spatial light modulator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
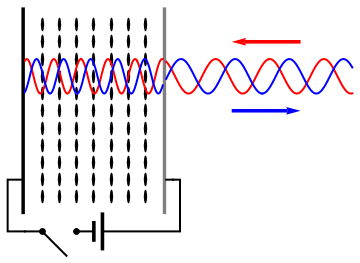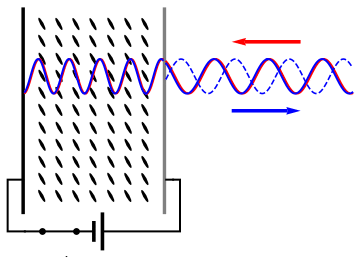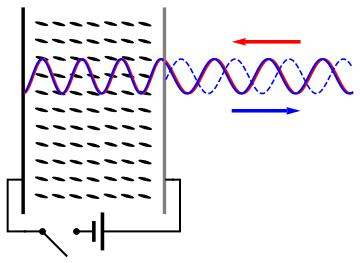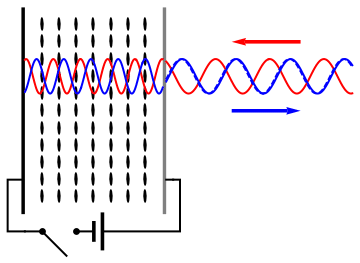 A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the
*Coomber, Stuart D.; Cameron, Colin D.; Hughes, Jonathon R.; Sheerin, David T.; Slinger, Christopher W.; Smith, Mark A.; Stanley, Maurice (
*Slinger, C.; Cameron, C.; Stanley, M.
"Computer-Generated Holography as a Generic Display Technology"
''IEEE Computer'', Volume 38, Issue 8, Aug. 2005, pp 46–53 {{Reflist
9781510613010/10.1117/3.2281295?SSO=1 How to Shape Light with Spatial Light Modulators
SLM ToolBox
A free Windows application for controlling phase-only spatial light modulators.
Phase calibration of a Spatial Light Modulator
Optical components Display technology Optical devices
 A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
* Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, m ...
, phase, or polarization of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
in a spatially varying manner. A simple example is an overhead projector
An overhead projector (often abbreviated to OHP), like a Movie projector, film or slide projector, uses light to Projector, project an enlarged image on a Projection screen, screen, allowing the view of a small document or picture to be shared ...
transparency. Usually when the term SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
.
SLMs are primarily marketed for image projection, displays devices, and maskless lithography. SLMs are also used in optical computing
Optical computing or photonic computing uses light waves produced by lasers or incoherent sources for data processing, data storage or data communication for computing. For decades, photons have shown promise to enable a higher bandwidth than the ...
and holographic optical tweezers.
Usually, an SLM modulates the intensity of the light beam. However, it is also possible to produce devices that modulate the phase of the beam or both the intensity and the phase simultaneously. It is also possible to produce devices that modulate the polarization of the beam, and modulate the polarization, phase, and intensity simultaneously.
SLMs are used extensively in holographic data storage setups to encode information into a laser beam similarly to the way a transparency does for an overhead projector. They can also be used as part of a holographic display technology.
In the 1980s, large SLMs were placed on overhead projectors to project computer monitor contents to the screen. Since then, more modern projectors
A projector or image projector is an optical device that projects an image (or moving images) onto a surface, commonly a projection screen. Most projectors create an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens, but some newer typ ...
have been developed where the SLM is built inside the projector. These are commonly used in meetings for presentations.
Liquid crystal SLMs can help solve problems related to laser microparticle manipulation. In this case spiral beam parameters can be changed dynamically.
Electrically-addressed spatial light modulator (EASLM)
As its name implies, the image on an electrically addressed spatial light modulator is created and changed electronically, as in most electronic displays. EASLMs usually receive input via a conventional interface such as VGA or DVI input. They are available at resolutions up to QXGA (2048 × 1536). Unlike ordinary displays, they are usually much smaller (having an active area of about 2 cm²) as they are not normally meant to be viewed directly. An example of an EASLM is the digital micromirror device (DMD) at the heart of DLP displays or LCoS Displays usingferroelectric
In physics and materials science, ferroelectricity is a characteristic of certain materials that have a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field. All ferroelectrics are also piezoel ...
liquid crystals
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as i ...
( FLCoS) or nematic liquid crystals (electrically controlled birefringence effect).
Spatial light modulators can be either reflective or transmissive depending on their design and purpose.
DMDs, short for digital micromirror devices, are spatial light modulators that specifically work with binary amplitude-only modulation. Each pixel on the SLM can only be in one of two states: "on" or "off". The main purpose of the SLM is to control and adjust the amplitude of the light.
Phase modulation can be achieved using a DMD by using Lee holography techniques, or by using the superpixel method.
Optically-addressed spatial light modulator (OASLM)
The image on an optically addressed spatial light modulator, also known as a light valve, is created and changed by shining light encoded with an image on its front or back surface. A photosensor allows the OASLM to sense the brightness of each pixel and replicate the image usingliquid crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as i ...
s. As long as the OASLM is powered, the image is retained even after the light is extinguished. An electrical signal is used to clear the whole OASLM at once.
They are often used as the second stage of a very-high-resolution display, such as one for a computer-generated holographic display. In a process called active tiling, images displayed on an EASLM are sequentially transferred to different parts on an OASLM, before the whole image on the OASLM is presented to the viewer. As EASLMs can run as fast as 2500 frames per second, it is possible to tile around 100 copies of the image on the EASLM onto an OASLM while still displaying full-motion video on the OASLM. This potentially gives images with resolutions of above 100 megapixels.
Application in ultrafast pulse measuring and shaping
Multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan (MIIPS) is a technique based on the computer-controlled phase scan of a linear-array spatial light modulator. Through the phase scan to an ultrashort pulse, MIIPS can not only characterize but also manipulate the ultrashort pulse to get the needed pulse shape at target spot (such as transform-limited pulse for optimized peak power, and other specific pulse shapes). This technique features with full calibration and control of the ultrashort pulse, with no moving parts, and simple optical setup. Linear array SLMs that use nematic liquid crystal elements are available that can modulate amplitude, phase, or both simultaneously.See also
*Active filters
An active filter is a type of analog circuit implementing an electronic filter using active components, typically an amplifier. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the cost, performance and predictability of a filter.
...
in femtosecond pulse shaping
* Photoelastic modulator
* Waveplate
A waveplate or retarder is an optics, optical device that alters the Polarization (waves), polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the ''half-wave plate'', which rotates the polarization direct ...
References
*Larry J. Hornbeck ( TI), ''Digital Light Processing for High-Brightness, High-Resolution Applications'', 21st century Archive*Coomber, Stuart D.; Cameron, Colin D.; Hughes, Jonathon R.; Sheerin, David T.; Slinger, Christopher W.; Smith, Mark A.; Stanley, Maurice (
QinetiQ
QinetiQ ( as in '' kinetic'') is a British defence technology company headquartered in Farnborough, Hampshire. It operates primarily in the defence, security and critical national infrastructure markets and run testing and evaluation capabili ...
), "Optically addressed spatial light modulators for replaying computer-generated holograms", ''Proc. SPIE
SPIE (formerly the Society of Photographic Instrumentation Engineers, later the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers) is an international not-for-profit professional society for optics and photonics technology, founded in 1955. It ...
'' Vol. '4457', p. 9-19 (2001)
*''Liquid Crystal Optically Addressed Spatial Light Modulator''*Slinger, C.; Cameron, C.; Stanley, M.
"Computer-Generated Holography as a Generic Display Technology"
''IEEE Computer'', Volume 38, Issue 8, Aug. 2005, pp 46–53 {{Reflist
External links
9781510613010/10.1117/3.2281295?SSO=1 How to Shape Light with Spatial Light Modulators
SLM ToolBox
A free Windows application for controlling phase-only spatial light modulators.
Phase calibration of a Spatial Light Modulator
Optical components Display technology Optical devices