anion-exchange on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, the purification of chemicals and separation of substances.
Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, the purification of chemicals and separation of substances.
Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid  Ion exchangers can have binding preferences for certain ions or classes of ions, depending on the physical properties and
Ion exchangers can have binding preferences for certain ions or classes of ions, depending on the physical properties and
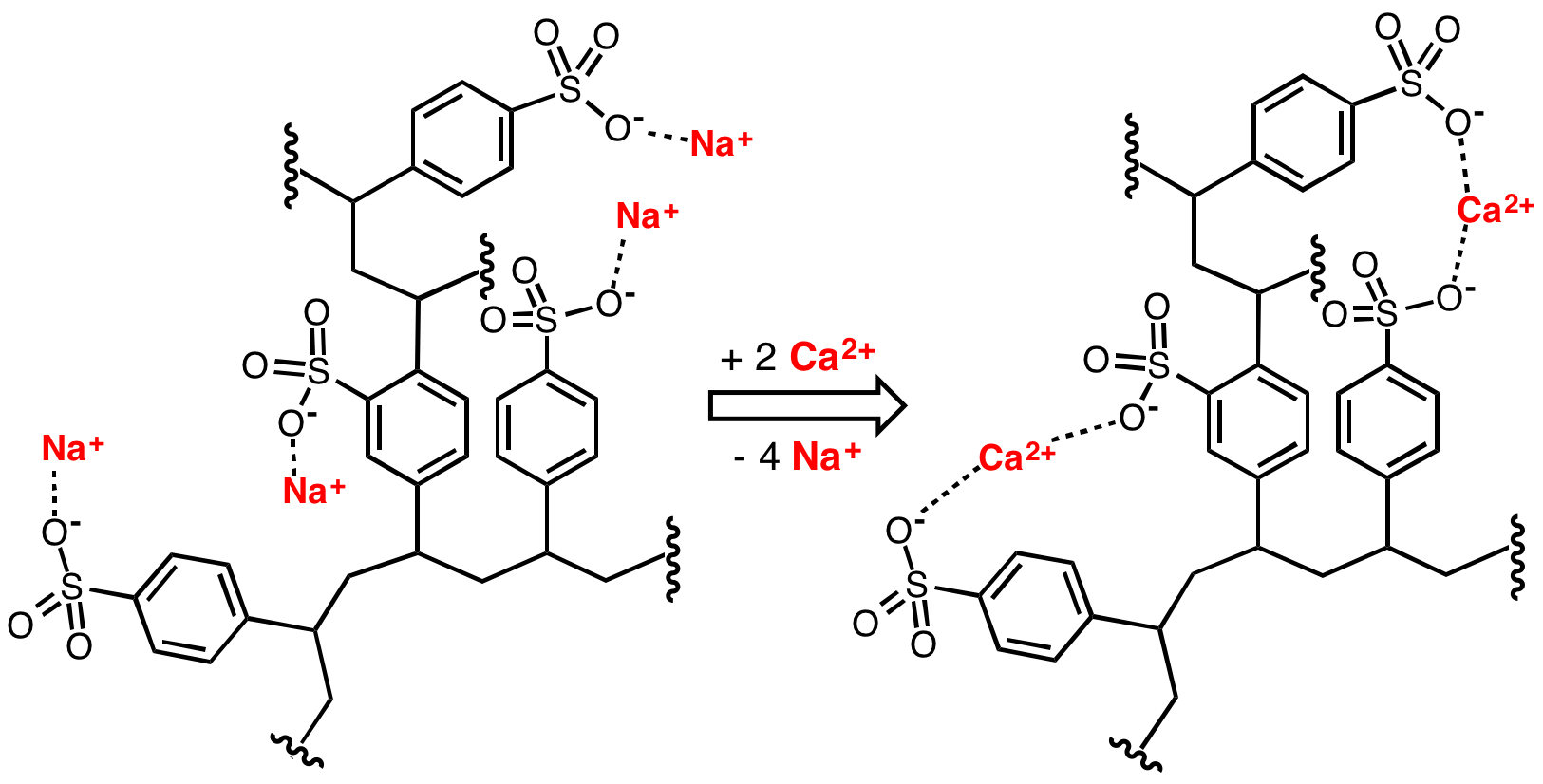 Ion exchange can also be used to remove hardness from water by exchanging calcium and magnesium ions for sodium ions in an ion-exchange column. Liquid-phase (aqueous) ion-exchange desalination has been demonstrated. In this technique anions and cations in salt water are exchanged for carbonate anions and calcium cations respectively using electrophoresis. Calcium and carbonate ions then react to form calcium carbonate, which then precipitates, leaving behind fresh water. The desalination occurs at ambient temperature and pressure and requires no membranes or solid ion exchangers. The theoretical energy efficiency of this method is on par with
Ion exchange can also be used to remove hardness from water by exchanging calcium and magnesium ions for sodium ions in an ion-exchange column. Liquid-phase (aqueous) ion-exchange desalination has been demonstrated. In this technique anions and cations in salt water are exchanged for carbonate anions and calcium cations respectively using electrophoresis. Calcium and carbonate ions then react to form calcium carbonate, which then precipitates, leaving behind fresh water. The desalination occurs at ambient temperature and pressure and requires no membranes or solid ion exchangers. The theoretical energy efficiency of this method is on par with
Ion Exchange Materials: Properties and Applications
Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006. *
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070428014113/http://www.ionexchange.books.kth.se/applets.html Some applets illustrating ion exchange processesbr>A simple explanation of deionizationIon exchange, BioMineWiki
{{Authority control Analytical chemistry General chemistry
 Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, the purification of chemicals and separation of substances.
Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, the purification of chemicals and separation of substances.
Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
ic ion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radius) microbeads, usually white or ye ...
. More precisely, the term encompasses a large variety of processes where ions are exchanged between two electrolytes. Aside from its use to purify drinking water, the technique is widely applied for purification and separation of a variety of industrially and medicinally important chemicals. Although the term usually refers to applications of synthetic (man-made) resins, it can include many other materials such as soil.
Typical ion exchangers are ion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radius) microbeads, usually white or ye ...
s (functionalized porous or gel
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still dif ...
polymer), zeolite
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a metal ion or H+. These p ...
s, montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite gro ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
, and soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
humus. Ion exchangers are either cation exchangers, which exchange positively charged ions ( cations), or anion exchangers, which exchange negatively charged ions (anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s). There are also amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.
One type of amphoteric species are amphipro ...
exchangers that are able to exchange both cations and anions simultaneously. However, the simultaneous exchange of cations and anions is often performed in ''mixed beds'', which contain a mixture of anion- and cation-exchange resins, or passing the solution through several different ion-exchange materials.
 Ion exchangers can have binding preferences for certain ions or classes of ions, depending on the physical properties and
Ion exchangers can have binding preferences for certain ions or classes of ions, depending on the physical properties and chemical structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of ...
of both the ion exchanger and ion. This can be dependent on the size, charge, or structure of the ions. Common examples of ions that can bind to ion exchangers are:
* H+ ( proton) and OH− (hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. I ...
).
* Singly charged monatomic (i.e., monovalent) ions like Na+, K+, and Cl−.
* Doubly charged monatomic (i.e., divalent) ions like Ca2+ and Mg2+.
* Polyatomic inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemist ...
ions like and .
* Organic base
An organic base is an organic compound which acts as a base. Organic bases are usually, but not always, proton acceptors. They usually contain nitrogen atoms, which can easily be protonated. For example, amines or nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ...
s, usually molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s containing the amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element wi ...
functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
−NR2H+.
* Organic acids, often molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s containing −COO− ( carboxylic acid) functional groups.
* Biomolecules that can be ionized: amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
s, peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
...
s, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, etc.
Along with absorption and adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which ...
, ion exchange is a form of sorption
Sorption is a physical and chemical process by which one substance becomes attached to another. Specific cases of sorption are treated in the following articles:
; Absorption: "the incorporation of a substance in one state into another of a d ...
.
Ion exchange is a reversible process, and the ion exchanger can be ''regenerated'' or ''loaded'' with desirable ions by washing with an excess of these ions.
Types
Cation exchange
# CM (Carboxymethyl group, weak cation exchange) # SP (sulphopropyl group, strong cation exchange)Anion exchange
* DEAE-Sepharose * QFFApplications
Ion exchange is widely used in the food and beverage industry, hydrometallurgy, metals finishing, chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical technology, sugar and sweetener production, ground- and potable-water treatment, nuclear, softening, industrial water treatment, semiconductor, power, and many other industries. A typical example of application is preparation of high-purity water forpower engineering
Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of electrical engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electric power, and the electrical apparatus connected to such sy ...
, electronic and nuclear industries; i.e. polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
ic or inorganic insoluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
ion exchangers are widely used for water softening
Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. The resulting soft water requires less soap for the same cleaning effort, as soap is not wasted bonding with calcium ions. Soft water also exten ...
, water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
, water decontamination
Decontamination (sometimes abbreviated as decon, dcon, or decontam) is the process of removing contaminants on an object or area, including chemicals, micro-organisms or radioactive substances. This may be achieved by chemical reaction, disinfecti ...
, etc.
Ion exchange is a method widely used in household filters to produce soft water for the benefit of laundry detergents, soaps, and water heaters. This is accomplished by exchanging divalent cations (such as calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
Ca2+ and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
Mg2+) with highly soluble monovalent cations (e.g., Na+ or H+) (see water softening
Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. The resulting soft water requires less soap for the same cleaning effort, as soap is not wasted bonding with calcium ions. Soft water also exten ...
). Another application for ion exchange in domestic water treatment is the removal of nitrate and natural organic matter. In domestic filtration systems ion exchange is one of the alternatives for water softening in households along with reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. Compared to RO membranes, ion exchange requires repetitive regeneration when inlet water is hard (has high mineral content).
Industrial and analytical ion-exchange chromatography
Ion chromatography (or ion-exchange chromatography) separates ions and polar molecules based on their affinity to the ion exchanger. It works on almost any kind of charged molecule—including large proteins, small nucleotides, and amino a ...
is another area to be mentioned.
Ion-exchange chromatography is a chromatographical method that is widely used for chemical analysis and separation of ions. For example, in biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
it is widely used to separate charged molecules such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s. An important area of the application is extraction and purification of biologically produced substances such as proteins ( amino acids) and DNA/ RNA.
Ion-exchange processes are used to separate and purify metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
s, including separating uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
from plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
and the other actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
s, including thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
, neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it bein ...
, and americium. This process is also used to separate the lanthanides, such as lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lant ...
, cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 ...
, neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishe ...
, praseodymium
Praseodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Pr and the atomic number 59. It is the third member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal, valued for i ...
, europium, and ytterbium
Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. However, like the othe ...
, from each other. The separation of neodymium and praseodymium was a particularly difficult one, and those were formerly thought to be just one element didymium
Didymium ( el, , twin) is a mixture of the elements praseodymium and neodymium. It is used in safety glasses for glassblowing and blacksmithing, especially with a gas ( propane)-powered forge, where it provides a filter that selectively block ...
– but that is an alloy of the two.
There are two series of rare-earth metal
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous sil ...
s, the lanthanides and the actinides, both of whose families all have very similar chemical and physical properties. Using methods developed by Frank Spedding
Frank Harold Spedding (22 October 1902 – 15 December 1984) was a Canadian American chemist. He was a renowned expert on rare earth elements, and on extraction of metals from minerals. The uranium extraction process helped make it possible for ...
in the 1940s, ion-exchange processes were formerly the only practical way to separate them in large quantities, until the development of the "solvent extraction" techniques that can be scaled up enormously.
A very important case of ion-exchange is the plutonium-uranium extraction process (PUREX
PUREX (plutonium uranium reduction extraction) is a chemical method used to purify fuel for nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons. PUREX is the ''de facto'' standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and plutonium ...
), which is used to separate the plutonium (mainly ) and the uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
(in that case known as reprocessed uranium
Reprocessed uranium (RepU) is the uranium recovered from nuclear reprocessing, as done commercially in France, the UK and Japan and by nuclear weapons states' military plutonium production programs. This uranium makes up the bulk of the material s ...
) contained in spent fuel
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor a ...
from americium, curium, neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it bein ...
(the minor actinide
The minor actinides are the actinide elements in used nuclear fuel other than uranium and plutonium, which are termed the major actinides. The minor actinides include neptunium (element 93), americium (element 95), curium (element 96), berkeliu ...
s), and the fission products that come from nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat fr ...
s. Thus the waste products can be separated out for disposal. Next, the plutonium and uranium are available for making nuclear-energy materials, such as new reactor fuel ( MOX-fuel) and (plutonium-based) nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s. Historically some fission products such as Strontium-90
Strontium-90 () is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.8 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine and ...
or Caesium-137
Caesium-137 (), cesium-137 (US), or radiocaesium, is a radioactive isotope of caesium that is formed as one of the more common fission products by the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and other fissionable isotopes in nuclear reactors and nucle ...
were likewise separated for use as radionuclides employed in industry or medicine.
The ion-exchange process is also used to separate other sets of very similar chemical elements, such as zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'' ...
and hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
, which is also very important for the nuclear industry. Physically, zirconium is practically transparent to free neutrons, used in building nuclear reactors, but hafnium is a very strong absorber of neutrons, used in reactor control rods.
Thus, ion-exchange is used in nuclear reprocessing and the treatment of radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons r ...
.
Ion-exchange resins in the form of thin membranes are also used in chloralkali process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodit ...
, fuel cells, and vanadium redox batteries.
 Ion exchange can also be used to remove hardness from water by exchanging calcium and magnesium ions for sodium ions in an ion-exchange column. Liquid-phase (aqueous) ion-exchange desalination has been demonstrated. In this technique anions and cations in salt water are exchanged for carbonate anions and calcium cations respectively using electrophoresis. Calcium and carbonate ions then react to form calcium carbonate, which then precipitates, leaving behind fresh water. The desalination occurs at ambient temperature and pressure and requires no membranes or solid ion exchangers. The theoretical energy efficiency of this method is on par with
Ion exchange can also be used to remove hardness from water by exchanging calcium and magnesium ions for sodium ions in an ion-exchange column. Liquid-phase (aqueous) ion-exchange desalination has been demonstrated. In this technique anions and cations in salt water are exchanged for carbonate anions and calcium cations respectively using electrophoresis. Calcium and carbonate ions then react to form calcium carbonate, which then precipitates, leaving behind fresh water. The desalination occurs at ambient temperature and pressure and requires no membranes or solid ion exchangers. The theoretical energy efficiency of this method is on par with electrodialysis
Electrodialysis (ED) is used to transport salt ions from one solution through ion-exchange membranes to another solution under the influence of an applied electric potential difference. This is done in a configuration called an electrodialysis ...
and reverse osmosis.
Other applications
* Insoil science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to th ...
, cation-exchange capacity
Cation-exchange capacity (CEC) is a measure of how many cations can be retained on soil particle surfaces. Negative charges on the surfaces of soil particles bind positively-charged atoms or molecules (cations), but allow these to exchange with ot ...
is the ion-exchange capacity of soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
for positively charged ions. Soils can be considered as natural weak cation exchangers.
* In pollution remediation and geotechnical engineering, ion-exchange capacity determines the swelling capacity of swelling or expansive clay
Expansive clay is a clay soil that is prone to large volume changes (swelling and shrinking) that are directly related to changes in water content. Soils with a high content of expansive minerals can form deep cracks in drier seasons or years; su ...
such as montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite gro ...
, which can be used to "capture" pollutants and charged ions.
* In planar waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities de ...
manufacturing, ion exchange is used to create the guiding layer of higher index of refraction.
* Dealkalization Dealkalization is a process of surface modification applicable to glasses containing alkali ions, wherein a thin surface layer is created that has a lower concentration of alkali ions than is present in the underlying, bulk glass. This change in s ...
, removal of alkali ions from a glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
surface.
* Chemically strengthened glass
Chemically strengthened glass is a type of glass that has increased strength as a result of a post-production chemical process. When broken, it still shatters in long pointed splinters similar to float glass. For this reason, it is not considered ...
, produced by exchanging K+ for Na+ in soda glass surfaces using KNO3 melts.
Waste water produced by resin regeneration
Most ion-exchange systems use columns of ion-exchangeresin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on n ...
that are operated on a cyclic basis.
During the filtration process, water flows through the resin column until the resin is considered exhausted. That happens only when water leaving the column contains more than the maximal desired concentration of the ions being removed. Resin is then regenerated by sequentially backwashing the resin bed to remove accumulated suspended solids, flushing removed ions from the resin with a concentrated solution of replacement ions, and rinsing the flushing solution from the resin. Production of backwash, flushing, and rinsing wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
during regeneration of ion-exchange media limits the usefulness of ion exchange for wastewater treatment.
Water softeners are usually regenerated with brine containing 10% sodium chloride. Aside from the soluble chloride salts of divalent cations removed from the softened water, softener regeneration wastewater contains the unused 50–70% of the sodium chloride regeneration flushing brine required to reverse ion-exchange resin equilibria. Deionizing resin regeneration with sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide is approximately 20–40% efficient. Neutralized deionizer regeneration wastewater contains all of the removed ions plus 2.5–5 times their equivalent concentration
In chemistry, the equivalent concentration or normality (N) of a solution is defined as the molar concentration ''ci'' divided by an equivalence factor ''f''eq:
:Normality =
Definition
Normality is defined as the number of gramme or mole e ...
as sodium sulfate.Kemmer, pp. 12–18.
See also
*Alkali anion exchange membrane
An anion exchange membrane (AEM) is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct anions but reject gases such as oxygen or hydrogen.
Applications
Anion exchange membranes are used in electrolytic cells and fuel ...
* Ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
* Ion chromatography
Ion chromatography (or ion-exchange chromatography) separates ions and polar molecules based on their affinity to the ion exchanger. It works on almost any kind of charged molecule—including large proteins, small nucleotides, and amino acid ...
* Ion-exchange membrane An ion-exchange membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that transports certain dissolved ions, while blocking other ions or neutral molecules.
Ion-exchange membranes are therefore electrically conductive. They are often used in desalination and c ...
s
* Ion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radius) microbeads, usually white or ye ...
* Desalination
* Reverse osmosis
References
Further information
* * Ion Exchangers (K. Dorfner, ed.), Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, 1991. * C. E. Harland, Ion exchange: Theory and Practice, The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 1994. * * * Ion exchange (D. Muraviev, V. Gorshkov, A. Warshawsky), M. Dekker, New York, 2000. * A. A. ZagorodniIon Exchange Materials: Properties and Applications
Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006. *
External links
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070428014113/http://www.ionexchange.books.kth.se/applets.html Some applets illustrating ion exchange processesbr>A simple explanation of deionization
{{Authority control Analytical chemistry General chemistry