|
Debir
A Bible, Biblical word, dvir () may refer to: __NOTOC__ Names * Debir King of Eglon, a Canaanite monarch, king of Eglon, Canaan, Eglon, slain by Joshua (). Aided by miracles, Joshua's army routed the Canaanite military, forcing Debir and the other kings to seek refuge in a cave. There they were trapped until later executed. Places * A royal Canaanite city, also known as Kiriath-Sepher () and Kiriath-Sannah. () It became a Kohen, Kohanic city. () Its location is unclear, but today it is commonly identified with Rabud, Khirbet Rabud southwest of Hebron. Claude Reignier Conder, Conder and Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener, Kitchener thought ''Debir'', mentioned in was present Ad-Dhahiriya.Conder and Kitchener, 1883, SWP III, p402/ref>C. R. Conder, Conder (1879), p93/ref> * A site mentioned to be in the low plain of Achor. () Though its exact location is not known, the name may have survived in Thogheret ed-Debr, southwest of Jericho. * A location in Gilead, at the border of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Of Holies
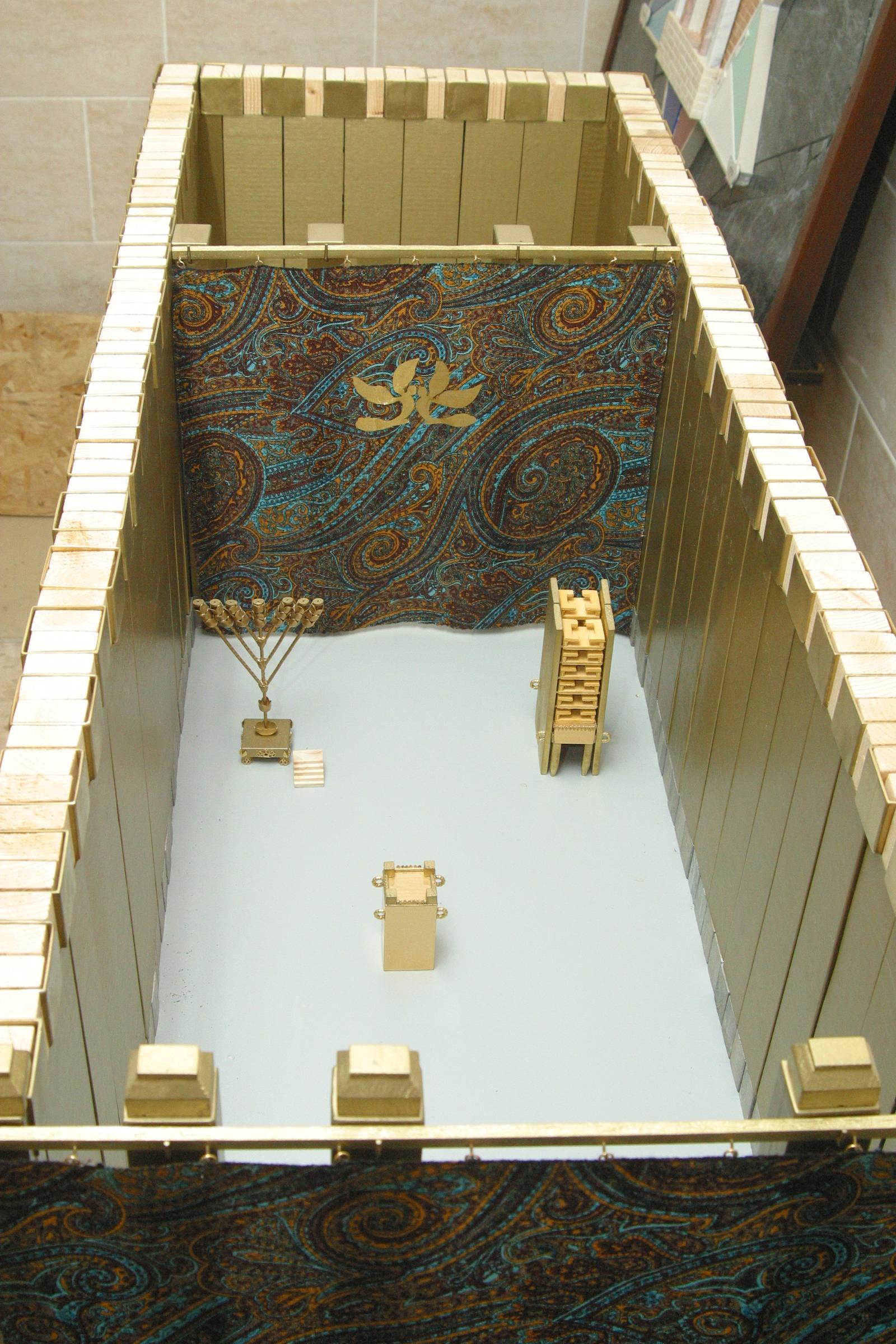
The Holy of Holies (Hebrew: ''Qōḏeš haqQŏḏāšīm'' or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also הַדְּבִיר ''haDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where God's presence appeared. According to Hebrew tradition, the area was defined by four pillars that held up the veil of the covering, under which the Ark of the Covenant was held above the floor. According to the Hebrew scripture, the Ark contained the Ten Commandments, which were given by God to Moses on Mount Sinai. The Temple in Jerusalem was said to have been built by King Solomon for keeping the Ark. Ancient Jewish traditions viewed the Holy of Holies as the spiritual junction of Heaven and Earth, the "axis mundi". As a part of the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem, the Holy of Holies was situated somewhere on Temple Mount; its precise location in the Mount being a matter of dispute, with some classical Jewish sources identifying its location with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephod
An ephod ( he, אֵפוֹד ''ʾēfōḏ''; or ) was a type of apron, which according to the Hebrew Bible, was worn by the Jewish high priest the kohen gadol, an artifact and an object to be revered in ancient Israelite culture, and was closely connected with oracular practices and priestly ritual. In the Books of Samuel and Books of Chronicles, David is described as wearing an ephod when dancing in the presence of the Ark of the Covenant (2 Samuel 6:14, 1 Chronicles 15:27) and one is described as standing in the sanctuary at Nob, with a sword behind it (1 Samuel 21:9). In the book of Exodus and in Leviticus one is described as being created for the High Priest to wear as part of his official vestments (Exodus 28:4+, 29:5, 39:2+; Leviticus 8:7). Description In the Bible, in the contexts where it is worn, the ephod is usually described as being linen, but did not constitute complete clothing of any kind, as the Books of Samuel describe.Cheyne and Black, ''Encyclopedia Biblica'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zechariah Ben Jehoiada
Zechariah ben Jehoiada ''Zəḵaryā ben-Yǝhōyāḏāʿ''; ar, زكريّا بن يهوياداع ''Zakariya bin Yehuyada'') is a figure in the Hebrew Bible described as a priest who was stoned to death by Jehoash of Judah and may possibly have been alluded to in the New Testament. Lineage Zechariah was the son of Jehoiada, the High Priest in the times of Ahaziah and Jehoash of Judah. After the death of Jehoiada, Zechariah condemned both King Jehoash and the people for their rebellion against God (). This so stirred up their resentment against him that at the king's commandment they stoned him, and he died "in the court of the house of the Lord" (). In rabbinical literature In rabbinical literature, Zechariah was the son-in-law of the king, and, being also a priest, prophet, and judge, he dared censure the monarch. He was killed in the priests' courtyard of the Temple on a Sabbath which was likewise the Day of Atonement. Later, when Nebuzar-adan, the captain of Nebuchadne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interpretes. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : Dt. Bibelges., 2006 . However, in modern Greek the accentuation is , while the current (28th) scholarly edition of the New Testament has . ar, كَنْعَانُ – ) was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period (14th century BC) as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eglon, Canaan
Eglon ( he, עֶגְלוֹן, translit=) was a Canaanite city-state mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. According to the Book of Joshua, Debir, king of Eglon, joined a confederation against Gibeon when that city made peace with Israel. The five kings involved were slain and Eglon was later conquered and its inhabitants condemned to destruction. It was thereafter included in the territory of the Tribe of Judah, although it is not mentioned outside of the Book of Joshua.. Note: this citation supports the claim that Eglon is only mentioned in Joshua. It does not make any comment as to whether Eglon stayed in the possession of the tribe of Judah. According to K. van Bekkum, the location of Eglon is unknown, but the most plausible candidate is Tel 'Eton. Tel 'Eton Tel 'Eton ( he, תל עיטון, translit=) is an archaeological site excavated by an the Bar Ilan University, managed by Avraham Faust Avraham Faust is an Israeli archaeologist and professor at Bar-Ilan University Bar-Ilan Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvir (other)
* Debir (other)
* Dvir (name)
Dvir is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Dvir'' may also refer to: *, now part of Kinneret Zmora-Bitan Dvir Kinneret Zmora-Bitan Dvir is one of Israel's largest book publishing companies. History The company's oldest imprint, Dvir, was founded in Odessa in 1919 by Hayim Nahman Bialik. See also * {{disambig ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabud
Rabud ( ar, رابود, also spelled Khirbet Rabud) is a Palestinian village in the southern West Bank, in the Hebron Governorate of the State of Palestine. The village was the site of an ancient Canaanite city. Etymology According to Palmer, the name ''Khirbet Rabud'' means "the ruin of the animal's lair". Demographics Part of the Hebron Governorate of Palestine, it is located 13 kilometers southwest of Hebron and about 5 km northwest of as-Samu. Rabud had a population of 2,262 in the 2007 census by the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS). The principal families are the Huraibat, Quteinah, al-Uqela and Shanan. History According to research by the Applied Research Institute-Jerusalem, Rabud's history dates back to the Canaanite period in Palestine, but the modern inhabitants of the village migrated from the Arabian Peninsula. It is thought to lie on the site of the ancient Judean Kohanic city of Kiryat Sefer or Debir.(Trevor Bryce (2009). The Routledge Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
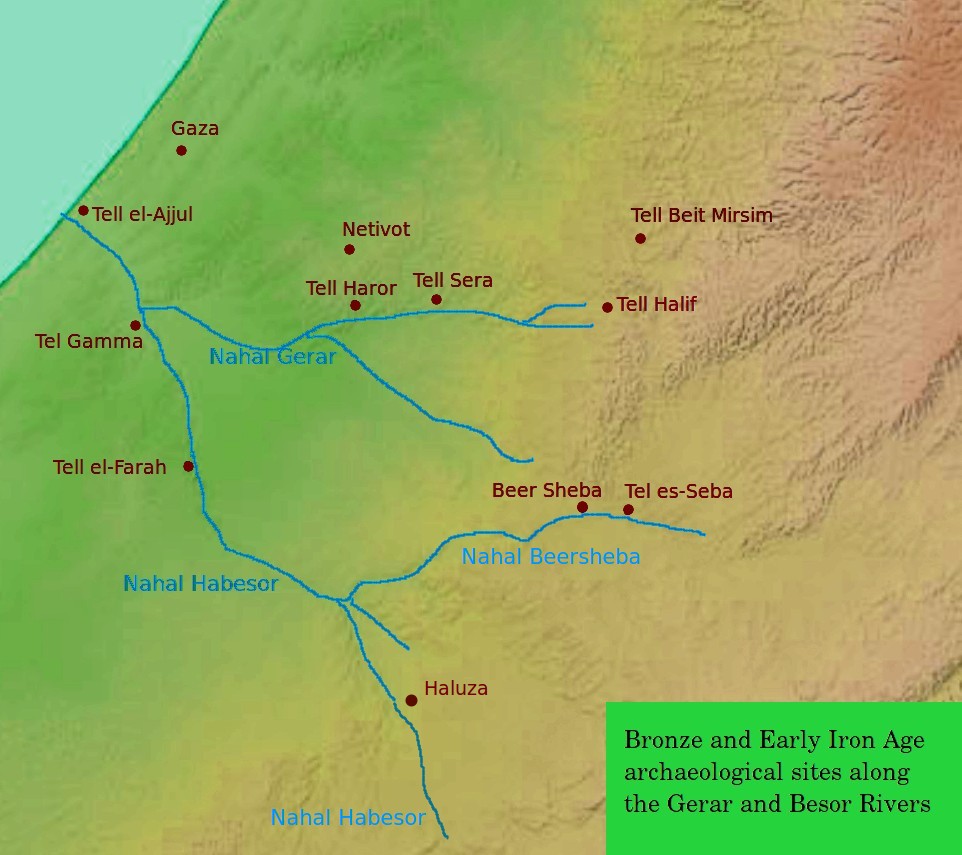
Tell Beit Mirsim
Tell Beit Mirsim is an archaeological site in Israel, on the border between the lowlands of Shfela and Mount Hebron. It is located in the eastern region of Lachish about 20 kilometers southwest of Hebron and about 13 kilometers southeast of Lachish. Excavations It was excavated for four seasons (1926, 1928, 1930 and 1932) by William F. Albright. The excavation revealed 10 or 11 strata dating from the late 3rd millennium BC to around 589 BC. The site is of particular importance for the archeology of Palestine, since the ceramics in the individual layers were observed particularly well and published quickly. This pottery corpus has long been considered the standard for archeology in the region. :"The strict separation of earth layers, or archaeological sediments, also allowed the strict separation of ceramic assemblages".Herr, Larry G. (2002)"W.F. Albright and the History of Pottery in Palestine".''Near Eastern Archaeology'' 65.1 (2002), 53. Town plan The site has "a town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lives Of The Prophets
The ''Lives of the Prophets'' is an ancient apocryphal account of the lives of the prophets of the Old Testament. It is not regarded as scripture by any Jewish or Christian denomination. The work may have been known by the author of some of the Pauline epistles, as there are similarities in the descriptions of the fates of the prophets, although without naming the individuals concerned. Manuscript tradition The work survives only in Christian manuscripts. There are two groups of Greek manuscripts: the first group includes many versions, well known in the past centuries, with heavy Christian additions. Some of these versions were attributed to Epiphanius of Salamis, others to Dorotheus of Tyre. The other group of Greek manuscripts is more stable and free from the interpolations found in the previous group: the best codex is a 6th-century CE manuscript usually referred to as ''Q'' or as ''anonymous recension'', which is the earliest Greek version of this work. D. R. A. Hare, ''The L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad-Dhahiriya
Ad-Dhahiriya (also Az-Zahiriya) ( ar, الظاهرية) is a Palestinian city in the Hebron Governorate of the State of Palestine, 23 km southwest of the city of Hebron in the southern West Bank. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, ad-Dhahiriya had a population of 38.002 in 2016. History According to Conder and Kitchener Ad-Dhahiriya was probably the site of the ancient biblical town of Debir.Conder and Kitchener, 1883, SWP III, p402/ref> They found the village undermined by caves. In the centre of Ad-Dhahiriya was a tower, which appeared to be from before the Crusader era, possibly from early Christian or Roman period. Local tradition, supported by archaeology, have that ad-Dhahiriya was founded by Baibars (1223/1228 – 1277). Ottoman era In the various Ottoman census in the sixteenth century, ''Darusiyya'' was noted as located in the ''nahiya'' of Halil. In the 932 AH/1525-1526 CE census, the villagers also cultivated the fields at ''Bayt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocrypha
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered too profound or too sacred to be disclosed to anyone other than the initiated. ''Apocrypha'' was later applied to writings that were hidden not because of their divinity but because of their questionable value to the church. In general use, the word ''apocrypha'' has come to mean "false, spurious, bad, or heretical". Biblical apocrypha are a set of texts included in the Septuagint and the Latin Vulgate, but not in the Hebrew Bible. While Catholic tradition considers some of these texts to be deuterocanonical, and the Orthodox Churches consider them all to be canonical, Protestants consider them apocryphal, that is, non-canonical books that are useful for instruction. Luther's Bible placed them in a separate section in between the Old Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)