|
Procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia; thus it is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes. In addition to blocking the ''I''Na current, it inhibits the ''I''Kr rectifier K+ current. Procainamide is also known to induce a voltage-dependent open channel block on the batrachotoxin (BTX)-activated sodium channels in cardiomyocytes. Uses Medical Procainamide is used for treating ventricular arrhythmias: ventricular ectopy and tachycardia and supraventricular arrhythmias: atrial fibrillation, and re-entrant and automatic supraventricular tachycardia. For example, it can be used to convert new-onset atrial fibrillation, and although was initially thought to be suboptimal for this purpose, a growing body of literature is amounting in support for this exact cause. It is administered by mouth, by intramuscular injection, or intravenously. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel Blocker
Sodium channel blockers are drugs which impair the conduction of sodium ions (Na+) through sodium channels. Extracellular The following naturally-produced substances block sodium channels by binding to and occluding the extracellular pore opening of the channel: * Alkaloids: ** Saxitoxin (STX) ** Neosaxitoxin (NSTX) ** Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Intracellular Drugs which block sodium channels by blocking from the intracellular side of the channel include: * Local anesthetics: ''lidocaine'' * Class I antiarrhythmic agents * Various anticonvulsants: ''phenytoin, oxcarbazepine (derivative of carbamazepine)'' Unknown mechanism * Calcium has been shown to block sodium channels which explains the effects of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia. * Lamotrigine is known to block sodium channels but it is not known whether it is extracellular or intracellular. * Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to cause inhibitory effects on sodium currents. This voltage-dependent inhibition is non-selective in nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug-induced Lupus Erythematosus
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder caused by chronic use of certain drugs. These drugs cause an autoimmune response (the body attacks its own cells) producing symptoms similar to those of systemic lupus erythematosus Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ... (SLE). There are 38 known medications to cause DIL but there are three that report the highest number of cases: hydralazine, procainamide, and quinidine. While the criteria for diagnosing DIL has not been thoroughly established, symptoms of DIL typically present as myalgia, muscle pain and arthralgia, joint pain. Generally, the symptoms recede after discontinuing use of the drugs. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of drug-induced lupus erythematosus include the following: * Joint pain (art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Vaughan Williams classification The Vaughan Williams classification was introduced in 1970 by Miles Vaughan Williams.Vaughan Williams, EM (1970) "Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs". In ''Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias'' (Eds. Sandoe E; Flensted-Jensen E; Olsen KH). Astra, Elsinore. Denmark (1970) Vaughan Williams was a pharmacology tutor at Hertford College, Oxford. One of his students, Bramah N. Singh, contributed to the development of the classification system. The system is therefore sometimes known as the Singh-Vaughan Williams classification. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaughan Williams Classification
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Vaughan Williams classification The Vaughan Williams classification was introduced in 1970 by Miles Vaughan Williams.Vaughan Williams, EM (1970) "Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs". In ''Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias'' (Eds. Sandoe E; Flensted-Jensen E; Olsen KH). Astra, Elsinore. Denmark (1970) Vaughan Williams was a pharmacology tutor at Hertford College, Oxford. One of his students, Bramah N. Singh, contributed to the development of the classification system. The system is therefore sometimes known as the Singh-Vaughan Williams classification. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylation
: In organic chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply '' acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite reaction, the removal of an acetyl group from a chemical compound. Organic synthesis Acetate esters and acetamides are generally prepared by acetylations. Acetylations are often used in making C-acetyl bonds in Friedel-Crafts reactions. Carbanions and their equivalents are susceptible to acetylations. Acetylation reagents Many acetylations are achieved using these three reagents: * Acetic anhydride. This reagent is common in the laboratory; its use cogenerates acetic acid. *Acetyl chloride. This reagent is also common in the laboratory, but its use cogenerates hydrogen chloride, which can be undesirable. *Ketene. At one time acetic anhydride was prepared by the reaction of ketene with acetic acid: :H2C=C=O + CH3COOH -> (CH3CO)2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergic Response
An allergic response is a hypersensitive immune reaction to a substance that normally is harmless or would not cause an immune response in everyone. An allergic response may cause harmful symptoms such as itching or inflammation or tissue injury. Mechanism Allergies are an abnormal immune reaction. The human immune system is designed to protect the body from potential harm and in people who have allergies the immune system will react to allergens (substances that trigger an immune response). The immune system will produce immunoglobulin E, IgE, antibodies for each allergen. The antibodies will cause cells in the body to produce histamine. This histamine will act on different areas of the body (eyes, throat, nose, gastrointestinal tract, skin or lungs) to produce symptoms of an allergic reaction. The allergic response is not limited to a certain amount of exposure. If the body is exposed to the allergen multiple times the immune system will react every time the allergen is prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthralgia
Arthralgia (from Greek ''arthro-'', joint + ''-algos'', pain) literally means ''joint pain''. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication. According to MeSH, the term "arthralgia" should only be used when the condition is non-inflammatory, and the term "arthritis" should be used when the condition is inflammatory. Causes The causes of ''arthralgia'' are varied and range, from a joints perspective, from degenerative and destructive processes such as osteoarthritis and sports injuries to inflammation of tissues surrounding the joints, such as bursitis. These might be triggered by other things, such as infections or vaccinations. Diagnosis Diagnosis involves interviewing the patient and performing physical exams. When attempting to establish the cause of the arthralgia, the emphasis is on the interview. The patient is asked questions intended to narrow the number of potential causes. Given th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myalgia
Myalgia (also called muscle pain and muscle ache in layman's terms) is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, especially when there has been no trauma. Long-lasting myalgia can be caused by metabolic myopathy, some nutritional deficiencies, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Causes The most common causes of myalgia are overuse, injury, and strain. Myalgia might also be caused by allergies, diseases, medications, or as a response to a vaccination. Dehydration at times results in muscle pain as well, especially for people involved in extensive physical activities such as workout. Muscle pain is also a common symptom in a variety of diseases, including infectious diseases, such as influenza, muscle abscesses, Lyme disease, malaria, trichinosis or poliomyelitis; autoimmune diseases, such as celiac disease, systemic lupus er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
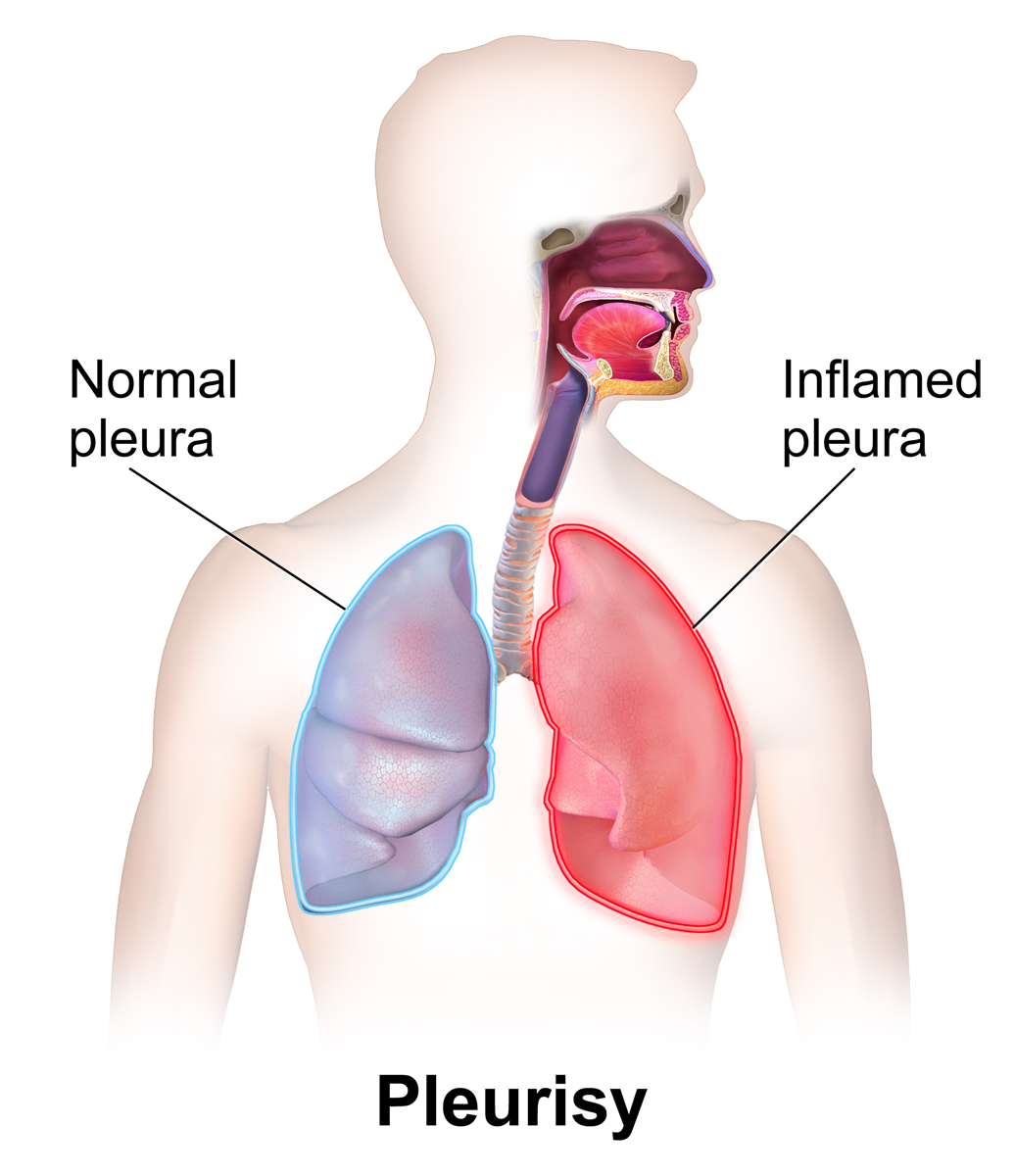
Pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever, or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause. The most common cause is a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infection, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, autoimmune disorders, lung cancer, following heart surgery, pancreatitis and asbestosis. Occasionally the cause remains unknown. The underlying mechanism involves the rubbing together of the pleurae instead of smooth gliding. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include pericarditis, heart attack, cholecystitis, pulmonary embolism, and pneumothorax. Diagnostic testing may include a chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood tests. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Paracetamol (acetaminop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock (circulatory)
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest, as complications worsen. Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: low volume, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Low volume shock, also known as hypovolemic shock, may be from bleeding, diarrhea, or vomiting. Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdoses. The diagnosis is generally based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. A decreased pulse pressure (systolic blood pressure m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |