Bristle Worm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Polychaeta () is a

 The outer surface of the body wall consists of a simple
The outer surface of the body wall consists of a simple



 Polychaetes are extremely variable in both form and lifestyle, and include a few taxa that swim among the
Polychaetes are extremely variable in both form and lifestyle, and include a few taxa that swim among the


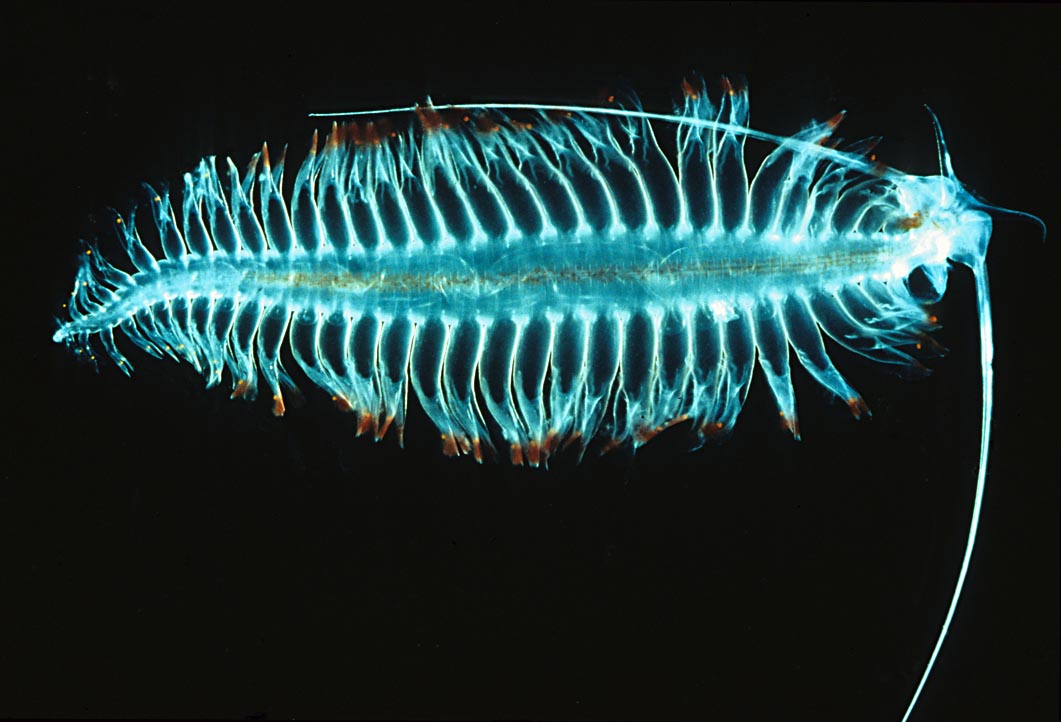



 Taxonomically, polychaetes are thought to be
Taxonomically, polychaetes are thought to be
World Polychaeta Database
Special issue of ''Marine Ecology''
dedicated to polychaetes
a guide to the marine zooplankton of south eastern Australia
paraphyletic
In taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
class of generally marine annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecolo ...
worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete wor ...
s, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; plural: parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointe ...
that bear many bristles, called chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such ...
e, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm
The lugworm or sandworm (''Arenicola marina'') is a large marine worm of the phylum Annelida. Its coiled castings are a familiar sight on a beach at low tide but the animal itself is rarely seen except by those who, from curiosity or to use as ...
(''Arenicola marina'') and the sandworm or clam worm ''Alitta''.
Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between and . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. T ...
, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep
The Challenger Deep is the deepest-known point of the seabed of Earth, with a depth of by direct measurement from deep-diving submersibles, remotely operated underwater vehicles and benthic landers, and (sometimes) slightly more by sonar bath ...
, the deepest known spot in the Earth's oceans. Only 168 species (less than 2% of all polychaetes) are known from fresh waters.
Description
Polychaetes are segmented worms, generally less than in length, although ranging at the extremes from to , in ''Eunice aphroditois
''Eunice aphroditois'' is a benthic bristle worm of warm marine waters. It lives mainly in the Atlantic Ocean, but can also be found in the Indo-Pacific. It ranges in length from less than to . Its iridescent cuticle produces a wide range of c ...
''. They can sometimes be brightly coloured, and may be iridescent
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
or even luminescent
Luminescence is spontaneous emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; or "cold light".
It is thus a form of cold-body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions or stress on a crystal ...
. Each segment bears a pair of paddle-like and highly vascularized parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; plural: parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointe ...
, which are used for movement and, in many species, act as the worm's primary respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gre ...
surfaces. Bundles of bristles, called chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such ...
e, project from the parapodia.
However, polychaetes vary widely from this generalised pattern, and can display a range of different body forms. The most generalised polychaetes are those that crawl along the bottom, but others have adapted to many different ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
s, including burrowing, swimming, pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or wa ...
life, tube-dwelling or boring, commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fro ...
ism, and parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has c ...
, requiring various modifications to their body structures.
The head, or prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) th ...
, is relatively well developed, compared with other annelids. It projects forward over the mouth, which therefore lies on the animal's underside. The head normally includes two to four pair of eyes, although some species are blind. These are typically fairly simple structures, capable of distinguishing only light and dark, although some species have large eyes with lenses that may be capable of more sophisticated vision, including the Alciopids' complex eyes which rival cephalopod and vertebrate eyes.
The head also includes a pair of antennae, tentacle-like palp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and ...
s, and a pair of pits lined with cilia, known as "nuchal organs". These latter appear to be chemoreceptor
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance (endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorecept ...
s, and help the worm to seek out food.
Internal anatomy and physiology
 The outer surface of the body wall consists of a simple
The outer surface of the body wall consists of a simple columnar epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
covered by a thin cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
. Underneath this, in order, are a thin layer of connective tissue, a layer of circular muscle, a layer of longitudinal muscle, and a peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothel ...
surrounding the body cavity
A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.
The two largest human body cavities are the ventral body cavity, and ...
. Additional oblique muscles move the parapodia. In most species the body cavity is divided into separate compartments by sheets of peritoneum between each segment, but in some species it's more continuous.
The mouth of polychaetes is located on the peristomium, the segment behind the prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) th ...
, and varies in form depending on their diets, since the group includes predators, herbivores, filter feeders, scavengers, and parasites. In general, however, they possess a pair of jaws and a pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
that can be rapidly everted, allowing the worms to grab food and pull it into their mouths. In some species, the pharynx is modified into a lengthy proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elong ...
. The digestive tract is a simple tube, usually with a stomach part way along.
The smallest species, and those adapted to burrowing, lack gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
s, breathing only through their body surfaces. Most other species have external gills, often associated with the parapodia.
A simple but well-developed circulatory system is usually present. The two main blood vessels furnish smaller vessels to supply the parapodia and the gut. Blood flows forward in the dorsal vessel, above the gut, and returns down the body in the ventral vessel, beneath the gut. The blood vessels themselves are contractile, helping to push the blood along, so most species have no need of a heart. In a few cases, however, muscular pumps analogous to a heart are found in various parts of the system. Conversely, some species have little or no circulatory system at all, transporting oxygen in the coelomic fluid that fills their body cavities.
The blood may be colourless, or have any of three different respiratory pigments. The most common of these is haemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyt ...
, but some groups have haemerythrin
Hemerythrin (also spelled haemerythrin; grc, αἷμα, haîma, blood, grc, ἐρυθρός, erythrós, red) is an oligomeric protein responsible for oxygen (O2) transport in the marine invertebrate phyla of sipunculids, priapulids, brachiop ...
or the green-coloured chlorocruorin, instead.
The nervous system consists of a single or double ventral nerve cord running the length of the body, with ganglia
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympathe ...
and a series of small nerves in each segment. The brain is relatively large, compared with that of other annelids, and lies in the upper part of the head. An endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
is attached to the ventral posterior surface of the brain, and appears to be involved in reproductive activity. In addition to the sensory organs on the head, photosensitive eye spots, statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in ''Xenoturbella''. The statocyst cons ...
s, and numerous additional sensory nerve endings, most likely in involved with the sense of touch, also occur on the body.
Polychaetes have a varying number of protonephridia
The nephridium (plural ''nephridia'') is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Neph ...
or metanephridia
The nephridium (plural ''nephridia'') is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Neph ...
for excreting waste, which in some cases can be relatively complex in structure. The body also contains greenish "chloragogen" tissue, similar to that found in oligochaete
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms ...
s, which appears to function in metabolism, in a similar fashion to that of the vertebrate liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
.
The cuticle is constructed from cross-linked fibres of collagen and may be 200 nm to 13 mm thick. Their jaws are formed from sclerotised collagen, and their setae
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. Th ...
from sclerotised chitin.
Ecology



 Polychaetes are extremely variable in both form and lifestyle, and include a few taxa that swim among the
Polychaetes are extremely variable in both form and lifestyle, and include a few taxa that swim among the plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
or above the abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between and . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface. T ...
. Most burrow or build tubes in the sediment, and some live as commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fro ...
s. A few are parasitic. The mobile forms (Errantia) tend to have well-developed sense organs and jaws, while the stationary forms (Sedentaria) lack them, but may have specialized gills or tentacles used for respiration and deposit or filter feeding, e.g., fanworm
Sabellida is an order of annelid worms in the class Polychaeta. They are filter feeders with no buccal organ. The prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") ...
s.
Underwater polychaetes have eversible mouthparts used to capture prey. A few groups have evolved to live in terrestrial environments, like Namanereidinae with many terrestrial species, but are restricted to humid areas. Some have even evolved cutaneous invaginations for aerial gas exchange.
Notable polychaetes
*One notable polychaete, thePompeii worm
''Alvinella pompejana'', the Pompeii worm, is a species of deep-sea polychaete worm (commonly referred to as "bristle worms"). It is an extremophile found only at hydrothermal vents in the Pacific Ocean, discovered in the early 1980s off the Gal� ...
(''Alvinella pompejana''), is endemic to the hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s of the Pacific Ocean. Pompeii worms are among the most heat-tolerant complex animals known.
*A recently discovered genus, ''Osedax
''Osedax'' is a genus of deep-sea siboglinid polychaetes, commonly called boneworms, zombie worms, or bone-eating worms. ''Osedax'' is Latin for "bone-eater". The name alludes to how the worms bore into the bones of whale carcasses to reach en ...
'', includes a species nicknamed the "bone-eating snot flower".
*Another remarkable polychaete is '' Hesiocaeca methanicola'', which lives on methane clathrate
Methane clathrate (CH4·5.75H2O) or (8CH4·46H2O), also called methane hydrate, hydromethane, methane ice, fire ice, natural gas hydrate, or gas hydrate, is a solid clathrate compound (more specifically, a clathrate hydrate) in which a large amou ...
deposits.
*''Lamellibrachia
''Lamellibrachia'' is a genus of tube worms related to the giant tube worm, ''Riftia pachyptila''. They live at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) leak out of the seafloor, and are entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxi ...
luymesi'' is a cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
tube worm
A tubeworm is any worm-like sessile invertebrate that anchors its tail to an underwater surface and secretes around its body a mineral tube, into which it can withdraw its entire body.
Tubeworms are found among the following taxa:
* Annelida, the ...
that reaches lengths of over 3 m and may be the most long-lived animal, being over 250 years old.
*A still unclassified multilegged predatory polychaete worm was identified only by observation from the underwater vehicle ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep
The Challenger Deep is the deepest-known point of the seabed of Earth, with a depth of by direct measurement from deep-diving submersibles, remotely operated underwater vehicles and benthic landers, and (sometimes) slightly more by sonar bath ...
, the greatest depth in the oceans, near in depth. It was about an inch long visually, but the probe failed to capture it, so it could not be studied in detail.
*The Bobbit worm (''Eunice aphroditois
''Eunice aphroditois'' is a benthic bristle worm of warm marine waters. It lives mainly in the Atlantic Ocean, but can also be found in the Indo-Pacific. It ranges in length from less than to . Its iridescent cuticle produces a wide range of c ...
'') is a predatory species that can achieve a length at ), with an average diameter of .
*''Dimorphilus gyrociliatus'', which has the smallest known genome of any annelid. The species shows an extreme sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most anim ...
, with females measuring just ~1 mm long and has a simplified segmented body with only six segments, reduced coelom, and no appendages, parapodia or chaetae. The males are only 50 µm long, consist of just a few hundred cells, lack a digestive system, only live for about a week and has just 68 neurons.
Reproduction
Most polychaetes have separate sexes, rather than being hermaphroditic. The most primitive species have a pair ofgonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sperm ...
s in every segment, but most species exhibit some degree of specialisation. The gonads shed immature gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce t ...
s directly into the body cavity, where they complete their development. Once mature, the gametes are shed into the surrounding water through ducts or openings that vary between species, or in some cases by the complete rupture of the body wall (and subsequent death of the adult). A few species copulate, but most fertilize their eggs externally.
The fertilized eggs typically hatch into trochophore
A trochophore (; also spelled trocophore) is a type of free-swimming planktonic marine larva with several bands of cilia.
By moving their cilia rapidly, they make a water eddy, to control their movement, and to bring their food closer, to captur ...
larvae, which float among the plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucia ...
, and eventually metamorphose
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
into the adult form by adding segments. A few species have no larval form, with the egg hatching into a form resembling the adult, and in many that do have larvae, the trochophore never feeds, surviving off the yolk that remains from the egg.
However, some polychaetes exhibit remarkable reproductive strategies. Some species reproduce by epitoky
Epitoky is a process that occurs in many species of polychaete marine worms wherein a sexually immature worm (the atoke) is modified or transformed into a sexually mature worm (the epitoke). Epitokes are pelagic morphs capable of sexual reproduc ...
. For much of the year, these worms look like any other burrow-dwelling polychaete, but as the breeding season approaches, the worm undergoes a remarkable transformation as new, specialized segments begin to grow from its rear end until the worm can be clearly divided into two halves. The front half, the atoke, is asexual. The new rear half, responsible for breeding, is known as the epitoke. Each of the epitoke segments is packed with eggs and sperm and features a single eyespot on its surface. The beginning of the last lunar quarter is the cue for these animals to breed, and the epitokes break free from the atokes and float to the surface. The eye spots sense when the epitoke reaches the surface and the segments from millions of worms burst, releasing their eggs and sperm into the water.
A similar strategy is employed by the deep sea worm ''Syllis ramosa
''Syllis ramosa'' is a species of polychaete worm in the family Syllidae. It is found in the deep sea where it lives within the tissues of a sponge. It was the first branching polychaete worm to be discovered, with each worm having a single head ...
'', which lives inside a sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through ...
. The rear end of the worm develops into a "stolon" containing the eggs or sperm; this stolon then becomes detached from the parent worm and rises to the sea surface, where fertilisation takes place.
Fossil record
Stem-group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. ...
polychaete fossils are known from the Sirius Passet
Sirius Passet is a Cambrian Lagerstätte in Peary Land, Greenland. The Sirius Passet Lagerstätte was named after the Sirius sledge patrol that operates in North Greenland. It comprises six places in Nansen Land, on the east shore of J.P. Koch ...
Lagerstätte
A Lagerstätte (, from ''Lager'' 'storage, lair' '' Stätte'' 'place'; plural ''Lagerstätten'') is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues. These for ...
, a rich, sedimentary deposit in Greenland tentatively dated to the late Atdabanian
Cambrian Stage 3 is the still unnamed third stage of the Cambrian. It succeeds Cambrian Stage 2 and precedes Cambrian Stage 4, although neither its base nor top have been formally defined. The plan is for its lower boundary to correspond approx ...
(early Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ( ...
). The oldest found is Phragmochaeta canicularis
''Phragmochaeta canicularis'' is an extinct animal belonging to the annelids and lived in the Early Cambrian (Atdabanian in the local timescale, about 520 million years ago).Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fos ...
organisms, such as '' Canadia'', may also have polychaete affinities. ''Wiwaxia
''Wiwaxia'' is a genus of soft-bodied animals that were covered in carbonaceous scales and spines that protected it from predators. ''Wiwaxia'' fossils – mainly isolated scales, but sometimes complete, articulated fossils – are known from ear ...
'', long interpreted as an annelid, is now considered to represent a mollusc. An even older fossil, '' Cloudina'', dates to the terminal Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ...
period; this has been interpreted as an early polychaete, although consensus is absent.
Being soft-bodied organisms
Soft-bodied organisms are animals that lack skeletons. The group roughly corresponds to the group Vermes as proposed by Carl von Linné. All animals have muscles but, since muscles can only pull, never push, a number of animals have developed hard ...
, the fossil record of polychaetes is dominated by their fossilized jaws, known as scolecodont
A scolecodont is the jaw of a polychaete annelid, a common type of fossil-producing segmented worm useful in invertebrate paleontology. Scolecodonts are common and diverse microfossils, which range from the Cambrian period (around half a billion ...
s, and the mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
ized tubes that some of them secrete. Most important biomineralising polychaetes
Biomineralising polychaetes are polychaetes that biomineralize.
The most important biomineralizing polychaetes are serpulids, sabellids and cirratulids. They secrete tubes of calcium carbonate. Serpulids have most advanced biomineralizatio ...
are serpulids, sabellids, and cirratulids. Polychaete cuticle does have some preservation potential; it tends to survive for at least 30 days after a polychaete's death. Although biomineralisation is usually necessary to preserve soft tissue after this time, the presence of polychaete muscle in the nonmineralised Burgess shale shows this need not always be the case. Their preservation potential is similar to that of jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella ...
.
Taxonomy and systematics






 Taxonomically, polychaetes are thought to be
Taxonomically, polychaetes are thought to be paraphyletic
In taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
, meaning the group excludes some descendants of its most recent common ancestor. Groups that may be descended from the polychaetes include the oligochaetes
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms ...
(earthworm
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. Th ...
s and leech
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodie ...
es), sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of unsegmented marine annelid worms. The name ''Sipuncula'' is from the genus name '' Sipunculus'', and comes from the Latin ...
ns, and echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lo ...
ns. The Pogonophora and Vestimentifera
Siboglinidae is a family of polychaete annelid worms whose members made up the former phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of about 100 species of vermiform creatures which live in thin tubes buried ...
were once considered separate phyla, but are now classified in the polychaete family Siboglinidae
Siboglinidae is a family of polychaete annelid worms whose members made up the former phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of about 100 species of vermiform creatures which live in thin tubes buri ...
.
Much of the classification below matches Rouse & Fauchald, 1998, although that paper does not apply ranks above family.
Older classifications recognize many more (sub)orders than the layout presented here. As comparatively few polychaete taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
have been subject to cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived cha ...
analysis, some groups which are usually considered invalid today may eventually be reinstated.
These divisions were shown to be mostly paraphyletic in recent years.
* Basal or ''incertae sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertaint ...
''
**Family Diurodrilidae
**Family Histriobdellidae
**Family Nerillidae
**Family Parergodrilidae
**Family Potamodrilidae
**Family Psammodrilidae
**Family Spintheridae
Spintheridae is a family of marine polychaete worms with a single genus, ''Spinther'', containing these species:
* '' Spinther alaskensis'' Hartman, 1948
* '' Spinther arcticus'' (M. Sars, 1851) (includes Spinther miniaceus'' Grube, 1860)
*'' S ...
**Family Protodriloididae
**Family Saccocirridae
**Order Haplodrili
**Order Myzostomida
The Myzostomida or Myzostomatida are an order of small marine worms, which are parasitic on echinoderms, mostly crinoids. These highly unusual and diverse annelids were first discovered by Friedrich Sigismund Leuckart in 1827.
Morphology
A ...
***Family Endomyzostomatidae
***Family Asteromyzostomatidae
***Family Myzostomidae
Myzostomatidae is a family of polychaetes
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that be ...
*Subclass Palpata
Palpata is a subclass of polychaete worm. Members of this subclass are mostly deposit feeders on marine detritus or filter feeders. Palpata has become superfluous with the elevation of Canalipalpata to subclass.
Characteristics
Palpata include ...
**Family Protodrilidae
**Family Polygordiidae
Polygordiidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the class Polychaeta
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protr ...
*Subclass Aciculata
Errantia is a diverse group of marine polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. Traditionally a subclass of the paraphyletic class "Polychaeta", it is currently regarded as a monophyletic group within the larger Pleistoannelida, composed of Err ...
**Family Levidoridae
Syllidae is a family of small to medium-sized polychaete worms. Syllids are distinguished from other polychaetes by the presence of a muscular region of the anterior digestive tract known as the ''proventricle''.
Syllid worms range in size from ...
**Order Amphinomida
Amphinomida is an order of marine polychaetes. The order contains two families:
* ''Amphinomidae'' Lamarck, 1818
* ''Euphrosinidae
The Euphrosinidae are a family of polychaete worms. The name is from Greek ''Euphrosyne'', meaning merriment; s ...
***Family Amphinomidae
Amphinomidae, also known as the bristle worms or sea mice, are a family of marine polychaetes, many species of which bear chaetae mineralized with carbonate. The best-known amphinomids are the fireworms, which can cause great pain if their toxin ...
***Family Euphrosinidae
The Euphrosinidae are a family of polychaete worms. The name is from Greek ''Euphrosyne'', meaning merriment; she was one of the three Graces.
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms t ...
**Order Eunicida
Eunicida is an order of polychaete worms.
Characteristics
Members of this order have an elongated, segmented body and a distinct head, normally with a separate peristomium and prostomium. Many, but not all, live in tubes which vary from a muco ...
***Family Dorvilleidae
***Family Eunicidae
Eunicidae is a family of marine polychaetes (bristle worms). The family comprises marine annelids distributed in diverse benthic habitats across Oceania, Europe, South America, North America, Asia and Africa. The Eunicid anatomy typically consi ...
***Family Hartmaniellidae
***Family Ichthyotomidae
***Family Lumbrineridae
Lumbrineridae is a family of polychaetes
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear ...
***Family Oenonidae
***Family Onuphidae
The Onuphidae are a family of polychaete worms.
Characteristics
Most onuphids have tubes. Some live semisubmerged in the substrate, but others carry their tubes around, and they can all rebuild their tubes if necessary. The tubes, thin and parch ...
**Order Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic creatures, moving over the surface or burrowing in sediments, or living in cr ...
***Suborder Aphroditiformia
****Family Acoetidae
Acoetidae is a family of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata.
Genera
* '' Acoetes'' Audouin & Milne Edwards, 1832
* '' Euarche'' Ehlers, 1887
* '' Eumolpe''
* '' Eupanthalis'' McIntosh, 1876
* '' Eupolyodontes'' Buchanan, 1894
* '' Eup ...
****Family Aphroditidae
Aphroditidae is a family of annelids belonging to the order Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic cr ...
****Family Eulepethidae
Eulepethidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthi ...
****Family Iphionidae
****Family Pholoidae
Pholoidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic cr ...
****Family Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but gene ...
****Family Sigalionidae
***Suborder Glyceriformia
****Family Glyceridae
****Family Goniadidae
****Family Lacydoniidae
****Family Paralacydoniidae
***Suborder Nereidiformia
****Family Antonbruunidae
****Family Chrysopetalidae
****Family Hesionidae
Hesionidae are a family of phyllodocid "bristle worms" ( class Polychaeta). They are (like almost all polychaetes) marine organisms. Most are found on the continental shelf; '' Hesiocaeca methanicola'' is found on methane ice, where it feeds ...
****Family Nereididae
Nereididae (formerly spelled Nereidae) are a family of polychaete worms. It contains about 500 – mostly marine – species grouped into 42 genera. They may be commonly called ragworms or clam worms.
Characteristics
The prostomium of ...
****Family Pilargidae
****Family Syllidae
***Suborder Phyllodocida incertae sedis
****Family Iospilidae
****Family Nautiliniellidae
****Family Nephtyidae
****Family Typhloscolecidae
****Family Tomopteridae
***Suborder Phyllodociformia
****Family Alciopidae
****Family Lopadorhynchidae
****Family Phyllodocidae
Phyllodocidae is a family of polychaete worms. Worms in this family live on the seabed and may burrow under the sediment.
Characteristics
Members of the Phyllodocidae are characterised by an eversible pharynx and leaf-like dorsal cirri. The hea ...
****Family Pontodoridae
*Subclass Sedentaria
Sedentaria is a diverse clade of annelid worms. It is traditionally treated as a subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, but it is also a monophyletic group uniting several polychaetes and the monophyletic class Clitellata. It is the siste ...
**Family Chaetopteridae
The Chaetopteridae are a family of marine filter-feeding polychaete worms that live in vertical or U-shaped tubes in tunnels buried in the sedimentary or hard substrate of marine environments. The worms are highly adapted to the hard tube they ...
**Infraclass Canalipalpata
Canalipalpata, also known as bristle-footed annelids or fan-head worms, is an order of polychaete worms, with 31 families in it including the suborder Sabellida (families Serpulidae (tubeworms) and Sabellidae (fanworms and feather duster worms) ...
***Order Sabellida
Sabellida is an order of annelid worms in the class Polychaeta. They are filter feeders with no buccal organ. The prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") ...
****Family Caobangidae
****Family Fabriciidae
****Family Oweniidae
Oweniidae is a family of marine polychaete worms in the suborder Sabellida. The worms live in tubes made of sand and are selective filter feeders, detritivores and grazers.
Characteristics
Members of this family live in tubes made of sand and sh ...
****Family Sabellariidae
Sabellariidae is a family of marine polychaete worms in the suborder Sabellida. The worms live in tubes made of sand and are filter feeders and detritivores.
Characteristics
Members of this family live in tubes made of sand and shell fragments c ...
****Family Sabellidae
Sabellidae, or feather duster worms, are a family of marine polychaete tube worms characterized by protruding feathery branchiae. Sabellids build tubes out of a tough, parchment-like exudate, strengthened with sand and bits of shell. Unlike the ...
****Family Serpulidae
The Serpulidae are a family of sessile, tube-building annelid worms in the class Polychaeta. The members of this family differ from other sabellid tube worms in that they have a specialized operculum that blocks the entrance of their tubes whe ...
****Family Siboglinidae
Siboglinidae is a family of polychaete annelid worms whose members made up the former phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of about 100 species of vermiform creatures which live in thin tubes buri ...
(formerly the phyla Pogonophora & Vestimentifera)
***Order Spionida
Spionida is an order of marine polychaete worms in the infraclass Canalipalpata. Spionids are cosmopolitan and live in soft substrates in the littoral or neritic zones.
Characteristics
Spionids have a single pair of flexible feeding tentacles w ...
****Suborder Spioniformia
*****Family Apistobranchidae
Apistobranchidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Spionida
Spionida is an order of marine polychaete worms in the infraclass Canalipalpata. Spionids are cosmopolitan and live in soft substrates in the littoral or neritic zone ...
*****Family Longosomatidae
Longosomatidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Spionida
Spionida is an order of marine polychaete worms in the infraclass Canalipalpata. Spionids are cosmopolitan and live in soft substrates in the littoral or neritic zone ...
*****Family Magelonidae
Magelonidae is a family of annelids belonging to the order Spionida
Spionida is an order of marine polychaete worms in the infraclass Canalipalpata. Spionids are cosmopolitan and live in soft substrates in the littoral or neritic zones.
Chara ...
*****Family Poecilochaetidae
Poecilochaetidae is a family of marine worms within the Polychaeta. It is a monotypic family containing the single genus '' Poecilochaetus''. Members of this family are benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a ...
*****Family Spionidae
Spionidae is a family of marine worms within the Polychaeta. Spionids are selective deposit feeders that use their two grooved palps to locate prey. However, some spionids are capable of interface feeding, i.e. switching between deposit and sus ...
*****Family Trochochaetidae
Trochochaetidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Spionida
Spionida is an order of marine polychaete worms in the infraclass Canalipalpata. Spionids are cosmopolitan and live in soft substrates in the littoral or neritic zon ...
*****Family Uncispionidae
Uncispionidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Spionida
Spionida is an order of marine polychaete worms in the infraclass Canalipalpata. Spionids are cosmopolitan and live in soft substrates in the littoral or neritic zones.
...
***Order Terebellida
Terebellida make up an order of the Polychaeta class, commonly referred to as "bristle worms". Together with the Sabellida, the Spionida and some enigmatic families of unclear taxonomic relationship (e.g. the Saccocirridae), they make up the ...
****Suborder Cirratuliformia
*****Family Acrocirridae (sometimes placed in Spionida)
*****Family Cirratulidae
Cirratulidae is a family of marine polychaete worms. Members of the family are found worldwide, mostly living in mud or rock crevices. Most are deposit feeders, but some graze on algae or are suspension feeders.
Description
Cirratulids vary in ...
(sometimes placed in Spionida)
*****Family Ctenodrilidae (sometimes own suborder Ctenodrilida)
*****Family Fauveliopsidae
Fauveliopsidae is a family of polychaetes belonging to the order Terebellida. The genus name honours Pierre Fauvel.
It is a small family, containing only three genera and about twenty species. They are benthic animals, noted for their habit of ...
(sometimes own suborder Fauveliopsida)
*****Family Flabelligeridae
Flabelligeridae is a family of polychaete worms, known as bristle-cage worms, notable for their cephalic cage: long slender chaetae forming a fan-like arrangement surrounding the eversible (able to be turned inside-out) head. Unlike many polychae ...
(sometimes suborder Flabelligerida)
*****Family Flotidae
Flotidae is a family of pelagic polychaete worms, sometimes synonymized with Flabelligeridae, which they closely resemble. Other sources consider them the sister taxon to Flabelligeridae and closely allied to the latter group.Zhadan, A. E., and A ...
(sometimes included in Flabelligeridae)
*****Family Poeobiidae (sometimes own suborder Poeobiida or included in Flabelligerida)
*****Family Sternaspidae (sometimes own suborder Sternaspida)
****Suborder Terebellomorpha
*****Family Alvinellidae
The Alvinellidae are a family of small, deep-sea polychaete worms endemic to hydrothermal vents in the Pacific Ocean. Belonging to the order Terebellida, the family contains two genera, ''Alvinella'' and ''Paralvinella''; the former genus conta ...
*****Family Ampharetidae
*****Family Pectinariidae
*****Family Terebellidae
The Terebellidae is a marine family of polychaete worms, of which the type taxon is '' Terebella'', described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1767 12th edition of ''Systema Naturae''.
Characteristics
Most terebellids live in burrows or crevices and ...
*****Family Trichobranchidae
Trichobranchidae is a family of annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species ...
**Infraclass Scolecida
Scolecida is an infraclass of polychaete worms. Scolecids are mostly unselective deposit feeders on marine detritus.
Characteristics
Scolecids have parapodia with rami that are all alike.
The prostomium is distinct. The head has no appendages ...
***Family Arenicolidae
Arenicolidae is a family of marine polychaete worms. They are commonly known as lugworms and the little coils of sand they produce are commonly seen on the beach. Arenicolids are found worldwide, mostly living in burrows in sandy substrates. Most ...
***Family Capitellidae
Capitellidae is a polychaete worm family in the subclass Scolecida.
Genera
* '' Abyssocapitella''
* '' Amastigos''
* '' Anotomastus''
* '' Baldia''
* '' Barantolla''
* '' Branchiocapitella''
* '' Capitella''
* '' Capitellethus''
* '' Capitobr ...
***Family Cossuridae
***Family Maldanidae
***Family Opheliidae
***Family Orbiniidae
Orbiniidae is a family of polychaete worms. Orbiniids are mostly unselective deposit feeders on marine detritus. They can be found from the neritic zone to abyssal depths.
The family was revised in 1957 by Hartman and some further revisions ...
***Family Paraonidae
***Family Scalibregmatidae
***Order Capitellida
Capitellida is an order of annelids belonging to the class Polychaeta.
Families:
* Arenicolidae Johnston, 1835
* Capitellidae
Capitellidae is a polychaete worm family in the subclass Scolecida.
Genera
* '' Abyssocapitella''
* '' Amastigos ...
(nomen dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application.
Zoology
In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a s ...
)
***Order Cossurida (nomen dubium)
***Order Opheliida (nomen dubium)
***Order Orbiniida
Orbiniida is an order of small polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. It is the earliest diverging clade in Sedentaria. Along with Protodriliformia (in Errantia), this order is composed of meiofaunal marine worms formerly known as " archianne ...
(nomen dubium)
***Order Questida (nomen dubium)
***Order Scolecidaformia (nomen dubium)
*Subclass Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lo ...
** Order Bonelliida
Bonelliida is a suborder of the order Echiuroidea, an order of polychaete worms.
Families
The following families are classified within the suborder:
* Bonelliidae Lacaze-Duthiers, 1858
* Ikedidae Bock
Bock is a strong beer in Germany, ...
*** Family Bonelliidae
Bonelliidae is a family of marine worms (Class Echiura, phylum Annelida) noted for being sexually dimorphic, with males being tiny in comparison with the females. They occupy burrows in the seabed in many parts of the world's oceans, often at gr ...
*** Family Ikedidae
Ikedidae is a family of spoon worms in the suborder Bonelliida. It is a monotypic family, the only genus being ''Ikeda''. These worms burrow into soft sediment on the seabed.
Examination of the original material of '' Ikeda taenoides'' by Ter ...
** Order Echiurida
*** Family Echiuridae
Echiuridae is a family of spoon worms in the suborder Echiurida. It is a monotypic family, the only genus being ''Echiurus''. These worms burrow into soft sediment on the seabed.
Species
The World Register of Marine Species recognises the fo ...
*** Family Thalassematidae
*** Family Urechidae
See also
* Aelosoma *Edith Berkeley
Edith Berkeley (1 September 1875–25 February 1963) was a Canadian marine biologist who specialized in the biology of polychaetes. The Edith Berkeley Memorial Lectures were established in the University of British Columbia in her memory in 1969.
...
*'' Australonuphis''
References
Bibliography
* Campbell, Reece, and Mitchell. Biology. 1999. *Notes
External links
World Polychaeta Database
Special issue of ''Marine Ecology''
dedicated to polychaetes
a guide to the marine zooplankton of south eastern Australia
Natural History Museum
A natural history museum or museum of natural history is a scientific institution with natural history collections that include current and historical records of animals, plants, fungi, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, climatology, and more ...
{{Authority control
*
Extant Cambrian first appearances
Paraphyletic groups