Wolff–Parkinson–White Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (WPWS) is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the

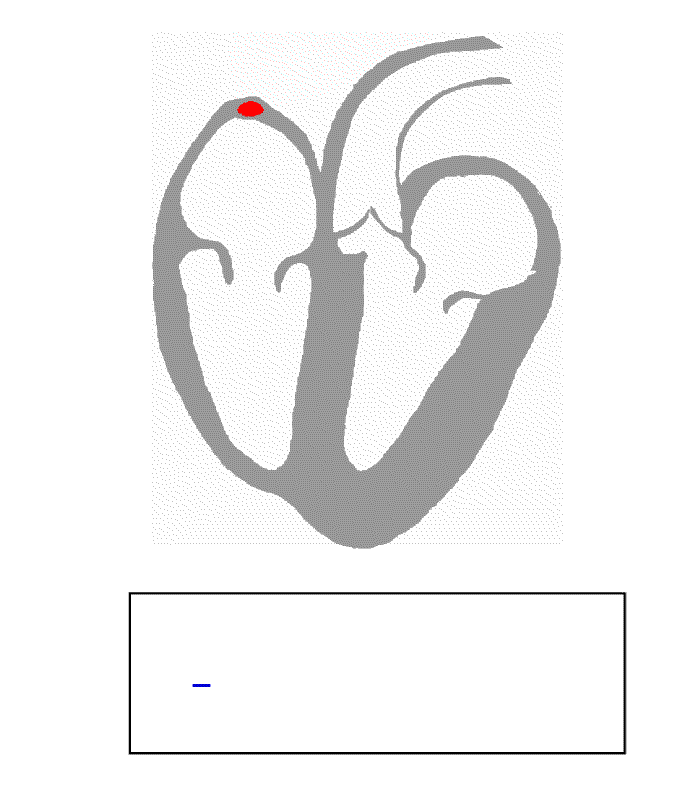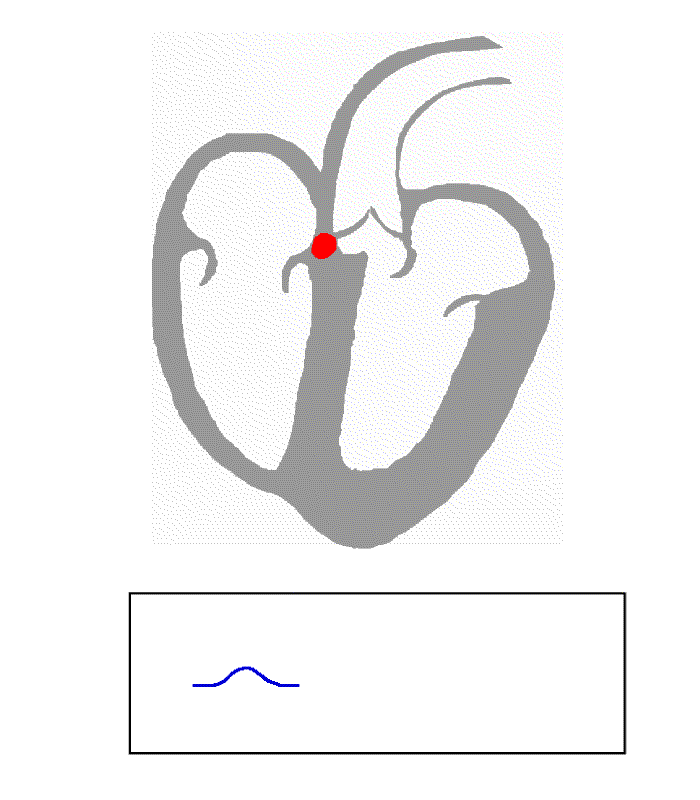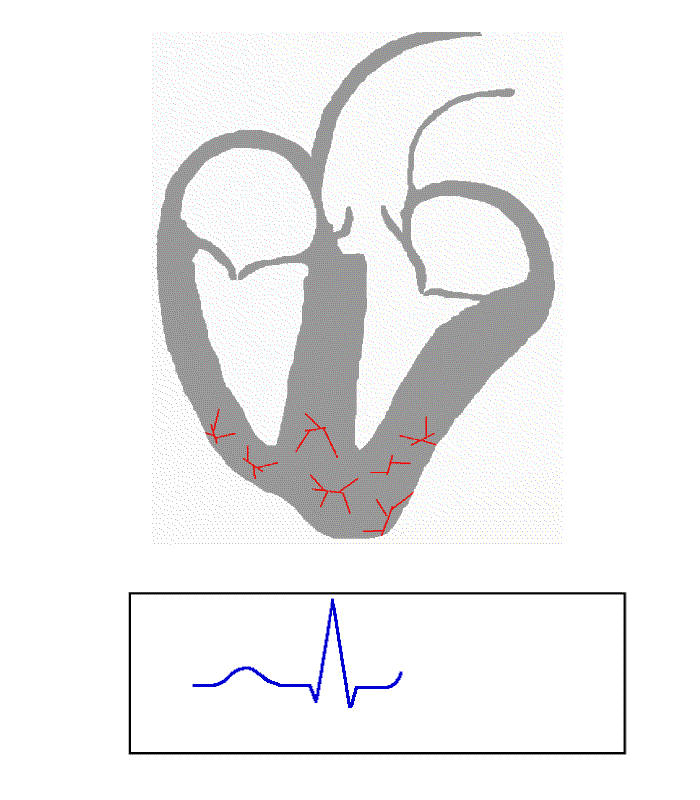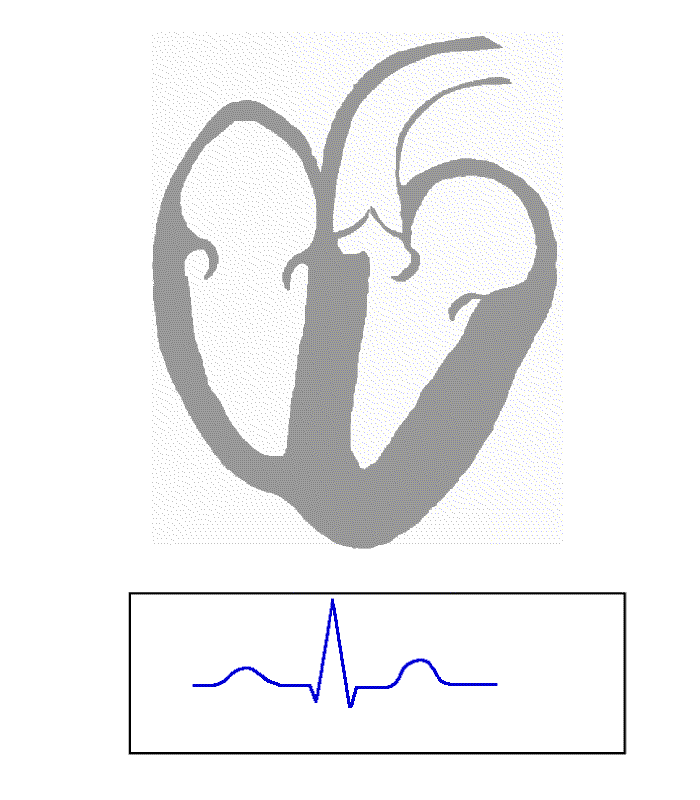 Electrical activity in the normal human heart begins when a
Electrical activity in the normal human heart begins when a
 The bundle of Kent is an abnormal extra or accessory conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles that is present in a small percentage (between 0.1 and 0.3%) of the general population. This pathway may communicate between the left atrium and the left ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type A pre-excitation", or between the right atrium and the right ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type B pre-excitation" in old, currently abandoned classification. Problems arise when this pathway creates an
The bundle of Kent is an abnormal extra or accessory conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles that is present in a small percentage (between 0.1 and 0.3%) of the general population. This pathway may communicate between the left atrium and the left ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type A pre-excitation", or between the right atrium and the right ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type B pre-excitation" in old, currently abandoned classification. Problems arise when this pathway creates an
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
(
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Clinic, The University of Wisconsin - Madison
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Cardiac arrhythmia Rare syndromes Syndromes affecting the heart Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
involving an accessory pathway
In cardiology, an accessory pathway is an additional electrical connection between two parts of the heart. These pathways can lead to abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmias) associated with symptoms of palpitations. Some pathways may activate a regi ...
able to conduct electrical current between the atria and the ventricles, thus bypassing the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
. About 60% of people with the electrical problem develop symptoms, which may include an abnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest.
Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as ...
, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, lightheadedness
Lightheadedness is a common and typically unpleasant sensation of dizziness or a feeling that one may faint. The sensation of lightheadedness can be short-lived, prolonged, or, rarely, recurring. In addition to dizziness, the individual may fee ...
, or syncope. Rarely, cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
may occur. The most common type of arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – ab ...
(abnormal heart rate) associated with WPWS is paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a type of supraventricular tachycardia, named for its intermittent episodes of abrupt onset and termination. Often people have no symptoms. Otherwise symptoms may include palpitations, feeling li ...
.
The cause of WPW is typically unknown and is likely due to a combination of chance and genetic factors. A small number of cases are due to a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
of the PRKAG2 gene which may be inherited in an autosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The firs ...
fashion. The underlying mechanism involves an accessory electrical conduction pathway between the atria and the ventricles. It is associated with other conditions such as Ebstein anomaly and hypokalemic periodic paralysis. The diagnosis of WPW occurs with a combination of palpitations and when an electrocardiogram (ECG) show a short PR interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization ...
and a delta wave. It is a type of pre-excitation syndrome.
WPW syndrome may be monitored or treated with either medications or an ablation (destroying the tissues) such as with radiofrequency catheter ablation. It affects between 0.1 and 0.3% in the population. The risk of death in those without symptoms is about 0.5% per year in children and 0.1% per year in adults. In some cases, non-invasive monitoring may help to more carefully risk stratify patients into a lower risk category. In those without symptoms ongoing observation may be reasonable. In those with WPW complicated by atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
, cardioversion
Cardioversion is a medical procedure by which an abnormally fast heart rate (tachycardia) or other cardiac arrhythmia is converted to a normal rhythm using electricity or drugs.
Synchronized electrical cardioversion uses a therapeutic dose of ...
or the medication procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes; thus it is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia. ...
may be used. The condition is named after Louis Wolff, John Parkinson, and Paul Dudley White who described the ECG findings in 1930.
Signs and symptoms
People with WPW are usually asymptomatic when not having a fast heart rate. However, individuals may experience palpitations,dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a ...
, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, or infrequently syncope (fainting or near fainting) during episodes of supraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower cham ...
. WPW is also associated with a very small risk of sudden death due to more dangerous heart rhythm disturbances.
Pathophysiology
 Electrical activity in the normal human heart begins when a
Electrical activity in the normal human heart begins when a cardiac action potential
Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells known as pacemaker cells, that have automatic action potential generati ...
arises in the sinoatrial
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node, sinus node or Keith–Flack node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sin ...
(SA) node, which is located in the right atrium
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.
...
. From there, the electrical stimulus is transmitted via internodal pathways to the atrioventricular (AV) node. After a brief delay at the AV node, the stimulus travels through the bundle of His
The bundle of His (BH) or His bundle (HB) ( "hiss"Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spiral bound Version'. Cengage Learning; 2016. . pp. 129–.) is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction. As part of ...
to the left and right bundle branches and then to the Purkinje fibers
The Purkinje fibers, named for Jan Evangelista Purkyně, ( ; ; Purkinje tissue or subendocardial branches) are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium in a space called the subendocardium. The Purki ...
and the endocardium
The endocardium (: endocardia) is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides prot ...
at the apex of the heart, then finally to the ventricular myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall o ...
.
The AV node serves an important function as a "gatekeeper", limiting the electrical activity that reaches the ventricles. In situations where the atria generate excessively rapid electrical activity (such as atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
or atrial flutter
Atrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). ...
), the AV node limits the number of signals conducted to the ventricles. For example, if the atria are electrically activated at 300 beats per minute, half those electrical impulses may be blocked by the AV node, so that the ventricles are stimulated at only 150 beats per minute – resulting in a pulse
In medicine, the pulse refers to the rhythmic pulsations (expansion and contraction) of an artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be felt ( palpated) in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surfac ...
of 150 beats per minute. Another important property of the AV node is that it slows down individual electrical impulses. This is manifested on the electrocardiogram as the PR interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization ...
(the time from electrical activation of the atria to electrical activation of the ventricles), which is usually shortened to less than 120 millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second or 1000 microseconds.
A millisecond is to one second, as one second i ...
s in duration.
Individuals with WPW have an accessory pathway that communicates between the atria and the ventricles, in addition to the AV node. This accessory pathway is known as the bundle of Kent. This accessory pathway does not share the rate-slowing properties of the AV node and may conduct electrical activity at a significantly higher rate than the AV node. For instance, in the example above, if an individual had an atrial rate of 300 beats per minute, the accessory bundle may conduct all the electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, causing the ventricles to contract at 300 beats per minute. Extremely rapid heart rates such as this may result in hemodynamic instability or cardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock is a medical emergency resulting from inadequate blood flow to the body's organs due to the dysfunction of the heart. Signs of inadequate blood flow include low urine production (<30 mL/hour), cool arms and legs, and decreased ...
. In some cases, the combination of an accessory pathway and abnormal heart rhythms can trigger ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the Ventricle (heart), ventricles of the heart Fibrillation, quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical activity. Ventricula ...
, a leading cause of sudden cardiac death.
WPW may be associated with PRKAG2, a protein kinase
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphates to them ( phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a f ...
enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
encoded by the ''PRKAG2'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
.
Bundle of Kent
 The bundle of Kent is an abnormal extra or accessory conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles that is present in a small percentage (between 0.1 and 0.3%) of the general population. This pathway may communicate between the left atrium and the left ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type A pre-excitation", or between the right atrium and the right ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type B pre-excitation" in old, currently abandoned classification. Problems arise when this pathway creates an
The bundle of Kent is an abnormal extra or accessory conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles that is present in a small percentage (between 0.1 and 0.3%) of the general population. This pathway may communicate between the left atrium and the left ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type A pre-excitation", or between the right atrium and the right ventricle, in which case it is termed a "type B pre-excitation" in old, currently abandoned classification. Problems arise when this pathway creates an electrical circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., battery (electricity), batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e. ...
that bypasses the AV node. The AV node is capable of slowing the rate of conduction of electrical impulses to the ventricles, whereas the bundle of Kent lacks this capability. When an aberrant electrical connection is made via the bundle of Kent, tachydysrhythmias may therefore result.
Diagnosis
WPW is commonly diagnosed on the basis of the electrocardiogram in an asymptomatic individual. In this case, it is manifested as a delta wave, which is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex that is associated with a short PR interval. The short PR interval and slurring of the QRS complex are reflective of the impulse making it to the ventricles early (via the accessory pathway) without the usual delay experienced in the AV node. If a person with WPW experiences episodes of atrial fibrillation, the ECG shows a rapid polymorphic wide-complex tachycardia (without ''torsades de pointes
''Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes'' or ''torsades des pointes'' (TdP; also called ''torsades'') (, , translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorph ...
''). This combination of atrial fibrillation and WPW is considered dangerous, and most antiarrhythmic drugs are contraindicated.
When an individual is in normal sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), a sinus rhythm ...
, the ECG characteristics of WPW are a short PR interval (less than 120 milliseconds in duration), widened QRS complex (greater than 120 milliseconds in duration) with slurred upstroke of the QRS complex, and secondary repolarization changes (reflected in ST segment
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.005 to 0.150 sec (5 to 150 ms).
It starts at the J point (junction between the QRS complex and ST segment) and ends at the beginning of the T ...
-T wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the ''absolute refractory period''. The last half of the T wav ...
changes).
In individuals with WPW, electrical activity that is initiated in the SA node travels through the accessory pathway, as well as through the AV node to activate the ventricles via both pathways. Since the accessory pathway does not have the impulse slowing properties of the AV node, the electrical impulse first activates the ventricles via the accessory pathway, and immediately afterwards via the AV node. This gives the short PR interval and slurred upstroke of the QRS complex known as the delta wave.
In case of type A pre-excitation (left atrioventricular connections), a positive R wave is seen in V1 ("positive delta") on the precordial leads of the electrocardiogram, while in type B pre-excitation (right atrioventricular connections), a predominantly negative delta wave is seen in lead V1 ("negative delta").
People with WPW may have more than one accessory pathwayin some cases, as many as eight abnormal pathways have been found. This has been seen in individuals with Ebstein's anomaly.
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome is sometimes associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a mitochondrially inherited (transmitted from mother to offspring) degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and their axons that leads to an acute or subacute loss of central vision; it predomin ...
, a form of mitochondrial disease
Mitochondrial disease is a group of disorders caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria are the organelles that generate energy for the cell and are found in every cell of the human body except red blood cells. They convert the energy o ...
.
Risk stratification
WPW carries a small risk of sudden death, presumably due to rapidly conducted atrial fibrillation causing ventricular fibrillation. While the overall risk is approximately 2.4 per 1000 person years, the risk in an individual is dependent on the properties of the accessory pathway causing pre-excitation. A higher risk accessory pathway may be suggested by a history of syncope, but risk stratification is best performed by assessing how frequently a pathway can conduct impulse to the ventricles, usually via programmed electrical stimulation (PES) in thecardiac electrophysiology
Cardiac electrophysiology is a branch of cardiology and Basic Science, basic science focusing on the electrical activities of the heart. The term is usually used in clinical context, to describe studies of such phenomena by invasive (intracardiac ...
laboratory. This is an invasive but generally low-risk procedure during which the atria are stimulated to try to induce tachycardia. If a tachycardia involving the accessory pathway can be triggered, the cardiologist can then assess how rapidly the accessory pathway is able to conduct. The faster it can conduct, the higher the likelihood the accessory pathway can conduct fast enough to trigger a lethal tachycardia.
High-risk features that may be present during PES include an effective refractory period of the accessory pathway less than 250 ms, multiple pathways, septal location of pathway, and inducibility of supraventricular tachycardia ( AVRT, atrial fibrillation). Individuals with any of these high-risk features are generally considered at increased risk for SCD or symptomatic tachycardia, and should be treated accordingly (i.e.: catheter ablation).
It is unclear whether invasive risk stratification (with PES) is necessary in the asymptomatic individual. While some groups advocate PES for risk stratification in all individuals under 35 years old, others only offer it to individuals who have history suggestive of a tachydysrhythmia, since the incidence of sudden cardiac death is so low (less than 0.6% in some reports).
Other methods of risk stratification include observing the ventricular rate during spontaneous atrial fibrillation on a 12-lead ECG. RR intervals of less than 250 ms suggest a higher risk pathway. During exercise testing, abrupt loss of pre-excitation as heart rate increases also suggest a lower risk pathway. However, this approach is hampered by the normal improvement in AV node conduction during exercise which can also mask pre-excitation despite ongoing conduction down the accessory pathway.
Treatment
According to the ACLS protocol, patients with WPW who become symptomatic with asupraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower cham ...
(SVT) with hemodynamic
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously ...
instability (along with a heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
R> 150 bpm during the SVT episode and the abnormal heart rhythm seen on a current ECG, hemodynamic instability is defined as hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
with a systolic blood pressure BP< 90 mm Hg or a rather-sudden drop in the SBP by > 40 mm Hg; other symptoms may include chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
OB confusion
In psychology, confusion is the quality or emotional state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
, delayed capillary refill
Capillary refill time (CRT) is defined as the time taken for color to return to an external capillary bed after pressure is applied to cause blanching. It can be measured by holding a hand higher than heart-level and pressing the soft pad of a ...
, acute drop in urinary output nowiki/>oliguria">oliguria.html" ;"title="nowiki/>oliguria">nowiki/>oliguria lethargic with a change in mentation, or altered mental status and Orientation (mental), disorientation) requires emergent medical intervention with an automated external defibrillator (AED) for prompt electrical synchronized cardioversion in an attempt to bring the patient back into a normal sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. On the electrocardiogram (ECG), a sinus rhythm ...
and/or prevent further decompensation, cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
, and mortality.
If the WPW patient is symptomatic but hemodynamically ''stable'', antiarrhythmic drugs, (i.e., Antiarrhythmic Drugs like Class IA drug like Procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes; thus it is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia. ...
, or a Class III drug like Amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and paroxys ...
) may be used in an attempt to chemically convert the patient back into normal sinus rhythm.
Medications
WPW pattern with hemodynamically stability and orthodromic AVRT leading to a regular narrow complex tachycardia may be managed similarly to other regular narrow complex supraventricular tachycardias: first withvagal maneuver
A vagal maneuver is an action used to stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system by activating the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system and helps regulate many critical aspects of human physiology, i ...
s followed by a trial of adenosine (first-line therapy). The 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS guidelines recommend beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers as second-line agents, electric cardioversion is reserved for refractory arrhythmias. However, if there is any doubt about the diagnosis of orthodromic AVRT or if aberrant conduction leading to a wide complex QRS is observed, it may be prudent to manage as undifferentiated wide complex tachycardia.
People with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response may be treated with amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and paroxys ...
or procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes; thus it is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia. ...
to stabilize their heart rate. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia found with WPW. Amiodarone in atrial fibrillation with WPW, is linked to ventricular fibrillation, and thus may be worse than procainamide.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with WPW or history of it; this includes adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside build ...
, diltiazem
Diltiazem, sold under the brand name Cardizem among others, is a nondihydropyridine calcium channel blocker medication used to treat high blood pressure, angina, and certain heart arrhythmias. It may also be used in hyperthyroidism if beta b ...
, verapamil
Verapamil, sold under various trade names, is a calcium channel blocker medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, angina (chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart), and supraventricular tachycardia. It may also be use ...
, other calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s, and beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart's normal electrical pathway (therefore favoring 1:1 atrial to ventricle conduction through the pre-excitation pathway, potentially leading to unstable ventricular arrhythmias).
Catheter ablation
The definitive treatment of WPW is the destruction of the abnormal electrical pathway bycatheter ablation
Catheter ablation is a procedure that uses radio-frequency energy or other sources to terminate or modify a faulty electrical pathway from sections of the heart of those who are prone to developing cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation ...
. Two main types of catheter ablation include radiofrequency ablation with heat or cryoablation with cold energy. This procedure is performed by cardiac electrophysiologists and has high success rate in the hands of an experienced electrophysiologist. Findings from 1994 indicate success rates of as high as 95% in people treated with radiofrequency catheter ablation for WPW. If radiofrequency catheter ablation is successfully performed, the condition is generally considered cured. Recurrence rates are typically less than 5% after a successful ablation. Some patients, such as the ones with underlying Ebstein's anomaly and inherited cardiomyopathies, may have multiple accessory pathways.
History
The bundle of Kent is eponymously named for British physiologist Albert Frank Stanley Kent (18631958), who described lateral branches in the atrioventricular groove of the monkey heart (erroneously believing these constituted the normal atrioventricular conduction system). In 1915, Frank Norman Wilson (18901952) became the first to describe the condition later called Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. Alfred M. Wedd (18871967) was the next to describe the condition in 1921. Cardiologists Louis Wolff (18981972), John Parkinson (18851976) and Paul Dudley White (18861973) are credited with the definitive description of the disorder in 1930.Notable cases
* LaMarcus Aldridge, Americanbasketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
player
* Michael Cera
Michael Austin Cera ( ; ; born June 7, 1988) is a Canadian actor. Over his career he has received nominations for a British Academy Film Award, three Critics' Choice Movie Awards, four Screen Actors Guild Awards, and a Tony Award.
Cera beca ...
, Canadian actor
* Jonathon Cooper, American football player
* Max Duggan, American football player
* Nathan Eagleton, former Australian rules football
Australian football, also called Australian rules football or Aussie rules, or more simply football or footy, is a contact sport played between two teams of 18 players on an Australian rules football playing field, oval field, often a modified ...
player
* Jeff Garlin
Jeffrey Garlin (born June 5, 1962) is an American stand-up comedy, stand-up comedian and actor. He is best known for playing List of Curb Your Enthusiasm characters#Jeff Greene, Jeff Greene on the HBO sitcom ''Curb Your Enthusiasm'', and Murray ...
, American actor, writer, and comedian
* Quentin Groves, American football player who died of a heart attack at age 32
* Dan Hardy, British UFC welterweight fighter, turned analyst and commentator
* Alicia Hoskin, New Zealand Olympic canoeist.
* Mitch Hurwitz, American television writer and producer, creator of ''Arrested Development
''Arrested Development'' is an American satire, satirical television sitcom created by Mitchell Hurwitz. It follows the Bluths, a formerly wealthy, dysfunctional family and is presented in a Serial (radio and television), serialized format, inco ...
''
* Jessie J
Jessica Ellen Cornish (born 27 March 1988), known professionally as Jessie J, is an English singer and songwriter. Born and raised in London, she began her career on stage, aged 11, with a role in the West End musical '' Whistle Down the Wind ...
, British musician
* Marilyn Manson
Brian Hugh Warner (born January 5, 1969), known professionally as Marilyn Manson, is an American rock musician. He is the lead singer and the only original member remaining of the Marilyn Manson (band), same-titled band he founded in 1989. Th ...
, American musician, painter, and actor
* Meat Loaf
Michael Lee Aday (born Marvin Lee Aday; September 27, 1947 – January 20, 2022), known professionally by his stage name Meat Loaf, was an American singer and actor. He was known for his powerful, wide-ranging voice and theatrical live shows. ...
, American musician
* Michael Montgomery, American football player
* Montel Vontavious Porter
Hassan Hamid Assad (born Alvin Antonio Burke Jr.; October 28, 1973), better known by his ring name Montel Vontavious Porter (MVP), is an American Professional wrestling, professional wrestler, Manager (professional wrestling), manager, and sub ...
, professional wrestler
Professional wrestling, often shortened to either pro wrestling or wrestling,The term "wrestling" is most often widely used to specifically refer to modern scripted professional wrestling, though it is also used to refer to real-life wrest ...
* Michael Rupp
Michael Ryan Rupp (born January 13, 1980) is an American former professional ice hockey center. He has played in the National Hockey League (NHL) for the New Jersey Devils, Phoenix Coyotes, Columbus Blue Jackets, Pittsburgh Penguins, New York Ra ...
, American ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
player
See also
* Re-entry ventricular arrhythmiaReferences
External links
* Genetics Home ReferenceWolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
(
United States National Library of Medicine
The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), operated by the United States federal government, is the world's largest medical library.
Located in Bethesda, Maryland, the NLM is an institute within the National Institutes of Health. I ...
, Bethesda, Maryland)
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Clinic, The University of Wisconsin - Madison
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Cardiac arrhythmia Rare syndromes Syndromes affecting the heart Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate