|
ITU-T Study Group 17
The ITU-T Study Group 17 (SG17) is a statutory group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with security. The group is concerned with a broad range of security-related standardization issues such as cybersecurity, security management, security architectures and frameworks, countering spam, identity management, biometrics, protection of personally identifiable information, and the security of applications and services for the Internet of Things (IoT). It is responsible for standardization of i.a. ASN.1 and X.509, it is also the parent body of the Focus Group on Quantum Information Technology (FG-QIT). The group is currently chaired by Heung Youl Youm of South Korea. Administratively, SG17 is a statutory meeting of the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), which creates the ITU-T Study Groups and appoints their management teams. The secretariat is provided by the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (under Director Chaesub L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standards Organization
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpreting, or otherwise contributing to the usefulness of technical standards to those who employ them. Such an organization works to create uniformity across producers, consumers, government agencies, and other relevant parties regarding terminology, product specifications (e.g. size, including units of measure), protocols, and more. Its goals could include ensuring that Company A's external hard drive works on Company B's computer, an individual's blood pressure measures the same with Company C's sphygmomanometer as it does with Company D's, or that all shirts that should not be ironed have the same icon (a clothes iron crossed out with an X) on the label. Most standards are voluntary in the sense that they are offered for adoption by people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaesub Lee
Chaesub Lee PhD (Korean: 이재섭) is the Director of ITU Telecommunication Standardization Bureau, the permanent secretariat of the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) and as such, an Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations. Early career In 1986 Lee started working at Korea Telecom, where he worked for 17 years. Following this, Lee worked at Korea's Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) for eight years. ITU involvement Lee was the Chairman of the ITU-T Focus Group Next-Generation Networks (FG-NGN), as well as the Vice-Chairman of the ITU-T Focus Group IPTV. Lee served as Vice-Chairman of ITU-T Study Group 13 "Future Networks and Cloud" (SG13) from 2001 until 2008, after which he became Chairman of that group in 2009. Director Telecommunication Standardization Bureau Lee was elected at the 2014 Plenipotentiary Conference in Busan (Republic of Korea), with the term beginning on January 1, 2015. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federated Learning
Federated learning (also known as collaborative learning) is a machine learning technique that trains an algorithm across multiple decentralized edge devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. This approach stands in contrast to traditional centralized machine learning techniques where all the local datasets are uploaded to one server, as well as to more classical decentralized approaches which often assume that local data samples are identically distributed. Federated learning enables multiple actors to build a common, robust machine learning model without sharing data, thus allowing to address critical issues such as data privacy, data security, data access rights and access to heterogeneous data. Its applications are spread over a number of industries including defense, telecommunications, IoT, and pharmaceutics. A major open question at the moment is how inferior models learned through federated data are relative to ones where the data are pooled. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-party Computation
Secure multi-party computation (also known as secure computation, multi-party computation (MPC) or privacy-preserving computation) is a subfield of cryptography with the goal of creating methods for parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. Unlike traditional cryptographic tasks, where cryptography assures security and integrity of communication or storage and the adversary is outside the system of participants (an eavesdropper on the sender and receiver), the cryptography in this model protects participants' privacy from each other. The foundation for secure multi-party computation started in the late 1970s with the work on mental poker, cryptographic work that simulates game playing/computational tasks over distances without requiring a trusted third party. Note that traditionally, cryptography was about concealing content, while this new type of computation and protocol is about concealing partial information about data while comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption is a form of encryption that permits users to perform computations on its encrypted data without first decrypting it. These resulting computations are left in an encrypted form which, when decrypted, result in an identical output to that produced had the operations been performed on the unencrypted data. Homomorphic encryption can be used for privacy-preserving outsourced storage and computation. This allows data to be encrypted and out-sourced to commercial cloud environments for processing, all while encrypted. For sensitive data, such as health care information, homomorphic encryption can be used to enable new services by removing privacy barriers inhibiting data sharing or increase security to existing services. For example, predictive analytics in health care can be hard to apply via a third party service provider due to medical data privacy concerns, but if the predictive analytics service provider can operate on encrypted data instead, these priva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trustworthy AI
Trustworthy AI is a programme of work of the ITU (United Nations Specialized Agency for ICT) under its AI for Good programme. The programme advances the standardization of a number of Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs), including homomorphic encryption, federated learning, secure multi-party computation, differential privacy, zero-knowledge proof. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies are complex and the working can be considered counterintuitive. For instance, homomorphic encryption enciphers data, yet if this data is numerical, it is still possible to compute on this data (the outcomes still being encrypted but decryptable by the data owner). Other PETs exhibit similar characteristics. Often these technologies are developed with the explicit goal of enabling their analysis in juristictions different from the data creation (under e.g. GDPR). As such, the programme being led by two international organizations develops international standards to work in this context. The PETs are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AI For Good
AI for Good is a year-round digital platform of the United Nations, where AI innovators and problem owners learn, discuss and connect to identify practical AI solutions to advance the UN Sustainable Development Goals, SDGs. The impetus for organizing global summits that are action oriented, came from existing discourse in artificial intelligence (AI) research being dominated by research streams such as the Netflix Prize (improve the movie recommendation algorithm). AI for Good aims to bring forward Artificial Intelligence research topics that contribute towards more global problems, in particular through the Sustainable Development Goals. AI for Good came out of the AI for Good Global Summit 2020 which had been moved online in 2020 due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. AI for Good is organized by the Standardization Sector of ITU (ITU-T). Since moving online, AI for Good developed into three main programme streams: Learn, Build, and Connect. AI for Good also helps organize ITU's Global Stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSI Model
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that 'provides a common basis for the coordination of SOstandards development for the purpose of systems interconnection'. In the OSI reference model, the communications between a computing system are split into seven different abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. The model partitions the flow of data in a communication system into seven abstraction layers to describe networked communication from the physical implementation of transmitting bits across a communications medium to the highest-level representation of data of a distributed application. Each intermediate layer serves a class of functionality to the layer above it and is served by the layer below it. Classes of functionality are realized in all software development through all and any standardized communication protocols. Each layer in the OSI model has its own well-defined functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
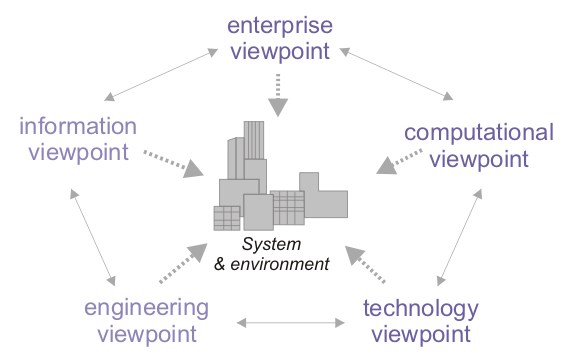
RM-ODP
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems. RM-ODP, also named ''ITU-T Rec. X.901-X.904'' and ''ISO/IEC 10746'', is a joint effort by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T). Overview The RM-ODP is a reference model based on precise concepts derived from current distributed processing developments and, as far as possible, on the use of formal description techniques for specification of the architecture. Many RM-ODP concepts, possibly under different names, have been around for a long time and have been rigorousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and adjacent islands. It has a population of 51.75 million, of which roughly half live in the Seoul Capital Area, the fourth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Other major cities include Incheon, Busan, and Daegu. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Its first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Silla and Balhae in the late 7th century, Korea was ruled by the Goryeo dynasty (918–1392) and the Joseon dynasty (1392–1897). The succeeding Korean Empire (1897–1910) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercive change) caused by others, by restraining the freedom of others to act. Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be of persons and social groups, objects and institutions, ecosystems or any other entity or phenomenon vulnerable to unwanted change. Security mostly refers to protection from hostile forces, but it has a wide range of other senses: for example, as the absence of harm (e.g. freedom from want); as the presence of an essential good (e.g. food security); as resilience against potential damage or harm (e.g. secure foundations); as secrecy (e.g. a secure telephone line); as containment (e.g. a secure room or cell); and as a state of mind (e.g. emotional security). The term is also used to refer to acts and systems whose purpose may be to provide security (security companies, security forces, security guard, cyber security systems, security cameras, remote guard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. The first meeting of the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), the sector's governing conference, took place on 1 March of that year. ITU-T has a permanent secretariat called the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB), which is based at the ITU headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. The current director of the TSB is Chaesub Lee (of South Korea), whose first 4-year term commenced on 1 January 2015, and whose second 4-year term commenced on 1 January 2019. Chaesub Lee succeeded Malcolm Johnson (Director), Malc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)