World War I (WWI or WW1), also known as the First World War or the Great War in historical contexts, was a
global conflict
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
from 1914 to 1918. It was fought between two coalitions: the
Allied Powers and the
Central Powers. Fighting took place throughout
Europe, the
Middle East,
Africa, the
Pacific, and parts of
Asia. One of the
deadliest wars in history, it resulted in an estimated 9 million soldiers dead and 23 million wounded, plus another 5 million civilian deaths from various causes. Millions more died as a result of
genocide, and the war was a major factor in the 1918
Spanish flu pandemic.
The first decade of the 20th century saw increasing diplomatic tension between the European great powers. This reached a
breaking point on 28 June 1914, when a
Bosnian Serb named
Gavrilo Princip assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne.
Austria-Hungary held
Serbia responsible, and declared war on 28 July.
Russia came to Serbia's defence, and by 4 August,
Germany,
France, and
Britain were drawn into the war, with the
Ottoman Empire joining in November of that same year.
Germany's strategy in 1914 was to first defeat France, then transfer forces to the Russian front. However, this
failed, and by the end of 1914, the
Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
consisted of a continuous line of
trenches stretching from the
English Channel to
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
. The
Eastern Front was more dynamic, but neither side could gain a decisive advantage, despite costly offensives. As the war expanded to more fronts,
Bulgaria,
Romania,
Greece,
Italy and others joined in from 1915 onward.
In early 1917, the
United States entered the war on the side of the Allies, and later the same year, the
Bolsheviks seized power in the Russian
October Revolution, making
peace with the Central Powers in early 1918. Germany launched an
offensive
Offensive may refer to:
* Offensive, the former name of the Dutch political party Socialist Alternative
* Offensive (military), an attack
* Offensive language
** Fighting words or insulting language, words that by their very utterance inflict inj ...
in the west in March 1918, and despite initial success, it left the
German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
exhausted and demoralised. A successful Allied
counter-offensive later that year caused a collapse of the German frontline. By the end of 1918, Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary agreed to armistices with the Allies, leaving Germany isolated. Facing
revolution at home and with his army on the verge of mutiny,
Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicated on 9 November.
Fighting ended with the
Armistice of 11 November 1918, while the subsequent
Paris Peace Conference Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include:
Listed by name
Paris Accords
may refer to:
* Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germ ...
imposed various settlements on the defeated powers, notably the
Treaty of Versailles. The dissolution of the Russian, German, Austro-Hungarian, and Ottoman Empires resulted in the creation of new independent states, including
Poland,
Finland,
Czechoslovakia, and
Yugoslavia. The inability to manage
post-war instability contributed to the outbreak of
World War II in September 1939.
Names
The term ''world war'' was first coined in September 1914 by German biologist and philosopher
Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new sp ...
. He claimed that "there is no doubt that the course and character of the feared 'European War' ... will become the first world war in the full sense of the word," in ''
The Indianapolis Star'' on 20 September 1914.
The term First World War had been used by Lt-Col.
Charles à Court Repington, as a title for his memoirs (published in 1920); he had noted his discussion on the matter with a Major Johnstone of
Harvard University in his diary entry of 10 September 1918.
Prior to
World War II, the events of 1914–1918 were generally known as the Great War or simply the World War. In August 1914, the magazine ''
The Independent'' wrote "This is the Great War. It names itself".
In October 1914, the Canadian magazine ''
Maclean's'' similarly wrote, "Some wars name themselves. This is the Great War." Contemporary Europeans also referred to it as "
the war to end war" and it was also described as "
the war to end all wars" due to their perception of its unparalleled scale, devastation, and loss of life.
Background
Political and military alliances
For much of the 19th century, the major European powers maintained a tenuous
balance of power among themselves, known as the
Concert of Europe. After 1848, this was challenged by a variety of factors, including Britain's withdrawal into so-called
splendid isolation, the
decline of the Ottoman Empire
In the late eighteenth century, the Ottoman Empire (Ottoman Old Regime) faced numerous enemies. In response to these threats, the empire initiated a period of internal reform which came to be known as the Tanzimat, which succeeded in significan ...
,
New Imperialism, and the rise of
Prussia under
Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
. The 1866
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
established Prussian hegemony in German states, while victory in the 1870–1871
Franco-Prussian War allowed Bismarck to
consolidate the German states into a
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
under Prussian leadership. Avenging the defeat of 1871, or
revanchism, and recovering the provinces of
Alsace-Lorraine became the principal objects of French policy for the next forty years.

In order to isolate France and avoid a war on two fronts, Bismarck negotiated the
League of the Three Emperors (German: ''Dreikaiserbund'') between
Austria-Hungary,
Russia and Germany. After Russian victory in the 1877–1878
Russo-Turkish War, the League was dissolved due to Austrian concerns over Russian influence in the
Balkans, an area they considered of vital strategic interest. Germany and Austria-Hungary then formed the 1879
Dual Alliance, which became the
Triple Alliance Triple Alliance may refer to:
* Aztec Triple Alliance (1428–1521), Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan and in central Mexico
* Triple Alliance (1596), England, France, and the Dutch Republic to counter Spain
* Triple Alliance (1668), England, the ...
when Italy joined in 1882. For Bismarck, the purpose of these agreements was to isolate France by ensuring the three Empires resolved any disputes between themselves; when this was threatened in 1880 by British and French attempts to negotiate directly with Russia, he reformed the League in 1881, which was renewed in 1883 and 1885. After the agreement lapsed in 1887, he replaced it with the
Reinsurance Treaty, a secret agreement between Germany and Russia to remain neutral if either were attacked by France or Austria-Hungary.
Bismarck viewed peace with Russia as the foundation of German foreign policy but after becoming
Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
in 1890,
Wilhelm II forced him to retire and was persuaded not to renew the Reinsurance Treaty by his new
Chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
,
Leo von Caprivi. This provided France an opportunity to counteract the Triple Alliance by signing the
Franco-Russian Alliance in 1894, followed by the 1904 ''
Entente Cordiale'' with Britain. The
Triple Entente was completed by the 1907
Anglo-Russian Convention. While these were not formal alliances, by settling long-standing colonial disputes in
Africa and
Asia, the notion of British entry into any future conflict involving France or Russia became a possibility. British and Russian support for France against Germany during the
Agadir Crisis in 1911 reinforced their relationship and increased Anglo-German estrangement, deepening the divisions that would erupt in 1914.
Arms race
German industrial strength and production significantly increased after 1871, driven by the creation of a unified Reich,
French indemnity payments, and the annexation of
Alsace-Lorraine. Backed by Wilhelm II, Admiral
Alfred von Tirpitz sought to use this growth in economic power to build a ''Kaiserliche Marine'', or
Imperial German Navy, which could compete with the British
Royal Navy for world naval supremacy. His thinking was influenced by US naval strategist
Alfred Thayer Mahan, who argued possession of a
blue-water navy
A blue-water navy is a maritime force capable of operating globally, essentially across the deep waters of open oceans. While definitions of what actually constitutes such a force vary, there is a requirement for the ability to exercise sea cont ...
was vital for global power projection; Tirpitz had his books translated into German, while Wilhelm made them required reading for his advisors and senior military personnel.
However, it was also an emotional decision, driven by Wilhelm's simultaneous admiration for the Royal Navy and desire to outdo and surpass it. Bismarck thought that the British would not interfere in Europe, so long as its maritime supremacy remained secure, but his dismissal in 1890 led to a change in policy and an
Anglo-German naval arms race began. Despite the vast sums spent by Tirpitz, the launch of in 1906 gave the British a technological advantage over their German rivals which they never lost. Ultimately, the race diverted huge resources into creating a German navy large enough to antagonise Britain, but not defeat it; in 1911, Chancellor
Theobald von Bethmann Hollweg acknowledged defeat, leading to the ''Rüstungswende'' or 'armaments turning point', when he switched expenditure from the navy to the army.

This decision was not driven by a reduction in political tensions, but German concern over Russia's quick recovery from its defeat in the
Russo-Japanese War and subsequent
1905 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
that same year. Economic reforms backed by funding from the French led to a significant post-1908 expansion of railways and transportation infrastructure, particularly in its western border regions. Since Germany and Austria-Hungary relied on faster mobilisation to compensate for their numerical inferiority compared to
Russia, the threat posed by the closing of this gap was more important than competing with the Royal Navy. After Germany expanded its standing army by 170,000 troops in 1913, France extended compulsory military service from two to three years; similar measures were taken by the
Balkan powers and Italy, which led to increased expenditure by the
Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
and Austria-Hungary. Absolute figures are hard to calculate due to differences in categorising expenditure, since they often omit civilian infrastructure projects like railways which also had logistical importance and military use. It is known, however, that from 1908 to 1913, military spending by the six major European powers increased by over 50% in real terms.
Conflicts in the Balkans

The years before 1914 were marked by a series of crises in the Balkans as other powers sought to benefit from Ottoman decline. While
Pan-Slavic and
Orthodox Russia considered itself the protector of
Serbia and other
Slav states, they preferred the strategically vital
Bosporus straits to be controlled by a weak Ottoman government, rather than an ambitious Slav power like
Bulgaria. Since Russia had its own ambitions in northeastern
Anatolia and their clients had over-lapping claims in the Balkans, balancing these divided Russian policy-makers and added to regional instability.
Austrian statesmen viewed the Balkans as essential for the continued existence of their Empire, and saw Serbian expansion as a direct threat. The 1908–1909
Bosnian Crisis began when Austria annexed the former Ottoman territory of
Bosnia and Herzegovina, which it
had occupied since 1878. Timed to coincide with the
Bulgarian Declaration of Independence
The ''de jure'' independence of Bulgaria ( bg, Независимост на България, ''Nezavisimost na Bǎlgariya'') from the Ottoman Empire was proclaimed on in the old capital of Tarnovo by Prince Ferdinand of Bulgaria, who afte ...
from the Ottoman Empire, this unilateral action was denounced by the European powers, but accepted as there was no consensus on how to resolve the situation. Some historians see this as a significant escalation, ending any chance of Austria co-operating with Russia in the Balkans while also damaging diplomatic relations between Serbia and Italy, both of whom had their own expansionist ambitions in the region.
Tensions increased after the 1911–1912
Italo-Turkish War demonstrated Ottoman weakness and led to the formation of the
Balkan League, an alliance of Serbia, Bulgaria,
Montenegro, and
Greece. The League quickly overran most of the Ottomans' territory in the Balkans during the 1912–1913
First Balkan War, much to the surprise of outside observers. The Serbian capture of ports on the
Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
resulted in partial Austrian mobilisation starting on 21 November 1912, including units along the Russian border in
Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
. In a meeting the next day, the
Russian government
The Government of Russia exercises executive power in the Russian Federation. The members of the government are the prime minister, the deputy prime ministers, and the federal ministers. It has its legal basis in the Constitution of the Russia ...
decided not to mobilise in response, unwilling to precipitate a war for which they were not as of yet prepared to handle.
The Great Powers sought to re-assert control through the 1913
Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
, which created an independent
Albania, while enlarging the territories of Bulgaria, Serbia, Montenegro and Greece. However, disputes between the victors sparked the 33-day
Second Balkan War, when Bulgaria attacked Serbia and Greece on 16 June 1913; it was defeated, losing most of
Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
to Serbia and Greece, and
Southern Dobruja to Romania. The result was that even countries which benefited from the Balkan Wars, such as Serbia and Greece, felt cheated of their "rightful gains", while for Austria it demonstrated the apparent indifference with which other powers viewed their concerns, including Germany. This complex mix of resentment, nationalism and insecurity helps explain why the pre-1914 Balkans became known as the "
powder keg of Europe
The powder keg of Europe or Balkan powder keg was the Balkans in the early part of the 20th century preceding World War I. There were many overlapping claims to territories and spheres of influence between the major European powers such as the ...
".
Prelude
Sarajevo assassination

On 28 June 1914,
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
F ...
, heir presumptive to Emperor
Franz Joseph, visited
Sarajevo, capital of the recently annexed provinces of
Bosnia and Herzegovina. Six assassins from the movement known as
Young Bosnia, or ''Mlada Bosna'', took up positions along the route taken by the Archduke's motorcade, with the intention of assassinating him. Supplied with arms by extremists within the Serbian
Black Hand
Black Hand or The Black Hand may refer to:
Extortionists and underground groups
* Black Hand (anarchism) (''La Mano Negra''), a presumed secret, anarchist organization based in the Andalusian region of Spain during the early 1880s
* Black Hand ...
intelligence organisation, they hoped his death would free Bosnia from Austrian rule, although there was little agreement on what would replace it.
Nedeljko Čabrinović threw a
grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade genera ...
at the Archduke's car and injured two of his aides, who were taken to hospital while the convoy carried on. The other assassins were also unsuccessful but an hour later, as Ferdinand was returning from visiting the injured officers, his car took a wrong turn into a street where
Gavrilo Princip was standing. He stepped forward and fired two pistol shots, fatally wounding Ferdinand and his wife
Sophie
Sophie is a version of the female given name Sophia, meaning "wise".
People with the name Born in the Middle Ages
* Sophie, Countess of Bar (c. 1004 or 1018–1093), sovereign Countess of Bar and lady of Mousson
* Sophie of Thuringia, Duchess o ...
, who both died shortly thereafter. Although Emperor Franz Joseph was shocked by the incident, political and personal differences meant the two men were not close; allegedly, his first reported comment was "A higher power has re-established the order which I, alas, could not preserve".
According to historian
Zbyněk Zeman
Zbyněk Anthony Bohuslav Zeman (18 October 1928 – 22 June 2011) was a Czech historian who later became a naturalized British citizen. He published widely on the history of Central and Eastern Europe in the 20th century. As an academic, he taugh ...
, his reaction was reflected more broadly in
Vienna, where "the event almost failed to make any impression whatsoever. On 28 and 29 June, the crowds listened to music and drank wine, as if nothing had happened." Nevertheless, the impact of the murder of the heir to the throne was significant, and has been described by historian
Christopher Clark
Sir Christopher Munro Clark (born 14 March 1960) is an Australian historian living in the United Kingdom and Germany. He is the twenty-second Regius Professor of History at the University of Cambridge. In 2015, he was knighted for his servi ...
as a "
9/11 effect, a terrorist event charged with historic meaning, transforming the political chemistry in Vienna".
Expansion of violence in Bosnia and Herzegovina

The Austro-Hungarian authorities encouraged the subsequent
anti-Serb riots in Sarajevo
The anti-Serb riots in Sarajevo consisted of large-scale anti-Serb violence in Sarajevo on 28 and 29 June 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. Encouraged by the Austro-Hungarian government, the violent demonstrations ass ...
, in which
Bosnian Croats
The Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina (), often referred to as Bosnian Croats () or Herzegovinian Croats () are the third most populous ethnic group in the country after Bosniaks and Serbs, and are one of the constitutive nations of Bosnia and ...
and
Bosniaks
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry ...
killed two
Bosnian Serbs
The Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sr-Cyrl, Срби у Босни и Херцеговини, Srbi u Bosni i Hercegovini) are one of the three constitutive nations (state-forming nations) of the country, predominantly residing in the politi ...
and damaged numerous Serb-owned buildings.
Violent actions against ethnic Serbs were also organised outside Sarajevo, in other cities in Austro-Hungarian-controlled Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia. Austro-Hungarian authorities in Bosnia and Herzegovina imprisoned and extradited approximately 5,500 prominent Serbs, 700 to 2,200 of whom died in prison. A further 460 Serbs were sentenced to death. A predominantly Bosniak special militia known as the ''
Schutzkorps'' was established and carried out the persecution of Serbs.
July Crisis
The assassination initiated the
July Crisis, a month of diplomatic manoeuvring between Austria-Hungary, Germany, Russia, France and Britain. Believing Serbian intelligence helped organise Franz Ferdinand's murder, Austrian officials wanted to use the opportunity to end their interference in Bosnia and saw war as the best way of achieving this. However, the
Foreign Ministry had no solid proof of Serbian involvement and a dossier used to make its case contained multiple errors. On 23July, Austria delivered an
ultimatum to Serbia, listing ten demands made intentionally unacceptable to provide an excuse for starting hostilities.

Serbia ordered general mobilisation on 25July, but accepted all the terms, except for those empowering Austrian representatives to suppress "subversive elements" inside Serbia, and take part in the investigation and trial of Serbians linked to the assassination. Claiming this amounted to rejection, Austria broke off diplomatic relations and ordered partial mobilisation the next day; on 28 July, they declared war on Serbia and began shelling
Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
. Having initiated war preparations on 25 July, Russia now ordered general mobilisation in support of Serbia on 30th.
Anxious to ensure backing from the
SPD political opposition by presenting Russia as the aggressor, German Chancellor Bethmann Hollweg delayed commencement of war preparations until 31 July. That afternoon the Russian government were handed a note requiring them to "cease all war measures against Germany and Austria-Hungary" within 12 hours. A further German demand for neutrality was refused by the French who ordered general mobilisation but delayed declaring war. The
German General Staff had long assumed they faced a war on two fronts; the
Schlieffen Plan envisaged using 80% of the army to defeat France in the west, then switch to Russia. Since this required them to move quickly, mobilisation orders were issued that afternoon.

At a meeting on 29 July, the British cabinet had narrowly decided its obligations to Belgium under the 1839
Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
did not require it to oppose a German invasion with military force. However, this was largely driven by Prime Minister
Asquith's desire to maintain unity; he and his senior Cabinet ministers were already committed to support France, the Royal Navy had been mobilised and public opinion was strongly in favour of intervention. On 31 July, Britain sent notes to Germany and France, asking them to respect Belgian neutrality; France pledged to do so, Germany did not reply.
Once the German ultimatum to Russia expired on the morning of 1 August, the two countries were at war. Later the same day, Wilhelm was informed by his ambassador in London,
Prince Lichnowsky
The House of Lichnowsky or House of Lichnovský is the name of an influential Czech aristocratic family of Silesian and Moravian origin, documented since the 14th century.
History
The noble family first appeared in the Duchy of Pless (Pszczyn ...
, that Britain would remain neutral if France was not attacked, and might not intervene at all given the ongoing
Home Rule Crisis in
Ireland. Jubilant at this news, he ordered General
Moltke, the German chief of staff, to "march the whole of the... army to the East". This allegedly brought Moltke to the verge of a nervous breakdown, before Lichnowsky realised he was mistaken. Once Wilhelm received a telegram from
George V, it confirmed there had been a misunderstanding, and he told Moltke, "Now do what you want."
Aware of German plans to attack through Belgium, French Commander-in-Chief
Joseph Joffre asked his government for permission to cross the border and pre-empt such a move. To avoid a violation of Belgian neutrality, he was told any advance could come only after a German invasion. On 2 August,
Germany occupied Luxembourg and exchanged fire with French units; on 3August, they declared war on France and demanded free passage across Belgium, which was refused. Early on the morning of 4August, the Germans invaded and
Albert I of Belgium
Albert I (8 April 1875 – 17 February 1934) was King of the Belgians from 23 December 1909 until his death in 1934.
Born in Brussels as the fifth child and second son of Prince Philippe, Count of Flanders and Princess Marie of Hohenzollern-S ...
called for assistance under the
Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
. Britain sent Germany an ultimatum demanding they withdraw from Belgium; when this expired at midnight without a response, the two empires were at war.
Progress of the war
Opening hostilities
Confusion among the Central Powers
The strategy of the Central Powers suffered from miscommunication. Germany had promised to support Austria-Hungary's invasion of Serbia, but interpretations of what this meant differed. Previously tested deployment plans had been replaced early in 1914, but those had never been tested in exercises. Austro-Hungarian leaders believed Germany would cover its northern flank against Russia.
Serbian campaign

Beginning on 12 August, the Austrian and Serbs clashed at the battles of the
Cer
Cer, or CER may refer to:
Environment
* Certified Emission Reduction, emission units
Statistics
* Control event rate, a statistical value in epidemiology
* Crossover error rate, a statistical value in a biometric system
Information Technology
...
and
Kolubara; over the next two weeks, Austrian attacks were repulsed with heavy losses, dashing their hopes of a swift victory and marking the first major Allied victories of the war. As a result, Austria had to keep sizeable forces on the Serbian front, weakening its efforts against Russia. Serbia's defeat of the 1914 invasion has been called one of the major upset victories of the twentieth century. In spring 1915, the campaign saw the first use of
anti-aircraft warfare after an Austrian plane was shot down with
ground-to-air fire, as well as the first
medical evacuation
Medical evacuation, often shortened to medevac or medivac, is the timely and efficient movement and en route care provided by medical personnel to wounded being evacuated from a battlefield, to injured patients being evacuated from the scene of a ...
by the Serbian army in autumn 1915.
German offensive in Belgium and France

Upon mobilisation in 1914, 80% of the
German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
was located on the Western Front, with the remainder acting as a screening force in the East; officially titled ''Aufmarsch II West,'' it is better known as the
Schlieffen Plan after its creator,
Alfred von Schlieffen, head of the
German General Staff from 1891 to 1906. Rather than a direct attack across their shared frontier, the German right wing would sweep through the
Netherlands and
Belgium, then swing south, encircling Paris and trapping the French army against the Swiss border. Schlieffen estimated this would take six weeks, after which the German army would transfer to the East and defeat the Russians.
The plan was substantially modified by his successor,
Helmuth von Moltke the Younger. Under Schlieffen, 85% of German forces in the west were assigned to the right wing, with the remainder holding along the frontier. By keeping his left wing deliberately weak, he hoped to lure the French into an offensive into the "lost provinces" of
Alsace-Lorraine, which was in fact the strategy envisaged by their
Plan XVII. However, Moltke grew concerned the French might push too hard on his left flank and as the German Army increased in size from 1908 to 1914, he changed the allocation of forces between the two wings from 85:15 to 70:30. He also considered Dutch neutrality essential for German trade and cancelled the incursion into the Netherlands, which meant any delays in Belgium threatened the entire viability of the plan. Historian
Richard Holmes argues these changes meant the right wing was not strong enough to achieve decisive success and thus led to unrealistic goals and timings.

The initial German advance in the West was very successful and by the end of August the Allied left, which included the
British Expeditionary Force (BEF), was in
full retreat. At the same time, the French offensive in Alsace-Lorraine was a disastrous failure, with casualties exceeding 260,000, including 27,000 killed on 22 August during the
Battle of the Frontiers. German planning provided broad strategic instructions, while allowing army commanders considerable freedom in carrying them out at the front; this worked well in 1866 and 1870 but in 1914,
von Kluck used this freedom to disobey orders, opening a gap between the German armies as they closed on Paris.
In 1911, the Russian
Stavka
The ''Stavka'' (Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка) is a name of the high command of the armed forces formerly in the Russian Empire, Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine.
In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrative staff, a ...
had agreed with the French to attack Germany within fifteen days of mobilisation, ten days before the Germans had anticipated, although it meant the two Russian armies that entered
East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
on 17 August did so without many of their support elements.
By the end of 1914, German troops held strong defensive positions inside France, controlled the bulk of France's domestic coalfields and had inflicted 230,000 more casualties than it lost itself. However, communications problems and questionable command decisions cost Germany the chance of a decisive outcome, while it had failed to achieve the primary objective of avoiding a long, two-front war. As was apparent to a number of German leaders, this amounted to a strategic defeat; shortly after the Marne,
Crown Prince Wilhelm told an American reporter; "We have lost the war. It will go on for a long time but lost it is already."
Asia and the Pacific

On 30 August 1914, New Zealand
occupied German Samoa, now the independent state of
Samoa. On 11 September, the
Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force
The Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force (AN&MEF) was a small volunteer force of approximately 2,000 men, raised in Australia shortly after the outbreak of World War I to seize and destroy German wireless stations in German New Guin ...
landed on the island of
New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dam ...
, then part of
German New Guinea. On 28 October, the German cruiser sank the
Russian cruiser ''Zhemchug'' in the
Battle of Penang. Japan declared war on Germany prior to seizing territories in the Pacific which later became the
South Seas Mandate
The South Seas Mandate, officially the Mandate for the German Possessions in the Pacific Ocean Lying North of the Equator, was a League of Nations mandate in the "South Seas" given to the Empire of Japan by the League of Nations following Wo ...
, as well as German
Treaty ports on the Chinese
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
peninsula at
Tsingtao. After Vienna refused to withdraw its cruiser from Tsingtao, Japan declared war on Austria-Hungary as well, and the ship was sunk at Tsingtao in November 1914. Within a few months, Allied forces had seized all German territories in the Pacific, leaving only isolated commerce raiders and a few holdouts in New Guinea.
African campaigns
Some of the first clashes of the war involved British, French, and German colonial forces in Africa. On 6–7 August, French and British troops invaded the German protectorate of
Togoland and
Kamerun. On 10 August, German forces in
South-West Africa
South West Africa ( af, Suidwes-Afrika; german: Südwestafrika; nl, Zuidwest-Afrika) was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1990, after which it became modern-day Namibia. It bordered Angola (Portuguese colony before 1 ...
attacked South Africa; sporadic and fierce fighting continued for the rest of the war. The German colonial forces in
German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
, led by Colonel
Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck, fought a
guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or Irregular military, irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, Raid (military), raids ...
campaign during World WarI and only surrendered two weeks after the armistice took effect in Europe.
Indian support for the Allies
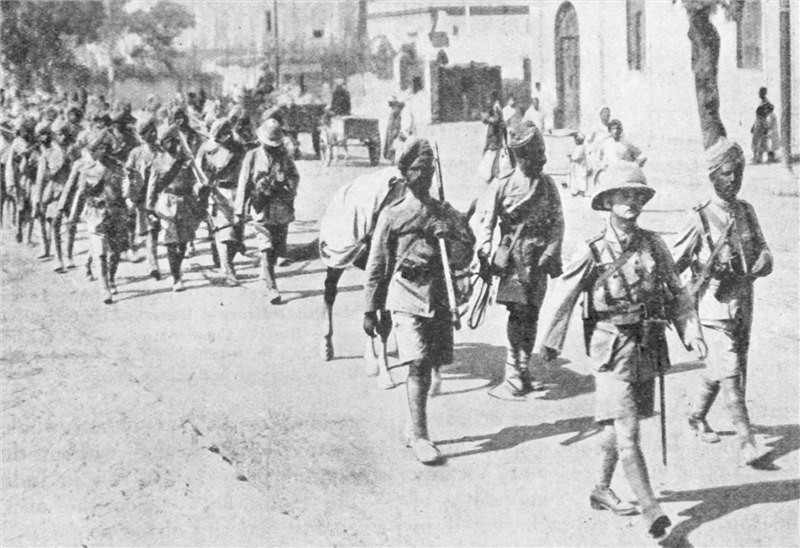

Prior to the war, Germany had attempted to use Indian nationalism and pan-Islamism to its advantage, a policy continued post-1914 by
instigating uprisings in India, while the
Niedermayer–Hentig Expedition
The Niedermayer–Hentig Expedition, also known as the Kabul Mission, was a diplomatic mission to Afghanistan sent by the Central Powers in 1915–1916. The purpose was to encourage Afghanistan to declare full independence from the British Emp ...
urged Afghanistan to join the war on the side of Central Powers. However, contrary to British fears of a revolt in India, the outbreak of the war saw a reduction in nationalist activity. This was largely because leaders from the
Indian National Congress and other groups believed support for the British war effort would hasten
Indian Home Rule, a promise allegedly made explicit in 1917 by
Edwin Montagu, the
Secretary of State for India.
In 1914, the
British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
was larger than the British Army itself, and between 1914 and 1918 an estimated 1.3 million Indian soldiers and labourers served in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, while the
Government of India and their
princely allies supplied large quantities of food, money, and ammunition. In all, 140,000 soldiers served on the Western Front and nearly 700,000 in the Middle East, with 47,746 killed and 65,126 wounded.
The suffering engendered by the war, as well as the failure of the British government to grant self-government to India after the end of hostilities, bred disillusionment and resulted in
the campaign for full independence led by
Mahatma Gandhi.
Western Front 1914 to 1916
Trench warfare begins

Pre-war military tactics that emphasised open warfare and the individual rifleman proved obsolete when confronted with conditions prevailing in 1914. Technological advances allowed the creation of strong defensive systems largely impervious to massed infantry advances, such as
barbed wire
A close-up view of a barbed wire
Roll of modern agricultural barbed wire
Barbed wire, also known as barb wire, is a type of steel fencing wire constructed with sharp edges or points arranged at intervals along the strands. Its primary use is t ...
,
machine guns and above all far more powerful
artillery, which dominated the battlefield and made crossing open ground extremely difficult. Both sides struggled to develop tactics for breaching entrenched positions without suffering heavy casualties. In time, however, technology enabled the production of new offensive weapons, such as
gas warfare and the
tank.
After the
First Battle of the Marne in September 1914, Allied and German forces unsuccessfully tried to outflank each other, a series of manoeuvres later known as the "
Race to the Sea". By the end of 1914, the opposing forces confronted each other along an uninterrupted line of entrenched positions from the
Channel to the Swiss border. Since the Germans were normally able to choose where to stand, they generally held the high ground, while their trenches tended to be better built; those constructed by the French and English were initially considered "temporary", only needed until an offensive would smash the German defences. Both sides tried to break the stalemate using scientific and technological advances. On 22 April 1915, at the
Second Battle of Ypres, the Germans (violating the
Hague Convention) used
chlorine gas for the first time on the Western Front. Several types of gas soon became widely used by both sides, and though it never proved a decisive, battle-winning weapon, it became one of the most-feared and best-remembered horrors of the war.
Continuation of trench warfare

In February 1916 the Germans attacked French defensive positions at the
Battle of Verdun, lasting until December 1916. The Germans made initial gains, before French counter-attacks returned matters to near their starting point. Casualties were greater for the French, but the Germans bled heavily as well, with anywhere from 700,000 to 975,000 casualties suffered between the two combatants. Verdun became a symbol of French determination and self-sacrifice.
The
Battle of the Somme
The Battle of the Somme ( French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place bet ...
was an Anglo-French offensive of July to November 1916. The
opening day
Opening Day is the day on which professional baseball leagues begin their regular season. For Major League Baseball (MLB) and most of the American minor leagues, this day typically falls during the first week of April, although in recent years ...
on 1 July 1916 was the bloodiest single day in the history of the
British Army, which suffered 57,470 casualties, including 19,240 dead. As a whole, the Somme offensive led to an estimated 420,000 British casualties, along with 200,000 French and 500,000 German. Gun fire was not the only factor taking lives; the diseases that emerged in the trenches were a major killer on both sides. The living conditions made it so that countless diseases and infections occurred, such as
trench foot,
shell shock, blindness/burns from
mustard gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
,
lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result o ...
,
trench fever, "
cooties" (
body lice) and the '
Spanish flu'.
Naval war

At the start of the war, German
cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hu ...
s were scattered across the globe, some of which were subsequently used to attack Allied
merchant shipping. These were systematically hunted down by the Royal Navy, although not before causing considerable damage. One of the most successful was the , part of the German
East Asia Squadron stationed at Qingdao, which seized or sank 15 merchantmen, as well as a Russian cruiser and a French destroyer. Most of the squadron was returning to Germany when it sank two British armoured cruisers at the
Battle of Coronel in November 1914, before being virtually destroyed at the
Battle of the Falkland Islands in December. The
SMS Dresden escaped with a few auxiliaries, but after the
Battle of Más a Tierra, these too were either destroyed or interned.
Soon after the outbreak of hostilities, Britain began a naval
blockade of Germany
The Blockade of Germany, or the Blockade of Europe, occurred from 1914 to 1919. The prolonged naval blockade was conducted by the Allies of World War I, Allies during and after World War I in an effort to restrict the maritime supply of goods t ...
. This proved effective in cutting off vital military and civilian supplies, although it violated accepted international law codified by several international agreements of the past two centuries. Britain also mined international waters which closed off entire sections of ocean, even to neutral ships. Since there was limited response to this tactic of the British, Germany expected a similar response to its unrestricted submarine warfare.
The
Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland (german: Skagerrakschlacht, the Battle of the Skagerrak) was a naval battle fought between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy ...
in May/June 1916 was the only full-scale clash of battleships during the war, and one of the largest in history. The clash was indecisive, although the Germans inflicted more damage than they received, since thereafter the bulk of the German
High Seas Fleet was confined to port for the duration of the war.

German
U-boats attempted to cut the supply lines between North America and Britain.
The nature of
submarine warfare
Submarine warfare is one of the four divisions of underwater warfare, the others being anti-submarine warfare, mine warfare and mine countermeasures.
Submarine warfare consists primarily of diesel and nuclear submarines using torpedoes, missi ...
meant that attacks often came without warning, giving the crews of the merchant ships little hope of survival.
The
United States launched a protest, and Germany changed its rules of engagement. After the sinking of the passenger ship
RMS ''Lusitania'' in 1915, Germany promised not to target passenger liners, while Britain armed its merchant ships, placing them beyond the protection of the "
cruiser rules
Cruiser rules is a colloquial phrase referring to the conventions regarding the attacking of a merchant ship by an armed vessel. Here ''cruiser'' is meant in its original meaning of a ship sent on an independent mission such as commerce raiding ...
", which demanded warning and movement of crews to "a place of safety" (a standard that lifeboats did not meet). Finally, in early 1917, Germany adopted a policy of
unrestricted submarine warfare, realising the Americans would eventually enter the war.
Germany sought to strangle Allied
sea lanes before the United States could transport a large army overseas, but after initial successes eventually failed to do so.
The U-boat threat lessened in 1917, when merchant ships began travelling in
convoys, escorted by
destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s. This tactic made it difficult for U-boats to find targets, which significantly lessened losses; after the
hydrophone and
depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive Shock factor, hydraulic shock. Most depth ...
s were introduced, accompanying destroyers could attack a submerged submarine with some hope of success. Convoys slowed the flow of supplies since ships had to wait as convoys were assembled. The solution to the delays was an extensive program of building new freighters. Troopships were too fast for the submarines and did not travel the North Atlantic in convoys. The U-boats had sunk more than 5,000 Allied ships, at a cost of 199 submarines.
World War I also saw the first use of
aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
s in combat, with launching
Sopwith Camels in a successful raid against the
Zeppelin hangars at
Tondern in July 1918, as well as
blimps for antisubmarine patrol.
Southern theatres
War in the Balkans


Faced with Russia in the east, Austria-Hungary could spare only one-third of its army to attack Serbia. After suffering heavy losses, the Austrians briefly occupied the Serbian capital,
Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
. A Serbian counter-attack in the Battle of Kolubara succeeded in driving them from the country by the end of 1914. For the first ten months of 1915, Austria-Hungary used most of its military reserves to fight
Italy. German and Austro-Hungarian diplomats, however, scored a coup by persuading Bulgaria to join the attack on Serbia. The Austro-Hungarian provinces of
Slovenia, Croatia and
Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
provided troops for Austria-Hungary in the fight with Serbia, Russia and Italy. Montenegro allied itself with Serbia.
Bulgaria declared war on Serbia on 14 October 1915 and joined in the attack by the Austro-Hungarian army under Mackensen's army of 250,000 that was already underway. Serbia was conquered in a little more than a month, as the Central Powers, now including Bulgaria, sent in 600,000 troops total. The Serbian army, fighting on two fronts and facing certain defeat, retreated into northern
Albania. The Serbs suffered defeat in the
Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo ( tr, Kosova Savaşı; sr, Косовска битка) took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan ...
. Montenegro covered the Serbian retreat towards the Adriatic coast in the
Battle of Mojkovac in 6–7 January 1916, but ultimately the Austrians also conquered Montenegro. The surviving Serbian soldiers were evacuated by ship to Greece. After conquest, Serbia was divided between Austro-Hungary and Bulgaria.
In late 1915, a Franco-British force landed at
Salonica in Greece to offer assistance and to pressure its government to declare war against the Central Powers. However, the pro-German
King Constantine I dismissed the pro-Allied government of
Eleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos ( el, Ελευθέριος Κυριάκου Βενιζέλος, translit=Elefthérios Kyriákou Venizélos, ; – 18 March 1936) was a Greek statesman and a prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movem ...
before the Allied expeditionary force arrived.
The Macedonian front was initially mostly static. French and Serbian forces retook limited areas of Macedonia by recapturing
Bitola
Bitola (; mk, Битола ) is a city in the southwestern part of North Macedonia. It is located in the southern part of the Pelagonia valley, surrounded by the Baba, Nidže, and Kajmakčalan mountain ranges, north of the Medžitlija-Níki ...
on 19 November 1916 following the costly
Monastir offensive, which brought stabilisation of the front.

Serbian and French troops finally made a breakthrough in September 1918 in the
Vardar offensive, after most of the German and Austro-Hungarian troops had been withdrawn. The Bulgarians were defeated at the
Battle of Dobro Pole
The Battle of Dobro Pole ( sr, Битка код Доброг Поља, Bitka kod Dobrog Polja; gr, Μάχη του Ντόμπρο Πόλε, Máchi tou Dóbro Póle), also known as the Breakthrough at Dobro Pole ( bg, Пробив при До� ...
, and by 25 September British and French troops had crossed the border into Bulgaria proper as the Bulgarian army collapsed. Bulgaria capitulated four days later, on 29 September 1918. The German high command responded by despatching troops to hold the line, but these forces were far too weak to re-establish a front.
The disappearance of the Macedonian front meant that the road to
Budapest and Vienna was now opened to Allied forces. Hindenburg and Ludendorff concluded that the strategic and operational balance had now shifted decidedly against the
Central Powers and, a day after the Bulgarian collapse, insisted on an immediate peace settlement.
Ottoman Empire

The Ottomans threatened Russia's
Caucasian
Caucasian may refer to:
Anthropology
*Anything from the Caucasus region
**
**
** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Caucasus region
*
*
*
Languages
* Northwest Caucasian l ...
territories and Britain's communications with India via the
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
. As the conflict progressed, the Ottoman Empire took advantage of the European powers' preoccupation with the war and conducted large-scale ethnic cleansing of the indigenous
Armenian,
Greek, and
Assyrian Christian populations, known as the
Armenian genocide,
Greek genocide, and
Sayfo respectively.
The British and French opened overseas fronts with the
Gallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula (; tr, Gelibolu Yarımadası; grc, Χερσόνησος της Καλλίπολης, ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles ...
(1915) and
Mesopotamian campaigns (1914). In Gallipoli, the Ottoman Empire successfully repelled the British, French, and
Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZACs). In
Mesopotamia, by contrast, after the defeat of the British defenders in the
siege of Kut by the Ottomans (1915–16), British Imperial forces reorganised and captured
Baghdad in March 1917. The British were aided in Mesopotamia by local Arab and Assyrian fighters, while the Ottomans employed local
Kurdish and
Turcoman tribes.
Further to the west, the
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
was defended from Ottoman attacks in 1915 and 1916; in August, a German and Ottoman force was defeated at the
Battle of Romani by the
ANZAC Mounted Division and the
52nd (Lowland) Infantry Division
The 52nd (Lowland) Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army that was originally formed as the Lowland Division, in 1908 as part of the Territorial Force. It later became the 52nd (Lowland) Division in 1915. The 52nd (Low ...
. Following this victory, an
Egyptian Expeditionary Force advanced across the
Sinai Peninsula, pushing Ottoman forces back in the
Battle of Magdhaba in December and the
Battle of Rafa on the border between the Egyptian
Sinai and Ottoman Palestine in January 1917.

Russian armies generally had success in the
Caucasus campaign.
Enver Pasha
İsmail Enver, better known as Enver Pasha ( ota, اسماعیل انور پاشا; tr, İsmail Enver Paşa; 22 November 1881 – 4 August 1922) was an Ottoman military officer, revolutionary, and convicted war criminal who formed one-third ...
, supreme commander of the Ottoman armed forces, was ambitious and dreamed of re-conquering central Asia and areas that had been lost to Russia previously. He was, however, a poor commander. He launched an offensive against the Russians in the Caucasus in December 1914 with 100,000 troops, insisting on a frontal attack against mountainous Russian positions in winter. He lost 86% of his force at the
Battle of Sarikamish
The Battle of Sarikamish (''Sarighamishi chakatamart''), russian: Сражение при Сарыкамыше; tr, Sarıkamış Harekatı, lit=''Operation Sarıkamış'' was an engagement between the Russian and Ottoman empires during World W ...
.

The Ottoman Empire, with German support, invaded Persia (modern
Iran) in December 1914 in an effort to cut off British and Russian access to
petroleum reservoir
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence ...
s around
Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world a ...
near the
Caspian Sea. Persia, ostensibly neutral, had long been under the spheres of British and Russian influence. The Ottomans and Germans were aided by
Kurdish and
Azeri forces, together with a large number of major Iranian tribes, such as the
Qashqai,
Tangistanis,
Lurs
Lurs () are an Iranian people living in the mountains of western Iran. The four Luri branches are the Bakhtiari, Mamasani, Kohgiluyeh and Lur proper, who are principally linked by the Luri language.
Lorestan Province is named after the Lu ...
, and
Khamseh, while the Russians and British had the support of Armenian and Assyrian forces. The
Persian campaign was to last until 1918 and end in failure for the Ottomans and their allies. However, the Russian withdrawal from the war in 1917 led to Armenian and Assyrian forces, who had hitherto inflicted a series of defeats upon the forces of the Ottomans and their allies, being cut off from supply lines, outnumbered, outgunned and isolated, forcing them to fight and flee towards British lines in northern Mesopotamia.
General
Yudenich
Nikolai Nikolayevich Yudenich ( – 5 October 1933) was a commander of the Russian Imperial Army during World War I. He was a leader of the anti-communist White movement in Northwestern Russia during the Civil War.
Biography
Early life
Yuden ...
, the Russian commander from 1915 to 1916, drove the Turks out of most of the southern
Caucasus with a string of victories.
The
Arab Revolt, instigated by the Arab bureau of the British
Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* Unit ...
, started June 1916 with the
Battle of Mecca, led by
Sharif Hussein of
Mecca, and ended with the Ottoman surrender of Damascus.
Fakhri Pasha, the Ottoman commander of
Medina, resisted for more than two and half years during the
siege of Medina before surrendering in January 1919.
The
Senussi
The Senusiyya, Senussi or Sanusi ( ar, السنوسية ''as-Sanūssiyya'') are a Muslim political-religious tariqa (Sufi order) and clan in colonial Libya and the Sudan region founded in Mecca in 1837 by the Grand Senussi ( ar, السنوسي ...
tribe, along the border of
Italian Libya and
British Egypt, incited and armed by the Turks, waged a small-scale
guerrilla war against Allied troops. The British were forced to dispatch 12,000 troops to oppose them in the
Senussi campaign. Their rebellion was finally crushed in mid-1916.
Total Allied casualties on the Ottoman fronts amounted 650,000 men. Total Ottoman casualties were 725,000, with 325,000 dead and 400,000 wounded.
Italian Front

Although Italy joined the Triple Alliance in 1882, a treaty with its traditional Austrian enemy was so controversial that subsequent governments denied its existence and the terms were only made public in 1915. This arose from
nationalist designs on Austro-Hungarian territory in
Trentino, the
Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
,
Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
and
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
, which were considered vital to secure the borders established in
1866
Events January–March
* January 1
** Fisk University, a historically black university, is established in Nashville, Tennessee.
** The last issue of the abolitionist magazine '' The Liberator'' is published.
* January 6 – Ottoman tr ...
. In 1902, Rome secretly agreed with France to remain neutral if the latter was attacked by Germany, effectively nullifying its role in the Triple Alliance.
When the war began in 1914, Italy argued the Triple Alliance was defensive in nature and it was not obliged to support an Austrian attack on Serbia. Opposition to joining the Central Powers increased when Turkey became a member in September, since in
1911
A notable ongoing event was the Comparison of the Amundsen and Scott Expeditions, race for the South Pole.
Events January
* January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory ...
Italy had occupied Ottoman possessions in
Libya and the
Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. ...
islands. To secure Italian neutrality, the Central Powers offered them the
French protectorate of Tunisia
The French protectorate of Tunisia (french: Protectorat français de Tunisie; ar, الحماية الفرنسية في تونس '), commonly referred to as simply French Tunisia, was established in 1881, during the French colonial Empire era, ...
, while in return for an immediate entry into the war, the Allies agreed to their demands for Austrian territory and sovereignty over the Dodecanese. Although they remained secret, these provisions were incorporated into the April 1915
Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
; Italy joined the Triple Entente and on 23 May declared war on Austria-Hungary, followed by Germany fifteen months later.

The pre-1914 Italian army was the weakest in Europe, short of officers, trained men, adequate transport and modern weapons; by April 1915, some of these deficiencies had been remedied but it was still unprepared for the major offensive required by the Treaty of London. The advantage of superior numbers was offset by the difficult terrain; much of the fighting took place at altitudes of over 3000 metres in the
Alps and
Dolomites, where trench lines had to be cut through rock and ice and keeping troops supplied was a major challenge. These issues were exacerbated by unimaginative strategies and tactics. Between 1915 and 1917, the Italian commander,
Luigi Cadorna, undertook
a series of frontal assaults along the Isonzo which made little progress and cost many lives; by the end of the war, total Italian combat deaths totalled around 548,000.
In the spring of 1916, the Austro-Hungarians counterattacked in
Asiago in the ''
Strafexpedition
The Battle of Asiago (Battle of the Plateaux) or the Südtirol Offensive (in Italian: Battaglia degli Altipiani), nicknamed ''Strafexpedition'' (" Punitive expedition") by the Italians, was a major counteroffensive launched by the Austro-Hunga ...
'', but made little progress and were pushed by the Italians back to the Tyrol. Although an Italian corps occupied southern
Albania in May 1916, their main focus was the Isonzo front which after the
capture of Gorizia in August 1916 remained static until October 1917. After a combined Austro-German force won a major victory at
Caporetto, Cadorna was replaced by
Armando Diaz who retreated more than before holding positions along the
Piave River. A second Austrian
offensive was repulsed in June 1918 and by October it was clear the Central Powers had lost the war. On 24 October, Diaz launched the
Battle of Vittorio Veneto and initially met stubborn resistance, but with Austria-Hungary collapsing, Hungarian divisions in Italy now demanded they be sent home. When this was granted, many others followed and the Imperial army disintegrated, the Italians taking over 300,000 prisoners. On 3November, the
Armistice of Villa Giusti ended hostilities between Austria-Hungary and Italy which occupied
Trieste and areas along the
Adriatic Sea awarded to it in 1915.
Romanian participation
Despite secretly agreeing to support the Triple Alliance in 1883, Romania increasingly found itself at odds with the Central Powers over their support for Bulgaria in the 1912 to 1913 Balkan Wars and the status of ethnic Romanian communities in
Hungarian-controlled
Transylvania, which comprised an estimated 2.8 million of the 5.0 million population. With the ruling elite split into pro-German and pro-Entente factions, Romania remained neutral in 1914, arguing like Italy that because Austria-Hungary had declared war on Serbia, it was under no obligation to join them. They maintained this position for the next two years, while allowing Germany and Austria to transport military supplies and advisors across Romanian territory.
In September 1914, Russia had acknowledged Romanian rights to Austro-Hungarian territories including Transylvania and
Banat, whose acquisition had widespread popular support, and Russian success against Austria led Romania to join the Entente in the August 1916 Treaty of Bucharest. Under the strategic plan known as
Hypothesis Z, the Romanian army planned an offensive into Transylvania, while defending Southern
Dobruja and
Giurgiu
Giurgiu (; bg, Гюргево) is a city in southern Romania. The seat of Giurgiu County, it lies in the historical region of Muntenia. It is situated amongst mud-flats and marshes on the left bank of the Danube facing the Bulgarian city ...
against a possible Bulgarian counterattack. On 27 August 1916, they
attacked Transylvania and occupied substantial parts of the province before being driven back by the recently formed
German 9th Army
The 9th Army (german: 9. Armee) was a World War II field army. It was activated on 15 May 1940 with General Johannes Blaskowitz in command.
History
1940
The 9th Army first saw service along the Siegfried Line during its involvement in the invas ...
, led by former Chief of Staff Falkenhayn. A combined German-Bulgarian-Turkish offensive captured Dobruja and Giurgiu, although the bulk of the Romanian army managed to escape encirclement and retreated to
Bucharest, which
surrendered
Surrender, in military terms, is the relinquishment of control over territory, combatants, fortifications, ships or armament to another power. A surrender may be accomplished peacefully or it may be the result of defeat in battle. A sovereign ...
to the Central Powers on 6 December 1916.
On 7 May 1918 Romania signed the
Treaty of Bucharest with the Central Powers, which recognised Romanian sovereignty over Bessarabia in return for ceding control of passes in the Carpathian Mountains to Austria-Hungary and granting oil concessions to Germany. Romania re-entered the war on 10 November 1918 on the side of the Allies and the Treaty of Bucharest was formally annulled by the Armistice of 11 November 1918.
Eastern Front
Initial actions

As previously agreed with France, Russian plans at the start of the war were to simultaneously advance into
Austrian Galicia and East Prussia as soon as possible. Although their
attack on Galicia was largely successful, and the invasions achieved their aim of forcing Germany to divert troops from the Western Front, the speed of mobilisation meant they did so without much of their heavy equipment and support functions. These weaknesses contributed to Russian defeats at
Tannenberg and the
Masurian Lakes in August and September 1914, forcing them to withdraw from East Prussia with heavy losses. By spring 1915, they had also retreated from Galicia, and the May 1915
Gorlice–Tarnów offensive then allowed the Central Powers to invade
Russian-occupied Poland.
Despite the successful June 1916
Brusilov offensive against the Austrians in eastern Galicia, shortages of supplies, heavy losses and command failures prevented the Russians from fully exploiting their victory. However, it was one of the most significant and impactful offensives of the war, diverting German resources from
Verdun, relieving Austro-Hungarian pressure on the Italians, and convincing Romania to enter the war on the side of the Allies on 27 August. It also fatally weakened both the Austrian and Russian armies, whose offensive capabilities were badly affected by their losses and increased the disillusionment with the war that ultimately led to the Russian revolutions.
Meanwhile, unrest grew in Russia as
the Tsar remained at the front, with the home front controlled by
Empress Alexandra. Her increasingly incompetent rule and food shortages in urban areas led to widespread protests and the murder of her favourite,
Grigori Rasputin
Grigori Yefimovich Rasputin (; rus, links=no, Григорий Ефимович Распутин ; – ) was a Russian mystic and self-proclaimed holy man who befriended the family of Nicholas II, the last Emperor of Russia, thus g ...
, at the end of 1916.
Central Powers peace overtures

On 12 December 1916, after ten brutal months of the
Battle of Verdun and a
successful offensive against Romania, Germany attempted to negotiate a peace with the Allies.
However, this attempt was rejected out of hand as a "duplicitous war ruse".
Soon after, US president
Woodrow Wilson attempted to intervene as a peacemaker, asking in a note for both sides to state their demands and start negotiations.
Lloyd George's War Cabinet considered the German offer to be a ploy to create divisions amongst the Allies. After initial outrage and much deliberation, they took Wilson's note as a separate effort, signalling that the United States was on the verge of entering the war against Germany following the "submarine outrages". While the Allies debated a response to Wilson's offer, the Germans chose to rebuff it in favour of "a direct exchange of views". Learning of the German response, the Allied governments were free to make clear demands in their response of 14 January. They sought restoration of damages, the evacuation of occupied territories, reparations for France, Russia and Romania, and a recognition of the principle of nationalities. This included the liberation of Italians, Slavs, Romanians, Czecho-Slovaks, and the creation of a "free and united Poland". On the question of security, the Allies sought guarantees that would prevent or limit future wars, complete with sanctions, as a condition of any peace settlement. The negotiations failed and the Entente powers rejected the German offer on the grounds that Germany had not put forward any specific proposals.
Final years of the war
Russian Revolution and withdrawal
By the end of 1916, Russian casualties totalled nearly five million killed, wounded or captured, with major urban areas affected by food shortages and high prices. In March 1917, Tsar Nicholas ordered the military to forcibly suppress a wave of strikes in
Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
but the troops refused to fire on the crowds. Revolutionaries set up the
Petrograd Soviet and fearing a left-wing takeover, the
State Duma
The State Duma (russian: Госуда́рственная ду́ма, r=Gosudárstvennaja dúma), commonly abbreviated in Russian as Gosduma ( rus, Госду́ма), is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Russia, while the upper house ...
forced Nicholas to abdicate and established the
Russian Provisional Government, which confirmed Russia's willingness to continue the war. However, the Petrograd Soviet refused to disband, creating
competing power centres and caused confusion and chaos, with frontline soldiers becoming increasingly demoralised and unwilling to fight on.
Following the Tsar's abdication,
Vladimir Lenin—with the help of the German government—was ushered by train from Switzerland into Russia on 16 April 1917. Discontent and the weaknesses of the Provisional Government led to a rise in the popularity of the Bolshevik Party, led by Lenin, which demanded an immediate end to the war. The Revolution of November was followed in December by an armistice and negotiations with Germany. At first, the Bolsheviks refused the German terms, but when German troops began marching across Ukraine unopposed, the new government acceded to the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk on 3March 1918. The treaty ceded vast territories, including Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, parts of Poland and Ukraine to the Central Powers.
With the
Russian Empire out of the war, Romania found itself alone on the Eastern Front and signed the
Treaty of Bucharest with the Central Powers in May 1918, ending the state of war between Romania and the
Central Powers. Under the terms of the treaty, Romania had to give territory to Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria, and lease its oil reserves to Germany. However, the terms also included the Central Powers recognition of the union of
Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
with Romania.
United States enters the war
The United States was a major supplier of war materiel to the Allies but remained neutral in 1914, in large part due to domestic opposition. The most significant factor in creating the support Wilson needed was the German submarine offensive, which not only cost American lives, but paralysed trade as ships were reluctant to put to sea.
On 6 April 1917, Congress
declared war on Germany as an "Associated Power" of the Allies. The
United States Navy sent a
battleship group to
Scapa Flow
Scapa Flow viewed from its eastern end in June 2009
Scapa Flow (; ) is a body of water in the Orkney Islands, Scotland, sheltered by the islands of Mainland, Graemsay, Burray,S. C. George, ''Jutland to Junkyard'', 1973. South Ronaldsay and ...
to join the Grand Fleet and provided convoy escorts. In April 1917, the
United States Army had fewer than 300,000 men, including
National Guard units, compared to British and French armies of 4.1 and 8.3 million respectively. The
Selective Service Act of 1917 drafted 2.8 million men, although training and equipping such numbers was a huge logistical challenge. By June 1918, over 667,000 members of the
American Expeditionary Forces (AEF), had been transported to France, a figure which reached 2 million by the end of November.
Despite his conviction Germany must be defeated, Wilson went to war to ensure the US played a leading role in shaping the peace, which meant preserving the AEF as a separate military force, rather than being absorbed into British or French units as his Allies wanted. He was strongly supported by AEF commander General
John J. Pershing
General of the Armies John Joseph Pershing (September 13, 1860 – July 15, 1948), nicknamed "Black Jack", was a senior United States Army officer. He served most famously as the commander of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) on the Wes ...
, a proponent of pre-1914 "open warfare" who considered the French and British emphasis on artillery as misguided and incompatible with American "offensive spirit". Much to the frustration of his Allies, who had suffered heavy losses in 1917, he insisted on retaining control of American troops and refused to commit them to the front line until able to operate as independent units. As a result, the first significant US involvement was the
Meuse–Argonne offensive in late September 1918.
Nivelle Offensive (April–May 1917)

In December 1916,
Robert Nivelle replaced Pétain as commander of French armies on the Western Front and began planning a
spring attack in
Champagne, part of a joint Franco-British operation. Nivelle claimed the capture of his main objective, the
Chemin des Dames, would achieve a massive breakthrough and cost no more than 15,000 casualties. Poor security meant German intelligence was well informed on tactics and timetables, but despite this, when the attack began on 16 April the French made substantial gains, before being brought to a halt by the newly built and extremely strong defences of the Hindenburg Line. Nivelle persisted with frontal assaults and by 25 April the French had suffered nearly 135,000 casualties, including 30,000 dead, most incurred in the first two days.

Concurrent British attacks at
Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
were more successful, although ultimately of little strategic value. Operating as a separate unit for the first time, the
Canadian Corps
The Canadian Corps was a World War I corps formed from the Canadian Expeditionary Force in September 1915 after the arrival of the 2nd Canadian Division in France. The corps was expanded by the addition of the 3rd Canadian Division in December ...
capture of
Vimy Ridge during the battle is viewed by many Canadians as a defining moment in creating a sense of national identity. Although Nivelle continued the offensive, on 3 May the
21st Division, which had been involved in some of the heaviest fighting at Verdun, refused orders to go into battle, initiating the
French Army mutinies; within days, acts of "collective indiscipline" had spread to 54 divisions, while over 20,000 deserted. Unrest was almost entirely confined to the infantry, whose demands were largely non-political, including better economic support for families at home, and regular periods of leave, which Nivelle had ended.
Sinai and Palestine campaign (1917–1918)

In March and April 1917, at the
First and
Second Battles of Gaza, German and Ottoman forces stopped the advance of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, which had begun in August 1916 at the Battle of Romani. At the end of October, the
Sinai and Palestine campaign resumed, when General
Edmund Allenby's
XXth Corps,
XXI Corps and
Desert Mounted Corps won the
Battle of Beersheba. Two Ottoman armies were defeated a few weeks later at the
Battle of Mughar Ridge and, early in December,
Jerusalem was captured following another Ottoman defeat at the
Battle of Jerusalem. About this time,
Friedrich Freiherr Kress von Kressenstein was relieved of his duties as the Eighth Army's commander, replaced by
Djevad Pasha, and a few months later the commander of the
Ottoman Army in Palestine,
Erich von Falkenhayn, was replaced by
Otto Liman von Sanders.
In early 1918, the front line was
extended
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate
* Exte ...
and the
Jordan Valley was occupied, following the
First Transjordan and the
Second Transjordan attacks by British Empire forces in March and April 1918.
German offensive and Allied counter-offensive (March–November 1918)

In December 1917, the Central Powers signed an armistice with Russia, thus freeing large numbers of German troops for use in the west. With German reinforcements and new American troops pouring in, the outcome was to be decided on the Western Front. The Central Powers knew that they could not win a protracted war, but they held high hopes for success based on a final quick offensive. Ludendorff drew up plans (
codenamed Operation Michael) for the 1918 offensive on the Western Front. The operation commenced on 21 March 1918 with an attack on British forces near
Saint-Quentin. German forces achieved an unprecedented advance of . The initial offensive a success; after heavy fighting, however, the offensive was halted. Lacking tanks or
motorised artillery, the Germans were unable to consolidate their gains. The problems of re-supply were also exacerbated by increasing distances that now stretched over terrain that was shell-torn and often impassable to traffic.
Following this, Germany launched
Operation Georgette against the northern
English Channel ports. The Allies halted the drive after limited territorial gains by Germany. The German Army to the south then conducted
Operations Blücher and Yorck, pushing broadly towards Paris. Germany launched Operation Marne (
Second Battle of the Marne) on 15 July, in an attempt to encircle
Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
. The resulting counter-attack, which started the
Hundred Days Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allies of World War I, Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (1918), Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Wester ...
on 8 August, caused a marked collapse in German morale.
= Allied advance to the Hindenburg Line
=

By September, the Germans had fallen back to the Hindenburg Line. The Allies had
advanced to the Hindenburg Line in the north and centre. German forces launch numerous counterattacks, but positions and outposts of the Line continued to fall, with the BEF alone taking 30,441 prisoners in the last week of September. On 24 September, Supreme Army Command informed the leaders in Berlin that armistice talks were inevitable.
The
final assault on the Hindenburg Line began with the
Meuse-Argonne offensive, launched by American and French troops on 26 September. Two days later the Allied armies (Belgian French and British)
attacked around Ypres and the day after the British Fourth and French First Army at St Quentin in the centre of the line. The following week, co-operating American and French units broke through in
Champagne at the
Battle of Blanc Mont Ridge
The Battle of Blanc Mont Ridge (3 October to 27 October 1918) occurred during World War I, northeast of Reims, in Champagne, France
Champagne () was a province in the northeast of the Kingdom of France, now best known as the Champagne w ...
(3 October - 27 October), forcing the Germans off the commanding heights, and closing towards the Belgian frontier. On 8October the Hindenburg Line was pierced again by British and Dominion troops of the First and Third British Armies at the
Second Battle of Cambrai
The Battle of Cambrai, 1918 (also known as the Second Battle of Cambrai) was a battle between troops of the British First Army (United Kingdom), First, Third Army (United Kingdom), Third and Fourth Army (United Kingdom), Fourth Armies and German ...
.
Breakthrough of Macedonian Front (September 1918)

Allied forces started the
Vardar offensive on 15 September at two key points:
Dobro Pole and near
Dojran Lake
Doiran Lake (, ''Dojransko Ezero''; , ''Límni Dhoïráni''), also spelled Dojran Lake is a lake with an area of shared between North Macedonia () and Greece ().
To the west is the city of Nov Dojran (Нов Дојран), to the east the vill ...
. In the
Battle of Dobro Pole
The Battle of Dobro Pole ( sr, Битка код Доброг Поља, Bitka kod Dobrog Polja; gr, Μάχη του Ντόμπρο Πόλε, Máchi tou Dóbro Póle), also known as the Breakthrough at Dobro Pole ( bg, Пробив при До� ...
, the Serbian and French armies had success after a three day long battle with relatively small casualties, and subsequently made a breakthrough in the front, something which was rarely seen in World War I. After the front was broken, Allied forces started to liberate Serbia and reached
Skopje at 29 September, after which
Bulgaria signed an armistice with the Allies on 30 September.
Armistices and capitulations

The collapse of the Central Powers came swiftly. Bulgaria was the first to sign an armistice, the
Armistice of Salonica on 29 September 1918.
German Emperor
Wilhelm II in a telegram to
Bulgarian Tsar Ferdinand I described the situation thus: "Disgraceful! 62,000 Serbs decided the war!". On the same day, the
German Supreme Army Command informed Kaiser Wilhelm II and the
Imperial Chancellor Count Georg von Hertling, that the military situation facing Germany was hopeless.
On 24 October, the Italians began a push that rapidly recovered territory lost after the Battle of Caporetto. This culminated in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, which marked the end of the Austro-Hungarian Army as an effective fighting force. The offensive also triggered the disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. During the last week of October, declarations of independence were made in Budapest, Prague, and Zagreb. On 29 October, the imperial authorities asked Italy for an armistice, but the Italians continued advancing, reaching Trento, Udine, and Trieste. On 3November, Austria-Hungary sent a
flag of truce to ask for an
armistice (
Armistice of Villa Giusti). The terms, arranged by telegraph with the Allied Authorities in Paris, were communicated to the Austrian commander and accepted. The Armistice with Austria was signed in the Villa Giusti, near
Padua, on 3November. Austria and Hungary signed separate armistices following the overthrow of the
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
. In the following days, the Italian Army occupied
Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
and all
Tyrol with over 20,000 soldiers.
On 30 October, the Ottoman Empire capitulated, signing the Armistice of Mudros.
German government surrenders

With the military faltering and with widespread loss of confidence in the Kaiser leading to his abdication and fleeing of the country, Germany moved towards surrender. Prince Maximilian of Baden took charge of a new government on 3October as Chancellor of Germany to negotiate with the Allies. Negotiations with President Wilson began immediately, in the hope that he would offer better terms than the British and French. Wilson demanded a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary control over the German military.
In northern Germany, the
German Revolution of 1918–1919
The German Revolution or November Revolution (german: Novemberrevolution) was a civil conflict in the German Empire at the end of the First World War that resulted in the replacement of the German federal constitutional monarchy with a dem ...
began at the end of October 1918. Units of the German Navy refused to set sail for a last, large-scale operation in a war they believed to be as good as lost, initiating the uprising. The
sailors' revolt, which then ensued in the naval ports of
Wilhelmshaven and
Kiel, spread across the whole country within days and led to the
proclamation of a republic on 9November 1918, shortly thereafter to the
abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, and to German surrender.
Aftermath
In the aftermath of the war, four empires disappeared: the German, Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman, and Russian. Numerous nations regained their former independence, and new ones were created. Four dynasties, together with their ancillary aristocracies, fell as a result of the war: the
Romanovs, the
Hohenzollerns, the
Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
, and the
Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
. Belgium and Serbia were badly damaged, as was France, with 1.4 million soldiers dead, not counting other casualties. Germany and Russia were similarly affected.
Formal end of the war
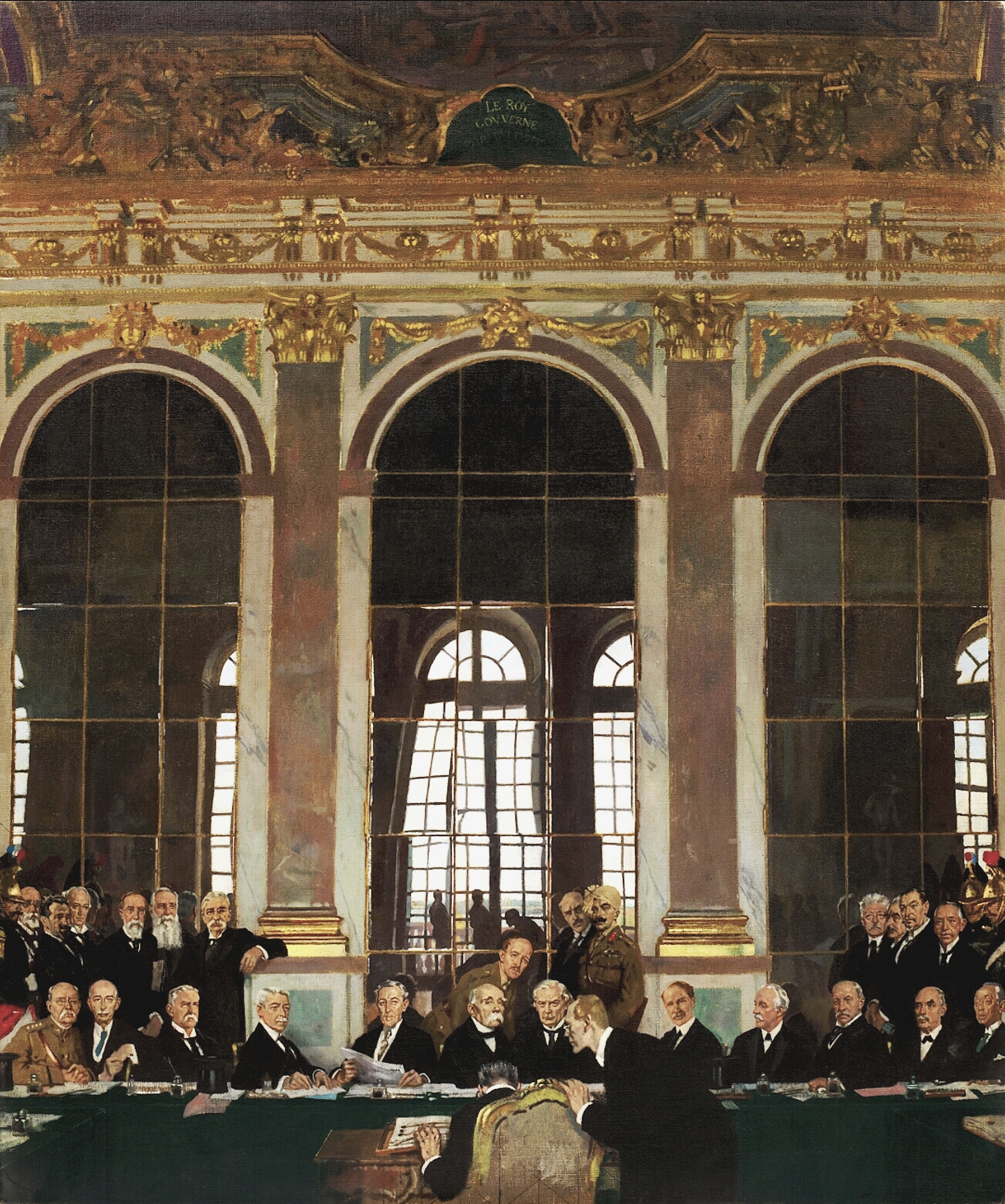

A formal state of war between the two sides persisted for another seven months, until the signing of the
Treaty of Versailles with Germany on 28 June 1919. The United States Senate did not ratify the treaty despite public support for it, and did not formally end its involvement in the war until the
Knox–Porter Resolution
The Knox–Porter Resolution () was a joint resolution of the United States Congress signed by President Warren G. Harding on July 2, 1921, officially ending United States involvement in World War I. The documents were signed on the estate of Jos ...
was signed on 2July 1921 by President
Warren G. Harding. For the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the state of war ceased under the provisions of the ''
Termination of the Present War (Definition) Act 1918'' with respect to:
:* Germany on 10 January 1920.
:* Austria on 16 July 1920.
:* Bulgaria on 9 August 1920.
:* Hungary on 26 July 1921.
:* Turkey on 6 August 1924.

Some
war memorials date the end of the war as being when the Versailles Treaty was signed in 1919, which was when many of the troops serving abroad finally returned home; by contrast, most commemorations of the war's end concentrate on the armistice of 11 November 1918.
Peace treaties and national boundaries

After the war, there grew a certain amount of academic focus on the causes of war and on the elements that could make peace flourish. In part, these led to the institutionalization of peace and conflict studies, security studies and International Relations (IR) in general. The
Paris Peace Conference Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include:
Listed by name
Paris Accords
may refer to:
* Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germ ...
imposed a series of peace treaties on the Central Powers officially ending the war. The 1919
Treaty of Versailles dealt with Germany and, building on
Wilson's 14th point, brought into being the
League of Nations on 28 June 1919.
The Central Powers had to acknowledge responsibility for "all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war imposed upon them by" their aggression. In the Treaty of Versailles, this statement was
Article 231
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article may also refer to:
G ...
. This article became known as the War Guilt clause as the majority of Germans felt humiliated and resentful. Overall the Germans felt they had been unjustly dealt with by what they called the "
diktat of Versailles". German historian Hagen Schulze said the Treaty placed Germany "under legal sanctions, deprived of military power, economically ruined, and politically humiliated." Belgian historian Laurence Van Ypersele emphasises the central role played by memory of the war and the Versailles Treaty in German politics in the 1920s and 1930s:
Active denial of war guilt in Germany and German resentment at both reparations and continued Allied occupation of the Rhineland made widespread revision of the meaning and memory of the war problematic. The legend of the "stab in the back
The stab-in-the-back myth (, , ) was an antisemitic conspiracy theory that was widely believed and promulgated in Germany after 1918. It maintained that the Imperial German Army did not lose World War I on the battlefield, but was instead ...
" and the wish to revise the "Versailles diktat", and the belief in an international threat aimed at the elimination of the German nation persisted at the heart of German politics. Even a man of peace such as Gustav
Gustav, Gustaf or Gustave may refer to:
*Gustav (name), a male given name of Old Swedish origin
Art, entertainment, and media
*Primeval (film), ''Primeval'' (film), a 2007 American horror film
*Gustav (film series), ''Gustav'' (film series), a Hu ...
] Stresemann publicly rejected German guilt. As for the Nazis, they waved the banners of domestic treason and international conspiracy in an attempt to galvanise the German nation into a spirit of revenge. Like a Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany sought to redirect the memory of the war to the benefit of its own policies.
Meanwhile, new nations liberated from German rule viewed the treaty as recognition of wrongs committed against small nations by much larger aggressive neighbours.
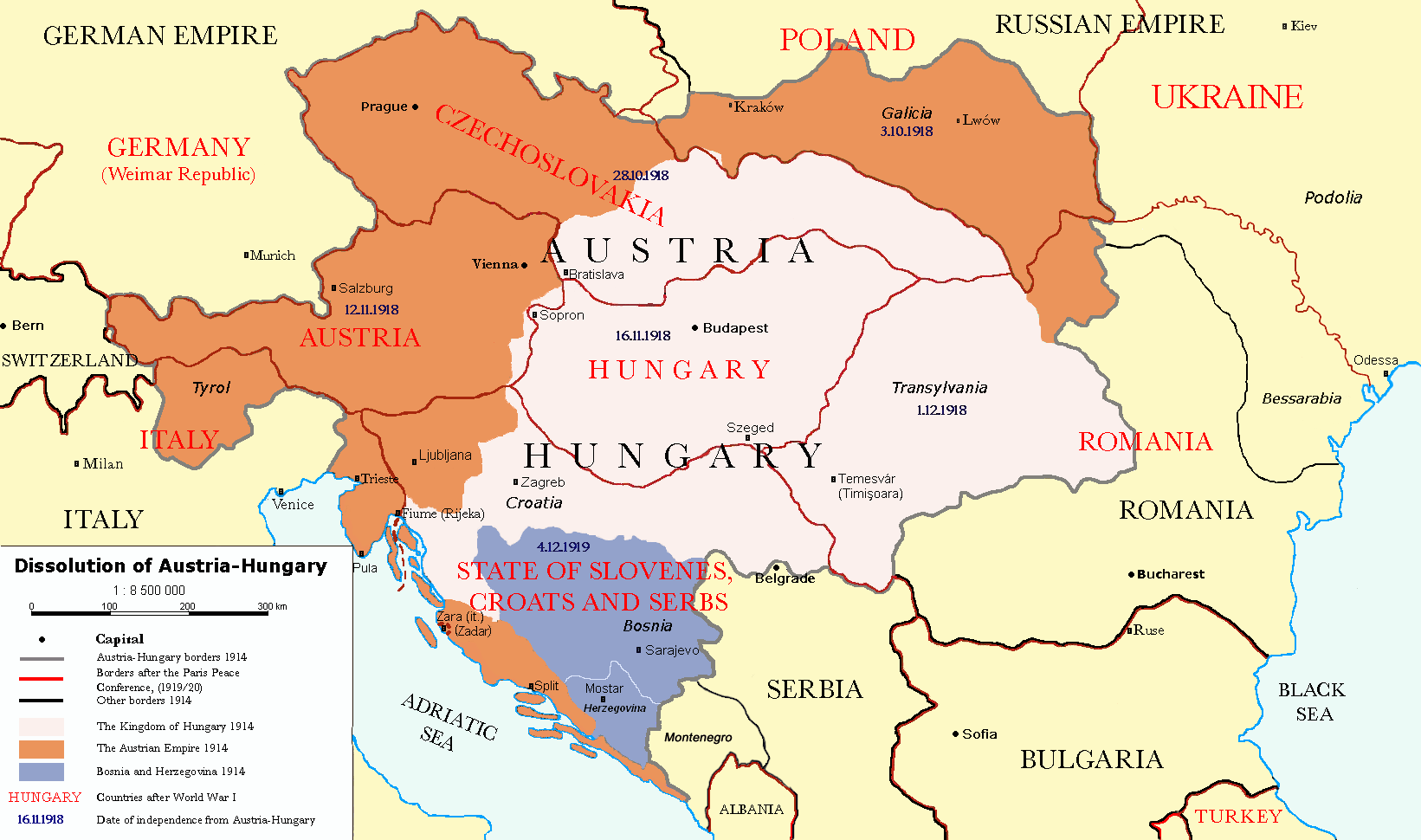
Austria-Hungary was partitioned into several successor states, largely but not entirely along ethnic lines. Apart from Austria and Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Italy, Poland, Romania and Yugoslavia received territories from the Dual Monarchy (the formerly separate and autonomous
Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia
The Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia ( hr, Kraljevina Hrvatska i Slavonija; hu, Horvát-Szlavónország or ; de-AT, Königreich Kroatien und Slawonien) was a nominally autonomous kingdom and constitutionally defined separate political nation with ...
was incorporated into Yugoslavia). The details were contained in the
Saint-Germain-en-Laye and the
Treaty of Trianon. As a result, Hungary lost 64% of its total population, decreasing from 20.9 million to 7.6 million and losing 31% (3.3 out of 10.7 million) of its ethnic
Hungarians. According to the 1910 census, speakers of the Hungarian language included approximately 54% of the entire population of the
Kingdom of Hungary. Within the country, numerous ethnic minorities were present: 16.1%
Romanians, 10.5%
Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
, 10.4%
Germans, 2.5%
Ruthenians, 2.5%
Serbs and 8% others.
[Frucht, p. 356.] Between 1920 and 1924, 354,000 Hungarians fled former Hungarian territories attached to Romania, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia.
The Russian Empire, which had withdrawn from the war in 1917 after the October Revolution, lost much of its western frontier as the newly independent nations of
Estonia,
Finland,
Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
,
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, and
Poland were carved from it. Romania took control of Bessarabia in April 1918.
National identities
After 123 years, Poland re-emerged as an independent country. The Kingdom of Serbia and its dynasty, as a "minor Entente nation" and the country with the most casualties per capita, became the backbone of a new multinational state, the
Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, later renamed Yugoslavia. Czechoslovakia, combining the
Kingdom of Bohemia with parts of the Kingdom of Hungary, became a new nation. Romania would
unite all Romanian-speaking people under a single state leading to
Greater Romania.
In the British Empire, the war unleashed new forms of nationalism. In Australia and New Zealand, the Battle of Gallipoli became known as those nations' "Baptism of Fire". It was the first major war in which the newly established countries fought, and it was one of the first times that Australian troops fought as Australians, not just subjects of the
British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
, and independent national identities for these nations took hold.
Anzac Day
, image = Dawn service gnangarra 03.jpg
, caption = Anzac Day Dawn Service at Kings Park, Western Australia, 25 April 2009, 94th anniversary.
, observedby = Australia Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Cook Islands New ...
, commemorating the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC), celebrates this defining moment.
In the aftermath of World War I, Greece
fought against Turkish nationalists led by
Mustafa Kemal, a war that eventually resulted in a
massive population exchange between the two countries under the Treaty of Lausanne. According to various sources, several hundred thousand Greeks died during this period, which was tied in with the Greek genocide.
Casualties
Of the 60 million European military personnel who were mobilised from 1914 to 1918,
8 million were killed, 7 million were permanently disabled, and 15 million were seriously injured. Germany lost 15.1% of its active male population, Austria-Hungary lost 17.1%, and France lost 10.5%. France mobilised 7.8 million men, of which 1.4 million died and 3.2 million were injured. Among the soldiers mutilated and surviving in the trenches, approximately 15,000 sustained horrific facial injuries, causing them to undergo social stigma and marginalisation; they were called the ''
gueules cassées
Gueules cassées (broken faces)Biernoff, S. and Stein, C. (2008); "Les Gueules cassées (review)", in: ''Bulletin of the History of Medicine'', Volume 82, Number 2, Summer 2008. Retrieved on-line throug 9 December 2015. is a French expression for f ...
''. In Germany, civilian deaths were 474,000 higher than in peacetime, due in large part to food shortages and malnutrition that weakened resistance to disease. These excess deaths are estimated as 271,000 in 1918, plus another 71,000 in the first half of 1919 when the blockade was still in effect. By the end of the war, starvation caused by famine had killed approximately 100,000 people in Lebanon. Between 5and 10 million people died in the
Russian famine of 1921. By 1922, there were between 4.5 million and 7million homeless children in Russia as a result of nearly a decade of devastation from World WarI, the Russian Civil War, and the subsequent famine of 1920–1922. Numerous anti-Soviet Russians fled the country after the Revolution; by the 1930s, the northern Chinese city of
Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
had 100,000 Russians.
Diseases flourished in the chaotic wartime conditions. In 1914 alone, louse-borne
epidemic typhus killed 200,000 in Serbia. From 1918 to 1922, Russia had about 25 million infections and 3million deaths from epidemic typhus. In 1923, 13 million Russians contracted malaria, a sharp increase from the pre-war years. Starting in early 1918, a major influenza epidemic known as
Spanish flu spread around the world, accelerated by the movement of large number of soldiers, often crammed together in camps and transport ships with poor sanitation. Overall, the Spanish flu killed at least 17 million to 25 million people, including an estimated 2.64 million Europeans and as many as 675,000 Americans.
Moreover, between 1915 and 1926, an epidemic of
encephalitis lethargica
Encephalitis lethargica is an atypical form of encephalitis. Also known as "sleeping sickness" or "sleepy sickness" (distinct from tsetse fly-transmitted sleeping sickness), it was first described in 1917 by neurologist Constantin von Economo a ...
spread around the world affecting nearly five million people.
War crimes
Chemical weapons in warfare
The German army was the first to successfully deploy chemical weapons during the Second Battle of Ypres (22 April – 25 May 1915), after German scientists working under the direction of
Fritz Haber at the
Kaiser Wilhelm Institute developed a method to weaponize
chlorine.
The use of chemical weapons was sanctioned by the German High Command in an effort to force Allied soldiers out of their entrenched positions, complementing rather than supplanting more lethal conventional weapons.
In time, chemical weapons were deployed by all major belligerents throughout the war, inflicting approximately 1.3 million casualties, but relatively few fatalities: About 90,000 in total.
For example, there were an estimated 186,000 British chemical weapons casualties during the war (80% of which were the result of exposure to the
vesicant '
mustard gas
Mustard gas or sulfur mustard is a chemical compound belonging to a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. The name ''mustard gas'' is technically incorrect: the substance, when dispersed, is often not actually a gas, b ...
', introduced to the battlefield by the Germans in July 1917, which burns the skin at any point of contact and inflicts more severe lung damage than chlorine or
phosgene
Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, espe ...
),
and up to one-third of American casualties were caused by them. The Russian Army reportedly suffered roughly 500,000 chemical weapon casualties in World WarI. The use of chemical weapons in warfare was in direct violation of the
1899 Hague Declaration Concerning Asphyxiating Gases and the
1907 Hague Convention on Land Warfare, which prohibited their use.
Genocides by the Ottoman Empire

The
ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
of the Ottoman Empire's Armenian population, including mass deportations and executions, during the final years of the Ottoman Empire is considered
genocide.
The Ottomans carried out organised and systematic massacres of the Armenian population at the beginning of the war and manipulated acts of Armenian resistance by portraying them as rebellions to justify further extermination.
In early 1915, a number of Armenians volunteered to join the Russian forces and the Ottoman government used this as a pretext to issue the
Tehcir Law (Law on Deportation), which authorised the deportation of Armenians from the Empire's eastern provinces to Syria between 1915 and 1918. The Armenians were intentionally
marched to death and a number were attacked by Ottoman brigands. While an exact number of deaths is unknown, the
International Association of Genocide Scholars estimates 1.5 million.
The government of Turkey has consistently
denied the genocide, arguing that those who died were victims of inter-ethnic fighting, famine, or disease during World WarI; these claims are rejected by most historians.
Other ethnic groups were similarly attacked by the Ottoman Empire during this period, including Assyrians and
Greeks, and some scholars consider those events to be part of the same policy of extermination. At least 250,000 Assyrian Christians, about half of the population, and 350,000–750,000
Anatolian and
Pontic Greeks were killed between 1915 and 1922.
Prisoners of war

About eight million soldiers surrendered and were held in
POW camps during the war. All nations pledged to follow the
Hague Conventions on fair treatment of
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
, and the survival rate for POWs was generally much higher than that of combatants at the front.
25–31% of Russian losses (as a proportion of those captured, wounded, or killed) were to prisoner status, for Austria-Hungary 32%, for Italy 26%, for France 12%, for Germany 9%; for Britain 7%. Prisoners from the Allied armies totalled about 1.4 million (not including Russia, which lost 2.5–3.5 million soldiers as prisoners). From the Central Powers about 3.3 million soldiers became prisoners; most of them surrendered to Russians.
Soldiers' experiences
Allied personnel was around 42,928,000 while Central personnel was near 25,248,000.
The British soldiers of the war were initially volunteers but increasingly were
conscripted into service. Surviving veterans, returning home, often found they could discuss their experiences only amongst themselves. Grouping together, they formed "veterans' associations" or "Legions". A small number of personal accounts of American veterans have been collected by the Library of Congress
Veterans History Project
The Veterans History Project of the Library of Congress American Folklife Center (commonly known as the Veterans History Project) was created by the United States Congress in 2000 to collect and preserve the firsthand remembrances of U.S. wartime ...
.
Conscription

Conscription was common in most European countries. However, it was controversial in English-speaking countries. It was especially unpopular among minority ethnic groups—especially the Irish Catholics in Ireland and Australia,
and the French Catholics in Canada.
In the United States, conscription began in 1917 and was generally well received, with a few pockets of opposition in isolated rural areas. The administration decided to rely primarily on conscription, rather than voluntary enlistment, to raise military manpower after only 73,000 volunteers enlisted out of the initial 1million target in the first six weeks of the war.
Military attachés and war correspondents
Military and civilian observers from every major power closely followed the course of the war. Many were able to report on events from a perspective somewhat akin to modern "
embedded" positions within the opposing land and naval forces.
Economic effects
Macro- and micro-economic consequences devolved from the war. Families were altered by the departure of many men. With the death or absence of the primary wage earner, women were forced into the workforce in unprecedented numbers. At the same time, industry needed to replace the lost labourers sent to war. This aided the struggle for
voting rights for women.

In all nations, the government's share of GDP increased, surpassing 50% in both Germany and France and nearly reaching that level in Britain. To pay for purchases in the United States, Britain cashed in its extensive investments in American railroads and then began borrowing heavily from
Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
. President Wilson was on the verge of cutting off the loans in late 1916 but allowed a great increase in
US government lending to the Allies. After 1919, the US demanded repayment of these loans. The repayments were, in part, funded by German reparations that, in turn, were supported by American loans to Germany. This circular system collapsed in 1931 and some loans were never repaid. Britain still owed the United States $4.4
billion of World WarI debt in 1934; the last installment was finally paid in 2015.
Britain turned to her colonies for help in obtaining essential war materials whose supply from traditional sources had become difficult. Geologists such as
Albert Kitson were called on to find new resources of precious minerals in the African colonies. Kitson discovered important new deposits of
manganese, used in munitions production, in the
Gold Coast.
Article 231 of the Treaty of Versailles (the so-called "war guilt" clause) stated Germany accepted responsibility for "all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war imposed upon them by the aggression of Germany and her allies." It was worded as such to lay a legal basis for reparations, and a similar clause was inserted in the treaties with Austria and Hungary. However, neither of them interpreted it as an admission of war guilt." In 1921, the total reparation sum was placed at 132 billion gold marks. However, "Allied experts knew that Germany could not pay" this sum. The total sum was divided into three categories, with the third being "deliberately designed to be chimerical" and its "primary function was to mislead public opinion ... into believing the "total sum was being maintained."
Thus, 50 billion gold marks (12.5 billion dollars) "represented the actual Allied assessment of German capacity to pay" and "therefore … represented the total German reparations" figure that had to be paid.
This figure could be paid in cash or in-kind (coal, timber, chemical dyes, etc.). In addition, some of the territory lost—via the treaty of Versailles—was credited towards the reparation figure as were other acts such as helping to restore the Library of Louvain. By 1929, the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
arrived, causing political chaos throughout the world. In 1932 the payment of reparations was suspended by the international community, by which point Germany had paid only the equivalent of 20.598 billion gold marks in reparations. With the rise of Adolf Hitler, all bonds and loans that had been issued and taken out during the 1920s and early 1930s were cancelled.
David Andelman notes "refusing to pay doesn't make an agreement null and void. The bonds, the agreement, still exist." Thus, following the Second World War, at the
London Conference
List of conferences in London (chronological):
* London Conference of 1830 guaranteed the independence of Belgium
* London Conference of 1832 convened to establish a stable government in Greece
* London Conference of 1838–1839 preceded the ...
in 1953, Germany agreed to resume payment on the money borrowed. On 3October 2010, Germany made the final payment on these bonds.
The Australian prime minister,
Billy Hughes
William Morris Hughes (25 September 1862 – 28 October 1952) was an Australian politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Australia, in office from 1915 to 1923. He is best known for leading the country during World War I, but ...
, wrote to the British prime minister,
David Lloyd George, "You have assured us that you cannot get better terms. I much regret it, and hope even now that some way may be found of securing agreement for demanding reparation commensurate with the tremendous sacrifices made by the British Empire and her Allies." Australia received £5,571,720 war reparations, but the direct cost of the war to Australia had been £376,993,052, and, by the mid-1930s, repatriation pensions, war gratuities, interest and sinking fund charges were £831,280,947. Of about 416,000 Australians who served, about 60,000 were killed and another 152,000 were wounded.
The war contributed to the evolution of the
wristwatch from women's jewellery to a practical everyday item, replacing the
pocketwatch, which requires a free hand to operate.
es were designed for use by the military as pocket watches were not as effective for combat. Military funding of advancements in radio contributed to the post-war popularity of the medium.
Support and opposition for the war
Support

In the Balkans,
Yugoslav nationalists
Yugoslav or Yugoslavian may refer to:
* Yugoslavia, or any of the three historic states carrying that name:
** Kingdom of Yugoslavia, a European monarchy which existed 1918–1945 (officially called "Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes" 1918–1 ...
such as the leader,
Ante Trumbić, strongly supported the war, desiring th
freedomof
Yugoslavs from Austria-Hungary and other foreign powers and the creation of an independent Yugoslavia. The
Yugoslav Committee, led by Trumbić, was formed in Paris on 30 April 1915 but shortly moved its office to London. In April 1918, the Rome Congress of Oppressed Nationalities met, including
Czechoslovak,
Italian,
Polish,
Transylvanian, and Yugoslav representatives who urged the Allies to support national
self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
for the peoples residing within Austria-Hungary.
In the Middle East,
Arab nationalism soared in Ottoman territories in response to the rise of Turkish nationalism during the war, with Arab nationalist leaders advocating the creation of a
pan-Arab
Pan-Arabism ( ar, الوحدة العربية or ) is an ideology that espouses the unification of the countries of North Africa and Western Asia from the Atlantic Ocean to the Arabian Sea, which is referred to as the Arab world. It is closely c ...
state. In 1916, the Arab Revolt began in Ottoman-controlled territories of the Middle East in an effort to achieve independence.
In East Africa,
Iyasu V of
Ethiopia was supporting the
Dervish state who were at war with the British in the
Somaliland campaign. Von Syburg, the German envoy in
Addis Ababa, said, "now the time has come for Ethiopia to regain the coast of the Red Sea driving the Italians home, to restore the Empire to its ancient size." The Ethiopian Empire was on the verge of entering World WarI on the side of the Central Powers before Iyasu's overthrow at the
Battle of Segale due to Allied pressure on the Ethiopian aristocracy. Iyasu was accused of converting to
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
. According to Ethiopian historian
Bahru Zewde, the evidence used to prove Iyasu's conversion was a doctored photo of Iyasu wearing a turban provided by the Allies. Some historians claim the British spy
T. E. Lawrence forged the Iyasu photo.

A number of socialist parties initially supported the war when it began in August 1914.
But European socialists split on national lines, with the concept of
class conflict
Class conflict, also referred to as class struggle and class warfare, is the political tension and economic antagonism that exists in society because of socio-economic competition among the social classes or between rich and poor.
The forms ...
held by radical socialists such as Marxists and
syndicalists being overborne by their patriotic support for the war. Once the war began, Austrian, British, French, German, and Russian socialists followed the rising nationalist current by supporting their countries' intervention in the war.
Italian nationalism was stirred by the outbreak of the war and was initially strongly supported by a variety of political factions. One of the most prominent and popular Italian nationalist supporters of the war was
Gabriele D'Annunzio, who promoted
Italian irredentism and helped sway the Italian public to support intervention in the war. The
Italian Liberal Party, under the leadership of
Paolo Boselli, promoted intervention in the war on the side of the Allies and used the Dante Alighieri Society to promote Italian nationalism. Italian socialists were divided on whether to support the war or oppose it; some were militant supporters of the war, including
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
and
Leonida Bissolati. However, the
Italian Socialist Party decided to oppose the war after anti-militarist protestors were killed, resulting in a
general strike
A general strike refers to a strike action in which participants cease all economic activity, such as working, to strengthen the bargaining position of a trade union or achieve a common social or political goal. They are organised by large co ...
called
Red Week.
The Italian Socialist Party purged itself of pro-war nationalist members, including Mussolini.
Mussolini, a syndicalist who supported the war on grounds of irredentist claims on Italian-populated regions of Austria-Hungary, formed the pro-interventionist ''
Il Popolo d'Italia'' and the ''Fasci Rivoluzionario d'Azione Internazionalista'' ("Revolutionary
Fasci for International Action") in October 1914 that later developed into the ''
Fasci Italiani di Combattimento'' in 1919, the origin of fascism. Mussolini's nationalism enabled him to raise funds from
Ansaldo
Ansaldo Energia S.p.A. is an Italian power engineering company. It is based in Genoa, Italy. The absorbed parent company, Gio. Ansaldo & C., started in 1853. It was taken over by Leonardo S.p.A. In 2011, Leonardo S.p.A. sold 45% stake in An ...
(an armaments firm) and other companies to create ''Il Popolo d'Italia'' to convince socialists and revolutionaries to support the war.
Patriotic funds
On both sides there was large scale fundraising for soldiers' welfare, their dependents and for those injured. The
Nail Men
Nail Men or Men of Nails (german: Nagelmänner) were a form of propaganda and fundraising for members of the armed forces and their dependents in the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the German Empire in World War I. They consisted of wooden statues (u ...
were a German example. Around the British Empire there were many patriotic funds, including the
Royal Patriotic Fund Corporation
The Royal Patriotic Fund Corporation (also known as the Royal Pat) was a charitable body set up by Royal Warrant in the United Kingdom during the Crimean War. It provided assistance to the widows, orphans and other dependants of members of the ar ...
,
Canadian Patriotic Fund,
Queensland Patriotic Fund
Formed in 1900, the Queensland Patriotic Fund was responsible for raising funds and fund administration to provide financial and other assistance to those who were serving or had served in the armed forces of Australia, as well as offering support ...
and, by 1919, there were 983 funds in New Zealand. At the start of the next world war the New Zealand funds were reformed, having been criticised as overlapping, wasteful and abused, but 11 were still functioning in 2002.
Opposition
Many countries jailed those who spoke out against the conflict. These included
Eugene Debs in the United States and
Bertrand Russell in Britain. In the US, the
Espionage Act of 1917 and
Sedition Act of 1918 made it a federal crime to oppose military recruitment or make any statements deemed "disloyal". Publications at all critical of the government were removed from circulation by postal censors,
and many served long prison sentences for statements of fact deemed unpatriotic.

A number of nationalists opposed intervention, particularly within states that the nationalists were hostile to. Although the vast majority of Irish people consented to participate in the war in 1914 and 1915, a minority of advanced
Irish nationalists staunchly opposed taking part. The war began amid the Home Rule crisis in Ireland that had resurfaced in 1912, and by July 1914 there was a serious possibility of an outbreak of civil war in Ireland. Irish nationalists and Marxists attempted to pursue Irish independence, culminating in the
Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the a ...
of 1916, with Germany sending 20,000 rifles to Ireland to stir unrest in Britain. The UK government placed Ireland under
martial law in response to the Easter Rising, though once the immediate threat of revolution had dissipated, the authorities did try to make concessions to nationalist feeling. However, opposition to involvement in the war increased in Ireland, resulting in the
Conscription Crisis of 1918.
Other opposition came from
conscientious objector
A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on the grounds of freedom of thought, conscience, or religion. The term has also been extended to object ...
s—some socialist, some religious—who refused to fight. In Britain, 16,000 people asked for conscientious objector status. Some of them, most notably prominent peace activist
Stephen Hobhouse
Stephen Henry Hobhouse (5 August 1881 – 2 April 1961) was a prominent English peace activist, prison reformer, and religious writer.
Family
Stephen Henry Hobhouse was born in Pitcombe, Somerset, England. He was the eldest son of Henry Hob ...
, refused both military and
alternative service. Many suffered years of prison, including
solitary confinement
Solitary confinement is a form of imprisonment in which the inmate lives in a single cell with little or no meaningful contact with other people. A prison may enforce stricter measures to control contraband on a solitary prisoner and use additi ...
and bread and water diets. Even after the war, in Britain many job advertisements were marked "No conscientious objectors need apply".
On 1–4 May 1917, about 100,000 workers and soldiers of
Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, and after them, the workers and soldiers of other Russian cities, led by the Bolsheviks, demonstrated under banners reading "Down with the war!" and "all power to the soviets!" The mass demonstrations resulted in a crisis for the
Russian Provisional Government. In
Milan, in May 1917, Bolshevik revolutionaries organised and engaged in rioting calling for an end to the war, and managed to close down factories and stop public transportation.
[Seton-Watson, Christopher. 1967. ''Italy from Liberalism to Fascism: 1870 to 1925''. London: Methuen & Co. Ltd. p. 471] The Italian army was forced to enter Milan with tanks and machine guns to face Bolsheviks and
anarchists, who fought violently until 23 May when the army gained control of the city. Almost 50 people (including three Italian soldiers) were killed and over 800 people arrested.
Technology

World War I began as a clash of 20th-century technology and 19th-century
tactics, with the inevitably large ensuing casualties. By the end of 1917, however, the major armies, now numbering millions of men, had modernised and were making use of telephone,
wireless communication,
armoured cars,
tanks (especially with the advent of the first prototype tank,
Little Willie), and aircraft.
Artillery also underwent a revolution. In 1914, cannons were positioned in the front line and fired directly at their targets. By 1917,
indirect fire with guns (as well as mortars and even machine guns) was commonplace, using new techniques for spotting and ranging, notably, aircraft and the often overlooked
field telephone.
Fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinc ...
were initially used for
reconnaissance and
ground attack. To shoot down enemy planes,
anti-aircraft guns and
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
were developed.
Strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombers, ...
s were created, principally by the Germans and British, though the former used
Zeppelins as well.
Towards the end of the conflict, aircraft carriers were used for the first time, with HMS ''Furious'' launching
Sopwith Camels in a raid to destroy the Zeppelin hangars at
Tønder in 1918.
Diplomacy
The non-military diplomatic and propaganda interactions among the nations were designed to build support for the cause or to undermine support for the enemy. For the most part, wartime diplomacy focused on five issues:
propaganda campaigns; defining and redefining the war goals, which became harsher as the war went on; luring neutral nations (Italy, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, Romania) into the coalition by offering slices of enemy territory; and encouragement by the Allies of nationalistic minority movements inside the Central Powers, especially among Czechs, Poles, and Arabs. In addition, there were multiple peace proposals coming from neutrals, or one side or the other; none of them progressed very far.
Legacy and memory
Memorials

Memorials were erected in thousands of villages and towns. Close to battlefields, those buried in improvised burial grounds were gradually moved to formal graveyards under the care of organisations such as the
Commonwealth War Graves Commission, the
American Battle Monuments Commission, the
German War Graves Commission
The German War Graves Commission ( in German) is responsible for the maintenance and upkeep of German war graves in Europe and North Africa. Its objectives are acquisition, maintenance and care of German war graves; tending to next of kin; youth ...
, and
Le Souvenir français. Many of these graveyards also have central monuments to the missing or
unidentified
''Unidentified'' is a 2006 science fiction Christian film produced by Rich Christiano and Alvin Mount. It was written and directed by Rich Christiano and stars Jonathan Aube, Josh Adamson, Michael Blain-Rozgay, Jenna Bailey, Lance Zitron, and t ...
dead, such as the
Menin Gate Memorial to the Missing and the
Thiepval Memorial to the Missing of the Somme.
In 1915,
John McCrae, a Canadian army doctor, wrote the poem ''
In Flanders Fields'' as a salute to those who perished in the Great War. Published in
''Punch'' on 8December 1915, it is still recited today, especially on
Remembrance Day and
Memorial Day.
 National World War I Museum and Memorial
National World War I Museum and Memorial in
Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City (abbreviated KC or KCMO) is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central ...
, is a memorial dedicated to all Americans who served in World WarI. The
Liberty Memorial was dedicated on 1November 1921, when the supreme Allied commanders spoke to a crowd of more than 100,000 people.
The UK Government has budgeted substantial resources to
the commemoration of the war during the period 2014 to 2018. The lead body is the
Imperial War Museum
Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military ...
. On 3August 2014, French President
François Hollande
François Gérard Georges Nicolas Hollande (; born 12 August 1954) is a French politician who served as President of France from 2012 to 2017. He previously was First Secretary of the Socialist Party (PS) from 1997 to 2008, Mayor of Tulle from ...
and German President
Joachim Gauck together marked
the centenary of Germany's declaration of war on France by laying the first stone of a memorial in Vieil Armand, known in German as
Hartmannswillerkopf
Hartmannswillerkopf, also known as the Vieil Armand (French) or Hartmannsweiler Kopf (German; English: Hartmansweiler Head) is a pyramidal rocky spur in the Vosges mountains of the Grand Est region, France. The peak stands at overlooking the Rhine ...
, for French and German soldiers killed in the war.
During the
Armistice centenary commemorations, French President
Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron (; born 21 December 1977) is a French politician who has served as President of France since 2017. ''Ex officio'', he is also one of the two Co-Princes of Andorra. Prior to his presidency, Macron served as Minister of Econ ...
and German Chancellor
Angela Merkel visited the site of the signing of the Armistice of Compiègne and unveiled a plaque to reconciliation.
Historiography
The first tentative efforts to comprehend the meaning and consequences of
modern warfare began during the initial phases of the war; this process continued throughout and after the end of hostilities, and is still underway more than a century later. Teaching World War I has presented special challenges. When compared with
World War II, the First World War is often thought to be "a wrong war fought for the wrong reasons"; it lacks the
metanarrative of
good versus evil that characterizes retellings of the Second World War. Lacking recognizable heroes and villains, it is often taught thematically, invoking
tropes
Trope or tropes may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Trope (cinema), a cinematic convention for conveying a concept
* Trope (literature), a figure of speech or common literary device
* Trope (music), any of a variety of different things ...
like the wastefulness of war, the folly of generals and the innocence of soldiers. The complexity of the conflict is mostly obscured by these oversimplifications.
George Kennan
George Frost Kennan (February 16, 1904 – March 17, 2005) was an American diplomat and historian. He was best known as an advocate of a policy of containment of Soviet expansion during the Cold War. He lectured widely and wrote scholarly histo ...
referred to the war as the "seminal catastrophe of the 20th century".
Historian Heather Jones argues that the
historiography has been reinvigorated by a cultural turn in the
21st century
The 21st (twenty-first) century is the current century in the ''Anno Domini'' era or Common Era, under the Gregorian calendar. It began on 1 January 2001 ( MMI) and will end on 31 December 2100 ( MMC).
Marking the beginning of the 21st centur ...
. Scholars have raised entirely new questions regarding
military occupation,
radicalisation of politics,
race,
medical science,
gender and
mental health. Among the major subjects that historians have long debated regarding the war include:
Why the war began; why the
Allies won; whether generals were responsible for
high casualty rates; how soldiers endured the poor conditions of
trench warfare; and to what extent the civilian
home front accepted and endorsed the war effort.
[see Christoph Cornelissen, and Arndt Weinrich, eds. ''Writing the Great War – The Historiography of World War I from 1918 to the Present'' (2020]
free download
; full coverage for major countries.
Unexploded ordnance
As late as 2007, signs warning visitors to keep off certain paths at battlefield sites like
Verdun and
Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
*Somme, Queensland, Australia
*Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), a ...
remained in place as
unexploded ordnance continued to pose a danger to farmers living near former battlegrounds. In France and Belgium locals who discover caches of unexploded munitions are assisted by weapons disposal units. In some places, plant life has still not returned to normal.
See also
*
Lists of World War I topics
This is a list of World War I-related lists:
* :List of Australian corps in World War I
* :List of Australian divisions in WWI
* :List of British armies in WWI
* :List of British corps in WWI
* :List of British divisions in WWI
* :List of Canadian ...
*
List of military engagements of World War I
List of military engagements of World War I encompasses land, naval, and air engagements as well as campaigns, operations, defensive lines and sieges. Campaigns generally refer to broader strategic operations conducted over a large bit of territory ...
*
Outline of World War I
*
World war
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Deals with technical developments, including the first dipping
hydrophones
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Links to other WWI Sites worldwide links from Brigham Young U.
The World War One Document Archive from Brigham Young U.
International Encyclopedia of the First World WarRecords on the outbreak of World War I from the UK Parliamentary CollectionsThe Heritage of the Great War / First World War. Graphic color photos, pictures and musicA multimedia history of World War I* European Newspapers from th
start of the First World Warand th
end of the warWWI Films on the European Film GatewayThe British Pathé WW1 Film Archive
World War I British press photograph collection– A sampling of images distributed by the British government during the war to diplomats overseas, from the UBC Library Digital Collections
Personal accounts of American World War I veterans Veterans History Project,
Library of Congress.
Library guides
National Library of New ZealandState Library of New South WalesIndiana University Bloomington
New York University
University of AlbertaCalifornia State Library, California History Room. Collection: California. State Council of Defense. California War History Committee. Records of Californians who served in World War I, 1918–1922.
{{Authority control
World Wars
Articles containing video clips
Global conflicts
Russo-Turkish wars
Wars involving Armenia
Wars involving Australia
Wars involving Azerbaijan
Wars involving Belgium
Wars involving Bolivia
Wars involving Brazil
Wars involving British India
Wars involving Bulgaria
Wars involving Canada
Wars involving Costa Rica
Wars involving Cuba
Wars involving France
Wars involving Germany
Wars involving Greece
Wars involving Guatemala
Wars involving Haiti
Wars involving Honduras
Wars involving Ireland
Wars involving Italy
Wars involving Japan
Wars involving Korea
Wars involving Liberia
Wars involving Malta
Wars involving Montenegro
Wars involving Nepal
Wars involving New Zealand
Wars involving Nicaragua
Wars involving Panama
Wars involving Portugal
Wars involving Rhodesia
Wars involving Romania
Wars involving the Russian Empire
Wars involving Soviet Russia (1917–1922)
White movement
Wars involving Serbia
Wars involving South Africa
Wars involving Sri Lanka
Wars involving Sudan
Wars involving Taiwan
Wars involving Thailand
Wars involving the Habsburg monarchy
Wars involving the Ottoman Empire
Wars involving the Republic of China
Wars involving the states and peoples of Oceania
Wars involving the United Kingdom
Wars involving the United States
Wars involving Slovenia
 This decision was not driven by a reduction in political tensions, but German concern over Russia's quick recovery from its defeat in the Russo-Japanese War and subsequent
This decision was not driven by a reduction in political tensions, but German concern over Russia's quick recovery from its defeat in the Russo-Japanese War and subsequent  The years before 1914 were marked by a series of crises in the Balkans as other powers sought to benefit from Ottoman decline. While Pan-Slavic and Orthodox Russia considered itself the protector of Serbia and other Slav states, they preferred the strategically vital Bosporus straits to be controlled by a weak Ottoman government, rather than an ambitious Slav power like Bulgaria. Since Russia had its own ambitions in northeastern Anatolia and their clients had over-lapping claims in the Balkans, balancing these divided Russian policy-makers and added to regional instability.
Austrian statesmen viewed the Balkans as essential for the continued existence of their Empire, and saw Serbian expansion as a direct threat. The 1908–1909 Bosnian Crisis began when Austria annexed the former Ottoman territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which it had occupied since 1878. Timed to coincide with the
The years before 1914 were marked by a series of crises in the Balkans as other powers sought to benefit from Ottoman decline. While Pan-Slavic and Orthodox Russia considered itself the protector of Serbia and other Slav states, they preferred the strategically vital Bosporus straits to be controlled by a weak Ottoman government, rather than an ambitious Slav power like Bulgaria. Since Russia had its own ambitions in northeastern Anatolia and their clients had over-lapping claims in the Balkans, balancing these divided Russian policy-makers and added to regional instability.
Austrian statesmen viewed the Balkans as essential for the continued existence of their Empire, and saw Serbian expansion as a direct threat. The 1908–1909 Bosnian Crisis began when Austria annexed the former Ottoman territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which it had occupied since 1878. Timed to coincide with the  On 28 June 1914,
On 28 June 1914,  The Austro-Hungarian authorities encouraged the subsequent
The Austro-Hungarian authorities encouraged the subsequent  At a meeting on 29 July, the British cabinet had narrowly decided its obligations to Belgium under the 1839
At a meeting on 29 July, the British cabinet had narrowly decided its obligations to Belgium under the 1839  Beginning on 12 August, the Austrian and Serbs clashed at the battles of the
Beginning on 12 August, the Austrian and Serbs clashed at the battles of the  Upon mobilisation in 1914, 80% of the
Upon mobilisation in 1914, 80% of the  The initial German advance in the West was very successful and by the end of August the Allied left, which included the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), was in full retreat. At the same time, the French offensive in Alsace-Lorraine was a disastrous failure, with casualties exceeding 260,000, including 27,000 killed on 22 August during the Battle of the Frontiers. German planning provided broad strategic instructions, while allowing army commanders considerable freedom in carrying them out at the front; this worked well in 1866 and 1870 but in 1914, von Kluck used this freedom to disobey orders, opening a gap between the German armies as they closed on Paris.
In 1911, the Russian
The initial German advance in the West was very successful and by the end of August the Allied left, which included the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), was in full retreat. At the same time, the French offensive in Alsace-Lorraine was a disastrous failure, with casualties exceeding 260,000, including 27,000 killed on 22 August during the Battle of the Frontiers. German planning provided broad strategic instructions, while allowing army commanders considerable freedom in carrying them out at the front; this worked well in 1866 and 1870 but in 1914, von Kluck used this freedom to disobey orders, opening a gap between the German armies as they closed on Paris.
In 1911, the Russian  Prior to the war, Germany had attempted to use Indian nationalism and pan-Islamism to its advantage, a policy continued post-1914 by instigating uprisings in India, while the
Prior to the war, Germany had attempted to use Indian nationalism and pan-Islamism to its advantage, a policy continued post-1914 by instigating uprisings in India, while the  Pre-war military tactics that emphasised open warfare and the individual rifleman proved obsolete when confronted with conditions prevailing in 1914. Technological advances allowed the creation of strong defensive systems largely impervious to massed infantry advances, such as
Pre-war military tactics that emphasised open warfare and the individual rifleman proved obsolete when confronted with conditions prevailing in 1914. Technological advances allowed the creation of strong defensive systems largely impervious to massed infantry advances, such as  In February 1916 the Germans attacked French defensive positions at the Battle of Verdun, lasting until December 1916. The Germans made initial gains, before French counter-attacks returned matters to near their starting point. Casualties were greater for the French, but the Germans bled heavily as well, with anywhere from 700,000 to 975,000 casualties suffered between the two combatants. Verdun became a symbol of French determination and self-sacrifice.
The
In February 1916 the Germans attacked French defensive positions at the Battle of Verdun, lasting until December 1916. The Germans made initial gains, before French counter-attacks returned matters to near their starting point. Casualties were greater for the French, but the Germans bled heavily as well, with anywhere from 700,000 to 975,000 casualties suffered between the two combatants. Verdun became a symbol of French determination and self-sacrifice.
The  At the start of the war, German
At the start of the war, German  German U-boats attempted to cut the supply lines between North America and Britain. The nature of
German U-boats attempted to cut the supply lines between North America and Britain. The nature of 
 Faced with Russia in the east, Austria-Hungary could spare only one-third of its army to attack Serbia. After suffering heavy losses, the Austrians briefly occupied the Serbian capital,
Faced with Russia in the east, Austria-Hungary could spare only one-third of its army to attack Serbia. After suffering heavy losses, the Austrians briefly occupied the Serbian capital,  The Ottomans threatened Russia's
The Ottomans threatened Russia's  Russian armies generally had success in the Caucasus campaign.
Russian armies generally had success in the Caucasus campaign.  The Ottoman Empire, with German support, invaded Persia (modern Iran) in December 1914 in an effort to cut off British and Russian access to
The Ottoman Empire, with German support, invaded Persia (modern Iran) in December 1914 in an effort to cut off British and Russian access to  Although Italy joined the Triple Alliance in 1882, a treaty with its traditional Austrian enemy was so controversial that subsequent governments denied its existence and the terms were only made public in 1915. This arose from nationalist designs on Austro-Hungarian territory in Trentino, the
Although Italy joined the Triple Alliance in 1882, a treaty with its traditional Austrian enemy was so controversial that subsequent governments denied its existence and the terms were only made public in 1915. This arose from nationalist designs on Austro-Hungarian territory in Trentino, the  The pre-1914 Italian army was the weakest in Europe, short of officers, trained men, adequate transport and modern weapons; by April 1915, some of these deficiencies had been remedied but it was still unprepared for the major offensive required by the Treaty of London. The advantage of superior numbers was offset by the difficult terrain; much of the fighting took place at altitudes of over 3000 metres in the Alps and Dolomites, where trench lines had to be cut through rock and ice and keeping troops supplied was a major challenge. These issues were exacerbated by unimaginative strategies and tactics. Between 1915 and 1917, the Italian commander, Luigi Cadorna, undertook a series of frontal assaults along the Isonzo which made little progress and cost many lives; by the end of the war, total Italian combat deaths totalled around 548,000.
In the spring of 1916, the Austro-Hungarians counterattacked in Asiago in the ''
The pre-1914 Italian army was the weakest in Europe, short of officers, trained men, adequate transport and modern weapons; by April 1915, some of these deficiencies had been remedied but it was still unprepared for the major offensive required by the Treaty of London. The advantage of superior numbers was offset by the difficult terrain; much of the fighting took place at altitudes of over 3000 metres in the Alps and Dolomites, where trench lines had to be cut through rock and ice and keeping troops supplied was a major challenge. These issues were exacerbated by unimaginative strategies and tactics. Between 1915 and 1917, the Italian commander, Luigi Cadorna, undertook a series of frontal assaults along the Isonzo which made little progress and cost many lives; by the end of the war, total Italian combat deaths totalled around 548,000.
In the spring of 1916, the Austro-Hungarians counterattacked in Asiago in the '' As previously agreed with France, Russian plans at the start of the war were to simultaneously advance into Austrian Galicia and East Prussia as soon as possible. Although their attack on Galicia was largely successful, and the invasions achieved their aim of forcing Germany to divert troops from the Western Front, the speed of mobilisation meant they did so without much of their heavy equipment and support functions. These weaknesses contributed to Russian defeats at Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes in August and September 1914, forcing them to withdraw from East Prussia with heavy losses. By spring 1915, they had also retreated from Galicia, and the May 1915 Gorlice–Tarnów offensive then allowed the Central Powers to invade Russian-occupied Poland.
Despite the successful June 1916 Brusilov offensive against the Austrians in eastern Galicia, shortages of supplies, heavy losses and command failures prevented the Russians from fully exploiting their victory. However, it was one of the most significant and impactful offensives of the war, diverting German resources from Verdun, relieving Austro-Hungarian pressure on the Italians, and convincing Romania to enter the war on the side of the Allies on 27 August. It also fatally weakened both the Austrian and Russian armies, whose offensive capabilities were badly affected by their losses and increased the disillusionment with the war that ultimately led to the Russian revolutions.
Meanwhile, unrest grew in Russia as the Tsar remained at the front, with the home front controlled by Empress Alexandra. Her increasingly incompetent rule and food shortages in urban areas led to widespread protests and the murder of her favourite,
As previously agreed with France, Russian plans at the start of the war were to simultaneously advance into Austrian Galicia and East Prussia as soon as possible. Although their attack on Galicia was largely successful, and the invasions achieved their aim of forcing Germany to divert troops from the Western Front, the speed of mobilisation meant they did so without much of their heavy equipment and support functions. These weaknesses contributed to Russian defeats at Tannenberg and the Masurian Lakes in August and September 1914, forcing them to withdraw from East Prussia with heavy losses. By spring 1915, they had also retreated from Galicia, and the May 1915 Gorlice–Tarnów offensive then allowed the Central Powers to invade Russian-occupied Poland.
Despite the successful June 1916 Brusilov offensive against the Austrians in eastern Galicia, shortages of supplies, heavy losses and command failures prevented the Russians from fully exploiting their victory. However, it was one of the most significant and impactful offensives of the war, diverting German resources from Verdun, relieving Austro-Hungarian pressure on the Italians, and convincing Romania to enter the war on the side of the Allies on 27 August. It also fatally weakened both the Austrian and Russian armies, whose offensive capabilities were badly affected by their losses and increased the disillusionment with the war that ultimately led to the Russian revolutions.
Meanwhile, unrest grew in Russia as the Tsar remained at the front, with the home front controlled by Empress Alexandra. Her increasingly incompetent rule and food shortages in urban areas led to widespread protests and the murder of her favourite,  On 12 December 1916, after ten brutal months of the Battle of Verdun and a successful offensive against Romania, Germany attempted to negotiate a peace with the Allies. However, this attempt was rejected out of hand as a "duplicitous war ruse".
Soon after, US president Woodrow Wilson attempted to intervene as a peacemaker, asking in a note for both sides to state their demands and start negotiations. Lloyd George's War Cabinet considered the German offer to be a ploy to create divisions amongst the Allies. After initial outrage and much deliberation, they took Wilson's note as a separate effort, signalling that the United States was on the verge of entering the war against Germany following the "submarine outrages". While the Allies debated a response to Wilson's offer, the Germans chose to rebuff it in favour of "a direct exchange of views". Learning of the German response, the Allied governments were free to make clear demands in their response of 14 January. They sought restoration of damages, the evacuation of occupied territories, reparations for France, Russia and Romania, and a recognition of the principle of nationalities. This included the liberation of Italians, Slavs, Romanians, Czecho-Slovaks, and the creation of a "free and united Poland". On the question of security, the Allies sought guarantees that would prevent or limit future wars, complete with sanctions, as a condition of any peace settlement. The negotiations failed and the Entente powers rejected the German offer on the grounds that Germany had not put forward any specific proposals.
On 12 December 1916, after ten brutal months of the Battle of Verdun and a successful offensive against Romania, Germany attempted to negotiate a peace with the Allies. However, this attempt was rejected out of hand as a "duplicitous war ruse".
Soon after, US president Woodrow Wilson attempted to intervene as a peacemaker, asking in a note for both sides to state their demands and start negotiations. Lloyd George's War Cabinet considered the German offer to be a ploy to create divisions amongst the Allies. After initial outrage and much deliberation, they took Wilson's note as a separate effort, signalling that the United States was on the verge of entering the war against Germany following the "submarine outrages". While the Allies debated a response to Wilson's offer, the Germans chose to rebuff it in favour of "a direct exchange of views". Learning of the German response, the Allied governments were free to make clear demands in their response of 14 January. They sought restoration of damages, the evacuation of occupied territories, reparations for France, Russia and Romania, and a recognition of the principle of nationalities. This included the liberation of Italians, Slavs, Romanians, Czecho-Slovaks, and the creation of a "free and united Poland". On the question of security, the Allies sought guarantees that would prevent or limit future wars, complete with sanctions, as a condition of any peace settlement. The negotiations failed and the Entente powers rejected the German offer on the grounds that Germany had not put forward any specific proposals.
 In December 1916, Robert Nivelle replaced Pétain as commander of French armies on the Western Front and began planning a spring attack in Champagne, part of a joint Franco-British operation. Nivelle claimed the capture of his main objective, the Chemin des Dames, would achieve a massive breakthrough and cost no more than 15,000 casualties. Poor security meant German intelligence was well informed on tactics and timetables, but despite this, when the attack began on 16 April the French made substantial gains, before being brought to a halt by the newly built and extremely strong defences of the Hindenburg Line. Nivelle persisted with frontal assaults and by 25 April the French had suffered nearly 135,000 casualties, including 30,000 dead, most incurred in the first two days.
In December 1916, Robert Nivelle replaced Pétain as commander of French armies on the Western Front and began planning a spring attack in Champagne, part of a joint Franco-British operation. Nivelle claimed the capture of his main objective, the Chemin des Dames, would achieve a massive breakthrough and cost no more than 15,000 casualties. Poor security meant German intelligence was well informed on tactics and timetables, but despite this, when the attack began on 16 April the French made substantial gains, before being brought to a halt by the newly built and extremely strong defences of the Hindenburg Line. Nivelle persisted with frontal assaults and by 25 April the French had suffered nearly 135,000 casualties, including 30,000 dead, most incurred in the first two days.
 Concurrent British attacks at
Concurrent British attacks at  In March and April 1917, at the First and Second Battles of Gaza, German and Ottoman forces stopped the advance of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, which had begun in August 1916 at the Battle of Romani. At the end of October, the Sinai and Palestine campaign resumed, when General Edmund Allenby's XXth Corps, XXI Corps and Desert Mounted Corps won the Battle of Beersheba. Two Ottoman armies were defeated a few weeks later at the Battle of Mughar Ridge and, early in December, Jerusalem was captured following another Ottoman defeat at the Battle of Jerusalem. About this time, Friedrich Freiherr Kress von Kressenstein was relieved of his duties as the Eighth Army's commander, replaced by Djevad Pasha, and a few months later the commander of the Ottoman Army in Palestine, Erich von Falkenhayn, was replaced by Otto Liman von Sanders.
In early 1918, the front line was
In March and April 1917, at the First and Second Battles of Gaza, German and Ottoman forces stopped the advance of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, which had begun in August 1916 at the Battle of Romani. At the end of October, the Sinai and Palestine campaign resumed, when General Edmund Allenby's XXth Corps, XXI Corps and Desert Mounted Corps won the Battle of Beersheba. Two Ottoman armies were defeated a few weeks later at the Battle of Mughar Ridge and, early in December, Jerusalem was captured following another Ottoman defeat at the Battle of Jerusalem. About this time, Friedrich Freiherr Kress von Kressenstein was relieved of his duties as the Eighth Army's commander, replaced by Djevad Pasha, and a few months later the commander of the Ottoman Army in Palestine, Erich von Falkenhayn, was replaced by Otto Liman von Sanders.
In early 1918, the front line was  In December 1917, the Central Powers signed an armistice with Russia, thus freeing large numbers of German troops for use in the west. With German reinforcements and new American troops pouring in, the outcome was to be decided on the Western Front. The Central Powers knew that they could not win a protracted war, but they held high hopes for success based on a final quick offensive. Ludendorff drew up plans ( codenamed Operation Michael) for the 1918 offensive on the Western Front. The operation commenced on 21 March 1918 with an attack on British forces near Saint-Quentin. German forces achieved an unprecedented advance of . The initial offensive a success; after heavy fighting, however, the offensive was halted. Lacking tanks or motorised artillery, the Germans were unable to consolidate their gains. The problems of re-supply were also exacerbated by increasing distances that now stretched over terrain that was shell-torn and often impassable to traffic.
Following this, Germany launched Operation Georgette against the northern English Channel ports. The Allies halted the drive after limited territorial gains by Germany. The German Army to the south then conducted Operations Blücher and Yorck, pushing broadly towards Paris. Germany launched Operation Marne ( Second Battle of the Marne) on 15 July, in an attempt to encircle
In December 1917, the Central Powers signed an armistice with Russia, thus freeing large numbers of German troops for use in the west. With German reinforcements and new American troops pouring in, the outcome was to be decided on the Western Front. The Central Powers knew that they could not win a protracted war, but they held high hopes for success based on a final quick offensive. Ludendorff drew up plans ( codenamed Operation Michael) for the 1918 offensive on the Western Front. The operation commenced on 21 March 1918 with an attack on British forces near Saint-Quentin. German forces achieved an unprecedented advance of . The initial offensive a success; after heavy fighting, however, the offensive was halted. Lacking tanks or motorised artillery, the Germans were unable to consolidate their gains. The problems of re-supply were also exacerbated by increasing distances that now stretched over terrain that was shell-torn and often impassable to traffic.
Following this, Germany launched Operation Georgette against the northern English Channel ports. The Allies halted the drive after limited territorial gains by Germany. The German Army to the south then conducted Operations Blücher and Yorck, pushing broadly towards Paris. Germany launched Operation Marne ( Second Battle of the Marne) on 15 July, in an attempt to encircle  By September, the Germans had fallen back to the Hindenburg Line. The Allies had advanced to the Hindenburg Line in the north and centre. German forces launch numerous counterattacks, but positions and outposts of the Line continued to fall, with the BEF alone taking 30,441 prisoners in the last week of September. On 24 September, Supreme Army Command informed the leaders in Berlin that armistice talks were inevitable.
The final assault on the Hindenburg Line began with the Meuse-Argonne offensive, launched by American and French troops on 26 September. Two days later the Allied armies (Belgian French and British) attacked around Ypres and the day after the British Fourth and French First Army at St Quentin in the centre of the line. The following week, co-operating American and French units broke through in Champagne at the
By September, the Germans had fallen back to the Hindenburg Line. The Allies had advanced to the Hindenburg Line in the north and centre. German forces launch numerous counterattacks, but positions and outposts of the Line continued to fall, with the BEF alone taking 30,441 prisoners in the last week of September. On 24 September, Supreme Army Command informed the leaders in Berlin that armistice talks were inevitable.
The final assault on the Hindenburg Line began with the Meuse-Argonne offensive, launched by American and French troops on 26 September. Two days later the Allied armies (Belgian French and British) attacked around Ypres and the day after the British Fourth and French First Army at St Quentin in the centre of the line. The following week, co-operating American and French units broke through in Champagne at the  Allied forces started the Vardar offensive on 15 September at two key points: Dobro Pole and near
Allied forces started the Vardar offensive on 15 September at two key points: Dobro Pole and near  The collapse of the Central Powers came swiftly. Bulgaria was the first to sign an armistice, the Armistice of Salonica on 29 September 1918. German Emperor Wilhelm II in a telegram to Bulgarian Tsar Ferdinand I described the situation thus: "Disgraceful! 62,000 Serbs decided the war!". On the same day, the German Supreme Army Command informed Kaiser Wilhelm II and the Imperial Chancellor Count Georg von Hertling, that the military situation facing Germany was hopeless.
On 24 October, the Italians began a push that rapidly recovered territory lost after the Battle of Caporetto. This culminated in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, which marked the end of the Austro-Hungarian Army as an effective fighting force. The offensive also triggered the disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. During the last week of October, declarations of independence were made in Budapest, Prague, and Zagreb. On 29 October, the imperial authorities asked Italy for an armistice, but the Italians continued advancing, reaching Trento, Udine, and Trieste. On 3November, Austria-Hungary sent a flag of truce to ask for an armistice ( Armistice of Villa Giusti). The terms, arranged by telegraph with the Allied Authorities in Paris, were communicated to the Austrian commander and accepted. The Armistice with Austria was signed in the Villa Giusti, near Padua, on 3November. Austria and Hungary signed separate armistices following the overthrow of the
The collapse of the Central Powers came swiftly. Bulgaria was the first to sign an armistice, the Armistice of Salonica on 29 September 1918. German Emperor Wilhelm II in a telegram to Bulgarian Tsar Ferdinand I described the situation thus: "Disgraceful! 62,000 Serbs decided the war!". On the same day, the German Supreme Army Command informed Kaiser Wilhelm II and the Imperial Chancellor Count Georg von Hertling, that the military situation facing Germany was hopeless.
On 24 October, the Italians began a push that rapidly recovered territory lost after the Battle of Caporetto. This culminated in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto, which marked the end of the Austro-Hungarian Army as an effective fighting force. The offensive also triggered the disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. During the last week of October, declarations of independence were made in Budapest, Prague, and Zagreb. On 29 October, the imperial authorities asked Italy for an armistice, but the Italians continued advancing, reaching Trento, Udine, and Trieste. On 3November, Austria-Hungary sent a flag of truce to ask for an armistice ( Armistice of Villa Giusti). The terms, arranged by telegraph with the Allied Authorities in Paris, were communicated to the Austrian commander and accepted. The Armistice with Austria was signed in the Villa Giusti, near Padua, on 3November. Austria and Hungary signed separate armistices following the overthrow of the  With the military faltering and with widespread loss of confidence in the Kaiser leading to his abdication and fleeing of the country, Germany moved towards surrender. Prince Maximilian of Baden took charge of a new government on 3October as Chancellor of Germany to negotiate with the Allies. Negotiations with President Wilson began immediately, in the hope that he would offer better terms than the British and French. Wilson demanded a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary control over the German military.
In northern Germany, the
With the military faltering and with widespread loss of confidence in the Kaiser leading to his abdication and fleeing of the country, Germany moved towards surrender. Prince Maximilian of Baden took charge of a new government on 3October as Chancellor of Germany to negotiate with the Allies. Negotiations with President Wilson began immediately, in the hope that he would offer better terms than the British and French. Wilson demanded a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary control over the German military.
In northern Germany, the  A formal state of war between the two sides persisted for another seven months, until the signing of the Treaty of Versailles with Germany on 28 June 1919. The United States Senate did not ratify the treaty despite public support for it, and did not formally end its involvement in the war until the
A formal state of war between the two sides persisted for another seven months, until the signing of the Treaty of Versailles with Germany on 28 June 1919. The United States Senate did not ratify the treaty despite public support for it, and did not formally end its involvement in the war until the  Some war memorials date the end of the war as being when the Versailles Treaty was signed in 1919, which was when many of the troops serving abroad finally returned home; by contrast, most commemorations of the war's end concentrate on the armistice of 11 November 1918.
Some war memorials date the end of the war as being when the Versailles Treaty was signed in 1919, which was when many of the troops serving abroad finally returned home; by contrast, most commemorations of the war's end concentrate on the armistice of 11 November 1918.
 Austria-Hungary was partitioned into several successor states, largely but not entirely along ethnic lines. Apart from Austria and Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Italy, Poland, Romania and Yugoslavia received territories from the Dual Monarchy (the formerly separate and autonomous
Austria-Hungary was partitioned into several successor states, largely but not entirely along ethnic lines. Apart from Austria and Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Italy, Poland, Romania and Yugoslavia received territories from the Dual Monarchy (the formerly separate and autonomous  Of the 60 million European military personnel who were mobilised from 1914 to 1918, 8 million were killed, 7 million were permanently disabled, and 15 million were seriously injured. Germany lost 15.1% of its active male population, Austria-Hungary lost 17.1%, and France lost 10.5%. France mobilised 7.8 million men, of which 1.4 million died and 3.2 million were injured. Among the soldiers mutilated and surviving in the trenches, approximately 15,000 sustained horrific facial injuries, causing them to undergo social stigma and marginalisation; they were called the ''
Of the 60 million European military personnel who were mobilised from 1914 to 1918, 8 million were killed, 7 million were permanently disabled, and 15 million were seriously injured. Germany lost 15.1% of its active male population, Austria-Hungary lost 17.1%, and France lost 10.5%. France mobilised 7.8 million men, of which 1.4 million died and 3.2 million were injured. Among the soldiers mutilated and surviving in the trenches, approximately 15,000 sustained horrific facial injuries, causing them to undergo social stigma and marginalisation; they were called the '' The
The  About eight million soldiers surrendered and were held in POW camps during the war. All nations pledged to follow the Hague Conventions on fair treatment of
About eight million soldiers surrendered and were held in POW camps during the war. All nations pledged to follow the Hague Conventions on fair treatment of  Conscription was common in most European countries. However, it was controversial in English-speaking countries. It was especially unpopular among minority ethnic groups—especially the Irish Catholics in Ireland and Australia, and the French Catholics in Canada.
In the United States, conscription began in 1917 and was generally well received, with a few pockets of opposition in isolated rural areas. The administration decided to rely primarily on conscription, rather than voluntary enlistment, to raise military manpower after only 73,000 volunteers enlisted out of the initial 1million target in the first six weeks of the war.
Conscription was common in most European countries. However, it was controversial in English-speaking countries. It was especially unpopular among minority ethnic groups—especially the Irish Catholics in Ireland and Australia, and the French Catholics in Canada.
In the United States, conscription began in 1917 and was generally well received, with a few pockets of opposition in isolated rural areas. The administration decided to rely primarily on conscription, rather than voluntary enlistment, to raise military manpower after only 73,000 volunteers enlisted out of the initial 1million target in the first six weeks of the war.
 In all nations, the government's share of GDP increased, surpassing 50% in both Germany and France and nearly reaching that level in Britain. To pay for purchases in the United States, Britain cashed in its extensive investments in American railroads and then began borrowing heavily from
In all nations, the government's share of GDP increased, surpassing 50% in both Germany and France and nearly reaching that level in Britain. To pay for purchases in the United States, Britain cashed in its extensive investments in American railroads and then began borrowing heavily from  In the Balkans,
In the Balkans,  A number of socialist parties initially supported the war when it began in August 1914. But European socialists split on national lines, with the concept of
A number of socialist parties initially supported the war when it began in August 1914. But European socialists split on national lines, with the concept of  World War I began as a clash of 20th-century technology and 19th-century tactics, with the inevitably large ensuing casualties. By the end of 1917, however, the major armies, now numbering millions of men, had modernised and were making use of telephone, wireless communication, armoured cars, tanks (especially with the advent of the first prototype tank, Little Willie), and aircraft.
Artillery also underwent a revolution. In 1914, cannons were positioned in the front line and fired directly at their targets. By 1917, indirect fire with guns (as well as mortars and even machine guns) was commonplace, using new techniques for spotting and ranging, notably, aircraft and the often overlooked field telephone.
World War I began as a clash of 20th-century technology and 19th-century tactics, with the inevitably large ensuing casualties. By the end of 1917, however, the major armies, now numbering millions of men, had modernised and were making use of telephone, wireless communication, armoured cars, tanks (especially with the advent of the first prototype tank, Little Willie), and aircraft.
Artillery also underwent a revolution. In 1914, cannons were positioned in the front line and fired directly at their targets. By 1917, indirect fire with guns (as well as mortars and even machine guns) was commonplace, using new techniques for spotting and ranging, notably, aircraft and the often overlooked field telephone.
 The non-military diplomatic and propaganda interactions among the nations were designed to build support for the cause or to undermine support for the enemy. For the most part, wartime diplomacy focused on five issues: propaganda campaigns; defining and redefining the war goals, which became harsher as the war went on; luring neutral nations (Italy, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, Romania) into the coalition by offering slices of enemy territory; and encouragement by the Allies of nationalistic minority movements inside the Central Powers, especially among Czechs, Poles, and Arabs. In addition, there were multiple peace proposals coming from neutrals, or one side or the other; none of them progressed very far.
The non-military diplomatic and propaganda interactions among the nations were designed to build support for the cause or to undermine support for the enemy. For the most part, wartime diplomacy focused on five issues: propaganda campaigns; defining and redefining the war goals, which became harsher as the war went on; luring neutral nations (Italy, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, Romania) into the coalition by offering slices of enemy territory; and encouragement by the Allies of nationalistic minority movements inside the Central Powers, especially among Czechs, Poles, and Arabs. In addition, there were multiple peace proposals coming from neutrals, or one side or the other; none of them progressed very far.
 National World War I Museum and Memorial in
National World War I Museum and Memorial in