Wiesbaden () is a city in central western Germany and the capital of the state of
Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major histor ...
. , it had 290,955 inhabitants, plus approximately 21,000 United States citizens (mostly associated with the
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
). The Wiesbaden urban area is home to approximately 560,000 people. Wiesbaden is the second-largest city in Hesse after
Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
.
The city, together with nearby Frankfurt am Main,
Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it th ...
, and
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
, is part of the
Frankfurt Rhine Main Region
The Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region, often simply referred to as Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Frankfurt Rhine-Main area or Rhine-Main area (German: ''Rhein-Main-Gebiet'' or ''Frankfurt/Rhein-Main'', abbreviated FRM), is the second-largest metropolitan re ...
, a
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
with a combined population of about 5.8 million people.
Wiesbaden is one of the oldest
spa town
A spa town is a resort town based on a mineral spa (a developed mineral spring). Patrons visit spas to "take the waters" for their purported health benefits.
Thomas Guidott set up a medical practice in the English town of Bath in 1668. He ...
s in Europe. Its name translates to "meadow baths", a reference to its famed
hot springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
. It is also internationally famous for its architecture and climate—it is also called the "
Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
of the North" in reference to the city in France. At one time, Wiesbaden had 26 hot springs. , fourteen of the springs are still flowing.
In 1970, the town hosted the tenth ''
Hessentag
The Hessentag (; en, Hesse Day) is an annual event, both fair and festival, organized by the German state of Hesse to represent the different regions of Hesse. The events are shown for a week to the visitors, with an emphasis on cultural disp ...
Landesfest'' (English: Hessian Day, a state festival).
The city is considered the tenth richest in Germany (2014) boasting 110.3% of the national average gross domestic product in 2017. The average annual buying power per citizen is €24,783.
Geographical setting

Wiesbaden is situated on the right (northern) bank of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, below the confluence of the
Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
, where the Rhine's main direction changes from north to west. The city is across the Rhine from Mainz, the capital of the state of
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
. Frankfurt am Main is located about east. To the north of the city are the
Taunus
The Taunus is a mountain range in Hesse, Germany, located north of Frankfurt. The tallest peak in the range is '' Großer Feldberg'' at 878 m; other notable peaks are ''Kleiner Feldberg'' (825 m) and '' Altkönig'' (798 m).
The Taunus range span ...
Mountains, which trend in a northeasterly direction.
The city center, the ''Stadtmitte'', is located in the north-easternmost part of the
Upper Rhine Valley
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the so ...
at the spurs of the Taunus mountains, about from the Rhine. The landscape is formed by a wide lowland between the Taunus heights in the north, the Bierstadter Höhe and the Hainerberg in the east, the Mosbacher Mountain in the south, and the Schiersteiner Mountain in the west, an offshoot of the Taunus range.
The downtown is drained only by the narrow valley of the Salzbach, a tributary of the Rhine, on the eastern flanks of the Mosbacher Mountain. The city's main railway line and the Mainz road (''Mainzer Straße'') follow this valley. Several other streams drain into the Salzbach within the city center: the Wellritzbach, the Kesselbach, the Schwarzbach, the Dambach, and the Tennelbach, as well as the outflow of many thermal and mineral springs in the ''Kurhaus'' (spa) district. Above the city center, the Salzbach is better known as the Rambach.
The highest point of the Wiesbaden municipality is located northwest of the city center near the summit of the Hohe Wurzel, with an elevation of
above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The lowest point is the harbour entrance of Schierstein at above sea level. The central square (the ''Schlossplatz'', or palace square) is at an elevation of .
Wiesbaden covers an area of . It is from north to south and from west to east. In the north are vast forest areas, which cover 27.4% of the urban area. In the west and east are
vineyards
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards ...
and agricultural land, which cover 31.1% of the area. Of the municipality's -long border, the Rhine makes up .
Climate
Wiesbaden has a
temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
-
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(
Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: Cfb) with relatively cold winters and warm summers. Its average annual temperature is , with monthly mean temperatures ranging from in January to in July.
History

Classical antiquity
While evidence of settlement at present-day Wiesbaden dates back to the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
era, historical records document continuous occupancy after the erection of a
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
fort in 6 AD which housed an auxiliary cavalry unit. The
thermal springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
of Wiesbaden are first mentioned in
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
's ''
Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' ( la, Naturalis historia) is a work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. ...
''. They were famous for their recreation pools for Roman army horses and possibly as the source of a mineral used for red hair dye (which was very fashionable around the turn of BC/AD among women in Rome).
The Roman settlement is first mentioned using the name ''Aquae Mattiacorum'' (
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "Waters of the Mattiaci") in 121. The
Mattiaci
The Mattiaci were by Tacitus recorded as an ancient Germanic tribe and related to the Chatti, their Germanic neighbors to the east. There is no clear definition of what the tribe's name meant. The ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography'' sugge ...
were a
Germanic tribe
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, beginn ...
, possibly a branch of the neighboring
Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the valle ...
, who lived in the vicinity at that time. The town also appears as Mattiacum in
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's
Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
(2.10). The Roman Empire built the
Limes Germanicus
The (Latin for ''Germanic frontier'') is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier () fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubd ...
, which was a line of Roman frontier fortifications in the
Taunus
The Taunus is a mountain range in Hesse, Germany, located north of Frankfurt. The tallest peak in the range is '' Großer Feldberg'' at 878 m; other notable peaks are ''Kleiner Feldberg'' (825 m) and '' Altkönig'' (798 m).
The Taunus range span ...
. Wiesbaden is just south of the Taunus.
The capital of the province of
Germania Superior,
Mogontiacum
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Main ...
(present-day
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
), base of 2 (at times 3) Roman legions, was just over the Rhine and connected by a bridge at the present-day borough of
Mainz-Kastel
Mainz-Kastel is a district of the city Wiesbaden, which is the capital of the German state Hesse in western Germany.
Kastel is the historical bridgehead of Mainz, the capital of the German state Rhineland-Palatinate and is located on the right si ...
(Roman "''castellum''"), a strongly fortified bridgehead.
The
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
, a coalition of Germanic tribes from beyond the ''Limes'', captured the fort around 260. Later, in the 370s, when the Romans and Alamanni were allied, the Alemanni gained control of the Wiesbaden area and were in charge of its defense against other Germanic tribes.
Middle Ages
After the
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
under
Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
defeated the Alamanni in the
Battle of Tolbiac in 496, the Franks eventually displaced the Alamanni in the Wiesbaden area over the course of the 6th century. In the 8th century, Wiesbaden became the site of a royal
palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
of the Frankish kingdom. The first documented use of the name Wiesbaden is by
Einhard
Einhard (also Eginhard or Einhart; la, E(g)inhardus; 775 – 14 March 840) was a Frankish scholar and courtier. Einhard was a dedicated servant of Charlemagne and his son Louis the Pious; his main work is a biography of Charlemagne, the ''Vita ...
, the biographer of
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
, whose writings mention "Wisabada" sometime between 828 and 830.
When the Frankish
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
broke up in 888, Wiesbaden was in the eastern half, called
East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided t ...
(which would evolve into the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
). The town was part of
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper Fr ...
, the heartland of East Francia. In the 1170s, the
Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
of
Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
, Walram I, received the area around Wiesbaden as a
fiefdom
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form o ...
. When Franconia fragmented in the early 13th century, Nassau emerged as an independent state as part of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1232 Wiesbaden became a
Reichsstadt
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
, an imperial city, of the Holy Roman Empire. However, in 1242, during the war of Emperor
Frederick II against the Pope, the
Archbishop of Mainz,
Siegfried III, ordered the city's destruction.
Wiesbaden returned to the control of the
House of Nassau
The House of Nassau is a diversified aristocratic dynasty in Europe. It is named after the lordship associated with Nassau Castle, located in present-day Nassau, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The lords of Nassau were originally titled "Count ...
in 1270 under Count
Walram II, Count of Nassau
Walram II of Nassau, german: Walram II. von Nassau (Cawley.Dek (1970). – 24 January 1276), was Count of Nassau and is the ancestor of the Walramian branch of the House of Nassau.
Life
Walram was the second son of Count Henry II of Nassau and ...
. However, Wiesbaden and the castle at
Sonnenberg
Sonnenberg is a municipality in the Oberhavel district, in Brandenburg, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, a ...
were again destroyed in 1283 in conflict with
Eppstein
Eppstein is a town in the Main-Taunus-Kreis, in Hesse, Germany. Eppstein lies west of Frankfurt am Main, around 12 km north east of the state capital Wiesbaden, and is at the edge of the Taunus mountains. The ruins of the Eppstein castle is ...
.
Walram's son and successor
Adolf
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo and when Latinised Adolphus) is a given name used in German-speaking countries, Scandinavia, the Netherlands and Flanders, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Latin America and to a lesser extent in vari ...
would later become king of
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
from 1292 until 1298. In 1329, under Adolf's son
Gerlach I of Nassau-Weilburg the House of Nassau and thereby, Wiesbaden, received the right of
coinage
Coinage may refer to:
* Coins, standardized as currency
* Neologism, coinage of a new word
* '' COINage'', numismatics magazine
* Tin coinage, a tax on refined tin
* Protologism
''Protologism'' is a term coined in 2003 by the American literary ...
from Holy Roman Emperor
Louis the Bavarian
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany ...
.
In 1355, the County of Nassau-Weilburg was divided among the sons of Gerlach. The County of Nassau's holdings would be subdivided many times among heirs, with the parts being brought together again whenever a line died out. Wiesbaden became the seat of the County of Nassau-Wiesbaden under Count Adolf I (1307–1370), eldest son of Gerlach. It would eventually fall back to Nassau-Weilburg in 1605.
Modern era
Due to its participation in the uprisings of the
German Peasants' War of 1525, Wiesbaden lost all its privileges for over 40 years. During this time, Wiesbaden became
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
with the nomination of Wolf Denthener as first
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
pastor on January 1, 1543. The same day, the first Latin school was opened, preparing pupils for the
gymnasium in
Idstein. In 1566, the privileges of the city were restored.
The oldest remaining building of Wiesbaden, the old city hall, was built in 1609 and 1610. No older buildings are preserved due to two fires in 1547 and 1561. In 1648, at the end of the devastating
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, chronicles tell that Wiesbaden had barely 40 residents left. In 1659, the County of Nassau-Weilburg was divided again. Wiesbaden became part of the
County of Nassau-Usingen
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
. In 1744, the seat of Nassau-Usingen was moved to
Biebrich. In 1771, the Count of Nassau-Usingen granted a concession for gambling in Wiesbaden. In 1810, the Wiesbaden Casino (German: ''Spielbank'') was opened in the old Kurhaus. Gambling was later outlawed by
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
n authorities in 1872.
As a result of
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's victory over Austria in the
Battle of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz in ...
, the Holy Roman Empire was dissolved in 1805. On July 12, 1806, 16 states in present-day Germany, including the remaining counties of Nassau-Usingen and Nassau-Weilburg, formally left the Holy Roman Empire and joined in the
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
. Napoleon was its "protector". Under pressure from Napoleon, both counties merged to form the
Duchy of Nassau
The Duchy of Nassau (German: ''Herzogtum Nassau'') was an independent state between 1806 and 1866, located in what is now the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse. It was a member of the Confederation of the Rhine and later of the G ...
on August 30, 1806.

At the 1815
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
, the Duchy of Nassau joined the
German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, w ...
. The capital of Nassau was moved from Weilburg to Wiesbaden, and the city became the ducal residence. Building activity started to give the city a magnificent appearance. Most of the historical center of Wiesbaden dates back to this time.

In the
Revolutions of 1848
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in Europea ...
, 30,000 citizens of Nassau assembled in Wiesbaden on March 4. They demanded a constitution from the Duke, which they received.
In the
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
of 1866, Nassau took Austria's side. This decision led to the end of the duchy. After the Austrian defeat, Nassau was annexed by
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
and became part of the Prussian
province of Hesse-Nassau
The Province of Hesse-Nassau () was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868 to 1918, then a province of the Free State of Prussia until 1944.
Hesse-Nassau was created as a consequence of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 by combining the p ...
. The deposed duke
Adolph of Nassau in 1890 became the
Grand Duke of Luxembourg
The Grand Duke of Luxembourg ( lb, Groussherzog vu Lëtzebuerg, french: Grand-duc de Luxembourg, german: Großherzog von Luxemburg) is the monarchical head of state of Luxembourg. Luxembourg has been a grand duchy since 15 March 1815, when it w ...
(see
House of Nassau
The House of Nassau is a diversified aristocratic dynasty in Europe. It is named after the lordship associated with Nassau Castle, located in present-day Nassau, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The lords of Nassau were originally titled "Count ...
). This turned out to be a fortunate change for the city, as it then became an international spa town. A rise in construction commenced after the aristocracy followed the lead of the Hohenzollern emperors, who began annual trips to Wiesbaden.
The period around the turn of the 20th century is regarded as the heyday of the city.
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and List of monarchs of Prussia, King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until Abdication of Wilhelm II, his abdication on 9 ...
visited the city regularly in summer, such that it became an unofficial "summer residence". The city was also popular among the Russian nobility. In the wake of the imperial court, numerous nobles, artists, and wealthy businessmen increasingly settled in the city. Many wealthy persons chose Wiesbaden as their retirement seat, as it offered leisure and medical treatment alike. In the latter part of the 19th century, Wiesbaden became the German city with the most millionaires.
In 1894, the present Hessian State Theater, designed by the Vienna architects Fellner and Helmer, was built on behalf of Kaiser Wilhelm II.
Weimar Republic and Third Reich (1919 to 1945)
After World War I, Wiesbaden fell under the Allied occupation of the Rhineland and was occupied by the French army in 1918. In 1921, the Wiesbaden Agreement on German reparations to France was signed in the city. In 1925, Wiesbaden became the headquarters of the
British Army of the Rhine
There have been two formations named British Army of the Rhine (BAOR). Both were originally occupation forces in Germany, one after the First World War and the other after the Second World War. Both formations had areas of responsibility located ...
until the withdrawal of occupying forces from the Rhineland in 1930.
In 1929, an airport was constructed in Erbenheim on the site of a horse-racing track. In 1936,
Fighter Squadron 53 of the
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
was stationed here.
In the
Kristallnacht
() or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (german: Novemberpogrome, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) paramilitary and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation from ...
pogrom on November 10, 1938, Wiesbaden's large synagogue on Michelsberg was destroyed. The synagogue had been designed by Phillip Hoffmann and built in 1869. Another synagogue in
Wiesbaden-Bierstadt was also destroyed. When the Nazis came to power in Germany, there were 2,700 Jews living in Wiesbaden. By June 1942 nearly all of them had been deported to the Nazi death camps in German-occupied Poland.
General
Ludwig Beck
Ludwig August Theodor Beck (; 29 June 1880 – 20 July 1944) was a German general and Chief of the German General Staff during the early years of the Nazi regime in Germany before World War II. Although Beck never became a member of the Na ...
from Wiesbaden was one of the planners of the
July 20, 1944 assassination attempt of
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
. Beck was designated by his fellow conspirators to be future Head of State (Regent) after elimination of Hitler. The plot failed, however, and Beck was forced to commit suicide. Today, the city annually awards the Ludwig Beck prize for civil courage in his honor.
Lutheran pastor and theologian
Martin Niemöller
Friedrich Gustav Emil Martin Niemöller (; 14 January 18926 March 1984) was a German theologian and Lutheran pastor. He is best known for his opposition to the Nazi regime during the late 1930s and for his widely quoted 1946 poem " First they ca ...
, founder of the
Confessing Church
The Confessing Church (german: link=no, Bekennende Kirche, ) was a movement within German Protestantism during Nazi Germany that arose in opposition to government-sponsored efforts to unify all Protestant churches into a single pro-Nazi German ...
resistance movement against the Nazis, is an Honorary Citizen of Wiesbaden. He presented his last sermon before his arrest in Wiesbaden's Market Church.
World War II
In World War II, Wiesbaden was the headquarters for Germany's
Wehrkreis XII
The military districts, also known in some English-language publications by their German name as Wehrkreise (singular: ''Wehrkreis''), were administrative territorial units in Nazi Germany before and during World War II. The task of military distr ...
.
This military district included the
Eifel
The Eifel (; lb, Äifel, ) is a low mountain range in western Germany and eastern Belgium. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Community of ...
, part of
Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major histor ...
, the
Palatinate, and the
Saarland
The Saarland (, ; french: Sarre ) is a state of Germany in the south west of the country. With an area of and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, and ...
. After the
Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
, this ''Wehrkreis'' was extended to include
Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gr ...
, including
Nancy, and the Grand Duchy of
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
. The commander was ''General der Infanterie''
Walther Schroth
__NOTOC__
Walther Schroth (3 June 1882 – 6 October 1944) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross.
Schroth served on the "Court of Military Honour," a drumh ...
.
''Wehrkreis'' XII was made up of three subordinate regions: ''Bereich Hauptsitze''
Koblenz
Koblenz (; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz''), spelled Coblenz before 1926, is a German city on the banks of the Rhine and the Moselle, a multi-nation tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman mili ...
,
Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 2 ...
and
Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand E ...
.
*''Bereich Hauptsitz'' Koblenz was the headquarters for 12 ''Unterregion-Hauptsitze'', namely
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
I, Trier II,
Koblenz
Koblenz (; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz''), spelled Coblenz before 1926, is a German city on the banks of the Rhine and the Moselle, a multi-nation tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman mili ...
,
Neuwied
Neuwied () is a town in the north of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, capital of the District of Neuwied. Neuwied lies on the east bank of the Rhine, 12 km northwest of Koblenz, on the railway from Frankfurt am Main to Cologne. Th ...
,
Kreuznach
Bad Kreuznach () is a town in the Bad Kreuznach district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a spa town, most well known for its medieval bridge dating from around 1300, the Alte Nahebrücke, which is one of the few remaining bridges in th ...
, Wiesbaden,
Limburg an der Lahn
Limburg an der Lahn (officially abbreviated ''Limburg a. d. Lahn'') is the district seat of Limburg-Weilburg in Hesse, Germany.
Geography
Location
Limburg lies in western Hessen between the Taunus and the Westerwald on the river Lahn.
The t ...
,
Lahn
The Lahn is a , right (or eastern) tributary of the Rhine in Germany. Its course passes through the federal states of North Rhine-Westphalia (23.0 km), Hesse (165.6 km), and Rhineland-Palatinate (57.0 km).
It has its source in t ...
,
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
,
Worms Worms may refer to:
*Worm, an invertebrate animal with a tube-like body and no limbs
Places
*Worms, Germany
Worms () is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main. It had ...
,
Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it th ...
, and
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
.
*''Bereich Hauptsitz'' Mannheim was the headquarters for 10 ''Unterregion-Hauptsitze'', namely
Saarlautern
Saarlouis (; french: link=no, Sarrelouis, ; formerly Sarre-Libre and Saarlautern) is a town in Saarland, Germany, capital of the district of Saarlouis (district), Saarlouis. In 2020, the town had a population of 34,409. Saarlouis, as the name imp ...
,
Saarbrücken
Saarbrücken (; french: link=no, Sarrebruck ; Rhine Franconian: ''Saarbrigge'' ; lb, Saarbrécken ; lat, Saravipons, lit=The Bridge(s) across the Saar river) is the capital and largest city of the state of Saarland, Germany. Saarbrücken is S ...
,
St. Wendel,
Zweibrücken
Zweibrücken (; french: Deux-Ponts, ; Palatinate German: ''Zweebrigge'', ; literally translated as "Two Bridges") is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, on the Schwarzbach river.
Name
The name ''Zweibrücken'' means 'two bridges'; olde ...
,
Kaiserslautern
Kaiserslautern (; Palatinate German: ''Lautre'') is a city in southwest Germany, located in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate at the edge of the Palatinate Forest. The historic centre dates to the 9th century. It is from Paris, from Frankfur ...
,
Neustadt an der Weinstraße,
Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning " Ludwig's Port upon Rhine"), is a city in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, on the river Rhine, opposite Mannheim. With Mannheim, Heidelberg, and the surrounding region, it form ...
(Rhein),
Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (german: Universitätsstadt Mannheim), is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 2 ...
I, Mannheim II, and
Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914 ...
.
*''Bereich Hauptsitz'' Metz was the headquarters for ''Unterregion-Hauptsitze''
Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand E ...
,
Diedenhofen
Thionville (; ; german: Diedenhofen ) is a city in the northeastern French department of Moselle. The city is located on the left bank of the river Moselle, opposite its suburb Yutz.
History
Thionville was settled as early as the time of t ...
(Thionville), and
Saint-Avold
Saint-Avold (; ; Lorraine Franconian: ''Sänt Avuur'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
It is situated twenty-eight miles (45 km) east of Metz, France and seventeen miles (27 km) southwest ...
.
During the war, Wiesbaden was, between August 1940 and the end of 1942, bombed by the
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
and from 1943 through to March 1945, was attacked by both RAF and United States Air Force bombers on 66 days. In the attacks, about 18% of the city's homes were destroyed. During the war, more than 25% of the city's buildings were damaged or worse and 1,700 people were killed.
Wiesbaden was captured by U.S. Army forces on March 28, 1945. The U.S. 317th Infantry Regiment attacked in assault boats across the Rhine from Mainz while the 319th Infantry attacked across the river Main near
Hochheim am Main
Hochheim am Main (; Old English: Hockamore) is a town in the Main-Taunus district of the German state of Hesse. It is located near the right bank of the river Main three miles above its confluence with the Rhine, as well as on the German Timber- ...
. The attack started at 0100 and by early afternoon the two forces of the
80th U.S. Infantry Division had linked up with the loss of only three dead and three missing. The Americans captured 900 German soldiers and a warehouse full of 4,000 cases of champagne.
After the war's end, American rock artist
Elvis Presley
Elvis Aaron Presley (January 8, 1935 – August 16, 1977), or simply Elvis, was an American singer and actor. Dubbed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, King of Rock and Roll", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Elvis Presley, one ...
was stationed in Friedberg and often visited Wiesbaden.
Cold War and contemporary history
After World War II, the state of Hesse was established (see
Greater Hesse
Greater Hesse (german: link=no, Groß-Hessen) was the provisional name given for a section of German territory created by the United States military administration in at the end of World War II. It was formed by the Allied Control Council on 19 ...
), and Wiesbaden became its capital, though nearby
Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
is much larger and works as Hesse's economic and financial centre. Wiesbaden however suffered much less than Frankfurt from air bombing. There is a persistent rumour that the U.S. Army Air Force spared the town with the intention of turning it into a postwar HQ, but USAAF sources claim this to be a myth, arguing that Wiesbaden's economic and strategic importance simply did not justify more bombing. Wiesbaden was host to the Headquarters, U.S. Air Forces, Europe based at the former
Lindsey Air Station
The Europaviertel (European quarter) in Wiesbaden is a former barracks area named ''Gersdorff Kaserne'' at the edge of the city center of the Hessian state capital, approximately 2 kilometers southwest of the Marktkirche.
Barracks (1868–1945)
...
from 1953 to 1973.
American armed forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
have been present in Wiesbaden since World War II. The
U.S. 1st Armored Division
The 1st Armored Division, nicknamed "Old Ironsides," is a combined arms division of the United States Army. The division is part of III Armored Corps and operates out of Fort Bliss in El Paso, Texas. It was the first armored division of the ...
was headquartered at the
Wiesbaden Army Airfield
Lucius D. Clay Kaserne (german: Flugplatz Wiesbaden-Erbenheim) , commonly known as Clay Kaserne, is an installation of the United States Army in Hesse, Germany. The ''kaserne'' is located within Wiesbaden-Erbenheim. Named for General Lucius D. C ...
, just off the
Autobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. ...
toward Frankfurt, until the Division completed relocation to Fort Bliss, Texas, in 2011. Wiesbaden is now home to the
U.S. Army Europe
United States Army Europe and Africa (USAREUR-AF) is an Army Service Component Command (ASCC) /Theater Army responsible for directing United States Army operations throughout the U.S. European Command (EUCOM) and U.S. Africa Command (AFRICO ...
Headquarters and Mission Command Center.
Bathing and gambling
Wiesbaden has long been famous for its thermal springs and spa. Use of the thermal springs was first documented by the Romans. The business of spring bathing became important for Wiesbaden near the end of the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. By 1370, 16 bath houses were in operation. By 1800, the city had 2,239 inhabitants and 23 bath houses.
By 1900, Wiesbaden, with a population of 86,100, hosted 126,000 visitors annually. Famous visitors to the springs included
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as trea ...
,
Fyodor Dostoevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
,
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
,
Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
, and
Henrik Pontoppidan
Henrik Pontoppidan (24 July 1857 – 21 August 1943) was a Danish realist writer who shared with Karl Gjellerup the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1917 for "his authentic descriptions of present-day life in Denmark." Pontoppidan's novels and shor ...
. In those years, more millionaires were living in Wiesbaden than in any other city in Germany.
Gambling followed bathing ''en suite'', and in the 19th century, Wiesbaden was famous for both. Its casino (''Spielbank'') rivalled those of
Bad Homburg
Bad Homburg vor der Höhe () is the district town of the Hochtaunuskreis, Hesse, on the southern slope of the Taunus mountains. Bad Homburg is part of the Frankfurt Rhein-Main Regional Authority, Frankfurt Rhein-Main urban area. The town's offic ...
,
Baden-Baden
Baden-Baden () is a spa town in the states of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, at the north-western border of the Black Forest mountain range on the small river Oos (river), Oos, ten kilometres (six miles) east of the ...
, and
Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Lig ...
. In 1872, the Prussian-dominated imperial government closed down all German gambling houses. The Wiesbaden casino was reopened in 1949.
Main sights
The Palace Square
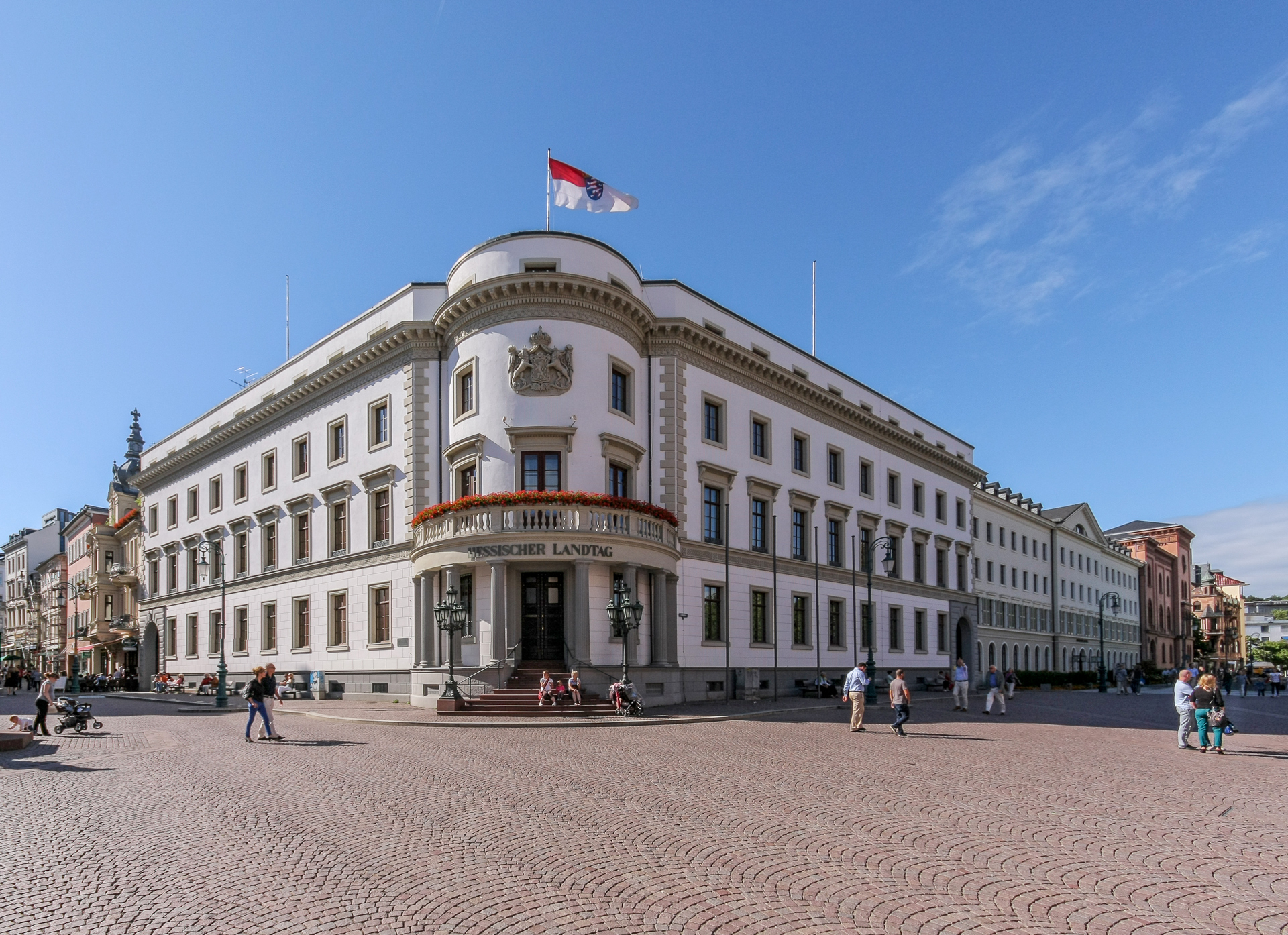

The ''
Schloßplatz'' ("palace square") is situated in the center of the city, surrounded by several outstanding buildings. The
ducal palace was begun under
William, Duke of Nassau
Wilhelm (Given names: ''Georg Wilhelm August Heinrich Belgicus''; 14 June 1792, Kirchheimbolanden – 20/30 August 1839, Bad Kissingen) was joint sovereign Duke of Nassau, along with his father's cousin Frederick Augustus, reigning from 1816 unt ...
. Its foundations were laid in 1837 and it was completed in November 1841 (two years after William's death). For the twenty-six remaining years of ducal authority it was the residence of the ruling family. It later served as a secondary residence for the King of
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
1866 to 1918. It was later used as a headquarters for French and British occupying forces after World War I, then as a museum.
Since 1945, the building has served as
Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non- ...
(parliamentary building) for the state of Hesse. The site of the palace had been that of a castle, probably from the early Middle Ages, around which the city had developed. While nothing is known of the former castle, remains of it were uncovered during excavations after World War II.
The new town hall was built in 1887. A tile mosaic in front of the town hall shows the
heraldic eagle
The eagle is used in heraldry as a charge, as a supporter, and as a crest. Heraldic eagles can be found throughout world history like in the Achaemenid Empire or in the present Republic of Indonesia. The European post-classical symbolism of the ...
of the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Re ...
(of which Wiesbaden was a part at the time), the
coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central ele ...
of the Prussian
Province of Hesse-Nassau
The Province of Hesse-Nassau () was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868 to 1918, then a province of the Free State of Prussia until 1944.
Hesse-Nassau was created as a consequence of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 by combining the p ...
, and the
fleur-de-lis
The fleur-de-lis, also spelled fleur-de-lys (plural ''fleurs-de-lis'' or ''fleurs-de-lys''), is a lily (in French, and mean 'flower' and 'lily' respectively) that is used as a decorative design or symbol.
The fleur-de-lis has been used in the ...
of Wiesbaden. The old town hall, built in 1610, is the oldest preserved building in the city center and now is used as a civil registry office.
The
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
''
Marktkirche'' ("market church") was built from 1852 to 1862 in a
neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
style. Its western steeple is in height, making the church the highest building in the city.
Kurhaus and Theater
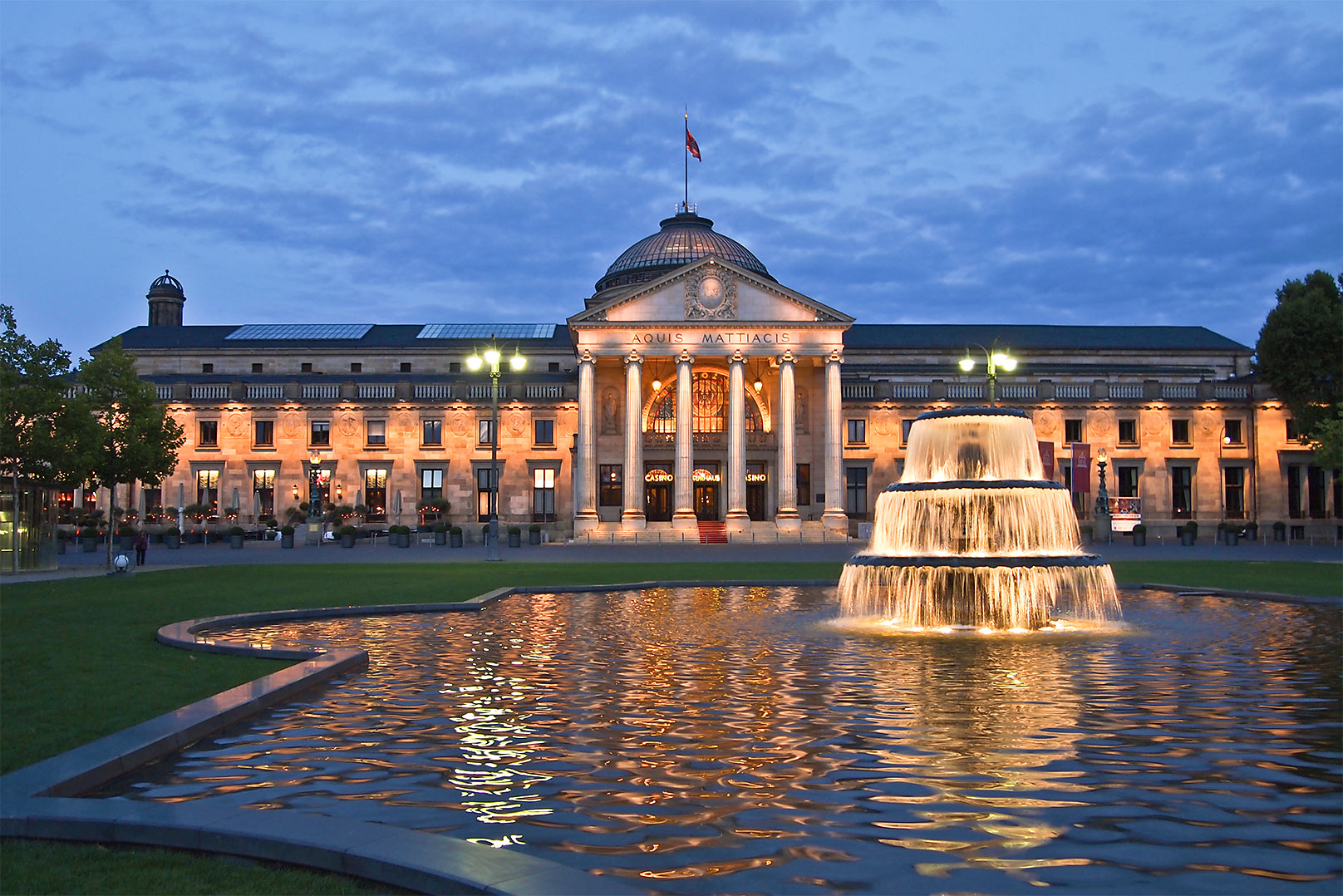

The monumental
Neo-Classical ''
Kurhaus
Kurhaus (German for "spa house" or "health resort") may refer to:
* Kurhaus of Baden-Baden in Germany
* Kurhaus, Wiesbaden in Germany
* Kurhaus, Meran in South Tyrol, Italy
* Kurhaus of Scheveningen in the Netherlands
* Kurhaus Bergün, a grand ho ...
'' ("spa house") was built at the request of Kaiser
Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until his abdication on 9 November 1918. Despite strengthening the German Empir ...
between 1904 and 1907. Its famous ''Spielbank'' (casino) is again in operation.
In front of the Kurhaus is a lawn known as the Bowling Green. To one side of the Bowling Green is the Kurhaus Kolonnade. Built in 1827, the 129 meter structure is the longest hall in Europe supported by pillars. To the other side is the Theater Kolonnade, built in 1839. It is adjacent to the
Hessisches Staatstheater Wiesbaden
The Hessisches Staatstheater Wiesbaden ('Hessian State Theatre Wiesbaden') is a German theatre located in Wiesbaden, in the German state Hesse. The company produces operas, plays, ballets, musicals and concerts on four stages. Known also as the ...
, built between 1892 and 1894.
St. Bonifatius
St. Bonifatius, the first church for the Catholic community after the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, was built from 1845 until 1849 by Philipp Hoffmann in
Gothic Revival style
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
and dedicated to
Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictines, Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant ...
.
St. Elizabeth's Church
The Russian Orthodox
Church of Saint Elizabeth, called ''Griechische Kapelle'' (Greek chapel) locally, was built on the
Neroberg from 1847 to 1855 by Duke Adolf of Nassau on the occasion of the early death of his wife
Elizabeth Mikhailovna, who died in childbirth. The architect was again Philipp Hoffmann.
Other sights
Another building from the regency of Duke Wilhelm is the Luisenplatz, a square named for the Duke's first wife. It is surrounded by
Neoclassicist
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was ...
buildings, and in the middle of the square is the
Waterloo Obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by Anc ...
, commemorating the 683 Nassauers who died on 18 June 1815 near
Hougoumont
Château d'Hougoumont (originally Goumont) is a walled manorial compound, situated at the bottom of an escarpment near the Nivelles road in the Braine-l'Alleud municipality, near Waterloo, Belgium. The site served as one of the advanced defens ...
Farm in the respective battle against
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
. Apart from the palace in the center, the ducal family had a large palace on the banks of the Rhine, known as
Schloss Biebrich
Biebrich Palace (german: link=no, Schloss Biebrich) is a Baroque residence (''Schloss'') in the borough of Biebrich in the city of Wiesbaden, Hesse, Germany. Built in 1702 by Prince Georg August Samuel of Nassau-Idstein, it served as the duca ...
. This
baroque building was erected in the first half of the 18th century.
North of the city is the
Neroberg. From the top of this hill it is possible to view a panorama of the city. The
Nerobergbahn funicular railway
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite en ...
connects the city with the hill. South of it, the
Nerotalanlagen are a park along a creek, created in 1897/98 as an
English landscape garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
.
One of the three Hessian state museums,
Museum Wiesbaden
The Museum Wiesbaden is a two-branch museum of art and natural history in the Hessian capital of Wiesbaden, Germany. It is one of the three Hessian State museums, in addition to the museums in Kassel and Darmstadt.
History
The foundation o ...
is located in Wiesbaden.
Other churches are the
Bergkirche, completed in 1879 in Gothic Revival style, and the
Lutherkirche, finished in 1910 in
Jugendstil
''Jugendstil'' ("Youth Style") was an artistic movement, particularly in the decorative arts, that was influential primarily in Germany and elsewhere in Europe to a lesser extent from about 1895 until about 1910. It was the German counterpart of ...
. The church
Mariä Heimsuchung is a tall concrete landmark in the Kohlheck suburb.
Oriental Christianity is also represented with the St. Isaiah
Syriac Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = syc
, image = St_George_Syriac_orthodox_church_in_Damascus.jpg
, imagewidth = 250
, alt = Cathedral of Saint George
, caption = Cathedral of Saint George, Damascus ...
on the Willi-Juppe-Straße in Dotzheim, built 2016 by Suryoye-
Assyrians.
The Warmer Damm park is a 4.5-hectare park on the east side of Wilhelmstrasse and south of the State theater and Kurhaus which features a lake, a fountain, various statues, and large grassy areas. The park was created in 1859–1860 and is named after the medieval fortifications around a pond into which the warm waters of the town's 26 warm springs flowed.
Gallery
Wiesbaden-biebrich-schloss.jpg, Biebrich Palace
Hessischer Landtag Stadtschloss Wiesbaden.jpg, City Palace
Wiesbaden Nerobergbahn 2010-05-01 17.08.21.jpg, Nerobergbahn funicular
Russ Orth Kirche Wiesbaden 865-h.jpg, ''Griechische Kapelle''
Nerotalanlagen, south.jpg, Nerotalanlagen
Wiesbad1.jpg, Marktkirche
Marktkirche seen from the Warmer Damm, Wiesbaden, Germany.JPG, Warmer Damm
Warmer Damm Pond and Fountain.JPG, Warmer Damm
St. Bonifatius Church, Wiesbaden, Germany.jpg, St. Bonifatius
Boroughs of Wiesbaden
The city of Wiesbaden is divided into 26 boroughs: five in the central city and 21 suburban districts. The 21 suburban districts were incorporated in four phases from 1926 to 1977. The former Mainz suburbs on the right bank of river Rhine viz. Amöneburg, Kastel and Kostheim have belonged to Wiesbaden since 1945.

Inner boroughs
Suburban boroughs
Historical population
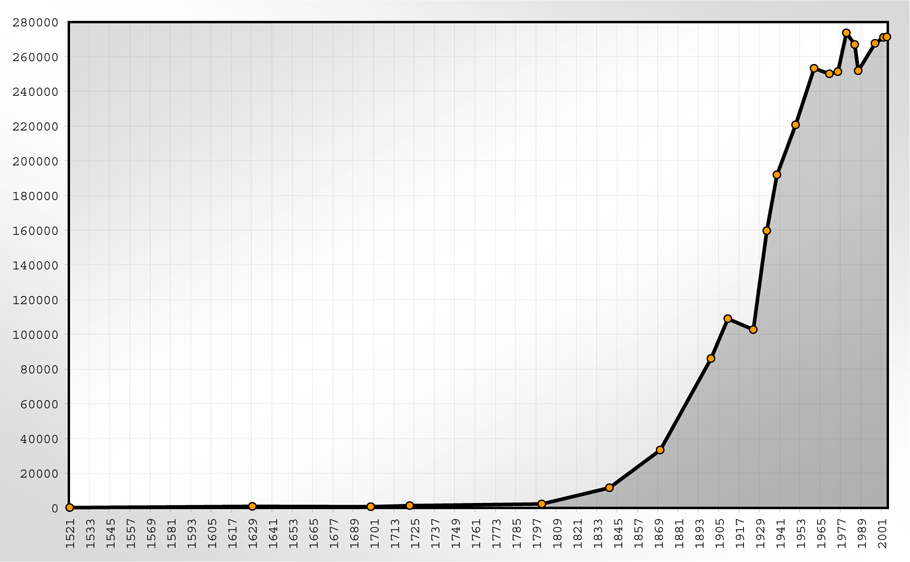
The population development of Wiesbaden is as follows:

List of largest groups of foreign residents of Wiesbaden:
Politics
Mayor

The current mayor of Wiesbaden is Gert-Uwe Mende of the
Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Fo ...
(SPD), who was elected in 2019.
The most recent mayoral election was held on 26 May 2019, with a runoff held on 16 June, and the results were as follows:
! rowspan=2 colspan=2, Candidate
! rowspan=2, Party
! colspan=2, First round
! colspan=2, Second round
, -
! Votes
! %
! Votes
! %
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Gert-Uwe Mende
, align=left,
Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Fo ...
, 29,940
, 27.1
, 41,000
, 62.0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Eberhard Seidensticker
, align=left,
Christian Democratic Union
, 26,997
, 24.5
, 25,104
, 38.0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christiane Hinninger
, align=left,
Alliance 90/The Greens
, 25,849
, 23.4
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Sebastian Rutten
, align=left,
Free Democratic Party
, 11,590
, 10.5
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Eckhard Müller
, align=left,
Alternative for Germany
, 6,859
, 6.2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Ingo von Seemen
, align=left,
The Left
, 5,336
, 4.8
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Bachmann
, align=left,
Free Voters
Free Voters (german: Freie Wähler, FW or FWG) in Germany may belong to an association of people which participates in an election without having the status of a registered political party. Usually it involves a locally organized group of voters ...
, 3,812
, 3.5
, -
! colspan=3, Valid votes
! 110,383
! 98.9
! 66,104
! 98.6
, -
! colspan=3, Invalid votes
! 1,202
! 1.1
! 937
! 1.4
, -
! colspan=3, Total
! 111,585
! 100.0
! 67,041
! 100.0
, -
! colspan=3, Electorate/voter turnout
! 208,686
! 53.5
! 208,821
! 32.1
, -
, colspan=7, Source: City of Wiesbaden
1st round
The following is a list of mayors since 1945:
*1849–1868: Heinrich Fischer
*1868–1882: Wilhelm Lanz
*1882–1883: Christian Schlichter
*1883–1913: Carl Bernhard von Ibell
*1913–1919: Karl Glässing
*1919–1929: Fritz Travers
*1930–1933: Georg Krücke
*1933–1937: Alfred Schulte
*1937–1945: Erich Mix
Erich Mix (27 June 1898 in Labuhnken (now Trzcińsk, Poland) in West Prussia (now Starogard Gdański) – 9 April 1971 in Wiesbaden) was a German flying ace during World War II, a politician, a member of the Nazi Party, and later a member of th ...
*1945–1946: Georg Krücke
*1946–1953: Hans Heinrich Redlhammer
*1951–1954: Georg Kluge
*1954–1960: Erich Mix
Erich Mix (27 June 1898 in Labuhnken (now Trzcińsk, Poland) in West Prussia (now Starogard Gdański) – 9 April 1971 in Wiesbaden) was a German flying ace during World War II, a politician, a member of the Nazi Party, and later a member of th ...
*1960–1968: Georg Buch
*1968–1980: Rudi Schmitt
*1980–1982: Georg-Berndt Oschatz
*1982–1985: Hans-Joachim Jentsch
*1985–1997: Achim Exner
*1997–2007: Hildebrand Diehl
*2007–2013: Helmut Müller
*2013–2019: Sven Gerich
Sven Gerich (born 30 October 1974 in Hannoversch Münden) is a German politician from Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD).
Life
Gerich worked in his father's company in Wiesbaden. He has been mayor of Wiesbaden since 1 July 2013 . On 24 ...
*2019– : Gert-Uwe Mende
City council
 The Wiesbaden city council (''Stadtverordnetenversammlung'') governs the city alongside the Mayor. The most recent city council election was held on 14 March 2021, and the results were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Lead candidate
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, align=left, Daniela Georgi
, 1,526,381
, 23.5
, 1.2
, 19
, 1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens (Grüne)
, align=left, Christiane Hinninger
, 1,390,605
, 21.4
, 7.3
, 17
, 6
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left,
The Wiesbaden city council (''Stadtverordnetenversammlung'') governs the city alongside the Mayor. The most recent city council election was held on 14 March 2021, and the results were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Lead candidate
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, align=left, Daniela Georgi
, 1,526,381
, 23.5
, 1.2
, 19
, 1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens (Grüne)
, align=left, Christiane Hinninger
, 1,390,605
, 21.4
, 7.3
, 17
, 6
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Fo ...
(SPD)
, align=left, Hendrik Schmehl
, 1,320,299
, 20.3
, 5.6
, 17
, 4
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, align=left, Christian Diers
, 675,021
, 10.4
, 0.6
, 8
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alternative for Germany (AfD)
, align=left, Eckhard Müller
, 423,519
, 6.5
, 6.3
, 5
, 6
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, The Left (Die Linke)
, align=left, Ingo von Seemen
, 402,735
, 6.2
, 0.0
, 5
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Volt Germany
Volt Germany (, mostly known by the abbreviated name Volt) is a social-liberal pro-European, eurofederalist political party in Germany. It is the German branch of Volt Europa, a political movement that operates on a European level.
Italian And ...
(Volt)
, align=left, Daniel Weber
, 246,454
, 3.8
, New
, 3
, New
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Free Voters
Free Voters (german: Freie Wähler, FW or FWG) in Germany may belong to an association of people which participates in an election without having the status of a registered political party. Usually it involves a locally organized group of voters ...
(FW)
, align=left, Christian Bachmann
, 163,942
, 2.5
, 1.1
, 2
, 1
, -
,
, align=left, Initiative Pro Auto Wiesbaden (Pro Auto)
, align=left, Christian Hill
, 105,047
, 1.6
, New
, 1
, New
, -
,
, align=left, Citizens' List Wiesbaden (BLW)
, align=left, Monika Becht
, 73,255
, 1.1
, 0.6
, 1
, ±0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Die PARTEI
(''Party for Labour, Rule of Law, Animal Protection, Promotion of Elites and Grassroots Democratic Initiative''), or Die PARTEI (''The PARTY''), is a German political party. It was founded in 2004 by the editors of the German satirical magazi ...
(PARTEI)
, align=left, Lukas Haker
, 51,343
, 0.8
, New
, 1
, New
, -
,
, align=left, Independent List Wiesbaden (ULW)
, align=left, Veit Wilhelmy
, 50,920
, 0.8
, 0.2
, 1
, ±0
, -
,
, align=left, Alliance for Innovation and Justice (BIG)
, align=left, Faissal Wardak
, 44,344
, 0.7
, 0.4
, 1
, 1
, -
,
, align=left, Liberal Conservative Reformers
The Liberal Conservative Reformers (german: Liberal-Konservative Reformer, LKR) is a centre-right to right-wing political party in Germany which was known from July 2015 to November 2016 as ALFA.
The party was established in July 2015 as a spli ...
(LKR)
, align=left, Thomas Preinl
, 25,988
, 0.4
, New
, 0
, New
, -
! colspan=3, Valid votes
! 83,885
! 95.9
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=3, Invalid votes
! 3,597
! 4.1
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=3, Total
! 87,482
! 100.0
!
! 81
! ±0
, -
! colspan=3, Electorate/voter turnout
! 209,347
! 41.8
! 1.6
!
!
, -
, colspan=8, Source
Statistics Hesse
Transport

Roads
Wiesbaden is well connected to the German motorway (''Autobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. ...
'') system. The Wiesbadener Kreuz
The Wiesbadener Kreuz is a full cloverleaf interchange near the Hessian state capital of Wiesbaden in Germany where the Autobahnen A3 and A66 meet. It lies within the northeastern edge of Hochheim am Main. The interchange was opened in 1939 an ...
is an Autobahn interchange east of the city where the Bundesautobahn 3
is an autobahn in Germany running from the Germany-Netherlands border near Wesel in the northwest to the Germany-Austria border near Passau.
Major cities along its total length of 778 km (483 mi) include Oberhausen, Duisburg, Düsse ...
(A 3), Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 m ...
to Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzburg is ...
, and the Bundesautobahn 66
is an autobahn in southwestern Germany. It connects the Taunus to Fulda, passing close to Frankfurt am Main. The first part of the autobahn between Wiesbaden and the Nordwestkreuz Frankfurt, was opened as early as 1934, then called the ''Rhein-M ...
(A 66), Rheingau to Fulda
Fulda () (historically in English called Fuld) is a town in Hesse, Germany; it is located on the river Fulda and is the administrative seat of the Fulda district (''Kreis''). In 1990, the town hosted the 30th Hessentag state festival.
History ...
, meet. With approximately 210,000 cars daily it is one of the most heavily used interchange in Germany. The Bundesautobahn 66
is an autobahn in southwestern Germany. It connects the Taunus to Fulda, passing close to Frankfurt am Main. The first part of the autobahn between Wiesbaden and the Nordwestkreuz Frankfurt, was opened as early as 1934, then called the ''Rhein-M ...
(A 66) connects Wiesbaden with Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
.
The Bundesautobahn 643
is a short autobahn in Germany. The motorway crosses the Rhine River, connecting the cities of Wiesbaden and Mainz, the capital cities of the German states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate, respectively. It is one of two autobahns in Germany th ...
(A 643) is mainly a commuter motorway which starts in the south of the city centre, runs through the southern part of Wiesbaden crosses the Rhine via the Schierstein Bridge
The Schierstein Bridge (German: ''Schiersteiner Brücke'') is long, four-lane highway bridge in Germany. It carries Bundesautobahn 643 over the Rhine River between Mainz-Mombach, Rhineland-Palatinate and Wiesbaden-Schierstein, Hesse (Rhine kilome ...
and connect in the northwestern part of Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
to the A60. The Bundesautobahn 671
is an autobahn in the federal state of Hesse, Germany. It begins as a continuation of Mainzer Straße (Bundesstraße 263) in Wiesbaden from its junction with A 66 and connects the center of the Hessian capital city with A 60.
...
(A 671) is a very short motorway in the southeastern part of Wiesbaden which primarily serves as a fast connection between the city centre and the Bundesautobahn 60
is an autobahn in Germany. During its entire course it forms a part of the E 42.
Overview
The A 60 begins at the former border crossing Steinebrück four lanes as a continuation of the Belgian A 27 from Liège. The state border runs on the 411 ...
to serve the cities like Rüsselsheim, Darmstadt and the Rhine-Neckar region (Mannheim, Ludwigshafen and Heidelberg).
The downtown area is bordered on the north side by , which has once featured many antique stores. The east side is constrained by Wilhelmstrasse, created by Christian Zais. This 1,000 meter-long street is named after Duke William of Nassau (German Wilhelm), not Emperor Wilhelm II, as many mistakenly believe.
The streets of central Wiesbaden are regularly congested with cars during rush hour. Besides some areas, especially the Ringroad and not directly in the centre, and the southern arterial roads like the Mainzer Straße Mainzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Amy Mainzer (born 1974), American astronomer
*Ferdinand Mainzer (1871–1943), German-Jewish gynaecologist and historical author
*Klaus Mainzer (born 1947), German scholar and philosop ...
, and Schiersteiner Straße.
Rail
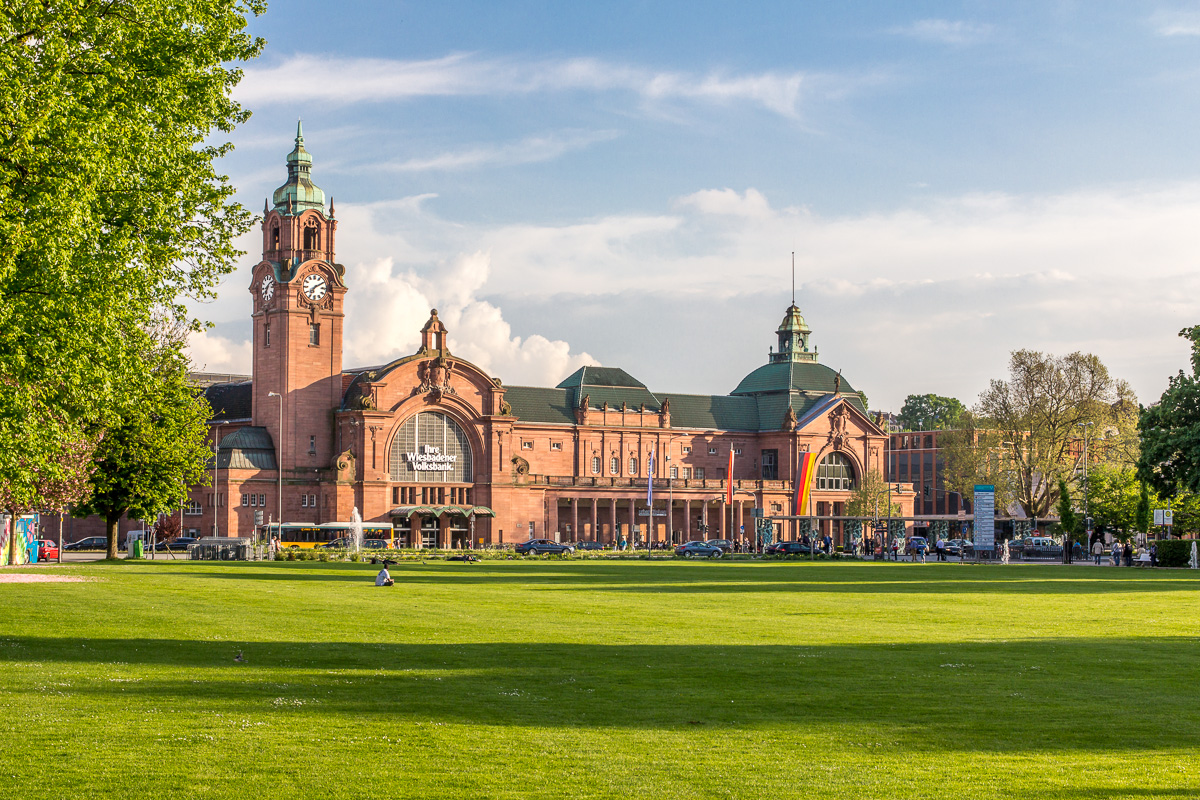 Wiesbaden's main railway station and several minor railway stops connect the town with
Wiesbaden's main railway station and several minor railway stops connect the town with Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
, Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it th ...
, Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
, Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
, and Koblenz
Koblenz (; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz''), spelled Coblenz before 1926, is a German city on the banks of the Rhine and the Moselle, a multi-nation tributary.
Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman mili ...
via Rüdesheim. Wiesbaden Hauptbahnhof is connected to the Cologne-Frankfurt high-speed rail line by a 13-kilometer branch line
A branch line is a phrase used in railway terminology to denote a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line.
Industrial spur
An industr ...
. Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
, München, Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as wel ...
, Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
, Stuttgart Central Station, Stuttgart, Mannheim Central Station, Mannheim, and Hanover Central Station, Hanover are connected directly to Wiesbaden via long-distance service of the Deutsche Bahn. More services to locations outside the immediate area connect through Mainz or Frankfurt Airport long-distance station, Frankfurt Airport or Frankfurt Hauptbahnhof. Regional trains and bus services are coordinated by the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund.
Public transport
 *S-Bahn
Wiesbaden is connected to the Frankfurt S-Bahn Rhein-Main, S-Bahn network and served by three lines (S1, S8 and S9) which connect Wiesbaden with the densely populated Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region, Rhine Main Region. All routes have an at least 30 minute service during the day, in the rush hour partially every 15 minutes schedule. It provides access to nearby cities such as
*S-Bahn
Wiesbaden is connected to the Frankfurt S-Bahn Rhein-Main, S-Bahn network and served by three lines (S1, S8 and S9) which connect Wiesbaden with the densely populated Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region, Rhine Main Region. All routes have an at least 30 minute service during the day, in the rush hour partially every 15 minutes schedule. It provides access to nearby cities such as Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
, Rüsselsheim, Frankfurt, Hanau, and Offenbach am Main, and smaller towns that are on the way.
*Bus
The city's public transportation service ESWE Verkehr connects all city districts to downtown by 45 bus lines in the daytime and 9 bus lines in the night. Five more bus lines, operated by the public transportation service of the city of Mainz, connects Wiesbaden's districts Mainz-Kastel, Kastel and Mainz-Kostheim, Kostheim to Mainz downtown.
Airports
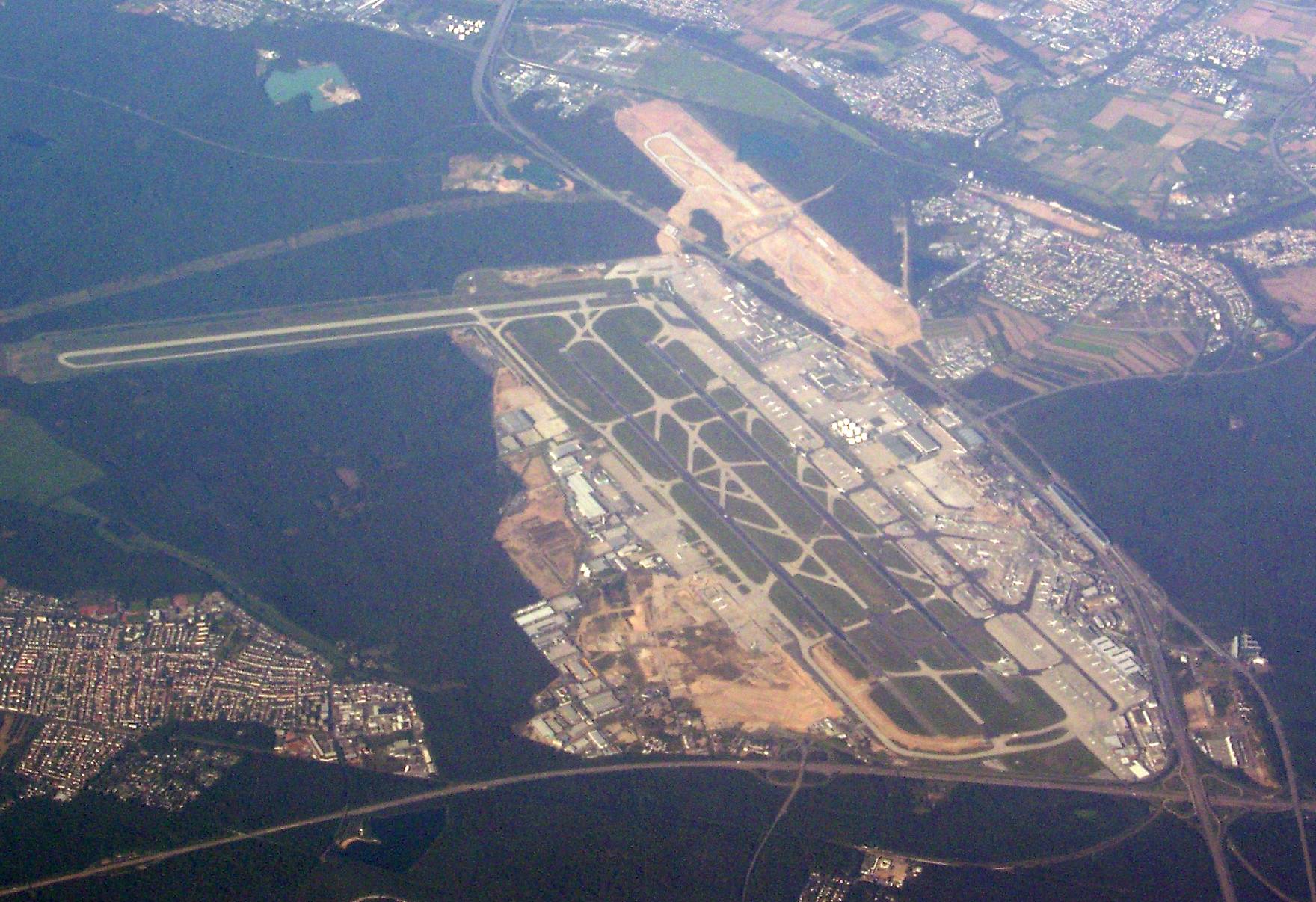 *Frankfurt Airport
The city can be accessed from around the world via Frankfurt Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt am Main'') which is located east of Wiesbaden. The airport has four runways and serves 265 non-stop destinations. Run by transport company Fraport it ranks among the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic and is the World's busiest airports by cargo traffic, second busiest airport by cargo traffic in Europe. The airport also serves as a hub for Condor Flugdienst, Condor and as the main hub for German flag carrier Lufthansa. Depending on whether total passengers or flights are used, it ranks second or third busiest in Europe alongside London Heathrow Airport and Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport. Passenger traffic at Frankfurt Airport in 2011 was 56.5 million.
The airport can be reached by car or train and has two railway stations, one for regional and one for long-distance traffic. The S-Bahn lines S8 and S9 (direction ''Offenbach Ost'' or ''Hanau Hbf'') departing at the Frankfurt Airport Regional Train Station, regional train station take 30 minutes from the airport to Wiesbaden Central Station, the Intercity-Express, ICE trains departing at the Frankfurt Airport long-distance station, long-distance railway station take also 30 minutes to the central station.
*Frankfurt Hahn Airport
Despite the name, Frankfurt Hahn Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt-Hahn'') is not located anywhere near Frankfurt but is instead situated approximately from the city in Lautzenhausen (
*Frankfurt Airport
The city can be accessed from around the world via Frankfurt Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt am Main'') which is located east of Wiesbaden. The airport has four runways and serves 265 non-stop destinations. Run by transport company Fraport it ranks among the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic and is the World's busiest airports by cargo traffic, second busiest airport by cargo traffic in Europe. The airport also serves as a hub for Condor Flugdienst, Condor and as the main hub for German flag carrier Lufthansa. Depending on whether total passengers or flights are used, it ranks second or third busiest in Europe alongside London Heathrow Airport and Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport. Passenger traffic at Frankfurt Airport in 2011 was 56.5 million.
The airport can be reached by car or train and has two railway stations, one for regional and one for long-distance traffic. The S-Bahn lines S8 and S9 (direction ''Offenbach Ost'' or ''Hanau Hbf'') departing at the Frankfurt Airport Regional Train Station, regional train station take 30 minutes from the airport to Wiesbaden Central Station, the Intercity-Express, ICE trains departing at the Frankfurt Airport long-distance station, long-distance railway station take also 30 minutes to the central station.
*Frankfurt Hahn Airport
Despite the name, Frankfurt Hahn Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt-Hahn'') is not located anywhere near Frankfurt but is instead situated approximately from the city in Lautzenhausen (Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
). Hahn Airport was a major base for low-cost carrier Ryanair. This airport can be reached by car or bus. The nearest train station is in Traben-Trarbach, it is ca. from the airport, on foot. The roads are not lit.
Port
There are small container port operations nearby on the rivers Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
and Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
.
Military
Lucius D. Clay Kaserne (formerly Wiesbaden Army Airfield or WAAF) is located adjacent to Wiesbaden-Erbenheim and is home to the US Army Europe, US Army in Europe (USAREUR) headquarters, the 2nd Signal Brigade and the 66th Military Intelligence Brigade. The airfield was one of the points of origin for flights to Berlin in support of Operation Vittles (the Berlin airlift) during the Berlin Blockade, Soviet blockade of Berlin. General Clay, the commander of the US occupation zone in Germany, was the architect of the airlift.
The United States Army runs a garrison in Wiesbaden. The facilities for US soldiers and families are spread across various locations including: Aukamn, Hainerberg, Mainz-Kastel and the Wiesbaden Army-Airfield, where the names of the streets are named after servicemen and women who sacrificed their lives during the Berlin Airlift.
Economy
Wiesbaden hosts a number of international companies, which have their German or European headquarters there including Abbott Laboratories, DXC Technology, Ferrari, Federal-Mogul, Melbourne IT, Porsche, Norwegian Cruise Line, and Svenska Cellulosa Aktiebolaget, SCA. Several German companies also have their headquarters in Wiesbaden, including SGL Carbon, Dyckerhoff, KION Group, DBV-Winterthur, and R + V Versicherung. Wiesbaden is also home to the "Industriepark Kalle-Albert", an industrial park in the southern quarter of Biebrich. It is one of the largest in Germany with over 80 companies from the pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and chemical industry, chemical industries, including Agfa-Gevaert, Clariant, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, and Shin-Etsu Chemical. The park was founded by chemical company Hoechst AG in 1997.
The Federal Criminal Police Office (Germany), Federal Criminal Police Office and the Federal Statistical Office of Germany are both based in Wiesbaden, along with many Hessian ministries such as the Hessian Landeskriminalamt, State Criminal Police Office.
At approximately €77,500, Wiesbaden has the second largest gross domestic product per inhabitant in Hesse, after Frankfurt, making it one of the richest cities in Germany. The purchasing power per inhabitant is €22,500.
Culture
Wiesbaden's most important stage is the Hessisches Staatstheater Wiesbaden
The Hessisches Staatstheater Wiesbaden ('Hessian State Theatre Wiesbaden') is a German theatre located in Wiesbaden, in the German state Hesse. The company produces operas, plays, ballets, musicals and concerts on four stages. Known also as the ...
. Concert halls include the Friedrich-von-Thiersch-Saal of the Kurhaus. Wiesbaden has a State Library and a conservatory, where Max Reger studied and taught as a young man. Choirs such as the Wiesbadener Knabenchor, Schiersteiner Kantorei and Chor von St. Bonifatius are known in the region and even internationally.
International May Festival
The International May Festival is an annual arts festival presented by the Hessisches Staatstheater Wiesbaden
The Hessisches Staatstheater Wiesbaden ('Hessian State Theatre Wiesbaden') is a German theatre located in Wiesbaden, in the German state Hesse. The company produces operas, plays, ballets, musicals and concerts on four stages. Known also as the ...
every May. Established in 1896, it is one of the most distinguished international theatre and music festivals in the world. The festival features performances of plays, musicals, operas, and ballets. Concerts from a wide array of music are featured, as are artistic circus acts and modern dance presentations. Lectures, recitals, cabaret performances, and readings are also featured.
Rheingau Wine Festival
The wines and sparkling wines of the close Rheingau are presented annually at the ten-day festival in August, ''Rheingauer Weinwoche'' (Rheingau Wine Week) around the Wiesbaden City Hall, on the Schlossplatz (Palace Square), the square ''Dern’sches Gelände'' and in the pedestrian area. At 118 booths, Rheingau and Wiesbaden vintners offer their wine and sparkling wine and invite to discover the already well known and favored, but also new vintages. Every year thousands of visitors use this opportunity to get acquainted with Rheingau Riesling wines and all their various facets and flavors. Regional specialities compatible with the wines are offered as well. A diversified musical program entertains the wine festival guests. Initiated more than 30 years ago by the Rheingau vintners, this wine festival has a long tradition.
Shooting Star Market
Wiesbaden's Sternschnuppenmarkt is located at the central #Main sights, Schlossplatz and the neighbouring streets of the #Main sights, parliamentary building, #Main sights, old town hall, and #Main sights, market church. The Sternschnuppenmarkt takes place from the end of November until December 23 every year and is open from Monday until Thursday 10:30 – 9:00 pm, Friday and Saturday 10:30 – 9:30 pm, and Sunday 12:00 – 9:00 pm.
The market is related to the city arms of Wiesbaden: the colours blue and gold and the three lilies are characteristic. Four gates and an illuminated floral roof symbolizing Fleur-de-lis, consisting of twelve over ten metre high and twelve metre wide luminous lilies, emboss the Sternschnuppenmarkt.
Over 110 booths are decorated in oriental style, coloured blue and gold, offering Christmas style goods, arts and crafts as well as nostalgic carousels and a toy train. A Christmas tree more than tall is decorated with 1000 blue and golden ties, 2500 electric bulbs and 30 flash bulbs. The nativity scene displays life-sized wooden figures.
Rheingau Musik Festival
 From the beginning in 1988 the Rheingau Musik Festival has staged summer concerts in the Marktkirche and in the concert hall of the
From the beginning in 1988 the Rheingau Musik Festival has staged summer concerts in the Marktkirche and in the concert hall of the Kurhaus
Kurhaus (German for "spa house" or "health resort") may refer to:
* Kurhaus of Baden-Baden in Germany
* Kurhaus, Wiesbaden in Germany
* Kurhaus, Meran in South Tyrol, Italy
* Kurhaus of Scheveningen in the Netherlands
* Kurhaus Bergün, a grand ho ...
now named Friedrich-von-Thiersch-Saal.
Sport
Since 2007 Wiesbaden has been home to SV Wehen Wiesbaden, an association football team that formerly played in nearby Taunusstein. The club was promoted to the 2. Bundesliga in 2019, but relegated back to the 3. Liga in 2020.
Twin towns – sister cities
Town twinning between Wiesbaden and other cities began with Klagenfurt in 1930, one of the first town-twinnings in Germany. Wiesbaden is Sister city, twinned with:
* Klagenfurt, Austria (1930)
* Montreux, Switzerland (1953)
* Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg, Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg (Berlin), Germany (1964)
* Ghent, Belgium (1969)
* Fondettes, France (1975)
* Ljubljana, Slovenia (1977)
* Kfar Saba, Israel (1981)
* San Sebastián, Spain (1981)
* Wrocław, Poland (1987)
* Royal Tunbridge Wells, Tunbridge Wells, England, United Kingdom (1989)
* Görlitz, Germany (1990)
* Ocotal, Nicaragua (1990)
* Fatih, Turkey (2012)
Coat of arms
Wiesbaden's coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central ele ...
features three fleur-de-lis, fleurs-de-lys, stylized representations of the city's heraldic symbol, the lily. The blazon is: "Azure, two and one fleurs-de-lys Or".
Notable people
*Adolphe, Grand Duke of Luxembourg (born 1817, Biebrich Palace), reign 23 November 1890 – 17 November 1905
*Norbert Becker (agroscientist), Norbert J. Becker (1937–2012), agricultural scientist and specialist in the area of vine breeding and viticulture
*Adolphus Busch (1839–1913), founder of Anheuser-Busch
*Sarah Colonna (born 1974), American stand-up comedian
*Shlomo Eckstein (1929–2020), Israeli economist and President of Bar-Ilan University
*Gisela Ehrensperger (born 1943), Swiss operatic soprano
*Petra Fuhrmann (1955–2019), member of the Hessian Landtag
*Biruté Galdikas (born 1946), Lithuanian-Canadian primatologist
*Jürgen Grabowski (1944-2022), footballer
*Peter Hanenberger (born 1942), automotive specialist for General Motors, previously chairman of Holden
*Franz Kaiser (1891–1962), astronomer, discoverer of asteroid 717 Wisibada and asteroid 765 Mattiaca, both named in honour of the city of Wiesbaden
*Wilhelm Kempf (bishop), Wilhelm Kempf (1906–1982), Catholic theologian, Bishop of Limburg 1949–1981
*Michael Kessler (born 1967), actor and comedian
*Alfred Koerppen (1926–2022), organist, music pedagogue, composer and academic teacher
*Otto Krebs (1873–1941), industrialist and art collector
*Günther Lütjens (1889–1941), admiral and commander of the World War II naval Operation Rheinübung, aboard the battleship
*Bruce Maxwell (born 1990), American baseball player (born on a U.S. military base)
*John McEnroe (born 1959), American tennis player (born on a U.S. military base)
*Melody Perkins (born 1974), American actress
*Emil Pfeiffer (1846–1921), physician
*Bud Pierce (born 1956), American politician
*Dieter Rams (born 1932), industrial designer, former head of design for Braun (company), Braun
*Rudolf von Ribbentrop (1921–2019), captain in the Waffen-SS, recipient of the Knights Cross of the Iron Cross for bravery
*Nico Rosberg (born 1985), Finnish-German racing driver, 2016 Formula One season, 2016 Formula One World Champion
*Volker Schlöndorff (born 1939), film director
*Kristina Schröder (born 1977), politician (CDU)
*Henry Schwarzschild (1925–1996), American activist for civil rights and human rights
*Kiki VanDeWeghe (born 1958), American basketball player, coach and executive
*Valerie Weigmann (born 1989), Filipino-German actress, host and Miss World Philippines 2014 titleholder
*Silvia Weiss, soprano
*William IV, Grand Duke of Luxembourg (born 1852, Biebrich Palace), reign 17 November 1905 - 25 February 1912
*Maria Yakunchikova (1870–1902), Russian painter and graphic artist
*Schoolboy Q (born 1986), American rapper (born on a U.S. military base)
Notable residents
*Peter Carl Fabergé, fled Russia to Germany, settled first in Bad Homburg and then in Wiesbaden
*Alexej von Jawlensky, Russian Expressionist painter, lived there in 1922–1941 and died there
*Hava Lazarus-Yafeh (1930–1998), Orientalism, Orientalist, scholar, editor, and educator; born in Wiesbaden.Elvis Presley
Elvis Aaron Presley (January 8, 1935 – August 16, 1977), or simply Elvis, was an American singer and actor. Dubbed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, King of Rock and Roll", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Elvis Presley, one ...
.
*Max Reger, studied in Wiesbaden
*Mickey Rourke, resides in Wiesbaden at least part-time with his Russian-born girlfriend Anastassija Makarenko
*Debby Ryan, American actress, lived in Wiesbaden for three years
*Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
, settled in Wiesbaden-Biebrich, Biebrich (now part of Wiesbaden) in 1861, after the political ban against him in Germany was lifted. It was there that he began work on Die Meistersinger von Nürnberg.
*Reese Witherspoon, lived in Wiesbaden with her parents
*Mayte Garcia, American belly dancer, actress, author, singer and choreographer, lived here in Wiesbaden with her parents. It was here that she met her future husband, the singer Prince, backstage at one of his concert
*Eno (rapper), Eno, rapper, lives in Wiesbaden
Notable visitors
*In the 19th century, visitors to the Wiesbaden's famous hot springs included Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as trea ...
and Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
. Brahms' Symphony No. 3 (Brahms), Symphony No. 3 (Op. 90) was composed in Wiesbaden in the summer of 1883.
*Washington Roebling, chief engineer of the Brooklyn Bridge, came to Wiesbaden—along with his wife, Emily Warren Roebling—in 1873, hoping that the warm springs would ameliorate the effects of the decompression sickness he suffered as a result of working in caissons of the bridge.
*Béla Kéler, Hungarian composer, died in Wiesbaden.
*Russian author Fyodor Dostoevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
, who suffered from an acute gambling compulsion, allegedly lost his travelling money in Wiesbaden's ''Spielbank'' casino in 1865. The experience became the inspiration of his 1866 novel The Gambler (novel), The Gambler (Russian Игрок), set in the fictitious place "Roulettenburg". Some historians have disputed this account, saying that Bad Homburg
Bad Homburg vor der Höhe () is the district town of the Hochtaunuskreis, Hesse, on the southern slope of the Taunus mountains. Bad Homburg is part of the Frankfurt Rhein-Main Regional Authority, Frankfurt Rhein-Main urban area. The town's offic ...
was the location for Dostoevsky's real-life misfortune.
*Wiesbaden's Bowling Green has been very popular in recent years since various open-air concerts have been held there by artists like Elton John (2009, 2011 & 2019), Rod Stewart (2009), Eric Clapton (2008), R.E.M. (2003), Sting (musician), Sting (2001), Bryan Adams (2000), Simply Red (1999), José Carreras (1992), and Luciano Pavarotti (1993). Lionel Richie and Plácido Domingo (2nd time in Wiesbaden) have also performed there.
Rivalry with Mainz
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
, on the opposite side of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, is Wiesbaden's archrival – the two cities are the capitals of their respective Bundesländer, and citizens of both cities joke, jokingly refer to those on the other one as "living on the wrong side of the river".
Fictional references
*In his short story "The Horror of the Heights" (1913), Sir Arthur Conan Doyle refers to an aerial region over Wiesbaden and Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Homburg in which aircraft mysteriously vanish.
*In the 1983 American television movie ''The Day After'', Wiesbaden was the first city to be destroyed by a nuclear weapon during the escalating war between NATO and Warsaw Pact forces that eventually leads to a full-scale nuclear exchange between the United States and the Soviet Union.
*The historical novel series ''Romanike'' (2006–2014) by Codex Regius features Wiesbaden in the Roman age, or Aquae Mattiacorum, as one of its main locations.
References
Notes
External links
Official websiteThe Jewish Community of Wiesbaden
on the Yad Vashem website
Wiesbaden City Panoramas
– Panoramic Views and virtual Tours
Photos of WiesbadenMore Photos of WiesbadenWiesbaden Daily PhotosWebcam to Wiesbaden (Remote-Control Pan-Tilt)Webcam to Railway-Station WiesbadenWiesbaden U.S. Army Garrison
*
{{Authority control
Wiesbaden,
120s establishments in the Roman Empire
German state capitals
Holocaust locations in Germany
Populated places established in the 2nd century
Populated places on the Rhine
Roman towns and cities in Germany
Spa towns in Germany
 Wiesbaden is situated on the right (northern) bank of the
Wiesbaden is situated on the right (northern) bank of the 
 Due to its participation in the uprisings of the German Peasants' War of 1525, Wiesbaden lost all its privileges for over 40 years. During this time, Wiesbaden became
Due to its participation in the uprisings of the German Peasants' War of 1525, Wiesbaden lost all its privileges for over 40 years. During this time, Wiesbaden became  At the 1815
At the 1815  In the
In the  The '' Schloßplatz'' ("palace square") is situated in the center of the city, surrounded by several outstanding buildings. The ducal palace was begun under
The '' Schloßplatz'' ("palace square") is situated in the center of the city, surrounded by several outstanding buildings. The ducal palace was begun under  The monumental Neo-Classical ''
The monumental Neo-Classical '' The population development of Wiesbaden is as follows:
The population development of Wiesbaden is as follows:
 Wiesbaden's main railway station and several minor railway stops connect the town with
Wiesbaden's main railway station and several minor railway stops connect the town with  *S-Bahn
Wiesbaden is connected to the Frankfurt S-Bahn Rhein-Main, S-Bahn network and served by three lines (S1, S8 and S9) which connect Wiesbaden with the densely populated Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region, Rhine Main Region. All routes have an at least 30 minute service during the day, in the rush hour partially every 15 minutes schedule. It provides access to nearby cities such as
*S-Bahn
Wiesbaden is connected to the Frankfurt S-Bahn Rhein-Main, S-Bahn network and served by three lines (S1, S8 and S9) which connect Wiesbaden with the densely populated Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region, Rhine Main Region. All routes have an at least 30 minute service during the day, in the rush hour partially every 15 minutes schedule. It provides access to nearby cities such as  *Frankfurt Airport
The city can be accessed from around the world via Frankfurt Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt am Main'') which is located east of Wiesbaden. The airport has four runways and serves 265 non-stop destinations. Run by transport company Fraport it ranks among the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic and is the World's busiest airports by cargo traffic, second busiest airport by cargo traffic in Europe. The airport also serves as a hub for Condor Flugdienst, Condor and as the main hub for German flag carrier Lufthansa. Depending on whether total passengers or flights are used, it ranks second or third busiest in Europe alongside London Heathrow Airport and Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport. Passenger traffic at Frankfurt Airport in 2011 was 56.5 million.
The airport can be reached by car or train and has two railway stations, one for regional and one for long-distance traffic. The S-Bahn lines S8 and S9 (direction ''Offenbach Ost'' or ''Hanau Hbf'') departing at the Frankfurt Airport Regional Train Station, regional train station take 30 minutes from the airport to Wiesbaden Central Station, the Intercity-Express, ICE trains departing at the Frankfurt Airport long-distance station, long-distance railway station take also 30 minutes to the central station.
*Frankfurt Hahn Airport
Despite the name, Frankfurt Hahn Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt-Hahn'') is not located anywhere near Frankfurt but is instead situated approximately from the city in Lautzenhausen (
*Frankfurt Airport
The city can be accessed from around the world via Frankfurt Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt am Main'') which is located east of Wiesbaden. The airport has four runways and serves 265 non-stop destinations. Run by transport company Fraport it ranks among the world's busiest airports by passenger traffic, world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic and is the World's busiest airports by cargo traffic, second busiest airport by cargo traffic in Europe. The airport also serves as a hub for Condor Flugdienst, Condor and as the main hub for German flag carrier Lufthansa. Depending on whether total passengers or flights are used, it ranks second or third busiest in Europe alongside London Heathrow Airport and Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport. Passenger traffic at Frankfurt Airport in 2011 was 56.5 million.
The airport can be reached by car or train and has two railway stations, one for regional and one for long-distance traffic. The S-Bahn lines S8 and S9 (direction ''Offenbach Ost'' or ''Hanau Hbf'') departing at the Frankfurt Airport Regional Train Station, regional train station take 30 minutes from the airport to Wiesbaden Central Station, the Intercity-Express, ICE trains departing at the Frankfurt Airport long-distance station, long-distance railway station take also 30 minutes to the central station.
*Frankfurt Hahn Airport
Despite the name, Frankfurt Hahn Airport (''Flughafen Frankfurt-Hahn'') is not located anywhere near Frankfurt but is instead situated approximately from the city in Lautzenhausen ( From the beginning in 1988 the Rheingau Musik Festival has staged summer concerts in the Marktkirche and in the concert hall of the
From the beginning in 1988 the Rheingau Musik Festival has staged summer concerts in the Marktkirche and in the concert hall of the