copper on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and

 Copper, silver, and gold are in group 11 of the periodic table; these three metals have one s-orbital electron on top of a filled d-
Copper, silver, and gold are in group 11 of the periodic table; these three metals have one s-orbital electron on top of a filled d-

 Copper does not react with water, but it does slowly react with atmospheric oxygen to form a layer of brown-black copper oxide which, unlike the rust that forms on iron in moist air, protects the underlying metal from further corrosion ( passivation). A green layer of verdigris (copper carbonate) can often be seen on old copper structures, such as the roofing of many older buildings and the Statue of Liberty. Copper
Copper does not react with water, but it does slowly react with atmospheric oxygen to form a layer of brown-black copper oxide which, unlike the rust that forms on iron in moist air, protects the underlying metal from further corrosion ( passivation). A green layer of verdigris (copper carbonate) can often be seen on old copper structures, such as the roofing of many older buildings and the Statue of Liberty. Copper
 Copper is produced in massive stars and is present in the Earth's crust in a proportion of about 50 parts per million (ppm). In nature, copper occurs in a variety of minerals, including
Copper is produced in massive stars and is present in the Earth's crust in a proportion of about 50 parts per million (ppm). In nature, copper occurs in a variety of minerals, including
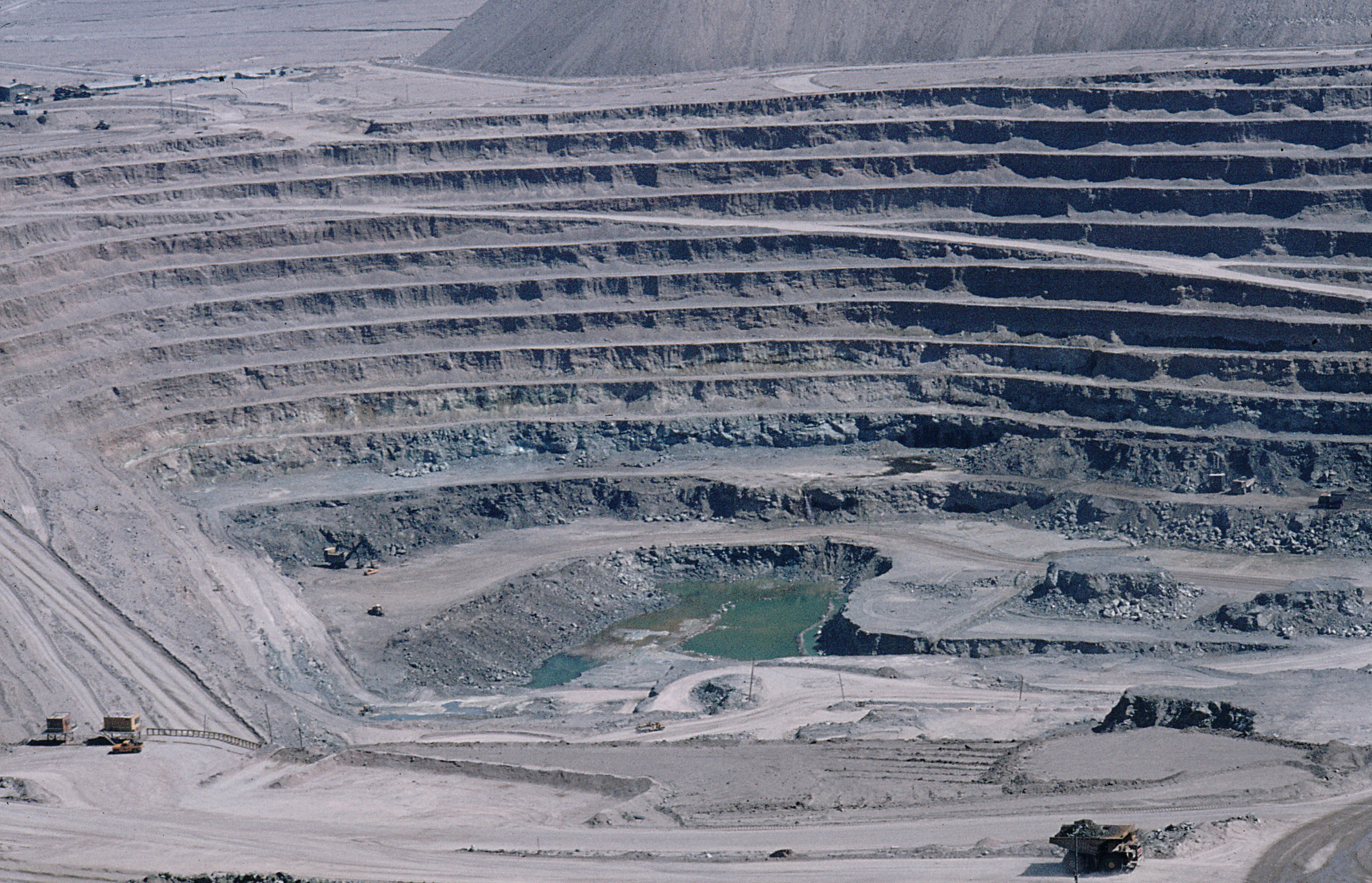

 Most copper is mined or extracted as copper sulfides from large
Most copper is mined or extracted as copper sulfides from large
 Copper has been in use at least 10,000 years, but more than 95% of all copper ever mined and smelted has been extracted since 1900. As with many natural resources, the total amount of copper on Earth is vast, with around 1014 tons in the top kilometer of Earth's crust, which is about 5 million years' worth at the current rate of extraction. However, only a tiny fraction of these reserves is economically viable with present-day prices and technologies. Estimates of copper reserves available for mining vary from 25 to 60 years, depending on core assumptions such as the growth rate. Recycling is a major source of copper in the modern world. Because of these and other factors, the future of copper production and supply is the subject of much debate, including the concept of
Copper has been in use at least 10,000 years, but more than 95% of all copper ever mined and smelted has been extracted since 1900. As with many natural resources, the total amount of copper on Earth is vast, with around 1014 tons in the top kilometer of Earth's crust, which is about 5 million years' worth at the current rate of extraction. However, only a tiny fraction of these reserves is economically viable with present-day prices and technologies. Estimates of copper reserves available for mining vary from 25 to 60 years, depending on core assumptions such as the growth rate. Recycling is a major source of copper in the modern world. Because of these and other factors, the future of copper production and supply is the subject of much debate, including the concept of
 The concentration of copper in ores averages only 0.6%, and most commercial ores are sulfides, especially chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), bornite (Cu5FeS4) and, to a lesser extent, covellite (CuS) and chalcocite (Cu2S). Conversely, the average concentration of copper in polymetallic nodules is estimated at 1.3%. The methods of extracting copper as well as other metals found in these nodules include sulphuric leaching, smelting and an application of the Cuprion process. For minerals found in land ores, they are concentrated from crushed ores to the level of 10–15% copper by
The concentration of copper in ores averages only 0.6%, and most commercial ores are sulfides, especially chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), bornite (Cu5FeS4) and, to a lesser extent, covellite (CuS) and chalcocite (Cu2S). Conversely, the average concentration of copper in polymetallic nodules is estimated at 1.3%. The methods of extracting copper as well as other metals found in these nodules include sulphuric leaching, smelting and an application of the Cuprion process. For minerals found in land ores, they are concentrated from crushed ores to the level of 10–15% copper by
 Numerous copper alloys have been formulated, many with important uses. Brass is an alloy of copper and
Numerous copper alloys have been formulated, many with important uses. Brass is an alloy of copper and
 Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called ''cuprous'' and ''cupric'', respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.
Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called ''cuprous'' and ''cupric'', respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.
 Copper forms coordination complexes with ligands. In aqueous solution, copper(II) exists as . This complex exhibits the fastest water exchange rate (speed of water ligands attaching and detaching) for any transition
Copper forms coordination complexes with ligands. In aqueous solution, copper(II) exists as . This complex exhibits the fastest water exchange rate (speed of water ligands attaching and detaching) for any transition  :Cu2+ + 2 OH− → Cu(OH)2
:Cu2+ + 2 OH− → Cu(OH)2



 Copper occurs naturally as native copper, native metallic copper and was known to some of the oldest civilizations on record. The history of copper use dates to 9000 BC in the Middle East; a copper pendant was found in northern Iraq that dates to 8700 BC. Evidence suggests that gold and meteoric iron (but not smelted iron) were the only metals used by humans before copper. The history of copper metallurgy is thought to follow this sequence: First, cold forming, cold working of native copper, then Annealing (metallurgy), annealing, smelting, and, finally, lost-wax casting. In southeastern Anatolia, all four of these techniques appear more or less simultaneously at the beginning of the Neolithic c. 7500 BC.
Copper smelting was independently invented in different places. It was probably discovered in China before 2800 BC, in Central America around 600 AD, and in West Africa about the 9th or 10th century AD. Investment casting was invented in 4500–4000 BC in Southeast Asia and carbon dating has established mining at Alderley Edge Mines, Alderley Edge in Cheshire, UK, at 2280 to 1890 BC. Ötzi the Iceman, a male dated from 3300 to 3200 BC, was found with an axe with a copper head 99.7% pure; high levels of arsenic in his hair suggest an involvement in copper smelting. Experience with copper has assisted the development of other metals; in particular, copper smelting led to the discovery of bloomery, iron smelting. Production in the Old Copper Complex in Michigan and Wisconsin is dated between 6000 and 3000 BC.Pleger, Thomas C. "A Brief Introduction to the Old Copper Complex of the Western Great Lakes: 4000–1000 BC",
Copper occurs naturally as native copper, native metallic copper and was known to some of the oldest civilizations on record. The history of copper use dates to 9000 BC in the Middle East; a copper pendant was found in northern Iraq that dates to 8700 BC. Evidence suggests that gold and meteoric iron (but not smelted iron) were the only metals used by humans before copper. The history of copper metallurgy is thought to follow this sequence: First, cold forming, cold working of native copper, then Annealing (metallurgy), annealing, smelting, and, finally, lost-wax casting. In southeastern Anatolia, all four of these techniques appear more or less simultaneously at the beginning of the Neolithic c. 7500 BC.
Copper smelting was independently invented in different places. It was probably discovered in China before 2800 BC, in Central America around 600 AD, and in West Africa about the 9th or 10th century AD. Investment casting was invented in 4500–4000 BC in Southeast Asia and carbon dating has established mining at Alderley Edge Mines, Alderley Edge in Cheshire, UK, at 2280 to 1890 BC. Ötzi the Iceman, a male dated from 3300 to 3200 BC, was found with an axe with a copper head 99.7% pure; high levels of arsenic in his hair suggest an involvement in copper smelting. Experience with copper has assisted the development of other metals; in particular, copper smelting led to the discovery of bloomery, iron smelting. Production in the Old Copper Complex in Michigan and Wisconsin is dated between 6000 and 3000 BC.Pleger, Thomas C. "A Brief Introduction to the Old Copper Complex of the Western Great Lakes: 4000–1000 BC",
Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh Annual Meeting of the Forest History Association of Wisconsin
', Oconto, Wisconsin, 5 October 2002, pp. 10–18. Natural bronze, a type of copper made from ores rich in silicon, arsenic, and (rarely) tin, came into general use in the Balkans around 5500 BC.

 In Greece, copper was known by the name (χαλκός). It was an important resource for the Romans, Greeks and other ancient peoples. In Roman times, it was known as ''aes Cyprium'', ''aes'' being the generic Latin term for copper alloys and ''Cyprium'' from Cyprus, where much copper was mined. The phrase was simplified to ''cuprum'', hence the English ''copper''. Aphrodite (Venus (goddess), Venus in Rome) represented copper in mythology and alchemy because of its lustrous beauty and its ancient use in producing mirrors; Cyprus, the source of copper, was sacred to the goddess. The seven heavenly bodies known to the ancients were associated with the seven metals known in antiquity, and Venus was assigned to copper, both because of the connection to the goddess and because Venus was the brightest heavenly body after the Sun and Moon and so corresponded to the most lustrous and desirable metal after gold and silver.
Copper was first mined in ancient Britain as early as 2100 BC. Mining at the largest of these mines, the Great Orme, continued into the late Bronze Age. Mining seems to have been largely restricted to supergene (geology), supergene ores, which were easier to smelt. The rich copper deposits of Cornwall seem to have been largely untouched, in spite of extensive tin mining in the region, for reasons likely social and political rather than technological.
In North America, copper mining began with marginal workings by Native Americans. Native copper is known to have been extracted from sites on Isle Royale with primitive stone tools between 800 and 1600. Copper metallurgy was flourishing in South America, particularly in Peru around 1000 AD. Copper burial ornamentals from the 15th century have been uncovered, but the metal's commercial production did not start until the early 20th century.
The cultural role of copper has been important, particularly in currency. Romans in the 6th through 3rd centuries BC used copper lumps as money. At first, the copper itself was valued, but gradually the shape and look of the copper became more important. Julius Caesar had his own coins made from brass, while Augustus, Octavianus Augustus Caesar's coins were made from Cu-Pb-Sn alloys. With an estimated annual output of around 15,000 t, Roman metallurgy, Roman copper mining and smelting activities reached a scale unsurpassed until the time of the Industrial Revolution; the Roman province, provinces most intensely mined were those of Hispania, Cyprus and in Central Europe.
The gates of the Temple of Jerusalem used Corinthian bronze treated with depletion gilding. The process was most prevalent in Alexandria, where alchemy is thought to have begun. In ancient India, copper was used in the holistic medical science Ayurveda for surgical instruments and other medical equipment. Ancient Egyptians (Old Kingdom, ~2400 BC) used copper for sterilizing wounds and drinking water, and later to treat headaches, burns, and itching.
In Greece, copper was known by the name (χαλκός). It was an important resource for the Romans, Greeks and other ancient peoples. In Roman times, it was known as ''aes Cyprium'', ''aes'' being the generic Latin term for copper alloys and ''Cyprium'' from Cyprus, where much copper was mined. The phrase was simplified to ''cuprum'', hence the English ''copper''. Aphrodite (Venus (goddess), Venus in Rome) represented copper in mythology and alchemy because of its lustrous beauty and its ancient use in producing mirrors; Cyprus, the source of copper, was sacred to the goddess. The seven heavenly bodies known to the ancients were associated with the seven metals known in antiquity, and Venus was assigned to copper, both because of the connection to the goddess and because Venus was the brightest heavenly body after the Sun and Moon and so corresponded to the most lustrous and desirable metal after gold and silver.
Copper was first mined in ancient Britain as early as 2100 BC. Mining at the largest of these mines, the Great Orme, continued into the late Bronze Age. Mining seems to have been largely restricted to supergene (geology), supergene ores, which were easier to smelt. The rich copper deposits of Cornwall seem to have been largely untouched, in spite of extensive tin mining in the region, for reasons likely social and political rather than technological.
In North America, copper mining began with marginal workings by Native Americans. Native copper is known to have been extracted from sites on Isle Royale with primitive stone tools between 800 and 1600. Copper metallurgy was flourishing in South America, particularly in Peru around 1000 AD. Copper burial ornamentals from the 15th century have been uncovered, but the metal's commercial production did not start until the early 20th century.
The cultural role of copper has been important, particularly in currency. Romans in the 6th through 3rd centuries BC used copper lumps as money. At first, the copper itself was valued, but gradually the shape and look of the copper became more important. Julius Caesar had his own coins made from brass, while Augustus, Octavianus Augustus Caesar's coins were made from Cu-Pb-Sn alloys. With an estimated annual output of around 15,000 t, Roman metallurgy, Roman copper mining and smelting activities reached a scale unsurpassed until the time of the Industrial Revolution; the Roman province, provinces most intensely mined were those of Hispania, Cyprus and in Central Europe.
The gates of the Temple of Jerusalem used Corinthian bronze treated with depletion gilding. The process was most prevalent in Alexandria, where alchemy is thought to have begun. In ancient India, copper was used in the holistic medical science Ayurveda for surgical instruments and other medical equipment. Ancient Egyptians (Old Kingdom, ~2400 BC) used copper for sterilizing wounds and drinking water, and later to treat headaches, burns, and itching.


 The Great Copper Mountain was a mine in Falun, Sweden, that operated from the 10th century to 1992. It satisfied two-thirds of Europe's copper consumption in the 17th century and helped fund many of Sweden's wars during that time. It was referred to as the nation's treasury; Sweden had a History of copper currency in Sweden, copper backed currency.
The Great Copper Mountain was a mine in Falun, Sweden, that operated from the 10th century to 1992. It satisfied two-thirds of Europe's copper consumption in the 17th century and helped fund many of Sweden's wars during that time. It was referred to as the nation's treasury; Sweden had a History of copper currency in Sweden, copper backed currency.
 Copper is used in roofing, currency, and for photographic technology known as the daguerreotype. Copper was used in Renaissance sculpture, and was used to construct the Statue of Liberty; copper continues to be used in construction of various types. Copper plating and copper sheathing were widely used to protect the under-water hulls of ships, a technique pioneered by the British Admiralty in the 18th century. The Norddeutsche Affinerie in Hamburg was the first modern electroplating plant, starting its production in 1876. The German scientist Gottfried Osann invented powder metallurgy in 1830 while determining the metal's atomic mass; around then it was discovered that the amount and type of alloying element (e.g., tin) to copper would affect bell tones.
During the rise in demand for copper for the Age of Electricity, from the 1880s until the Great Depression of the 1930s, the United States produced one third to half the world's newly mined copper. Major districts included the Keweenaw district of northern Michigan, primarily native copper deposits, which was eclipsed by the vast sulphide deposits of Butte, Montana in the late 1880s, which itself was eclipsed by porphyry deposits of the Souhwest United States, especially at Bingham Canyon, Utah and Morenci, Arizona. Introduction of open pit steam shovel mining and innovations in smelting, refining, flotation concentration and other processing steps led to mass production. Early in the twentieth century, Arizona ranked first, followed by Montana, then Utah and Michigan.
Flash smelting was developed by Outokumpu in Finland and first applied at Harjavalta in 1949; the energy-efficient process accounts for 50% of the world's primary copper production.
The Intergovernmental Council of Copper Exporting Countries, formed in 1967 by Chile, Peru, Zaire and Zambia, operated in the copper market as OPEC does in oil, though it never achieved the same influence, particularly because the second-largest producer, the United States, was never a member; it was dissolved in 1988.
Copper is used in roofing, currency, and for photographic technology known as the daguerreotype. Copper was used in Renaissance sculpture, and was used to construct the Statue of Liberty; copper continues to be used in construction of various types. Copper plating and copper sheathing were widely used to protect the under-water hulls of ships, a technique pioneered by the British Admiralty in the 18th century. The Norddeutsche Affinerie in Hamburg was the first modern electroplating plant, starting its production in 1876. The German scientist Gottfried Osann invented powder metallurgy in 1830 while determining the metal's atomic mass; around then it was discovered that the amount and type of alloying element (e.g., tin) to copper would affect bell tones.
During the rise in demand for copper for the Age of Electricity, from the 1880s until the Great Depression of the 1930s, the United States produced one third to half the world's newly mined copper. Major districts included the Keweenaw district of northern Michigan, primarily native copper deposits, which was eclipsed by the vast sulphide deposits of Butte, Montana in the late 1880s, which itself was eclipsed by porphyry deposits of the Souhwest United States, especially at Bingham Canyon, Utah and Morenci, Arizona. Introduction of open pit steam shovel mining and innovations in smelting, refining, flotation concentration and other processing steps led to mass production. Early in the twentieth century, Arizona ranked first, followed by Montana, then Utah and Michigan.
Flash smelting was developed by Outokumpu in Finland and first applied at Harjavalta in 1949; the energy-efficient process accounts for 50% of the world's primary copper production.
The Intergovernmental Council of Copper Exporting Countries, formed in 1967 by Chile, Peru, Zaire and Zambia, operated in the copper market as OPEC does in oil, though it never achieved the same influence, particularly because the second-largest producer, the United States, was never a member; it was dissolved in 1988.
 The major applications of copper are electrical wire (60%), roofing and plumbing (20%), and industrial machinery (15%). Copper is used mostly as a pure metal, but when greater hardness is required, it is put into such alloys as brass and bronze (5% of total use). For more than two centuries, copper paint has been used on boat hulls to control the growth of plants and shellfish. A small part of the copper supply is used for nutritional supplements and fungicides in agriculture. Machining of copper is possible, although alloys are preferred for good machinability in creating intricate parts.
The major applications of copper are electrical wire (60%), roofing and plumbing (20%), and industrial machinery (15%). Copper is used mostly as a pure metal, but when greater hardness is required, it is put into such alloys as brass and bronze (5% of total use). For more than two centuries, copper paint has been used on boat hulls to control the growth of plants and shellfish. A small part of the copper supply is used for nutritional supplements and fungicides in agriculture. Machining of copper is possible, although alloys are preferred for good machinability in creating intricate parts.
 Integrated circuits and printed circuit boards increasingly feature copper in place of aluminium because of its superior electrical conductivity; heat sinks and heat exchangers use copper because of its superior heat dissipation properties. Electromagnets, vacuum tubes, cathode ray tubes, and magnetrons in microwave ovens use copper, as do waveguides for microwave radiation.
Integrated circuits and printed circuit boards increasingly feature copper in place of aluminium because of its superior electrical conductivity; heat sinks and heat exchangers use copper because of its superior heat dissipation properties. Electromagnets, vacuum tubes, cathode ray tubes, and magnetrons in microwave ovens use copper, as do waveguides for microwave radiation.


 Copper has been used since ancient times as a durable, corrosion resistance, corrosion resistant, and weatherproof architectural material. Roofing material, Roofs, flashing (weatherproofing), flashings, rain gutters, downspouts, domes, spires, vaults, and doors have been made from copper for hundreds or thousands of years. Copper's architectural use has been expanded in modern times to include interior and exterior Copper in architecture#Wall cladding, wall cladding, building expansion joints, RF shielding, radio frequency shielding, and Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces, antimicrobial and decorative indoor products such as attractive handrails, bathroom fixtures, and counter tops. Some of copper's other important benefits as an architectural material include low thermal expansion, thermal movement, light weight, lightning rod, lightning protection, and recyclability
The metal's distinctive natural green patina has long been coveted by architects and designers. The final patina is a particularly durable layer that is highly resistant to atmospheric corrosion, thereby protecting the underlying metal against further weathering. It can be a mixture of carbonate and sulfate compounds in various amounts, depending upon environmental conditions such as sulfur-containing acid rain. Architectural copper and its alloys can also be Copper in architecture#Finishes, 'finished' to take on a particular look, feel, or color. Finishes include mechanical surface treatments, chemical coloring, and coatings.
Copper has excellent brazing and soldering properties and can be welded; the best results are obtained with gas metal arc welding.
Copper has been used since ancient times as a durable, corrosion resistance, corrosion resistant, and weatherproof architectural material. Roofing material, Roofs, flashing (weatherproofing), flashings, rain gutters, downspouts, domes, spires, vaults, and doors have been made from copper for hundreds or thousands of years. Copper's architectural use has been expanded in modern times to include interior and exterior Copper in architecture#Wall cladding, wall cladding, building expansion joints, RF shielding, radio frequency shielding, and Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces, antimicrobial and decorative indoor products such as attractive handrails, bathroom fixtures, and counter tops. Some of copper's other important benefits as an architectural material include low thermal expansion, thermal movement, light weight, lightning rod, lightning protection, and recyclability
The metal's distinctive natural green patina has long been coveted by architects and designers. The final patina is a particularly durable layer that is highly resistant to atmospheric corrosion, thereby protecting the underlying metal against further weathering. It can be a mixture of carbonate and sulfate compounds in various amounts, depending upon environmental conditions such as sulfur-containing acid rain. Architectural copper and its alloys can also be Copper in architecture#Finishes, 'finished' to take on a particular look, feel, or color. Finishes include mechanical surface treatments, chemical coloring, and coatings.
Copper has excellent brazing and soldering properties and can be welded; the best results are obtained with gas metal arc welding.
. Copper Touch Surfaces. Retrieved on 8 November 2011. Indians have been using copper vessels since ancient times for storing water, even before modern science realized its antimicrobial properties. Some copper alloys were proven to kill more than 99.9% of disease-causing bacteria within just two hours when cleaned regularly. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has approved the registrations of these copper alloys as "antimicrobial materials with public health benefits"; that approval allows manufacturers to make legal claims to the public health benefits of products made of registered alloys. In addition, the EPA has approved a long list of antimicrobial copper products made from these alloys, such as bedrails, handrails, over-bed tables, sinks, faucets, door knobs, toilet hardware, computer keyboards, health club equipment, and shopping cart handles (for a comprehensive list, see: Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces#Approved products). Copper doorknobs are used by hospitals to reduce the transfer of disease, and Legionnaires' disease is suppressed by copper tubing in plumbing systems. Antimicrobial copper alloy products are now being installed in healthcare facilities in the U.K., Ireland, Japan, Korea, France, Denmark, and Brazil, as well as being called for in the US, and in the subway transit system in Santiago, Chile, where copper-zinc alloy handrails were installed in some 30 stations between 2011 and 2014. Textile fibers can be blended with copper to create antimicrobial protective fabrics.

 A unique tetranuclear copper center has been found in nitrous-oxide reductase.
Chemical compounds which were developed for treatment of Wilson's disease have been investigated for use in cancer therapy.
A unique tetranuclear copper center has been found in nitrous-oxide reductase.
Chemical compounds which were developed for treatment of Wilson's disease have been investigated for use in cancer therapy.
Material: Copper (Cu), bulk
MEMS and Nanotechnology Clearinghouse. *
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Copper and compounds fact sheet
from the National Pollutant Inventory of Australia
Copper.org
– official website of the Copper Development Association with an extensive site of properties and uses of copper
Price history of copper, according to the IMF
{{good article Copper, Chemical elements Transition metals Dietary minerals Electrical conductors Cubic minerals Crystals in space group 225 Native element minerals Symbols of Arizona Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure
ductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
metal with very high thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver
Sterling silver is an alloy of silver containing 92.5% by weight of silver and 7.5% by weight of other metals, usually copper. The sterling silver standard has a minimum millesimal fineness of 925.
'' Fine silver'', which is 99.9% pure silver, i ...
used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement.
Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. 3500 BC.
In the Roman era, copper was mined principally on Cyprus, the origin of the name of the metal, from ''aes cyprium'' (metal of Cyprus), later corrupted to ''cuprum'' (Latin). ''Coper'' (Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
) and ''copper'' were derived from this, the later spelling first used around 1530.
Commonly encountered compounds are copper(II) salts, which often impart blue or green colors to such minerals as azurite, malachite, and turquoise, and have been used widely and historically as pigments.
Copper used in buildings, usually for roofing, oxidizes to form a green verdigris (or patina). Copper is sometimes used in decorative art, both in its elemental metal form and in compounds as pigments. Copper compounds are used as bacteriostatic agents, fungicides, and wood preservatives.
Copper is essential to all living organisms as a trace dietary mineral because it is a key constituent of the respiratory enzyme complex cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV, (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and mitochondria of eukaryotes.
It is the last enzyme in the respiratory elect ...
. In molluscs
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ...
and crustaceans, copper is a constituent of the blood pigment hemocyanin, replaced by the iron-complexed hemoglobin in fish and other vertebrates. In humans, copper is found mainly in the liver, muscle, and bone. The adult body contains between 1.4 and 2.1 mg of copper per kilogram of body weight.
Characteristics
Physical
 Copper, silver, and gold are in group 11 of the periodic table; these three metals have one s-orbital electron on top of a filled d-
Copper, silver, and gold are in group 11 of the periodic table; these three metals have one s-orbital electron on top of a filled d-electron shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or ...
and are characterized by high ductility, and electrical and thermal conductivity. The filled d-shells in these elements contribute little to interatomic interactions, which are dominated by the s-electrons through metallic bond
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be des ...
s. Unlike metals with incomplete d-shells, metallic bonds in copper are lacking a covalent character and are relatively weak. This observation explains the low hardness and high ductility of single crystals of copper. At the macroscopic scale, introduction of extended defects to the crystal lattice, such as grain boundaries, hinders flow of the material under applied stress, thereby increasing its hardness. For this reason, copper is usually supplied in a fine-grained polycrystalline
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
form, which has greater strength than monocrystalline forms.
The softness of copper partly explains its high electrical conductivity () and high thermal conductivity, second highest (second only to silver) among pure metals at room temperature. This is because the resistivity to electron transport in metals at room temperature originates primarily from scattering of electrons on thermal vibrations of the lattice, which are relatively weak in a soft metal. The maximum permissible current density of copper in open air is approximately of cross-sectional area, above which it begins to heat excessively.
Copper is one of a few metallic elements with a natural color other than gray or silver. Pure copper is orange-red and acquires a reddish tarnish
Tarnish is a thin layer of corrosion that forms over copper, brass, aluminum, magnesium, neodymium and other similar metals as their outermost layer undergoes a chemical reaction. Tarnish does not always result from the sole effects of oxygen in ...
when exposed to air. The characteristic color of copper results from the electronic transitions between the filled 3d and half-empty 4s atomic shells – the energy difference between these shells corresponds to orange light.
As with other metals, if copper is put in contact with another metal, galvanic corrosion will occur.
Chemical
 Copper does not react with water, but it does slowly react with atmospheric oxygen to form a layer of brown-black copper oxide which, unlike the rust that forms on iron in moist air, protects the underlying metal from further corrosion ( passivation). A green layer of verdigris (copper carbonate) can often be seen on old copper structures, such as the roofing of many older buildings and the Statue of Liberty. Copper
Copper does not react with water, but it does slowly react with atmospheric oxygen to form a layer of brown-black copper oxide which, unlike the rust that forms on iron in moist air, protects the underlying metal from further corrosion ( passivation). A green layer of verdigris (copper carbonate) can often be seen on old copper structures, such as the roofing of many older buildings and the Statue of Liberty. Copper tarnish
Tarnish is a thin layer of corrosion that forms over copper, brass, aluminum, magnesium, neodymium and other similar metals as their outermost layer undergoes a chemical reaction. Tarnish does not always result from the sole effects of oxygen in ...
es when exposed to some sulfur compounds, with which it reacts to form various copper sulfide
Copper sulfides describe a family of chemical compounds and minerals with the formula CuxSy. Both minerals and synthetic materials comprise these compounds. Some copper sulfides are economically important ores.
Prominent copper sulfide mineral ...
s.
Isotopes
There are 29isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numb ...
s of copper. and are stable, with comprising approximately 69% of naturally occurring copper; both have a spin of . The other isotopes are radioactive, with the most stable being with a half-life of 61.83 hours. Seven metastable isotopes have been characterized; is the longest-lived with a half-life of 3.8 minutes. Isotopes with a mass number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word ''Atomgewicht'' tomic weight, also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approxima ...
above 64 decay by β−, whereas those with a mass number below 64 decay by β+. , which has a half-life of 12.7 hours, decays both ways.
and have significant applications. is used in Cu-PTSM as a radioactive tracer for positron emission tomography.
Occurrence
 Copper is produced in massive stars and is present in the Earth's crust in a proportion of about 50 parts per million (ppm). In nature, copper occurs in a variety of minerals, including
Copper is produced in massive stars and is present in the Earth's crust in a proportion of about 50 parts per million (ppm). In nature, copper occurs in a variety of minerals, including native copper
Native copper is an uncombined form of copper that occurs as a natural mineral. Copper is one of the few metallic elements to occur in native form, although it most commonly occurs in oxidized states and mixed with other elements. Native coppe ...
, copper sulfides such as chalcopyrite
Chalcopyrite ( ) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mo ...
, bornite, digenite, covellite
Covellite (also known as covelline) is a rare copper sulfide mineral with the formula CuS. This indigo blue mineral is commonly a secondary mineral in limited abundance and although it is not an important ore of copper itself, it is well known t ...
, and chalcocite, copper sulfosalts such as tetrahedite-tennantite, and enargite, copper carbonates such as azurite and malachite, and as copper(I) or copper(II) oxides such as cuprite and tenorite, respectively. The largest mass of elemental copper discovered weighed 420 tonnes and was found in 1857 on the Keweenaw Peninsula in Michigan, US. Native copper is a polycrystal
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
, with the largest single crystal ever described measuring . Copper is the 25th most abundant element in Earth's crust, representing 50 ppm compared with 75 ppm for zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, and 14 ppm for lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
.
Typical background concentrations of copper do not exceed in the atmosphere; in soil; in vegetation; 2 μg/L in freshwater and in seawater.
Production

open pit mine
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow.
This form of mining ...
s in porphyry copper
Porphyry copper deposits are copper ore bodies that are formed from hydrothermal fluids that originate from a voluminous magma chamber several kilometers below the deposit itself. Predating or associated with those fluids are vertical dikes of ...
deposits that contain 0.4 to 1.0% copper. Sites include Chuquicamata, in Chile, Bingham Canyon Mine
The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest m ...
, in Utah, United States, and El Chino Mine, in New Mexico, United States. According to the British Geological Survey, in 2005, Chile was the top producer of copper with at least one-third of the world share followed by the United States, Indonesia and Peru. Copper can also be recovered through the in-situ leach
In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, ''in situ''. In situ leach works by artificially disso ...
process. Several sites in the state of Arizona are considered prime candidates for this method. The amount of copper in use is increasing and the quantity available is barely sufficient to allow all countries to reach developed world levels of usage. An alternative source of copper for collection currently being researched are polymetallic nodules, which are located at the depths of the Pacific Ocean approximately 3000–6500 meters below sea level. These nodules contain other valuable metals such as cobalt and nickel.
Reserves and prices
 Copper has been in use at least 10,000 years, but more than 95% of all copper ever mined and smelted has been extracted since 1900. As with many natural resources, the total amount of copper on Earth is vast, with around 1014 tons in the top kilometer of Earth's crust, which is about 5 million years' worth at the current rate of extraction. However, only a tiny fraction of these reserves is economically viable with present-day prices and technologies. Estimates of copper reserves available for mining vary from 25 to 60 years, depending on core assumptions such as the growth rate. Recycling is a major source of copper in the modern world. Because of these and other factors, the future of copper production and supply is the subject of much debate, including the concept of
Copper has been in use at least 10,000 years, but more than 95% of all copper ever mined and smelted has been extracted since 1900. As with many natural resources, the total amount of copper on Earth is vast, with around 1014 tons in the top kilometer of Earth's crust, which is about 5 million years' worth at the current rate of extraction. However, only a tiny fraction of these reserves is economically viable with present-day prices and technologies. Estimates of copper reserves available for mining vary from 25 to 60 years, depending on core assumptions such as the growth rate. Recycling is a major source of copper in the modern world. Because of these and other factors, the future of copper production and supply is the subject of much debate, including the concept of peak copper
Peak copper is the point in time at which the maximum global copper production rate is reached. Since copper is a finite resource, at some point in the future new production from mining will diminish, and at some earlier time production will rea ...
, analogous to peak oil
Peak oil is the hypothetical point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production is reached, after which it is argued that production will begin an irreversible decline. It is related to the distinct concept of oil depletion; whil ...
.
The price of copper has historically been unstable, and its price increased from the 60-year low of US$0.60/lb (US$1.32/kg) in June 1999 to $3.75 per pound ($8.27/kg) in May 2006. It dropped to $2.40/lb ($5.29/kg) in February 2007, then rebounded to $3.50/lb ($7.71/kg) in April 2007. In February 2009, weakening global demand and a steep fall in commodity prices since the previous year's highs left copper prices at $1.51/lb ($3.32/kg). Between September 2010 and February 2011, the price of copper rose from £5,000 a metric ton to £6,250 a metric ton.
Methods
froth flotation
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, wher ...
or bioleaching
Bioleaching is the extraction of metals from their ores through the use of living organisms. This is much cleaner than the traditional heap leaching using cyanide. Bioleaching is one of several applications within biohydrometallurgy and several ...
. Heating this material with silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
in flash smelting removes much of the iron as slag. The process exploits the greater ease of converting iron sulfides into oxides, which in turn react with the silica to form the silicate slag that floats on top of the heated mass. The resulting ''copper matte,'' consisting of Cu2S, is roasted to convert the sulfides into oxides:
:2 Cu2S + 3 O2 → 2 Cu2O + 2 SO2
The cuprous oxide reacts with cuprous sulfide to converted to ''blister'' copper upon heating:
:2 Cu2O + Cu2S → 6 Cu + 2 SO2
The Sudbury matte process converted only half the sulfide to oxide and then used this oxide to remove the rest of the sulfur as oxide. It was then electrolytically refined and the anode mud exploited for the platinum and gold it contained. This step exploits the relatively easy reduction of copper oxides to copper metal. Natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
is blown across the blister to remove most of the remaining oxygen and electrorefining is performed on the resulting material to produce pure copper:
:Cu2+ + 2 e− → Cu
Recycling
Like aluminium, copper is recyclable without any loss of quality, both from raw state and from manufactured products. In volume, copper is the third most recycled metal after iron and aluminium. An estimated 80% of all copper ever mined is still in use today. According to the International Resource Panel's Metal Stocks in Society report, the global per capita stock of copper in use in society is 35–55 kg. Much of this is in more-developed countries (140–300 kg per capita) rather than less-developed countries (30–40 kg per capita). The process of recycling copper is roughly the same as is used to extract copper but requires fewer steps. High-purity scrap copper is melted in a furnace and then reduced and cast into billets andingot
An ingot is a piece of relatively pure material, usually metal, that is cast into a shape suitable for further processing. In steelmaking, it is the first step among semi-finished casting products. Ingots usually require a second procedure of sha ...
s; lower-purity scrap is refined by electroplating in a bath of sulfuric acid.
Alloys
 Numerous copper alloys have been formulated, many with important uses. Brass is an alloy of copper and
Numerous copper alloys have been formulated, many with important uses. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
. Bronze usually refers to copper- tin alloys, but can refer to any alloy of copper such as aluminium bronze
Aluminium bronze is a type of bronze in which aluminium is the main alloying metal added to copper, in contrast to standard bronze (copper and tin) or brass (copper and zinc). A variety of aluminium bronzes of differing compositions have found in ...
. Copper is one of the most important constituents of silver and karat
The fineness of a precious metal object (coin, bar, jewelry, etc.) represents the weight of ''fine metal'' therein, in proportion to the total weight which includes alloying base metals and any impurities. Alloy metals are added to increase hardne ...
gold solders used in the jewelry industry, modifying the color, hardness and melting point of the resulting alloys. Some lead-free solders consist of tin alloyed with a small proportion of copper and other metals.
The alloy of copper and nickel, called cupronickel, is used in low-denomination coins, often for the outer cladding. The US five-cent coin (currently called a ''nickel'') consists of 75% copper and 25% nickel in homogeneous composition. Prior to the introduction of cupronickel, which was widely adopted by countries in the latter half of the 20th century, alloys of copper and silver were also used, with the United States using an alloy of 90% silver and 10% copper until 1965, when circulating silver was removed from all coins with the exception of the Half dollar - these were debased to an alloy of 40% silver and 60% copper between 1965 and 1970. The alloy of 90% copper and 10% nickel, remarkable for its resistance to corrosion, is used for various objects exposed to seawater, though it is vulnerable to the sulfides sometimes found in polluted harbors and estuaries. Alloys of copper with aluminium (about 7%) have a golden color and are used in decorations. ''Shakudō
''Shakudō'' (赤銅) is a Japanese billon of gold and copper (typically 4–10% gold, 96–90% copper), one of the '' irogane'' class of colored metals, which can be treated to develop a black, or sometimes indigo, patina, resembling lacquer. ...
'' is a Japanese decorative alloy of copper containing a low percentage of gold, typically 4–10%, that can be patinated to a dark blue or black color.
Compounds
 Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called ''cuprous'' and ''cupric'', respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.
Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called ''cuprous'' and ''cupric'', respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.
Binary compounds
As with other elements, the simplest compounds of copper are binary compounds, i.e. those containing only two elements, the principal examples being oxides, sulfides, and halides. Bothcuprous
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish- ...
and cupric oxides are known. Among the numerous copper sulfide
Copper sulfides describe a family of chemical compounds and minerals with the formula CuxSy. Both minerals and synthetic materials comprise these compounds. Some copper sulfides are economically important ores.
Prominent copper sulfide mineral ...
s, important examples include copper(I) sulfide
Copper(I) sulfide is a copper sulfide, a chemical compound of copper and sulfur. It has the chemical compound Cu2S. It is found in nature as the mineral chalcocite. It has a narrow range of stoichiometry ranging from Cu1.997S to Cu2.000S.
Prepara ...
and copper(II) sulfide.
Cuprous halides with fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are known, as are cupric halides with fluorine, chlorine, and bromine. Attempts to prepare copper(II) iodide yield only copper(I) iodide and iodine.
:2 Cu2+ + 4 I− → 2 CuI + I2
Coordination chemistry
 Copper forms coordination complexes with ligands. In aqueous solution, copper(II) exists as . This complex exhibits the fastest water exchange rate (speed of water ligands attaching and detaching) for any transition
Copper forms coordination complexes with ligands. In aqueous solution, copper(II) exists as . This complex exhibits the fastest water exchange rate (speed of water ligands attaching and detaching) for any transition metal aquo complex
In chemistry, metal aquo complexes are coordination compounds containing metal ions with only water as a ligand. These complexes are the predominant species in aqueous solutions of many metal salts, such as metal nitrates, sulfates, and perchlorat ...
. Adding aqueous sodium hydroxide causes the precipitation of light blue solid copper(II) hydroxide. A simplified equation is: Aqueous ammonia
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although ...
results in the same precipitate. Upon adding excess ammonia, the precipitate dissolves, forming tetraamminecopper(II):
: + 4 NH3 → + 2 H2O + 2 OH−
Many other oxyanion An oxyanion, or oxoanion, is an ion with the generic formula (where A represents a chemical element and O represents an oxygen atom). Oxyanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxyanions are determine ...
s form complexes; these include copper(II) acetate
Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is availab ...
, copper(II) nitrate
Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu( NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hy ...
, and copper(II) carbonate. Copper(II) sulfate forms a blue crystalline penta hydrate, the most familiar copper compound in the laboratory. It is used in a fungicide called the Bordeaux mixture.

Polyol
In organic chemistry, a polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups (). The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, thr ...
s, compounds containing more than one alcohol functional group, generally interact with cupric salts. For example, copper salts are used to test for reducing sugars. Specifically, using Benedict's reagent
Benedict's reagent (often called Benedict's qualitative solution or Benedict's solution) is a chemical reagent and complex mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. It is often used in place of Fehling's ...
and Fehling's solution
In organic chemistry, Fehling's solution is a chemical reagent used to differentiate between water-soluble carbohydrate and ketone () functional groups, and as a test for reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars, supplementary to the Tollens' reag ...
the presence of the sugar is signaled by a color change from blue Cu(II) to reddish copper(I) oxide. Schweizer's reagent and related complexes with ethylenediamine and other amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element wi ...
s dissolve cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
. Amino acids form very stable chelate complex
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
es with copper(II). including in the form of metal-organic biohybrids (MOBs). Many wet-chemical tests for copper ions exist, one involving potassium ferrocyanide, which gives a brown precipitate with copper(II) salts.
Organocopper chemistry
Compounds that contain a carbon-copper bond are known as organocopper compounds. They are very reactive towards oxygen to form copper(I) oxide and have many uses in chemistry. They are synthesized by treating copper(I) compounds withGrignard reagents
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . ...
, terminal alkynes or organolithium reagents; in particular, the last reaction described produces a Gilman reagent
A Gilman reagent is a lithium and copper ( diorganocopper) reagent compound, R2CuLi, where R is an alkyl or aryl. These reagents are useful because, unlike related Grignard reagents and organolithium reagents, they react with organic halides to ...
. These can undergo substitution with alkyl halides
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely us ...
to form coupling products; as such, they are important in the field of organic synthesis. Copper(I) acetylide
Copper(I) acetylide, or cuprous acetylide, is a chemical compound with the formula Cu2 C2. Although never characterized by X-ray crystallography, the material has been claimed at least since 1856. One form is claimed to be a monohydrate with for ...
is highly shock-sensitive but is an intermediate in reactions such as the Cadiot-Chodkiewicz coupling and the Sonogashira coupling. Conjugate addition
Nucleophilic conjugate addition is a type of organic reaction. Ordinary nucleophilic additions or 1,2-nucleophilic additions deal mostly with additions to carbonyl compounds. Simple alkene compounds do not show 1,2 reactivity due to lack of polari ...
to enones and carbocupration of alkynes can also be achieved with organocopper compounds. Copper(I) forms a variety of weak complexes with alkenes and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
, especially in the presence of amine ligands.
Copper(III) and copper(IV)
Copper(III) is most often found in oxides. A simple example is potassiumcuprate
Cuprate loosely refers to a material that can be viewed as containing anionic copper complexes. Examples include tetrachloridocuprate ( uCl4sup>2−), the superconductor YBa2Cu3O7, and the organocuprates (e.g., dimethylcuprate u(CH3)2sup>� ...
, KCuO2, a blue-black solid. The most extensively studied copper(III) compounds are the cuprate superconductor
Cuprate superconductors are a family of high-temperature superconducting materials made of layers of copper oxides (CuO2) alternating with layers of other metal oxides, which act as charge reservoirs. At ambient pressure, cuprate superconductors ...
s. Yttrium barium copper oxide
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen ...
(YBa2Cu3O7) consists of both Cu(II) and Cu(III) centres. Like oxide, fluoride is a highly basic anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
and is known to stabilize metal ions in high oxidation states. Both copper(III) and even copper(IV) fluorides are known, K3CuF6 and Cs2CuF6, respectively.
Some copper proteins form oxo complexes, which also feature copper(III). With tetrapeptide
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in p ...
s, purple-colored copper(III) complexes are stabilized by the deprotonated amide ligands.
Complexes of copper(III) are also found as intermediates in reactions of organocopper compounds. For example, in the Kharasch–Sosnovsky reaction.
History
A timeline of copper illustrates how this metal has advanced human civilization for the past 11,000 years.Prehistoric
Copper Age


 Copper occurs naturally as native copper, native metallic copper and was known to some of the oldest civilizations on record. The history of copper use dates to 9000 BC in the Middle East; a copper pendant was found in northern Iraq that dates to 8700 BC. Evidence suggests that gold and meteoric iron (but not smelted iron) were the only metals used by humans before copper. The history of copper metallurgy is thought to follow this sequence: First, cold forming, cold working of native copper, then Annealing (metallurgy), annealing, smelting, and, finally, lost-wax casting. In southeastern Anatolia, all four of these techniques appear more or less simultaneously at the beginning of the Neolithic c. 7500 BC.
Copper smelting was independently invented in different places. It was probably discovered in China before 2800 BC, in Central America around 600 AD, and in West Africa about the 9th or 10th century AD. Investment casting was invented in 4500–4000 BC in Southeast Asia and carbon dating has established mining at Alderley Edge Mines, Alderley Edge in Cheshire, UK, at 2280 to 1890 BC. Ötzi the Iceman, a male dated from 3300 to 3200 BC, was found with an axe with a copper head 99.7% pure; high levels of arsenic in his hair suggest an involvement in copper smelting. Experience with copper has assisted the development of other metals; in particular, copper smelting led to the discovery of bloomery, iron smelting. Production in the Old Copper Complex in Michigan and Wisconsin is dated between 6000 and 3000 BC.Pleger, Thomas C. "A Brief Introduction to the Old Copper Complex of the Western Great Lakes: 4000–1000 BC",
Copper occurs naturally as native copper, native metallic copper and was known to some of the oldest civilizations on record. The history of copper use dates to 9000 BC in the Middle East; a copper pendant was found in northern Iraq that dates to 8700 BC. Evidence suggests that gold and meteoric iron (but not smelted iron) were the only metals used by humans before copper. The history of copper metallurgy is thought to follow this sequence: First, cold forming, cold working of native copper, then Annealing (metallurgy), annealing, smelting, and, finally, lost-wax casting. In southeastern Anatolia, all four of these techniques appear more or less simultaneously at the beginning of the Neolithic c. 7500 BC.
Copper smelting was independently invented in different places. It was probably discovered in China before 2800 BC, in Central America around 600 AD, and in West Africa about the 9th or 10th century AD. Investment casting was invented in 4500–4000 BC in Southeast Asia and carbon dating has established mining at Alderley Edge Mines, Alderley Edge in Cheshire, UK, at 2280 to 1890 BC. Ötzi the Iceman, a male dated from 3300 to 3200 BC, was found with an axe with a copper head 99.7% pure; high levels of arsenic in his hair suggest an involvement in copper smelting. Experience with copper has assisted the development of other metals; in particular, copper smelting led to the discovery of bloomery, iron smelting. Production in the Old Copper Complex in Michigan and Wisconsin is dated between 6000 and 3000 BC.Pleger, Thomas C. "A Brief Introduction to the Old Copper Complex of the Western Great Lakes: 4000–1000 BC", Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh Annual Meeting of the Forest History Association of Wisconsin
', Oconto, Wisconsin, 5 October 2002, pp. 10–18. Natural bronze, a type of copper made from ores rich in silicon, arsenic, and (rarely) tin, came into general use in the Balkans around 5500 BC.
Bronze Age
Alloying copper with tin to make bronze was first practiced about 4000 years after the discovery of copper smelting, and about 2000 years after "natural bronze" had come into general use. Bronze artifacts from the Vinča culture date to 4500 BC. Sumerian and Ancient Egypt, Egyptian artifacts of copper and bronze alloys date to 3000 BC. The Bronze Age began in Southeastern Europe around 3700–3300 BC, in Northwestern Europe about 2500 BC. It ended with the beginning of the Iron Age, 2000–1000 BC in the Near East, and 600 BC in Northern Europe. The transition between the Neolithic period and the Bronze Age was formerly termed the Chalcolithic period (copper-stone), when copper tools were used with stone tools. The term has gradually fallen out of favor because in some parts of the world, the Chalcolithic and Neolithic are coterminous at both ends. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is of much more recent origin. It was known to the Greeks, but became a significant supplement to bronze during the Roman Empire.Ancient and post-classical

Modern

 The Great Copper Mountain was a mine in Falun, Sweden, that operated from the 10th century to 1992. It satisfied two-thirds of Europe's copper consumption in the 17th century and helped fund many of Sweden's wars during that time. It was referred to as the nation's treasury; Sweden had a History of copper currency in Sweden, copper backed currency.
The Great Copper Mountain was a mine in Falun, Sweden, that operated from the 10th century to 1992. It satisfied two-thirds of Europe's copper consumption in the 17th century and helped fund many of Sweden's wars during that time. It was referred to as the nation's treasury; Sweden had a History of copper currency in Sweden, copper backed currency.
 Copper is used in roofing, currency, and for photographic technology known as the daguerreotype. Copper was used in Renaissance sculpture, and was used to construct the Statue of Liberty; copper continues to be used in construction of various types. Copper plating and copper sheathing were widely used to protect the under-water hulls of ships, a technique pioneered by the British Admiralty in the 18th century. The Norddeutsche Affinerie in Hamburg was the first modern electroplating plant, starting its production in 1876. The German scientist Gottfried Osann invented powder metallurgy in 1830 while determining the metal's atomic mass; around then it was discovered that the amount and type of alloying element (e.g., tin) to copper would affect bell tones.
During the rise in demand for copper for the Age of Electricity, from the 1880s until the Great Depression of the 1930s, the United States produced one third to half the world's newly mined copper. Major districts included the Keweenaw district of northern Michigan, primarily native copper deposits, which was eclipsed by the vast sulphide deposits of Butte, Montana in the late 1880s, which itself was eclipsed by porphyry deposits of the Souhwest United States, especially at Bingham Canyon, Utah and Morenci, Arizona. Introduction of open pit steam shovel mining and innovations in smelting, refining, flotation concentration and other processing steps led to mass production. Early in the twentieth century, Arizona ranked first, followed by Montana, then Utah and Michigan.
Flash smelting was developed by Outokumpu in Finland and first applied at Harjavalta in 1949; the energy-efficient process accounts for 50% of the world's primary copper production.
The Intergovernmental Council of Copper Exporting Countries, formed in 1967 by Chile, Peru, Zaire and Zambia, operated in the copper market as OPEC does in oil, though it never achieved the same influence, particularly because the second-largest producer, the United States, was never a member; it was dissolved in 1988.
Copper is used in roofing, currency, and for photographic technology known as the daguerreotype. Copper was used in Renaissance sculpture, and was used to construct the Statue of Liberty; copper continues to be used in construction of various types. Copper plating and copper sheathing were widely used to protect the under-water hulls of ships, a technique pioneered by the British Admiralty in the 18th century. The Norddeutsche Affinerie in Hamburg was the first modern electroplating plant, starting its production in 1876. The German scientist Gottfried Osann invented powder metallurgy in 1830 while determining the metal's atomic mass; around then it was discovered that the amount and type of alloying element (e.g., tin) to copper would affect bell tones.
During the rise in demand for copper for the Age of Electricity, from the 1880s until the Great Depression of the 1930s, the United States produced one third to half the world's newly mined copper. Major districts included the Keweenaw district of northern Michigan, primarily native copper deposits, which was eclipsed by the vast sulphide deposits of Butte, Montana in the late 1880s, which itself was eclipsed by porphyry deposits of the Souhwest United States, especially at Bingham Canyon, Utah and Morenci, Arizona. Introduction of open pit steam shovel mining and innovations in smelting, refining, flotation concentration and other processing steps led to mass production. Early in the twentieth century, Arizona ranked first, followed by Montana, then Utah and Michigan.
Flash smelting was developed by Outokumpu in Finland and first applied at Harjavalta in 1949; the energy-efficient process accounts for 50% of the world's primary copper production.
The Intergovernmental Council of Copper Exporting Countries, formed in 1967 by Chile, Peru, Zaire and Zambia, operated in the copper market as OPEC does in oil, though it never achieved the same influence, particularly because the second-largest producer, the United States, was never a member; it was dissolved in 1988.
Applications
 The major applications of copper are electrical wire (60%), roofing and plumbing (20%), and industrial machinery (15%). Copper is used mostly as a pure metal, but when greater hardness is required, it is put into such alloys as brass and bronze (5% of total use). For more than two centuries, copper paint has been used on boat hulls to control the growth of plants and shellfish. A small part of the copper supply is used for nutritional supplements and fungicides in agriculture. Machining of copper is possible, although alloys are preferred for good machinability in creating intricate parts.
The major applications of copper are electrical wire (60%), roofing and plumbing (20%), and industrial machinery (15%). Copper is used mostly as a pure metal, but when greater hardness is required, it is put into such alloys as brass and bronze (5% of total use). For more than two centuries, copper paint has been used on boat hulls to control the growth of plants and shellfish. A small part of the copper supply is used for nutritional supplements and fungicides in agriculture. Machining of copper is possible, although alloys are preferred for good machinability in creating intricate parts.
Wire and cable
Despite competition from other materials, copper remains the preferred electrical conductor in nearly all categories of electrical wiring except overhead electric power transmission where aluminium is often preferred. Copper wire is used in power generation, power transmission, power distribution, telecommunications, electronics circuitry, and countless types of electrical equipment. Electrical wiring is the most important market for the copper industry. This includes structural power wiring, power distribution cable, appliance wire, communications cable, automotive wire and cable, and magnet wire. Roughly half of all copper mined is used for electrical wire and cable conductors. Many electrical devices rely on copper wiring because of its multitude of inherent beneficial properties, such as its high electrical conductivity, tensile strength, ductility, creep (deformation) resistance, corrosion resistance, low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, ease of soldering, malleability, and ease of installation. For a short period from the late 1960s to the late 1970s, copper wiring was replaced by aluminium wiring in many housing construction projects in America. The new wiring was implicated in a number of house fires and the industry returned to copper.Electronics and related devices
 Integrated circuits and printed circuit boards increasingly feature copper in place of aluminium because of its superior electrical conductivity; heat sinks and heat exchangers use copper because of its superior heat dissipation properties. Electromagnets, vacuum tubes, cathode ray tubes, and magnetrons in microwave ovens use copper, as do waveguides for microwave radiation.
Integrated circuits and printed circuit boards increasingly feature copper in place of aluminium because of its superior electrical conductivity; heat sinks and heat exchangers use copper because of its superior heat dissipation properties. Electromagnets, vacuum tubes, cathode ray tubes, and magnetrons in microwave ovens use copper, as do waveguides for microwave radiation.
Electric motors
Copper's superior Copper wire and cable#Electrical conductivity, conductivity enhances the efficiency of electrical motor (device), motors. This is important because motors and motor-driven systems account for 43%–46% of all global electricity consumption and 69% of all electricity used by industry. Increasing the mass and cross section of copper in a Inductor, coil increases the efficiency of the motor. Induction motor, Copper motor rotors, a new technology designed for motor applications where energy savings are prime design objectives, are enabling general-purpose induction motors to meet and exceed National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) premium efficiency standards.Renewable energy production
Architecture


 Copper has been used since ancient times as a durable, corrosion resistance, corrosion resistant, and weatherproof architectural material. Roofing material, Roofs, flashing (weatherproofing), flashings, rain gutters, downspouts, domes, spires, vaults, and doors have been made from copper for hundreds or thousands of years. Copper's architectural use has been expanded in modern times to include interior and exterior Copper in architecture#Wall cladding, wall cladding, building expansion joints, RF shielding, radio frequency shielding, and Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces, antimicrobial and decorative indoor products such as attractive handrails, bathroom fixtures, and counter tops. Some of copper's other important benefits as an architectural material include low thermal expansion, thermal movement, light weight, lightning rod, lightning protection, and recyclability
The metal's distinctive natural green patina has long been coveted by architects and designers. The final patina is a particularly durable layer that is highly resistant to atmospheric corrosion, thereby protecting the underlying metal against further weathering. It can be a mixture of carbonate and sulfate compounds in various amounts, depending upon environmental conditions such as sulfur-containing acid rain. Architectural copper and its alloys can also be Copper in architecture#Finishes, 'finished' to take on a particular look, feel, or color. Finishes include mechanical surface treatments, chemical coloring, and coatings.
Copper has excellent brazing and soldering properties and can be welded; the best results are obtained with gas metal arc welding.
Copper has been used since ancient times as a durable, corrosion resistance, corrosion resistant, and weatherproof architectural material. Roofing material, Roofs, flashing (weatherproofing), flashings, rain gutters, downspouts, domes, spires, vaults, and doors have been made from copper for hundreds or thousands of years. Copper's architectural use has been expanded in modern times to include interior and exterior Copper in architecture#Wall cladding, wall cladding, building expansion joints, RF shielding, radio frequency shielding, and Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces, antimicrobial and decorative indoor products such as attractive handrails, bathroom fixtures, and counter tops. Some of copper's other important benefits as an architectural material include low thermal expansion, thermal movement, light weight, lightning rod, lightning protection, and recyclability
The metal's distinctive natural green patina has long been coveted by architects and designers. The final patina is a particularly durable layer that is highly resistant to atmospheric corrosion, thereby protecting the underlying metal against further weathering. It can be a mixture of carbonate and sulfate compounds in various amounts, depending upon environmental conditions such as sulfur-containing acid rain. Architectural copper and its alloys can also be Copper in architecture#Finishes, 'finished' to take on a particular look, feel, or color. Finishes include mechanical surface treatments, chemical coloring, and coatings.
Copper has excellent brazing and soldering properties and can be welded; the best results are obtained with gas metal arc welding.
Antibiofouling
Copper is biostatic, meaning bacteria and many other forms of life will not grow on it. For this reason it has long been used to line parts of ships to protect against barnacles and mussels. It was originally used pure, but has since been superseded by Muntz metal and copper-based paint. Similarly, as discussed in copper alloys in aquaculture, copper alloys have become important netting materials in the aquaculture industry because they are antimicrobial and prevent biofouling, even in extreme conditionsEdding, Mario E., Flores, Hector, and Miranda, Claudio, (1995), Experimental Usage of Copper-Nickel Alloy Mesh in Mariculture. Part 1: Feasibility of usage in a temperate zone; Part 2: Demonstration of usage in a cold zone; Final report to the International Copper Association Ltd. and have strong structural and corrosion-resistant properties in marine environments.Antimicrobial
Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces, Copper-alloy touch surfaces have natural properties that destroy a wide range of microorganisms (e.g., ''Escherichia coli, E. coli'' O157:H7, methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA), ''Staphylococcus'', ''Clostridium difficile (bacteria), Clostridium difficile'', influenza A virus, Adenoviridae, adenovirus, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, SARS-Cov-2, and Fungus, fungi).Copper Touch Surfaces. Copper Touch Surfaces. Retrieved on 8 November 2011. Indians have been using copper vessels since ancient times for storing water, even before modern science realized its antimicrobial properties. Some copper alloys were proven to kill more than 99.9% of disease-causing bacteria within just two hours when cleaned regularly. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has approved the registrations of these copper alloys as "antimicrobial materials with public health benefits"; that approval allows manufacturers to make legal claims to the public health benefits of products made of registered alloys. In addition, the EPA has approved a long list of antimicrobial copper products made from these alloys, such as bedrails, handrails, over-bed tables, sinks, faucets, door knobs, toilet hardware, computer keyboards, health club equipment, and shopping cart handles (for a comprehensive list, see: Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces#Approved products). Copper doorknobs are used by hospitals to reduce the transfer of disease, and Legionnaires' disease is suppressed by copper tubing in plumbing systems. Antimicrobial copper alloy products are now being installed in healthcare facilities in the U.K., Ireland, Japan, Korea, France, Denmark, and Brazil, as well as being called for in the US, and in the subway transit system in Santiago, Chile, where copper-zinc alloy handrails were installed in some 30 stations between 2011 and 2014. Textile fibers can be blended with copper to create antimicrobial protective fabrics.
Speculative investing
Copper may be used as a speculative investment due to the predicted increase in use from worldwide infrastructure growth, and the important role it has in producing wind turbines, solar panels, and other renewable energy sources. Another reason predicted demand increases is the fact that electric cars contain an average of 3.6 times as much copper as conventional cars, although the effect of electric cars on copper demand is debated. Some people invest in copper through copper mining stocks, Exchange-traded fund, ETFs, and Futures contract, futures. Others store physical copper in the form of copper bars or rounds although these tend to carry a higher premium in comparison to precious metals. Those who want to avoid the premiums of copper bullion alternatively store old copper wire, copper tubing or American Penny (United States coin), pennies made before 1982.Folk medicine
Copper is commonly used in jewelry, and according to some folklore, copper bracelets relieve arthritis symptoms. In one trial for osteoarthritis and one trial for rheumatoid arthritis, no differences is found between copper bracelet and control (non-copper) bracelet. No evidence shows that copper can be absorbed through the skin. If it were, it might lead to Copper toxicity, copper poisoning.Compression clothing
Recently, some compression bandage, compression clothing with inter-woven copper has been marketed with health claims similar to the folk medicine claims. Because compression clothing is a valid treatment for some ailments, the clothing may have that benefit, but the added copper may have no benefit beyond a placebo effect.Degradation
''Chromobacterium violaceum'' and ''Pseudomonas fluorescens'' can both mobilize solid copper as a cyanide compound. The ericoid mycorrhizal fungi associated with ''Calluna'', ''Erica'' and ''Vaccinium'' can grow in metalliferous soils containing copper. The ectomycorrhizal fungus ''Suillus luteus'' protects young pine trees from copper toxicity. A sample of the fungus ''Aspergillus niger'' was found growing from gold mining solution and was found to contain cyano complexes of such metals as gold, silver, copper, iron, and zinc. The fungus also plays a role in the solubilization of heavy metal sulfides.Biological role

Biochemistry
Copper proteins have diverse roles in biological electron transport and oxygen transportation, processes that exploit the easy interconversion of Cu(I) and Cu(II). Copper is essential in the aerobic Cellular respiration, respiration of all eukaryotes. In mitochondria, it is found incytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV, (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and mitochondria of eukaryotes.
It is the last enzyme in the respiratory elect ...
, which is the last protein in oxidative phosphorylation. Cytochrome c oxidase is the protein that binds the O2 between a copper and an iron; the protein transfers 8 electrons to the O2 molecule to reduce it to two molecules of water. Copper is also found in many superoxide dismutases, proteins that catalyze the decomposition of superoxides by converting it (by disproportionation) to oxygen and hydrogen peroxide:
* Cu2+-SOD + O2− → Cu+-SOD + O2 (reduction of copper; oxidation of superoxide)
* Cu+-SOD + O2− + 2H+ → Cu2+-SOD + H2O2 (oxidation of copper; reduction of superoxide)
The protein hemocyanin is the oxygen carrier in most mollusks and some arthropods such as the horseshoe crab (''Limulus polyphemus''). Because hemocyanin is blue, these organisms have blue blood rather than the red blood of iron-based hemoglobin. Structurally related to hemocyanin are the laccases and tyrosinases. Instead of reversibly binding oxygen, these proteins hydroxylate substrates, illustrated by their role in the formation of lacquers.S.J. Lippard, J.M. Berg "Principles of bioinorganic chemistry" University Science Books: Mill Valley, CA; 1994. . The biological role for copper commenced with the appearance of oxygen in earth's atmosphere. Several copper proteins, such as the "blue copper proteins", do not interact directly with substrates; hence they are not enzymes. These proteins relay electrons by the process called electron transfer.
 A unique tetranuclear copper center has been found in nitrous-oxide reductase.
Chemical compounds which were developed for treatment of Wilson's disease have been investigated for use in cancer therapy.
A unique tetranuclear copper center has been found in nitrous-oxide reductase.
Chemical compounds which were developed for treatment of Wilson's disease have been investigated for use in cancer therapy.
Nutrition
Copper is an essential trace element in plants and animals, but not all microorganisms. The human body contains copper at a level of about 1.4 to 2.1 mg per kg of body mass.Absorption
Copper is absorbed in the gut, then transported to the liver bound to serum albumin, albumin. After processing in the liver, copper is distributed to other tissues in a second phase, which involves the protein ceruloplasmin, carrying the majority of copper in blood. Ceruloplasmin also carries the copper that is excreted in milk, and is particularly well-absorbed as a copper source. Copper in the body normally undergoes enterohepatic circulation (about 5 mg a day, vs. about 1 mg per day absorbed in the diet and excreted from the body), and the body is able to excrete some excess copper, if needed, via bile, which carries some copper out of the liver that is not then reabsorbed by the intestine.Dietary recommendations
The U.S. Institute of Medicine (IOM) updated the estimated average requirements (EARs) and recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) for copper in 2001. If there is not sufficient information to establish EARs and RDAs, an estimate designated Adequate Intake (AI) is used instead. The AIs for copper are: 200 μg of copper for 0–6-month-old males and females, and 220 μg of copper for 7–12-month-old males and females. For both sexes, the RDAs for copper are: 340 μg of copper for 1–3 years old, 440 μg of copper for 4–8 years old, 700 μg of copper for 9–13 years old, 890 μg of copper for 14–18 years old and 900 μg of copper for ages 19 years and older. For pregnancy, 1,000 μg. For lactation, 1,300 μg. As for safety, the IOM also sets tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. In the case of copper the UL is set at 10 mg/day. Collectively the EARs, RDAs, AIs and ULs are referred to as Dietary Reference Intakes. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL defined the same as in United States. For women and men ages 18 and older the AIs are set at 1.3 and 1.6 mg/day, respectively. AIs for pregnancy and lactation is 1.5 mg/day. For children ages 1–17 years the AIs increase with age from 0.7 to 1.3 mg/day. These AIs are higher than the U.S. RDAs. The European Food Safety Authority reviewed the same safety question and set its UL at 5 mg/day, which is half the U.S. value. For U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For copper labeling purposes 100% of the Daily Value was 2.0 mg, but it was revised to 0.9 mg to bring it into agreement with the RDA. A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.Deficiency
Because of its role in facilitating iron uptake, copper deficiency can produce anemia-like symptoms, neutropenia, bone abnormalities, hypopigmentation, impaired growth, increased incidence of infections, osteoporosis, hyperthyroidism, and abnormalities in glucose and cholesterol metabolism. Conversely, Wilson's disease causes an accumulation of copper in body tissues. Severe deficiency can be found by testing for low plasma or serum copper levels, low ceruloplasmin, and low red blood cell superoxide dismutase levels; these are not sensitive to marginal copper status. The "cytochrome c oxidase activity of leucocytes and platelets" has been stated as another factor in deficiency, but the results have not been confirmed by replication.Toxicity
Gram quantities of various copper salts have been taken in suicide attempts and produced acute copper toxicity in humans, possibly due to redox cycling and the generation of reactive oxygen species that damage DNA. Corresponding amounts of copper salts (30 mg/kg) are toxic in animals. A minimum dietary value for healthy growth in rabbits has been reported to be at least 3 Parts per million, ppm in the diet. However, higher concentrations of copper (100 ppm, 200 ppm, or 500 ppm) in the diet of rabbits may favorably influence Feed conversion ratio, feed conversion efficiency, growth rates, and carcass dressing percentages. Chronic copper toxicity does not normally occur in humans because of transport systems that regulate absorption and excretion. Autosomal recessive mutations in copper transport proteins can disable these systems, leading to Wilson's disease with copper accumulation and cirrhosis of the liver in persons who have inherited two defective genes. Elevated copper levels have also been linked to worsening symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.Human exposure
In the US, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has designated a permissible exposure limit (PEL) for copper dust and fumes in the workplace as a time-weighted average (TWA) of 1 mg/m3. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 1 mg/m3, time-weighted average. The IDLH (immediately dangerous to life and health) value is 100 mg/m3. Copper is a constituent of tobacco smoke. The tobacco plant readily absorbs and accumulates heavy metals, such as copper from the surrounding soil into its leaves. These are readily absorbed into the user's body following smoke inhalation. The health implications are not clear.See also
* Copper in renewable energy * Copper nanoparticle * Erosion corrosion of copper water tubes ** Cold water pitting of copper tube * List of countries by copper production * Metal theft ** Operation Tremor * Anaconda Copper * Antofagasta PLC * Codelco * El Boleo, El Boleo mine * Grasberg mineReferences
Notes
Further reading
* * * Current Medicinal Chemistry, Volume 12, Number 10, May 2005, pp. 1161–1208(48) Metals, Toxicity and Oxidative Stress *Material: Copper (Cu), bulk
MEMS and Nanotechnology Clearinghouse. *
External links
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Copper and compounds fact sheet
from the National Pollutant Inventory of Australia
Copper.org
– official website of the Copper Development Association with an extensive site of properties and uses of copper
Price history of copper, according to the IMF
{{good article Copper, Chemical elements Transition metals Dietary minerals Electrical conductors Cubic minerals Crystals in space group 225 Native element minerals Symbols of Arizona Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure