|
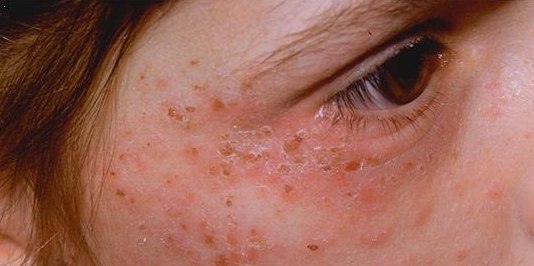
Hepatoerythropoietic Porphyria
Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria is a very rare form of hepatic porphyria caused by a disorder in both genes which code Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase (UROD). It has a similar presentation to porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT), but with earlier onset. In classifications which define PCT type 1 as "sporadic" and PCT type 2 as "familial", hepatoerythropoietic porphyria is more similar to type 2. See also * Hereditary coproporphyria * List of cutaneous conditions * List of dental abnormalities associated with cutaneous conditions Many conditions of or affecting the human integumentary system have associated abnormalities of the teeth. See also * List of cutaneous conditions * List of contact allergens * List of cutaneous conditions associated with internal malignan ... References External links * * Porphyrias Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism {{endocrine-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Porphyria
Hepatic porphyrias is a form of porphyria in which toxic porphyrin molecules build up in the liver. Hepatic porphyrias can result from a number of different enzyme deficiencies. Examples include (in order of synthesis pathway): * Acute intermittent porphyria * Porphyria cutanea tarda Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fift ... and Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria * Hereditary coproporphyria * Variegate porphyria See also * Erythropoietic porphyria * Givosiran References External links * * www.drugs-porphyria.com * www.porphyria-europe.com Porphyrias {{endocrine-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen III Decarboxylase
Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase (uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, or UROD) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''UROD'' gene. Function Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase is a homodimeric enzyme () that catalyzes the fifth step in heme biosynthesis, which corresponds to the elimination of carboxyl groups from the four acetate side chains of uroporphyrinogen III to yield coproporphyrinogen III: :uroporphyrinogen III \rightleftharpoons coproporphyrinogen III + 4 CO2 Clinical significance Mutations and deficiency in this enzyme are known to cause familial porphyria cutanea tarda Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fift ... and hepatoerythropoietic porphyria. At least 65 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Mechanism At low substr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translational Research (journal)
''Translational Research: The Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering translational research. It was established in 1915 as ''The Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine'' obtaining its current title in 2006. Jeffrey Laurence (Weill Cornell Medical College) has been editor-in-chief since 2006. He was preceded by Dale Hammerschmidt. It is the official journal of the Central Society for Clinical and Translational Research. It is published by Mosby. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports ''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publicationby Clarivate Analytics (previously the intellectual property of Thomson Reuters). It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science-Core Collect ...'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor of 5.03, ranking it second out of 30 journals in the category "Medical Lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fifth step in heme production. Heme is a vital molecule for all of the body's organs. It is a component of hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in the blood. Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria has been described as a homozygous form of porphyria cutanea tarda, although it can also be caused if two different mutations occur at the same locus. Symptoms and signs Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is recognized as the most prevalent subtype of porphyritic diseases. PCT is characterized by onycholysis and blistering of the skin in areas that receive higher levels of exposure to sunlight. The primary cause is a deficiency of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (UROD), a cytosolic enzyme that is a step in the enzymatic pathway that leads to the synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Coproporphyria
Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the ''CPOX'' gene, and is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, although homozygous individuals have been identified. Unlike acute intermittent porphyria, individuals with HCP can present with cutaneous findings similar to those found in porphyria cutanea tarda in addition to the acute attacks of abdominal pain, vomiting and neurological dysfunction characteristic of acute porphyrias. Like other porphyrias, attacks of HCP can be induced by certain drugs, environmental stressors or diet changes. Biochemical and molecular testing can be used to narrow down the diagnosis of a porphyria and identify the specific genetic defect. Overall, porphyrias are rare diseases. The combined incidence for all forms of the disease has been estimated at 1:20,000. The exact incidence of HCP is dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dental Abnormalities Associated With Cutaneous Conditions
Many conditions of or affecting the human integumentary system have associated abnormalities of the teeth. See also * List of cutaneous conditions * List of contact allergens * List of cutaneous conditions associated with internal malignancy * List of cutaneous conditions caused by mutations in keratins * List of cutaneous conditions caused by problems with junctional proteins * List of genes mutated in cutaneous conditions * List of histologic stains that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions * List of immunofluorescence findings for autoimmune bullous conditions * List of inclusion bodies that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions * List of keratins expressed in the human integumentary system * List of radiographic findings associated with cutaneous conditions * List of specialized glands within the human integumentary system * List of target antigens in pemphigoid * List of target antigens in pemphigus Circulating auto-antibodies in the human body can target n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ILDS
The International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) is a non-governmental organization that works closely with the World Health Organization. It was founded in 1935, but because of World War II no congresses were held until 1952. It is governed by the International Committee of Dermatology. The ILDS is the parent organization of the International Foundation for Dermatology, founded in 1987. After the publication of ICD-10, the ILDS produced a series of compatible extensions for use in dermatology Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical .... References External links Official site HistoryInternational Foundation for DermatologyApplication to Dermatology of International Classification of Disease (ICD-11) Organizations established in 1935 Dermatology organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrias
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure. Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked dominant manner. One type, ''porphyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |