Way Of The Patriarchs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
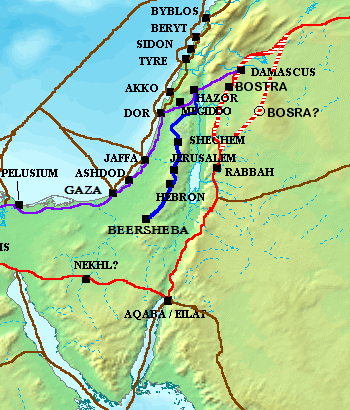 The Road of the Patriarchs or Way of the Patriarchs ( he, דֶּרֶךְ הֲאָבוֹת ''Derech haʾAvot'' Lit. ''Way (of) the Fathers''), is an ancient north–south route traversing the land of Israel. The name is used by biblical scholars because of mentions in biblical narratives that it was frequently travelled by
The Road of the Patriarchs or Way of the Patriarchs ( he, דֶּרֶךְ הֲאָבוֹת ''Derech haʾAvot'' Lit. ''Way (of) the Fathers''), is an ancient north–south route traversing the land of Israel. The name is used by biblical scholars because of mentions in biblical narratives that it was frequently travelled by



 The route connected to Via Maris and the King's Highway by way of several east-west roads:
An important connection was "The Sunset Road" ( he, דֶּרֶךְ מְבוֹא הַשֶּמֶש ''Derech Mevo HaShemesh'') () leading from The King's Highway, crossing the Jordan River at the location of today's Adam Bridge (Jisr Damiat) and ascending through the Tirtza Valley (Wadi Al Fara) to Mount Gerizim and
The route connected to Via Maris and the King's Highway by way of several east-west roads:
An important connection was "The Sunset Road" ( he, דֶּרֶךְ מְבוֹא הַשֶּמֶש ''Derech Mevo HaShemesh'') () leading from The King's Highway, crossing the Jordan River at the location of today's Adam Bridge (Jisr Damiat) and ascending through the Tirtza Valley (Wadi Al Fara) to Mount Gerizim and
 The Road of the Patriarchs or Way of the Patriarchs ( he, דֶּרֶךְ הֲאָבוֹת ''Derech haʾAvot'' Lit. ''Way (of) the Fathers''), is an ancient north–south route traversing the land of Israel. The name is used by biblical scholars because of mentions in biblical narratives that it was frequently travelled by
The Road of the Patriarchs or Way of the Patriarchs ( he, דֶּרֶךְ הֲאָבוֹת ''Derech haʾAvot'' Lit. ''Way (of) the Fathers''), is an ancient north–south route traversing the land of Israel. The name is used by biblical scholars because of mentions in biblical narratives that it was frequently travelled by Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
, Isaac
Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was th ...
and Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
.
It is also called the Hill Road or the Ridge Route because it follows the watershed ridge line of the Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first ...
n and Judaean Mountains
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel wh ...
. It runs from Megiddo Megiddo may refer to:
Places and sites in Israel
* Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley
* Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel
* Megiddo church (Israel)
* Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel
* Megiddo Junctio ...
and Hazor south to Beersheba
Beersheba or Beer Sheva, officially Be'er-Sheva ( he, בְּאֵר שֶׁבַע, ''Bəʾēr Ševaʿ'', ; ar, بئر السبع, Biʾr as-Sabʿ, Well of the Oath or Well of the Seven), is the largest city in the Negev desert of southern Israel. ...
by way of Shechem
Shechem ( ), also spelled Sichem ( ; he, שְׁכֶם, ''Šəḵem''; ; grc, Συχέμ, Sykhém; Samaritan Hebrew: , ), was a Canaanite and Israelite city mentioned in the Amarna Letters, later appearing in the Hebrew Bible as the first c ...
, Bethel, Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, Ephrath
Ephrath or Ephrathah or Ephratah ( he, אֶפְרָת \ אֶפְרָתָה) is a biblically-referenced former name of Bethlehem, meaning "fruitful". It is also a personal name.
Biblical place
A very old tradition is that Ephrath refers to Bethleh ...
and Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after Eas ...
. Unlike the Via Maris
Via Maris is one modern name for an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia — along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Egypt, Israel, Turkey and Syr ...
and the King's Highway King's Highway or Kings Highway may refer to:
Roads Australia
* Kings Highway (Australia), connecting Queanbeyan to Batemans Bay
Canada
* King's Highways, an alternative designation for the primary provincial highway system in Ontario
* King's ...
which were international roads crossing the territories of many peoples, the Ridge Route was wholly within the territory of ancient Israel.
Modern equivalent
The modern Highway 60 follows roughly the route of the Way of the Patriarchs (without the more recentbypasses
Bypass may refer to:
* Bypass (road), a road that avoids a built-up area (not to be confused with passing lane)
* Flood bypass of a river
Science and technology Medicine
* Bypass surgery, a class of surgeries including for example:
** Heart bypa ...
), passing through Afula
Afula ( he, עפולה Arabic: العفولة) is a city in the Northern District of Israel, often known as the "Capital of the Valley" due to its strategic location in the Jezreel Valley. As of , the city had a population of .
Afula's ancient ...
, Jenin, Nablus, Ramallah, Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
, Halhul
Halhul ( ar, حلحول, transliteration: ''Ḥalḥūl'') is a Palestinian city located in the southern West Bank, north of Hebron in the Hebron Governorate of the State of Palestine. The town, bordered by Sa'ir and Ash-Shuyukh to the east, ...
, Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after Eas ...
and Dhahiriya.
Archaeological findings



Ritual baths
Way stations were discovered along the route between Beersheba and Jerusalem from the time of the ancientTemple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
and later during the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
and Roman eras. Ritual baths ( mikvaot, Hebrew: מקוואות) served pilgrims during their journey.
Milestones
Milestones have been discovered along the route signalling that, even in Roman times, the route was used as a major road. The stones represent the distance to Jerusalem.Biblical events
The Maccabees' Battle of Beth Zechariah
The Way of the Patriarchs passes byKhirbet Beit Zakariyyah
Khirbet Beit Zakariyyah (variants: Beit Iskâria, Khirbet Zakariah, Beit Skâria) is a small Palestinian village in the West Bank, perched on a hill that rises about above sea level. It is located in between the larger Israeli settlements of Al ...
, a small Palestinian village near the Israeli settlement of Alon Shevut, possibly the site of the Battle of Beth Zechariah
The Battle of Beth Zechariah was a battle around May 162 BC during the Maccabean revolt fought between Jewish rebels under the leadership of Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) against an army of the Seleucid Empire, the Greek successor state (diadoch ...
between Judas Maccabeus and the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
Greeks. It was there that Judah's brother, Eleazar Avaran
Eleazar Avaran, also known as Eleazar Maccabeus, Eleazar Hachorani/Chorani (Hebrew: אלעזר המכבי ''Eleazar HaMakabi'', אלעזר החורני ''Eleazar HaChorani''; died 162 BC) was the fourth son of Mattathias and the younger brother of ...
, was killed after stabbing and killing one of the Greek elephants. This incident is commemorated by the name of the adjacent community, Elazar
Eleazar (; ) or Elʽazar was a priest in the Hebrew Bible, the second High Priest, succeeding his father Aaron after he died. He was a nephew of Moses.
Biblical narrative
Eleazar played a number of roles during the course of the Exodus, fro ...
.
Battle of Gibeah
The biblical story of the Concubine of the Hill from theBook of Judges
The Book of Judges (, ') is the seventh book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. In the narrative of the Hebrew Bible, it covers the time between the conquest described in the Book of Joshua and the establishment of a kingdom ...
, leading up to the battle of Gibeah (), tells of a small family caravan journeying on the ridge route from Bethlehem towards Jerusalem. Gibeah
Gibeah (; he, גִּבְעָה ''Gīḇəʿā''; he, גִּבְעַת, link=no ''Gīḇəʿaṯ'') is the name of three places mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, in the tribes of Benjamin, Judah, and Ephraim respectively.
Gibeah of Benjamin is th ...
is generally identified with Tell el-Fūl.
Route near ancient Jerusalem
Ancient Jerusalem (today's Old City) was not situated on the mountain watershed. Indeed, the Ridge Route did not pass directly through the ancient city but was situated just to the west, about a 20-minute walk from the city walls. The route from Bethel southwards would have passed through today's neighborhoods ofBeit Hanina
Beit Hanina ( ar, بيت حنينا , he, בית חנינא) is an Arab Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem. It is on the road to Ramallah, eight kilometers north of central Jerusalem, at an elevation of 780 meters above sea level. Bei ...
, Shuafat
Shuafat ( ar, شعفاط '), also ''Shu'fat'' and ''Sha'fat'', is a mostly Palestinian Arab neighborhood of East Jerusalem, forming part of north-eastern Jerusalem. Located on the old Jerusalem–Ramallah road about three miles north of the Old ...
, French Hill
French Hill ( he, הגבעה הצרפתית, ''HaGiv'a HaTzarfatit'', ar, التلة الفرنسية, ''at-tel al-faransiya''), also Giv'at Shapira ( he, גִּבְעַת שַׁפִּירָא) is an Israeli settlement in northern East Jerusa ...
, Givat HaMivtar
Givat HaMivtar () is an Israeli settlement and a neighborhood in East Jerusalem established in 1970 between Ramat Eshkol and French Hill. It is located on a hill where an important battle took place in the Six Day War. Archaeological excavation ...
and Kerem Avraham, crossing Jaffa Road
Jaffa Road ( he, רחוב יפו, Rehov Yaffo; ar, شارع يافا) is one of the longest and oldest major streets in Jerusalem. It crosses the city from east to west, from the Old City walls to downtown Jerusalem, the western portal of Jer ...
at the center of modern down-town Jerusalem behind the HaMashbir Department Store building, and continuing along Shmuel HaNagid St. (peak height: Ratisbonne Monastery), King George St., Keren HaYesod St., and finally the Hebron Road to Bethlehem.
East-west connections
 The route connected to Via Maris and the King's Highway by way of several east-west roads:
An important connection was "The Sunset Road" ( he, דֶּרֶךְ מְבוֹא הַשֶּמֶש ''Derech Mevo HaShemesh'') () leading from The King's Highway, crossing the Jordan River at the location of today's Adam Bridge (Jisr Damiat) and ascending through the Tirtza Valley (Wadi Al Fara) to Mount Gerizim and
The route connected to Via Maris and the King's Highway by way of several east-west roads:
An important connection was "The Sunset Road" ( he, דֶּרֶךְ מְבוֹא הַשֶּמֶש ''Derech Mevo HaShemesh'') () leading from The King's Highway, crossing the Jordan River at the location of today's Adam Bridge (Jisr Damiat) and ascending through the Tirtza Valley (Wadi Al Fara) to Mount Gerizim and Shechem
Shechem ( ), also spelled Sichem ( ; he, שְׁכֶם, ''Šəḵem''; ; grc, Συχέμ, Sykhém; Samaritan Hebrew: , ), was a Canaanite and Israelite city mentioned in the Amarna Letters, later appearing in the Hebrew Bible as the first c ...
. Today's eastern leg of Route 57 roughly follows the ancient track.
The "Red Ascent" ( he, מַעֲלֵה אֲדֻמִּים ''Ma'ale Adumim
Ma'ale Adumim ( he, מַעֲלֵה אֲדֻמִּים; ar, معالي أدوميم) is an urban Israeli settlement organized as a city council in the West Bank, seven kilometers () east of Jerusalem. Ma'ale Adumim achieved city status in 1991. ...
'') ( and ) formed a boundary of the tribe of Judah ''ascending from the Valley of Achor
Achor ( he, עכור "muddy, turbid: gloomy, dejected") is the name of a valley in the vicinity of Jericho.
History
The Book of Joshua, chapter seven, relates the story from which the valley's name comes. After the problems the Israelites ha ...
to Debir A Biblical word, dvir () may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Names
* Debir King of Eglon, a Canaanite king of Eglon, slain by Joshua (). Aided by miracles, Joshua's army routed the Canaanite military, forcing Debir and the other kings to seek refuge in a cave ...
and turning north to Gilgal
Gilgal ( he, גִּלְגָּל ''Gilgāl''), also known as Galgala or Galgalatokai of the 12 Stones ( grc-gre, Γαλαγα or , ''Dōdekalithōn''), is the name of one or more places in the Hebrew Bible. Gilgal is mentioned 39 times, in particula ...
''. It takes its name from the red rock lining the ascent. Highway 1 between Jerusalem and the Jordan Valley follows the ancient route.
To the west of Shechem, the ancient " Aphek Ascent" from the Via Maris and the coastal plain passed through Aphek, Soco and today's Kfar Saba
Kfar Saba ( he, כְּפַר סָבָא), officially Kefar Sava, is a city in the Sharon region, of the Central District of Israel. In 2019 it had a population of 110,456, making it the 16th-largest city in Israel. The population of Kfar Saba i ...
and Qalqilyah
Qalqilya or Qalqiliya ( ar, قلقيلية, Qalqīlyaḧ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank which serves as the administrative center of the Qalqilya Governorate of the State of Palestine. In the 2007 census, the city had a population of 41, ...
. Highway 55
The following highways are numbered 55:
International
* European route E55
* Arab Mashreq route M55
Argentina
* San Luis Provincial Route 55
Australia
* Carnarvon Highway
* Castlereagh Highway
* Karoonda Highway
Belgium
* N55 road (Belgiu ...
duplicates the eastern part of this route.
"The Bethoron
Bethoron ( he, בֵית־חוֹרֹ֔ן, lit=house of Horon; grc, Ὡρωνείν), also Beth-Horon, was the name of two adjacent ancient towns strategically located on the Gibeon-Aijalon road, guarding the "ascent of Beth-Horon". The towns are ...
Ascent" ( he, מַעֲלֵה בֵּית חוֹרוֹן ''Ma'ale Beit Horon'') () from the coastal plain passes today's Ben Gurion Airport, then rose along an offshoot of the watershed ridge leading to today's Beit Hanina
Beit Hanina ( ar, بيت حنينا , he, בית חנינא) is an Arab Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem. It is on the road to Ramallah, eight kilometers north of central Jerusalem, at an elevation of 780 meters above sea level. Bei ...
as it approached Jerusalem. Today's Route 443 follows the ancient road with minor deviations.
The ascent from Jaffa to Jerusalem through the Plain of Ayalon is now duplicated by Route 412, Highway 44 and Route 1.
Further south, Highway 35
The following highways are numbered 35:
International
* European route E35
Canada
* Alberta Highway 35
* British Columbia Highway 35
* Ontario Highway 35
* Quebec Autoroute 35
*Saskatchewan Highway 35
China
* G35 Expressway
Costa Rica
* ...
roughly follows the path of the ancient "Lachish
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. Th ...
Road" from Gaza, Ashkelon and Ashdod through the Lachish region to Hebron.
See also
*Incense Route
The Incense Trade Route was an ancient network of major land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levan ...
*King's Highway King's Highway or Kings Highway may refer to:
Roads Australia
* Kings Highway (Australia), connecting Queanbeyan to Batemans Bay
Canada
* King's Highways, an alternative designation for the primary provincial highway system in Ontario
* King's ...
*Nablus Road Nablus Road (, ''Derekh Shekhem'', "Shechem Road") is one of the traditional routes radiating from Jerusalem's walled city. Starting at the Damascus Gate, it is the ancient road north.
Places of interest
* American Colony Hotel
* Armenian Ceramics ...
inside East Jerusalem
*Via Maris
Via Maris is one modern name for an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia — along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Egypt, Israel, Turkey and Syr ...
References
{{Trade route 2 Ancient roads and tracks Trade routes Ancient Israel and Judah Archaeological sites in Israel