Zoological Institute on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the
 The history of zoology traces the study of the animal kingdom from ancient to modern times. Prehistoric people needed to study the animals and plants in their environment in order to exploit them and survive. There are cave paintings, engravings and sculptures in France dating back 15,000 years showing bison, horses and deer in carefully rendered detail. Similar images from other parts of the world illustrated mostly the animals hunted for food, but also the savage animals.
The
The history of zoology traces the study of the animal kingdom from ancient to modern times. Prehistoric people needed to study the animals and plants in their environment in order to exploit them and survive. There are cave paintings, engravings and sculptures in France dating back 15,000 years showing bison, horses and deer in carefully rendered detail. Similar images from other parts of the world illustrated mostly the animals hunted for food, but also the savage animals.
The
 Many scientists now consider the five-kingdom system outdated. Modern alternative classification systems generally start with the three-domain system:
Many scientists now consider the five-kingdom system outdated. Modern alternative classification systems generally start with the three-domain system:
 Physiology studies the mechanical, physical, and biochemical processes of living organisms by attempting to understand how all of the structures function as a whole. The theme of "structure to function" is central to biology. Physiological studies have traditionally been divided into
Physiology studies the mechanical, physical, and biochemical processes of living organisms by attempting to understand how all of the structures function as a whole. The theme of "structure to function" is central to biology. Physiological studies have traditionally been divided into


Books on Zoology
at Project Gutenberg *
Online Dictionary of Invertebrate Zoology
' {{Authority control Branches of biology
structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
, embryology, evolution, classification Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organizat ...
, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study').
Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the onset of the Early Middle Ages, the Greek tradition of medicine and scientific study went into decline in Western Europe, although it continued in the medieval Islamic world
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
. Modern zoology has its origins during the Renaissance and early modern period, with Carl Linnaeus, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " the ...
, Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
, Charles Darwin, Gregor Mendel and many others.
The study of animals has largely moved on to deal with form and function, adaptations, relationships between groups, behaviour and ecology. Zoology has increasingly been subdivided into disciplines such as classification Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organizat ...
, physiology, biochemistry and evolution. With the discovery of the structure of DNA by Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
and James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and ...
in 1953, the realm of molecular biology opened up, leading to advances in cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
, developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
and molecular genetics.
History
 The history of zoology traces the study of the animal kingdom from ancient to modern times. Prehistoric people needed to study the animals and plants in their environment in order to exploit them and survive. There are cave paintings, engravings and sculptures in France dating back 15,000 years showing bison, horses and deer in carefully rendered detail. Similar images from other parts of the world illustrated mostly the animals hunted for food, but also the savage animals.
The
The history of zoology traces the study of the animal kingdom from ancient to modern times. Prehistoric people needed to study the animals and plants in their environment in order to exploit them and survive. There are cave paintings, engravings and sculptures in France dating back 15,000 years showing bison, horses and deer in carefully rendered detail. Similar images from other parts of the world illustrated mostly the animals hunted for food, but also the savage animals.
The Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
, which is characterized by the domestication of animals
The domestication of animals is the mutual relationship between non-human animals and the humans who have influence on their care and reproduction.
Charles Darwin recognized a small number of traits that made domesticated species different from t ...
, continued over the period of Antiquity. Ancient knowledge of wildlife is illustrated by the realistic depictions of wild and domestic animals in the Near East, Mesopotamia and Egypt, including husbandry practices and techniques, hunting and fishing. The invention of writing is reflected in zoology by the presence of animals in Egyptian hieroglyphics.
Although the concept of ''zoology'' as a single coherent field arose much later, the zoological sciences emerged from natural history reaching back to the biological works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
. Aristotle, in the fourth century BC, looked at animals as living organisms, studying their structure, development and vital phenomena. He divided them into two groups: animals with blood, equivalent to our concept of vertebrates, and animals without blood, invertebrates. He spent two years on Lesbos, observing and describing the animals and plants, considering the adaptations of different organisms and the function of their parts. Four hundred years later, Roman physician Galen dissected animals to study their anatomy and the function of the different parts, because the dissection of human cadavers was prohibited at the time. This resulted in some of his conclusions being false, but for many centuries it was considered heretical to challenge any of his views, so the study of anatomy stultified.
During the post-classical era, Middle Eastern science and medicine was the most advanced in the world, integrating concepts from Ancient Greece, Rome, Mesopotamia and Persia as well as the ancient Indian tradition of Ayurveda, while making numerous advances and innovations. In the 13th century, Albertus Magnus produced commentaries and paraphrases of all Aristotle's works; his books on topics like botany, zoology, and minerals included information from ancient sources, but also the results of his own investigations. His general approach was surprisingly modern, and he wrote, "For it is he task
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
of natural science not simply to accept what we are told but to inquire into the causes of natural things." An early pioneer was Conrad Gessner, whose monumental 4,500-page encyclopedia of animals, '' Historia animalium'', was published in four volumes between 1551 and 1558.
In Europe, Galen's work on anatomy remained largely unsurpassed and unchallenged up until the 16th century. During the Renaissance and early modern period, zoological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological theory that holds that knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience. It is one of several views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empir ...
and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Andreas Vesalius and William Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Carl Linnaeus, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as studying the development and behavior of organisms. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " the ...
did pioneering work in microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
and revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. van Leeuwenhoek's observations were endorsed by Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
; all living organisms were composed of one or more cells and could not generate spontaneously. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life.
Having previously been the realm of gentlemen naturalists, over the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries, zoology became an increasingly professional scientific discipline. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography, laying the foundations for biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism
Essentialism is the view that objects have a set of attributes that are necessary to their identity. In early Western thought, Plato's idealism held that all things have such an "essence"—an "idea" or "form". In ''Categories'', Aristotle sim ...
and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species.
These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection; in this Darwin placed the theory of organic evolution on a new footing, by explaining the processes by which it can occur, and providing observational evidence that it had done so. Darwin's theory
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
was rapidly accepted by the scientific community and soon became a central axiom of the rapidly developing science of biology. The basis for modern genetics began with the work of Gregor Mendel on peas in 1865, although the significance of his work was not realized at the time.
Darwin gave a new direction to morphology and physiology, by uniting them in a common biological theory: the theory of organic evolution. The result was a reconstruction of the classification of animals upon a genealogical
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinsh ...
basis, fresh investigation of the development of animals, and early attempts to determine their genetic relationships. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery. In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the modern synthesis created evolutionary biology.
Research in cell biology is interconnected to other fields such as genetics, biochemistry, medical microbiology
Medical microbiology, the large subset of microbiology that is applied to medicine, is a branch of medical science concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. In addition, this field of science studies various ...
, immunology, and cytochemistry. With the sequencing of the DNA molecule by Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
and James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and ...
in 1953, the realm of molecular biology opened up, leading to advances in cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
, developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
and molecular genetics. The study of systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre ...
was transformed as DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Th ...
elucidated the degrees of affinity between different organisms.
Scope
Zoology is the branch of science dealing with animals. A species can be defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sex can produce fertile offspring; about 1.5 million species of animal have been described and it has been estimated that as many as 8 million animal species may exist. An early necessity was to identify the organisms and group them according to their characteristics, differences and relationships, and this is the field of the taxonomist. Originally it was thought that species were immutable, but with the arrival of Darwin's theory of evolution, the field of cladistics came into being, studying the relationships between the different groups orclade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s. Systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre ...
is the study of the diversification of living forms, the evolutionary history of a group is known as its phylogeny, and the relationship between the clades can be shown diagrammatically in a cladogram.
Although someone who made a scientific study of animals would historically have described themselves as a zoologist, the term has come to refer to those who deal with individual animals, with others describing themselves more specifically as physiologists, ethologists, evolutionary biologists, ecologists, pharmacologists, endocrinologists or parasitologists.
Branches of zoology
Although the study of animal life is ancient, its scientific incarnation is relatively modern. This mirrors the transition from natural history to biology at the start of the 19th century. SinceHunter
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
and Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, Baron Cuvier (; 23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier, was a French naturalist and zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in nat ...
, comparative anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
study has been associated with morphography, shaping the modern areas of zoological investigation: anatomy, physiology, histology, embryology, teratology and ethology. Modern zoology first arose in German and British universities. In Britain, Thomas Henry Huxley was a prominent figure. His ideas were centered on the morphology of animals. Many consider him the greatest comparative anatomist of the latter half of the 19th century. Similar to Hunter
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
, his courses were composed of lectures and laboratory practical classes in contrast to the previous format of lectures only.
Classification
Scientific classification in zoology, is a method by which zoologists group and categorize organisms bybiological type
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the ...
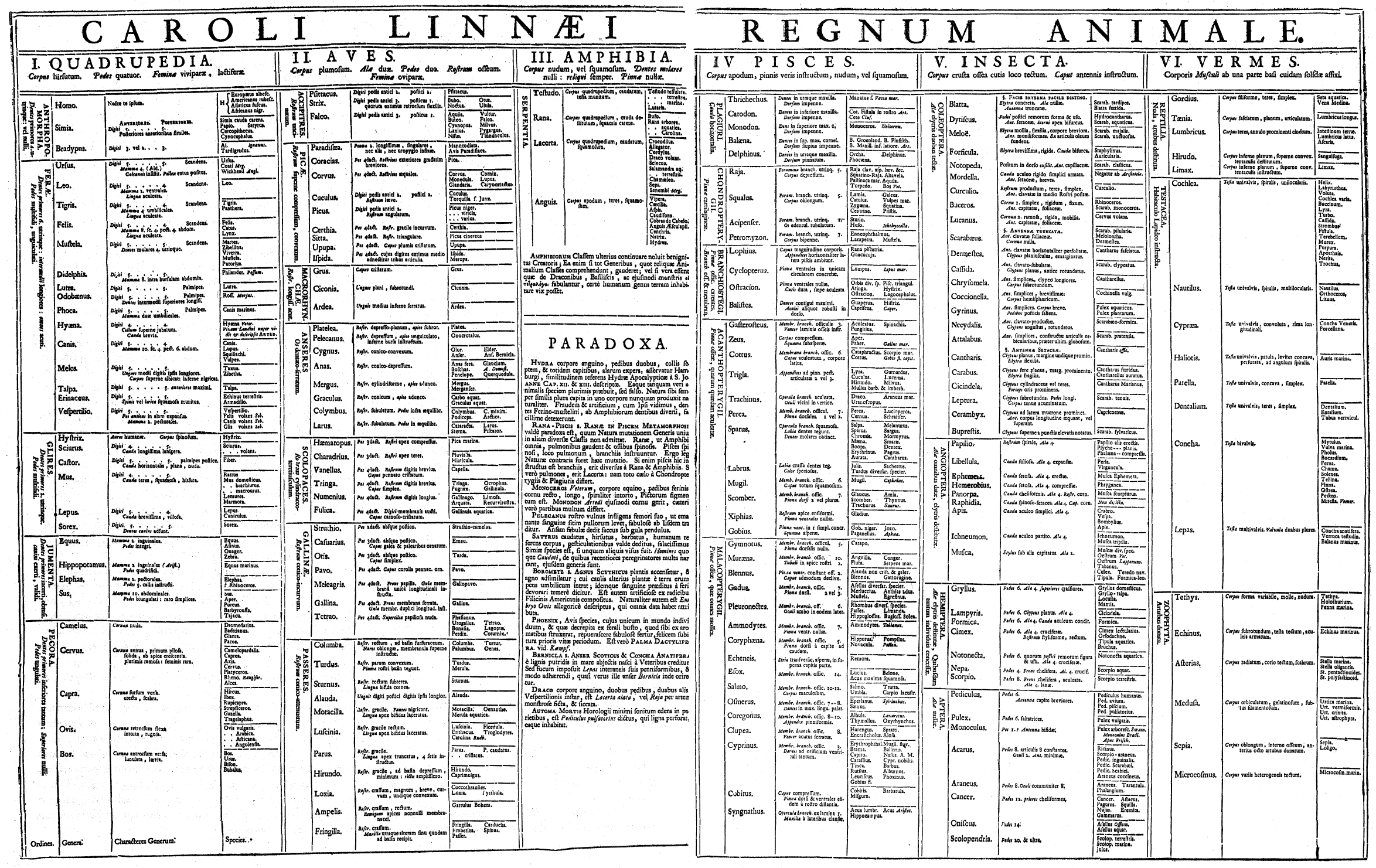
, such as genus or species. Biological classification is a form of scientific taxonomy. Modern biological classification has its root in the work of Carl Linnaeus, who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics. These groupings have since been revised to improve consistency with the Darwinian principle of common descent
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
. Molecular phylogenetics, which uses nucleic acid sequence
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of Nucleobase, bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequence ...
as data, has driven many recent revisions and is likely to continue to do so. Biological classification belongs to the science of zoological systematics.
 Many scientists now consider the five-kingdom system outdated. Modern alternative classification systems generally start with the three-domain system:
Many scientists now consider the five-kingdom system outdated. Modern alternative classification systems generally start with the three-domain system: Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
(originally Archaebacteria); Bacteria (originally Eubacteria); Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
(including protists, fungi, plants, and animals) These domains reflect whether the cells have nuclei or not, as well as differences in the chemical composition of the cell exteriors.
Further, each kingdom is broken down recursively until each species is separately classified. The order is:
Domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
; kingdom; phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature f ...
; class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differentl ...
; order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
; family; genus; species. The scientific name of an organism is generated from its genus and species. For example, humans are listed as '' Homo sapiens''. ''Homo'' is the genus, and ''sapiens'' the specific epithet, both of them combined make up the species name. When writing the scientific name of an organism, it is proper to capitalize the first letter in the genus and put all of the specific epithet in lowercase. Additionally, the entire term may be italicized or underlined.
The dominant classification system is called the Linnaean taxonomy. It includes ranks and binomial nomenclature. The classification, taxonomy, and nomenclature of zoological organisms is administered by the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. A merging draft, BioCode, was published in 1997 in an attempt to standardize nomenclature, but has yet to be formally adopted.
Vertebrate and invertebrate zoology
Vertebrate zoology is thebiological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
discipline
Discipline refers to rule following behavior, to regulate, order, control and authority. It may also refer to punishment. Discipline is used to create habits, routines, and automatic mechanisms such as blind obedience. It may be inflicted on ot ...
that consists of the study of vertebrate animals, that is animals with a backbone, such as fish, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s, birds and mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s. The various taxonomically oriented disciplines such as mammalogy In zoology, mammalogy is the study of mammals – a class of vertebrates with characteristics such as homeothermic metabolism, fur, four-chambered hearts, and complex nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part o ...
, biological anthropology, herpetology
Herpetology (from Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is the branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians (gymnophiona)) and rept ...
, ornithology, and ichthyology
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish ( Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha). According to FishBase, 33,400 species of fish had been described as of Octob ...
seek to identify and classify species and study the structures and mechanisms specific to those groups. The rest of the animal kingdom is dealt with by invertebrate zoology Invertebrate zoology is the subdiscipline of zoology that consists of the study of invertebrates, animals without a backbone (a structure which is found only in fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals).
Invertebrates are a vast and very di ...
, a vast and very diverse group of animals that includes sponges, echinoderms, tunicates, worms, mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
s, arthropods and many other phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
, but single-celled organisms or protists are not usually included.
Structural zoology
Cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
studies the structural and physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
properties of cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, including their behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as wel ...
, interactions, and environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
. This is done on both the microscopic and molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
levels for single-celled organisms such as bacteria as well as the specialized cells in multicellular organisms such as humans. Understanding the structure and function of cells is fundamental to all of the biological sciences. The similarities and differences between cell types are particularly relevant to molecular biology.
Anatomy considers the forms of macroscopic structures such as organs and organ systems. It focuses on how organs and organ systems work together in the bodies of humans and animals, in addition to how they work independently. Anatomy and cell biology are two studies that are closely related, and can be categorized under "structural" studies. Comparative anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species).
The science began in the classical era, continuing in t ...
is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different groups. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species).
Physiology
 Physiology studies the mechanical, physical, and biochemical processes of living organisms by attempting to understand how all of the structures function as a whole. The theme of "structure to function" is central to biology. Physiological studies have traditionally been divided into
Physiology studies the mechanical, physical, and biochemical processes of living organisms by attempting to understand how all of the structures function as a whole. The theme of "structure to function" is central to biology. Physiological studies have traditionally been divided into plant physiology
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (bi ...
and animal physiology, but some principles of physiology are universal, no matter what particular organism is being studied. For example, what is learned about the physiology of yeast cells can also apply to human cells. The field of animal physiology extends the tools and methods of human physiology to non-human species. Physiology studies how, for example, the nervous, immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
, endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
, respiratory, and circulatory
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
systems function and interact.
Developmental biology
Developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
is the study of the processes by which animals and plants reproduce and grow. The discipline includes the study of embryonic development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
, cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
, regeneration
Regeneration may refer to:
Science and technology
* Regeneration (biology), the ability to recreate lost or damaged cells, tissues, organs and limbs
* Regeneration (ecology), the ability of ecosystems to regenerate biomass, using photosynthesis
...
, asexual and sexual reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
, metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
, and the growth and differentiation of stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
s in the adult organism. Development of both animals and plants is further considered in the articles on evolution, population genetics, heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
, genetic variability, Mendelian inheritance, and reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
.
Evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. Evolutionary research is concerned with the origin and descent of species, as well as their change over time, and includes scientists from manytaxonomically
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given ...
oriented disciplines. For example, it generally involves scientists who have special training in particular organisms such as mammalogy In zoology, mammalogy is the study of mammals – a class of vertebrates with characteristics such as homeothermic metabolism, fur, four-chambered hearts, and complex nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part o ...
, ornithology, herpetology
Herpetology (from Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is the branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians (gymnophiona)) and rept ...
, or entomology
Entomology () is the science, scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such ...
, but use those organisms as systems to answer general questions about evolution.
Evolutionary biology is partly based on paleontology, which uses the fossil record to answer questions about the mode and tempo of evolution, and partly on the developments in areas such as population genetics and evolutionary theory. Following the development of DNA fingerprinting
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's DNA characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is called DNA barcoding.
DNA profiling is a forensic tec ...
techniques in the late 20th century, the application of these techniques in zoology has increased the understanding of animal populations. In the 1980s, developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
re-entered evolutionary biology from its initial exclusion from the modern synthesis through the study of evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved.
The field grew from 19th-century beginni ...
. Related fields often considered part of evolutionary biology are phylogenetics, systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre ...
, and taxonomy.
Ethology
Ethology is the scientific and objective study of animal behavior under natural conditions, as opposed tobehaviorism
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understanding the behavior of humans and animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex evoked by the pairing of certain antecedent (behavioral psychology), antecedent stimuli in the environment, o ...
, which focuses on behavioral response studies in a laboratory setting. Ethologists have been particularly concerned with the evolution of behavior and the understanding of behavior in terms of the theory of natural selection. In one sense, the first modern ethologist was Charles Darwin, whose book, '' The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals,'' influenced many future ethologists.
A subfield of ethology is behavioral ecology
Behavioral ecology, also spelled behavioural ecology, is the study of the evolutionary basis for animal behavior due to ecological pressures. Behavioral ecology emerged from ethology after Niko Tinbergen outlined four questions to address when ...
which attempts to answer Nikolaas Tinbergen's four questions
Ma Nishtana ( he, מה נשתנה) are the first two words in a phrase meaning "Why is tonight different from all other nights?" The phrase appears at the beginning of each line of The Four Questions, traditionally asked via song by the youngest ...
with regard to animal behavior: what are the proximate causes of the behavior, the developmental history of the organism, the survival value and phylogeny of the behavior? Another area of study is animal cognition, which uses laboratory experiments and carefully controlled field studies to investigate an animal's intelligence and learning.

Biogeography
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
studies the spatial distribution of organisms on the Earth, focusing on topics like dispersal and migration, plate tectonics, climate change, and cladistics. It is an integrative field of study, uniting concepts and information from evolutionary biology, taxonomy, ecology, physical geography, geology, paleontology and climatology. The origin of this field of study is widely accredited to Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural se ...
, a British biologist who had some of his work jointly published with Charles Darwin.
Molecular biology
Molecular biology studies the common genetic and developmental mechanisms of animals and plants, attempting to answer the questions regarding the mechanisms of genetic inheritance and the structure of the gene. In 1953,James Watson
James Dewey Watson (born April 6, 1928) is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist. In 1953, he co-authored with Francis Crick the academic paper proposing the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Watson, Crick and ...
and Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical struc ...
described the structure of DNA and the interactions within the molecule, and this publication jump-started research into molecular biology and increased interest in the subject. While researchers practice techniques specific to molecular biology, it is common to combine these with methods from genetics and biochemistry. Much of molecular biology is quantitative, and recently a significant amount of work has been done using computer science techniques such as bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combi ...
and computational biology
Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has fo ...
. Molecular genetics, the study of gene structure and function, has been among the most prominent sub-fields of molecular biology since the early 2000s. Other branches of biology are informed by molecular biology, by either directly studying the interactions of molecules in their own right such as in cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
and developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
, or indirectly, where molecular techniques are used to infer historical attributes of populations or species, as in fields in evolutionary biology such as population genetics and phylogenetics. There is also a long tradition of studying biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include large ...
s "from the ground up", or molecularly, in biophysics.
See also
*Animal science
Animal science is described as "studying the biology of animals that are under the control of humankind". It can also be described as the production and management of farm animals. Historically, the degree was called animal husbandry and the ...
, the biology of domesticated animals
* Astrobiology
Astrobiology, and the related field of exobiology, is an interdisciplinary scientific field that studies the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. Astrobiology is the multidisciplinary field that investig ...
* Cognitive zoology
* Evolutionary biology
* List of zoologists
This is a list of notable zoology, zoologists who have published names of new taxon, taxa under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.
A
* Abe – Tokiharu Abe (1911–1996)
* Abeille de Perrin, Ab. – Elzéar Abeille de Perrin (1 ...
* Outline of zoology
* Palaeontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
* Timeline of zoology
This is a chronologically organized listing of notable zoological events and discoveries.
Ancient world
*28000 BC. Cave painting (e.g. Chauvet Cave) in southern France and northern Spain depicts animals in a stylized fashion. These European ...
* Zoological distribution
Zoogeography is the branch of the science of biogeography that is concerned with geographic distribution (present and past) of animal species.
As a multifaceted field of study, zoogeography incorporates methods of molecular biology, genetics, mor ...
Notes
References
External links
Books on Zoology
at Project Gutenberg *
Online Dictionary of Invertebrate Zoology
' {{Authority control Branches of biology