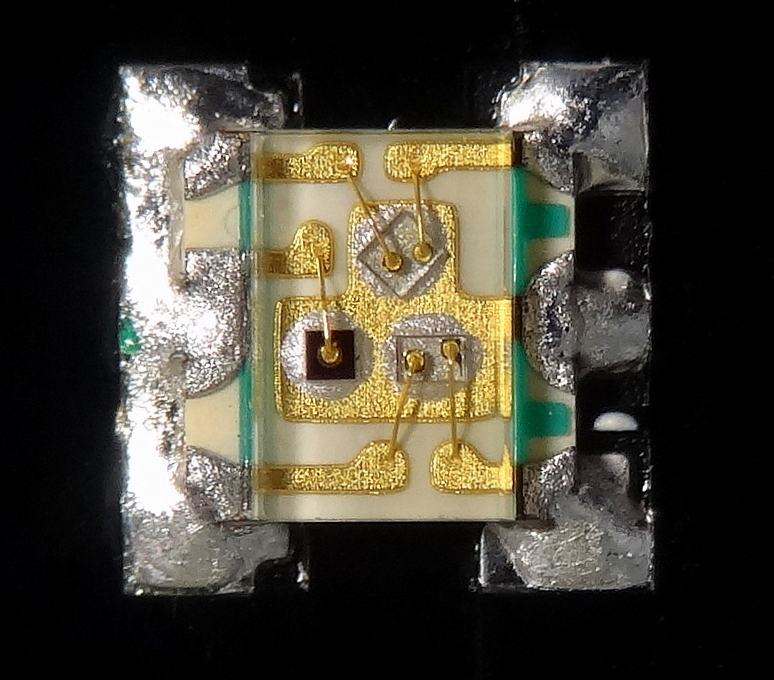 Pure gold wire doped with controlled amounts of
Pure gold wire doped with controlled amounts of
April 2016. The purpose of the test is as MIL-STD-883 2011.9 describes it: "To measure bond strengths, evaluate bond strength distributions, or determine compliance with specified bond strength requirements". A wire can be pulled to destruction, but there are also non-destructive variants whereby one tests whether the wire can withstand a certain force. Non-destructive test methods are typically used for 100% testing of safety critical, high quality and high cost products, avoiding damage to the acceptable wired bonds tested. The term wire pull usually refers to the act of pulling a wire with a hook mounted on a pull sensor on a bond tester. However, to promote certain failure modes, wires can be cut and then pulled by tweezers, also mounted on a pull sensor on a bond tester. Usually wires up to 75 μm diameter (3 mil) are classified as thin wire. Beyond that size, we speak about thick wire testing.
Amkor Copper (Cu) WirebondingJ-Devices Copper (Cu) Wirebonding
Amkor Silver (Ag) Wirebonding
{{Authority control Semiconductor device fabrication Packaging (microfabrication) Welding Electronics manufacturing Articles containing video clips
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(IC) or other semiconductor device
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material (primarily silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors) for its function. Its conductivit ...
and its packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a coo ...
during semiconductor device fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and memories (such as Random-access memory, RAM and flash memory). It is a ...
. Wire bonding can also be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
(PCB) to another, although these are less common. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages. Wire bonding can be used at frequencies above 100 GHz.V. Valenta et al., "Design and experimental evaluation of compensated bondwire interconnects above 100 GHz", International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 2015Materials
Bondwires usually consist of one of the following materials: *Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
*Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
*Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
*Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
Wire diameters start from under 10 μm and can be up to several hundred micrometres for high-powered applications.
The wire bonding industry is transitioning from gold to copper. This change has been instigated by the rising cost of gold and the comparatively stable, and much lower, cost of copper. While possessing higher thermal and electrical conductivity than gold, copper had previously been seen as less reliable due to its hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
and susceptibility to corrosion. By 2015, it is expected that more than a third of all wire bonding machines in use will be set up for copper.
Copper wire has become one of the preferred materials for wire bonding interconnects in many semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
and microelectronic applications. Copper is used for fine wire ball bonding in sizes from up to . Copper wire has the ability of being used at smaller diameters providing the same performance as gold without the high material cost. Smaller diameters are possible due to copper's higher electrical conductivity. Copper wire bonds are at least as reliable if not more reliable than gold wire bonds.
Copper wire up to can be successfully wedge bonded. Large diameter copper wire can and does replace aluminium wire where high current carrying capacity is needed or where there are problems with complex geometry. Annealing and process steps used by manufacturers enhance the ability to use large diameter copper wire to wedge bond to silicon without damage occurring to the die.
Copper wire does pose some challenges in that it is harder than both gold and aluminium, so bonding parameters must be kept under tight control. The amount of power used during ultrasonic bonding must be higher and copper has a higher fusing current so it has a higher current carrying capacity. The formation of oxides is inherent with this material, so storage and shelf life are issues that must be considered. Special packaging is required in order to protect copper wire and achieve a longer shelf life. Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), ...
coated copper wire is a common alternative which has shown significant resistance to corrosion, albeit at a higher hardness than pure copper and a greater price, though still less than gold. During the fabrication of wire bonds, copper wire, as well as its plated varieties, must be worked in the presence of forming gas
Forming gas is a mixture of hydrogen (mole fraction varies) and nitrogen. It is sometimes called a "dissociated ammonia atmosphere" due to the reaction which generates it:
:2 NH3 → 3 H2 + N2
It can also be manufactured by thermal cra ...
5% nitrogen and 5% hydrogenor a similar anoxic gas in order to prevent corrosion. A method for coping with copper's relative hardness is the use of high purity N+varieties.
Long-term corrosion effects (Cu2Si) and other stability topics led to increased quality requirements when used in automotive applications.
 Pure gold wire doped with controlled amounts of
Pure gold wire doped with controlled amounts of beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with ...
and other elements is normally used for ball bonding
Ball bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a bare silicon die and the lead frame of the package it is placed in during Fabrication (semiconductor), semiconductor device fabrica ...
. This process brings together the two materials that are to be bonded using heat, pressure and ultrasonic energy referred to as thermosonic bonding. The most common approach in thermosonic bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoul ...
is to ball-bond to the chip, then stitch-bond to the substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
. Very tight controls during processing enhance looping characteristics and eliminate sagging.
Junction size, bond strength and conductivity requirements typically determine the most suitable wire size for a specific wire bonding application. Typical manufacturers make gold wire in diameters from and larger. Production tolerance on gold wire diameter is +/-3%.
Alloyed aluminium wires are generally preferred to pure aluminium wire except in high-current devices because of greater drawing ease to fine sizes and higher pull-test strengths in finished devices. Pure aluminium and 0.5% magnesium-aluminium are most commonly used in sizes larger than .
All-aluminium systems in semiconductor fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and memories (such as RAM and flash memory). It is a multiple-step photol ...
eliminate the " purple plague" (brittle gold-aluminium intermetallic compound) sometimes associated with pure gold bonding wire. Aluminium is particularly suitable for thermosonic bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoul ...
.
In order to assure that high quality bonds can be obtained at high production speeds, special controls are used in the manufacture of 1% silicon-aluminium wire. One of the most important characteristics of high grade bonding wire of this type is homogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the Uniformity (chemistry), uniformity of a Chemical substance, substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, ...
of the alloy system. Homogeneity is given special attention during the manufacturing process. Microscopic checks of the alloy structure of finished lots of 1% silicon-aluminium wire are performed routinely. Processing also is carried out under conditions which yield the ultimate in surface cleanliness and smooth finish and permits entirely snag-free de-reeling.
Attachment techniques
The main classes of wire bonding: *Ball bonding
Ball bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a bare silicon die and the lead frame of the package it is placed in during Fabrication (semiconductor), semiconductor device fabrica ...
* Wedge bonding
* Compliant bonding
Ball bonding usually is restricted to gold and copper wire and usually requires heat. For wedge bonding, only gold wire requires heat. Wedge bonding can use large diameter wires or wire ribbons for power electronics application. Ball bonding is limited to small diameter wires, suitable for interconnect application.
In either type of wire bonding, the wire is attached at both ends using a combination of downward pressure, ultrasonic energy, and in some cases heat, to make a weld. Heat is used to make the metal softer. The correct combination of temperature and ultrasonic energy is used in order to maximize the reliability and strength of a wire bond. If heat and ultrasonic energy is used, the process is called thermosonic bonding.
In wedge bonding, the wire must be drawn in a straight line according to the first bond. This slows down the process due to time needed for tool alignment. Ball bonding, however, creates its first bond in a ball shape with the wire sticking out at the top, having no directional preference. Thus, the wire can be drawn in any direction, making it a faster process.
Compliant bondingA.Coucoulas, "Compliant Bonding" Proceedings 1970 IEEE 20th Electronic Components Conference, pp. 380-89, 1970. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:CompliantBondingPublic_1-10.pdf https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225284187_Compliant_Bonding_Alexander_Coucoulas_1970_Proceeding_Electronic_Components_Conference_Awarded_Best_Paper transmits heat and pressure through a compliant or indentable aluminium tape and therefore is applicable in bonding gold wires and the beam leads that have been electroformed to the silicon integrated circuit (known as the beam leaded integrated circuit).
Manufacturing and reliability challenges
There are multiple challenges when it comes to wire bond manufacturing and reliability. These challenges tend of be a function of several parameters such as the material systems, bonding parameters, and use environment. Different wire bond- bond pad metal systems such asAluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
-Aluminium (Al-Al), Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
-Aluminium (Au-Al), and Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
-Aluminium (Cu-Al) require different manufacturing parameters and behave differently under the same use environments.
Wire bond manufacturing
Much work has been done to characterize various metal systems, review critical manufacturing parameters, and identify typical reliability issues that occur in wire bonding. When it comes to material selection, the application and use environment will dictate the metal system. Often the electrical properties, mechanical properties, and cost are taken into account when making a decision. For example, a high current device for a space application might require a large diameter aluminium wire bond in a hermetically sealed ceramic package. If cost is a large constraint, then avoiding gold wire bonds may be a necessity. Some recent work has been done to look at copper wire bonds in automotive applications. This is only a small sampling, as there is a vast body of work reviewing and testing what material systems work best in different applications. From a manufacturing perspective, the bonding parameters play a critical role in bond formation and bond quality. Parameters such bond force, ultrasonic energy, temperature, and loop geometry, to name a few, can have a significant effect on bond quality. There are various wire bonding techniques (thermosonic bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoul ...
, ultrasonic bonding, thermocompression bonding) and types of wire bonds (ball bonding
Ball bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a bare silicon die and the lead frame of the package it is placed in during Fabrication (semiconductor), semiconductor device fabrica ...
, wedge bonding) that affect susceptibility to manufacturing defects and reliability issues. Certain materials and wire diameters are more practical for fine pitch or complex layouts. The bond pad also plays an important role as the metallization and barrier layer(s) stackup will impact the bond formation.
Typical failure modes that result from poor bond quality and manufacturing defects include: fracture at the ball bond neck, heel cracking (wedge bonds), pad liftoff, pad peel, overcompression, and improper intermetallic formation. A combination of wire bond pull/shear testing, nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
, and destructive physical analysis (DPA) can be used to screen manufacturing and quality issues.
Wire bond reliability
While wirebond manufacturing tends to focus on bond quality, it often does not account for wearout mechanisms related to wire bond reliability. In this case, an understanding of the application and use environment can help prevent reliability issues. Common examples of environments that lead to wire bond failures include elevated temperature, humidity, and temperature cycling. Under elevated temperatures, excessive intermetallics (IMC) growth can create brittle points of fracture. Much work that has been done to characterize the intermetallic formation and aging for various metal systems. This not a problem in metal systems where the wire bond and bond pad are the same material such as Al-Al. This does become a concern in dissimilar metal systems. One of the most well known examples is the brittle intermetallics formed in gold-aluminium IMCs such as purple plague. Additionally, diffusion related issues, such as Kirkendall voiding and Horsting voiding, can also lead to wire bond failures. Under elevated temperature and humidity environments,corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
can be a concern. This is most common in Au-Al metal systems and is driven by galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, different metal, when both in the prese ...
. The presence of halides such as chlorine can accelerate this behavior. This Au-Al corrosion is often characterized with Peck's law for temperature and humidity. This is not as common in other metal systems.
Under temperature cycling, thermomechanical stress is generated in the wire bond as a result of coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between the epoxy molding compound (EMC), the leadframe, the die, the die adhesive, and the wire bond. This leads to low cycle fatigue due to shear or tensile stresses in the wire bond. Various fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
models have been used to predict the fatigue life of wire bonds under such conditions, such as Paris' law. Fatigue models can be coupled with data-driven
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous value (semiotics), values that convey information, describing the quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols t ...
approaches, such as physics-informed Markov-Chains, to account for uncertainty and to better generalize for predictions on lower temperature.
Proper understanding of the use environment and metal systems are often the most important factors for increasing wire bond reliability.
Testing
While there are some wire bond pull and shear testing techniques such as MIL-STD-883, ASTM F459-13, and JESD22-B116,JESD22-B116: Wire Bond Shear Test Method these tend to be applicable for manufacturing quality rather than reliability. They are often monotonic overstress techniques, where peak force and fracture location are the critical outputs. In this case the damage is plasticity dominated, and does not reflect some wearout mechanisms that might be seen under environmental conditions. Wire pull testing applies an upward force under the wire, effectively pulling it away from the substrate or die.How to test bonds: How to Wire Pull?April 2016. The purpose of the test is as MIL-STD-883 2011.9 describes it: "To measure bond strengths, evaluate bond strength distributions, or determine compliance with specified bond strength requirements". A wire can be pulled to destruction, but there are also non-destructive variants whereby one tests whether the wire can withstand a certain force. Non-destructive test methods are typically used for 100% testing of safety critical, high quality and high cost products, avoiding damage to the acceptable wired bonds tested. The term wire pull usually refers to the act of pulling a wire with a hook mounted on a pull sensor on a bond tester. However, to promote certain failure modes, wires can be cut and then pulled by tweezers, also mounted on a pull sensor on a bond tester. Usually wires up to 75 μm diameter (3 mil) are classified as thin wire. Beyond that size, we speak about thick wire testing.
See also
* Purple plague (intermetallic) *Kirkendall effect
The Kirkendall effect is the motion of the interface between two metals that occurs due to the difference in diffusion rates of the metal atoms. The effect can be observed, for example, by placing insoluble markers at the interface between a pure m ...
* Ball Bonding
Ball bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a bare silicon die and the lead frame of the package it is placed in during Fabrication (semiconductor), semiconductor device fabrica ...
* Wedge bonding
* Thermosonic Bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoul ...
* Pull off test
References
Resources
Amkor Copper (Cu) Wirebonding
Amkor Silver (Ag) Wirebonding
{{Authority control Semiconductor device fabrication Packaging (microfabrication) Welding Electronics manufacturing Articles containing video clips