congenital erythropoetic porphyria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as
 In humans, porphyrins are the main precursors of heme, an essential constituent of hemoglobin,
In humans, porphyrins are the main precursors of heme, an essential constituent of hemoglobin,
File:Allan Ramsay - King George III in coronation robes - Google Art Project.jpg, George III in his coronation robes
File:Mary, Queen of Scots after Nicholas Hilliard.jpg, Mary, Queen of Scots .
File:Maria I, Queen of Portugal - Giuseppe Troni, atribuído (Turim, 1739-Lisboa, 1810) - Google Cultural Institute.jpg, Maria I of Portugal in a c. 1790s portrait attributed to
The Drug Database for Acute Porphyria - comprehensive database on drug porphyrinogenicity
Orphanet's disease page on Porphyria
{{Heme metabolism disorders Red blood cell disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism Diseases of liver
acute porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are ra ...
, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled wi ...
s or itching may occur with sunlight exposure.
Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
, autosomal recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
, or X-linked dominant manner. One type, '' porphyria cutanea tarda'', may also be due to hemochromatosis (increased iron in the liver), hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
, alcohol, or HIV/AIDS. The underlying mechanism results in a decrease in the amount of heme produced and a build-up of substances involved in making heme. Porphyrias may also be classified by whether the liver or bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
is affected. Diagnosis is typically made by blood, urine, and stool tests. Genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
may be done to determine the specific mutation.
Treatment depends on the type of porphyria and the person's symptoms. Treatment of porphyria of the skin generally involves the avoidance of sunlight, while treatment for acute porphyria may involve giving intravenous heme or a glucose solution. Rarely, a liver transplant may be carried out.
The precise prevalence of porphyria is unclear, but it is estimated to affect between 1 and 100 per 50,000 people. Rates are different around the world. Porphyria cutanea tarda is believed to be the most common type. The disease was described as early as 370 BC by Hippocrates. The underlying mechanism was first described by German physiologist and chemist Felix Hoppe-Seyler in 1871. The name ''porphyria'' is from the Greek πορφύρα, ''porphyra'', meaning " purple", a reference to the color of the urine that may be present during an attack.
Signs and symptoms

Acute porphyrias
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP),variegate porphyria
Variegate porphyria, also known by several other names, is an autosomal dominant porphyria that can have acute (severe but usually not long-lasting) symptoms along with symptoms that affect the skin. The disorder results from low levels of the en ...
(VP), aminolevulinic acid dehydratase deficiency porphyria
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase deficiency porphyria (also known as "Doss porphyria", "plumboporphyria", or "ADP") is an extremely rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that results from inappropriately low levels of the enzyme delta-aminole ...
(ALAD) and hereditary coproporphyria
Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the ''CPOX'' gene, and is inherited in an autosom ...
(HCP). These diseases primarily affect the nervous system, resulting in episodic crises known as acute attacks. The major symptom of an acute attack is abdominal pain, often accompanied by vomiting, hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
(elevated blood pressure), and tachycardia (an abnormally rapid heart rate).
The most severe episodes may involve neurological complications: typically motor neuropathy (severe dysfunction of the peripheral nerves that innervate muscle), which leads to muscle weakness and potentially to quadriplegia (paralysis of all four limbs) and central nervous system symptoms such as seizures and coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
. Occasionally, there may be short-lived psychiatric symptoms such as anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, and, very rarely, overt psychosis. All these symptoms resolve once the acute attack passes.
Given the many presentations and the relatively low occurrence of porphyria, patients may initially be suspected to have other, unrelated conditions. For instance, the polyneuropathy of acute porphyria may be mistaken for Guillain–Barré syndrome, and porphyria testing is commonly recommended in those situations. Elevation of aminolevulinic acid from lead-induced disruption of heme synthesis results in lead poisoning having symptoms similar to acute porphyria.
Chronic porphyrias
The non-acute porphyrias are X-linked dominant protoporphyria (XLDPP), congenitalerythropoietic porphyria
Erythropoietic porphyria is a type of porphyria associated with erythropoietic cells. In erythropoietic porphyrias, the enzyme deficiency occurs in the red blood cells. Types
There are three types:
Presentation
X-linked dominant erythropoietic pr ...
(CEP), porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT), and erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP). None of these are associated with acute attacks; their primary manifestation is with skin disease. For this reason, these four porphyrias—along with two acute porphyrias, VP and HCP, that may also involve skin manifestations—are sometimes called cutaneous porphyrias.
Skin disease is encountered where excess porphyrins accumulate in the skin. Porphyrins are photoactive molecules, and exposure to light results in promotion of electrons to higher energy levels. When these return to the resting energy level or ground state, energy is released. This accounts for the property of fluorescence typical of the porphyrins. This causes local skin damage.
Two distinct patterns of skin disease are seen in porphyria:
* Immediate photosensitivity. This is typical of XLDPP and EPP. Following a variable period of sun exposure
The ultraviolet radiation in sunlight has both positive and negative health effects, as it is required for the synthesis of vitamin D3 and is a mutagen. A dietary supplement can supply vitamin D without this mutagenic effect, but supplementati ...
—typically about 30 minutes—patients complain of severe pain, burning, and discomfort in exposed areas. Typically, the effects are not visible, though occasionally there may be some redness and swelling of the skin.
* Vesiculo-erosive skin disease. This—a reference to the characteristic blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled wi ...
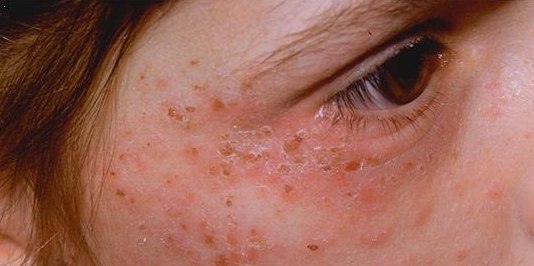
ing (vesicles) and open sores (erosions) noted in patients—is the pattern seen in CEP, PCT, VP, and HCP. The changes are noted only in sun-exposed areas such as the face and back of the hands. Milder skin disease, such as that seen in VP and HCP, consists of increased skin fragility in exposed areas with a tendency to form blisters and erosions, particularly after minor knocks or scrapes. These heal slowly, often leaving small scars that may be lighter or darker than normal skin. More severe skin disease is sometimes seen in PCT, with prominent lesions, darkening of exposed skin such as the face, and hypertrichosis: abnormal hair growth on the face, particularly the cheeks. The most severe disease is seen in CEP and a rare variant of PCT known as hepatoerythropoietic porphyria
Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria is a very rare form of hepatic porphyria caused by a disorder in both genes which code Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase (UROD).
It has a similar presentation to porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT), but with earlier onse ...
(HEP); symptoms include severe shortening of digits, loss of skin appendages such as hair and nails, and severe scarring of the skin with progressive disappearance of ears, lips, and nose. Patients may also show deformed, discolored teeth or gum and eye abnormalities.
Cause
The porphyrias are generally considered genetic in nature.Genetics
Subtypes of porphyrias depend on which enzyme is deficient. X-linked dominant protoporphyria is a rare form of erythropoietic protoporphyria caused by a gain-of-function mutation in ALAS2 characterized by severe photosensitivity. In the autosomal recessive types, if a person inherits a single gene they may become a carrier. Generally they do not have symptoms, but may pass the gene onto offspring.Triggers
Acute porphyria can be triggered by a number of drugs, most of which are believed to trigger it by interacting with enzymes in the liver which are made with heme. Such drugs include: *Sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
s, including sulfadiazine
Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic. Used together with pyrimethamine, a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, it is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis, which is caused by a protozoan parasite. It is a second-line treatment for otitis media, p ...
, sulfasalazine and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.
* Sulfonylureas like glibenclamide, gliclazide and glimepiride
Glimepiride, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is less preferred than metformin. Use is recommended together with diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth. Glimepiride takes up to three hours for maximum effect and l ...
, although glipizide
Glipizide, sold under the brand name Glucotrol among others, is an anti-diabetic medication of the sulfonylurea class used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is used together with a diabetic diet and exercise. It is not indicated for use by itself in ...
is thought to be safe.
* Barbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as ...
including thiopental
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal (a trademark of Abbott Laboratories), thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal (also a trademark), is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pe ...
, phenobarbital, primidone
Primidone, sold under various brand names, is a barbiturate medication that is used to treat partial and generalized seizures, as well as essential tremors. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include sleepiness, poor coordination, nause ...
, etc.
* Systemic treatment with antifungals
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as crypto ...
including fluconazole, griseofulvin, ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral among others, is an antiandrogen and antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous candid ...
and voriconazole
Voriconazole, sold under the brand name Vfend among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, penicilliosis, and infections by '' ...
. (Topical use of these agents is thought to be safe due to minimal systemic absorption.)
* Certain antibiotics like rifapentine, rifampicin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires’ disease. ...
, rifabutine
Rifabutin (Rfb) is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and prevent and treat Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex. It is typically only used in those who cannot tolerate rifampin such as people with HIV/AIDS on antiret ...
, isoniazid, nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin is an antibacterial medication used to treat urinary tract infections, but it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and headaches. Rarely ...
and, possibly, metronidazole.
* Ergot
Ergot ( ) or ergot fungi refers to a group of fungi of the genus ''Claviceps''.
The most prominent member of this group is ''Claviceps purpurea'' ("rye ergot fungus"). This fungus grows on rye and related plants, and produces alkaloids that ca ...
derivatives including dihydroergotamine
Dihydroergotamine (DHE), sold under the brand names D.H.E. 45 and Migranal among others, is an ergot alkaloid used to treat migraines. It is a derivative of ergotamine. It is administered as a nasal spray or injection and has an efficacy simil ...
, ergometrine, ergotamine, methysergide, etc.
* Certain antiretroviral
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multipl ...
medications (''e.g.'' indinavir, nevirapine, ritonavir, saquinavir, etc.)
* Progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. ...
s
* Some anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
including: carbamazepine, ethosuximide, phenytoin, topiramate, valproate.
* Some painkillers like dextropropoxyphene, ketorolac
Ketorolac, sold under the brand names Toradol, and Biorolac among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain. Specifically it is recommended for moderate to severe pain. Recommended duration of treatment is less ...
, metamizole
Metamizole, or dipyrone, is a painkiller, spasm reliever, and fever reliever that also has anti-inflammatory effects. It is most commonly given by mouth or by intravenous infusion.
Although it is available over-the-counter in some countries, ...
, pentazocine
Pentazocine, sold under the brand name Talwin among others, is a painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is believed to work by activating (agonizing) κ-opioid receptors (KOR) and μ-opioid receptors (MOR). As such it is called an ...
* Some cancer treatments like bexarotene, busulfan, chlorambucil
Chlorambucil, sold under the brand name Leukeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Hodgkin lymphoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. For CLL it is a preferred treatment. It is given by mouth.
...
, estramustine, etoposide, flutamide, idarubicin, ifosfamide, irinotecan, ixabepilone
Ixabepilone (INN; also known as azaepothilone B, codenamed BMS-247550) is a pharmaceutical drug developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb as a chemotherapeutic medication for cancer.
History
Ixabepilone is a semi-synthetic analog of epothilone B, a natura ...
, letrozole, lomustine
Lomustine (INN); abbreviated as CCNU; original brand name CeeNU, now marketed as Gleostine) is an alkylating nitrosourea compound used in chemotherapy. It is closely related to semustine and is in the same family as streptozotocin. It is a highly ...
, megestrol
Megestrol (, ) is a progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was never marketed and is not currently used clinically. Its acylated derivative megestrol acetate is also a progestogen, which, in contrast to megestrol itself, has been ...
, mitomycin
The mitomycins are a family of aziridine-containing natural products isolated from ''Streptomyces caespitosus'' or ''Streptomyces lavendulae.'' They include mitomycin A, mitomycin B, and mitomycin C. When the name mitomycin occurs alone, it usually ...
, mitoxantrone
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent.
Uses
Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the ...
, paclitaxel, procarbazine, tamoxifen, topotecan
Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form o ...
* Some antidepressants like imipramine
Imipramine, sold under the brand name Tofranil, among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) mainly used in the treatment of depression. It is also effective in treating anxiety and panic disorder. The drug is also used to treat bedwetting. ...
, phenelzine, trazodone
* Some antipsychotics like risperidone, ziprasidone
* Some retinoids
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.
Retinoids have many important functions throughout ...
used for skin conditions like acitretin and isotretinoin
* Miscellaneous others including: cocaine, methyldopa, fenfluramine
Fenfluramine, sold under the brand name Fintepla, is a serotonergic medication used for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome.https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/212102s003lb ...
, disulfiram
Disulfiram is a medication used to support the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to ethanol (drinking alcohol). Disulfiram works by inhibiting the enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, causing many of the effects of ...
, orphenadrine
Orphenadrine (sold under many brand names) is an anticholinergic drug of the ethanolamine antihistamine class; it is closely related to diphenhydramine. It is a muscle relaxant that is used to treat muscle pain and to help with motor control in Pa ...
, pentoxifylline
Pentoxifylline, also known as oxpentifylline, is a xanthine derivative used as a drug to treat muscle pain in people with peripheral artery disease. It is generic and sold under many brand names worldwide.Drugs.codrugs.com international listings ...
, and sodium aurothiomalate.
Pathogenesis
myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobi ...
, catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting t ...
, peroxidase, and P450 liver cytochromes.
The body requires porphyrins to produce heme, which is used to carry oxygen in the blood among other things, but in the porphyrias there is a deficiency (inherited or acquired) of the enzymes that transform the various porphyrins into others, leading to abnormally high levels of one or more of these substances. Porphyrias are classified in two ways, by symptoms and by pathophysiology. Physiologically, porphyrias are classified as liver or erythropoietic based on the sites of accumulation of heme precursors, either in the liver or in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
and red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek language, Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''k ...
.
Deficiency in the enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
of the porphyrin pathway leads to insufficient production of heme. Heme function plays a central role in cellular metabolism. This is not the main problem in the porphyrias; most heme synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
** Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organ ...
enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
—even dysfunctional enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
—have enough residual activity to assist in heme biosynthesis. The principal problem in these deficiencies is the accumulation of porphyrins, the heme precursors, which are toxic to tissue in high concentrations. The chemical properties of these intermediates determine the location of accumulation, whether they induce photosensitivity, and whether the intermediate is excreted (in the urine or feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
).
There are eight enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway, four of which—the first one and the last three—are in the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
, while the other four are in the cytosol. Defects in any of these can lead to some form of porphyria. The hepatic porphyria
Hepatic porphyrias is a form of porphyria in which toxic porphyrin molecules build up in the liver. Hepatic porphyrias can result from a number of different enzyme deficiencies.
Examples include (in order of synthesis pathway):
* Acute intermitten ...
s are characterized by acute neurological attacks ( seizures, psychosis, extreme back and abdominal pain, and an acute polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy ( poly- + neuro- + -pathy) is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hand ...
), while the erythropoietic forms present with skin problems, usually a light-sensitive blistering rash and increased hair growth.''Variegate porphyria
Variegate porphyria, also known by several other names, is an autosomal dominant porphyria that can have acute (severe but usually not long-lasting) symptoms along with symptoms that affect the skin. The disorder results from low levels of the en ...
'' (also ''porphyria variegata'' or ''mixed porphyria''), which results from a partial deficiency in PROTO oxidase
Protoporphyrinogen oxidase or protox is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PPOX'' gene.
Protoporphyrinogen oxidase is responsible for the seventh step in biosynthesis of protoporphyrin IX. This porphyrin is the precursor to hemoglobin, ...
, manifests itself with skin lesions similar to those of porphyria cutanea tarda combined with acute neurologic attacks. Hereditary coproporphyria
Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the ''CPOX'' gene, and is inherited in an autosom ...
, which is characterized by a deficiency in coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the CPOX gene, may also present with both acute neurologic attacks and cutaneous lesions. All other porphyrias are either skin- or nerve-predominant.
Diagnosis
Porphyrin studies
Porphyria is diagnosed through biochemical analysis of blood, urine, and stool. In general, urine estimation of porphobilinogen (PBG) is the first step if acute porphyria is suspected. As a result of feedback, the decreased production of heme leads to increased production of precursors, PBG being one of the first substances in the porphyrin synthesis pathway. In nearly all cases of acute porphyria syndromes, urinary PBG is markedly elevated except for the very rareALA dehydratase deficiency
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase deficiency porphyria (also known as "Doss porphyria", "plumboporphyria", or "ADP") is an extremely rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that results from inappropriately low levels of the enzyme delta-aminolev ...
or in patients with symptoms due to hereditary tyrosinemia type I. In cases of
mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
- or arsenic poisoning-induced porphyria, other changes in porphyrin profiles appear, most notably elevations of uroporphyrins I & III, coproporphyrins I & III, and pre-coproporphyrin.
Repeat testing during an attack and subsequent attacks may be necessary in order to detect a porphyria, as levels may be normal or near-normal between attacks. The urine screening test has been known to fail in the initial stages of a severe, life-threatening attack of acute intermittent porphyria.
Up to 90% of the genetic carriers of the more common, dominantly inherited acute hepatic porphyrias (acute intermittent porphyria, hereditary coproporphyria
Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the ''CPOX'' gene, and is inherited in an autosom ...
, variegate porphyria) have been noted in DNA tests to be latent for classic symptoms and may require DNA or enzyme testing. The exception to this may be latent post-puberty genetic carriers of hereditary coproporphyria
Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the ''CPOX'' gene, and is inherited in an autosom ...
.
As most porphyrias are rare conditions, general hospital labs typically do not have the expertise, technology, or staff time to perform porphyria testing. In general, testing involves sending samples of blood, stool, and urine to a reference laboratory. All samples to detect porphyrins must be handled properly. Samples should be taken during an acute attack; otherwise a false negative result may occur. Samples must be protected from light and either refrigerated or preserved.
If all the porphyrin studies are negative, one must consider pseudoporphyria
Pseudoporphyria is a bullous photosensitivity that clinically and histologically mimics porphyria cutanea tarda. The difference is that no abnormalities in urine or serum porphyrin is noted on laboratories. Pseudoporphyria has been reported in p ...
. A careful medication review often will find the cause of pseudoporphyria.
Additional tests
Further diagnostic tests of affected organs may be required, such as nerve conduction studies forneuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
or an ultrasound of the liver. Basic biochemical tests may assist in identifying liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
, and other organ problems.
Management
Acute porphyria
Carbohydrate administration
Often, empirical treatment is required if the diagnostic suspicion of a porphyria is high since acute attacks can be fatal. A high-carbohydrate diet is typically recommended; in severe attacks, adextrose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
10% infusion is commenced, which may aid in recovery by suppressing heme synthesis, which in turn reduces the rate of porphyrin accumulation. However, this can worsen cases of low blood sodium levels (hyponatraemia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be abs ...
) and should be done with extreme caution as it can prove fatal.
Heme analogs
Hematin
Haematin (also known as hematin, ferriheme, hematosin, hydroxyhemin, oxyheme, phenodin, or oxyhemochromogen) is a dark bluish or brownish pigment containing iron in the ferric state, obtained by the oxidation of haem.
Haematin inhibits the synth ...
(trade name Panhematin) and heme arginate
Heme arginate (or haem arginate) is a compound of heme and arginine used in the treatment of acute porphyrias. This heme product is only available outside the United States and is equivalent to hematin.
Heme arginate is a heme compound, whereby ...
(trade name NormoSang) are the drugs of choice in acute porphyria, in the United States and the United Kingdom, respectively. These drugs need to be given very early in an attack to be effective; effectiveness varies amongst individuals. They are not curative drugs but can shorten attacks and reduce the intensity of an attack. Side effects are rare but can be serious. These heme-like substances theoretically inhibit ALA synthase and hence the accumulation of toxic precursors. In the United Kingdom, supplies of NormoSang are kept at two national centers; emergency supply is available from St Thomas's Hospital, London. In the United States, Lundbeck manufactures and supplies Panhematin for infusion.
Heme arginate (NormoSang) is used during crises but also in preventive treatment to avoid crises, one treatment every 10 days.
Any sign of low blood sodium ( hyponatremia) or weakness should be treated with the addition of hematin, heme arginate, or even tin mesoporphyrin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, as these are signs of impending syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) or peripheral nervous system involvement that may be localized or severe, progressing to bulbar paresis and respiratory paralysis.
Cimetidine
Cimetidine
Cimetidine, sold under the brand name Tagamet among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is mainly used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers.
The development of longer-acting H2 rec ...
has also been reported to be effective for acute porphyric crisis and possibly effective for long-term prophylaxis.
Symptom control
Pain is severe, frequently out of proportion to physical signs, and often requires the use of opiates to reduce it to tolerable levels. Pain should be treated as early as medically possible. Nausea can be severe; it may respond to phenothiazine drugs but is sometimes intractable. Hot baths and showers may lessen nausea temporarily, though caution should be used to avoid burns or falls.Early identification
It is recommended that patients with a history of acute porphyria, and even genetic carriers, wear an alert bracelet or other identification at all times. This is in case they develop severe symptoms, or in case of accidents where there is a potential for drug exposure, and as a result they are unable to explain their condition to healthcare professionals. Some drugs are absolutely contraindicated for patients with any form of porphyria.Neurologic and psychiatric disorders
Patients who experience frequent attacks can develop chronic neuropathic pain in extremities as well as chronic pain in the abdomen.Intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO) is a clinical syndrome caused by severe impairment in the ability of the intestines to push food through. It is characterized by the signs and symptoms of Bowel obstruction, intestinal obstruction without any les ...
, ileus, intussusception Intussusception may refer to:
* Intussusception (medical disorder)
Intussusception is a medical condition in which a part of the intestine folds into the section immediately ahead of it. It typically involves the small bowel and less commonly t ...
, hypoganglionosis, and encopresis in children have been associated with porphyrias. This is thought to be due to axonal nerve deterioration in affected areas of the nervous system and vagal nerve dysfunction. Pain treatment with long-acting opioids, such as morphine, is often indicated, and, in cases where seizure or neuropathy is present, gabapentin is known to improve outcome.
Seizures often accompany this disease. Most seizure medications exacerbate this condition. Treatment can be problematic: barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as we ...
s especially must be avoided. Some benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s are safe and, when used in conjunction with newer anti-seizure medications such as gabapentin, offer a possible regimen for seizure control. Gabapentin has the additional feature of aiding in the treatment of some kinds of neuropathic pain. Magnesium sulfate and bromides have also been used in porphyria seizures; however, development of status epilepticus
Status epilepticus (SE), or status seizure, is a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes or 2 or more seizures within a 5-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The s ...
in porphyria may not respond to magnesium alone. The addition of hematin
Haematin (also known as hematin, ferriheme, hematosin, hydroxyhemin, oxyheme, phenodin, or oxyhemochromogen) is a dark bluish or brownish pigment containing iron in the ferric state, obtained by the oxidation of haem.
Haematin inhibits the synth ...
or heme arginate
Heme arginate (or haem arginate) is a compound of heme and arginine used in the treatment of acute porphyrias. This heme product is only available outside the United States and is equivalent to hematin.
Heme arginate is a heme compound, whereby ...
has been used during status epilepticus
Status epilepticus (SE), or status seizure, is a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes or 2 or more seizures within a 5-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The s ...
.
Depression often accompanies the disease and is best dealt with by treating the offending symptoms and if needed the judicious use of antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
s. Some psychotropic drugs are porphyrinogenic, limiting the therapeutic scope. Other psychiatric symptoms such as anxiety, restlessness, insomnia, depression, mania, hallucinations, delusions, confusion, catatonia, and psychosis may occur.
Underlying liver disease
Some liver diseases may cause porphyria even in the absence of genetic predisposition. These include hemochromatosis andhepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
. Treatment of iron overload may be required.
Patients with the acute porphyrias (AIP
AIP may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Action International Pictures
* Afghan Islamic Press
* AIP Records, a record label
* American International Pictures, an independent film production/distribution company, now a subsidiary of MGM ...
, HCP, VP) are at increased risk over their life for hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
(primary liver cancer) and may require monitoring. Other typical risk factors for liver cancer need not be present.
Hormone treatment
Hormonal fluctuations that contribute to cyclical attacks in women have been treated with oral contraceptives and luteinizing hormones to shut down menstrual cycles. However, oral contraceptives have also triggered photosensitivity and withdrawal of oral contraceptives has triggered attacks. Androgens and fertility hormones have also triggered attacks. In 2019,givosiran
Givosiran, sold under the brand name Givlaari, is a medication used for the treatment of adults with acute hepatic porphyria. Givosiran is a small interfering RNA (siRNA) directed towards delta-aminolevulinate synthase 1 (ALAS1), an important ...
was approved in the United States for the treatment of acute hepatic porphyria.
Erythropoietic porphyria
These are associated with accumulation of porphyrins in erythrocytes and are rare. The pain, burning, swelling, and itching that occur in erythropoietic porphyrias generally require avoidance of bright sunlight. Most kinds ofsunscreen
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock or sun cream, is a photoprotective topical product for the skin that mainly absorbs, or to a much lesser extent reflects, some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn and ...
are not effective, but SPF-rated long-sleeve shirts, hats, bandanas, and gloves can help. Chloroquine may be used to increase porphyrin secretion in some EPs. Blood transfusion is occasionally used to suppress innate heme production.
The rarest is congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP), otherwise known as Gunther's disease
Gunther disease is a congenital form of erythropoietic porphyria. The word porphyria originated from the Greek word porphura. Porphura actually means "purple pigment", which, in suggestion, the color that the body fluid changes when a person has Gu ...
. The signs may present from birth and include severe photosensitivity, brown teeth that fluoresce in ultraviolet light due to deposition of Type 1 porphyrins, and later hypertrichosis. Hemolytic anemia usually develops. Pharmaceutical-grade beta carotene may be used in its treatment. A bone marrow transplant has also been successful in curing CEP in a few cases, although long-term results are not yet available.
In December 2014, afamelanotide received authorization from the European Commission as a treatment for the prevention of phototoxicity in adult patients with EPP.
Epidemiology
Rates of all types of porphyria taken together have been estimated to be approximately one in 25,000 in the United States. The worldwide prevalence has been estimated to be between one in 500 and one in 50,000 people. Porphyrias have been detected in all races and in multiple ethnic groups on every continent. There are high incidence reports of AIP in areas of India and Scandinavia. More than 200 genetic variants of AIP are known, some of which are specific to families, although some strains have proven to be repeated mutations.History
The underlying mechanism was first described by Felix Hoppe-Seyler in 1871, and acute porphyrias were described by the Dutch physician Barend Stokvis in 1889. The links between porphyrias and mental illness have been noted for decades. In the early 1950s, patients with porphyrias (occasionally referred to as "porphyric hemophilia") and severe symptoms of depression or catatonia were treated with electroshock therapy.Vampires and werewolves
Porphyria has been suggested as an explanation for the origin of vampire and werewolf legends, based upon certain perceived similarities between the condition and the folklore. In January 1964, L. Illis's 1963 paper, "On Porphyria and the Aetiology of Werewolves," was published in '' Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. ''Later,Nancy Garden
Nancy Garden (May 15, 1938 – June 23, 2014) was an American writer of fiction for children and young adults, best known for the lesbian novel '' Annie on My Mind''. She received the 2003 Margaret Edwards Award from the American Library Associa ...
argued for a connection between porphyria and the vampire belief in her 1973 book, ''Vampires''. In 1985, biochemist David Dolphin
David H. Dolphin, (born January 15, 1940) is a Canadian biochemist.
He is an internationally recognized expert in porphyrin chemistry and biochemistry. He was the lead creator of Visudyne, a medication used in conjunction with laser treatment t ...
's paper for the American Association for the Advancement of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is an American international non-profit organization with the stated goals of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific respons ...
, "Porphyria, Vampires, and Werewolves: The Aetiology of European Metamorphosis Legends," gained widespread media coverage, popularizing the idea.
The theory has been rejected by a few folklorists and researchers as not accurately describing the characteristics of the original werewolf and vampire legends or the disease, and as potentially stigmatizing people with porphyria.
A 1995 article from the ''Postgraduate Medical Journal
The ''Postgraduate Medical Journal'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal that was established in 1925 by the Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, of which it is the official journal. It is currently published on behalf of the Fellowship by ...
'' (via NIH) explains:
As it was believed that the folkloric vampire could move about freely in daylight hours, as opposed to the 20th century variant, congenital erythropoietic porphyria cannot readily explain the folkloric vampire but may be an explanation of the vampire as we know it in the 20th century. In addition, the folkloric vampire, when unearthed, was always described as looking quite healthy ("as they were in life"), while due to disfiguring aspects of the disease, sufferers would not have passed the exhumation test. Individuals with congenital erythropoietic porphyria do not crave blood. The enzyme (hematin) necessary to alleviate symptoms is not absorbed intact on oral ingestion, and drinking blood would have no beneficial effect on the sufferer. Finally, and most important, the fact that vampire reports were literally rampant in the 18th century, and that congenital erythropoietic porphyria is an extremely rare manifestation of a rare disease, makes it an unlikely explanation of the folkloric vampire.
Notable cases
* King George III. The mental illness exhibited by George III in theregency crisis of 1788
Charles James Fox (24 January 1749 – 13 September 1806), styled ''The Honourable'' from 1762, was a prominent British Whig statesman whose parliamentary career spanned 38 years of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He was the arch-riv ...
has inspired several attempts at retrospective diagnosis
A retrospective diagnosis (also retrodiagnosis or posthumous diagnosis) is the practice of identifying an illness after the death of the patient (sometimes in a historical figure) using modern knowledge, methods and disease classifications. Altern ...
. The first, written in 1855, thirty-five years after his death, concluded that he had acute mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wit ...
. M. Guttmacher, in 1941, suggested manic-depressive
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
psychosis as a more likely diagnosis. The first suggestion that a physical illness was the cause of King George's mental derangement came in 1966, in a paper called "The Insanity of King George III: A Classic Case of Porphyria", with a follow-up in 1968, "Porphyria in the Royal Houses of Stuart, Hanover and Prussia". The papers, by a mother/son psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry, the branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, study, and treatment of mental disorders. Psychiatrists are physicians and evaluate patients to determine whether their sy ...
team, were written as though the case for porphyria had been proven, but the response demonstrated that many experts, including those more intimately familiar with the manifestations of porphyria, were unconvinced. Many psychiatrists disagreed with the diagnosis, suggesting bipolar disorder as far more probable. The theory is treated in ''Purple Secret,'' which documents the ultimately unsuccessful search for genetic evidence of porphyria in the remains of royals suspected to have had it. In 2005, it was suggested that arsenic (which is known to be porphyrogenic) given to George III with antimony may have caused his porphyria. This study found high levels of arsenic in King George's hair. In 2010, one analysis of historical records argued that the porphyria claim was based on spurious and selective interpretation of contemporary medical and historical sources. The mental illness of George III is the basis of the plot in '' The Madness of King George'', a 1994 British film based upon the 1991 Alan Bennett play, ''The Madness of George III''. The closing credits of the film include the comment that the King's symptoms suggest that he had porphyria and notes that the disease is "periodic, unpredictable, and hereditary". The traditional argument that George III did NOT have porphyria, but rather bipolar disorder, is thoroughly defended by Andrew Roberts in his new biography, "The Last King of America."
* Descendants of George III. Among other descendants of George III theorized by the authors of ''Purple Secret'' to have had porphyria (based on analysis of their extensive and detailed medical correspondence) were his great-great-granddaughter Princess Charlotte of Prussia (Emperor William II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until his abdication on 9 November 1918. Despite strengthening the German Empi ...
's eldest sister) and her daughter Princess Feodora of Saxe-Meiningen
, spouse =
, house = Wettin
, father = Bernhard III, Duke of Saxe-Meiningen
, mother = Princess Charlotte of Prussia
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Potsdam, German Empire
, death_date =
, death_place = Hirschberg, Silesia, Provisional Gover ...
. They uncovered better evidence that George III's great-great-great-grandson Prince William of Gloucester
Prince William of Gloucester (William Henry Andrew Frederick; 18 December 1941 – 28 August 1972) was a grandson of King George V and paternal cousin of Queen Elizabeth II. At birth he was fourth in line to the throne; he was ninth in lin ...
was reliably diagnosed with variegate porphyria.
* Mary, Queen of Scots. It is believed that Mary, Queen of Scots, King George III's ancestor, also had acute intermittent porphyria, although this is subject to much debate. It is assumed she inherited the disorder, if indeed she had it, from her father, James V of Scotland. Both father and daughter endured well-documented attacks that could fall within the constellation of symptoms of porphyria.
* Maria I of Portugal. Maria I—known as "Maria the Pious" or "Maria the Mad" because of both her religious fervor and her acute mental illness, which made her incapable of handling state affairs after 1792 – is also thought to have had porphyria. Francis Willis, the same physician who treated George III, was even summoned by the Portuguese court but returned to England after the court limited the treatments he could oversee. Contemporary sources, such as Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs Luís Pinto de Sousa Coutinho, noted that the queen had ever-worsening stomach pains and abdominal spasms: hallmarks of porphyria.
* Vlad III Dracula, “The Impaler.” Vlad III was also said to have had acute porphyria, which may have started the notion that vampires were allergic to sunlight.
* Vincent van Gogh. Other commentators have suggested that Vincent van Gogh may have had acute intermittent porphyria.
* King Nebuchadnezzar of Babylon. The description of this king in Daniel 4
Daniel 4, the fourth chapter of the Bible's Book of Daniel, is presented in the form of a letter from king Nebuchadnezzar II in which he learns a lesson of God's sovereignty, "who is able to bring low those who walk in pride". Nebuchadnezzar dre ...
suggests to some that he had porphyria.
* Physician Archie Cochrane. He was born with porphyria, which caused health problems throughout his life.
* Paula Frías Allende
Paula Frías Allende (22 October 1963 – 6 December 1992) was an educator and humanitarian who was the daughter of Chilean-American author Isabel Allende. Her grandfather was first cousin to Salvador Allende, President of Chile from 1970 to 19 ...
. The daughter of the Chilean novelist Isabel Allende. She fell into a porphyria-induced coma in 1991, which inspired Isabel to write the memoir '' Paula'', dedicated to her.
Giuseppe Troni
Giuseppe Troni (Portuguese: ''José Troni''; Turin, 1739 – Lisbon, 1810) was an Italian court painter. He was initially a pupil of his father, Alessandro Trono, but completed his studies in Rome. He was portrait painter to the court of Naples, ...
or Thomas Hickey.
Uses in Literature
Stated or implied references to porphyria are included in some literature, particularly gothic literature. These include the following: * The condition is the name of the title character in the gothic poem " Porphyria's Lover," byRobert Browning
Robert Browning (7 May 1812 – 12 December 1889) was an English poet and playwright whose dramatic monologues put him high among the Victorian poets. He was noted for irony, characterization, dark humour, social commentary, historical settings ...
.
* The condition is heavily implied to be the cause of the symptoms suffered by the narrator in the gothic short story "Lusus Naturae
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in dysmorphology. The related t ...
," by Margaret Atwood
Margaret Eleanor Atwood (born November 18, 1939) is a Canadian poet, novelist, literary critic, essayist, teacher, environmental activist, and inventor. Since 1961, she has published 18 books of poetry, 18 novels, 11 books of non-fiction, nin ...
. Some of the narrator's symptoms resemble those of porphyria, and one passage of the story states that the name of the narrator's disease "had some Ps and Rs in it."
References
External links
*The Drug Database for Acute Porphyria - comprehensive database on drug porphyrinogenicity
Orphanet's disease page on Porphyria
{{Heme metabolism disorders Red blood cell disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism Diseases of liver