RM-ODP on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in
UML4ODP
defines use of the
RM-ODP Resource site
Open Distributed Processing - Reference Model
RM-ODP information at LAMS
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland.
Official Record of the ANSA project
Computing Laboratory
University of Kent, Canterbury UK.
(Formalisation of ODP Systems Architecture), University of Stirling, UK.
Distributed and Cooperative Systems
UMPC, Paris, France.
Networks and ComputerScience Department of ENST, Paris France.
Distributed Systems Technology Center
Australia. Distributed computing architecture Reference models Enterprise architecture frameworks ITU-T recommendations ITU-T X Series Recommendations ISO standards
 Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to Applied science, practical discipli ...
, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* Open (Blues Image album), ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* Open (Gotthard album), ''Open'' (Gotthard album), 1999
* Open (C ...
distributed Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
processing (ODP). It supports distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
* Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
, interworking, platform
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework
An enterprise architecture framework (EA framework) defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It struct ...
for the specification
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
There are different types of technical or engineering specificati ...
of ODP systems.
RM-ODP, also named ''ITU-T Rec. X.901-X.904'' and ''ISO/IEC 10746'', is a joint effort by the International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in A ...
(ISO), the International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and ...
(IEC) and the Telecommunication Standardization Sector
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Commu ...
(ITU-T).
Overview
The RM-ODP is a reference model based on precise concepts derived from current distributed processing developments and, as far as possible, on the use of formal description techniques for specification of thearchitecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
. Many RM-ODP concepts, possibly under different names, have been around for a long time and have been rigorously described and explained in exact philosophy (for example, in the works of Mario Bunge
Mario Augusto Bunge (; ; September 21, 1919 – February 24, 2020) was an Argentine-Canadian philosopher and physicist. His philosophical writings combined scientific realism, systemism, materialism, emergentism, and other principles.
He was ...
) and in systems thinking
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts. It has been used as a way of exploring and developing effective actio ...
(for example, in the works of Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek ( , ; 8 May 189923 March 1992), often referred to by his initials F. A. Hayek, was an Austrian–British economist, legal theorist and philosopher who is best known for his defense of classical liberalism. Hayek ...
). Some of these concepts—such as abstraction
Abstraction in its main sense is a conceptual process wherein general rules and concepts are derived from the usage and classification of specific examples, literal ("real" or " concrete") signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abst ...
, composition, and emergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole.
Emergenc ...
—have recently been provided with a solid mathematical foundation in category theory
Category theory is a general theory of mathematical structures and their relations that was introduced by Samuel Eilenberg and Saunders Mac Lane in the middle of the 20th century in their foundational work on algebraic topology. Nowadays, ca ...
.
RM-ODP has four fundamental elements:
* an object modelling approach to system specification;
* the specification of a system in terms of separate but interrelated viewpoint specifications;
* the definition of a system infrastructure providing distribution transparencies for system applications; and
* a framework for assessing system conformance.
The RM-ODP family of recommendations and international standards defines a system of interrelated essential concepts necessary to specify open
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* Open (Blues Image album), ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* Open (Gotthard album), ''Open'' (Gotthard album), 1999
* Open (C ...
distributed Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
processing systems and provides a well-developed enterprise architecture framework for structuring the specifications for any large-scale systems including software systems.
History
Much of the preparatory work that led into the adoption of RM-ODP as an ISO standard was carried out by theAdvanced Networked Systems Architecture
Andrew James Herbert, OBE, FREng (born 1954) is a British computer scientist, formerly Chairman of Microsoft Research, for the Europe, Middle East and Africa region.
Biography
Herbert received a bachelor's of science degree in computational ...
(ANSA) project. This ran from 1984 until 1998 under the leadership of Andrew Herbert
Andrew James Herbert, OBE, FREng (born 1954) is a British computer scientist, formerly Chairman of Microsoft Research, for the Europe, Middle East and Africa region.
Biography
Herbert received a bachelor's of science degree in computational ...
(now MD of Microsoft Research in Cambridge), and involved a number of major computing and telecommunication companies. Parts 2 and 3 of the RM-ODP were eventually adopted as ISO standard
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in A ...
s in 1996. Parts 1 and 4 were adopted in 1998.
RM-ODP topics
RM-ODP standards
RM-ODP consists of four basicITU-T Recommendations
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Comm ...
and
ISO/IEC International Standards:
# Overview: Contains a motivational overview of ODP, giving scoping, justification and explanation of key concepts, and an outline of the ODP architecture. It contains explanatory material on how the RM-ODP is to be interpreted and applied by its users, who may include standard writers and architects of ODP systems.
# Foundations: Contains the definition of the concepts and analytical framework for normalized description of (arbitrary) distributed processing systems. It introduces the principles of conformance to ODP standards and the way in which they are applied. In only 18 pages, this standard sets the basics of the whole model in a clear, precise and concise way.
# Architecture: Contains the specification of the required characteristics that qualify distributed processing as open. These are the constraints to which ODP standards must conform. This recommendation also defines RM-ODP viewpoints, subdivisions of the specification of a whole system, established to bring together those particular pieces of information relevant to some particular area of concern.
# Architectural Semantics: Contains a formalization of the ODP modeling concepts by interpreting many concepts in terms of the constructs of the different standardized formal description techniques.
Viewpoints modeling and the RM-ODP framework
Most complex system specifications are so extensive that no single individual can fully comprehend all aspects of the specifications. Furthermore, we all have different interests in a given system and different reasons for examining the system's specifications. A business executive will ask different questions of a system make-up than would a system implementer. The concept of RM-ODP viewpoints framework, therefore, is to provide separate viewpoints into the specification of a given complex system. These viewpoints each satisfy an audience with interest in a particular set of aspects of the system. Associated with each viewpoint is a viewpoint language that optimizes the vocabulary and presentation for the audience of that viewpoint.Viewpoint modeling
A view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of ''views'' to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture ...
has become an effective approach for dealing with the inherent complexity of large distributed systems. Current software architectural practices, as described in IEEE 1471
IEEE 1471 is a superseded IEEE standard for describing the architecture of a "software-intensive system", also known as software architecture.
In 2011 it was superseded by ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010, ''Systems and software engineering — Architecture de ...
, divide the design activity into several areas of concerns, each one focusing on a specific aspect of the system. Examples include the "4+1" view model, the Zachman Framework, TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is the most used framework for enterprise architecture as of 2020 that provides an approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing an enterprise information technology architecture. TOG ...
, DoDAF
The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized b ...
and, of course, RM-ODP.
A viewpoint
Viewpoint may refer to:
* Scenic viewpoint, a high place where people can gather to view scenery
In computing
* Viewpoint model, a computer science technique for making complex systems more comprehensible to human engineers
* Viewpoint Corporat ...
is a subdivision of the specification of a complete system, established to bring together those particular pieces of information relevant to some particular area of concern during the analysis or design of the system. Although separately specified, the viewpoints are not completely independent; key items in each are identified as related to items in the other viewpoints. Moreover, each viewpoint substantially uses the same foundational concepts (defined in Part 2 of RM-ODP). However, the viewpoints are sufficiently independent to simplify reasoning about the complete specification. The mutual consistency among the viewpoints is ensured by the architecture defined by RM-ODP, and the use of a common object model provides the glue that binds them all
together.
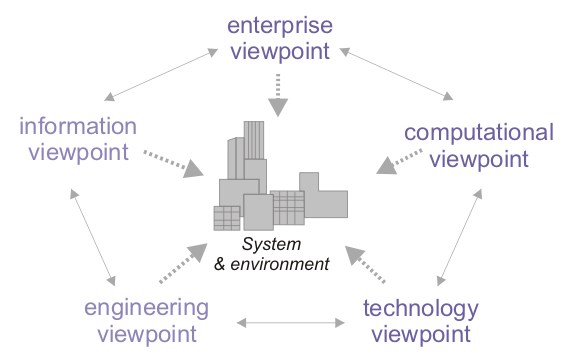
More specifically, the RM-ODP framework provides five generic and complementary viewpoints on the system and its environment:
* The ''enterprise viewpoint'', which focuses on the purpose, scope and policies for the system. It describes the business requirements and how to meet them.
* The ''information viewpoint'', which focuses on the semantics of the information and the information processing performed. It describes the information managed by the system and the structure and content type of the supporting data.
* The ''computational viewpoint'', which enables distribution through functional decomposition on the system into objects which interact at interfaces. It describes the functionality provided by the system and its functional decomposition.
* The ''engineering viewpoint'', which focuses on the mechanisms and functions required to support distributed interactions between objects in the system. It describes the distribution of processing performed by the system to manage the information and provide the functionality.
* The ''technology viewpoint'', which focuses on the choice of technology of the system. It describes the technologies chosen to provide the processing, functionality and presentation of information.
RM-ODP and UML
Currently there is growing interest in the use of UML for system modelling. However, there is no widely agreed approach to the structuring of such specifications. This adds to the cost of adopting the use of UML for system specification, hampers communication between system developers and makes it difficult to relate or merge system specifications where there is a need to integrate IT systems. Although the ODP reference model provides abstract languages for the relevant concepts, it does not prescribe particular notations to be used in the individual viewpoints. The viewpoint languages defined in the reference model are abstract languages in the sense that they define what concepts should be used, not how they should be represented. This lack of precise notations for expressing the different models involved in a multi-viewpoint specification of a system is a common feature for most enterprise architectural approaches, including the Zachman Framework, the " 4+1" model, or the RM-ODP. These approaches were consciously defined in a notation- and representation-neutral manner to increase their use and flexibility. However, this makes more difficult, among other things, the development of industrial tools for modeling the viewpoint specifications, the formal analysis of the specifications produced, and the possible derivation of implementations from the system specifications. In order to address these issues, ISO/IEC and the ITU-T started a joint project in 2004: "ITU-T Rec. X.906, ISO/IEC 19793: Information technology - Open distributed processing - Use of UML for ODP system specifications". This document (usually referred to aUML4ODP
defines use of the
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally m ...
2 (UML 2; ISO/IEC 19505), for expressing the specifications of open distributed systems in terms of the viewpoint specifications defined by the RM-ODP.
It defines a set of UML Profiles, one for each viewpoint language and one to express the correspondences between viewpoints, and an approach for structuring them according to the RM-ODP principles. The purpose of "UML4ODP" to allow ODP modelers to use the UML notation for expressing their ODP specifications in a standard graphical way; to allow UML modelers to use the RM-ODP concepts and mechanisms to structure their large UML system specifications according to a mature and standard proposal; and to allow UML tools to be used to process viewpoint specifications, thus facilitating the software design process and the enterprise architecture specification of large software systems.
In addition, ITU-T Rec. X.906 , ISO/IEC 19793 enables the seamless integration of the RM-ODP enterprise architecture framework
An enterprise architecture framework (EA framework) defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It struct ...
with the Model-Driven Architecture (MDA) initiative from the OMG, and with the service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provid ...
(SOA).
Applications
In addition, there are several projects that have used or currently use RM-ODP for effectively structuring their systems specifications: * The COMBINE project * The ENVRI and ENVRIplus projects for common operations of environmental research infrastructures are developing the ENVRI Reference Model * The Reference Architecture for Space Data Systems (RASDS) From the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems. * Interoperability Technology Association for Information Processing (INTAP), Japan. *The European Advanced Informatics in Medicine (AIM) OpenLabs project. * The Synapses European project. A 239-item reference list covering RM-ODP standards as well as related research, applications and case studies was included in.Kilov, H., Linington, P.F., Romero, J.R., Tanaka, A., Vallecillo, A.: The reference model of open distributed processing: foundations, experience and applications. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 35, 247–256 (2013)See also
*Enterprise Architecture framework
An enterprise architecture framework (EA framework) defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It struct ...
* Enterprise Collaboration Architecture The first version of the Enterprise Collaboration Architecture (ECA) has been published by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
The vision of the (ECA) is to simplify the development of component based and services oriented systems by providi ...
* Enterprise Modelling Methodology/Open Distributed Processing (EMM/ODP)
* Reference model
* Triune Continuum Paradigm The Triune Continuum Paradigm is a paradigm for general system modeling published in 2002.A. Naumenko''Triune Continuum Paradigm: a paradigm for general system modeling and its applications for UML and RM-ODP'' Doctoral thesis 2581, Swiss Federal ...
* View model
A view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of ''views'' to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architectur ...
* ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7
Notes and references
{{reflistExternal links
RM-ODP Resource site
Open Distributed Processing - Reference Model
RM-ODP information at LAMS
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland.
Official Record of the ANSA project
Computing Laboratory
University of Kent, Canterbury UK.
(Formalisation of ODP Systems Architecture), University of Stirling, UK.
Distributed and Cooperative Systems
UMPC, Paris, France.
Networks and ComputerScience Department of ENST, Paris France.
Distributed Systems Technology Center
Australia. Distributed computing architecture Reference models Enterprise architecture frameworks ITU-T recommendations ITU-T X Series Recommendations ISO standards