X.509 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
''X.520 The Directory: Selected attribute types''
recommendation. ITU-T introduced issuer and subject unique identifiers in version 2 to permit the reuse of issuer or subject name after some time. An example of reuse will be when a CA goes bankrupt and its name is deleted from the country's public list. After some time another CA with the same name may register itself, even though it is unrelated to the first one. However,
RFC gives the specific example of a certificate containing both keyUsage and extendedKeyUsage: in this case, both must be processed and the certificate can only be used if both extensions are coherent in specifying the usage of a certificate. For example, NSS uses both extensions to specify certificate usage.

 Examining how certificate chains are built and validated, it is important to note that a concrete certificate can be part of very different certificate chains (all of them valid). This is because several CA certificates can be generated for the same subject and public key, but be signed with different private keys (from different CAs or different private keys from the same CA). So, although a single X.509 certificate can have only one issuer and one CA signature, it can be validly linked to more than one certificate, building completely different certificate chains. This is crucial for cross-certification between PKIs and other applications.
See the following examples:
Examining how certificate chains are built and validated, it is important to note that a concrete certificate can be part of very different certificate chains (all of them valid). This is because several CA certificates can be generated for the same subject and public key, but be signed with different private keys (from different CAs or different private keys from the same CA). So, although a single X.509 certificate can have only one issuer and one CA signature, it can be validly linked to more than one certificate, building completely different certificate chains. This is crucial for cross-certification between PKIs and other applications.
See the following examples:
OpenCable security specification
defines its own profile of X.509 for use in the cable industry. Devices like
ITU-T's X.509 standards
* Peter Gutmann's articles: *
Overview of PKI
*
X.509 implementation notes and style guide
*
Sun * - Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure: Certification Path Building * {{IETF RFC, 5280, link=no - Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Profile
Understanding Digital Certificates
Microsoft TechNet Cryptographic protocols Public-key cryptography ITU-T recommendations ITU-T X Series Recommendations X.500
cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logy, -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of Adversary (cryptography), ...
, X.509 is an International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU)In the other common languages of the ITU:
*
* is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information ...
(ITU) standard defining the format of public key certificate
In cryptography, a public key certificate, also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate, is an electronic document used to prove the validity of a Key authentication, public key. The certificate includes the public key and informati ...
s. X.509 certificates are used in many Internet protocols, including TLS/SSL, which is the basis for HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It uses encryption for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protoc ...
, the secure protocol for browsing the web
Web most often refers to:
* Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal
* World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system
Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to:
Computing
* WEB, a literate programming system created by ...
. They are also used in offline applications, like electronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
s.
An X.509 certificate binds an identity to a public key using a digital signature. A certificate contains an identity (a hostname, or an organization, or an individual) and a public key ( RSA, DSA, ECDSA, ed25519, etc.), and is either signed by a certificate authority or is self-signed. When a certificate is signed by a trusted certificate authority, or validated by other means, someone holding that certificate can use the public key it contains to establish secure communications with another party, or validate documents digitally signed by the corresponding private key
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic alg ...
.
X.509 also defines certificate revocation list
In cryptography, a certificate revocation list (CRL) is "a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing certificate authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted".
Publicly trusted C ...
s, which are a means to distribute information about certificates that have been deemed invalid by a signing authority, as well as a certification path validation algorithm, which allows for certificates to be signed by intermediate CA certificates, which are, in turn, signed by other certificates, eventually reaching a trust anchor.
X.509 is defined by the ITU's "Standardization Sector" (ITU-T
The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating Standardization, standards fo ...
's SG17), in ITU-T Study Group 17 and is based on Abstract Syntax Notation One
Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) is a standard interface description language (IDL) for defining data structures that can be serialized and deserialized in a cross-platform way. It is broadly used in telecommunications and computer networ ...
(ASN.1), another ITU-T standard.
History and usage
X.509 was initially issued on July 3, 1988, and was begun in association with the X.500 standard. The first tasks of it was providing users with secure access to information resources and avoiding a cryptographicman-in-the-middle attack
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, or on-path attack, is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communi ...
. It assumes a strict hierarchical system of certificate authorities
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. Thi ...
(CAs) for issuing the certificates. This contrasts with web of trust
In cryptography, a web of trust is a concept used in PGP, GnuPG, and other OpenPGP-compatible systems to establish the authenticity of the binding between a public key and its owner. Its decentralized trust model is an alternative to the ...
models, like PGP, where anyone (not just special CAs) may sign and thus attest to the validity of others' key certificates.
Version 3 of X.509 includes the flexibility to support other topologies like bridges
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somet ...
and meshes. It can be used in a peer-to-peer, OpenPGP
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is an encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is used for signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partit ...
-like web of trust, but was rarely used that way . The X.500 system has only been implemented by sovereign nations for state identity information sharing treaty fulfillment purposes, and the IETF
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster ...
's Public-Key Infrastructure (X.509) (PKIX) working group has adapted the standard to the more flexible organization of the Internet. In fact, the term ''X.509 certificate'' usually refers to the IETF's PKIX certificate and CRL profile of the X.509 v3 certificate standard, as specified in , commonly called PKIX for ''Public Key Infrastructure (X.509)''.
An early issue with Public Key Infrastructure
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption.
The purpose of a PKI is to fac ...
(PKI) and X.509 certificates was the well known "which directory" problem. The problem is the client does not know where to fetch missing intermediate certificates because the global X.500 directory never materialized. The problem was mitigated by including all intermediate certificates in a request. For example, early web servers only sent the web server's certificate to the client. Clients that lacked an intermediate CA certificate or where to find them failed to build a valid path from the CA to the server's certificate. To work around the problem, web servers now send all the intermediate certificates along with the web server's certificate.
While PKIX refers to the IETF's or Internet's PKI standard, there are many other PKIs with different policies. For example, the US Government has its own PKI with its own policies, and the CA/Browser Forum has its own PKI with its own policies. The US Government's PKI is a massive book of over 2500 pages. If an organization's PKI diverges too much from that of the IETF or CA/Browser Forum, then the organization risks losing interoperability with common tools like web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
s, cURL
cURL (pronounced like "curl", ) is a free and open source computer program for transferring data to and from Internet servers. It can download a URL from a web server over HTTP, and supports a variety of other network protocols, URI scheme ...
, and Wget
GNU Wget (or just Wget, formerly Geturl, also written as its package name, wget) is a computer program that retrieves content from web servers. It is part of the GNU Project. Its name derives from "World Wide Web" and " ''get''", a HTTP reque ...
. For example, if a PKI has a policy of only issuing certificates on Monday, then common tools like cURL and Wget will not enforce the policy and allow a certificate issued on a Tuesday.
Certificates
X.509 certificates bind an identity to a public key using a digital signature. In the X.509 system, there are two types of certificates. The first is a CA certificate. The second is an end-entity certificate. A CA certificate can issue other certificates. The top level, self-signed CA certificate is sometimes called the Root CA certificate. Other CA certificates are called intermediate CA or subordinate CA certificates. An end-entity certificate identifies the user, like a person, organization or business. An end-entity certificate ''cannot'' issue other certificates. An end-entity certificate is sometimes called a leaf certificate since no other certificates can be issued below it. An organization that wants a signed certificate requests one from a CA using a protocol like Certificate Signing Request (CSR), Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) or Certificate Management Protocol (CMP). The organization first generates a key pair, keeping theprivate key
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic alg ...
secret and using it to sign the CSR. The CSR contains information identifying the applicant and the applicant's public key
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic alg ...
that is used to verify the signature of the CSR - and the Distinguished Name (DN) that is unique for the person, organization or business. The CSR may be accompanied by other credentials or proofs of identity required by the certificate authority.
The CSR will be validated using a Registration Authority (RA), and then the certification authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. Thi ...
will issue a certificate binding a public key to a particular distinguished name. The roles registration authority and certification authority are usually separate business units under separation of duties
Separation of duties (SoD), also known as segregation of duties, is the concept of having more than one person required to complete a task. It is an administrative control used by organisations to prevent fraud, sabotage, theft, misuse of informa ...
to reduce the risk of fraud.
An organization's trusted root certificates can be distributed to all employees so that they can use the company PKI system. Browsers such as Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated as IE or MSIE) is a deprecation, retired series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were u ...
, Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements curr ...
, Opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
, Safari
A safari (; originally ) is an overland journey to observe wildlife, wild animals, especially in East Africa. The so-called big five game, "Big Five" game animals of Africa – lion, African leopard, leopard, rhinoceros, African elephant, elep ...
and Chrome come with a predetermined set of root certificates pre-installed, so SSL certificates from major certificate authorities will work instantly; in effect the browsers' developers determine which CAs are trusted third parties for the browsers' users. For example, Firefox provides a CSV and/or HTML file containing a list of Included CAs.
X.509 and also include standards for certificate revocation list (CRL) implementations. Another IETF
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster ...
-approved way of checking a certificate's validity is the Online Certificate Status Protocol
The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is an Internet Communication protocol, protocol used for obtaining the revocation status of an X.509 digital certificate. It was created as an alternative to certificate revocation lists (CRL), specif ...
(OCSP). Firefox 3.0 enabled OCSP checking by default, as did versions of Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
from at least Vista
Vista may refer to:
Software
*Windows Vista, the line of Microsoft Windows client operating systems released in 2006 and 2007
* VistA, (Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture) a medical records system of the United States ...
and later.
Structure of a certificate
The structure foreseen by the standards is expressed in a formal language,Abstract Syntax Notation One
Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) is a standard interface description language (IDL) for defining data structures that can be serialized and deserialized in a cross-platform way. It is broadly used in telecommunications and computer networ ...
(ASN.1).
The structure of an X.509 v3 digital certificate
In cryptography, a public key certificate, also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate, is an electronic document used to prove the validity of a public key. The certificate includes the public key and information about it, informa ...
is as follows:
* Certificate
**Version Number
**Serial Number
**Signature Algorithm ID
**Issuer Name
**Validity period
***Not Before
***Not After
**Subject name
**Subject Public Key Info
***Public Key Algorithm
***Subject Public Key
**Issuer Unique Identifier (optional)
**Subject Unique Identifier (optional)
**Extensions (optional)
*** ...
*Certificate Signature Algorithm
*Certificate Signature
The Extensions field, if present, is a sequence of one or more certificate extensions. Each extension has its own unique ID, expressed as object identifier (OID), which is a set of values, together with either a critical or non-critical indication. A certificate-using system must reject the certificate if it encounters a critical extension that it does not recognize, or a critical extension that contains information that it cannot process. A non-critical extension may be ignored if it is not recognized, but must be processed if it is recognized.
The structure of version 1 is given in .
The inner format of issuer and subject unique identifiers specified i''X.520 The Directory: Selected attribute types''
recommendation. ITU-T introduced issuer and subject unique identifiers in version 2 to permit the reuse of issuer or subject name after some time. An example of reuse will be when a CA goes bankrupt and its name is deleted from the country's public list. After some time another CA with the same name may register itself, even though it is unrelated to the first one. However,
IETF
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster ...
recommends that no issuer and subject names be reused. Therefore, version 2 is not widely deployed in the Internet.
Extensions were introduced in version 3. A CA can use extensions to issue a certificate only for a specific purpose (e.g. only for signing digital objects).
In all versions, the serial number must be unique for each certificate issued by a specific CA (as mentioned in ).
Extensions informing a specific usage of a certificate
(and its predecessors) defines a number of certificate extensions which indicate how the certificate should be used. Most of them are arcs from thejoint-iso-ccitt(2) ds(5) id-ce(29) OID. Some of the most common, defined in section 4.2.1, are:
* Basic Constraints, Extended Validation certificates
Certification authorities operating under the CA/Browser Forum's PKI issue certificates with varying levels of validation. The different validations provide different levels of assurances that a certificate represents what it is supposed to. For example, a web server can be validated at the lowest level of assurances using an email called ''Domain Validation (DV)''. Or a web server can be validated at a higher level of assurances using more detailed methods called ''Extended Validation (EV)''. In practice, a DV certificate means a certificate was issued for a domain likeexample.com after someone responded to an email sent to webmaster@example.com. An EV certificate means a certificate was issued for a domain like example.com, and a company like Example, LLC is the owner of the domain, and the owner was verified by Articles of Incorporation
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article(s) may also refer to:
...
.
Extended validation does not add any additional security controls, so the secure channel setup using an EV certificate is not "stronger" than a channel setup using a different level of validation like DV.
Extended validation is signaled in a certificate using X.509 v3 extension. Each CA uses a different Object Identifier (OID) to assert extended validation. There is no single OID to indicate extended validation, which complicates user agent programming. Each user agent must have a list of OIDs that indicate extended validation.
The CA/Browser Forum's PKI recognizes extended validation and many browsers provide visual feedback to the user to indicate a site provides an EV certificate. Other PKIs, like the Internet's PKI (PKIX), do not place any special emphasis on extended validation. Tools using PKIX policies, like cURL and Wget, simply treat an EV certificate like any other certificate.
Security expert Peter Gutmann states CA's created EV certificates to restore profit levels after the Race to the Bottom
Race to the bottom is a Socioeconomics, socio-economic concept describing a scenario in which individuals or companies compete in a manner that incrementally reduces the utility of a product or service in response to perverse incentives. This pheno ...
cut into profits. During the race to the bottom CA's cut prices to lure consumers to purchase their certificates. As a result, profits were reduced and CA's dropped the level of validation they were performing to the point there were nearly no assurances on a certificate.
Certificate filename extensions
There are several commonly usedfilename extension
A filename extension, file name extension or file extension is a suffix to the name of a computer file (for example, .txt, .mp3, .exe) that indicates a characteristic of the file contents or its intended use. A filename extension is typically d ...
s for X.509 certificates. Some of these extensions are also used for other data such as private keys.
* .pem – ( Privacy-enhanced Electronic Mail) Base64
In computer programming, Base64 is a group of binary-to-text encoding schemes that transforms binary data into a sequence of printable characters, limited to a set of 64 unique characters. More specifically, the source binary data is taken 6 bits ...
encoded DER certificate, enclosed between and
* .cer, .crt, .der – usually in binary DER form, but Base64-encoded certificates are common too (see .pem above)
* .p8, .p8e, .pk8 – exported private key as specified in PKCS#8. May be in DER or PEM form that starts with . The encrypted key starts with and may have the .p8e extension.
* .p10, .csr – PKCS#10 a certificate signing request
In public key infrastructure (PKI) systems, a certificate signing request (CSR or certification request) is a message sent from an applicant to a certificate authority of the public key infrastructure (PKI) in order to apply for a digital identity ...
(CSR). In PEM form starts with . These are generated for submission to certificate-authorities (CA). It includes key details of the requested certificate such as Common Name (/CN), subject, organization, state, country, as well as the ''public key'' of the certificate to get signed. These get signed by the CA and a certificate is returned. The returned certificate is the public ''certificate'' (which includes the public key but not the private key), which itself can be in a couple of formats but usually in .p7r.
* .p7r – PKCS#7 response to CSR. Contains the newly-signed certificate, and the CA's own cert.
* .p7s – PKCS#7 Digital Signature. May contain the original signed file or message. Used in S/MIME
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is a standard for public-key encryption and signing of MIME data. S/MIME is on an IETF standards track and defined in a number of documents, most importantly . It was originally developed by ...
for email signing. Defined in RFC 2311.
* .p7m – PKCS#7 (SignedData, EnvelopedData) Message e.g. encrypted ("enveloped") file, message or MIME email letter. Defined in RFC 2311.
* .p7c – PKCS#7 degenerated SignedData "certs-only" structure, without any data to sign. Defined in RFC 2311.
* .p7b, .keystore – PKCS#7 SignedData structure without data, just certificate(s) bundle and/or CRLs (rarely) but not a private key. Uses DER form or BER or PEM that starts with . The format used by Windows for certificate interchange. Supported by Java but often has .keystore as an extension instead. Unlike .pem style certificates, this format has a ''defined'' way to include certification-path certificates.
* .p12, .pfx, .pkcs12 – PKCS#12, may contain certificate(s) (public) and private keys (password protected) in a single file. .pfx – ''Personal Information eXchange'' PFX, predecessor of PKCS#12 (usually contains data in PKCS#12 format, e.g. with PFX files generated in IIS).
* .crl – A Certificate Revocation List
In cryptography, a certificate revocation list (CRL) is "a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing certificate authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted".
Publicly trusted C ...
(CRL). Certificate Authorities produce these as a way to de-authorize certificates before expiration.
PKCS#7 is a standard for signing or encrypting (officially called "enveloping") data. Since the certificate is needed to verify signed data, it is possible to include them in the SignedData structure.
Certificate chains and cross-certification
A certificate chain (see the equivalent concept of "certification path" defined by section 3.2) is a list of certificates (usually starting with an end-entity certificate) followed by one or more CA certificates (usually the last one being a self-signed certificate), with the following properties: # The Issuer of each certificate (except the last one) matches the Subject of the next certificate in the list # Each certificate (except the last one) is signed by the secret key corresponding to the next certificate in the chain (i.e. the signature of one certificate can be verified using the public key contained in the following certificate) # The last certificate in the list is a trust anchor: a certificate that you trust because it was delivered to you by some trustworthy procedure Certificate chains are used in order to check that the public key (PK) contained in a target certificate (the first certificate in the chain) and other data contained in it effectively belongs to its subject. In order to ascertain this, the signature on the target certificate is verified by using the PK contained in the following certificate, whose signature is verified using the next certificate, and so on until the last certificate in the chain is reached. As the last certificate is a trust anchor, successfully reaching it will prove that the target certificate can be trusted. The description in the preceding paragraph is a simplified view on the certification path validation process as defined by section 6, which involves additional checks, such as verifying validity dates on certificates, looking up CRLs, etc. Examining how certificate chains are built and validated, it is important to note that a concrete certificate can be part of very different certificate chains (all of them valid). This is because several CA certificates can be generated for the same subject and public key, but be signed with different private keys (from different CAs or different private keys from the same CA). So, although a single X.509 certificate can have only one issuer and one CA signature, it can be validly linked to more than one certificate, building completely different certificate chains. This is crucial for cross-certification between PKIs and other applications.
See the following examples:
Examining how certificate chains are built and validated, it is important to note that a concrete certificate can be part of very different certificate chains (all of them valid). This is because several CA certificates can be generated for the same subject and public key, but be signed with different private keys (from different CAs or different private keys from the same CA). So, although a single X.509 certificate can have only one issuer and one CA signature, it can be validly linked to more than one certificate, building completely different certificate chains. This is crucial for cross-certification between PKIs and other applications.
See the following examples:
Examples
In these diagrams: * Each box represents a certificate, with its Subject in bold * A → B means "A is signed by B" (or, more precisely, "A is signed by the secret key corresponding to the public key contained in B"). * Certificates with the same color (that are not white/transparent) contain the same public keyExample 1: Cross-certification at root Certification Authority (CA) level between two PKIs
In order to manage that user certificates existing in PKI 2 (like "User 2") are trusted by PKI 1, CA1 generates a certificate (cert2.1) containing the public key of CA2. Now both "cert2 and cert2.1 (in green) have the same subject and public key, so there are two valid chains for cert2.2 (User 2): "cert2.2 → cert2" and "cert2.2 → cert2.1 → cert1". Similarly, CA2 can generate a certificate (cert1.1) containing the public key of CA1 so that user certificates existing in PKI 1 (like "User 1") are trusted by PKI 2.Example 2: CA certificate renewal
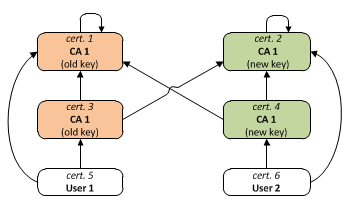
Since both cert1 and cert3 contain the same public key (the old one), there are two valid certificate chains for cert5: "cert5 → cert1" and "cert5 → cert3 → cert2", and analogously for cert6. This allows that old user certificates (such as cert5) and new certificates (such as cert6) can be trusted indifferently by a party having either the new root CA certificate or the old one as trust anchor during the transition to the new CA keys.Sample X.509 certificates
This is an example of a decoded X.509 certificate that was used in the past by wikipedia.org and several other Wikipedia websites. It was issued by GlobalSign, as stated in the Issuer field. Its Subject field describes Wikipedia as an organization, and its Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field for DNS describes the hostnames for which it could be used. The Subject Public Key Info field contains an ECDSA public key, while the signature at the bottom was generated by GlobalSign's RSA private key. (The signatures in these examples are truncated.)End-entity certificate
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
10:e6:fc:62:b7:41:8a:d5:00:5e:45:b6
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=BE, O=GlobalSign nv-sa, CN=GlobalSign Organization Validation CA - SHA256 - G2
Validity
Not Before: Nov 21 08:00:00 2016 GMT
Not After : Nov 22 07:59:59 2017 GMT
Subject: C=US, ST=California, L=San Francisco, O=Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., CN=*.wikipedia.org
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: id-ecPublicKey
Public-Key: (256 bit)
pub:
00:c9:22:69:31:8a:d6:6c:ea:da:c3:7f:2c:ac:a5:
af:c0:02:ea:81:cb:65:b9:fd:0c:6d:46:5b:c9:1e:
9d:3b:ef
ASN1 OID: prime256v1
NIST CURVE: P-256
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Agreement
Authority Information Access:
CA Issuers - URI:http://secure.globalsign.com/cacert/gsorganizationvalsha2g2r1.crt
OCSP - URI:http://ocsp2.globalsign.com/gsorganizationvalsha2g2
X509v3 Certificate Policies:
Policy: 1.3.6.1.4.1.4146.1.20
CPS: https://www.globalsign.com/repository/
Policy: 2.23.140.1.2.2
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:FALSE
X509v3 CRL Distribution Points:
Full Name:
URI:http://crl.globalsign.com/gs/gsorganizationvalsha2g2.crl
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.wikipedia.org, DNS:*.m.mediawiki.org, DNS:*.m.wikibooks.org, DNS:*.m.wikidata.org, DNS:*.m.wikimedia.org, DNS:*.m.wikimediafoundation.org, DNS:*.m.wikinews.org, DNS:*.m.wikipedia.org, DNS:*.m.wikiquote.org, DNS:*.m.wikisource.org, DNS:*.m.wikiversity.org, DNS:*.m.wikivoyage.org, DNS:*.m.wiktionary.org, DNS:*.mediawiki.org, DNS:*.planet.wikimedia.org, DNS:*.wikibooks.org, DNS:*.wikidata.org, DNS:*.wikimedia.org, DNS:*.wikimediafoundation.org, DNS:*.wikinews.org, DNS:*.wikiquote.org, DNS:*.wikisource.org, DNS:*.wikiversity.org, DNS:*.wikivoyage.org, DNS:*.wiktionary.org, DNS:*.wmfusercontent.org, DNS:*.zero.wikipedia.org, DNS:mediawiki.org, DNS:w.wiki, DNS:wikibooks.org, DNS:wikidata.org, DNS:wikimedia.org, DNS:wikimediafoundation.org, DNS:wikinews.org, DNS:wikiquote.org, DNS:wikisource.org, DNS:wikiversity.org, DNS:wikivoyage.org, DNS:wiktionary.org, DNS:wmfusercontent.org, DNS:wikipedia.org
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication, TLS Web Client Authentication
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
28:2A:26:2A:57:8B:3B:CE:B4:D6:AB:54:EF:D7:38:21:2C:49:5C:36
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:96:DE:61:F1:BD:1C:16:29:53:1C:C0:CC:7D:3B:83:00:40:E6:1A:7C
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
8b:c3:ed:d1:9d:39:6f:af:40:72:bd:1e:18:5e:30:54:23:35:
...
To validate this end-entity certificate, one needs an intermediate certificate that matches its Issuer and Authority Key Identifier:
In a TLS connection, a properly-configured server would provide the intermediate as part of the handshake. However, it's also possible to retrieve the intermediate certificate by fetching the "CA Issuers" URL from the end-entity certificate.
Intermediate certificate
This is an example of an intermediate certificate belonging to acertificate authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. Thi ...
. This certificate signed the end-entity certificate above, and was signed by the root certificate below. Note that the subject field of this intermediate certificate matches the issuer field of the end-entity certificate that it signed. Also, the "subject key identifier" field in the intermediate matches the "authority key identifier" field in the end-entity certificate.
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
04:00:00:00:00:01:44:4e:f0:42:47
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=BE, O=GlobalSign nv-sa, OU=Root CA, CN=GlobalSign Root CA
Validity
Not Before: Feb 20 10:00:00 2014 GMT
Not After : Feb 20 10:00:00 2024 GMT
Subject: C=BE, O=GlobalSign nv-sa, CN=GlobalSign Organization Validation CA - SHA256 - G2
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
00:c7:0e:6c:3f:23:93:7f:cc:70:a5:9d:20:c3:0e:
...
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Certificate Sign, CRL Sign
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:TRUE, pathlen:0
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
96:DE:61:F1:BD:1C:16:29:53:1C:C0:CC:7D:3B:83:00:40:E6:1A:7C
X509v3 Certificate Policies:
Policy: X509v3 Any Policy
CPS: https://www.globalsign.com/repository/
X509v3 CRL Distribution Points:
Full Name:
URI:http://crl.globalsign.net/root.crl
Authority Information Access:
OCSP - URI:http://ocsp.globalsign.com/rootr1
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:60:7B:66:1A:45:0D:97:CA:89:50:2F:7D:04:CD:34:A8:FF:FC:FD:4B
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
46:2a:ee:5e:bd:ae:01:60:37:31:11:86:71:74:b6:46:49:c8:
...
Root certificate
This is an example of a self-signed root certificate representing acertificate authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. Thi ...
. Its issuer and subject fields are the same, and its signature can be validated with its own public key. Validation of the trust chain has to end here. If the validating program has this root certificate in its trust store, the end-entity certificate can be considered trusted for use in a TLS connection. Otherwise, the end-entity certificate is considered untrusted.
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
04:00:00:00:00:01:15:4b:5a:c3:94
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=BE, O=GlobalSign nv-sa, OU=Root CA, CN=GlobalSign Root CA
Validity
Not Before: Sep 1 12:00:00 1998 GMT
Not After : Jan 28 12:00:00 2028 GMT
Subject: C=BE, O=GlobalSign nv-sa, OU=Root CA, CN=GlobalSign Root CA
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
00:da:0e:e6:99:8d:ce:a3:e3:4f:8a:7e:fb:f1:8b:
...
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Certificate Sign, CRL Sign
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:TRUE
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
60:7B:66:1A:45:0D:97:CA:89:50:2F:7D:04:CD:34:A8:FF:FC:FD:4B
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
d6:73:e7:7c:4f:76:d0:8d:bf:ec:ba:a2:be:34:c5:28:32:b5:
...
Security
There are a number of publications about PKI problems byBruce Schneier
Bruce Schneier (; born January 15, 1963) is an American cryptographer, computer security professional, privacy specialist, and writer. Schneier is an Adjunct Lecturer in Public Policy at the Harvard Kennedy School and a Fellow at the Berkman ...
, Peter Gutmann and other security experts.
Architectural weaknesses
*Use of blocklisting invalid certificates (using CRLs and OCSP), **If the client only trusts certificates when CRLs are available, then they lose the offline capability that makes PKI attractive. So most clients do trust certificates when CRLs are not available, but in that case an attacker that controls the communication channel can disable the CRLs. Adam Langley of Google has said soft-fail CRL checks are like a safety belt that works except when you have an accident. *CRLs are notably a poor choice because of large sizes and convoluted distribution patterns, *Ambiguous OCSP semantics and lack of historical revocation status, *Revocation of root certificates is not addressed, *Aggregation problem: Identity claims (authenticate with an identifier), attribute claims (submit a bag of vetted attributes), and policy claims are combined in a single container. This raises privacy, policy mapping, and maintenance issues. *Delegation problem: CAs cannot technically restrict subordinate CAs from issuing certificates outside a limited namespaces or attribute set; this feature of X.509 is not in use. Therefore, a large number of CAs exist on the Internet, and classifying them and their policies is an insurmountable task. Delegation of authority within an organization cannot be handled at all, as in common business practice. *Federation problem: Certificate chains that are the result of subordinate CAs, bridge CAs, and cross-signing make validation complex and expensive in terms of processing time. Path validation semantics may be ambiguous. The hierarchy with a third-party trusted party is the only model. This is inconvenient when a bilateral trust relationship is already in place. *Issuance of an Extended Validation (EV) certificate for a hostname doesn't prevent issuance of a lower-validation certificate valid for the same hostname, which means that the higher validation level of EV doesn't protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.Problems with certification authorities
* The person or organization that purchases a certificate will often utilize the least expensive certification authority. In response, CA's have cut prices and removed more expensive validation checks in what is known as aRace to the Bottom
Race to the bottom is a Socioeconomics, socio-economic concept describing a scenario in which individuals or companies compete in a manner that incrementally reduces the utility of a product or service in response to perverse incentives. This pheno ...
. The Race to the Bottom is partly addressed by Extended Validation (EV) certificates, yet trust value in the eyes of security experts are diminishing. According to Peter Gutmann, EV certificates do not add any additional security controls. Rather, EV certificates merely restore CA profits to levels prior to the Race to the Bottom by allowing a CA to charge more for a service they should have been providing all along. The Race to the Bottom is also partly addressed by certificate authorities like Let's Encrypt
Let's Encrypt is a Non-profit organisation, non-profit certificate authority run by Internet Security Research Group (ISRG) that provides X.509 public key certificate, certificates for Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption at no charge. It is ...
that provide certificates free of charge. Let's Encrypt has also become the largest provider of certificates with over 500 million websites using it.
* Certification authorities attempt to deny almost all warranties to the user and relying parties in their Certification Practice Statement (CPS). For example, Apple Inc
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer ...
states in their CPS, "To the extent permitted by applicable law, Subscriber agreements, if applicable, disclaim warranties from Apple, including any warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose".
* According to Peter Gutmann, "Users use an undefined certification request protocol to obtain a certificate which is published in an unclear location in a nonexistent directory with no real means to revoke it"
* Like all businesses, CAs are subject to the legal jurisdictions they operate within, and may be legally compelled to compromise the interests of their customers and their users. Intelligence agencies have also made use of false certificates issued through extralegal compromise of CAs, such as DigiNotar, to carry out man-in-the-middle attack
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, or on-path attack, is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communi ...
s. Another example is a revocation request of the CA of the Dutch government, because of a Dutch law passed in 2018, giving new powers for the Dutch intelligence and security services
Implementation issues
Implementations suffer from design flaws, bugs, different interpretations of standards and lack of interoperability of different standards. Some problems are: * Many implementations turn off revocation check: ** Seen as obstacle, policies are not enforced ** If it was turned on in all browsers by default, including code signing, it would probably crash the infrastructure * DNs are complex and little understood (lack of canonicalization, internationalization problems) * rfc822Name has two notations * Name and policy constraints hardly supported * Key usage ignored, first certificate in a list being used * Enforcement of custom OIDs is difficult * Attributes should not be made critical because it makes clients crash * Unspecified length of attributes lead to product-specific limits * There are implementation errors with X.509 that allow e.g. falsified subject names using null-terminated strings or code injection attacks in certificates * By using illegal 0x80 padded subidentifiers ofobject identifier
In computing, object identifiers or OIDs are an identifier mechanism standardized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and ISO/IEC for naming any object, concept, or "thing" with a globally unambiguous persistent name.
Syntax and lex ...
s, wrong implementations or by using integer overflows of the client's browsers, an attacker can include an unknown attribute in the CSR, which the CA will sign, which the client wrongly interprets as "CN" (OID=2.5.4.3). Dan Kaminsky demonstrated this at the 26th Chaos Communication Congress
The Chaos Communication Congress is an annual hacker conference organized by the Chaos Computer Club. The congress features a variety of lectures and workshops on technical and political issues related to security, cryptography, privacy and ...
"Black OPs of PKI"
Cryptographic weaknesses
Digital signature systems depend on securecryptographic hash function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map (mathematics), map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for a cryptography, cryptographic application: ...
s to work. When a public key infrastructure allows the use of a hash function that is no longer secure, an attacker can exploit weaknesses in the hash function to forge certificates. Specifically, if an attacker is able to produce a hash collision
In computer science, a hash collision or hash clash is when two distinct pieces of data in a hash table share the same hash value. The hash value in this case is derived from a hash function which takes a data input and returns a fixed length of ...
, they can convince a CA to sign a certificate with innocuous contents, where the hash of those contents is identical to the hash of another, malicious set of certificate contents, created by the attacker with values of their choosing. The attacker can then append the CA-provided signature to their malicious certificate contents, resulting in a malicious certificate that appears to be signed by the CA. Because the malicious certificate contents are chosen solely by the attacker, they can have different validity dates or hostnames than the innocuous certificate. The malicious certificate can even contain a "CA: true" field making it able to issue further trusted certificates.
* MD2-based certificates were used for a long time and were vulnerable to preimage attack
In cryptography, a preimage attack on cryptographic hash functions tries to find a message that has a specific hash value. A cryptographic hash function should resist attacks on its preimage (set of possible inputs).
In the context of attack, the ...
s. Since the root certificate already had a self-signature, attackers could use this signature and use it for an intermediate certificate.
* In 2005, Arjen Lenstra
Arjen Klaas Lenstra (born 2 March 1956, in Groningen) is a Dutch mathematician, cryptographer and computational number theorist. He is a professor emeritus from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) where he headed of the Labora ...
and Benne de Weger demonstrated "how to use hash collisions to construct two X.509 certificates that contain identical signatures and that differ only in the public keys", achieved using a collision attack
In cryptography, a collision attack on a cryptographic hash tries to find two inputs producing the same hash value, i.e. a hash collision. This is in contrast to a preimage attack where a specific target hash value is specified.
There are roughly ...
on the MD5
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. MD5 was designed by Ronald Rivest in 1991 to replace an earlier hash function MD4, and was specified in 1992 as Request for Comments, RFC 1321.
MD5 ...
hash function.
* In 2008, Alexander Sotirov
Alexander Sotirov is a computer security researcher. He has been employed by Determina and VMware. In 2012, Sotirov co-founded New York based Trail of Bits with Dino Dai Zovi and Dan Guido, where he currently serves as co-CEO.
He is well known f ...
and Marc Stevens presented at the Chaos Communication Congress
The Chaos Communication Congress is an annual hacker conference organized by the Chaos Computer Club. The congress features a variety of lectures and workshops on technical and political issues related to security, cryptography, privacy and ...
a practical attack that allowed them to create a rogue Certificate Authority, accepted by all common browsers, by exploiting the fact that RapidSSL was still issuing X.509 certificates based on MD5.
* In April 2009 at the Eurocrypt Conference, Australian Researchers of Macquarie University presented "Automatic Differential Path Searching for SHA-1
In cryptography, SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a hash function which takes an input and produces a 160-bit (20-byte) hash value known as a message digest – typically rendered as 40 hexadecimal digits. It was designed by the United States ...
". The researchers were able to deduce a method which increases the likelihood of a collision by several orders of magnitude.
* In February 2017, a group of researchers led by Marc Stevens produced a SHA-1 collision, demonstrating SHA-1's weakness.
Mitigations for cryptographic weaknesses
Exploiting a hash collision to forge X.509 signatures requires that the attacker be able to predict the data that the certificate authority will sign. This can be somewhat mitigated by the CA generating a random component in the certificates it signs, typically the serial number. The CA/Browser Forum has required serial number entropy in its Baseline Requirements Section 7.1 since 2011. , the Baseline Requirements forbid issuance of certificates using SHA-1. , Chrome and Firefox reject certificates that use SHA-1. both Edge and Safari are also rejecting SHA-1 certificate. OpenSSL began rejecting SHA-1 certificates by default in version 3.0, released September 2021.PKI standards for X.509
* PKCS7 (Cryptographic Message Syntax Standard — public keys with proof of identity for signed and/or encrypted message for PKI) *Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network, such as the Internet. The protocol is widely used in applications such as email, instant messaging, and voice over ...
(TLS) and its predecessor SSL — cryptographic protocols for Internet secure communications.
* Online Certificate Status Protocol
The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is an Internet Communication protocol, protocol used for obtaining the revocation status of an X.509 digital certificate. It was created as an alternative to certificate revocation lists (CRL), specif ...
(OCSP) / certificate revocation list (CRL) — this is to check certificate revocation status
* PKCS12 (Personal Information Exchange Syntax Standard) — used to store a private key with the appropriate public key certificate
* — Certification Path Building — guidance and recommendations for building X.509 public-key certification paths within applications (i.e., validating an end-entity certificate using a CA certificate)
PKIX Working Group
In 1995, theInternet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster ...
in conjunction with the National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of p ...
formed the Public-Key Infrastructure (X.509) working group. The working group, concluded in June 2014, is commonly referred to as "PKIX." It produced RFCs and other standards documentation on using and deploying X.509 in practice. In particular it produced and its successor RFC 5280, which define how to use X.509 in Internet protocols.
Major protocols and standards using X.509 certificates
TLS/SSL andHTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It uses encryption for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protoc ...
use the profile of X.509, as do S/MIME
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is a standard for public-key encryption and signing of MIME data. S/MIME is on an IETF standards track and defined in a number of documents, most importantly . It was originally developed by ...
(Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) and the EAP-TLS
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is an authentication framework frequently used in network and internet connections. It is defined in , which made obsolete, and is updated by .
EAP is an authentication framework for providing the transport ...
method for WiFi authentication. Any protocol that uses TLS, such as SMTP, POP, IMAP, LDAP, XMPP, and many more, inherently uses X.509.
IPsec can use the profile for authenticating peers.
ThOpenCable security specification
defines its own profile of X.509 for use in the cable industry. Devices like
smart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
s and TPMs often carry certificates to identify themselves or their owners. These certificates are in X.509 form.
The WS-Security standard defines authentication either through TLS or through its own certificate profile. Both methods use X.509.
The Microsoft Authenticode code signing system uses X.509 to identify authors of computer programs. Secure Boot feature of UEFI
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI, as an acronym) is a Specification (technical standard), specification for the firmware Software architecture, architecture of a computing platform. When a computer booting, is powered on, the UEFI ...
uses X.509 to authenticate UEFI drivers or bootloaders during booting
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via Computer hardware, hardware such as a physical button on the computer or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) h ...
and disallow blocklisted drivers or bootloaders (by using Forbidden Key Exchange or dbx database).
The OPC UA industrial automation communication standard uses X.509.
SSH generally uses a Trust On First Use security model and doesn't have need for certificates. However, the popular OpenSSH implementation does support a CA-signed identity model based on its own non-X.509 certificate format.
See also
*Abstract Syntax Notation One
Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) is a standard interface description language (IDL) for defining data structures that can be serialized and deserialized in a cross-platform way. It is broadly used in telecommunications and computer networ ...
* Certificate policy
* Code Access Security Code Access Security (CAS), in the Microsoft .NET framework, is Microsoft's solution to prevent untrusted code from performing privileged actions. When the CLR loads an assembly it will obtain evidence for the assembly and use this to identify th ...
* Communications security
Communications security is the discipline of preventing unauthorized interceptors from accessing telecommunications in an intelligible form, while still delivering content to the intended recipients.
In the North Atlantic Treaty Organization ...
* Information security
Information security is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It is part of information risk management. It typically involves preventing or reducing the probability of unauthorized or inappropriate access to data ...
* ISO/IEC JTC 1
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain an ...
* PKI Resource Query Protocol
* Public-key cryptography
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic alg ...
* Public Key Infrastructure
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption.
The purpose of a PKI is to fac ...
* Time stamp protocol
* Trusted timestamping
Trusted timestamping is the process of computer security, securely keeping track of the creation and modification time of a document. Security here means that no one—not even the owner of the document—should be able to change it once it has bee ...
* EdDSA
References
External links
ITU-T's X.509 standards
* Peter Gutmann's articles: *
Overview of PKI
*
X.509 implementation notes and style guide
*
Sun * - Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure: Certification Path Building * {{IETF RFC, 5280, link=no - Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Profile
Understanding Digital Certificates
Microsoft TechNet Cryptographic protocols Public-key cryptography ITU-T recommendations ITU-T X Series Recommendations X.500