West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The
United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
,
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
,
Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
,
The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
,
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
,
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
,
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
,
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
,
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
,
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
,
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...](_blank)
,
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
,
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
, and
Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
, as well as
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territory located in the South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and the archipelago of Tristan da Cunha including Gough Island. Its name wa ...
(
United Kingdom Overseas Territory).
[Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. ] The population of West Africa is estimated at about million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 are female and 192,309,000 male.
The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent.
Early history in West Africa included a number of prominent regional powers that dominated different parts of both the coastal and internal trade networks, such as the
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
and
Gao Empire
The Gao Empire preceded the Songhai Empire in the region of the Middle Niger. It owes its name to the town of Gao located at the eastern Niger bend. In the ninth century CE, it was considered to be the most powerful West African kingdom.
Gao was ...
s. West Africa sat at the intersection of trade routes between
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
-dominated
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and specialized goods from further south on the continent, including
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, advanced
iron-working
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
, and
ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is ...
. After European exploration encountered rich local economies and kingdoms, the
European slave trade exploited already existing slave systems to provide labor for colonies in the Americas. After the
end of the slave trade in the early 19th century, European nations, especially
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, continued to
exploit the region through colonial relationships. For example, they continued exporting a number of
extractive goods, including labor-intensive agricultural crops like
cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
and
coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulant, stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
S ...
, forestry products like
tropical timber
Tropical timber may refer to any type of timber or wood that grows in tropical rainforests and tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests and is Harvester (forery), harvested there. Typical examples of worldwide industrial significance inclu ...
, and mineral resources like gold. Since independence, many West African countries, like
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
, have played important roles in the regional and global economies.
West Africa has a rich
ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
, with strong
biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
and several distinct regions. The area's climate and ecology are heavily influenced by the dry
Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
to the North and East, which provides dry winds during the
Harmattan
The Harmattan is a season in West Africa that occurs between the end of November and the middle of March. It is characterized by the dry and dusty northeasterly trade wind, of the same name, which blows from the Sahara over West Africa into the ...
, as well as the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the South and West, which provides seasonal monsoons. This mixture of climates gives West Africa a rich array of
biomes, from biodiversity-rich
tropical forests
Tropical forests (a.k.a. jungle) are forested landscapes in tropical regions: ''i.e.'' land areas approximately bounded by the tropic of Cancer and Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing winds.
Some tropical fores ...
to
drylands
Drylands are defined by a scarcity of water. Drylands are zones where precipitation is balanced by evaporation from surfaces and by transpiration by plants (evapotranspiration). The United Nations Environment Program defines drylands as tropical ...
supporting rare and endangered fauna such as
pangolins
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: ''Manis'', ''Phataginus'', and ''Smutsia'' ...
,
rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...
, and
elephants
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and ...
. Because of the pressure for economic development, many of these ecologies are threatened by processes like
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
,
biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
,
overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
,
pollution from mining,
plastics and other industries, and extreme changes resulting from
climate change in West Africa.
West Africa went from roughly 5% of
gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
in 2016 to over 10% of gross domestic product in 2019.
History
The history of West Africa can be divided into five major periods: first, its prehistory, in which the first
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
settlers arrived, developed
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, and made contact with peoples to the north; the second, the Iron Age empires that consolidated both intra-Africa, and extra-Africa trade, and developed centralized states; third, major polities flourished, which would undergo an extensive history of contact with non-Africans; fourth, the colonial period, in which
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
controlled nearly the entire region; and fifth, the post-independence era, in which the current nations were formed.
Prehistory
Acheulean tool-using
archaic humans
A number of varieties of ''Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
may have dwelled throughout West Africa since at least between 780,000 BP and 126,000 BP (
Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The ...
).
During the
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
,
Middle Stone Age
The Middle Stone Age (or MSA) was a period of African prehistory between the Early Stone Age and the Late Stone Age. It is generally considered to have begun around 280,000 years ago and ended around 50–25,000 years ago. The beginnings of pa ...
peoples (e.g.,
Iwo Eleru people,
possibly
Aterians), who dwelled throughout West Africa between
MIS 4
Marine isotope stages (MIS), marine oxygen-isotope stages, or oxygen isotope stages (OIS), are alternating warm and cool periods in the Earth's paleoclimate, deduced from oxygen isotope data reflecting changes in temperature derived from data f ...
and
MIS 2
Marine isotope stages (MIS), marine oxygen-isotope stages, or oxygen isotope stages (OIS), are alternating warm and cool periods in the Earth's paleoclimate, deduced from oxygen isotope data reflecting changes in temperature derived from data f ...
,
were gradually replaced by incoming
Late Stone Age peoples, who migrated into West Africa
as an increase in humid conditions resulted in the subsequent expansion of the
West African forest.
West African hunter-gatherers
West African hunter-gatherers, West African foragers, or West African pygmies dwelled in western Central Africa earlier than 32,000 BP and dwelled in West Africa between 16,000 BP and 12,000 BP until as late as 1000 BP or some period of time after ...
occupied western
Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
(e.g.,
Shum Laka
The archaeological site of Shum Laka is the most prominent rockshelter site in the Grasslands region of the Laka Valley, northwest Cameroon. Occupations at this rockshelter date to the Later Stone Age. This region is important to investigations of ...
) earlier than 32,000 BP,
dwelled throughout
coastal West Africa by 12,000 BP,
and migrated northward between 12,000 BP and 8000 BP as far as Mali, Burkina Faso,
and Mauritania.
During the
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
,
Niger-Congo speakers independently created pottery in
Ounjougou
Ounjougou is the name of a lieu-dit found in the middle of an important complex of archaeological sites in the Upper Yamé Valley on the Bandiagara Plateau, in Dogon Country, Mali. The Ounjougou archaeological complex consists of over a hundred s ...
, Mali
– the earliest
pottery in Africa – by at least 9400 BCE,
and along with their pottery,
as well as wielding
bows and arrows
The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles ( arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was com ...
,
migrated into the Central Sahara,
which became their primary region of residence by 10,000 BP.
The emergence and expansion of ceramics in the Sahara may be linked with the origin of Round Head and Kel Essuf rock art, which occupy rockshelters in the same regions (e.g.,
Djado
Djado is a ghost town in Bilma Department, Bilma in Niger. The settlement lies on the Djado Plateau, plateau with the same name. The settlement likely wasn't called Djado during its existence. The site is quite remote. No excavation has been done ...
,
Acacus,
Tadrart).
Hunters in the Central Sahara farmed, stored, and cooked untamed central Saharan
flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
as well as tamed and shepherded
Barbary sheep
The Barbary sheep (''Ammotragus lervia''), also known as aoudad (pronounced �ɑʊdæd is a species of caprine native to rocky mountains in North Africa. While this is the only species in genus ''Ammotragus'', six subspecies have been descri ...
.
After the
Kel Essuf Period
Kel Essuf rock art is the earliest form of engraved anthropomorphic Central Saharan rock art, which was produced prior to 9800 BP, at least as early as 12,000 BP amid the Late Pleistocene, late period of the Pleistocene. The Kel Essuf Period is pr ...
and
Round Head Period
Round Head rock art is the earliest painted, monumental form of Central Saharan rock art, which was largely created from 9500 BP to 7500 BP and ceased being created by 3000 BP. The Round Head Period is preceded by the Kel Essuf Period and fol ...
of the Central Sahara, the
Pastoral Period followed.
Some of the hunter-gatherers who created the Round Head rock art may have adopted pastoral culture, and others may have not.
As a result of increasing
aridification
Aridification is the process of a region becoming increasingly arid, or dry. It refers to long term change, rather than seasonal variation.
It is often measured as the reduction of average soil moisture content.
It can be caused by reduced precip ...
of the
Green Sahara, Central Saharan
hunter-gatherers
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
and cattle
herders
A herder is a pastoral worker responsible for the care and management of a herd or flock of domestic animals, usually on open pasture. It is particularly associated with nomadic or transhumant management of stock, or with common land grazing. ...
may have used seasonal waterways as the migratory route taken to the
Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through ...
and
Chad Basin of West Africa.
Migration of Saharan peoples south of the Sahelian region resulted in seasonal interaction with and gradual absorption of West African hunter-gatherers, who primarily dwelt in the
savannas
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
and
forests
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
of West Africa.
After having persisted as late as 1000 BP,
or some period of time after 1500 CE,
remaining West African hunter-gatherers, many of whom dwelt in the
forest-savanna region, were ultimately acculturated and admixed into the larger groups of West African
agriculturalists
An agriculturist, agriculturalist, agrologist, or agronomist (abbreviated as agr.), is a professional in the science, practice, and management of agriculture and agribusiness. It is a regulated profession in Canada, India, the Philippines, the U ...
, akin to the migratory
Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
agriculturalists and their
encounters
Encounter or Encounters may refer to:
Film
*''Encounter'', a 1997 Indian film by Nimmala Shankar
*Encounter (2013 film), ''Encounter'' (2013 film), a Bengali film
*Encounter (2018 film), ''Encounter'' (2018 film), an American sci-fi film
*Encounte ...
with
Central African hunter-gatherers.
Empires

The development of the region's economy allowed more centralized states and civilizations to form, beginning with
Dhar Tichitt
Dhar Tichitt is a Neolithic archaeological site located in the southwestern region of the Sahara Desert, in Mauritania. It is one of several settlement locations along the sandstone cliffs in the area. Dhar Tichitt, Dhar Walata, Dhar Néma, an ...
that began in 1600 B.C. followed by
Djenné-Djenno
Djenné-Djenno (also Jenne-Jeno; ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Niger River Valley in the country of Mali. Literally translated to "ancient Djenné", it is the original site of both Djenné and Mali and is considered to be among ...
beginning in 300 B.C. This was then succeeded by the
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, ...
that first flourished between the 9th and 12th centuries, which later gave way to the
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ...
. In current-day Mauritania, there exist archaeological sites in the towns of
Tichit
Tichit or Tichitt ( ber, Ticit, ar, تيشيت) is a partly abandoned village at the foot of the Tagant Plateau in central southern Mauritania that is known for its vernacular architecture. The main agriculture in Tichit is date farming, and the ...
and
Oualata
, settlement_type = Communes of Mauritania, Commune and town
, image_skyline = Oualata 03.jpg
, imagesize = 300px
, image_caption = View of the town looking in a southeas ...
that were initially constructed around 2000 B.C., and were found to have originated from the
Soninke branch of the
Mandé peoples
The Mandé peoples are ethnic groups who are speakers of Mande languages. Various Mandé speaking ethnic groups are found particularly toward the west of West Africa. The Mandé Speaking languages are divided into two primary groups: East Mandé ...
. Also, based on the archaeology of the city of
Kumbi Saleh
Koumbi Saleh, sometimes Kumbi Saleh is the site of a ruined medieval town in south east Mauritania that may have been the capital of the Ghana Empire.
From the ninth century, Arab authors mention the Ghana Empire in connection with the trans-Sah ...
in modern-day Mauritania, the Mali empire came to dominate much of the region until its defeat by
Almoravid
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
invaders in 1052.
Three great kingdoms were identified in ''Bilad al-Sudan'' by the ninth century. They included Ghana,
Gao
Gao , or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an impor ...
and
Kanem.
The
Sosso Empire
The Sosso Empire was a twelfth-century Kaniaga kingdom of West Africa.
The Kingdom of Sosso, also written as Soso or Susu, was an ancient kingdom on the coast of west Africa. During its empire, reigned their most famous leader, Sumaoro Kan ...
sought to fill the void but was defeated (c. 1240) by the
Mandinka forces of
Sundiata Keita
Sundiata Keita ( Mandinka, Malinke: ; 1217 – c. 1255) (also known as Manding Diara, Lion of Mali, Sogolon Djata, son of Sogolon, Nare Maghan and Sogo Sogo Simbon Salaba) was a prince and founder of the Mali Empire. He is also the great-uncle ...
, founder of the new Mali Empire. The Mali Empire continued to flourish for several centuries, most particularly under Sundiata's grandnephew
Musa I, before a succession of weak rulers led to its collapse under
Mossi,
Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern A ...
and
Songhai invaders. In the 15th century, the Songhai would form a new dominant state based on
Gao
Gao , or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an impor ...
, in the
Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
, under the leadership of
Sonni Ali
Sunni Ali, also known as Si Ali, Sunni Ali Ber (Ber meaning "the Great"), was born in Ali Kolon. He reigned from about 1464 to 1492. Sunni Ali was the first king of the Songhai Empire, located in Africa and the 15th ruler of the Sunni dynasty. ...
and
Askia Mohammed
Askia Muhammad I (b. 1443 – d. 1538), born Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr al-Turi or Muhammad Ture, was the first ruler of the Askia dynasty of the Songhai Empire, reigning from 1493 to 1528. He is also known as Askia the Great, and his name in modern ...
.

Meanwhile, south of the Sudan, strong city-states arose in
Igboland
Igboland (Standard ), also known as Southeastern Nigeria (but extends into South-Southern Nigeria), is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people.
It is a cultural and common linguistic region in southern Nigeria. Geographically, it is divided b ...
, such as the 10th-century
Kingdom of Nri
The Kingdom of Nri () was a medieval polity located in what is now Nigeria. The kingdom existed as a sphere of religious and political influence over a third of Igboland, and was administered by a priest-king called an '' Eze Nri''. The ''Eze Nri ...
, which helped birth the arts and customs of the
Igbo people
The Igbo people ( , ; also spelled Ibo" and formerly also ''Iboe'', ''Ebo'', ''Eboe'',
*
*
* ''Eboans'', ''Heebo'';
natively ) are an ethnic group in Nigeria. They are primarily found in Abia, Anambra, Ebonyi, Enugu, and Imo States. A ...
,
Bono State
Bono State (or Bonoman) was a trading state created by the Bono people, located in what is now southern Ghana. Bonoman was a medieval Akan kingdom in what is now Bono, Bono East and Ahafo region respectively named after the (Bono and Ahafo) an ...
in the 11th century, which gave birth to the numerous
Akan Akan may refer to:
People and languages
*Akan people, an ethnic group in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire
*Akan language, a language spoken by the Akan people
*Kwa languages, a language group which includes Akan
* Central Tano languages, a language group ...
States, while
Ife rose to prominence around the 12th century. Further east,
Oyo arose as the dominant
Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
state and the
Aro Confederacy
The Aro Confederacy (1690–1902) was a political union orchestrated by the Aro people, Igbo subgroup, centered in Arochukwu in present-day southeastern Nigeria. Their influence and presence was all over Eastern Nigeria, lower Middle Belt, an ...
as a dominant
Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a ...
state in modern-day Nigeria.
The Kingdom of Nri was a West African medieval state in present-day southeastern Nigeria and a subgroup of the Igbo people. The Kingdom of Nri was unusual in the history of world government in that its leader exercised no military power over his subjects. The kingdom existed as a sphere of religious and political influence over a third of Igboland and was administered by a priest-king called as an
Eze Nri
The following is a list of rulers of Nri. The title of the ruler of Nri is ''Eze Nri''. He held religious and political authority over the Kingdom of Nri.
The Nri culture is believed to stretch back to at least the 13th century, with a traditiona ...
. The Eze Nri managed trade and diplomacy on behalf of the Nri people and possessed divine authority in religious matters.
The
Oyo Empire
The Oyo Empire was a powerful Yoruba empire of West Africa made up of parts of present-day eastern Benin and western Nigeria (including Southwest zone and the western half of Northcentral zone). It grew to become the largest Yoruba-speaking s ...
was a
Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
empire of what is today Western,North central
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and southern
Republic of Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Republic of Dahomey, Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burki ...
. Established in the 14th century, the Oyo Empire grew to become one of the largest West African states. It rose through the outstanding organizational skills of the Yoruba, wealth gained from trade and its powerful
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
. The Oyo Empire was the most politically important state in the region from the mid-17th to the late 18th century, holding sway not only over most of the other kingdoms in
Yorubaland
Yorubaland () is the homeland and cultural region of the Yoruba people in West Africa. It spans the modern-day countries of Nigeria, Togo and Benin, and covers a total land area of 142,114 km2 or about 60% of the land area of Ghana. Of this ...
, but also over nearby African states, notably the
Fon Kingdom of Dahomey in the modern
Republic of Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Republic of Dahomey, Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burki ...
to the west.
The Benin Empire was a
post-classical
In world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 AD to 1500, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically and development of trade ...
empire located in what is now southern
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
. Its capital was Edo, now known as
Benin City
Benin City is the capital and largest city of Edo State, Edo State, Nigeria. It is the fourth-largest city in Nigeria according to the 2006 census, after Lagos, Kano (city), Kano, and Ibadan, with a population estimate of about 3,500,000 as of ...
,
Edo. It should not be confused with the modern-day country called
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
, formerly called
Dahomey. The Benin Empire was "one of the oldest and most highly developed states in the coastal hinterland of West Africa, dating perhaps to the eleventh century CE",. The Benin Empire was governed by a sovereign Emperor with hundreds of thousands of soldiers and a powerful council rich in resources, wealth, ancient science and technology with cities described as beautiful and large as
Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English) is a city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland. Haarlem is situated at the northern edge of the Randstad, one of the most populated metropoli ...
. "
Olfert Dapper
Olfert Dapper (January 1636 – 29 December 1689) was a Dutch physician and writer. He wrote books about world history and geography, although he never travelled outside the Netherlands.
Biography
Olfert Dapper was born in early 1636 in the ...
, a Dutch writer, describing Benin in his book ''
Description of Africa'' (1668) ". Its craft was the most adored and treasured bronze casting in the history of Africa. It was annexed by the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
in 1897 during the invasion and scramble of Africa.
European contact and enslavement

Portuguese traders began establishing settlements along the coast in 1445, followed by the
French,
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
,
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
,
Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
and
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
; the
African slave trade
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa in ancient times, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Indian Ocean ...
began not long after, which over the following centuries would debilitate the region's economy and population. The slave trade also encouraged the formation of states such as the
Bono State
Bono State (or Bonoman) was a trading state created by the Bono people, located in what is now southern Ghana. Bonoman was a medieval Akan kingdom in what is now Bono, Bono East and Ahafo region respectively named after the (Bono and Ahafo) an ...
,
Bambara Empire and
Dahomey, whose economic activities include but not limited to exchanging slaves for European
firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s.
Colonialism
In the early 19th century, a series of Fulani reformist
jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
s swept across Western Africa. The most notable include
Usman dan Fodio
Usman Ɗan Fodio ( ar, عثمان بن فودي, translit=ʿUthmān ibn Fodio; 15 December 1754 – 20 April 1817) was a Fulani scholar, Sunni Islamic religious teacher, revolutionary, and philosopher who founded the Sokoto Caliphate and ruled ...
's
Fulani Empire
The Sokoto Caliphate (), also known as the Fulani Empire or the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fulani jihads after defeating the Hausa Kingdoms in the F ...
, which replaced the
Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
...
city-states,
Seku Amadu
Sheikhu Ahmadu ( ar-at, شيخ أحمد بن محمّد لبّو, Shaykh Aḥmadu bin Muḥammadu Lobbo; ff, Seeku Aamadu ; ) (c. 1776 – 20 April 1845) was the Fulbe founder of the Massina Empire (Diina of Hamdullahi) in the Inner Niger D ...
's
Massina Empire, which defeated the Bambara, and El Hadj
Umar Tall
Hadji Oumarûl Foutiyou Tall (Umar ibn Sa'id al-Futi Tal, ar, حاج عمر بن سعيد طعل), ( – 1864 CE), born in Futa Tooro, present day Senegal, was a West African political leader, Islamic scholar, Tijani Sufi and Toucouleur ...
's
Toucouleur Empire
The Tidjaniya Caliphate ( ar, الخلافة التجانية; also known as the Tijaniyya Jihad state or the Segu Tukulor or the Toucouleur Empire) (1861–1890) was founded in the mid-nineteenth century by Elhadj Oumar Foutiyou Tall of the T ...
, which briefly conquered much of modern-day Mali.
However, the
French and
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
continued to advance in the
Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
, subjugating kingdom after kingdom. With the fall of
Samory Ture's new-founded
Wassoulou Empire
The Wassoulou Empire, sometimes referred to as the Mandinka Empire, was a short-lived (1878–1898) empire of West Africa built from the conquests of Malinke ruler Samori Ture and destroyed by the French colonial army.
In 1864, Toucouleu ...
in 1898 and the
Ashanti queen
Yaa Asantewaa
Yaa Asantewaa I (born 17 October 1840 – 17 October 1921) was the Queen Mother of Ejisu in the Ashanti Empirenow part of modern-day Ghana – appointed by her brother Nana Akwasi Afrane Opese, the Edwesuhene, or ruler, of Edwesu. In 1900 she l ...
in 1902, most West African military resistance to colonial rule resulted in failure.
Part of the West-African regions underwent an increase in the
numeracy level throughout the 19th century. The reason for such a growth was predetermined by a number of factors. Namely, the
peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
production and trade, which was boosted by the
demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item ...
of the
colonial states. Importantly, the rise of the numeracy was higher in the regions which were less
hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
and had less dependent from the
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
trade (e.g. Sine and Salum). Whereas areas with the opposite trends illustrated opposite tendencies (e.g. central and northern Senegal). Those patterns were further even more stimulated with the French colonial campaign.
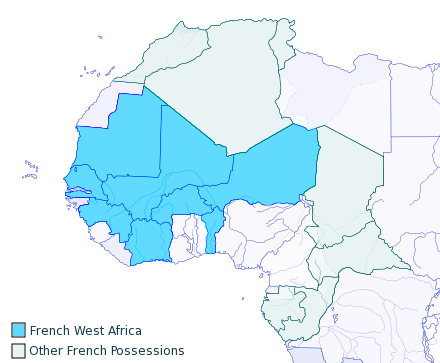
Britain controlled the Gambia, Sierra Leone, Ghana, and Nigeria throughout the colonial era, while France unified Senegal, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso, Benin, Ivory Coast, and Niger into
French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burki ...
.
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
founded the colony of
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
, while
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
claimed
Togoland
Togoland was a German Empire protectorate in West Africa from 1884 to 1914, encompassing what is now the nation of Togo and most of what is now the Volta Region of Ghana, approximately 90,400 km2 (29,867 sq mi) in size. During the period kn ...
, but was forced to divide it between France and Britain following
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
due to the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
. Only
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
retained its independence, at the price of major territorial concessions.
Postcolonial eras
Following
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, nationalist movements arose across West Africa. In 1957, Ghana, under
Kwame Nkrumah, became the first West African colony to achieve its independence, followed the next year by France's colonies (Guinea in 1958 under the leadership of President Ahmed Sekou Touré); by 1974, West Africa's nations were entirely autonomous.
Since independence, many West African nations have been submerged under political instability, with notable civil wars in Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Ivory Coast, and a succession of military coups in
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
.
Since the end of colonialism, the region has been the stage for some brutal conflicts, including:
*
Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Nigerian–Biafran War or the Biafran War, was a civil war fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state which had declared its independence f ...
*
First Liberian Civil War
*
Second Liberian Civil War
*
Guinea-Bissau Civil War
The Guinea-Bissau Civil War was fought from 7 June 1998 to 10 May 1999 and was triggered by an attempted coup d'état against the government of President João Bernardo Vieira led by Brigadier-General Ansumane Mané.Uppsala Conflict Data Progra ...
*
Ivorian Civil War
*
Sierra Leone Rebel War
*
Mali War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Mali War
, partof = the Islamist insurgency in the Sahel and the War on terror
, image = MaliWar.svg
, image_size = 380
, caption = Military situation ...
States
The
Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
, established in May 1975, has defined the region of West Africa since 1999 as including the following 15 states:

Geopolitically
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
, the
United Nations definition of
subregion
A subregion is a part of a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south are commonly used to define a subregion.
United Nations subregions
The United Nations Statistics Division, Statistics ...
Western Africa includes the preceding states with the addition of
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
(which withdrew from ECOWAS in 1999), comprising an area of approximately 6.1 million square km. The UN region also includes the
United Kingdom Overseas Territory of
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territory located in the South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and the archipelago of Tristan da Cunha including Gough Island. Its name wa ...
in the south
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
.
Area
In the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
scheme of African regions, the region of Western Africa includes 16
states and the
United Kingdom Overseas Territory of
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territory located in the South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and the archipelago of Tristan da Cunha including Gough Island. Its name wa ...
:
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
,
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
,
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
and the
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...](_blank)
, a transition zone between the
Sahara desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
and the
Sudanian Savanna;
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
,
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
,
The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
,
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
,
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
,
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
,
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
,
Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
and
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
compose most of
Guinea (region), Guinea, the traditional name for the area near the
Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the ...
;
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
lies in the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, the northwestern region of Africa that has historically been inhabited by West African groups such as the
Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
,
Soninke,
Wolof
Wolof or Wollof may refer to:
* Wolof people, an ethnic group found in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* Wolof language, a language spoken in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* The Wolof or Jolof Empire, a medieval West African successor of the Mal ...
,
Serer and
Toucouleur people
__NOTOC__
The Tukulor people ( ar, توكولور), also called Toucouleur or Haalpulaar, are a West African ethnic group native to Futa Tooro region of Senegal. There are smaller communities in Mali and Mauritania. The Toucouleur were Islamized ...
, along with
Arab-Berber
Arab-Berbers ( ar, العرب والبربر ''al-ʿarab wa-l-barbar'') are a population of the Maghreb, a vast region of North Africa in the western part of the Arab world along the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Arab-Berbers are peop ...
Maghrebi people
Maghrebis or Maghrebians ( ar, المغاربيون) is a modern Arabic term meaning "Westerners", mainly referring to the western part of the Arab world and North Africa. Maghrebis are predominantly of Arab and Berber or mixed Arab-Berber orig ...
such as the
Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern A ...
;
Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
is an island country in the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
; and
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territory located in the South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island and the archipelago of Tristan da Cunha including Gough Island. Its name wa ...
consists of eight main islands located in four different parts of the Atlantic. Due to Mauritania's increasingly close ties to the
Arab World
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
and its 1999 withdrawal from the
Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS), in modern times it is often considered, especially in Africa, as now part of western
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
.
List of countries
Cities
Major cities in West Africa include:
*
Abidjan
Abidjan ( , ; N'Ko script, N’ko: ߊߓߌߖߊ߲߬) is the economic capital of the Ivory Coast. As of the Demographics of Ivory Coast, 2021 census, Abidjan's population was 6.3 million, which is 21.5 percent of overall population of the country, ...
,
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
*
Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , ...
,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
*
Bamako
Bamako ( bm, ߓߡߊ߬ߞߐ߬ ''Bàmakɔ̌'', ff, 𞤄𞤢𞤥𞤢𞤳𞤮 ''Bamako'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Mali, with a 2009 population of 1,810,366 and an estimated 2022 population of 2.81 million. It is located on t ...
,
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
*
Port Harcourt,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
*
,
The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
*
Conakry
Conakry (; ; sus, Kɔnakiri; N’ko: ߞߐߣߊߞߙߌ߫, Fula: ''Konaakiri'' 𞤑𞤮𞤲𞤢𞥄𞤳𞤭𞤪𞤭) is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its p ...
,
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
*
Cotonou,
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
*
Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 2 ...
,
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
*
Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
,
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
*
Kumasi
Kumasi (historically spelled Comassie or Coomassie, usually spelled Kumase in Twi) is a city in the Ashanti Region, and is among the largest metropolitan areas in Ghana. Kumasi is located in a rain forest region near Lake Bosomtwe, and is the ...
,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
*
Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
* Ibadan, Nigeria
*
Lomé
Lomé is the capital and largest city of Togo. It has an urban population of 837,437 ,
Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
*
Calabar
Calabar (also referred to as Callabar, Calabari, Calbari and Kalabar) is the capital city of Cross River State, Nigeria. It was originally named Akwa Akpa, in the Efik language. The city is adjacent to the Calabar and Great Kwa rivers and cre ...
,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
*
Ouagadougou
Ouagadougou ( , , ) is the capital and largest city of Burkina Faso and the administrative, communications, cultural, and economic centre of the nation. It is also the country's largest city, with a population of 2,415,266 in 2019. The city's ...
,
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
*
Monrovia
Monrovia () is the capital city of the West African country of Liberia. Founded in 1822, it is located on Cape Mesurado on the Atlantic coast and as of the 2008 census had 1,010,970 residents, home to 29% of Liberia’s total population. As the ...
,
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
*
Abuja
Abuja () is the capital and eighth most populous city of Nigeria. Situated at the centre of the country within the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), it is a planned city built mainly in the 1980s based on a master plan by International Plann ...
,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
*
Cape Coast,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
*
Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou;
Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ ...
,
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
Environment
Nature
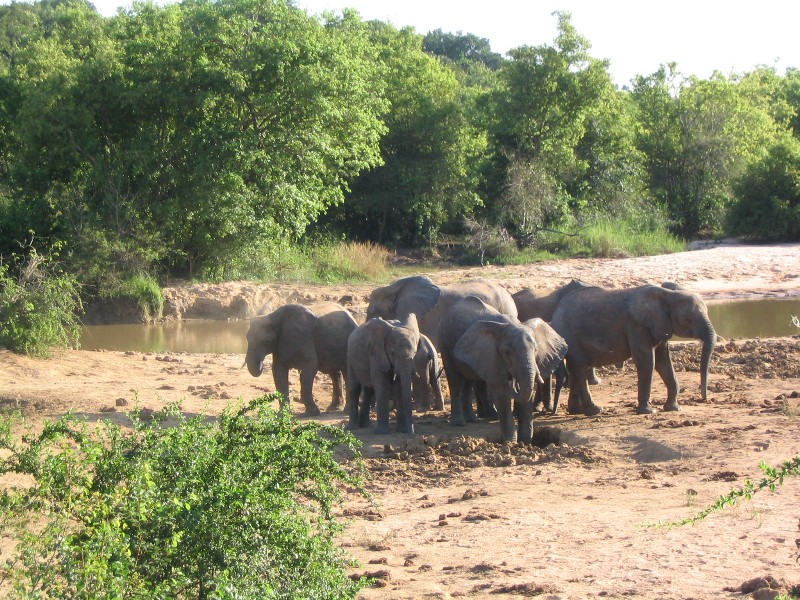


Before
European colonisation, West African countries such as those from the
Senegambia region (Senegal and the Gambia) used to have a diverse
wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animal species (biology), species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous ...
including
lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
s,
hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
,
elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae an ...
s,
antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals ...
s,
leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
s etc. However, during colonization, the European colonizers such as the French and British killed most of the wildlife particularly the lions, using their body parts as trophies. By the turn of the 20th century, the Senegambia region had lost most of its lion population and other exotic animals due to
poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
. By the 1930s, the Gambian elephant population became extinct. That phenomenon was not only limited to the Senegambia region but affected much of West African as the region lost much of its "natural resources once tied so closely to its cultural identity.
Poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
has stolen most of its wildlife." The British issued poaching licenses, and although they would later try to reverse the damage that had been done by attempting to preserve what was left of the local wildlife, but by that time, it was too late.
['']The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''
"Across Senegal, the Beloved Baobab Tree Is the 'Pride of the Neighborhood
by Dionne Searcey (Sept. 30, 2018) (Retrieved 1 April 2019)[Somerville, Keith, ''Ivory: Power and Poaching in Africa'', ]Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
(2016), p. 84-85
(Retrieved 1 April 2019) During the 1930s, the elephant population in the
Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast was about 300, and Sierra Leona between 500 and 600. Although a small number of elephants survived in Nigeria, hunting,
agricultural expansion
Agricultural expansion describes the growth of agricultural land (arable land, pastures, etc.) especially in the 20th and 21st centuries.
The agricultural expansion is often explained as a direct consequence of the global increase in food and ene ...
and
clearing of forest in that country drastically affected its wildlife population, particularly elephants.
Despite the historical damage that has been done to the region's wildlife populations, there are still some protected nature reserves within the region. Some of these include:
* The Bandia Nature Reserve in Senegal (French: ''Réserve de Bandia''), animal life includes:
giraffes
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, '' Giraffa camelopardal ...
,
zebras
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. zebr ...
,
rhinos, a variety of antelopes,
buffaloes,
monkeys,
crocodiles
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant memb ...
,
tortoises
Tortoises () are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin: ''tortoise''). Like other turtles, tortoises have a turtle shell, shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, ...
. apes and a variety of exotic birds.
* The
Yankari National Park in Nigeria, animal life includes: the
African bush elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana'') is one of two extant African elephant species and one of three extant elephant species. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with bulls reaching a shoulder height of up to and a body ...
,
olive baboon
The olive baboon (''Papio anubis''), also called the Anubis baboon, is a member of the family Cercopithecidae Old World monkeys. The species is the most wide-ranging of all baboons, being native to 25 countries throughout Africa, extending fr ...
,
patas monkey
The common patas monkey (''Erythrocebus patas''), also known as the wadi monkey or hussar monkey, is a ground-dwelling monkey distributed over semi-arid areas of West Africa, and into East Africa.
Taxonomy
There is some confusion surrounding ...
,
Tantalus monkey
The tantalus monkey (''Chlorocebus tantalus'') is an Old World monkey from Africa that ranges from Ghana to Sudan. It was originally described as a subspecies of the grivet (''Chlorocebus aethiops''). All species in ''Chlorocebus'' were formerly ...
,
roan antelope,
western hartebeest
The western hartebeest (''Alcelaphus buselaphus major'') is an antelope native to the medium to tall grassland plains of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, ...
,
West African lion
''Panthera leo leo'' is a lion subspecies, which is present in West Africa, northern Central Africa and India. In West and Central Africa it is restricted to fragmented and isolated populations with a declining trajectory. It has been referred to ...
,
African buffalo,
waterbuck
The waterbuck (''Kobus ellipsiprymnus'') is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus '' Kobus'' of the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies ar ...
,
bushbuck
The Cape bushbuck (''Tragelaphus sylvaticus'') is a common and a widespread species of antelope in sub-Saharan Africa.Wronski T, Moodley Y. (2009)Bushbuck, harnessed antelope or both? ''Gnusletter'', 28(1):18-19. Bushbuck are found in a wide ra ...
and
hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
.
#The
Ankasa Conservation Area in Ghana, animal life includes: the elephant,
bongo, leopard,
chimpanzee,
Diana monkey
The Diana monkey (''Cercopithecus diana'') is an Old World monkey found in the high canopy forests in Sierra Leone, Liberia, and western Côte d’Ivoire. Named for its white brow which is said to resemble the bow of the Roman goddess Diana, thi ...
, and other primates.
* The
Mole National Park
Mole National Park is Ghana's largest wildlife refuge. The park is located in the Savannah region of Ghana on savanna and riparian ecosystems at an elevation of 50 m, with a sharp escarpment forming the southern boundary of the park. The par ...
is Ghana's biggest wildlife refuge. It is home to over 83 mammal species including about 800 resident elephants, buffalo, hippos, and warthogs as well as various fauna and flora.
West Africa is also home to several
baobab
''Adansonia'' is a genus made up of eight species of medium-to-large deciduous trees known as baobabs ( or ). They are placed in the Malvaceae family, subfamily Bombacoideae. They are native to Madagascar, mainland Africa, and Australia.Trop ...
trees and other
plant life
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclu ...
. Some baobab trees are several centuries old and form part of the local folklore, for example, a mythical baobab tree named ''Ngoye njuli'' in Senegal which is regarded as a sacred site by the
Serer. The tree itself is rather majestic and looks like a huge
phallus and a deformed animal or thing is protruding from it. It is said to be the dwelling place of a
pangool
Pangool (in Serer and Cangin) singular: Fangool (var : ''Pangol'' and ''Fangol''), are the ancient saints and ancestral spirits of the Serer people of Senegal, the Gambia and Mauritania. The Pangool play a crucial role in Serer religion and hist ...
. Ngoye njuli is protected by the Senegalese authorities and attracts visitors. In West Africa, as in other parts of Africa where the baobab tree is found, the leaves are mixed with couscous and eaten, the bark of the tree is used to make ropes, and the fruit and seeds used for drinks and oils.

Deforestation
West Africa is greatly affected by
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
and has one of worst deforestation rate.
Even "the beloved baobab tree" which is viewed as sacred by some West African cultures are under threat due to
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
,
urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
and population growth. "Huge swaths of forest are being razed to clear space for palm oil and cocoa plantations. Mangroves are being killed off by pollution. Even wispy
acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia. The genus na ...
s are hacked away for use in cooking fires to feed growing families."
Nigeria, Liberia, Guinea, Ghana and the Ivory Coast, have lost large areas of their
rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
. In 2005, the
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
of the United Nations ranked
Nigeria as the state with the worst deforestation rate in the entire world. Causes include logging,
subsistence agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no su ...
, and the collection of fuelwoods.
According to a
ThoughtCo
Dotdash Meredith (formerly About.com) is an American digital media company based in New York City. The company publishes online articles and videos about various subjects across categories including health, home, food, finance, tech, beauty, l ...
publication authored Steve Nix (2018), almost 90 percent of West Africa's original rainforest has been destroyed, and the rest "heavily fragmented and in a degraded state, being poorly used."
ThoughtCo
Dotdash Meredith (formerly About.com) is an American digital media company based in New York City. The company publishes online articles and videos about various subjects across categories including health, home, food, finance, tech, beauty, l ...
, ''The Territory and Current Status of the African Rainforest'' by Steve Nix (November 04, 2018
(Retrieved 2 April 2019)
Overfishing
Overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
is a major issue in West Africa. Besides reducing fish stocks in the region, it also threatens
food security
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World F ...
and the livelihoods of many coastal communities who largely depend on
artisanal fishing
Artisanal fishing (or traditional/subsistence fishing) consists of various small-scale, low-technology, low-capital, fishing practices undertaken by individual fishing households (as opposed to commercial fishing). Many of these households are ...
. The overfishing generally comes from
foreign trawlers operating in the region.
To combat the overfishing,
Greenpeace
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning network, founded in Canada in 1971 by Irving Stowe and Dorothy Stowe, immigrant environmental activists from the United States. Greenpeace states its goal is to "ensure the ability of the Earth t ...
has recommended countries reduce the number of registered trawlers operating in African waters, increase the monitoring and control and set up regional fisheries organizations. Some steps have already been taken in the form of
WARFP (the World Bank's West Africa Regional Fisheries Program which empowers west-African countries (i.e. Liberia, Sierra Leone, Cape Verde, and Senegal) with information, training and monitoring systems. Furthermore, Liberia enacted a fisheries regulations Act in 2010 and installed a satellite-based monitoring system and Senegal enacted a fisheries code in 2015. In Cape Verde, the fishermen communities of Palmiera and Santa Maria have organized themselves to protect fishing zones. Mozambique finally created a
conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and managem ...
area, including a coastline.
Geography and climate
West Africa, broadly defined to include the western portion of the
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
(
Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the r ...
,
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
,
Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and
Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
), occupies an area in excess of 6,140,000 km
2, or approximately one-fifth of Africa. The vast majority of this land is plains lying less than 300 meters above sea level, though isolated high points exist in numerous states along the southern shore of West Africa.

The northern section of West Africa (narrowly defined to exclude the western Maghreb) is composed of semi-arid terrain known as
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
, a transitional zone between the Sahara and the
West Sudanian savanna
The West Sudanian savanna is a tropical savanna ecoregion that extends across West Africa.
Geography
The ecoregion stretches east and west across West Africa, from the Atlantic coast of Senegal to the Mandara Mountains on Nigeria's eastern borde ...
.
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s form a belt between the savannas and the southern coast, ranging from 160 km to 240 km in width.
The northwest African region of
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
periodically suffers country-wide plagues of
locust
Locusts (derived from the Vulgar Latin ''locusta'', meaning grasshopper) are various species of short-horned grasshoppers in the family Acrididae that have a swarming phase. These insects are usually solitary, but under certain circumstanc ...
s which consume water, salt and crops on which the human population relies.
Background
West Africa is west of an imagined north–south axis lying close to
10° east longitude.
[Peter Speth. ''Impacts of Global Change on the Hydrological Cycle in West and Northwest Africa'', p. 33. Springer, 2010. ] The Atlantic
Ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
forms the western as well as the southern borders of the West African region.
The northern border is the
Sahara Desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, with the Ranishanu Bend generally considered the northernmost part of the region. The eastern border is less precise, with some placing it at the
Benue Trough
The Benue Trough is a major geological structure underlying a large part of Nigeria and extending about 1,000 km northeast from the Bight of Benin to Lake Chad. It is part of the broader West and Central African Rift System.
Location
The ...
, and others on a line running from
Mount Cameroon
Mount Cameroon is an active volcano in the South West region of Cameroon next to the city of Buea near the Gulf of Guinea. Mount Cameroon is also known as Cameroon Mountain or Fako (the name of the higher of its two peaks) or by its indigenous n ...
to
Lake Chad
Lake Chad (french: Lac Tchad) is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Central Africa, which has varied in size over the centuries. According to the ''Global Resource Information Database'' of the United Nations Environment Programme, ...
.
Colonial boundaries are reflected in the modern boundaries between contemporary West African states, cutting across ethnic and cultural lines, often dividing single ethnic groups between two or more states.
In contrast to most of Central, Southern, and Southeast Africa, West Africa is not populated by
Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
-speaking peoples.
Climate change
Transport
Rail transport

A Trans-ECOWAS project, established in 2007, plans to upgrade railways in this zone. One of the goals of the
Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS) is the development of an integrated
railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
network.
Aims include the extension of railways in member countries, the interconnection of previously isolated railways and the standardization of gauge, brakes, couplings, and other parameters. The first line would connect the cities and ports of
Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
,
Cotonou,
Lomé
Lomé is the capital and largest city of Togo. It has an urban population of 837,437 and
Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , ...
and would allow the largest container ships to focus on a smaller number of large ports, while efficiently serving a larger
hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated ...
. This line connects gauge and systems, which would require four rail
dual gauge, which can also provide
standard gauge.
["Proposed Ecowas railway"](_blank)
. ''railwaysafrica.com''.

Road transport

The ''Trans–West African Coastal Highway'' is a transnational
highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
project to link 12 West African coastal states, from
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
in the north-west of the region to
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
in the east, with feeder roads already existing to two landlocked countries,
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
and
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
.
[Itai Madamombe (2006): "NEPAD promotes better transport networks"](_blank)
''Africa Renewal'', Vol. 20, No. 3 (October 2006), p. 14.
The eastern end of the highway terminates at
Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
.
Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS) consider its western end to be
Nouakchott
, image_skyline = Nouakchott.jpg
, image_caption = City view of Nouakchott
, pushpin_map = Mauritania#Arab world#Africa
, pushpin_relief = 1
, mapsize =
, map_caption ...
,
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, or to be
Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 2 ...
,
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
, giving rise to these alternative names for the road:
* Nouakchott–Lagos Highway
* Lagos–Nouakchott Highway
* Dakar–Lagos Highway
* Lagos–Dakar Highway
* Trans-African Highway 7 in the
Trans-African Highway
The Trans-African Highway network comprises transcontinental road projects in Africa being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union in conjunction with re ...
network
Air transport
The capitals' airports include:
*
Cadjehoun Airport
Cotonou Cadjehoun Airport is an airport in the Cadjehoun neighborhood of Cotonou, the largest city in Benin, in West Africa. The airport is the largest in the country, and as such, is the primary entry point into the country by air, with fligh ...
(COO) International; Cotonou, Benin
*
Ouagadougou Airport
Ouagadougou Airport , officially Thomas Sankara International Airport Ouagadougou, is an international airport in the center of the capital city of Ouagadougou in Burkina Faso. It was built in the 1960s, and it is approximately southeast of t ...
(OUA); Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
*
Amílcar Cabral International Airport
Amílcar Cabral International Airport , also known as Sal International Airport, is the main international airport of Cape Verde. The airport is named after the revolutionary leader Amílcar Cabral. It is located two km west-southwest from Espa ...
(SID); Praia, Cape Verde
*
Banjul International Airport
Banjul International Airport, also known as Yundum International , is the international airport of Banjul, capital of the Gambia, built during World War II.
History
The only airport in Gambia is at Yundum. After World War II, Yundum airport ...
(BJL) International; Banjul, Gambia
*
Kotoka International Airport
Kotoka International Airport is an international airport in Accra, the capital of Ghana. The airport is operated by Ghana Airports Company Limited (GACL), which has its offices on the airport property. It is the sole international airport in ...
(ACC); Accra; Ghana
*
Conakry International Airport
Conakry (; ; sus, Kɔnakiri; N’ko: ߞߐߣߊߞߙߌ߫, Fula: ''Konaakiri'' 𞤑𞤮𞤲𞤢𞥄𞤳𞤭𞤪𞤭) is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its po ...
(CKY); Conakry, Guinea
*
Osvaldo Vieira International Airport
Osvaldo Vieira International Airport , also known as Bissau-Bissalanca Airport, is an international airport that serves the city of Bissau, the capital of Guinea-Bissau, as well as the Metropolitan Region of Bissau. It is the only international ai ...
(OXB); Bissau, Guinea-Bissau
*
Port Bouet Airport
A port is a maritime law, maritime facility comprising one or more Wharf, wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge Affreightment, cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can a ...
(ABJ); Abidjan, Ivory Coast
*
Roberts International Airport (ROB); Monrovia, Liberia
*
Bamako–Sénou International Airport
Modibo Keita International Airport (formerly Bamako–Sénou International Airport) is Mali's main airport located approximately south of downtown Bamako, the capital of Mali in West Africa. It is the country's only international airport. It ...
(BKO); Bamako, Mali
*
Diori Hamani International Airport
Diori Hamani International Airport is an airport in Niamey, the capital of Niger. It is located from Niamey in the south eastern suburbs of the city, along the Route Nationale 1, the major highway linking Niamey with the east of the nation. Th ...
(NIM); Niamey, Niger
*
Murtala Muhammed International Airport
Murtala Muhammed International Airport (MMIA) ( yo, Pápá Ọkọ̀ Òfurufú Káríayé Múrítàlá Mùhammẹ̀d) is an international airport located in Ikeja, Lagos State, Nigeria, and is the major airport serving the entire state. The ai ...
(LOS); Lagos, Nigeria
*
Saint Helena Airport
Saint Helena Airport is an international airport on Saint Helena, a remote island in the south Atlantic Ocean, in the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha.
The construction of the runway was finishe ...
; Jamestown, Saint Helena
*
Blaise Diagne International Airport
Blaise Diagne International Airport (french: link=no, Aéroport international Blaise Diagne, ) is an international airport near the town of Diass in Thiès Region, Senegal, east of downtown Dakar. It serves as the main airport for Dakar, replac ...
(DSS); Dakar, Senegal
*
Lungi International Airport
Freetown International Airport (officially), locally known as Lungi International Airport, is an international airport located in the coastal town of Lungi, Sierra Leone. It is the only international airport in Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone Rive ...
(FNA); Freetown, Sierra Leone
*
Lomé–Tokoin Airport (LFW); Lomé, Togo
Of the sixteen, the most important hub and entry point to West Africa are
Kotoka International Airport
Kotoka International Airport is an international airport in Accra, the capital of Ghana. The airport is operated by Ghana Airports Company Limited (GACL), which has its offices on the airport property. It is the sole international airport in ...
, and
Murtala Muhammed International Airport
Murtala Muhammed International Airport (MMIA) ( yo, Pápá Ọkọ̀ Òfurufú Káríayé Múrítàlá Mùhammẹ̀d) is an international airport located in Ikeja, Lagos State, Nigeria, and is the major airport serving the entire state. The ai ...
, offering many international connections.
Health
West Africa has made considerably improvement in the health outcomes of its populations, in spite of the challenges posed by pervasive poverty, epidemic diseases, and food insecurity. The traditional communicable diseases of HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis are still the major reasons of mortality. Primary health care is the best answer to curing diseases, as it provides the basic preventive strategies as it reduce the rate of child and maternal morbidity and mortality—two of the most preventable outcomes that can prolong life expectancy at birth. Recently, mental health problems are on the rise in West Africa, as they are in many other world regions. However, the subject is largely a taboo, and professional treatment is still rare.
Culture
Despite the wide variety of cultures in West Africa, from
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
through to
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
, there are general similarities in
dress
A dress (also known as a frock or a gown) is a garment traditionally worn by women or girls consisting of a skirt with an attached bodice (or a matching bodice giving the effect of a one-piece garment). It consists of a top piece that co ...
,
cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
,
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
and culture that are not shared extensively with groups outside the geographic region. This long history of cultural exchange predates the colonization era of the region and can be approximately placed at the time of the
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, ...
(proper:
Wagadou
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, and ...
Empire),
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ...
or perhaps before these empires.
Art
Traditional architecture

The main traditional styles of building (in conjunction with modern styles) are the distinct
Sudano-Sahelian style in inland areas, and the coastal forest styles more reminiscent of other sub-Saharan areas. They differ greatly in construction due to the demands made by the variety of climates in the area, from tropical humid forests to arid grasslands and deserts. Despite the architectural differences, buildings perform similar functions, including the
compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
structure central to West African family life or strict distinction between the private and public worlds needed to maintain taboos or social etiquette.
Clothing

In contrast to other parts of the continent south of the
Sahara Desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, the concepts of
hem
A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the g ...
ming and
embroidering clothing have been traditionally common to West Africa for centuries, demonstrated by the production of various
breeches
Breeches ( ) are an article of clothing covering the body from the waist down, with separate coverings for each human leg, leg, usually stopping just below the knee, though in some cases reaching to the ankles. Formerly a standard item of Weste ...
,
shirts,
tunic
A tunic is a garment for the body, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the knees. The name derives from the Latin ''tunica'', the basic garment worn by both men and women in Ancient Rome ...
s and
jackets
A jacket is a garment for the upper body, usually extending below the hips. A jacket typically has sleeves, and fastens in the front or slightly on the side. A jacket is generally lighter, tighter-fitting, and less insulating than a coat, which ...
. As a result, the peoples of the region's diverse nations wear a wide variety of clothing with underlying similarities. Typical pieces of west African formal attire include the knee-to-ankle-length, flowing
Boubou robe,
Dashiki
The dashiki is a colorful garment that covers the top half of the body, worn mostly in West Africa. It is also known as a Kitenge in East Africa and is a common item of clothing in Tanzania and Kenya. It has formal and informal versions and var ...
, and
Senegalese
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
Kaftan
A kaftan or caftan (; fa, خفتان, ) is a variant of the robe or tunic. Originating in Asia, it has been worn by a number of cultures around the world for thousands of years. In Russian usage, ''kaftan'' instead refers to a style of men's l ...
(also known as ''Agbada'' and ''Babariga''), which has its origins in the clothing of nobility of various West African empires in the 12th century. Traditional half-sleeved, hip-long, woven smocks or tunics (known as ''fugu'' in Gurunsi, ''riga'' in Hausa) – worn over a pair of baggy trousers—is another popular garment. In the coastal regions stretching from southern Ivory Coast to Benin, a huge rectangular cloth is wrapped under one arm, draped over a shoulder, and held in one of the wearer's hands—coincidentally, reminiscent of
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
'
toga
The toga (, ), a distinctive garment of ancient Rome, was a roughly semicircular cloth, between in length, draped over the shoulders and around the body. It was usually woven from white wool, and was worn over a tunic. In Roman historical tra ...
s. The best-known of these toga-like garments is the
Kente
Kente ( ak, kente or ''nwetoma''; ee, kete; Dagbani: Chinchini) refers to a Ghanaian textile, made of handwoven cloth, strips of silk and cotton. Historically the fabric was worn in a toga-like fashion by royalty among ethnic groups such as the ...
(made by the
Akan people
The Akan () people live primarily in present-day Ghana and Ivory Coast in West Africa. The Akan language (also known as ''Twi/Fante'') are a group of dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo ...
of
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
), who wear them as a gesture of national pride.
Cuisine

Scores of foreign visitors to West African nations (e.g.,
traders,
historians
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the stu ...
,
emigrant
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
s, colonists, missionaries) have benefited from its citizens' generosity, and even left with a piece of its cultural heritage, via its foods. West African cuisines have had a significant influence on those of
Western civilization
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
for centuries; several dishes of West African origin are currently enjoyed in the
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
(e.g., the
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
and
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
); Australia; the USA (particularly
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
,
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
,
North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
); Italy; and other countries. Although some of these recipes have been altered to suit the sensibilities of their adopters, they retain a distinct West African essence.
West Africans cuisines include fish (especially among the coastal areas), meat, vegetables, and fruits—most of which are grown by the nations' local farmers. In spite of the obvious differences among the various local cuisines in this multinational region, the foods display more similarities than differences. The small difference may be in the ingredients used. Most foods are cooked via boiling or frying. Commonly featured, starchy vegetables include
yams,
plantain
Plantain may refer to:
Plants and fruits
* Cooking banana, banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking
** True plantains, a group of cultivars of the genus ''Musa''
* ''Plantaginaceae'', a family of flowerin ...
s,
cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively ...
, and sweet potatoes. Rice is also a staple food, as is the
Serer people's
sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
couscous
Couscous ( '; ber, ⵙⴽⵙⵓ, translit=Seksu) – sometimes called kusksi or kseksu – is a Maghrebi dish of small steamed granules of rolled durum wheat semolina that is often served with a stew spooned on top. Pearl millet, sorghum, ...
(called ''Chereh'' in
Serer) particularly in Senegal and
the Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
.
Jollof rice
Jollof (), or jollof rice, is a rice dish from West Africa. The dish is typically made with long-grain rice, tomatoes, onions, spices, vegetables and meat in a single pot, although its ingredients and preparation methods vary across different re ...
—originally from the
Kingdom of Jolof
The Kingdom of Jolof ( ar, جولوف), also known as Wolof and Wollof, was a West African rump state located in what is today the nation of Senegal. For nearly two hundred years, the Wolof rulers of the Jolof Empire collected tribute from vassal ...
(now part of modern-day Senegal) but has spread to the Wolofs of Gambia—is also enjoyed in many Western nations, as well;
Mafé (proper: ''Tigh-dege-na'' or ''Domodah'') from
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
(via the
Bambara and
Mandinka)—a peanut-butter stew served with rice;
Akara
Àkàrà (Yoruba)(English: Bean cake Hausa: kosai, Portuguese: Acarajé () is a type of fritter made from cowpeas or beans (black eye peas). It is found throughout West African, Caribbean, and Brazilian cuisines. The dish is traditionally encoun ...
(fried bean balls seasoned with spices served with sauce and bread) from Nigeria is a favorite breakfast for Gambians and Senegalese, as well as a favorite side snack or side dish in
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and the
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
just as it is in West Africa. It is said that its exact origin may be from
Yorubaland
Yorubaland () is the homeland and cultural region of the Yoruba people in West Africa. It spans the modern-day countries of Nigeria, Togo and Benin, and covers a total land area of 142,114 km2 or about 60% of the land area of Ghana. Of this ...
in Nigeria.
Fufu
Fufu (or fufuo, foofoo, foufou ) is a dough-like food found in West African cuisine. In addition to Ghana, it is also found in Sierra Leone, Guinea, Liberia, Cote D'Ivoire, Benin, Togo, Nigeria, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, t ...
(from the
Twi language
Twi () is a dialect of the Akan language spoken in southern and central Ghana by several million people, mainly of the Akan people, the largest of the seventeen major ethnic groups in Ghana. Twi has about 17-18 million speakers in total, includ ...
, a dough served with a spicy stew or sauce for example
okra
Okra or Okro (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in many English-speaking countries as ladies' fingers or ochro, is a flowering plant in the mallow family. It has edible green seed pods. The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with su ...
stew etc.) from
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
is enjoyed throughout the region and beyond even in
Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
with their own versions of it. Dishes such as
taguella,
eghajira, etc. are popular among the
Tuareg people
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern Alg ...
.
Recreation and sports

The board game
oware
Oware is an abstract strategy game among the mancala family of board games (pit and pebble games) played worldwide with slight variations as to the layout of the game, number of players and strategy of play. Its origin is uncertain but it is wide ...
is quite popular in many parts of Southern Africa. The word ''"Oware"'' originates from the
Akan people
The Akan () people live primarily in present-day Ghana and Ivory Coast in West Africa. The Akan language (also known as ''Twi/Fante'') are a group of dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo ...
of Ghana. However, virtually all African peoples have a version of this board game. The major
multi-sport event
A multi-sport event is an organized sporting event, often held over multiple days, featuring competition in many different sports among organized teams of athletes from (mostly) nation-states. The first major, modern, multi-sport event of interna ...
of West Africa is the ECOWAS Games which commenced at the
2012 ECOWAS Games.
Football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
is also a pastime enjoyed by many, either spectating or playing. The major national teams of West Africa, the
Ghana national football team
The Ghana national football team represents Ghana in men's international football, doing it since 1957. The team consists of twenty players including the technical team. The team is nicknamed the Black Stars after the Black Star of Africa in ...
, the
Ivory Coast national football team
The Ivory Coast national football team ( French: ''Équipe de football de Côte d'Ivoire'', recognized as the Côte d'Ivoire by FIFA) represents Ivory Coast in men's international football. Nicknamed ''the Elephants'', the team is managed by ...
, and the
Nigeria national football team
The Nigeria national football team represents Nigeria in men's international Association football, football. Governed by the Nigeria Football Federation (NFF), they are three-time Africa Cup of Nations winners, with their most recent title in ...
regularly win the
Africa Cup of Nations
The Africa Cup of Nations referred to as AFCON (french: Coupe d'Afrique des Nations, sometimes referred to as CAN, or TotalEnergies Africa Cup of Nations for sponsorship reasons), and sometimes as African Cup of Nations, is the main internati ...
. Major
football team
A football team is a group of players selected to play together in the various team sports known as football. Such teams could be selected to play in a match against an opposing team, to represent a football club, group, state or nation, an All-st ...
s of West Africa are
Asante Kotoko SC
Asante Kotoko Sporting Club, simply known as Asante Kotoko, is a professional football club founded on 31 August 1935 and based in Kumasi in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. Nicknamed the ''Porcupine Warriors'', they compete in the Ghana Premier Lea ...
and
Accra Hearts of Oak SC
Accra Hearts of Oak Sporting Club, commonly referred to as Hearts of Oak or just Hearts, is a professional sports club based in Accra (Greater Accra), Ghana. Founded in 1911, the club is the oldest surviving football club in Ghana and its tra ...
of the
Ghana Premier League
The is the top professional association football division of the football league system in Ghana. Officially formed in 1956 to replace a previous league incarnation, the Gold Coast Club Competition (which began in 1933 and ended in 1953–54), t ...
,
Enyimba International of the
Nigerian Premier League
The Nigeria Professional Football League (NPFL) is the highest level of the Nigerian football league system, for the Nigerian club-football championships.
The Nigerian league has suffered, like many others, from the financial impact and dwind ...
and
ASEC Mimosas
The Association Sportive des Employés de Commerce Mimosas, literally Mimosas Commerce Employees' Sporting Association, is an Côte d'Ivoire, Ivorian Association football, football club based in Abidjan. The club is also known as ''ASEC Mimosas A ...
of the
Ligue 1 (Ivory Coast)
The Ivory Coast MTN Ligue 1 is the top division of the Ivorian Football Federation. It was created in 1960.
2021−22 Ligue 1 clubs
* AF Amadou Diallo
* AS Indenié Abengourou
* ASEC Mimosas
* Bouaké FC
* CO Korhogo
* ES Bafing
* FC San Pedro
* ...
. The
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
governing body of West Africa is the
West African Football Union
The West African Football Union (french: Union des Fédérations Ouest-Africaines de Football; pt, União das Federações Oeste Africanas), officially abbreviated as WAFU-UFOA and WAFU, is an association of the football playing nations in West ...
(WAFU) and the major tournament is the
West African Club Championship
The West African Club Championship (UFOA Cup), also known as the General Eyadéma Cup, was a West African Club tournament from 1977 to 1999. It was open to league runners-up in the West Africa (or ''Zone 3'') region of the CAF. While the first mat ...
and
WAFU Nations Cup, along with the annual individual award of
West African Footballer of the Year.
Music

Mbalax
Mbalax (or mbalakh) is the national popular dance music of Senegal and the Gambia. In the 1970s, mbalax emerged as the distinctive sound of postcolonial Senegal. Derived from a fusion of indigenous Wolof sabar drumming with popular music principa ...
,
Highlife
Highlife is a music genre that started in present-day Ghana in the 19th century, during its Gold Coast (British colony), history as a colony of the British Empire and through its trade routes in coastal areas. It describes multiple local fusions ...
,
Fuji Fuji may refer to:
Places China
* Fuji, Xiangcheng City (付集镇), town in Xiangcheng City, Henan
Japan
* Mount Fuji, the tallest mountain in Japan
* Fuji River
* Fuji, Saga, town in Saga Prefecture
* Fuji, Shizuoka, city in Shizuoka Prefec ...
,
Afrobeat
Afrobeat is a Nigerian music genre that involves the combination of West African musical styles (such as traditional Yoruba music and highlife) and American funk, jazz, and soul influences, with a focus on chanted vocals, complex intersectin ...
, and
Afrobeats are modern musical genres of West Africa and its diaspora.
Traditional
folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has b ...
is also well-preserved. Some types of folk music are religious in nature such as the "Tassou" tradition used in
Serer religion
The Serer religion, or ''a ƭat Roog'' ("the way of the Divine"), is the original religious beliefs, practices, and teachings of the Serer people of Senegal in West Africa. The Serer religion believes in a universal supreme deity called Roog ...
.
Griot artists

Griot
A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel or kewel / okawul; Wolof: gewel) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician.
The griot is a repos ...
artists and praise-singing is an important musical tradition related to the oral history of West African culture. Traditionally, musical and oral history as conveyed over generations by griots are typical of West African culture in
Mande,
Wolof
Wolof or Wollof may refer to:
* Wolof people, an ethnic group found in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* Wolof language, a language spoken in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* The Wolof or Jolof Empire, a medieval West African successor of the Mal ...
,
Songhay,
Serer and, to some extent,
Fula
Fula may refer to:
*Fula people (or Fulani, Fulɓe)
*Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani)
**The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language
**The Fula variety known as the Pular language
**The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde
*Al-Fula ...
areas in the far west. A hereditary caste occupying the fringes of society, the griots were charged with memorizing the histories of local rulers and personages and the caste was further broken down into music-playing griots (similar to
bard
In Celtic cultures, a bard is a professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's ancestors and to praise t ...
s) and non-music-playing griots. Like Praise-singers, the griot's main profession was musical acquisition and prowess, and patrons were the sole means of financial support. Modern griots enjoy higher status in the patronage of rich individuals in places such as
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
,
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
,
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
and
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
, and to some extent make up the vast majority of musicians in these countries. Examples of modern popular griot artists include
Youssou N'Dour
Youssou N'Dour (, wo, Yuusu Nduur; also known as Youssou Madjiguène Ndour; born 1 October 1959) is a Senegalese singer, songwriter, musician, composer, occasional actor, businessman, and politician. In 2004, ''Rolling Stone'' magazine describe ...
,
Mamadou Diabate Mamadou is a common given name in West Africa among predominantly Muslim ethnic groups such as the Mandé and Wolof people. It is a variant of the Arabic name Muhammad.
Academics
* Mamadou Diouf (historian), Senegalese professor of West African h ...
,
Sona Jobareteh, and
Toumani Diabate.
In other areas of West Africa, primarily among the
Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
...
,
Mossi,
Dagomba and
Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
in the area encompassing
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
, northern
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[minstrels
A minstrel was an entertainer, initially in Middle Ages, medieval Europe. It originally described any type of entertainer such as a musician, juggler, acrobatics, acrobat, singer or jester, fool; later, from the sixteenth century, it came to ...](_blank)
, bards and poets play a vital role in extending the public show of power, lineage and prestige of traditional rulers through their exclusive patronage. Like the griot tradition, praise singers are charged with knowing the details of specific historical events and royal lineages, but more importantly need to be capable of poetic improvisation and creativity, with knowledge of traditional songs directed towards showing a patron's financial and political or religious power. Competition between Praise-singing ensembles and artistes are high, and artists responsible for any extraordinarily skilled prose, musical compositions, and panegyric songs are lavishly rewarded with money, clothing, provisions and other luxuries by patrons who are usually politicians, rulers, Islamic clerics and merchants; these successful praise-singers rise to national stardom. Examples include
Mamman Shata,
Souley Konko,
Fati Niger,
Saadou Bori and
Dan Maraya
Dan Maraya Jos (also known as Adamu Danmaraya Jos; born Adamu Wayya in 1946 – 20 June 2015) was a Nigerian Hausa griot best known for playing the kontigi.
Life
Dan Maraya Jos, whose name means "The Orphan of Jos", was born in 1946 in Buku ...
. In the case of Niger, numerous praise songs are composed and shown on television in praise of local rulers, Islamic clerics, and politicians.
Theatre
Film industry
Nollywood
Nollywood is a sobriquet that originally referred to the Nigerian film industry. The origin of the term dates back to the early 2000s, traced to an article in ''The New York Times''. Due to the history of evolving meanings and contexts, there ...
of Nigeria, is the main film industry of West Africa. The Nigerian cinema industry is the second largest film industry in terms of number of annual film productions, ahead of the
American film industry
The cinema of the United States, consisting mainly of major film studios (also known as Hollywood) along with some independent film, has had a large effect on the global film industry since the early 20th century. The dominant style of Ame ...
in
Hollywood.
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
and
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
also have long traditions of producing films. The late
Ousmane Sembène
Ousmane Sembène (; 1 January 1923 or 8 January 1923 – 9 June 2007), often credited in the French style as Sembène Ousmane in articles and reference works, was a Senegalese film director, producer and writer. The ''Los Angeles Times'' consider ...
, the Senegalese film director, producer and writer is from the region, as is the
Ghanaian
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in Ghana–Ivory Coast border, the west, Burkina ...
Shirley Frimpong-Manso.
Religion
Islam

Islam is the predominant religion of the West African interior and the far west coast of the continent (60% of West Africans); and was introduced to the region by traders in the 9th century. Islam is the religion of the region's biggest ethnic groups by population. Islamic rules on livelihood, values, dress and practices had a profound effect on the populations and cultures in their predominant areas, so much so that the concept of tribalism is less observed by Islamized groups like the
Mande,
Wolof
Wolof or Wollof may refer to:
* Wolof people, an ethnic group found in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* Wolof language, a language spoken in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* The Wolof or Jolof Empire, a medieval West African successor of the Mal ...
,
Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
...
,
Fula
Fula may refer to:
*Fula people (or Fulani, Fulɓe)
*Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani)
**The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language
**The Fula variety known as the Pular language
**The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde
*Al-Fula ...
,
Songhai, Zarma people, Zarma or
Soninke, than they are by non-Islamized groups. Ethnic intermarriage and shared cultural icons are established through a superseded commonality of belief or community, known as ummah. Traditional Muslim areas include
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 � ...
, Gambia,
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
,
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
,
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
,
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...](_blank)
and inland
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
; the western, northern and far-eastern regions of
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
; and the northern halves of the coastal nations of
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
,
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
,
Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
,
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
.
African traditional

Traditional African religions (noting the many different belief systems) are the oldest belief systems among the populations of this region, and include Akan religion, Yoruba religion, Odinani-
Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a ...
, and
Serer religion
The Serer religion, or ''a ƭat Roog'' ("the way of the Divine"), is the original religious beliefs, practices, and teachings of the Serer people of Senegal in West Africa. The Serer religion believes in a universal supreme deity called Roog ...
. They are Spirituality, spiritual but also linked to the historical and cultural heritage of the people. Although traditional beliefs vary from one place to the next, there are more similarities than differences.
Christianity
In 2010 around 36.5% of Western Africans identified as Christians. Christianity was largely introduced from the late 19th century onward, when missionaries from European countries brought the religion to the region. West African Christians are predominantly Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic or Anglicanism, Anglican; some Evangelical Christianity, Evangelical churches have also been established. Christianity has become the predominant religion in the Middle Belt, central and southern part of Religion in Nigeria, Nigeria, southern
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
, and the coastal regions stretching from southern
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
to coastal parts of
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
. Like Islam, elements of traditional African religion are mixed with Christianity.
Demographics and languages

West Africans primarily speak Niger–Congo languages, belonging mostly, though not exclusively, to its non-Bantu branches, though some Nilo-Saharan and Afroasiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic speaking groups are also found in West Africa. The Niger–Congo-speaking Yoruba language, Yoruba, Igbo language, Igbo,
Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
, Akan language, Akan and
Wolof
Wolof or Wollof may refer to:
* Wolof people, an ethnic group found in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* Wolof language, a language spoken in Senegal, Gambia, and Mauritania
* The Wolof or Jolof Empire, a medieval West African successor of the Mal ...
ethnic groups are the largest and most influential. The Tiv people found in Nigeria and partly in Cameroon are also among the largest. In the central Sahara,
Mandinka or
Mande groups are most significant. Chadic-speaking groups, including the
Hausa
Hausa may refer to:
* Hausa people, an ethnic group of West Africa
* Hausa language, spoken in West Africa
* Hausa Kingdoms, a historical collection of Hausa city-states
* Hausa (horse) or Dongola horse, an African breed of riding horse
See also
...
, are found in more northerly parts of the region nearest to the Sahara, and Nilo-Saharan communities, such as the
Songhai, Kanuri people, Kanuri and Zarma people, Zarma, are found in the eastern parts of West Africa bordering
Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
. The population of West Africa is estimated at million people as of . In
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
,
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...](_blank)
, the nomadic
Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern A ...
speak the Tuareg language, a Berber language.
Colonial languages also play a pivotal cultural and political role, being adopted as the official languages of most countries in the region, as well as ''linguae franca'' in communication between the region's various ethnic groups. For historical reasons, Western European languages such as French language, French, English language, English and Portuguese language, Portuguese predominate in Southern and Coastal subregions, whilst Arabic language, Arabic (in its Maghrebi Arabic, Maghrebi varieties) spreads inland northwards.
Science and technology
''Further information in the sections of History of science and technology in Africa:''
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel, Education
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 2, Astronomy
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 3, Mathematics
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa, Metallurgy
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 4, Medicine
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 5, Agriculture
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 6, Textiles
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 7, Maritime technology
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa 2, Architecture
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa 3, Communication systems
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa 4, Warfare
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa and the Sahel 8, Commerce
* History of science and technology in Africa#West Africa 5, By country
Economic and regional organizations

Economic Community of West Africa
West African Monetary Union
The West African Monetary Union (or UEMOA from its name in French, ''Union économique et monétaire ouest-africaine'') is limited to the eight, mostly Francophone countries that employ the CFA franc as their common currency. The Liptako-Gourma Authority of Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso seeks to jointly develop the contiguous areas of the three countries.
Women's peace movement
Since the adoption of the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 in 2000, women have been engaged in rebuilding war-torn Africa. Starting with the Women of Liberia Mass Action for Peace and Women in Peacebuilding Network (WIPNET), the peace movement has grown to include women across West Africa.
Established on May 8, 2006, Women Peace and Security Network – Africa (WIPSEN-Africa), is a women-focused, women-led Pan-African non-governmental organization based in
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
.
The organization focuses on empowering women to have a role in political and peace governance in Africa.
It has a presence in Ghana,
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
,
Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
,
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
. Regional leaders of nonviolent resistance include Leymah Gbowee, Comfort Freeman, and Aya Virginie Toure.
''Pray the Devil Back to Hell'' is a documentary film about the origin of this peace movement. The film has been used as an advocacy tool in post-conflict zones like Sudan and Zimbabwe, mobilizing African women to petition for peace and security.
November 2009 MEDIAGLOBAL
Gallery
Cityscapes of the largest cities
Capital cities of West Africa
File:Praia coast Cape Verde.jpg, Praia, Cape Verde
File:Dakar - Panorama_urbain.jpg, Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 2 ...
, Senegal
File:Imagelomé20.jpg, Lomé
Lomé is the capital and largest city of Togo. It has an urban population of 837,437 , Togo
File:Grande mosquee porto-novo.jpg, Porto-Novo, Benin
File:Street scene niamey 2006 002.jpg, Niamey, Niger
File:Kwamenkrumah av2.JPG, Ouagadougou
Ouagadougou ( , , ) is the capital and largest city of Burkina Faso and the administrative, communications, cultural, and economic centre of the nation. It is also the country's largest city, with a population of 2,415,266 in 2019. The city's ...
, Burkina Faso
File:Fort Thornton - Freetown - Sierra Leone.jpg, Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and p ...
, Sierra Leone
File:Banjul great mosque.jpg, , Gambia
File:Conakry street (3329204314).jpg, Conakry
Conakry (; ; sus, Kɔnakiri; N’ko: ߞߐߣߊߞߙߌ߫, Fula: ''Konaakiri'' 𞤑𞤮𞤲𞤢𞥄𞤳𞤭𞤪𞤭) is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its p ...
, Guinea
File:Praça Che Guevara, Bissau.jpg, Bissau, Guinea-Bissau
File:Monrovia Street.jpg, Monrovia
Monrovia () is the capital city of the West African country of Liberia. Founded in 1822, it is located on Cape Mesurado on the Atlantic coast and as of the 2008 census had 1,010,970 residents, home to 29% of Liberia’s total population. As the ...
, Liberia
File:Place des explorateurs, Koulouba - Bamako.jpg, Bamako
Bamako ( bm, ߓߡߊ߬ߞߐ߬ ''Bàmakɔ̌'', ff, 𞤄𞤢𞤥𞤢𞤳𞤮 ''Bamako'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Mali, with a 2009 population of 1,810,366 and an estimated 2022 population of 2.81 million. It is located on t ...
, Mali
File:Nouakchott.jpg, Nouakchott
, image_skyline = Nouakchott.jpg
, image_caption = City view of Nouakchott
, pushpin_map = Mauritania#Arab world#Africa
, pushpin_relief = 1
, mapsize =
, map_caption ...
, Mauritania
File:View_of_Abuja_from_Katampe_hill_01.jpg, Abuja
Abuja () is the capital and eighth most populous city of Nigeria. Situated at the centre of the country within the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), it is a planned city built mainly in the 1980s based on a master plan by International Plann ...
, Nigeria
File:A_drone_footage_of_Accra_central,_Ghana.jpg, Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , ...
, Ghana
File:Quartier_d'Affaires_au_Plateau_à_Abidjan_(29916932210).jpg, Abidjan
Abidjan ( , ; N'Ko script, N’ko: ߊߓߌߖߊ߲߬) is the economic capital of the Ivory Coast. As of the Demographics of Ivory Coast, 2021 census, Abidjan's population was 6.3 million, which is 21.5 percent of overall population of the country, ...
, Ivory Coast
File:Yamoussoukro_downtown.jpg, Yamoussoukro, Ivory Coast
File:Overlooking_Jamestown_from_the_south.jpg, Jamestown, Saint Helena, Jamestown, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
See also
*
*
*
*
*
*
* , a form of archaic money unique to West Africa
*
*
* , an indigenously developed West African writing system
*
**
**
**
*
*
*
References
Further reading
* Akyeampong, Emmanuel Kwaku. ''Themes in West Africa's History'' (2006).
* Brydon, Lynne. "Constructing Avatime: questions of history and identity in a West African polity, c. 1690s to the twentieth century." ''Journal of African History'' 49.1 (2008): 23–42
online
* Collins, Robert O. ''African History: Western African History'' (1990).
* Davidson, Basil. ''A History of West Africa, 1000–1800'' (1978), numerous editions
* Delavignette, Robert. ''Freedom and Authority in French West Africa'' (Routledge, 2018).
* Dueppen, Stephen A. "The archaeology of West Africa, ca. 800 BCE to 1500 CE." ''History Compass'' 14.6 (2016): 247–263.
* Edgerton, Robert B. ''The Fall of the Asante Empire: The Hundred-Year War For Africa'S Gold Coast'' (2002).
* Fage, J. D. ''A Guide to Original Sources for Precolonial Western Africa Published in European Languages'' (2nd ed. 1994); updated in Stanley B. Alpern, ed. ''Guide to Original Sources for Precolonial Western Africa'' (2006).
* Festus, Jacob et al. eds. ''History of West Africa'' (Vol. 1, 1989).
* Greene, S. E. ''Sacred Sites and the Colonial Encounter: A History of Meaning and Memory in Ghana'' (2002).
* Griswold, Wendy. ''Writing African women: Gender, popular culture and literature in West Africa'' (Zed Books Ltd., 2017).
* Ham, Anthony. ''West Africa'' (2013
online
* Hayward, Derek F., and Julius Oguntoyinbo. ''Climatology of West Africa'' (Routledge, 2019).
* Hopkins, Antony Gerald. ''An economic history of West Africa'' (2014
online
* Huber, Caroline, Lyn Finelli, and Warren Stevens. "The economic and social burden of the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa." ''Journal of infectious diseases 218.Supplement_5'' (2018): S698-S704.
* Kane, Ousmane Oumar, ''Beyond Timbuktu: An Intellectual History of Muslim West Africa'' (2016).
* Lavallée, Emmanuelle, and François Roubaud. "Corruption in the informal sector: evidence from West Africa." ''Journal of Development Studies'' 55.6 (2019): 1067–1080
online
* Law, Robin. "Human sacrifice in pre-colonial West Africa." ''African Affairs'' 84.334 (1985): 53–87
online
* Mann, Gregory. "Locating colonial histories: between France and West Africa." ''American Historical Review'' 110.2 (2005): 409–434. focus on local memories and memorial
online
* Martinez-Alvarez, Melisa, et al. "COVID-19 pandemic in West Africa." ''The Lancet Global Health'' 8.5 (2020): e631-e632
online
* Mazrui, Ali A. ''Islam and the English language in East and West Africa'' (Routledge, 2017).
* Meillassoux, Claude, ed. ''The development of indigenous trade and markets in West Africa: studies presented and discussed at the tenth International African seminar at Fourah Bay college, Freetown, december 1969'' (Routledge, 2018).
* Mendonsa, Eugene L. ''West Africa: An Introduction to Its History'' (2002)
* O'Brien, Donal Cruise, Richard Rathbone, John Dunn, eds. ''Contemporary West African States'' (2002
online free to borrow
* Soares, Benjamin. "The historiography of Islam in West Africa: an anthropologist's view." ''Journal of African History'' 55.1 (2014): 27–36
online
* Tonkin, Elizabeth. ''Narrating our pasts: The social construction of oral history'' (Cambridge university press, 1995), on West Africa
* Westermann, Diedrich, and Margaret Arminel Bryan. ''The Languages of West Africa: Handbook of African Languages'' (Routledge, 2017).
External links
– African Studies at Columbia University
ouestaf.com
– Ouestaf, a West African online newspaper
Loccidental
– An online West African newspaper
West Africa Review
– An e-journal on West Africa research and scholarship
The Voyage of the Sieur Le Maire, to the Canary Islands, Cape-Verde, Senegal, and Gambia
is the first published writing about Western Africa, dating from 1695
{{coord, 12, N, 3, E, source:wikidata, display=title
West Africa,
Regions of Africa
 The development of the region's economy allowed more centralized states and civilizations to form, beginning with
The development of the region's economy allowed more centralized states and civilizations to form, beginning with  Meanwhile, south of the Sudan, strong city-states arose in
Meanwhile, south of the Sudan, strong city-states arose in  In the early 19th century, a series of Fulani reformist
In the early 19th century, a series of Fulani reformist 

 Before European colonisation, West African countries such as those from the Senegambia region (Senegal and the Gambia) used to have a diverse
Before European colonisation, West African countries such as those from the Senegambia region (Senegal and the Gambia) used to have a diverse 
 The northern section of West Africa (narrowly defined to exclude the western Maghreb) is composed of semi-arid terrain known as
The northern section of West Africa (narrowly defined to exclude the western Maghreb) is composed of semi-arid terrain known as  A Trans-ECOWAS project, established in 2007, plans to upgrade railways in this zone. One of the goals of the
A Trans-ECOWAS project, established in 2007, plans to upgrade railways in this zone. One of the goals of the 
 The main traditional styles of building (in conjunction with modern styles) are the distinct Sudano-Sahelian style in inland areas, and the coastal forest styles more reminiscent of other sub-Saharan areas. They differ greatly in construction due to the demands made by the variety of climates in the area, from tropical humid forests to arid grasslands and deserts. Despite the architectural differences, buildings perform similar functions, including the
The main traditional styles of building (in conjunction with modern styles) are the distinct Sudano-Sahelian style in inland areas, and the coastal forest styles more reminiscent of other sub-Saharan areas. They differ greatly in construction due to the demands made by the variety of climates in the area, from tropical humid forests to arid grasslands and deserts. Despite the architectural differences, buildings perform similar functions, including the  In contrast to other parts of the continent south of the
In contrast to other parts of the continent south of the  Scores of foreign visitors to West African nations (e.g., traders,
Scores of foreign visitors to West African nations (e.g., traders,  The board game
The board game 

 Islam is the predominant religion of the West African interior and the far west coast of the continent (60% of West Africans); and was introduced to the region by traders in the 9th century. Islam is the religion of the region's biggest ethnic groups by population. Islamic rules on livelihood, values, dress and practices had a profound effect on the populations and cultures in their predominant areas, so much so that the concept of tribalism is less observed by Islamized groups like the Mande,
Islam is the predominant religion of the West African interior and the far west coast of the continent (60% of West Africans); and was introduced to the region by traders in the 9th century. Islam is the religion of the region's biggest ethnic groups by population. Islamic rules on livelihood, values, dress and practices had a profound effect on the populations and cultures in their predominant areas, so much so that the concept of tribalism is less observed by Islamized groups like the Mande,  Traditional African religions (noting the many different belief systems) are the oldest belief systems among the populations of this region, and include Akan religion, Yoruba religion, Odinani-
Traditional African religions (noting the many different belief systems) are the oldest belief systems among the populations of this region, and include Akan religion, Yoruba religion, Odinani- West Africans primarily speak Niger–Congo languages, belonging mostly, though not exclusively, to its non-Bantu branches, though some Nilo-Saharan and Afroasiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic speaking groups are also found in West Africa. The Niger–Congo-speaking Yoruba language, Yoruba, Igbo language, Igbo,
West Africans primarily speak Niger–Congo languages, belonging mostly, though not exclusively, to its non-Bantu branches, though some Nilo-Saharan and Afroasiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic speaking groups are also found in West Africa. The Niger–Congo-speaking Yoruba language, Yoruba, Igbo language, Igbo,