Zodiac Fighters on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
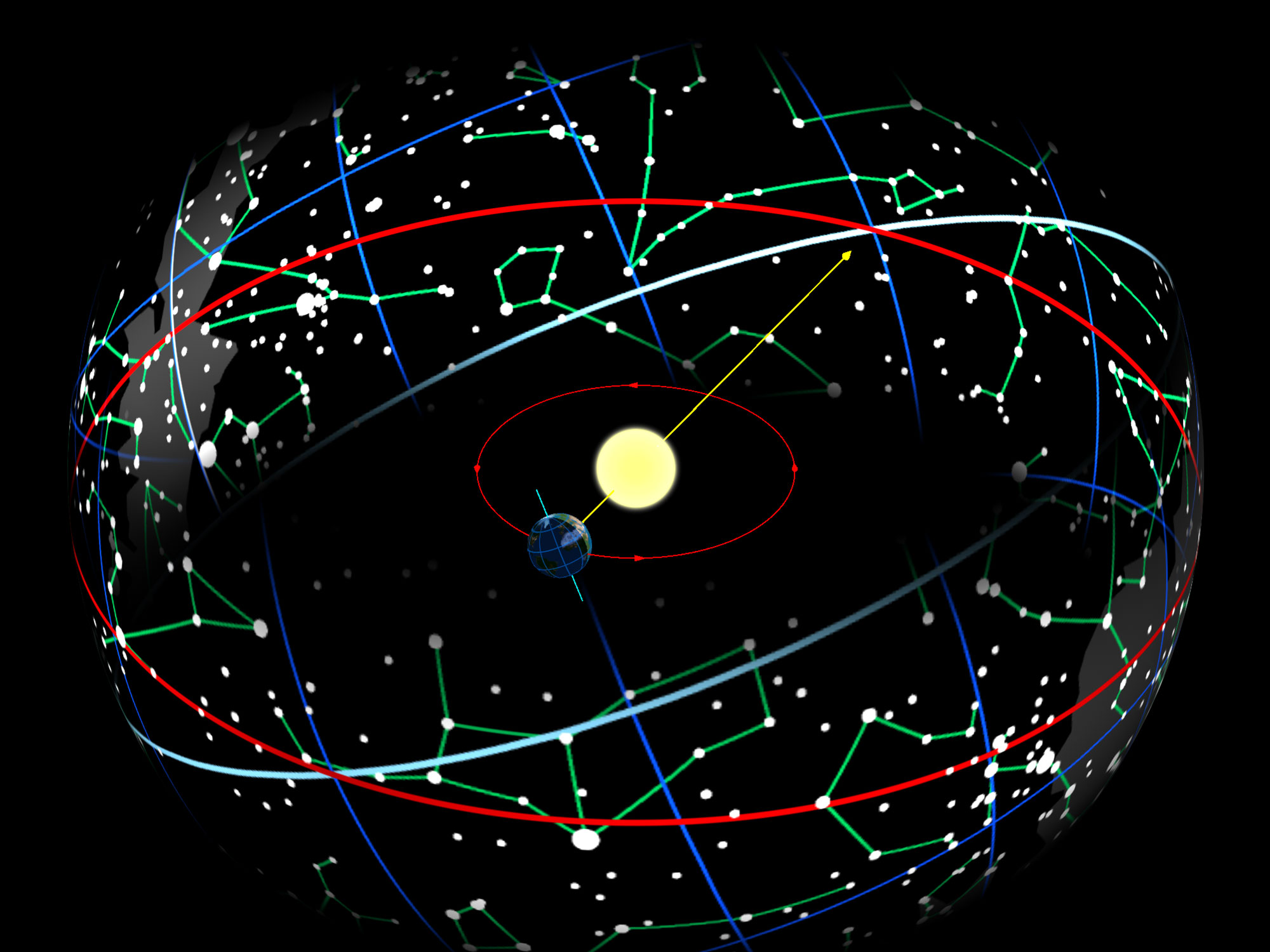 The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in
 The zodiac was in use by the Roman era, based on concepts inherited by Hellenistic astronomy from Babylonian astronomy of the Chaldean period (mid-1st millennium BC), which, in turn, derived from an earlier system of lists of stars along the ecliptic. The construction of the zodiac is described in Ptolemy's comprehensive 2nd century AD work, the ''
The zodiac was in use by the Roman era, based on concepts inherited by Hellenistic astronomy from Babylonian astronomy of the Chaldean period (mid-1st millennium BC), which, in turn, derived from an earlier system of lists of stars along the ecliptic. The construction of the zodiac is described in Ptolemy's comprehensive 2nd century AD work, the ''

 The division of the ecliptic into the zodiacal signs originates in Babylonian astronomy during the first half of the
The division of the ecliptic into the zodiacal signs originates in Babylonian astronomy during the first half of the
 The Babylonian star catalogs entered Greek astronomy in the 4th century BC, via
The Babylonian star catalogs entered Greek astronomy in the 4th century BC, via
 During the Abbasid era, Greek reference books were systematically translated into Arabic, and Islamic astronomers then did their own observations, correcting Ptolemy's Almagest. One such book was Al-Sufi's '' Book of Fixed Stars'', which has pictorial depictions of 48 constellations. The book was divided into three sections: constellations of the zodiac, constellations north of the zodiac, and southern constellations. When Al-Sufi's book, and other works, were translated in the 11th century, there were mistakes made in the translations. As a result, some stars ended up with the names of the constellation they belong to (e.g. Hamal in Aries).
The High Middle Ages saw a revival of interest in Greco-Roman magic, first in
During the Abbasid era, Greek reference books were systematically translated into Arabic, and Islamic astronomers then did their own observations, correcting Ptolemy's Almagest. One such book was Al-Sufi's '' Book of Fixed Stars'', which has pictorial depictions of 48 constellations. The book was divided into three sections: constellations of the zodiac, constellations north of the zodiac, and southern constellations. When Al-Sufi's book, and other works, were translated in the 11th century, there were mistakes made in the translations. As a result, some stars ended up with the names of the constellation they belong to (e.g. Hamal in Aries).
The High Middle Ages saw a revival of interest in Greco-Roman magic, first in
 Astrology emerged in the 8th century CE as a distinct discipline in Islam, with a mix of Indian, Hellenistic Iranian and other traditions blended with Greek and Islamic astronomical knowledge, for example Ptolemy's work and Al-Sufi's Book of Fixed Stars. A knowledge of the influence that the stars have on events on the earth was important in Islamic civilization. As a rule, it was believed that the signs of the zodiac and the planets control the destiny not only of people but also of nations, and that the zodiac has the ability to determine a person's physical characteristics as well as intelligence and personal traits.
The practice of astrology at this time could be divided into 4 broader categories: Genethlialogy, Catarchic Astrology, Interrogational Astrology and General Astrology. However the most common type of astrology was Genethlialogy, which examined all aspects of a person's life in relation to the planetary positions at their birth; more commonly known as our horoscope.
Astrology services were offered widely across the empire, mainly in bazaars, where people could pay for a reading. Astrology was valued in the royal courts, for example, the Abbasid Caliph Al-Mansur used astrology to determine the best date for founding the new capital of Baghdad. Whilst horoscopes were generally widely accepted by society, many scholars condemned the use of astrology and divination, linking it to occult influences. Many theologians and scholars thought that it went against the tenets of Islam; as only God should be able to determine events rather than astrologers looking at the positions of the planets.
In order to calculate someone's horoscope, an astrologer would use 3 tools: an astrolabe, ephemeris and a takht. First, the astrologer would use an astrolabe to find the position of the sun, align the rule with the persons time of birth and then align the rete to establish the altitude of the sun on that date. Next, the astrologer would use an Ephemeris, a table denoting the mean position of the planets and stars within the sky at any given time. Finally, the astrologer would add the altitude of the sun taken from the astrolabe, with the mean position of the planets on the person's birthday, and add them together on the takht (also known as the dustboard). The dust board was merely a tablet covered in sand; on which the calculations could be made and erased easily. Once this had been calculated, the astrologer was then able to interpret the horoscope. Most of these interpretations were based on the zodiac in literature. For example, there were several manuals on how to interpret each zodiac sign, the treatise relating to each individual sign and what the characteristics of these zodiacs were.
Astrology emerged in the 8th century CE as a distinct discipline in Islam, with a mix of Indian, Hellenistic Iranian and other traditions blended with Greek and Islamic astronomical knowledge, for example Ptolemy's work and Al-Sufi's Book of Fixed Stars. A knowledge of the influence that the stars have on events on the earth was important in Islamic civilization. As a rule, it was believed that the signs of the zodiac and the planets control the destiny not only of people but also of nations, and that the zodiac has the ability to determine a person's physical characteristics as well as intelligence and personal traits.
The practice of astrology at this time could be divided into 4 broader categories: Genethlialogy, Catarchic Astrology, Interrogational Astrology and General Astrology. However the most common type of astrology was Genethlialogy, which examined all aspects of a person's life in relation to the planetary positions at their birth; more commonly known as our horoscope.
Astrology services were offered widely across the empire, mainly in bazaars, where people could pay for a reading. Astrology was valued in the royal courts, for example, the Abbasid Caliph Al-Mansur used astrology to determine the best date for founding the new capital of Baghdad. Whilst horoscopes were generally widely accepted by society, many scholars condemned the use of astrology and divination, linking it to occult influences. Many theologians and scholars thought that it went against the tenets of Islam; as only God should be able to determine events rather than astrologers looking at the positions of the planets.
In order to calculate someone's horoscope, an astrologer would use 3 tools: an astrolabe, ephemeris and a takht. First, the astrologer would use an astrolabe to find the position of the sun, align the rule with the persons time of birth and then align the rete to establish the altitude of the sun on that date. Next, the astrologer would use an Ephemeris, a table denoting the mean position of the planets and stars within the sky at any given time. Finally, the astrologer would add the altitude of the sun taken from the astrolabe, with the mean position of the planets on the person's birthday, and add them together on the takht (also known as the dustboard). The dust board was merely a tablet covered in sand; on which the calculations could be made and erased easily. Once this had been calculated, the astrologer was then able to interpret the horoscope. Most of these interpretations were based on the zodiac in literature. For example, there were several manuals on how to interpret each zodiac sign, the treatise relating to each individual sign and what the characteristics of these zodiacs were.

 An example of the use of signs as astronomical coordinates may be found in the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris for the year 1767''. The "Longitude of the Sun" columns show the sign (represented as a digit from 0 to and including 11), degrees from 0 to 29, minutes, and seconds.
The zodiac symbols are Early Modern simplifications of conventional pictorial representations of the signs, attested since Hellenistic times.
An example of the use of signs as astronomical coordinates may be found in the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris for the year 1767''. The "Longitude of the Sun" columns show the sign (represented as a digit from 0 to and including 11), degrees from 0 to 29, minutes, and seconds.
The zodiac symbols are Early Modern simplifications of conventional pictorial representations of the signs, attested since Hellenistic times.
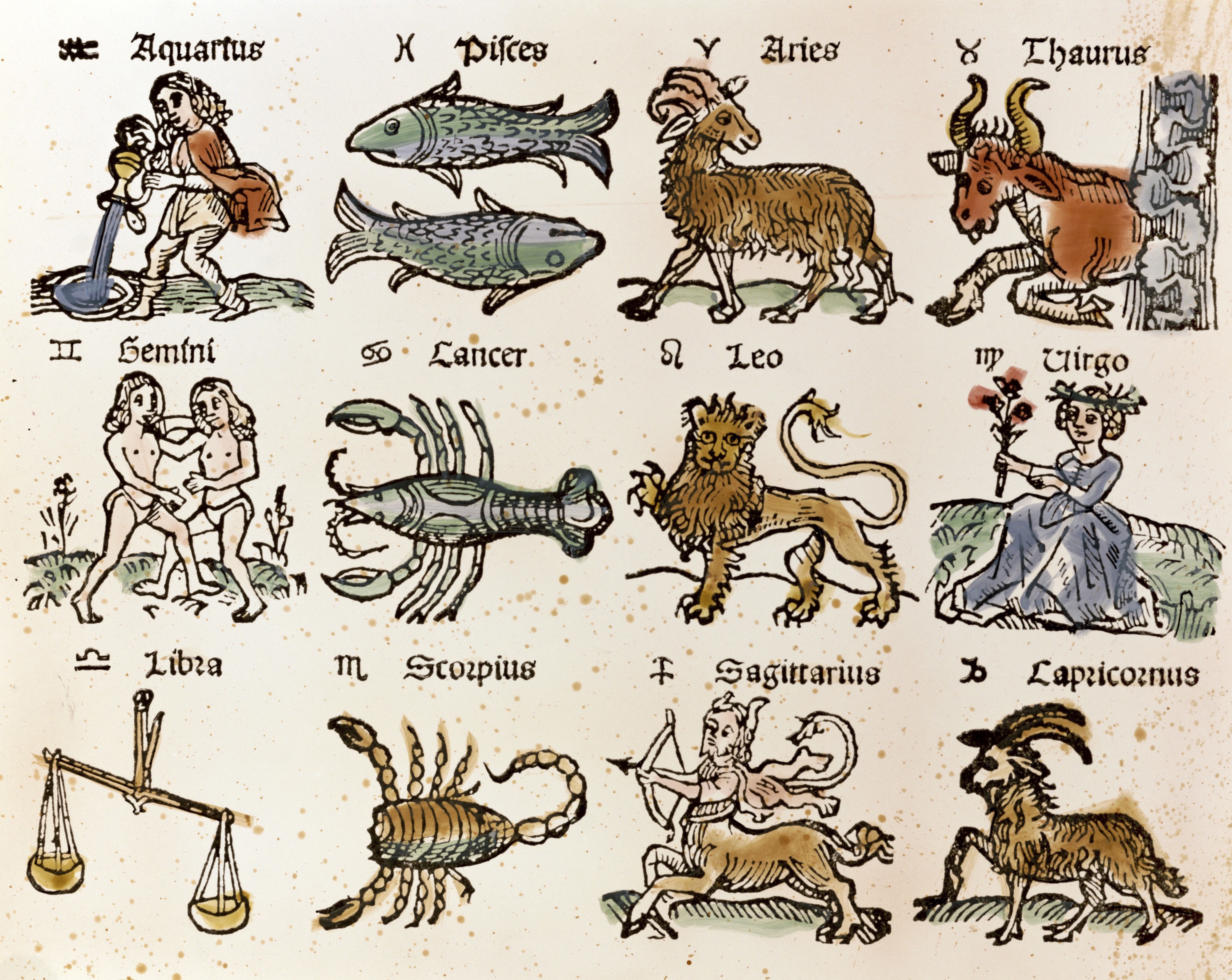 The beginning of Aries is defined as the moment of
The beginning of Aries is defined as the moment of  As each sign takes up exactly 30 degrees of the zodiac, the average duration of the solar stay in each sign is one twelfth of a
As each sign takes up exactly 30 degrees of the zodiac, the average duration of the solar stay in each sign is one twelfth of a
 In tropical astrology, the zodiacal signs are distinct from the
In tropical astrology, the zodiacal signs are distinct from the
Corvus is the Crow or Raven mysteriously perched on the tail of Hydra.
 The zodiac system was developed in
The zodiac system was developed in
"A Treatise on Zodiacal Signs and Constellations: Unique Jewels on the Benefits of Keeping Time"
is a manuscript that dates back to 1831 with a focus on Arabic, Coptic and Syriac calendars.
Zodiac Constellations at Constellation Guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zodiac, The Z + Ancient astronomy Astrology Astronomical coordinate systems Birthdays Early scientific cosmologies Western astrology
 The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude
Astronomical coordinate systems are organized arrangements for specifying positions of Natural satellite, satellites, planets, stars, galaxy, galaxies, and other celestial objects relative to physical reference points available to a situated obse ...
) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac.
In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
s: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius
Sagittarius ( ) may refer to:
*Sagittarius (constellation)
*Sagittarius (astrology), a sign of the Zodiac
Ships
*''SuperStar Sagittarius'', a cruise ship
* USS ''Sagittarius'' (AKN-2), a World War II US Navy cargo ship
Music
*Sagittarius (ban ...
, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces.
These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate system, which takes the ecliptic as the origin of latitude and the Sun's position at vernal equinox Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
* March equinox, the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* September equinox, the spring equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Nowruz, Persian/Iranian new year which be ...
as the origin of longitude.
Name
The English word ' derives from , the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ( ), meaning "cycle or circle of little animals". () is the diminutive of (, "animal"). The name reflects the prominence of animals (and mythological hybrids) among the twelve signs.Usage
 The zodiac was in use by the Roman era, based on concepts inherited by Hellenistic astronomy from Babylonian astronomy of the Chaldean period (mid-1st millennium BC), which, in turn, derived from an earlier system of lists of stars along the ecliptic. The construction of the zodiac is described in Ptolemy's comprehensive 2nd century AD work, the ''
The zodiac was in use by the Roman era, based on concepts inherited by Hellenistic astronomy from Babylonian astronomy of the Chaldean period (mid-1st millennium BC), which, in turn, derived from an earlier system of lists of stars along the ecliptic. The construction of the zodiac is described in Ptolemy's comprehensive 2nd century AD work, the ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
''.
Although the zodiac remains the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system in use in astronomy besides the equatorial one, the term and the names of the twelve signs are today mostly associated with horoscopic astrology
Horoscopic astrology is a form of astrology that uses a horoscope, a visual representation of the heavens, for a specific moment in time in order to interpret the inherent meaning underlying the alignment of the planets in astrology, planets at th ...
. The term "zodiac" may also refer to the region of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
encompassing the paths of the planets corresponding to the band of about 8 arc degrees above and below the ecliptic. The zodiac of a given planet is the band that contains the path of that particular body; e.g., the "zodiac of the Moon" is the band of 5° above and below the ecliptic. By extension, the "zodiac of the comets" may refer to the band encompassing most short-period comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are ...
s.
History
Early history
As early as the 14th century BC a complete list of the 36 Egyptian decans was placed among the hieroglyphs adorning the tomb of Seti I; they figured again in the temple of Ramesses II, and characterize every Egyptian astrological monument. Both the famous zodiacs of Dendera display their symbols, identified byKarl Richard Lepsius
Karl Richard Lepsius ( la, Carolus Richardius Lepsius) (23 December 181010 July 1884) was a pioneering Prussian Egyptologist, linguist and modern archaeologist.
He is widely known for his magnum opus ''Denkmäler aus Ägypten und Äthiopien'' ...
.

 The division of the ecliptic into the zodiacal signs originates in Babylonian astronomy during the first half of the
The division of the ecliptic into the zodiacal signs originates in Babylonian astronomy during the first half of the 1st millennium BC
The 1st millennium BC, also known as the last millennium BC, was the period of time lasting from the years 1000 BC to 1 BC (10th to 1st centuries BC; in astronomy: JD – ). It encompasses the Iron Age in the Old World and sees the transit ...
. The zodiac draws on stars in earlier Babylonian star catalogues, such as the MUL.APIN catalogue, which was compiled around 1000 BC. Some constellations can be traced even further back, to Bronze Age ( First Babylonian dynasty) sources, including Gemini "The Twins," from MAŠ.TAB.BA.GAL.GAL "The Great Twins," and Cancer "The Crab," from AL.LUL "The Crayfish," among others.
Around the end of the 5th century BC, Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n astronomers divided the ecliptic into 12 equal "signs", by analogy to 12 schematic months of 30 days each. Each sign contained 30° of celestial longitude, thus creating the first known celestial coordinate system. According to calculations by modern astrophysics, the zodiac was introduced between 409 and 398 BC, during Persian rule, and probably within a very few years of 401 BC. Unlike modern astrologers, who place the beginning of the sign of Aries at the position of the Sun at the vernal equinox Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
* March equinox, the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* September equinox, the spring equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Nowruz, Persian/Iranian new year which be ...
in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
( March equinox), Babylonian astronomers fixed the zodiac in relation to stars, placing the beginning of Cancer at the "Rear Twin Star" ( β Geminorum) and the beginning of Aquarius at the "Rear Star of the Goat-Fish" ( δ Capricorni).
Due to the precession of the equinoxes, the time of year the Sun is in a given constellation has changed since Babylonian times, the point of March equinox has moved from Aries into Pisces.
Because the division was made into equal arcs, 30° each, they constituted an ideal system of reference for making predictions about a planet's longitude. However, Babylonian techniques of observational measurements were in a rudimentary stage of evolution. They measured the position of a planet in reference to a set of "normal stars" close to the ecliptic (±9° of latitude) as observational reference points to help positioning a planet within this ecliptic coordinate system.
In Babylonian astronomical diaries, a planet position was generally given with respect to a zodiacal sign alone, less often in specific degrees within a sign. When the degrees of longitude were given, they were expressed with reference to the 30° of the zodiacal sign, i.e., not with a reference to the continuous 360° ecliptic. In astronomical ephemerides, the positions of significant astronomical phenomena were computed in sexagesimal fractions of a degree (equivalent to minutes and seconds of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The ...
). For daily ephemerides, the daily positions of a planet were not as important as the astrologically significant dates when the planet crossed from one zodiacal sign to the next.
Hebrew astronomy and astrology
Knowledge of the Babylonian zodiac is said to be reflected in the Hebrew Bible;E. W. Bullinger
Ethelbert William Bullinger (15 December 1837 – 6 June 1913) was an Anglican clergyman, biblical scholar, and ultradispensationalist theologian.
Early life
He was born in Canterbury, Kent, England, the youngest of five children of William ...
interpreted the creatures appearing in the book of Ezekiel as the middle signs of the four quarters of the zodiac, with the Lion as Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
, the Bull is Taurus, the Man representing Aquarius and the Eagle representing Scorpio. Some authors have linked the twelve tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( he, שִׁבְטֵי־יִשְׂרָאֵל, translit=Šīḇṭēy Yīsrāʾēl, lit=Tribes of Israel) are, according to Hebrew scriptures, the descendants of the biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, throu ...
with the same signs or the lunar Hebrew calendar having twelve lunar months in a lunar year. Martin and others have argued that the arrangement of the tribes around the Tabernacle (reported in the Book of Numbers) corresponded to the order of the zodiac, with Judah, Reuben, Ephraim
Ephraim (; he, ''ʾEp̄rayīm'', in pausa: ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was, according to the Book of Genesis, the second son of Joseph ben Jacob and Asenath. Asenath was an Ancient Egyptian woman whom Pharaoh gave to Joseph as wife, and the daughte ...
, and Dan representing the middle signs of Leo, Aquarius, Taurus, and Scorpio, respectively. Such connections were taken up by Thomas Mann, who in his novel '' Joseph and His Brothers'' attributes characteristics of a sign of the zodiac to each tribe in his rendition of the Blessing of Jacob.
Hellenistic and Roman era
 The Babylonian star catalogs entered Greek astronomy in the 4th century BC, via
The Babylonian star catalogs entered Greek astronomy in the 4th century BC, via Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; grc, Εὔδοξος ὁ Κνίδιος, ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar, and student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments are ...
.
Babylonia or Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
in the Hellenistic world came to be so identified with astrology that "Chaldean wisdom" became among Greeks and Romans the synonym of divination
Divination (from Latin ''divinare'', 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout histor ...
through the planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young ...
and star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s. Hellenistic astrology
Hellenistic astrology is a tradition of horoscopic astrology that was developed and practiced in the late Hellenistic period in and around the Mediterranean Basin region, especially in Egypt. The texts and technical terminology of this tradition o ...
derived in part from Babylonian and Egyptian astrology.
Horoscopic astrology
Horoscopic astrology is a form of astrology that uses a horoscope, a visual representation of the heavens, for a specific moment in time in order to interpret the inherent meaning underlying the alignment of the planets in astrology, planets at th ...
first appeared in Ptolemaic Egypt (305 BC–30 BC). The Dendera zodiac, a relief dating to ca. 50 BC, is the first known depiction of the classical zodiac of twelve signs.
The earliest extant Greek text using the Babylonian division of the zodiac into 12 signs of 30 equal degrees each is the ''Anaphoricus'' of Hypsicles of Alexandria (fl.190BC). Particularly important in the development of Western horoscopic astrology was the astrologer and astronomer Ptolemy, whose work ''Tetrabiblos'' laid the basis of the Western astrological tradition
Western astrology is the system of astrology most popular in Western countries. Western astrology is historically based on Ptolemy's ''Tetrabiblos'' (2nd century CE), which in turn was a continuation of Hellenistic and ultimately Babylonian tra ...
. Under the Greeks, and Ptolemy in particular, the planets, Houses, and signs of the zodiac were rationalized and their function set down in a way that has changed little to the present day. Ptolemy lived in the 2nd century AD, three centuries after the discovery of the precession of the equinoxes by Hipparchus around 130 BC. Hipparchus's lost work on precession never circulated very widely until it was brought to prominence by Ptolemy, and there are few explanations of precession outside the work of Ptolemy until late Antiquity, by which time Ptolemy's influence was widely established. Ptolemy clearly explained the theoretical basis of the western zodiac as being a tropical coordinate system, by which the zodiac is aligned to the equinoxes and solstices, rather than the visible constellations that bear the same names as the zodiac signs.
Hindu zodiac
According to mathematician-historian Montucla, the Hindu zodiac was adopted from the Greek zodiac through communications between ancient India and the Greek empire ofBactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
. The Hindu zodiac uses the sidereal coordinate system
Sidereal, meaning "of the stars", may refer to:
* Sidereal time
* Sidereal day
* Sidereal month
* Sidereal year
* Sidereal period of an object orbiting a star
* Sidereal and tropical astrology
'' Sidereal'' and ''tropical'' are terms used to ...
, which makes reference to the fixed stars. The tropical zodiac (of Mesopotamian origin) is divided by the intersections of the ecliptic and equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
, which shifts in relation to the backdrop of fixed stars at a rate of 1° every 72 years, creating the phenomenon known as precession of the equinoxes. The Hindu zodiac, being sidereal, does not maintain this seasonal alignment, but there are still similarities between the two systems. The Hindu zodiac signs and corresponding Greek signs sound very different, being in Sanskrit and Greek respectively, but their symbols are nearly identical. For example, ''dhanu'' means "bow" and corresponds to Sagittarius, the "archer", and ''kumbha'' means "water-pitcher" and corresponds to Aquarius, the "water-carrier".
Middle Ages
 During the Abbasid era, Greek reference books were systematically translated into Arabic, and Islamic astronomers then did their own observations, correcting Ptolemy's Almagest. One such book was Al-Sufi's '' Book of Fixed Stars'', which has pictorial depictions of 48 constellations. The book was divided into three sections: constellations of the zodiac, constellations north of the zodiac, and southern constellations. When Al-Sufi's book, and other works, were translated in the 11th century, there were mistakes made in the translations. As a result, some stars ended up with the names of the constellation they belong to (e.g. Hamal in Aries).
The High Middle Ages saw a revival of interest in Greco-Roman magic, first in
During the Abbasid era, Greek reference books were systematically translated into Arabic, and Islamic astronomers then did their own observations, correcting Ptolemy's Almagest. One such book was Al-Sufi's '' Book of Fixed Stars'', which has pictorial depictions of 48 constellations. The book was divided into three sections: constellations of the zodiac, constellations north of the zodiac, and southern constellations. When Al-Sufi's book, and other works, were translated in the 11th century, there were mistakes made in the translations. As a result, some stars ended up with the names of the constellation they belong to (e.g. Hamal in Aries).
The High Middle Ages saw a revival of interest in Greco-Roman magic, first in Kabbalism
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The defi ...
and later continued in Renaissance magic. This included magical uses of the zodiac, as found, e.g., in the Sefer Raziel HaMalakh.
The zodiac is found in medieval stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
as at Angers Cathedral, where the master glass maker, André Robin, made the ornate rosettes for the North and South transepts after the fire there in 1451.
Mughal king Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
issued an attractive series of coins in gold and silver depicting the twelve signs of the zodiac.
Medieval Islamic era
 Astrology emerged in the 8th century CE as a distinct discipline in Islam, with a mix of Indian, Hellenistic Iranian and other traditions blended with Greek and Islamic astronomical knowledge, for example Ptolemy's work and Al-Sufi's Book of Fixed Stars. A knowledge of the influence that the stars have on events on the earth was important in Islamic civilization. As a rule, it was believed that the signs of the zodiac and the planets control the destiny not only of people but also of nations, and that the zodiac has the ability to determine a person's physical characteristics as well as intelligence and personal traits.
The practice of astrology at this time could be divided into 4 broader categories: Genethlialogy, Catarchic Astrology, Interrogational Astrology and General Astrology. However the most common type of astrology was Genethlialogy, which examined all aspects of a person's life in relation to the planetary positions at their birth; more commonly known as our horoscope.
Astrology services were offered widely across the empire, mainly in bazaars, where people could pay for a reading. Astrology was valued in the royal courts, for example, the Abbasid Caliph Al-Mansur used astrology to determine the best date for founding the new capital of Baghdad. Whilst horoscopes were generally widely accepted by society, many scholars condemned the use of astrology and divination, linking it to occult influences. Many theologians and scholars thought that it went against the tenets of Islam; as only God should be able to determine events rather than astrologers looking at the positions of the planets.
In order to calculate someone's horoscope, an astrologer would use 3 tools: an astrolabe, ephemeris and a takht. First, the astrologer would use an astrolabe to find the position of the sun, align the rule with the persons time of birth and then align the rete to establish the altitude of the sun on that date. Next, the astrologer would use an Ephemeris, a table denoting the mean position of the planets and stars within the sky at any given time. Finally, the astrologer would add the altitude of the sun taken from the astrolabe, with the mean position of the planets on the person's birthday, and add them together on the takht (also known as the dustboard). The dust board was merely a tablet covered in sand; on which the calculations could be made and erased easily. Once this had been calculated, the astrologer was then able to interpret the horoscope. Most of these interpretations were based on the zodiac in literature. For example, there were several manuals on how to interpret each zodiac sign, the treatise relating to each individual sign and what the characteristics of these zodiacs were.
Astrology emerged in the 8th century CE as a distinct discipline in Islam, with a mix of Indian, Hellenistic Iranian and other traditions blended with Greek and Islamic astronomical knowledge, for example Ptolemy's work and Al-Sufi's Book of Fixed Stars. A knowledge of the influence that the stars have on events on the earth was important in Islamic civilization. As a rule, it was believed that the signs of the zodiac and the planets control the destiny not only of people but also of nations, and that the zodiac has the ability to determine a person's physical characteristics as well as intelligence and personal traits.
The practice of astrology at this time could be divided into 4 broader categories: Genethlialogy, Catarchic Astrology, Interrogational Astrology and General Astrology. However the most common type of astrology was Genethlialogy, which examined all aspects of a person's life in relation to the planetary positions at their birth; more commonly known as our horoscope.
Astrology services were offered widely across the empire, mainly in bazaars, where people could pay for a reading. Astrology was valued in the royal courts, for example, the Abbasid Caliph Al-Mansur used astrology to determine the best date for founding the new capital of Baghdad. Whilst horoscopes were generally widely accepted by society, many scholars condemned the use of astrology and divination, linking it to occult influences. Many theologians and scholars thought that it went against the tenets of Islam; as only God should be able to determine events rather than astrologers looking at the positions of the planets.
In order to calculate someone's horoscope, an astrologer would use 3 tools: an astrolabe, ephemeris and a takht. First, the astrologer would use an astrolabe to find the position of the sun, align the rule with the persons time of birth and then align the rete to establish the altitude of the sun on that date. Next, the astrologer would use an Ephemeris, a table denoting the mean position of the planets and stars within the sky at any given time. Finally, the astrologer would add the altitude of the sun taken from the astrolabe, with the mean position of the planets on the person's birthday, and add them together on the takht (also known as the dustboard). The dust board was merely a tablet covered in sand; on which the calculations could be made and erased easily. Once this had been calculated, the astrologer was then able to interpret the horoscope. Most of these interpretations were based on the zodiac in literature. For example, there were several manuals on how to interpret each zodiac sign, the treatise relating to each individual sign and what the characteristics of these zodiacs were.
Early modern

 An example of the use of signs as astronomical coordinates may be found in the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris for the year 1767''. The "Longitude of the Sun" columns show the sign (represented as a digit from 0 to and including 11), degrees from 0 to 29, minutes, and seconds.
The zodiac symbols are Early Modern simplifications of conventional pictorial representations of the signs, attested since Hellenistic times.
An example of the use of signs as astronomical coordinates may be found in the ''Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris for the year 1767''. The "Longitude of the Sun" columns show the sign (represented as a digit from 0 to and including 11), degrees from 0 to 29, minutes, and seconds.
The zodiac symbols are Early Modern simplifications of conventional pictorial representations of the signs, attested since Hellenistic times.
Twelve signs
What follows is a list of the signs of the modern zodiac (with the ecliptic longitudes of their first points), where 0° Aries is understood as the vernal equinox, with their Latin, Greek, Sanskrit, and Babylonian names. But note that the Sanskrit and the name equivalents (after c.500 BC) denote the constellations only, not the tropical zodiac signs. The "English translation" isn't usually used by English speakers. The Latin names are standard English usage (except that "Capricorn" is used rather than "Capricornus"). The following table compares the Gregorian dates on which the Sun enters a sign in the Ptolemaic tropical zodiac, and a sign in the sidereal system proposed by Cyril Fagan. The beginning of Aries is defined as the moment of
The beginning of Aries is defined as the moment of vernal equinox Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
* March equinox, the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* September equinox, the spring equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Nowruz, Persian/Iranian new year which be ...
, and all other dates shift accordingly.
The precise Gregorian times and dates vary slightly from year to year as the Gregorian calendar shifts relative to the tropical year. These variations remain within less than two days' difference in the recent past and the near-future, vernal equinox in UT always falling either on 20 or 21 March in the period of 1797 to 2043, falling on 19 March in 1796 the last time and in 2044 the next. The vernal equinox has fallen on 20 March UT since 2008, and will continue to do so until 2043.
 As each sign takes up exactly 30 degrees of the zodiac, the average duration of the solar stay in each sign is one twelfth of a
As each sign takes up exactly 30 degrees of the zodiac, the average duration of the solar stay in each sign is one twelfth of a sidereal year
A sidereal year (, ; ), also called a sidereal orbital period, is the time that Earth or another planetary body takes to orbit the Sun once with respect to the fixed stars.
Hence, for Earth, it is also the time taken for the Sun to return to the ...
, or 30.43 standard day
A day is the time period of a full rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours, 1440 minutes, or 86,400 seconds. In everyday life, the word "day" often refers to a solar day, which is the length between two so ...
s. Due to Earth's slight orbital eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values betwee ...
, the duration of each sign varies appreciably,
between about 29.4 days for Capricorn and about 31.4 days for Cancer (see Equation of time).
In addition, because the Earth's axis is at an angle, some signs take longer to rise than others, and the farther away from the equator the observer is situated, the greater the difference. Thus, signs are spoken of as "long" or "short" ascension.
Constellations
 In tropical astrology, the zodiacal signs are distinct from the
In tropical astrology, the zodiacal signs are distinct from the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
s associated with them, not only because of their drifting apart due to the precession of equinoxes but because the physical constellations take up varying widths of the ecliptic, so the Sun is not in each constellation for the same amount of time. Thus, Virgo takes up 5 times as much ecliptic longitude as Scorpius. The zodiacal signs are an abstraction from the physical constellations, and each represent exactly th of the full circle, but the time spent by the Sun in each sign varies slightly due to the eccentricity of the Earth's orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth ...
.
Sidereal astrology remedies this by assigning the zodiac sign approximately to the corresponding constellation. This alignment needs re calibrating every so often to keep the alignment in place.
The ecliptic intersects with 13 constellations of Ptolemy's ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
'', as well as of the more precisely delineated IAU designated constellations. In addition to the twelve constellations after which the twelve zodiac signs are named, the ecliptic intersects Ophiuchus, the bottom part of which interjects between Scorpio and Sagittarius.
Occasionally this difference between the astronomical constellations and the astrological signs is mistakenly reported in the popular press as a "change" to the list of traditional signs by some astronomical body like the IAU, NASA, or the Royal Astronomical Society. This happened in a 1995 report of the '' BBC Nine O'Clock News'' and various reports in 2011 and 2016.
Some "parazodiacal" constellations are touched by the paths of the planets, leading to counts of up to 25 "constellations of the zodiac". The ancient Babylonian MUL.APIN catalog lists Orion, Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (Help:IPA/English, /ˈpɜːrsiəs, -sjuːs/; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of Mycenae and of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus ...
, Auriga, and Andromeda. Modern astronomers have noted that planets pass through Crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
*Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
*Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surfac ...
, Sextans, Cetus, Pegasus
Pegasus ( grc-gre, Πήγασος, Pḗgasos; la, Pegasus, Pegasos) is one of the best known creatures in Greek mythology. He is a winged divine stallion usually depicted as pure white in color. He was sired by Poseidon, in his role as hor ...
, Corvus, Hydra
Hydra generally refers to:
* Lernaean Hydra, a many-headed serpent in Greek mythology
* ''Hydra'' (genus), a genus of simple freshwater animals belonging to the phylum Cnidaria
Hydra or The Hydra may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Hydra (constel ...
, and Scutum, with Venus very rarely passing through Aquila
Aquila may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Aquila'', a series of books by S.P. Somtow
* ''Aquila'', a 1997 book by Andrew Norriss
* ''Aquila'' (children's magazine), a UK-based children's magazine
* ''Aquila'' (journal), an or ...
, Canis Minor
Canis Minor is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellation ...
, Auriga, and Serpens.
Some other constellations are mythologically associated with the zodiacal ones: Piscis Austrinus, The Southern Fish, is attached to Aquarius. In classical maps, it swallows the stream poured out of Aquarius' pitcher, but perhaps it formerly just swam in it. Aquila
Aquila may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Aquila'', a series of books by S.P. Somtow
* ''Aquila'', a 1997 book by Andrew Norriss
* ''Aquila'' (children's magazine), a UK-based children's magazine
* ''Aquila'' (journal), an or ...
, The Eagle, was possibly associated with the zodiac by virtue of its main star, Altair. Hydra
Hydra generally refers to:
* Lernaean Hydra, a many-headed serpent in Greek mythology
* ''Hydra'' (genus), a genus of simple freshwater animals belonging to the phylum Cnidaria
Hydra or The Hydra may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Hydra (constel ...
in the Early Bronze Age marked the celestial equator and was associated with Leo, which is shown standing on the serpent on the Dendera zodiac.Corvus is the Crow or Raven mysteriously perched on the tail of Hydra.
Precession of the equinoxes
 The zodiac system was developed in
The zodiac system was developed in Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
, some 2,500 years ago, during the "Age of Aries
An astrological age is a time period in astrological theory which astrologers say, parallels major changes in the development of Earth's inhabitants, particularly relating to culture, society, and politics. There are twelve astrological ages cor ...
". At the time, it is assumed, the precession of the equinoxes was unknown. Contemporary use of the coordinate system is presented with the choice of interpreting the system either as sidereal, with the signs fixed to the stellar background, or as tropical, with the signs fixed to the point ( vector of the Sun) at the March equinox.
Western astrology takes the tropical approach, whereas Hindu astrology takes the sidereal one. This results in the originally unified zodiacal coordinate system drifting apart gradually, with a clockwise (westward) precession of 1.4 degrees per century.
For the tropical zodiac used in Western astronomy and astrology, this means that the tropical ''sign'' of Aries currently lies somewhere within the ''constellation'' Pisces (" Age of Pisces").
The sidereal coordinate system takes into account the ayanamsa, ''ayan'' meaning "transit' or 'movement', and ''amsa'' meaning 'small part', i.e. movement of equinoxes in small parts. It is unclear when Indians became aware of the precession of the equinoxes, but Bhāskara II
Bhāskara II (c. 1114–1185), also known as Bhāskarāchārya ("Bhāskara, the teacher"), and as Bhāskara II to avoid confusion with Bhāskara I, was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. From verses, in his main work, Siddhānta Shiroman ...
's 12th-century treatise ''Siddhanta Shiromani
''Siddhānta'' is a Sanskrit term denoting the established and accepted view of any particular school within Indian philosophy; literally "settled opinion or doctrine, dogma, axiom, received or admitted truth; any fixed or established or canonica ...
'' gives equations for measurement of precession of equinoxes, and says his equations are based on some lost equations of ''Suryasiddhanta
The ''Surya Siddhanta'' (; ) is a Sanskrit treatise in Indian astronomy dated to 505 CE,Menso Folkerts, Craig G. Fraser, Jeremy John Gray, John L. Berggren, Wilbur R. Knorr (2017)Mathematics Encyclopaedia Britannica, Quote: "(...) its Hindu inven ...
'' plus the equation of Munjaala.
The discovery of precession is attributed to Hipparchus around 130 BC. Ptolemy quotes from Hipparchus's now-lost work entitled "On the Displacement of the Solstitial and Equinoctial Points" in the seventh book of his 2nd century astronomical text, ''Almagest'', where he describes the phenomenon of precession and estimates its value. Ptolemy clarified that the convention of Greek mathematical astronomy was to commence the zodiac from the point of the vernal equinox and to always refer to this point as "the first degree" of Aries. This is known as the "tropical zodiac" (from the Greek word trópos, turn) because its starting point revolves through the circle of background constellations over time.
The principle of the vernal point acting as the first degree of the zodiac for Greek astronomers is described in the 1st century BC astronomical text of Geminus of Rhodes. Geminus explains that Greek astronomers of his era associate the first degrees of the zodiac signs with the two solstices and the two equinoxes, in contrast to the older Chaldean (Babylonian) system, which placed these points within the zodiac signs. This illustrates that Ptolemy merely clarified the convention of Greek astronomers and did not originate the principle of the tropical zodiac, as is sometimes assumed.
Ptolemy demonstrates that the principle of the tropical zodiac was well known to his predecessors within his astrological text, the '' Tetrabiblos'', where he explains why it would be an error to associate the regularly spaced signs of the seasonally aligned zodiac with the irregular boundaries of the visible constellations:
In modern astronomy
Astronomically, the zodiac defines a belt of space extending 8° or 9° in celestial latitude to the north and south of the ecliptic, within which the orbits of the Moon and the principal planets remain. It is a feature of the ecliptic coordinate system – a celestial coordinate system centered upon the ecliptic (the plane of the Earth's orbit and the Sun's apparent path), by which celestial longitude is measured in degrees east of the vernal equinox (the ascending intersection of the ecliptic and equator). The zodiac is narrow in angular terms because most of the Sun's planets have orbits that have only a slight inclination to the orbital plane of the Earth. Stars within the zodiac are subject to occultations by the Moon and other solar system bodies. These events can be useful, for example, to estimate the cross-sectional dimensions of a minor planet, or check a star for a close companion. The Sun's placement upon the vernal equinox, which occurs annually around 21 March, defines the starting point for measurement, the first degree of which is historically known as the " first point of Aries". The first 30° along the ecliptic is nominally designated as the zodiac sign Aries, which no longer falls within the proximity of the constellation Aries since the effect of precession is to move the vernal point through the backdrop of visible constellations (it is currently located near the end of the constellation Pisces, having been within that constellation since the 2nd century AD). The subsequent 30° of the ecliptic is nominally designated the zodiac sign Taurus, and so on through the twelve signs of the zodiac so that each occupies th (30°) of the zodiac's great circle. Zodiac signs have never been used to determine the boundaries of astronomical constellations that lie in the vicinity of the zodiac, which are, and always have been, irregular in their size and shape. The convention of measuring celestial longitude within individual signs was still being used in the mid-19th century, but modern astronomy now numbers degrees of celestial longitude continuously from 0° to 360°, rather than 0° to 30° within each sign. This coordinate system is primary used by astronomers for observations of solar system objects. The use of the zodiac as a means to determine astronomical measurement remained the main method for defining celestial positions by Western astronomers until the Renaissance, at which time preference moved to the equatorial coordinate system, which measures astronomical positions byright ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
and declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
rather than the ecliptic-based definitions of celestial longitude and celestial latitude
Astronomical coordinate systems are organized arrangements for specifying positions of Natural satellite, satellites, planets, stars, galaxy, galaxies, and other celestial objects relative to physical reference points available to a situated obse ...
. The orientation of equatorial coordinates are aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation, rather than the plane of the planet's orbit around the Sun.
The word "zodiac" is used in reference to the zodiacal cloud
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small dust, particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar S ...
of dust grains that move among the planets, and the zodiacal light that originates from their scattering of sunlight. While its name is derived from the zodiac, the zodiacal light covers the entire night sky, with enhancements in certain directions.
Unicode characters
In Unicode, the symbols of zodiac signs are encoded in block "Miscellaneous Symbols". They can be forced to look like text by appending U+FE0E, or like emojis by appending U+FE0F:See also
* Astronomical symbols * Chinese zodiac * Circle of stars * Cusp (astrology) * Elements of the zodiac * History of astrology * Jewish astrology *Mazzaroth
''Mazzaroth'' (Hebrew Transliteration: מַזָּרוֹת ''Mazzārōṯ'', LXX Μαζουρωθ, ''Mazourōth'') is a Biblical Hebrew Word found in the Book of Job (38:32) and literally meaning "constellations," according to 10th-century biblic ...
References
External links
"A Treatise on Zodiacal Signs and Constellations: Unique Jewels on the Benefits of Keeping Time"
is a manuscript that dates back to 1831 with a focus on Arabic, Coptic and Syriac calendars.
Zodiac Constellations at Constellation Guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zodiac, The Z + Ancient astronomy Astrology Astronomical coordinate systems Birthdays Early scientific cosmologies Western astrology