Women at the Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
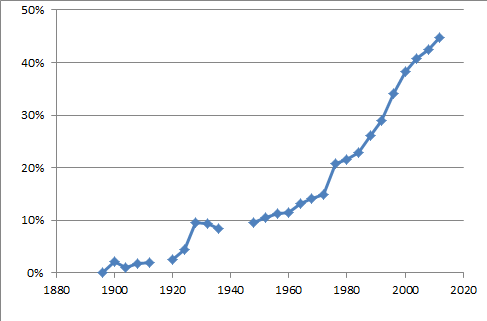
The rate of participation of women in the Olympic Games has been increasing since their first participation in
 The first modern Olympic Games to feature female athletes was the 1900 Games in Paris.
The first modern Olympic Games to feature female athletes was the 1900 Games in Paris.
 In 1920, 65 women competed at the Games.
In 1920, 65 women competed at the Games.
 At the
At the
 The women's 20 kilometre cross-country skiing event was added to the programme for the 1984 Winter Games in Sarajevo.
The women's 20 kilometre cross-country skiing event was added to the programme for the 1984 Winter Games in Sarajevo.
 At the
At the
 At the
At the
 At the
At the


 Women have competed in the following sports at the Olympic Games.
Women have competed in the following sports at the Olympic Games.
International Olympic Committee Men are excluded from the 25 metres pistol event. From 1996 to 2004, women participated in the double trap competition. The women's event was taken off the Olympic program after the 2004 Summer Olympics. Final shooting for women was discontinued in international competition as a result.
 The
The
 A goal of the IOC is to encourage these traditional countries to support women's participation in sport because two of the IOC's Olympic values that it must uphold are ensuring the lack of discrimination in sports and promoting women's involvement in sport. The commission that was created to promote the combination of these values was the Women in Sport Commission. This commission declares its role as "advis ngthe IOC Executive Board on the policy to deploy in the area of promoting women in sport". This commission did not become fully promoted to its status until 2004, and it meets once a year to discuss its goals and implementations. This commission also presents a Women and Sport Trophy annually which recognizes a woman internationally who has embodied the values of the IOC and who has supported efforts to increase women's participation in sport at all levels. This trophy is supposed to symbolize the IOC's commitment to honoring those who are beneficial to gender equality in sports.
Another way that the IOC tried to support women's participation in sport was allowing women to become members. In 1990,
A goal of the IOC is to encourage these traditional countries to support women's participation in sport because two of the IOC's Olympic values that it must uphold are ensuring the lack of discrimination in sports and promoting women's involvement in sport. The commission that was created to promote the combination of these values was the Women in Sport Commission. This commission declares its role as "advis ngthe IOC Executive Board on the policy to deploy in the area of promoting women in sport". This commission did not become fully promoted to its status until 2004, and it meets once a year to discuss its goals and implementations. This commission also presents a Women and Sport Trophy annually which recognizes a woman internationally who has embodied the values of the IOC and who has supported efforts to increase women's participation in sport at all levels. This trophy is supposed to symbolize the IOC's commitment to honoring those who are beneficial to gender equality in sports.
Another way that the IOC tried to support women's participation in sport was allowing women to become members. In 1990,
 In 1919, French translator and amateur rower,
In 1919, French translator and amateur rower,
1900
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 17), when the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 13 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 15), 2 ...
. Some sports are uniquely for women, others are contested by both sexes, while some older sports remain for men only. Studies of media coverage of the Olympics consistently show differences in the ways in which women and men are described and the ways in which their performances are discussed. The representation of women on the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
has run well behind the rate of female participation, and it continues to miss its target of a 20% minimum presence of women on their committee.
History of women at the Olympics
1900
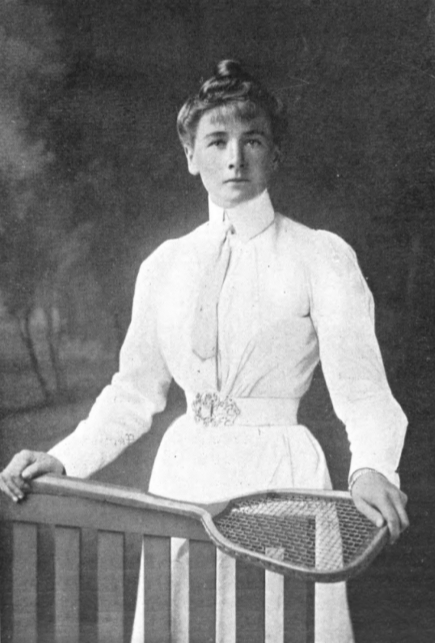
 The first modern Olympic Games to feature female athletes was the 1900 Games in Paris.
The first modern Olympic Games to feature female athletes was the 1900 Games in Paris. Hélène de Pourtalès
Countess Hélène de Pourtalès (April 28, 1868 – November 2, 1945), born Helen Barbey, was an American-born sailor who competed in the 1900 Summer Olympics representing Switzerland and became the first woman to win an Olympic gold medal. S ...
of Switzerland became the first woman to compete at the Olympic Games and became the first female Olympic champion, as a member of the winning team in the first 1 to 2 ton sailing event on May 22, 1900. Briton Charlotte Cooper became the first female individual champion by winning the women's singles tennis competition on July 11. Tennis and golf were the only sports where women could compete in individual disciplines. 22 women competed at the 1900 Games, 2.2% of all the competitors. Alongside sailing, golf and tennis, women also competed in croquet
Croquet ( or ; french: croquet) is a sport that involves hitting wooden or plastic balls with a mallet through hoops (often called "wickets" in the United States) embedded in a grass playing court.
Its international governing body is the Wor ...
.
There were several firsts in the women's golf. This was the first time ever that women competed in the Olympic Games. The women's division was won by Margaret Abbott of Chicago Golf Club
Chicago Golf Club is a private golf club in the central United States, located in Wheaton, Illinois, a suburb west of Chicago. The oldest 18-hole course in North America, it was one of the five founding clubs of the United States Golf Association ...
. Abbott shot a 47 to win and became the first ever American female to win a gold medal
A gold medal is a medal awarded for highest achievement in a non-military field. Its name derives from the use of at least a fraction of gold in form of plating or alloying in its manufacture.
Since the eighteenth century, gold medals have bee ...
in the Olympic Games, though she received a gilded porcelain bowl as a prize instead of a medal. She is also the second overall American woman to receive an Olympic medal. Abbott's mother, Mary Abbott, also competed in this Olympic event and finished tied for seventh, shooting a 65. They were the first and only mother and daughter that have ever competed in the same Olympic event at the same time. Margaret never knew that they were competing in the Olympics; she thought it was a normal golf tournament and died not knowing. Her historic victory was not known until University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
professor Paula Welch began to do research into the history of the Olympics and discovered that Margaret Abbott had placed first. Over the course of ten years, she contacted Abbott's children and informed them of their mother's victory.
Two women also competed in the hacks and hunter combined (''chevaux de selle'') equestrian event at the 1900 Games (Jane Moulin and Elvira Guerra
Elvira Guerra (; 1855–1937) was an Italian equestrienne and circus performer, notable for competing at the 1900 Summer Olympics, the first Games at which women were allowed to compete. She was the first woman to represent Italy at the Olympics. ...
). Originally only the jumping equestrian events were counted as "Olympic", but IOC records later added the hacks and hunter and mail coach
A mail coach is a stagecoach that is used to deliver mail. In Great Britain, Ireland, and Australia, they were built to a General Post Office-approved design operated by an independent contractor to carry long-distance mail for the Post Office. M ...
races to the official list of 1900 events, retroactively making Moulin and Guerra among the first female Olympians.
1904–1916
In1904
Events
January
* January 7 – The distress signal ''CQD'' is established, only to be replaced 2 years later by ''SOS''.
* January 8 – The Blackstone Library is dedicated, marking the beginning of the Chicago Public Library system.
* ...
, the women's archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
event was added.
London 1908
The 1908 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the IV Olympiad and also known as London 1908) were an international multi-sport event held in London, England, United Kingdom, from 27 April to 31 October 1908. The 1908 Games were ori ...
had 37 female athletes who competed in archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
, tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
and figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
.
Stockholm 1912
The 1912 Summer Olympics ( sv, Olympiska sommarspelen 1912), officially known as the Games of the V Olympiad ( sv, Den V olympiadens spel) and commonly known as Stockholm 1912, were an international multi-sport event held in Stockholm, Sweden, bet ...
featured 47 women in sports events. Swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
and diving
Diving most often refers to:
* Diving (sport), the sport of jumping into deep water
* Underwater diving, human activity underwater for recreational or occupational purposes
Diving or Dive may also refer to:
Sports
* Dive (American football), a ...
were added, but figure skating and archery were removed. The Art competitions that were introduced at those Olympics were also open to women, but full records of the entrants were not kept.
The 1916 Summer Olympics
The 1916 Summer Olympics (german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1916), officially known as the Games of the VI Olympiad, were scheduled to be held in Berlin, German Empire, but were eventually cancelled for the first time in its 20-year history due to ...
were due to be held in Berlin but were cancelled following the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
1920–1928
 In 1920, 65 women competed at the Games.
In 1920, 65 women competed at the Games. Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
was added back into the programme.
A record 135 female athletes competed at Paris 1924. At the 1924 Summer Olympics
The 1924 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1924), officially the Games of the VIII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIIe olympiade) and also known as Paris 1924, were an international multi-sport event held in Paris, France. The op ...
held the same year in Paris, women's fencing made its debut with Dane, Ellen Osiier winning the inaugural gold. Archery was again removed from the programme of sports. Dorothy Margaret Stuart was the first woman to gain a medal in the Arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both hi ...
, winning silver in Mixed Literature.
In 1924
Events
January
* January 12 – Gopinath Saha shoots Ernest Day, whom he has mistaken for Sir Charles Tegart, the police commissioner of Calcutta, and is arrested soon after.
* January 20– 30 – Kuomintang in China hol ...
the first Winter Olympics also took place, with women competing only in the figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
. Herma Szabo
Herma Szabo (22 February 1902 – 7 May 1986) was an Austrian figure skater who competed in ladies' singles and pairs. As a single skater, she became the 1924 Olympic champion and a five-time world champion (1922–1926). She also won two worl ...
became the first ever female Winter Olympic champion when she won the ladies' singles competition.
At the 1928 Winter Olympics in St Moritz
St. Moritz (also german: Sankt Moritz, rm, , it, San Maurizio, french: Saint-Moritz) is a high Alpine resort town in the Engadine in Switzerland, at an elevation of about above sea level. It is Upper Engadine's major town and a municipality in ...
, no changes were made to any female events. Fifteen year old Sonja Henie
Sonja Henie (8 April 1912 – 12 October 1969) was a Norway, Norwegian figure skating, figure skater and film star. She was a three-time List of Olympic medalists in figure skating, Olympic champion (Figure skating at the 1928 Winter Olympics, ...
won her inaugural of three Olympic gold medals.
At the Summer Games of the same year, women's athletics and gymnastics made their debut. In athletics, women competed in the 100 metres
The 100 metres, or 100-meter dash, is a sprint race in track and field competitions. The shortest common outdoor running distance, the dash is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. It has been conteste ...
, 800 metres
The 800 metres, or meters ( US spelling), is a common track running event. It is the shortest commonly run middle-distance running event. The 800 metres is run over two laps of an outdoor (400-metre) track and has been an Olympic event since the ...
, 4 × 100 metres relay
The 4 × 100 metres relay or sprint relay is an athletics track event run in lanes over one lap of the track with four runners completing 100 metres each. The first runners must begin in the same stagger as for the individu ...
, high jump
The high jump is a track and field event in which competitors must jump unaided over a horizontal bar placed at measured heights without dislodging it. In its modern, most-practiced format, a bar is placed between two standards with a crash mat f ...
and discus throw
The discus throw (), also known as disc throw, is a track and field event in which an athlete throws a heavy disk (mathematics), disc—called a discus—in an attempt to mark a farther distance than their competitors. It is an classical antiqui ...
. The 800-metre race was controversial as many competitors were reportedly exhausted or unable to complete the race. Consequently, the IOC decided to drop the 800 metres from the programme; it was not reinstated until 1960. Halina Konopacka
Halina Konopacka (Leonarda Kazimiera Konopacka-Matuszewska-Szczerbińska) (26 February 1900 – 28 January 1989) was a Polish athlete. She won the discus throw event at the 1928 Summer Olympics, defeating American silver medal winner Lillian C ...
of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
became the first female Olympic champion in athletics by winning the discus throw. At the gymnastics competition, the host Dutch team won the first gold medal for women in the sport. Tennis was removed from the program.
1932–1936
For the1932 Summer Olympics
The 1932 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the X Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1932) were an international multi-sport event held from July 30 to August 14, 1932 in Los Angeles, California, United States. The Games were held duri ...
, held in Los Angeles, the javelin throw
The javelin throw is a track and field event where the javelin, a spear about in length, is thrown. The javelin thrower gains momentum by running within a predetermined area. Javelin throwing is an event of both the men's decathlon and the ...
and 80 meters hurdles
80 metres hurdles is a distance in hurdling ran by women until 1972 in international competitions.
Since the 1972 Summer Olympics, the event has been permanently replaced by the 100 metre hurdles.
Masters athletics
The distance, with different sp ...
were added. At the 1936 Winter Games in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, women competed in the alpine skiing combined event for the first time, with German Christl Cranz
Christl Franziska Antonia Cranz-Borchers (1 July 1914 – 28 September 2004) was a German alpine ski racer. Cranz dominated international competition in the 1930s, winning twelve world championship titles between 1934 and 1939. At the 1936 Winte ...
winning the gold medal. At the 1936 Summer Olympics
The 1936 Summer Olympics (German: ''Olympische Sommerspiele 1936''), officially known as the Games of the XI Olympiad (German: ''Spiele der XI. Olympiade'') and commonly known as Berlin 1936 or the Nazi Olympics, were an international multi-sp ...
held in Berlin, gymnastics
Gymnastics is a type of sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, shou ...
returned to the programme for women.
1940–1944
The1940 Winter Olympics
The 1940 Winter Olympics, which would have been officially known as the and as Sapporo 1940 (札幌1940), were to have been celebrated from 3 to 12 February 1940 in Sapporo, Japan, but the games were eventually cancelled due to the onset of Wo ...
due to be held in Sapporo, 1940 Summer Olympics
The 1940 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XII Olympiad, were originally scheduled to be held from September 21 to October 6, 1940, in Tokyo City, Empire of Japan. They were rescheduled for Helsinki, Finland, to be held from ...
due to be held in Tokyo, 1944 Winter Olympics due to be held in Cortina d'Ampezzo and the 1944 Summer Olympics
The 1944 Summer Olympics, which were to be officially known as the Games of the XIII Olympiad, were cancelled because of World War II. They would have been held in London, England, United Kingdom, which won the bid on the first ballot in a June ...
due to be held in London were all cancelled due to the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Six female Olympic athletes died due to World War II:
1948–1956
 At the
At the 1948 Winter Olympics
The 1948 Winter Olympics, officially known as the V Olympic Winter Games (german: V. Olympische Winterspiele; french: Ves Jeux olympiques d'hiver; it, V Giochi olimpici invernali; rm, V Gieus olimpics d'enviern) and commonly known as St. Moritz ...
in St. Moritz, women made their debut in the downhill
Downhill may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Downhill'' (1927 film), a British film by Alfred Hitchcock
* ''Downhill'' (2014 film), a British comedy directed by James Rouse
* ''Downhill'' (2016 film), a Chilean thriller directed by Patrici ...
and slalom
To slalom is to zigzag between obstacles. It may refer to:
Sports
;Alpine skiing and/or snowboarding
* Slalom skiing, an alpine skiing and alpine snowboarding discipline
* Giant slalom, an alpine skiing and alpine snowboarding discipline
* Super-G ...
disciplines, having only competed in the combined event in 1936. In 1948, women competed in all of the same alpine skiing disciplines as the men. Barbara Ann Scott
Barbara Ann Scott (May 9, 1928 – September 30, 2012) was a Canadian figure skater. She was the 1948 Olympic champion, a two-time World champion (1947–1948), and a four-time Canadian national champion (1944–46, 48) in ladies' singles. Kn ...
of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
won the ladies' singles figure skating competition, marking the first time a non-European won the gold medal in the event. At the London 1948 Summer Olympics
The 1948 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XIV Olympiad and also known as London 1948) were an international multi-sport event held from 29 July to 14 August 1948 in London, England, United Kingdom. Following a twelve-year hiatus ca ...
, women competed in canoeing for the first time. The women competed in the K-1 500 metres discipline. Alice Coachman won a gold medal in the women's high jump at the 1948 Summer Olympics
The 1948 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XIV Olympiad and also known as London 1948) were an international multi-sport event held from 29 July to 14 August 1948 in London, England, United Kingdom. Following a twelve-year hiatus ca ...
, marking the first gold medal won by a Black woman for the United States. At the 1952 Winter Olympics
The 1952 Winter Olympics, officially known as the VI Olympic Winter Games ( no, De 6. olympiske vinterleker; nn, Dei 6. olympiske vinterleikane) and commonly known as Oslo 1952, was a winter multi-sport event held from 14 to 25 February 195 ...
held in Oslo, women competed in cross-country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreation ...
for the first time. They competed in the 10 kilometre distance. At the 1952 Summer Olympics
The 1952 Summer Olympics ( fi, Kesäolympialaiset 1952; sv, Olympiska sommarspelen 1952), officially known as the Games of the XV Olympiad ( fi, XV olympiadin kisat; sv, Den XV olympiadens spel) and commonly known as Helsinki 1952 ( sv, Helsin ...
held in Helsinki, women were allowed to compete in equestrian
The word equestrian is a reference to equestrianism, or horseback riding, derived from Latin ' and ', "horse".
Horseback riding (or Riding in British English)
Examples of this are:
* Equestrian sports
*Equestrian order, one of the upper classes i ...
for the first time. They competed in the dressage event which was open to both men and women to compete against one another. Danish equestrian Lis Hartel
Lis Hartel (March 14, 1921 – February 12, 2009) was an equestrian from Denmark. She was originally coached by her mother, Else Holst, but began to be coached by professional horseman Gunnar Andersen when she became nationally competitive.
She ...
of Denmark won the silver medal in the individual competition alongside men. At the 1956 Winter Olympics
The 1956 Winter Olympics, officially known as the VII Olympic Winter Games ( it, VII Giochi Olimpici invernali) and commonly known as Cortina d'Ampezzo 1956 ( lld, Anpezo 1956 or ), was a multi-sport event held in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy, from ...
held in Cortina d'Ampezzo, the 3 × 5 kilometre relay cross country event was added to the program. The 1956 Summer Olympics
The 1956 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVI Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, from 22 November to 8 December 1956, with the exception of the equestrian events, whi ...
held in Melbourne, had a programme identical to that of the prior Olympiad.The equestrian events for these Games were held in Stockholm due to Australia's strict equine quarantine laws.
1960–1968

Speed skating
Speed skating is a competitive form of ice skating in which the competitors racing, race each other in travelling a certain distance on Ice skate, skates. Types of speed skating are long track speed skating, short track speed skating, and marath ...
for women. made its debut at the 1960 Winter Olympics
The 1960 Winter Olympics (officially the VIII Olympic Winter Games and also known as Squaw Valley 1960) were a winter multi-sport event held from February 18 to 28, 1960, at the Squaw Valley Resort (now known as Palisades Tahoe) in Squaw Vall ...
held in Squaw Valley. Helga Haase
Helga Haase ( Obschernitzki; 9 June 1934 – 16 June 1989) was a speed skater in East Germany. She was born in Danzig and died in East Berlin.
Career
Haase's career began 1952, when she introduced herself at 18 years at the SC Dynamo Berlin ...
, representing the United Team of Germany
The United Team of Germany (german: Gesamtdeutsche Mannschaft) was a combined team of athletes from West Germany and East Germany that competed in the 1956, 1960 and 1964 Winter and Summer Olympic Games. In 1956, the team also included athletes f ...
, won the inaugural gold medal for women, in the 500 metres event. The programme remained the same for the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics ( it, Giochi Olimpici estivi del 1960), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad ( it, Giochi della XVII Olimpiade) and commonly known as Rome 1960 ( it, Roma 1960), were an international multi-sport event held ...
held in Rome. At the 1964 Winter Olympics
The 1964 Winter Olympics, officially known as the IX Olympic Winter Games (german: IX. Olympische Winterspiele) and commonly known as Innsbruck 1964 ( bar, Innschbruck 1964, label=Austro-Bavarian), was a winter multi-sport event which was celebr ...
in Innsbruck, the women's 5km cross-country skiing event debuted. At the 1964 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and commonly known as Tokyo 1964 ( ja, 東京1964), were an international multi-sport event held from 10 to 24 October 1964 in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had been awarded the organization of the 1940 Summer Olympics, but this ho ...
held in Tokyo, Volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summ ...
made its debut with the host Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
taking the gold. At the 1968 Winter Olympics
The 1968 Winter Olympics, officially known as the X Olympic Winter Games (french: Les Xes Jeux olympiques d'hiver), were a winter multi-sport event held from 6 to 18 February 1968 in Grenoble, France. Thirty-seven countries participated. Frenchm ...
held in Grenoble, women's luge appeared for the first time. Erika Lechner
Erika Lechner (sometimes listed as Erica Lechner, born 28 May 1947 in Bolzano) is an Italian luger who competed during the late 1960s and early 1970s. At the 1968 Winter Olympics in Grenoble, she originally finished third in the women's singles ...
of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
won the gold after East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
racers Ortrun Enderlein
Ortrun Zöphel-Enderlein (born 1 December 1943) is a former East German (GDR) luger, and one of the most successful lugers in the 1960s. Enderlein started her working career at the SC Traktor Oberwiesenthal, and was first introduced to luge in ...
, Anna-Maria Müller
Anna-Maria Müller (later Murach, 23 February 1949 – 23 August 2009) was an East German luger who competed in the late 1960s and early 1970s. She won the gold medal in the women's singles event at the 1972 Winter Olympics in Sapporo. At the pr ...
and Angela Knösel
Angela Knösel (born 29 August 1949) is a German luger who competed for East Germany in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
She won two silver medals in the women's singles event at the FIL European Luge Championships (1970, 1971).
At the 196 ...
allegedly heated the runners on their sleds and were disqualified. Whether the East Germans actually heated their sleds or if the situation was fabricated by the West Germans remains a mystery. At the 1968 Summer Olympics
The 1968 Summer Olympics ( es, Juegos Olímpicos de Verano de 1968), officially known as the Games of the XIX Olympiad ( es, Juegos de la XIX Olimpiada) and commonly known as Mexico 1968 ( es, México 1968), were an international multi-sport eve ...
in Mexico City, women competed in shooting
Shooting is the act or process of discharging a projectile from a ranged weapon (such as a gun, bow, crossbow, slingshot, or blowpipe). Even the acts of launching flame, artillery, darts, harpoons, grenades, rockets, and guided missiles can ...
for the first time. The women competed in mixed events with the men and were allowed to compete in all seven disciplines.
1972–1980
At the1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Europe ...
held in Sapporo there were no changes to the sports open to women. At the 1972 Summer Olympics
The 1972 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XX Olympiad () and commonly known as Munich 1972 (german: München 1972), was an international multi-sport event held in Munich, West Germany, from 26 August to 11 September 1972. ...
in Munich, archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
was held for the first time since 1920. At the 1976 Winter Olympics
The 1976 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XII Olympic Winter Games (german: XII. Olympische Winterspiele, french: XIIes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Innsbruck 1976 ( bar, Innschbruck 1976, label=Austro-Bavarian), was a ...
in Innsbruck, ice dancing was added to the programme.Ice dancing is a pairs event with one male and one female. Women competed in three new events at the 1976 Summer Olympics
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phi ...
held in Montreal. Women debuted in basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
and handball
Handball (also known as team handball, European handball or Olympic handball) is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outcourt players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of throwing it into the g ...
. Women also competed for the first time in rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically atta ...
, participating in six of the eight disciplines. There were no new events for women at the 1980 Winter Olympics
The 1980 Winter Olympics, officially the XIII Olympic Winter Games and also known as Lake Placid 1980, were an international multi-sport event held from February 13 to 24, 1980, in Lake Placid, New York, United States.
Lake Placid was elected ...
held in Lake Placid. At the 1980 Summer Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics (russian: Летние Олимпийские игры 1980, Letniye Olimpiyskiye igry 1980), officially known as the Games of the XXII Olympiad (russian: Игры XXII Олимпиады, Igry XXII Olimpiady) and commo ...
held in Moscow, women's field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ci ...
debuted. The underdog Zimbabwean team pulled off a major upset, winning the gold, the nation's first ever Olympic medal. However, these Olympics were marred by the US-led boycott of the games due to the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
.
1984–1992
Marja-Liisa Hämäläinen
Marja-Liisa Kirvesniemi (née Hämäläinen; born 10 September 1955) is a Finland, Finnish former cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skier.
Career
She was the big figure at the 1984 Winter Olympics, 1984 Olympics in Sarajevo, winning all ...
of Finland dominated the cross-country events, winning gold in all three distances.
Multiple new events for women were competed in at the 1984 Summer Olympics
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international multi-sport event held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. It marked the secon ...
in Los Angeles. Synchronized swimming
Synchronized swimming (in British English, synchronised swimming) or artistic swimming is a sport where swimmers perform a synchronized choreographed routine, accompanied by music. The sport is governed internationally by FINA (the ''Fédérati ...
made its debut, with only women competing in the competition. The host Americans won gold in both the solo
Solo or SOLO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Comics
* ''Solo'' (DC Comics), a DC comics series
* Solo, a 1996 mini-series from Dark Horse Comics
Characters
* Han Solo, a ''Star Wars'' character
* Jacen Solo, a Jedi in the non-canonical ''S ...
and duet
A duet is a musical composition for two performers in which the performers have equal importance to the piece, often a composition involving two singers or two pianists. It differs from a harmony, as the performers take turns performing a solo ...
events. Women also made their debut in cycling, competing in the road race. This event was also won by an American, Connie Carpenter
Connie Carpenter-Phinney (born February 26, 1957) is an American retired racing cyclist and speed skater who won four medals in World Cycling Championship competitions (both road and track cycling) in the late 1970s and early 1980s. She also won ...
. Also, rhythmic gymnastics
Rhythmic gymnastics is a sport in which gymnasts perform on a floor with an apparatus: hoop, ball, clubs, ribbon. The sport combines elements of gymnastics, dance and calisthenics; gymnasts must be strong, flexible, agile, dexterous and coord ...
appeared for the first time with only women competing; the winner was Canadian Lori Fung. The women's marathon also made its first appearance in these Games, with American Joan Benoit
Joan Benoit Samuelson (born May 16, 1957) is an American marathon runner who was the first women's Olympic Games marathon champion, winning the gold medal at the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. She held the fastest time for an American woma ...
winning gold in 2:24:52, a time many thought was impossible for women just a few years earlier. These were also the first Games where women competed only against other women in shooting
Shooting is the act or process of discharging a projectile from a ranged weapon (such as a gun, bow, crossbow, slingshot, or blowpipe). Even the acts of launching flame, artillery, darts, harpoons, grenades, rockets, and guided missiles can ...
. These games were boycotted by the Soviet Union and its satellite states.
There were no new events at the 1988 Winter Olympics
The 1988 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XV Olympic Winter Games (french: XVes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Calgary 1988 ( bla, Mohkínsstsisi 1988; sto, Wîchîspa Oyade 1988 or ; cr, Otôskwanihk 1998/; srs, Guts� ...
held in Calgary. At the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul, table tennis
Table tennis, also known as ping-pong and whiff-whaff, is a sport in which two or four players hit a lightweight ball, also known as the ping-pong ball, back and forth across a table using small solid rackets. It takes place on a hard table div ...
appeared for the first time for both men and women. They competed in the singles
Singles are people not in a committed relationship.
Singles may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''Singles'' (miniseries), a 1984 Australian television series
* ''Singles'' (1992 film), written and directed by Cameron Crowe
* ''Singles'' ...
and doubles disciplines. Also, a female specific sailing event debuted at these Games, the women's 470 discipline. For the first time women competed in a track cycling event, the sprint.
In 1991, the IOC made it mandatory for all new sports applying for Olympic recognition to have female competitors. However, this rule only applied to new sports applying for Olympic recognition. This meant that any sports that were included in the Olympic programme prior to 1991 could continue to exclude female participants at the discretion of the sport's federation. At the 1992 Winter Olympics
)
, nations = 64
, athletes = 1,801 (1313 men, 488 women)
, events = 57 in 6 sports (12 disciplines)
, opening = 8 February 1992
, closing = 23 February 1992
, opened_by = President François Mitterrand
, cauldron ...
in Albertville, women competed in biathlon
The biathlon is a winter sport that combines cross-country skiing and rifle shooting. It is treated as a race, with contestants skiing through a cross-country trail whose distance is divided into shooting rounds. The shooting rounds are not tim ...
for the first time. The athletes competed in the individual
An individual is that which exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of being an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) of being a person unique from other people and possessing one's own Maslow ...
, sprint and relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
disciplines. Freestyle skiing also debuted at the 1992 Games, where women competed in the moguls discipline. Short track speed skating
Short-track speed skating is a form of competitive ice skating, ice speed skating. In competitions, multiple skaters (typically between four and six) skate on an oval ice track with a length of . The rink itself is long by wide, which is the s ...
first appeared at these Games. Women competed in the 500 metres
The 500 metres is a rarely run middle-distance running event in track and field competitions.
All-time top 25
*i = indoor performance
*OT = oversized track (exceeding 200m in circumference)
*A = affected by altitude
*h = hand timing
Men
*C ...
and the 3000 metre relay. At the 1992 Summer Olympics
The 1992 Summer Olympics ( es, Juegos Olímpicos de Verano de 1992, ca, Jocs Olímpics d'estiu de 1992), officially known as the Games of the XXV Olympiad ( es, Juegos de la XXV Olimpiada, ca, Jocs de la XXV Olimpíada) and commonly known as ...
held in Barcelona, badminton
Badminton is a racquet sport played using racquets to hit a shuttlecock across a net. Although it may be played with larger teams, the most common forms of the game are "singles" (with one player per side) and "doubles" (with two players pe ...
appeared on the programme for the first time. Women competed in the singles
Singles are people not in a committed relationship.
Singles may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''Singles'' (miniseries), a 1984 Australian television series
* ''Singles'' (1992 film), written and directed by Cameron Crowe
* ''Singles'' ...
and doubles competition. Women also competed in the sport of judo
is an unarmed gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponi ...
for the first time at these Games. 35 nations still sent all-male delegations to these Games. 1992 was the last Olympic games that skeet competition opens to both men and women, and the only mixed shooting competition at the Olympics ever won by a woman: Zhang Shan
Zhang Shan (; born March 23, 1968) is a Chinese sports shooter and Olympic champion.
Career
Zhang Shan was born in the city of Nanchong in Sichuan province in Southwest China. She began shooting skeet at age 16. In 1989, she joined the Chines ...
.
1994–2002
 At the
At the 1994 Winter Olympics
The 1994 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XVII Olympic Winter Games ( no, De 17. olympiske vinterleker; nn, Dei 17. olympiske vinterleikane) and commonly known as Lillehammer '94, was an international winter multi-sport event held fro ...
in Lillehammer, the aerials discipline of freestyle skiing
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, Mogul Skiing, moguls, Ski Cross, cross, Half-pipe skiing, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Freestyle skiing at the Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics. It can consist of a ...
officially debuted. Lina Cheryazova
Lina Anatolyevna Cheryazova (russian: Лина Анатольевна Черязова, 1 November 1968 – 23 March 2019) was an Uzbek freestyle skier who competed in aerials. She won a bronze medal at the 1990 European Championship and a gold ...
of Uzbekistan won the gold medal, which is to date her nation's sole medal at an Olympic Winter Games. Women's soccer
Women's association football, more commonly known simply as women's football or women's soccer, is a team sport of association football when played by women only. It is played at the women's professional sports, professional level in multiple c ...
and softball
Softball is a game similar to baseball played with a larger ball on a smaller field. Softball is played competitively at club levels, the college level, and the professional level. The game was first created in 1887 in Chicago by George Hanc ...
made their first appearances at the 1996 Games in Atlanta, where the hosts won gold in both. At the 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 ( ja, 長野1998), was a winter multi-sport event held from 7 to 22 February 1998, mainly in Nagano, Japan, with some events taking place in the ...
in Nagano, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hock ...
(with the United States winning gold) and curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
(with Canada winning gold) debuted for women. Numerous new events made their premieres at the 2000 Summer Olympics
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad and also known as Sydney 2000 (Dharug: ''Gadigal 2000''), the Millennium Olympic Games or the Games of the New Millennium, was an international multi-sport event held from 1 ...
in Sydney. Weightlifting
Weightlifting generally refers to activities in which people lift Weight training#Equipment, weights, often in the form of dumbbells or barbells. People lift various kinds of weights for a variety of different reasons. These may include various t ...
, modern pentathlon
The modern pentathlon is an Olympic sport consisting of fencing (one-touch épée), freestyle swimming, equestrian show jumping, pistol shooting, and cross country running. The event is inspired by the traditional pentathlon held during the anci ...
, taekwondo
''Taekwondo'', ''Tae Kwon Do'' or ''Taekwon-Do'' (; ko, 태권도/跆拳道 ) is a Korean form of martial arts involving punching and kicking techniques, with emphasis on head-height kicks, spinning jump kicks, and fast kicking techniques. T ...
, triathlon
A triathlon is an endurance multisport race consisting of Swimming (sport), swimming, Cycle sport, cycling, and running over various distances. Triathletes compete for fastest overall completion time, racing each segment sequentially with the t ...
and trampoline
A trampoline is a device consisting of a piece of taut, strong fabric stretched between a steel frame using many coiled spring (device), springs. Not all trampolines have springs, as the Springfree Trampoline uses glass-reinforced plastic rods. ...
all debuted in Australia. At the 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
in Salt Lake City, women's bobsleigh
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Feder ...
made its first appearance. Jill Bakken
Jill Bakken (born January 25, 1977) is an American Olympic bobsledder who has competed since 1994. As the driver, she and partner Vonetta Flowers won the gold medal in Bobsleigh at the 2002 Winter Olympics for the U.S. Bakken's best Bobsleigh W ...
and Vonetta Flowers of the USA won the two-woman competition, the sole bobsleigh event for women at the 2002 Games.
2004–2012
 At the
At the 2004 Summer Olympics
The 2004 Summer Olympics ( el, Θερινοί Ολυμπιακοί Αγώνες 2004, ), officially the Games of the XXVIII Olympiad ( el, Αγώνες της 28ης Ολυμπιάδας, ) and also known as Athens 2004 ( el, Αθήνα 2004), ...
in Athens, women appeared in wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
for the first time competing in the freestyle weight classes of 48 kg, 55 kg, 63 kg and 72 kg. Women also competed in the sabre discipline of fencing for the first time, with Mariel Zagunis
Mariel Leigh Zagunis (born March 3, 1985) is an American sabre fencer. She is a two-time Olympic champion in the individual sabre ( 2004 and 2008) and the first American to win a gold medal in Olympic fencing. She was Team USA flag bearer in t ...
of the USA winning gold. In 2004, women from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
competed at the Olympics for the first time in their history after the nation was banned from Sydney 2000 by the IOC due to the Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state (polity), state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalism, Islamic fundamentalist, m ...
government's opposition to women in sports. At the 2006 Winter Olympics
The 2006 Winter Olympics, officially the XX Olympic Winter Games ( it, XX Giochi olimpici invernali) and also known as Torino 2006, were a winter multi-sport event held from 10 to 26 February 2006 in Turin, Italy. This marked the second t ...
in Turin, the programme remained unchanged. At the 2008 Summer Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and also known as Beijing 2008 (), were an international multisport event held from 8 to 24 August 2008, in Beijing, China. A total of 10,942 athletes from 204 Na ...
in Beijing, a few new events were added. BMX cycling was held for the first time in 2008, debuting with the men's event. Women also competed in the 3000 m steeplechase
The 3000 metres steeplechase or 3000-meter steeplechase (usually abbreviated as ) is the most common distance for the steeplechase in track and field. It is an obstacle race over the distance of the 3000 metres, which derives its name from the h ...
and the 10 kilometre marathon swim for the first time. Baseball and boxing remained the only sports not open to women at these Games.
At the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May DoanNancy GreeneWayne Gretz ...
in Vancouver, ski cross
Ski cross is a skiing competition which incorporates terrain features traditionally found in freestyle skiing with courses which include big-air jumps and high-banked turns. In spite of the fact that it is a timed racing event, it is often cons ...
debuted for both women and men. Ashleigh McIvor
Ashleigh McIvor DeMerit (born September 15, 1983) is a Canadian retired freestyle skier currently residing in Whistler, British Columbia. McIvor was a member of the Canadian national ski cross team and became the first gold medal winner of women ...
of Canada won the inaugural gold for women in the sport. Controversy was created when women's ski jumping
Ski jumping is a winter sport in which competitors aim to achieve the farthest jump after sliding down on their skis from a specially designed curved ramp. Along with jump length, competitor's aerial style and other factors also affect the final ...
was excluded from the programme by the IOC due to the low number of athletes and participating nations in the sport. A group of fifteen competitive female ski jumpers later filed a suit against the Vancouver Organizing Committee for the 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games
The Vancouver Organizing Committee for the 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games (VANOC) (french: Comité d’organisation des Jeux olympiques et paralympiques d’hiver de 2010 à Vancouver - COVAN) was the non-profit organization responsible ...
on the grounds that it violated the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms
The ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms'' (french: Charte canadienne des droits et libertés), often simply referred to as the ''Charter'' in Canada, is a bill of rights entrenched in the Constitution of Canada, forming the first part o ...
since men were competing in the same event. The suit failed, with the judge ruling that the situation was not governed by the Charter. The 2012 Summer Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012) was an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
saw women's boxing
Although women have participated in boxing for almost as long as the sport has existed, female fights have been effectively outlawed for most of boxing's history until recently, with athletic commissioners refusing to sanction or issue licenses ...
make its debut. This, combined with the decision by the IOC to drop baseball from the programme for 2012, meant that women competed in every sport at a Summer Games for the first time. London 2012 also marked the first time that all national Olympic committees sent a female athlete to the Games. Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
and Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
all had female athletes as a part of their delegations for the first time.
2014–2018
 At the
At the 2014 Winter Olympics
, ''Zharkie. Zimnie. Tvoi'')
, nations = 88
, events = 98 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, athletes = 2,873
, opening = 7 February 2014
, closing = 23 February 2014
, opened_by = President Vladimir Putin
, cauldron =
, stadium = Fisht Olympic ...
in Sochi, women's ski jumping made its first appearance. Carina Vogt
Carina Vogt (born 5 February 1992) is a German former ski jumper.
Career
She won the first Olympic gold medal ever awarded for women's ski jumping, at the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympic Games. Vogt's international debut was in the Meinerzhagen compe ...
of Germany won the first gold medal for women in the sport. The 2016 Summer Olympics
The 2016 Summer Olympics ( pt, Jogos Olímpicos de Verão de 2016), officially the Games of the XXXI Olympiad ( pt, Jogos da XXXI Olimpíada) and also known as Rio 2016, was an international multi-sport event held from 5 to 21 August 20 ...
in Rio de Janeiro saw the first rugby sevens competition. The tournament was won by the Australian team. Golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping wi ...
was also re-added to the programme for the first time for women since 1900. Inbee Park
Inbee Park (, or ; born 12 July 1988) is a South Korean professional golfer who plays on the LPGA Tour and the LPGA of Japan Tour. She has been the number one ranked player in the Women's World Golf Rankings for four separate runs: April 201 ...
of South Korea won the tournament. The 2018 Winter Olympics
, nations = 93
, athletes = 2,922 (1,680 men and 1,242 women)
, events = 102 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening =
, closing =
, opened_by = President Moon Jae-in
, cauldron = Kim Yun-a
, stadium = Pyeongchang Olympic Stadium
, winte ...
in PyeongChang saw the addition of big air snowboarding, mixed doubles curling, mass start speed skating, and mixed team alpine skiing. Jamie Anderson of the USA was the silver medalist of the big air, also winning gold in slopestysle, becoming the most medaled female snowboarder at those games.
2020
Transgender
A transgender (often abbreviated as trans) person is someone whose gender identity or gender expression does not correspond with their sex assigned at birth. Many transgender people experience dysphoria, which they seek to alleviate through tr ...
athletes have been permitted at the Olympics since 2004, however, Tokyo 2020 was the first Olympics in which a trans woman
A trans woman or a transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity, may experience gender dysphoria, and may transition; this process commonly includes hormone replacement therapy and so ...
competed, with Laurel Hubbard
Laurel Hubbard (born 9 February 1978) is a New Zealand weightlifter. Selected to compete at the 2020 Summer Olympics, she was the first openly transgender woman to compete in the Olympic Games. Prior to making her Olympic debut, Hubbard achieved ...
entering the women's super heavyweight weightlifting
Weightlifting generally refers to activities in which people lift Weight training#Equipment, weights, often in the form of dumbbells or barbells. People lift various kinds of weights for a variety of different reasons. These may include various t ...
event.
Women competed in softball, karate, sport climbing, surfing, and skateboarding
Skateboarding is an extreme sport, action sport originating in the United States that involves riding and performing tricks using a skateboard, as well as a recreational activity, an art form, an entertainment industry Profession, job, and a ...
at the 2020 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and also known as , was an international multi-sport event held from 23 July to 8 August 2021 in Tokyo, Japan, with some preliminary events that began on 21 July.
Tokyo was selected as the host city during the ...
in Tokyo.
The new sports climbing events - speed climbing, bouldering, and lead climbing - all had men's and women's categories. Several sports, such as swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
, introduced mixed events.
The length of tennis matches were changed so that men played three sets, the same as women in all previous Olympics.
The 2020 Olympics was the first Olympics in which women were allowed to compete in canoe sprint. Before this Olympics, women were allowed to do sprint kayak, but not sprint canoe.
The 2020 Olympics was the first Olympics in which there was a women's 1500 meter freestyle swimming event.
Future Olympics
TheInternational Ski Federation
The ''Fédération internationale de ski et de snowboard'' (FIS; en, International Ski and Snowboard Federation) is the highest international governing body for skiing and snowboarding. Founded on 2 February 1924 in Chamonix, France during the ...
has stated that it is aiming to include women's Nordic combined in the Olympic program for the first time at the 2022 Winter Olympics
The 2022 Winter Olympics (2022年冬季奥林匹克运动会), officially called the XXIV Olympic Winter Games () and commonly known as Beijing 2022 (2022), was an international winter multi-sport event held from 4 to 20 February 2022 in Beij ...
in Beijing. However, Nordic combined at the 2022 Winter Olympics
Nordic combined at the 2022 Winter Olympics was held at the Kuyangshu Nordic Center and Biathlon Center. The three events took place between 9 and 17 February 2022.
A total of 55 quota spots (all men) were distributed to the sport, the same as ...
ended up having three men only events, just as in 2018.
Sports



 Women have competed in the following sports at the Olympic Games.
Women have competed in the following sports at the Olympic Games.
Gender differences
Athletics
In combined events at the Olympics, women compete in the seven-eventheptathlon
A heptathlon is a track and field combined events contest made up of seven events. The name derives from the Greek επτά (hepta, meaning "seven") and ἄθλος (áthlos, or ἄθλον, áthlon, meaning "competition"). A competitor in a hept ...
but men compete in three more events in the decathlon
The decathlon is a combined event in Athletics (sport), athletics consisting of ten track and field events. The word "decathlon" was formed, in analogy to the word "pentathlon", from Greek language, Greek δέκα (''déka'', meaning "ten") and ...
. A women's pentathlon
The pentathlon or women's pentathlon is a combined track and field event in which each woman competes in five separate events over one day (formerly two days). The distance or time for each event is converted to points via scoring tables, with ...
was held from 1964 to 1980, before being expanded to the heptathlon.
In sprint hurdles at the Olympics
The sprint hurdles at the Summer Olympics have been contested over a variety of distances at the multi-sport event. The men's 110 metres hurdles has been present on the Olympic athletics programme since the first edition in 1896. A men's 200 me ...
, men compete in the 110 metres hurdles, while women cover 100 metres. Women ran 80 metres up to the 1968 Olympics; this was extended to 100 metres in 1961, albeit on a trial basis, the new distance of 100 metres became official in 1969. No date has been given for the addition of the 10 metres. Both men and women clear a total of ten hurdles during the races and both genders take three steps between the hurdles at elite level. Any amendment to the women's distance to match the men's would impact either the athlete technique or number of hurdles in the event, or result in the exclusion of women with shorter strides.
Historically, women competed over 3000 metres
The 3000 metres or 3000-metre run is a track running event, also commonly known as the "3K" or "3K run", where 7.5 laps are run around an outdoor 400 m track, or 15 laps around a 200 m indoor track.
It is debated whether the 3000m shoul ...
until this was matched to the men's 5000 metres
The 5000 metres or 5000-metre run is a common long-distance running event in track and field, approximately equivalent to or . It is one of the track events in the Olympic Games and the World Championships in Athletics, run over laps of a stan ...
event in 1996. Similarly, women competed in a 10 kilometres race walk in 1992 and 1996 before this was changed to the standard men's distance of 20 km. The expansion of the women's athletics programme to match the men's was a slow one. Triple jump was added in 1996, hammer throw and pole vault in 2000, and steeplechase in 2008. The sole difference remaining is the men-only 50 kilometres race walk
The 50 kilometre race walk was an Olympic athletics event that first appeared in 1932 and made its final Olympic appearance in 2021. The racewalking event is competed as a road race. Athletes must always keep in contact with the ground and the ...
event. While the inclusion of a women's 50 km event has been advocated, proposals have also been mooted to remove the men's event entirely from the Olympics.
Boxing
At the summer Olympics, men's boxing competitions take place over three three-minute rounds and women's over four rounds of two minutes each. Women also compete in three weight categories against 10 for men.Canoeing
Canoeing excluded women at the Olympics from both the sprint and slalom disciplines until Tokyo 2020.Shooting
Women are excluded from the 25 metres rapid fire pistol, the 50 metres pistol and the 50 metres rifle prone events.ShootingInternational Olympic Committee Men are excluded from the 25 metres pistol event. From 1996 to 2004, women participated in the double trap competition. The women's event was taken off the Olympic program after the 2004 Summer Olympics. Final shooting for women was discontinued in international competition as a result.
Road cycling
Since 1984, when women's cycling events were introduced, the women's road race has been 140 kilometres to the men's 250 kilometres. The time trials are 29 kilometres and 44 kilometres respectively. Each country is limited to sending five men and four women to the Summer Games.Tennis
Until the 2020 games, women competed in three-set matches at the Olympics as opposed to five sets for men. The men's matches were shortened for Tokyo 2020.Soccer
In Olympic soccer, there is no age restriction for women, whereas the men's teams field under-23 teams with a maximum of three over-aged players.Gender equality
Historically, female athletes have been treated, portrayed and looked upon differently from their male counterparts. In the early days of the Olympic Games, many NOCs sent fewer female competitors because they would incur the cost of a chaperone, which was not necessary for the male athletes. While inequality in participation has declined throughout history, women are still sometimes treated differently at the Games themselves. For example, in 2012, theJapan women's national soccer team
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
travelled to the Games in economy class, while the men's team travelled in business class. Although women compete in all sports at the summer Olympics, there are still 39 events that are not open to women. Men have to compete in longer and tougher events, such as 110 meters hurdles, compared to 100 meters hurdles for women.
Media
Historically, coverage and inclusion of women's team sports in the Olympics has been limited. It has been shown that commentators are more likely to refer to female athletes using "non-sporting terminology" than they are for men. A 2016 study published byCambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
found that women were more likely to be described using physical features, age, marital status and aesthetics than men were, as opposed to sport related adjectives and descriptions. The same study found that women were also more likely to be referred to as "girls" than men were to be called "boys" in commentary. This disparity in the quality of coverage for women's Olympic sports has been attributed to the fact that 90% of sports journalists are male.
Coverage of women's sports has typically been lower than men's. From 1992 to 1998, American women have always had less raw clock time when being covered on television. Compared to American men, the women have only had 44, 47, and 40 percent of the Olympic television coverage, respectively.
Role of the International Olympic Committee
International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
(IOC) was created by Pierre, Baron de Coubertin, in 1894 and is now considered "the supreme authority of the Olympic movement". Its headquarters are located in Lausanne, Switzerland
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
. The title of supreme authority of the Olympic movement consists of many different duties, which include promoting Olympic values, maintaining the regular celebration of the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
, and supporting any organization that is connected with the Olympic movement.
Some of the Olympic values that the IOC promotes are practicing sport ethically, eliminating discrimination from sports, encouraging women's involvement in sport, fighting the use of drugs in sport, and blending sport, culture, and education. The IOC supports these values by creating different commissions that focus on a particular area. These commissions hold conferences throughout the year where different people around the world discuss ideas and ways to implement the Olympic values into the lives of people internationally. The commissions also have the responsibility of reporting their findings to the President of the IOC and its executive board. The President has the authority to assign members to different commissions based on the person's interests and specialties.
The first two female IOC members were the Venezuelan Flor Isava-Fonseca and the Norwegian Pirjo Häggman
Airi Pirjo Maritta Wilmi-Rokkanen (née Wilmi, formerly Häggman; born 8 June 1951) is a retired Finnish sprinter who specialized in the 400 metres.
Häggman was a member of the Finnish silver medal 4 × 400 m relay team at the 1974 European Athl ...
and were co-opted as IOC members in 1981.
The IOC can contain up to 115 members, and currently, the members of the IOC come from 79 countries. The IOC is considered a powerful authority throughout the world as it creates policies that become standards for other countries to follow in the sporting arena.
Only 20 of the current 106 members of the IOC are women.
Women in Sport Commission
 A goal of the IOC is to encourage these traditional countries to support women's participation in sport because two of the IOC's Olympic values that it must uphold are ensuring the lack of discrimination in sports and promoting women's involvement in sport. The commission that was created to promote the combination of these values was the Women in Sport Commission. This commission declares its role as "advis ngthe IOC Executive Board on the policy to deploy in the area of promoting women in sport". This commission did not become fully promoted to its status until 2004, and it meets once a year to discuss its goals and implementations. This commission also presents a Women and Sport Trophy annually which recognizes a woman internationally who has embodied the values of the IOC and who has supported efforts to increase women's participation in sport at all levels. This trophy is supposed to symbolize the IOC's commitment to honoring those who are beneficial to gender equality in sports.
Another way that the IOC tried to support women's participation in sport was allowing women to become members. In 1990,
A goal of the IOC is to encourage these traditional countries to support women's participation in sport because two of the IOC's Olympic values that it must uphold are ensuring the lack of discrimination in sports and promoting women's involvement in sport. The commission that was created to promote the combination of these values was the Women in Sport Commission. This commission declares its role as "advis ngthe IOC Executive Board on the policy to deploy in the area of promoting women in sport". This commission did not become fully promoted to its status until 2004, and it meets once a year to discuss its goals and implementations. This commission also presents a Women and Sport Trophy annually which recognizes a woman internationally who has embodied the values of the IOC and who has supported efforts to increase women's participation in sport at all levels. This trophy is supposed to symbolize the IOC's commitment to honoring those who are beneficial to gender equality in sports.
Another way that the IOC tried to support women's participation in sport was allowing women to become members. In 1990, Flor Isava Fonseca
Flor Isava Fonseca (20 May 1921 – 25 July 2020) was a Venezuelan sportswoman, journalist, writer and TV presenter as well as prominent member of Venezuelan society.
For a number of years, she was the vice president of the Venezuelan Red Cros ...
became the first woman elected to the executive board of the IOC. The first American woman member of the IOC was Anita DeFrantz
Anita Lucette DeFrantz (born October 4, 1952) is an American Olympic rower, member of the International Olympic Committee, and twice Vice-President of International Rowing Federation (FISA).
Biography
DeFrantz was born in 1952 in Philadelphia, ...
, who became a member in 1986 and in 1992 began chairing the prototype of the IOC Commission on Women in Sport. DeFrantz not only worked towards promoting gender equality in sports, but she also wanted to move toward gender equality in the IOC so women could be equally represented. She believed that without equal representation in the IOC that women's voices would not get an equal chance to be heard. She was instrumental in creating a new IOC policy that required the IOC membership to be composed of at least 20 percent women by 2005. She also commissioned a study conducted in 1989 and again in 1994 that focused on the difference between televised coverage of men's and women's sports. Inequality
Inequality may refer to:
Economics
* Attention inequality, unequal distribution of attention across users, groups of people, issues in etc. in attention economy
* Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups
* ...
still exists in this area, but her study was deemed to be eye opening to how substantial the problem was and suggested ways to increase reporting on women's sporting events. DeFrantz is now head of the Women in Sport Commission.
The IOC failed in its policy requiring 20 percent of IOC members to be women by 2005. By June 2012, the policy had still not been achieved, with only 20 out of 106 IOC members women, an 18.8 percent ratio. Only 4 percent of National Olympic Committee
A National Olympic Committee (NOC) is a national constituent of the worldwide Olympic movement. Subject to the controls of the International Olympic Committee, NOCs are responsible for organizing their people's participation in the Olympic Games ...
s have female presidents.
Impact of the Women's World Games
Background
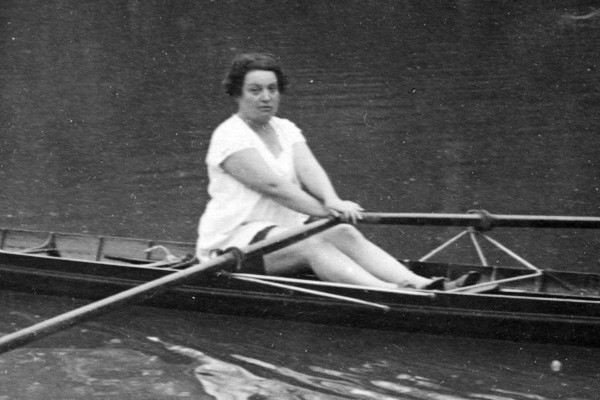
 In 1919, French translator and amateur rower,
In 1919, French translator and amateur rower, Alice Milliat
Alice Joséphine Marie Milliat née Million (5 May 1884 – 19 May 1957) was a pioneer of women's sport. Her lobbying on behalf of female athletes led to the accelerated inclusion of more women's events in the Olympic Games.
A member of , a cl ...
initiated talks with the IOC and International Association of Athletics Federations
World Athletics, formerly known as the International Amateur Athletic Federation (from 1912 to 2001) and International Association of Athletics Federations (from 2001 to 2019, both abbreviated as the IAAF) is the international governing body for ...
with the goal of having women's athletics included at the 1924 Summer Olympics. After her request was refused, she organized the first "Women's Olympiad
The Women's World Games were the first international women's sports events in track and field. The games were held four times between 1922 and 1934. They were established by Alice Milliat and the Fédération Sportive Féminine Internationale (FSF ...
", hosted in Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo (; ; french: Monte-Carlo , or colloquially ''Monte-Carl'' ; lij, Munte Carlu ; ) is officially an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco, specifically the ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is ...
. This would become the precursor to the first Women's World Games. The event was seen as a protest against the IOC's refusal to include females in athletics and a message to their President Pierre de Coubertin
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin (; born Pierre de Frédy; ...
who was opposed to women at the Olympics. Milliat went on to found the International Women's Sports Federation The Fédération Sportive Féminine Internationale (FSFI) – or, in English, the International Women's Sports Federation – was founded in October 1921 by Alice Milliat because of the unwillingness of existing sports organisations, such as ...
who organized the first Women's World Games.
The Games
The first ever "Women's Olympic Games" were held in Paris in 1922. The athletes competed in eleven events:60 metres
60 metres, or 60-meter dash, is a sprint event in track and field. It is a championship event for indoor championships, normally dominated by the best outdoor 100 metres runners. At outdoor venues it is a rare distance, at least for senior at ...
, 100 yards, 300 metres The 300 metres is an uncommon sprinting event in track and field competitions.
All-time top 25
*+ = en route to 400 m performance
*i = indoor performance
*A = affected by altitude
*OT = oversized track (> 200 m in circumference)
*h = hand timi ...
, 1000 metres
The 1000 metres is an uncommon middle-distance running event in track and field competitions.
The 1000 yards, an imperial alternative, was sometimes also contested.
All-time top 25
*h = hand timed
*i = indoor performance
*A = affected by ...
, 4 x 110 yards relay, Hurdling
Hurdling is the act of jumping over an obstacle at a high speed or in a sprint. In the early 19th century, hurdlers ran at and jumped over each hurdle (sometimes known as 'burgles'), landing on both feet and checking their forward motion. Today, ...
100 yards, high jump
The high jump is a track and field event in which competitors must jump unaided over a horizontal bar placed at measured heights without dislodging it. In its modern, most-practiced format, a bar is placed between two standards with a crash mat f ...
, long jump
The long jump is a track and field event in which athletes combine speed, strength and agility in an attempt to leap as far as possible from a takeoff point. Along with the triple jump, the two events that measure jumping for distance as a gr ...
, standing long jump
The standing long jump, also known as the standing broad jump, is an athletics event. It was an Olympic event until 1912. It is one of three standing variants of track and field jumping events, which also include the standing high jump and ...
, javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with th ...
and shot put
The shot put is a track and field event involving "putting" (throwing) a heavy spherical ball—the ''shot''—as far as possible. The shot put competition for men has been a part of the modern Olympics since their revival in 1896, and women's ...
. 20,000 people attended the Games and 18 world records were set. Despite the successful outcome of the event, the IOC still refused to include women's athletics at the 1924 Summer Olympics. On top of this, the IOC and IAAF objected to the use of the term "Olympic" in the event, so the IWSF changed the name of the event to the Women's World Games for the 1926 version. The 1926 Women's World Games
The 1926 Women's World Games (Swedish II. Internationella kvinnliga idrottsspelen, French 2èmes jeux féminins mondiaux ) were the second regular international Women's World Games, the tournament was held between 27
would be held in Gothenburg, Sweden. The discus throw was added to the programme. These Games were also attended by 20,000 spectators and finally convinced the IOC to allow women to compete in the Olympics in some athletics events. The IOC let women compete in 100 metres, 800 metres, 4 × 100 metres relay, high jump and discus throw in 1928. There would be two more editions of the Women's World Games, 1930
Events
January
* January 15 – The Moon moves into its nearest point to Earth, called perigee, at the same time as its fullest phase of the Lunar Cycle. This is the closest moon distance at in recent history, and the next one will be ...
in Prague and 1934
Events
January–February
* January 1 – The International Telecommunication Union, a specialist agency of the League of Nations, is established.
* January 15 – The 8.0 1934 Nepal–Bihar earthquake, Nepal–Bihar earthquake strik ...
in London. The IWSF was forced to fold after the Government of France
The Government of France ( French: ''Gouvernement français''), officially the Government of the French Republic (''Gouvernement de la République française'' ), exercises executive power in France. It is composed of the Prime Minister, who ...
pulled funding in 1936. Pierre de Coubertin
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin (; born Pierre de Frédy; ...
, founder of the International Olympic Committee, was quoted with saying "I do not approve of the participation of women in public competitions. In the Olympic Games, their primary role should be to crown the victors."
See also
*20th century women's fitness culture
The 20th century saw multiple trends and changes in women's fitness culture.
1900 to 1920
During the 19th century women participated in many forms of recreational fitness. Specific activities depended largely on the culture and social class, ...
* Olympic games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
* Women's sports
The participation of women and girls in sports, physical Physical fitness, fitness and exercise, has been recorded to have existed throughout history. However, participation rates and activities vary in accordance with nation, era, geography, ...
* Women's professional sports
Women's professional sports are a relatively new phenomenon, having largely emerged within the latter part of the 20th century. Unlike amateur women athletes, professional women athletes are able to acquire an income which allows them to earn a ...
* LGBT issues at the Olympic and Paralympic Games
* List of LGBT Olympians
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority controlOlympics
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
Olympics
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
Women
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or Adolescence, adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female hum ...