WWW Prefix on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an
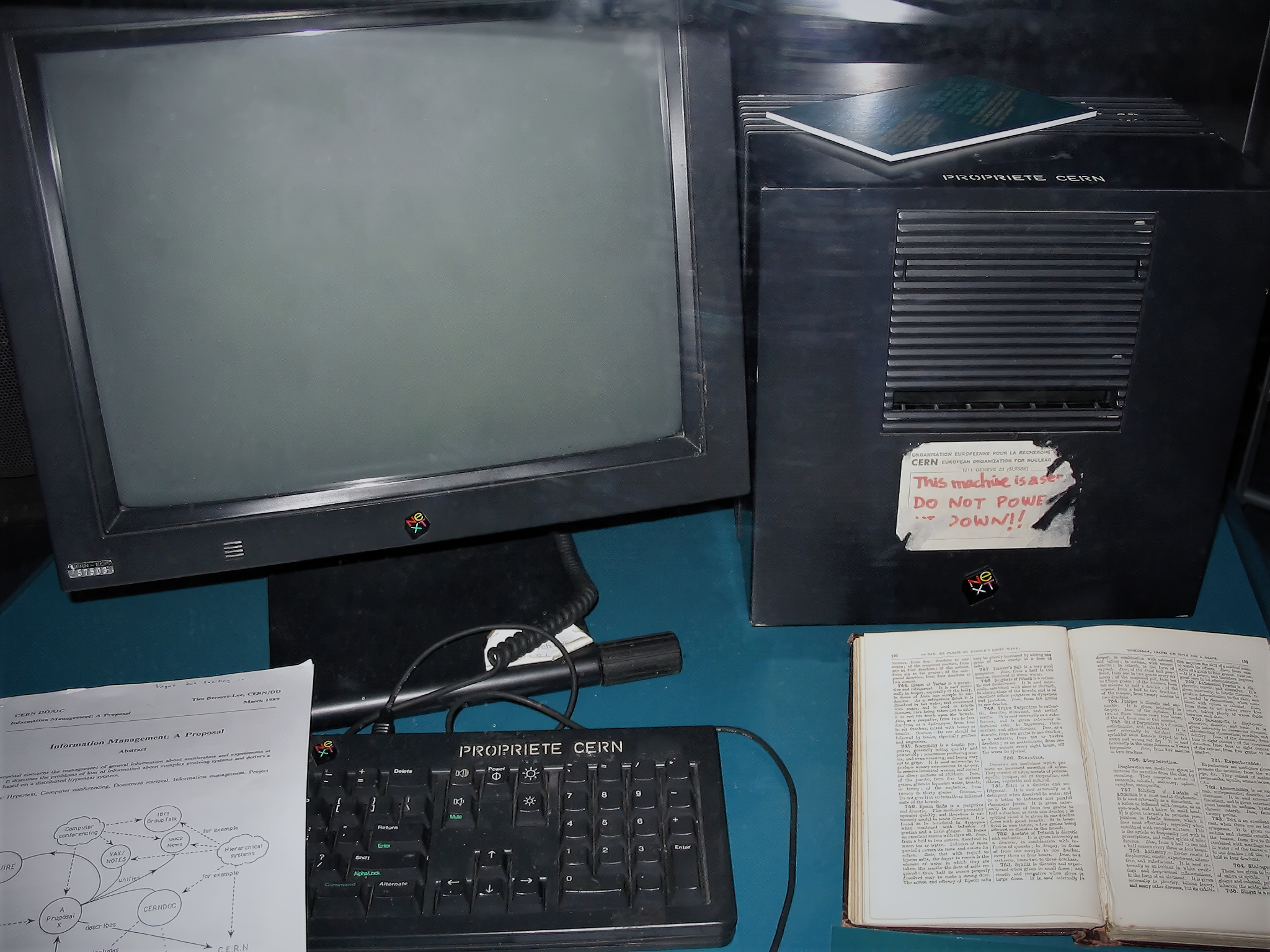 The Web was invented by English computer scientist
The Web was invented by English computer scientist
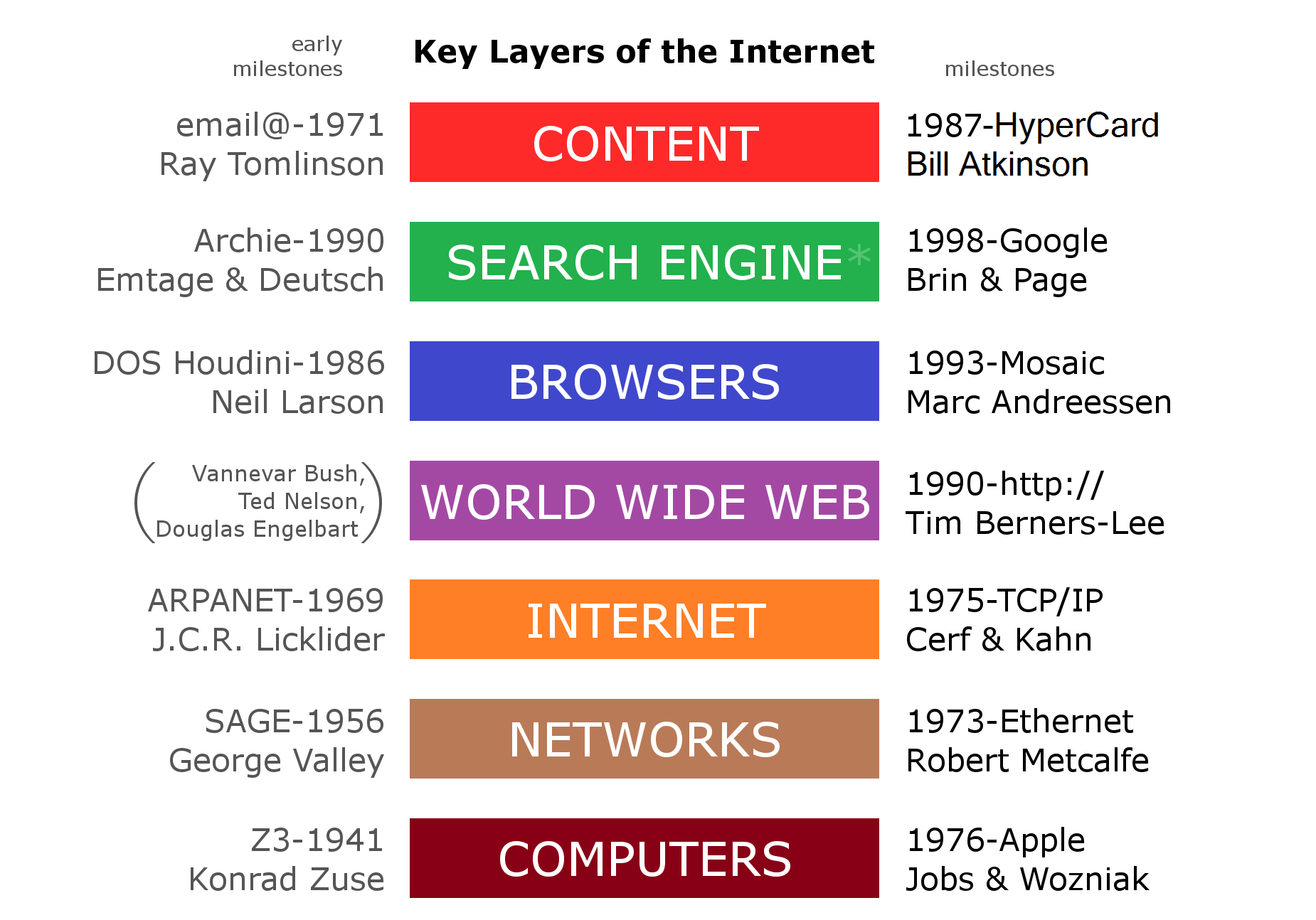 The terms ''Internet'' and ''World Wide Web'' are often used without much distinction. However, the two terms do not mean the same thing. The Internet is a global system of
The terms ''Internet'' and ''World Wide Web'' are often used without much distinction. However, the two terms do not mean the same thing. The Internet is a global system of
GET /home.html HTTP/1.1
Host: example.org
The computer receiving the HTTP request delivers it to web server software listening for requests on port 80. If the webserver can fulfill the request it sends an HTTP response back to the browser indicating success:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
followed by the content of the requested page. Hypertext Markup Language (
Example.org – The World Wide Web
The web browser parses the HTML and interprets the markup (</syntaxhighlight>, <syntaxhighlight lang="HTML" inline><p></syntaxhighlight> for paragraph, and such) that surrounds the words to format the text on the screen. Many web pages use HTML to reference the URLs of other resources such as images, other embedded media, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/C/Client-side_scripting.html" "title="Client-side scripting">scripts</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of handw ...<br></span></div> that affect page behaviour, and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/C/Cascading_Style_Sheets.html" "title="Cascading Style Sheets">Cascading Style Sheets</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML (including XML dialects such as SVG, MathML or XHTML). CSS is a cornerstone techno ...<br></span></div> that affect page layout. The browser makes additional HTTP requests to the web server for these other <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_media_type.html" "title="Internet media type">Internet media type</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A media type (also known as a MIME type) is a two-part identifier for file formats and format contents transmitted on the Internet. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the official authority for the standardization and publication o ...<br></span></div>s. As it receives their content from the web server, the browser progressively <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/B/Browser_engine.html" ;"title="Browser engine">renders</a> the page onto the screen as specified by its HTML and these additional resources.
<h2><br><p> HTML </h2></p>
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/m/markup_language.html" "title="markup language">markup language</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Markup language refers to a text-encoding system consisting of a set of symbols inserted in a text document to control its structure, formatting, or the relationship between its parts. Markup is often used to control the display of the document ...<br></span></div> for creating <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_page.html" ;"title="web page">web page</a>s and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_application.html" "title="web application">web application</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...<br></span></div>s. With <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/C/Cascading_Style_Sheets.html" "title="Cascading Style Sheets">Cascading Style Sheets</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML (including XML dialects such as SVG, MathML or XHTML). CSS is a cornerstone techno ...<br></span></div> (CSS) and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/J/JavaScript.html" "title="JavaScript">JavaScript</a><span class="linkinfotext">
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...<br></span></div>, it forms a triad of <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/c/cornerstone.html" ;"title="cornerstone">cornerstone</a> technologies for the World Wide Web.
<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_browser.html" "title="Web browser">Web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div>s receive HTML documents from a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">web server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...<br></span></div> or from local storage and <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/b/browser_engine.html" ;"title="browser engine">render</a> the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/S/Semantic_Web.html" "title="Semantic Web">semantically</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and comput ...<br></span></div> and originally included cues for the appearance of the document.
<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTML_element.html" "title="HTML element">HTML element</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An HTML element is a type of HTML (HyperText Markup Language) document component, one of several types of HTML nodes (there are also text nodes, comment nodes and others). The first used version of HTML was written by Tim Berners-Lee in 1993 ...<br></span></div>s are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTML_element#Images_and_objects.html" ;"title="HTML element#Images and objects">images</a> and other objects such as <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/F/Fieldset.html" ;"title="Fieldset">interactive forms</a> may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/structured_document.html" "title="structured document">structured document</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A structured document is an electronic document where some method of markup is used to identify the whole and parts of the document as having various meanings beyond their formatting. For example, a structured document might identify a certain por ...<br></span></div>s by denoting structural <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/semantics.html" "title="semantics">semantics</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy
Philosophy (f ...<br></span></div> for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hyperlink.html" ;"title="Hyperlink">links</a>, quotes and other items. HTML elements are delineated by ''tags'', written using <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/B/Bracket#Angle_brackets.html" "title="Bracket#Angle brackets">angle brackets</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'r ...<br></span></div>. Tags such as and directly introduce content into the page. Other tags such as surround and provide information about document text and may include other tags as sub-elements. Browsers do not display the HTML tags, but use them to interpret the content of the page.
HTML can embed programs written in a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/scripting_language.html" "title="scripting language">scripting language</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scripting ...<br></span></div> such as <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/J/JavaScript.html" "title="JavaScript">JavaScript</a><span class="linkinfotext">
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...<br></span></div>, which affects the behavior and content of web pages. Inclusion of CSS defines the look and layout of content. The <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/World_Wide_Web_Consortium.html" "title="World Wide Web Consortium">World Wide Web Consortium</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 and led by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working to ...<br></span></div> (W3C), maintainer of both the HTML and the CSS standards, has encouraged the use of CSS over explicit presentational HTML <ref name="deprecated"></ref>
<h2><br><p> Linking </h2></p>
Most web pages contain hyperlinks to other related pages and perhaps to downloadable files, source documents, definitions and other web resources. In the underlying HTML, a hyperlink looks like this:
<syntaxhighlight lang="html" inline=""><a href="http://example.org/home.html">Example.org Homepage</a>.</syntaxhighlight>
<img title="WorldWideWebAroundWikipedia"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b9/WorldWideWebAroundWikipedia.png" >
Such a collection of useful, related resources, interconnected via hypertext links is dubbed a ''web'' of information. Publication on the Internet created what Tim Berners-Lee first called the ''WorldWideWeb'' (in its original <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/C/CamelCase.html" "title="CamelCase">CamelCase</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Camel case (sometimes stylized as camelCase or CamelCase, also known as camel caps or more formally as medial capitals) is the practice of writing phrases without spaces or punctuation. The format indicates the separation of words with a single ...<br></span></div>, which was subsequently discarded) in November 1990.<ref name="W90"></ref>
The hyperlink structure of the web is described by the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/webgraph.html" ;"title="webgraph">webgraph</a>: the nodes of the web graph correspond to the web pages (or URLs) the directed edges between them to the hyperlinks. Over time, many web resources pointed to by hyperlinks disappear, relocate, or are replaced with different content. This makes hyperlinks obsolete, a phenomenon referred to in some circles as link rot, and the hyperlinks affected by it are often called <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/dead_link.html" ;"title="dead link">dead link</a>s. The ephemeral nature of the Web has prompted many efforts to archive websites. The <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_Archive.html" "title="Internet Archive">Internet Archive</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...<br></span></div>, active since 1996, is the best known of such efforts.
<h2><br><p> WWW prefix </h2></p>
Many hostnames used for the World Wide Web begin with ''www'' because of the long-standing practice of naming <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet.html" "title="Internet">Internet</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...<br></span></div> hosts according to the services they provide. The <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/h/hostname.html" ;"title="hostname">hostname</a> of a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">web server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...<br></span></div> is often ''www'', in the same way that it may be ''ftp'' for an <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/F/FTP_server.html" ;"title="FTP server">FTP server</a>, and ''news'' or ''nntp'' for a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/Usenet.html" "title="Usenet">Usenet</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Usenet () is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was ...<br></span></div> <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/n/news_server.html" "title="news server">news server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A news server is a collection of software used to handle Usenet articles. It may also refer to a computer itself which is primarily or solely used for handling Usenet. Access to Usenet is only available through news server providers.
Articles and ...<br></span></div>. These hostnames appear as Domain Name System (DNS) or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/subdomain.html" "title="subdomain">subdomain</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In the Domain Name System (DNS) hierarchy, a subdomain is a domain that is a part of another (main) domain. For example, if a domain offered an online store as part of their website example.com, it might use the subdomain shop.example.com .
Ov ...<br></span></div> names, as in ''www.example.com''. The use of ''www'' is not required by any technical or policy standard and many web sites do not use it; the first web server was ''nxoc01.cern.ch''. According to Paolo Palazzi, who worked at CERN along with Tim Berners-Lee, the popular use of ''www'' as subdomain was accidental; the World Wide Web project page was intended to be published at www.cern.ch while info.cern.ch was intended to be the CERN home page; however the DNS records were never switched, and the practice of prepending ''www'' to an institution's website domain name was subsequently copied. Many established websites still use the prefix, or they employ other subdomain names such as ''www2'', ''secure'' or ''en'' for special purposes. Many such web servers are set up so that both the main domain name (e.g., example.com) and the ''www'' subdomain (e.g., www.example.com) refer to the same site; others require one form or the other, or they may map to different web sites. The use of a subdomain name is useful for <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/l/load_balancing_(computing).html" ;"title="load balancing (computing)">load balancing</a> incoming web traffic by creating a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/CNAME_record.html" ;"title="CNAME record">CNAME record</a> that points to a cluster of web servers. Since, currently, only a subdomain can be used in a CNAME, the same result cannot be achieved by using the bare domain root.
When a user submits an incomplete domain name to a web browser in its address bar input field, some web browsers automatically try adding the prefix "www" to the beginning of it and possibly ".com", ".org" and ".net" at the end, depending on what might be missing. For example, entering "" may be transformed to ''<nowiki>http://www.microsoft.com/</nowiki>'' and "openoffice" to ''<nowiki>http://www.openoffice.org</nowiki>''. This feature started appearing in early versions of <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/F/Firefox.html" ;"title="Firefox">Firefox</a>, when it still had the working title 'Firebird' in early 2003, from an earlier practice in browsers such as <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/L/Lynx_(web_browser).html" "title="Lynx (web browser)">Lynx</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A lynx is a type of wild cat.
Lynx may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Lynx (constellation)
* Lynx (Chinese astronomy)
* Lynx X-ray Observatory, a NASA-funded mission concept for a next-generation X-ray space observatory
Places Canada
* Lynx, Ontar ...<br></span></div>. It is reported that Microsoft was granted a US patent for the same idea in 2008, but only for mobile devices.
In English, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/P/Pronunciation_of_"www".html" ;"title="Pronunciation of "www"">''www'' is usually read as</a> ''double-u double-u double-u''. Some users pronounce it ''dub-dub-dub'', particularly in New Zealand. Stephen Fry, in his "Podgrams" series of podcasts, pronounces it ''wuh wuh wuh''. The English writer <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/D/Douglas_Adams.html" ;"title="Douglas Adams">Douglas Adams</a> once quipped in ''<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/T/The_Independent.html" "title="The Independent">The Independent</a><span class="linkinfotext">
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publis ...<br></span></div> on Sunday'' (1999): "The World Wide Web is the only thing I know of whose shortened form takes three times longer to say than what it's short for".<ref name="Sim"></ref> In Mandarin Chinese, ''World Wide Web'' is commonly translated via a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/phono-semantic_matching.html" "title="phono-semantic matching">phono-semantic matching</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Phono-semantic matching (PSM) is the incorporation of a word into one language from another, often creating a neologism, where the word's non-native quality is hidden by replacing it with Phonetics, phonetically and semantically similar words or ...<br></span></div> to ''wàn wéi wǎng'' (), which satisfies ''www'' and literally means "myriad-dimensional net", a translation that reflects the design concept and proliferation of the World Wide Web. Tim Berners-Lee's web-space states that ''World Wide Web'' is officially spelled as three separate words, each capitalised, with no intervening hyphens. Nonetheless, it is often called simply ''the Web'', and also often ''the web''; see '' <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Capitalization_of_Internet.html" ;"title="Capitalization of Internet">Capitalization of ''Internet''</a>'' for details. Use of the www prefix has been declining, especially when <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_2.0.html" ;"title="Web 2.0">Web 2.0</a> <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_application.html" "title="web application">web application</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...<br></span></div>s sought to brand their domain names and make them easily pronounceable.<ref name="cas"></ref>
As the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/m/mobile_Web.html" "title="mobile Web">mobile Web</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The mobile web refers to mobile browser-based World Wide Web services accessed from handheld mobile devices, such as smartphones or feature phones, through a mobile or other wireless network.
History and development
Traditionally, the World ...<br></span></div> grew in popularity, services like <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/G/Gmail.html" ;"title="Gmail">Gmail</a>.com, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/O/Outlook.com.html" "title="Outlook.com">Outlook.com</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Outlook.com is a webmail service that is part of the Microsoft 365 product family. It offers mail, Calendaring software, calendaring, Address book, contacts, and Task management, tasks services.
Founded in 1996 by Sabeer Bhatia and Jack Smit ...<br></span></div>, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/M/Myspace.html" ;"title="Myspace">Myspace</a>.com, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/F/Facebook.html" "title="Facebook">Facebook</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin M ...<br></span></div>.com and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/T/Twitter.html" "title="Twitter">Twitter</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Twitter is an online social media and social networking service owned and operated by American company Twitter, Inc., on which users post and interact with 280-character-long messages known as "tweets". Registered users can post, like, and ...<br></span></div>.com are most often mentioned without adding "www." (or, indeed, ".com") to the domain.
<h2><br><p> Scheme specifiers </h2></p>
The scheme specifiers ''<code><nowiki>http://</nowiki></code>'' and ''<code><nowiki>https://</nowiki></code>'' at the start of a web <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/Uniform_Resource_Identifier.html" "title="Uniform Resource Identifier">URI</a><span class="linkinfotext"> Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), an island off Malakula Islan ...<br></span></div> refer to <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol.html" "title="Hypertext Transfer Protocol">Hypertext Transfer Protocol</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...<br></span></div> or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTTP_Secure.html" "title="HTTP Secure">HTTP Secure</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is enc ...<br></span></div>, respectively. They specify the communication protocol to use for the request and response. The HTTP protocol is fundamental to the operation of the World Wide Web, and the added encryption layer in HTTPS is essential when browsers send or retrieve confidential data, such as passwords or banking information. Web browsers usually automatically prepend <nowiki>http://</nowiki> to user-entered URIs, if omitted.
<h2><br><p> Pages</h2></p>
<img title="Commons"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b0/Commons.png" >
A ''web page'' (also written as ''webpage'') is a document that is suitable for the World Wide Web and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_browser.html" "title="web browser">web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div>s. A web browser displays a web page on a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/computer_display.html" "title="computer display">monitor</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West Vir ...<br></span></div> or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/m/mobile_device.html" "title="mobile device">mobile device</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physical ...<br></span></div>.
The term ''web page'' usually refers to what is visible, but may also refer to the contents of the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/computer_file.html" "title="computer file">computer file</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A computer file is a computer resource for recording data in a computer storage device, primarily identified by its file name. Just as words can be written to paper, so can data be written to a computer file. Files can be shared with and transfe ...<br></span></div> itself, which is usually a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/t/text_file.html" ;"title="text file">text file</a> containing <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/h/hypertext.html" "title="hypertext">hypertext</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typi ...<br></span></div> written in <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTML.html" "title="HTML">HTML</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...<br></span></div> or a comparable <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/m/markup_language.html" "title="markup language">markup language</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Markup language refers to a text-encoding system consisting of a set of symbols inserted in a text document to control its structure, formatting, or the relationship between its parts. Markup is often used to control the display of the document ...<br></span></div>. Typical web pages provide <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/h/hypertext.html" "title="hypertext">hypertext</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typi ...<br></span></div> for browsing to other web pages via <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/h/hyperlink.html" "title="hyperlink">hyperlink</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text wit ...<br></span></div>s, often referred to as ''links''. Web browsers will frequently have to access multiple <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_resource.html" ;"title="web resource">web resource</a> elements, such as reading <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Cascading_Style_Sheets.html" ;"title="Cascading Style Sheets">style sheets</a>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/client-side_scripting.html" "title="client-side scripting">scripts</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of handw ...<br></span></div>, and images, while presenting each web page.
On a network, a web browser can retrieve a web page from a remote <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">web server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...<br></span></div>. The web server may restrict access to a private network such as a corporate intranet. The web browser uses the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol.html" "title="Hypertext Transfer Protocol">Hypertext Transfer Protocol</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...<br></span></div> (HTTP) to make such requests to the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">web server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...<br></span></div>.
A <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/static_web_page.html" ;"title="static web page">''static'' web page</a> is delivered exactly as stored, as <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_content.html" ;"title="web content">web content</a> in the web server's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/f/file_system.html" "title="file system">file system</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, file system or filesystem (often abbreviated to fs) is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one larg ...<br></span></div>. In contrast, a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/dynamic_web_page.html" ;"title="dynamic web page">''dynamic'' web page</a> is generated by a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_application.html" "title="web application">web application</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...<br></span></div>, usually driven by <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/server-side_scripting.html" ;"title="server-side scripting">server-side software</a>. Dynamic web pages are used when each user may require completely different information, for example, bank websites, web email etc.
<h3><br><p> Static page </h3></p>
A ''static web page'' (sometimes called a ''flat page/stationary page'') is a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_page.html" ;"title="web page">web page</a> that is delivered to the user exactly as stored, in contrast to <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/dynamic_web_page.html" ;"title="dynamic web page">dynamic web page</a>s which are generated by a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_application.html" "title="web application">web application</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...<br></span></div>.
Consequently, a static web page displays the same information for all users, from all contexts, subject to modern capabilities of a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">web server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...<br></span></div> to <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/content_negotiation.html" "title="content negotiation">negotiate</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more people or parties to reach the desired outcome regarding one or more issues of conflict. It is an interaction between entities who aspire to agree on matters of mutual interest. The agreement c ...<br></span></div> <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/M/MIME_type.html" "title="MIME type">content-type</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A media type (also known as a MIME type) is a two-part identifier for file formats and format contents transmitted on the Internet. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the official authority for the standardization and publication o ...<br></span></div> or language of the document where such versions are available and the server is configured to do so.
<h3><br><p> Dynamic pages </h3></p>
<img title="Scheme dynamic page en"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4f/Scheme_dynamic_page_en.svg" >
A ''server-side dynamic web page'' is a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_page.html" ;"title="web page">web page</a> whose construction is controlled by an <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/a/application_server.html" "title="application server">application server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An application server is a server that hosts applications or software that delivers a business application through a communication protocol.
An application server framework is a service layer model. It includes software components available to a ...<br></span></div> processing server-side scripts. In server-side scripting, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/P/Parameter_(computer_programming).html" ;"title="Parameter (computer programming)">parameters</a> determine how the assembly of every new web page proceeds, including the setting up of more client-side processing.
A ''client-side dynamic web page'' processes the web page using JavaScript running in the browser. JavaScript programs can interact with the document via <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/D/Document_Object_Model.html" ;"title="Document Object Model">Document Object Model</a>, or DOM, to query page state and alter it. The same client-side techniques can then dynamically update or change the DOM in the same way.
A dynamic web page is then reloaded by the user or by a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/computer_program.html" "title="computer program">computer program</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program ...<br></span></div> to change some variable content. The updating information could come from the server, or from changes made to that page's DOM. This may or may not truncate the browsing history or create a saved version to go back to, but a ''dynamic web page update'' using <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/A/Ajax_(programming).html" ;"title="Ajax (programming)">Ajax</a> technologies will neither create a page to go back to nor truncate the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_browsing_history.html" ;"title="web browsing history">web browsing history</a> forward of the displayed page. Using Ajax technologies the end <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/User_(computing).html" "title="User (computing)">user</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Ancient Egyptian roles
* User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty
* Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User"
Other uses
* User (computing), a person (or software) using an ...<br></span></div> gets ''one dynamic page'' managed as a single page in the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_browser.html" "title="web browser">web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div> while the actual <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_content.html" ;"title="web content">web content</a> rendered on that page can vary. The Ajax engine sits only on the browser requesting parts of its DOM, ''the'' DOM, for its client, from an application server.
Dynamic HTML, or DHTML, is the umbrella term for technologies and methods used to create web pages that are not <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/static_web_page.html" ;"title="static web page">static web page</a>s, though it has fallen out of common use since the popularization of <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/A/Ajax_(programming).html" ;"title="Ajax (programming)">AJAX</a>, a term which is now itself rarely used. Client-side-scripting, server-side scripting, or a combination of these make for the dynamic web experience in a browser.
<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/J/JavaScript.html" "title="JavaScript">JavaScript</a><span class="linkinfotext">
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...<br></span></div> is a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/scripting_programming_language.html" "title="scripting programming language">scripting language</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scripting ...<br></span></div> that was initially developed in 1995 by <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/B/Brendan_Eich.html" ;"title="Brendan Eich">Brendan Eich</a>, then of <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/N/Netscape.html" "title="Netscape">Netscape</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Netscape Communications Corporation (originally Mosaic Communications Corporation) was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was onc ...<br></span></div>, for use within web pages.<ref name=Hamilton></ref> The standardised version is <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/E/ECMAScript.html" "title="ECMAScript">ECMAScript</a><span class="linkinfotext">
ECMAScript (; ES) is a JavaScript standard intended to ensure the interoperability of web pages across different browsers. It is standardized by Ecma International in the documenECMA-262
ECMAScript is commonly used for client-side scripting o ...<br></span></div>.<ref name=Hamilton /> To make web pages more interactive, some web applications also use JavaScript techniques such as <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/A/Ajax_(programming).html" ;"title="Ajax (programming)">Ajax</a> (<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/A/Asynchronous_I_O.html" "title="Asynchronous I/O">asynchronous</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Asynchrony is the state of not being in synchronization.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and computing
* Asynchrony (computer programming), the occurrence of events independent of the main program flow, and ways to deal with ...<br></span></div> JavaScript and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/X/XML.html" "title="XML">XML</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. T ...<br></span></div>). <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/C/Client-side_scripting.html" "title="Client-side scripting">Client-side script</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A server-side dynamic web page is a web page whose construction is controlled by an application server processing server-side scripts. In server-side scripting, Parameter (computer programming), parameters determine how the assembly of every new ...<br></span></div> is delivered with the page that can make additional HTTP requests to the server, either in response to user actions such as mouse movements or clicks, or based on elapsed time. The server's responses are used to modify the current page rather than creating a new page with each response, so the server needs only to provide limited, incremental information. Multiple Ajax requests can be handled at the same time, and users can interact with the page while data is retrieved. Web pages may also regularly <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/p/polling_(computer_science).html" ;"title="polling (computer science)">poll</a> the server to check whether new information is available.
<h2><br><p> Website</h2></p>
<img title="United States Antarctic Program website from 2018 02 22"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/87/United_States_Antarctic_Program_website_from_2018_02_22.png" >
A ''website'' is a collection of related web resources including <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_page.html" ;"title="web page">web page</a>s, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/m/multimedia.html" "title="multimedia">multimedia</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, or video into a single interactive presentation, in contrast to tradition ...<br></span></div> content, typically identified with a common <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/domain_name.html" ;"title="domain name">domain name</a>, and published on at least one <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">web server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...<br></span></div>. Notable examples are <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/wikipedia.html" "title="wikipedia">wikipedia</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Wikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read refer ...<br></span></div>.org, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/g/google.html" "title="google">google</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...<br></span></div>.com, and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/A/Amazon_(company).html" "title="Amazon (company)">amazon.com</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Amazon.com, Inc. ( ) is an American multinational technology company focusing on e-commerce, cloud computing, online advertising, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence. It has been referred to as "one of the most influential economi ...<br></span></div>.
A website may be accessible via a public <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_Protocol.html" "title="Internet Protocol">Internet Protocol</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
IP h ...<br></span></div> (IP) network, such as the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet.html" "title="Internet">Internet</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...<br></span></div>, or a private <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/l/local_area_network.html" "title="local area network">local area network</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger ...<br></span></div> (LAN), by referencing a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/URL.html" "title="URL">uniform resource locator</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifi ...<br></span></div> (URL) that identifies the site.
Websites can have many functions and can be used in various fashions; a website can be a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/personal_website.html" "title="personal website">personal website</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Personal web pages are World Wide Web pages created by an individual to contain content of a personal nature rather than content pertaining to a company, organization or institution. Personal web pages are primarily used for informative or enter ...<br></span></div>, a corporate website for a company, a government website, an organization website, etc. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, ranging from entertainment and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/social_networking.html" "title="social networking">social networking</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for an ...<br></span></div> to providing news and education. All publicly accessible websites collectively constitute the World Wide Web, while private websites, such as a company's website for its employees, are typically a part of an <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/i/intranet.html" "title="intranet">intranet</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An intranet is a computer network for sharing information, easier communication, collaboration tools, operational systems, and other computing services within an organization, usually to the exclusion of access by outsiders. The term is used in c ...<br></span></div>.
Web pages, which are the building blocks of websites, are <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/d/document.html" "title="document">document</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A document is a written, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ''Documentum'', which denotes a "teaching" or ...<br></span></div>s, typically composed in <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/p/plain_text.html" ;"title="plain text">plain text</a> interspersed with <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/F/Formatted_text.html" ;"title="Formatted text">formatting instructions</a> of Hypertext Markup Language (<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTML.html" "title="HTML">HTML</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...<br></span></div>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/X/XHTML.html" "title="XHTML">XHTML</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
While HTML, prior ...<br></span></div>). They may incorporate elements from other websites with suitable <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTML_anchor.html" ;"title="HTML anchor">markup anchors</a>. Web pages are accessed and transported with the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol.html" "title="Hypertext Transfer Protocol">Hypertext Transfer Protocol</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...<br></span></div> (HTTP), which may optionally employ encryption (<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTTP_Secure.html" "title="HTTP Secure">HTTP Secure</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is enc ...<br></span></div>, HTTPS) to provide security and privacy for the user. The user's application, often a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_browser.html" "title="web browser">web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div>, renders the page content according to its HTML markup instructions onto a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Computer_monitor.html" ;"title="Computer monitor">display terminal</a>.
<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hyperlink.html" "title="Hyperlink">Hyperlink</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text wit ...<br></span></div>ing between web pages conveys to the reader the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/site_map.html" ;"title="site map">site structure</a> and guides the navigation of the site, which often starts with a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/h/home_page.html" "title="home page">home page</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A home page (or homepage) is the main web page of a website. The term may also refer to the start page shown in a web browser when the application first opens. Usually, the home page is located at the root of the website's domain or subdomain ...<br></span></div> containing a directory of the site <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_content.html" ;"title="web content">web content</a>. Some websites require user registration or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/subscription.html" "title="subscription">subscription</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The subscription business model is a business model in which a customer must pay a recurring price at regular intervals for access to a product or service. The model was pioneered by publishers of books and periodicals in the 17th century, and ...<br></span></div> to access content. Examples of <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/p/paywall.html" ;"title="paywall">subscription websites</a> include many business sites, news websites, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/a/academic_journal.html" "title="academic journal">academic journal</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and d ...<br></span></div> websites, gaming websites, file-sharing websites, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_forum.html" "title="Internet forum">message boards</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are often longer than one line of text, and are at least temporar ...<br></span></div>, web-based <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/e/email.html" "title="email">email</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant ...<br></span></div>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/social_networking.html" "title="social networking">social networking</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for an ...<br></span></div> websites, websites providing real-time price quotations for different types of markets, as well as sites providing various other services. <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/E/End_user.html" "title="End user">End user</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrat ...<br></span></div>s can access websites on a range of devices, including <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/desktop_computer.html" ;"title="desktop computer">desktop</a> and <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/l/laptop.html" ;"title="laptop">laptop computers</a>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/t/tablet_computer.html" "title="tablet computer">tablet computer</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being comput ...<br></span></div>s, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/smartphone.html" "title="smartphone">smartphone</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...<br></span></div>s and <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/smart_TV.html" ;"title="smart TV">smart TV</a>s.
<h2><br><p> Browser</h2></p>
A ''web browser'' (commonly referred to as a ''browser'') is a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/software_application.html" "title="software application">software</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...<br></span></div> <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/u/user_agent.html" "title="user agent">user agent</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a user agent is any software, acting on behalf of a user, which "retrieves, renders and facilitates end-user interaction with Web content". A user agent is therefore a special kind of software agent.
Some prominent examples of us ...<br></span></div> for accessing information on the World Wide Web. To connect to a website's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_server.html" "title="web server">server</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called clients
Role
* Waiting staff, those who work at a restaurant or a bar attending customers and su ...<br></span></div> and display its pages, a user needs to have a web browser program. This is the program that the user runs to download, format, and display a web page on the user's computer.
In addition to allowing users to find, display, and move between web pages, a web browser will usually have features like keeping bookmarks, recording history, managing cookies (see below), and home pages and may have facilities for recording passwords for logging into web sites.
The most popular browsers are <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/G/Google_Chrome.html" ;"title="Google Chrome">Chrome</a>, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/F/Firefox.html" ;"title="Firefox">Firefox</a>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/S/Safari_(web_browser).html" "title="Safari (web browser)">Safari</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A safari (; ) is an overland journey to observe wild animals, especially in eastern or southern Africa. The so-called "Big Five" game animals of Africa – lion, leopard, rhinoceros, elephant, and Cape buffalo – particularly form an importa ...<br></span></div>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_Explorer.html" "title="Internet Explorer">Internet Explorer</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated IE or MSIE) is a series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft which was used in the Microsoft Wind ...<br></span></div>, and <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/M/Microsoft_Edge.html" ;"title="Microsoft Edge">Edge</a>.
<h2><br><p> Server</h2></p>
<img title="Inside and Rear of Webserver"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/38/Inside_and_Rear_of_Webserver.jpg" >
A ''Web server'' is <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/server_software.html" "title="server software">server software</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a server is a piece of computer hardware or software (computer program) that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called " clients". This architecture is called the client–server model. Servers can provide variou ...<br></span></div>, or hardware dedicated to running said software, that can satisfy World Wide Web client requests. A web server can, in general, contain one or more websites. A web server processes incoming network requests over <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol.html" "title="Hypertext Transfer Protocol">HTTP</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...<br></span></div> and several other related protocols.
The primary function of a web server is to store, process and deliver <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_page.html" ;"title="web page">web page</a>s to <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Client_(computing).html" ;"title="Client (computing)">clients</a>. The communication between client and server takes place using the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol.html" ;"title="Hypertext Transfer Protocol">Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)</a>. Pages delivered are most frequently <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTML.html" ;"title="HTML">HTML documents</a>, which may include <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/i/image.html" "title="image">image</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...<br></span></div>s, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/S/Style_sheet_(web_development).html" ;"title="Style sheet (web development)">style sheets</a> and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/J/JavaScript.html" "title="JavaScript">scripts</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of handw ...<br></span></div> in addition to the text content.
<img title="Wikimedia Foundation Servers-8055 35"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/69/Wikimedia_Foundation_Servers-8055_35.jpg" >
A <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/u/user_agent.html" "title="user agent">user agent</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a user agent is any software, acting on behalf of a user, which "retrieves, renders and facilitates end-user interaction with Web content". A user agent is therefore a special kind of software agent.
Some prominent examples of us ...<br></span></div>, commonly a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_browser.html" "title="web browser">web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div> or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_crawler.html" "title="web crawler">web crawler</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Web crawler, sometimes called a spider or spiderbot and often shortened to crawler, is an Internet bot that systematically browses the World Wide Web and that is typically operated by search engines for the purpose of Web indexing (''web spid ...<br></span></div>, initiates communication by making a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/H/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol#Request_message.html" ;"title="Hypertext Transfer Protocol#Request message">request</a> for a specific resource using HTTP and the server responds with the content of that resource or an <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/L/List_of_HTTP_status_codes#4xx_client_errors.html" ;"title="List of HTTP status codes#4xx client errors">error message</a> if unable to do so. The resource is typically a real file on the server's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/secondary_memory.html" "title="secondary memory">secondary storage</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer ...<br></span></div>, but this is not necessarily the case and depends on how the webserver is <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/I/Implementation.html" ;"title="Implementation">implemented</a>.
While the primary function is to serve content, full implementation of HTTP also includes ways of receiving content from clients. This feature is used for submitting <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/F/Form_(web).html" "title="Form (web)">web forms</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A webform, web form or HTML form on a web page allows a user to enter data that is sent to a server for processing. Forms can resemble paper or database forms because web users fill out the forms using checkboxes, radio buttons, or text fields. F ...<br></span></div>, including <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/u/upload.html" ;"title="upload">upload</a>ing of files.
Many generic web servers also support <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/server-side_scripting.html" ;"title="server-side scripting">server-side scripting</a> using <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/A/Active_Server_Pages.html" "title="Active Server Pages">Active Server Pages</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Active Server Pages (ASP) is Microsoft's first server-side scripting language and engine for dynamic web pages.
It was first released in December 1996, before being superseded in January 2002 by ASP.NET.
History
Initially released as an add ...<br></span></div> (ASP), <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/P/PHP.html" "title="PHP">PHP</a><span class="linkinfotext">
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared toward web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group ...<br></span></div> (Hypertext Preprocessor), or other <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/scripting_language.html" "title="scripting language">scripting language</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scripting ...<br></span></div>s. This means that the behavior of the webserver can be scripted in separate files, while the actual server software remains unchanged. Usually, this function is used to generate HTML documents <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/D/Dynamic_web_page.html" ;"title="Dynamic web page">dynamically</a> ("on-the-fly") as opposed to returning <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/S/Static_web_page.html" ;"title="Static web page">static documents</a>. The former is primarily used for retrieving or modifying information from <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/d/database.html" "title="database">database</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases sp ...<br></span></div>s. The latter is typically much faster and more easily <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_cache.html" ;"title="web cache">cached</a> but cannot deliver <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/dynamic_content.html" ;"title="dynamic content">dynamic content</a>.
Web servers can also frequently be found <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/e/embedded_system.html" ;"title="embedded system">embedded</a> in devices such as <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/printer_(computing).html" "title="printer (computing)">printers</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Printer may refer to:
Technology
* Printer (publishing), a person or a company
* Printer (computing), a hardware device
* Optical printer for motion picture films
People
* Nariman Printer ( fl. c. 1940), Indian journalist and activist
* Jame ...<br></span></div>, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/R/Router_(computing).html" ;"title="Router (computing)">routers</a>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/webcam.html" "title="webcam">webcam</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A webcam is a video camera which is designed to record or stream to a computer or computer network. They are primarily used in videotelephony, livestreaming and social media, and security. Webcams can be built-in computer hardware or peripheral d ...<br></span></div>s and serving only a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/L/Local_area_network.html" "title="Local area network">local network</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger ...<br></span></div>. The web server may then be used as a part of a system for monitoring or administering the device in question. This usually means that no additional software has to be installed on the client computer since only a web browser is required (which now is included with most <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/o/operating_system.html" "title="operating system">operating system</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also in ...<br></span></div>s).
<h2><br><p> Cookie</h2></p>
An ''HTTP cookie'' (also called ''web cookie'', ''Internet cookie'', ''browser cookie'', or simply ''cookie'') is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored on the user's computer by the user's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_browser.html" "title="web browser">web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div> while the user is browsing. Cookies were designed to be a reliable mechanism for websites to remember <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/program_state.html" "title="program state">stateful</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In information technology and computer science, a system is described as stateful if it is designed to remember preceding events or user interactions; the remembered information is called the state of the system.
The set of states a system can oc ...<br></span></div> information (such as items added in the shopping cart in an online store) or to record the user's browsing activity (including clicking particular buttons, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/a/access_control.html" "title="access control">logging in</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computer security, logging in (or logging on, signing in, or signing on) is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system by identifying and authenticating themselves. The user credentials are typically some form ...<br></span></div>, or recording which pages were visited in the past). They can also be used to remember arbitrary pieces of information that the user previously entered into form fields such as names, addresses, passwords, and credit card numbers.
Cookies perform essential functions in the modern web. Perhaps most importantly, ''authentication cookies'' are the most common method used by web servers to know whether the user is logged in or not, and which account they are logged in with. Without such a mechanism, the site would not know whether to send a page containing sensitive information or require the user to authenticate themselves by logging in. The security of an authentication cookie generally depends on the security of the issuing website and the user's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/comparison_of_web_browsers#Vulnerabilities.html" "title="comparison of web browsers#Vulnerabilities">web browser</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...<br></span></div>, and on whether the cookie data is encrypted. Security vulnerabilities may allow a cookie's data to be read by a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/h/hacker_(computer_security).html" ;"title="hacker (computer security)">hacker</a>, used to gain access to user data, or used to gain access (with the user's credentials) to the website to which the cookie belongs (see <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/c/cross-site_scripting.html" ;"title="cross-site scripting">cross-site scripting</a> and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/cross-site_request_forgery.html" "title="cross-site request forgery">cross-site request forgery</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Cross-site request forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding and abbreviated as CSRF (sometimes pronounced ''sea-surf'') or XSRF, is a type of malicious exploit of a website or web application where unauthorized commands are submitt ...<br></span></div> for examples).
Tracking cookies, and especially <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/#/#Cookie.html" ;"title="#Cookie">third-party tracking cookies</a>, are commonly used as ways to compile long-term records of individuals' browsing histories a potential <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_privacy#HTTP_cookies.html" ;"title="Internet privacy#HTTP cookies">privacy concern</a> that prompted European and U.S. lawmakers to take action in 2011.<ref name="eulaw"></ref> European law requires that all websites targeting <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/E/European_Union.html" "title="European Union">European Union</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...<br></span></div> member states gain "informed consent" from users before storing non-essential cookies on their device.
Google <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/P/Project_Zero_(Google).html" "title="Project Zero (Google)">Project Zero</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Project Zero is a team of security analysts employed by Google tasked with finding zero-day vulnerabilities. It was announced on 15 July 2014.
History
After finding a number of flaws in software used by many end-users while researching other p ...<br></span></div> researcher Jann Horn describes ways cookies can be read by <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/M/Man-in-the-middle_attack.html" "title="Man-in-the-middle attack">intermediaries</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An intermediary (or go-between) is a third party that offers intermediation services between two parties, which involves conveying messages between principals in a dispute, preventing direct contact and potential escalation of the issue. In law ...<br></span></div>, like <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/Wi-Fi.html" "title="Wi-Fi">Wi-Fi</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio wave ...<br></span></div> hotspot providers. He recommends using the browser in <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/i/incognito_mode.html" ;"title="incognito mode">incognito mode</a> in such circumstances.
<h2><br><p> Search engine</h2></p>
<img title="Mayflower Wikimedia Commons image search engine screenshot"; style="text-decoration: none; height:150px;float: left; padding: 0px 3px 0px 0px;"src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/ba/Mayflower_Wikimedia_Commons_image_search_engine_screenshot.png" >
A ''web search engine'' or ''Internet search engine'' is a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/software_system.html" "title="software system">software system</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A software system is a system of intercommunicating components based on software forming part of a computer system (a combination of hardware and software). It "consists of a number of separate programs, configuration files, which are used to se ...<br></span></div> that is designed to carry out ''web search'' (''Internet search''), which means to search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_search_query.html" ;"title="web search query">web search query</a>. The search results are generally presented in a line of results, often referred to as <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/search_engine_results_page.html" ;"title="search engine results page">search engine results page</a>s (SERPs). The information may be a mix of <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_page.html" ;"title="web page">web page</a>s, images, videos, infographics, articles, research papers, and other types of files. Some search engines also <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/data_mining.html" ;"title="data mining">mine data</a> available in <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/d/database.html" "title="database">database</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases sp ...<br></span></div>s or <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_directory.html" ;"title="web directory">open directories</a>. Unlike <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_directories.html" "title="web directories">web directories</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A web directory or link directory is an online list or catalog of websites. That is, it is a directory on the World Wide Web of (all or part of) the World Wide Web. Historically, directories typically listed entries on people or businesses, and th ...<br></span></div>, which are maintained only by human editors, search engines also maintain <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/r/real-time_computing.html" "title="real-time computing">real-time</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Real-time or real time describes various operations in computing or other processes that must guarantee response times within a specified time (deadline), usually a relatively short time. A real-time process is generally one that happens in defined ...<br></span></div> information by running an <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/a/algorithm.html" "title="algorithm">algorithm</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specificat ...<br></span></div> on a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_crawler.html" "title="web crawler">web crawler</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Web crawler, sometimes called a spider or spiderbot and often shortened to crawler, is an Internet bot that systematically browses the World Wide Web and that is typically operated by search engines for the purpose of Web indexing (''web spid ...<br></span></div>.
Internet content that is not capable of being searched by a web search engine is generally described as the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/d/deep_web.html" "title="deep web">deep web</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The deep web, invisible web, or hidden web are parts of the World Wide Web whose contents are not indexed by standard web search-engine programs. This is in contrast to the " surface web", which is accessible to anyone using the Internet. Co ...<br></span></div>.
<h2><br><p> Deep web</h2></p>
The deep web,<ref name="nhamilton"></ref> ''invisible web'',<ref name="jal"></ref> or ''hidden web''<ref name="cthw"></ref> are parts of the World Wide Web whose contents are not <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/S/Search_engine_indexing.html" ;"title="Search engine indexing">indexed</a> by standard <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_search_engine.html" "title="web search engine">web search engine</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A search engine is a software system designed to carry out web searches. They search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. The search results are generally presented in a ...<br></span></div>s. The opposite term to the deep web is the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/surface_web.html" "title="surface web">surface web</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Surface Web (also called the Visible Web, Indexed Web, Indexable Web or Lightnet) is the portion of the World Wide Web that is readily available to the general public and searchable with standard web search engines. It is the opposite of the ...<br></span></div>, which is accessible to anyone using the Internet. <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/C/Computer_scientist.html" "title="Computer scientist">Computer scientist</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A computer scientist is a person who is trained in the academic study of computer science.
Computer scientists typically work on the theoretical side of computation, as opposed to the hardware side on which computer engineers mainly focus (al ...<br></span></div> Michael K. Bergman is credited with coining the term ''deep web'' in 2001 as a search indexing term.<ref name="wright2009"/>
The content of the deep web is hidden behind <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTTP.html" "title="HTTP">HTTP</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...<br></span></div> forms, and includes many very common uses such as <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_mail.html" "title="web mail">web mail</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Webmail (or web-based email) is an email service that can be accessed using a standard web browser. It contrasts with email service accessible through a specialised email client software. Examples of webmail providers are 1&1 Ionos, AOL Mail, ...<br></span></div>, <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/o/online_banking.html" ;"title="online banking">online banking</a>, and services that users must pay for, and which is protected by a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/paywall.html" "title="paywall">paywall</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A paywall is a method of restricting access to content, with a purchase or a paid subscription, especially news. Beginning in the mid-2010s, newspapers started implementing paywalls on their websites as a way to increase revenue after years of ...<br></span></div>, such as <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/v/video_on_demand.html" "title="video on demand">video on demand</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of o ...<br></span></div>, some online magazines and newspapers, among others.
The content of the deep web can be located and accessed by a direct <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/URL.html" "title="URL">URL</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifie ...<br></span></div> or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/IP_address.html" "title="IP address">IP address</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.. Updated by . An IP address serves two main functions: network interface ident ...<br></span></div>, and may require a password or other security access past the public website page.
<h2><br><p> Caching </h2></p>
A <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_cache.html" "title="web cache">web cache</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Web cache (or HTTP cache) is a system for optimizing the World Wide Web. It is implemented both client-side and server-side. The caching of multimedias and other files can result in less overall delay when browsing the Web.
Parts of the syste ...<br></span></div> is a server computer located either on the public Internet or within an enterprise that stores recently accessed web pages to improve response time for users when the same content is requested within a certain time after the original request. Most web browsers also implement a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/b/browser_cache.html" "title="browser cache">browser cache</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Web cache (or HTTP cache) is a system for optimizing the World Wide Web. It is implemented both client-side and server-side. The caching of multimedias and other files can result in less overall delay when browsing the Web.
Parts of the syste ...<br></span></div> by writing recently obtained data to a local data storage device. HTTP requests by a browser may ask only for data that has changed since the last access. Web pages and resources may contain expiration information to control caching to secure sensitive data, such as in <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/o/online_banking.html" ;"title="online banking">online banking</a>, or to facilitate frequently updated sites, such as news media. Even sites with highly dynamic content may permit basic resources to be refreshed only occasionally. Web site designers find it worthwhile to collate resources such as CSS data and JavaScript into a few site-wide files so that they can be cached efficiently. Enterprise <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/F/Firewall_(networking).html" ;"title="Firewall (networking)">firewalls</a> often cache Web resources requested by one user for the benefit of many users. Some <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/s/search_engines.html" "title="search engines">search engines</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A search engine is a software system designed to carry out web searches. They search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. The search results are generally presented in a ...<br></span></div> store cached content of frequently accessed websites.
<h1><br><p> Security </h1></p>
For <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/criminal.html" "title="criminal">criminal</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Can ...<br></span></div>s, the Web has become a venue to spread <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/m/malware.html" "title="malware">malware</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Malware (a portmanteau for ''malicious software'') is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server, client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, depri ...<br></span></div> and engage in a range of <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/cybercrime.html" "title="cybercrime">cybercrime</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A cybercrime is a crime that involves a computer or a computer network.Moore, R. (2005) "Cyber crime: Investigating High-Technology Computer Crime," Cleveland, Mississippi: Anderson Publishing. The computer may have been used in committing the ...<br></span></div>s, including (but not limited to) <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/i/identity_theft.html" "title="identity theft">identity theft</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Identity theft occurs when someone uses another person's personal identifying information, like their name, identifying number, or credit card number, without their permission, to commit fraud or other crimes. The term ''identity theft'' was co ...<br></span></div>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/f/fraud.html" "title="fraud">fraud</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In law, fraud is intentional deception to secure unfair or unlawful gain, or to deprive a victim of a legal right. Fraud can violate civil law (e.g., a fraud victim may sue the fraud perpetrator to avoid the fraud or recover monetary compens ...<br></span></div>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/e/espionage.html" "title="espionage">espionage</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tangibl ...<br></span></div> and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/i/intelligence_gathering.html" "title="intelligence gathering">intelligence gathering</a><span class="linkinfotext">
This is a list of intelligence gathering disciplines.
HUMINT
Human intelligence (HUMINT) are gathered from a person in the location in question. Sources can include the following:
* Advisors or foreign internal defense (FID) personnel wor ...<br></span></div>.<ref name=Ben-Itzhak /> Web-based <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/v/vulnerability_(computing).html" "title="vulnerability (computing)">vulnerabilities</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Vulnerability refers to "the quality or state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed, either physically or emotionally."
A window of vulnerability (WOV) is a time frame within which defensive measures are diminished, com ...<br></span></div> now outnumber traditional computer security concerns, and as measured by <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/G/Google.html" "title="Google">Google</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...<br></span></div>, about one in ten web pages may contain malicious code. Most web-based <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/a/attack_(computing).html" ;"title="attack (computing)">attacks</a> take place on legitimate websites, and most, as measured by <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/S/Sophos.html" "title="Sophos">Sophos</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Sophos Group plc is a British based security software and hardware company. Sophos develops products for communication endpoint, encryption, network security, email security, mobile security and unified threat management. Sophos is primarily ...<br></span></div>, are hosted in the United States, China and Russia.<ref name=Sophos-Q1-2008></ref> The most common of all malware <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/T/Threat_(computer).html" ;"title="Threat (computer)">threats</a> is <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/S/SQL_injection.html" ;"title="SQL injection">SQL injection</a> attacks against websites. Through HTML and URIs, the Web was vulnerable to attacks like <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/c/cross-site_scripting.html" ;"title="cross-site scripting">cross-site scripting</a> (XSS) that came with the introduction of JavaScript<ref name=FGHR></ref> and were exacerbated to some degree by <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_2.0.html" ;"title="Web 2.0">Web 2.0</a> and Ajax <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_design.html" ;"title="web design">web design</a> that favours the use of scripts. Today by one estimate, 70% of all websites are open to XSS attacks on their users. <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/P/Phishing.html" ;"title="Phishing">Phishing</a> is another common threat to the Web. In February 2013, RSA (the security division of EMC) estimated the global losses from phishing at $1.5 billion in 2012.<ref name="First_Post"></ref> Two of the well-known phishing methods are Covert Redirect and Open Redirect.
Proposed solutions vary. Large security companies like <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/M/McAfee.html" ;"title="McAfee">McAfee</a> already design governance and compliance suites to meet post-9/11 regulations, and some, like <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/F/Finjan.html" "title="Finjan">Finjan</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Finjan Holdings (Finjan) is a company that focuses on the licensing of intellectual property. Finjan claims to own patented technology used in enterprise web security tools. Formerly a publicly traded company on NASDAQ (FNJN), it was acquired by t ...<br></span></div> have recommended active real-time inspection of programming code and all content regardless of its source.<ref name="Ben-Itzhak"></ref> Some have argued that for enterprises to see Web security as a business opportunity rather than a <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/c/cost_centre_(business).html" ;"title="cost centre (business)">cost centre</a>, while others call for "ubiquitous, always-on <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/d/digital_rights_management.html" "title="digital rights management">digital rights management</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures (TPM) such as access control technologies can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted works. ...<br></span></div>" enforced in the infrastructure to replace the hundreds of companies that secure data and networks. <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/J/Jonathan_Zittrain.html" "title="Jonathan Zittrain">Jonathan Zittrain</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Jonathan L. Zittrain (born December 24, 1969) is an American professor of Internet law and the George Bemis Professor of International Law at Harvard Law School. He is also a professor at the Harvard Kennedy School, a professor of computer scie ...<br></span></div> has said users sharing responsibility for computing safety is far preferable to locking down the Internet.
<h1><br><p> Privacy </h1></p>
Every time a client requests a web page, the server can identify the request's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/IP_address.html" "title="IP address">IP address</a><span class="linkinfotext">
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.. Updated by . An IP address serves two main functions: network interface ident ...<br></span></div>. Web servers usually log IP addresses in a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/l/log_file.html" "title="log file">log file</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In computing, logging is the act of keeping a log of events that occur in a computer system, such as problems, errors or just information on current operations. These events may occur in the operating system or in other software. A message or lo ...<br></span></div>. Also, unless set not to do so, most web browsers record requested web pages in a viewable ''history'' feature, and usually <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_cache.html" ;"title="Web cache">cache</a> much of the content locally. Unless the server-browser communication uses HTTPS encryption, web requests and responses travel in plain text across the Internet and can be viewed, recorded, and cached by intermediate systems. Another way to hide <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/personally_identifiable_information.html" "title="personally identifiable information">personally identifiable information</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Personal data, also known as personal information or personally identifiable information (PII), is any information related to an identifiable person.
The abbreviation PII is widely accepted in the United States, but the phrase it abbreviates ha ...<br></span></div> is by using a <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/v/virtual_private_network.html" "title="virtual private network">virtual private network</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. The be ...<br></span></div>. A VPN <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/e/encryption.html" ;"title="encryption">encrypts</a> online traffic and masks the original IP address lowering the chance of user identification.
When a web page asks for, and the user supplies, personally identifiable information—such as their real name, address, e-mail address, etc. web-based entities can associate current web traffic with that individual. If the website uses <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/H/HTTP_cookie.html" "title="HTTP cookie">HTTP cookie</a><span class="linkinfotext">
HTTP cookies (also called web cookies, Internet cookies, browser cookies, or simply cookies) are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and placed on the user's computer or other device by the user's w ...<br></span></div>s, username, and password authentication, or other tracking techniques, it can relate other web visits, before and after, to the identifiable information provided. In this way, a web-based organization can develop and build a profile of the individual people who use its site or sites. It may be able to build a record for an individual that includes information about their leisure activities, their shopping interests, their profession, and other aspects of their <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/d/demographic_profile.html" ;"title="demographic profile">demographic profile</a>. These profiles are of potential interest to marketers, advertisers, and others. Depending on the website's <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/t/terms_and_conditions.html" "title="terms and conditions">terms and conditions</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A contractual term is "any provision forming part of a contract". Each term gives rise to a contractual obligation, the breach of which may give rise to litigation. Not all terms are stated expressly and some terms carry less legal gravity as t ...<br></span></div> and the local laws that apply information from these profiles may be sold, shared, or passed to other organizations without the user being informed. For many ordinary people, this means little more than some unexpected e-mails in their in-box or some uncannily relevant advertising on a future web page. For others, it can mean that time spent indulging an unusual interest can result in a deluge of further targeted marketing that may be unwelcome. Law enforcement, counter-terrorism, and espionage agencies can also identify, target, and track individuals based on their interests or proclivities on the Web.
<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/S/Social_networking.html" "title="Social networking">Social networking</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for an ...<br></span></div> sites usually try to get users to use their real names, interests, and locations, rather than pseudonyms, as their executives believe that this makes the social networking experience more engaging for users. On the other hand, uploaded photographs or unguarded statements can be identified to an individual, who may regret this exposure. Employers, schools, parents, and other relatives may be influenced by aspects of social networking profiles, such as text posts or digital photos, that the posting individual did not intend for these audiences. <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Cyberbullying.html" ;"title="Cyberbullying">Online bullies</a> may make use of personal information to harass or <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/c/cyberstalking.html" ;"title="cyberstalking">stalk</a> users. Modern social networking websites allow fine-grained control of the privacy settings for each posting, but these can be complex and not easy to find or use, especially for beginners. Photographs and videos posted onto websites have caused particular problems, as they can add a person's face to an online profile. With modern and potential <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/F/Facial_recognition_system.html" "title="Facial recognition system">facial recognition technology</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A facial recognition system is a technology capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and ...<br></span></div>, it may then be possible to relate that face with other, previously anonymous, images, events, and scenarios that have been imaged elsewhere. Due to image caching, mirroring, and copying, it is difficult to remove an image from the World Wide Web.
<h1><br><p> Standards </h1></p>
Web standards include many interdependent standards and specifications, some of which govern aspects of the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet.html" "title="Internet">Internet</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...<br></span></div>, not just the World Wide Web. Even when not web-focused, such standards directly or indirectly affect the development and administration of websites and <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_service.html" ;"title="web service">web service</a>s. Considerations include the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/i/interoperability.html" ;"title="interoperability">interoperability</a>, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/a/accessibility.html" "title="accessibility">accessibility</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i. ...<br></span></div> and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/u/usability.html" "title="usability">usability</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a soft ...<br></span></div> of web pages and web sites.
Web standards, in the broader sense, consist of the following:
* ''Recommendations'' published by the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/World_Wide_Web_Consortium.html" "title="World Wide Web Consortium">World Wide Web Consortium</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 and led by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working to ...<br></span></div> (W3C)
* "Living Standard" made by the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_Hypertext_Application_Technology_Working_Group.html" "title="Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group">Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG) is a community of people interested in evolving HTML and related technologies. The WHATWG was founded by individuals from Apple Inc., the Mozilla Foundation and Opera Software, lea ...<br></span></div> (WHATWG)
* ''<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/R/Request_for_Comments.html" "title="Request for Comments">Request for Comments</a><span class="linkinfotext">
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or g ...<br></span></div>'' (RFC) documents published by the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_Engineering_Task_Force.html" "title="Internet Engineering Task Force">Internet Engineering Task Force</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and a ...<br></span></div> (IETF)
* ''Standards'' published by the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/International_Organization_for_Standardization.html" "title="International Organization for Standardization">International Organization for Standardization</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Ar ...<br></span></div> (ISO)
* ''Standards'' published by <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/E/Ecma_International.html" ;"title="Ecma International">Ecma International</a> (formerly ECMA)
* ''The <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/Unicode.html" "title="Unicode">Unicode</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expre ...<br></span></div> Standard'' and various ''Unicode Technical Reports'' (UTRs) published by the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/Unicode_Consortium.html" "title="Unicode Consortium">Unicode Consortium</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Unicode Consortium (legally Unicode, Inc.) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization incorporated and based in Mountain View, California. Its primary purpose is to maintain and publish the Unicode Standard which was developed with the intenti ...<br></span></div>
* Name and number registries maintained by the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_Assigned_Numbers_Authority.html" "title="Internet Assigned Numbers Authority">Internet Assigned Numbers Authority</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is a standards organization that oversees global IP address allocation, autonomous system number allocation, root zone management in the Domain Name System (DNS), media types, and other Interne ...<br></span></div> (IANA)
Web standards are not fixed sets of rules but are constantly evolving sets of finalized technical specifications of web technologies. Web standards are developed by <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/s/standards_organization.html" ;"title="standards organization">standards organization</a>s—groups of interested and often competing parties chartered with the task of standardization—not technologies developed and declared to be a standard by a single individual or company. It is crucial to distinguish those specifications that are under development from the ones that already reached the final development status (in the case of <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/W3C.html" "title="W3C">W3C</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 and led by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working to ...<br></span></div> specifications, the highest maturity level).
<h1><br><p> Accessibility </h1></p>
There are methods for accessing the Web in alternative mediums and formats to facilitate use by individuals with <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/d/disability.html" "title="disability">disabilities</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, se ...<br></span></div>. These disabilities may be visual, auditory, physical, speech-related, cognitive, neurological, or some combination. Accessibility features also help people with temporary disabilities, like a broken arm, or ageing users as their abilities change.<ref name=WAI></ref> The Web receives information as well as providing information and interacting with society. The World Wide Web Consortium claims that it is essential that the Web be accessible, so it can provide equal access and <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/e/equal_opportunity.html" ;"title="equal opportunity">equal opportunity</a> to people with disabilities. Tim Berners-Lee once noted, "The power of the Web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disability is an essential aspect."<ref name=WAI /> Many countries regulate <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/w/web_accessibility.html" ;"title="web accessibility">web accessibility</a> as a requirement for websites. International co-operation in the W3C <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_Accessibility_Initiative.html" ;"title="Web Accessibility Initiative">Web Accessibility Initiative</a> led to simple guidelines that web content authors as well as software developers can use to make the Web accessible to persons who may or may not be using <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/a/assistive_technology.html" "title="assistive technology">assistive technology</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Assistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for people with disabilities and the elderly. Disabled people often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, or even with ...<br></span></div>.<ref name=WAI />
<h1><br><p> Internationalisation </h1></p>
The W3C <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internationalization_and_localization.html" "title="Internationalization and localization">Internationalisation</a><span class="linkinfotext">
In economics, internationalization or internationalisation is the process of increasing involvement of enterprises in international markets, although there is no agreed definition of internationalization. Internationalization is a crucial strateg ...<br></span></div> Activity assures that web technology works in all languages, scripts, and cultures. Beginning in 2004 or 2005, <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/Unicode.html" "title="Unicode">Unicode</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expre ...<br></span></div> gained ground and eventually in December 2007 surpassed both <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/A/ASCII.html" "title="ASCII">ASCII</a><span class="linkinfotext">
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of ...<br></span></div> and Western European as the Web's most frequently used <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/c/character_encoding.html" "title="character encoding">character encoding</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to Graphics, graphical character (computing), characters, especially the written characters of Language, human language, allowing them to be Data storage, stored, Data communication, transmi ...<br></span></div>. Originally allowed resources to be identified by <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/URI.html" "title="URI">URI</a><span class="linkinfotext"> Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), an island off Malakula Islan ...<br></span></div> in a subset of US-ASCII. allows more characters—any character in the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/U/Universal_Character_Set.html" ;"title="Universal Character Set">Universal Character Set</a>—and now a resource can be identified by <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internationalized_Resource_Identifier.html" "title="Internationalized Resource Identifier">IRI</a><span class="linkinfotext">
IRI or I.R.I. refers to:
Businesses and organizations
* Iringa Airport, an airport in Tanzania serving Iringa and the surrounding Iringa Region by IATA airport code
* India Rejuvenation Initiative, an Indian anti-corruption organization forme ...<br></span></div> in any language.
<!--</h1></p> Statistics </h1></p>
Between 2005 and 2010, the number of Web users doubled, and was expected to surpass two billion in 2010. Early studies in 1998 and 1999 estimating the size of the Web using capture/recapture methods showed that much of the Web was not indexed by search engines and the Web was much larger than expected. According to a 2001 study, there was a massive number, over 550 billion, of documents on the Web, mostly in the invisible Web, or <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/D/Deep_Web_(search_indexing).html" "title="Deep Web (search indexing)">Deep Web</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The deep web, invisible web, or hidden web are parts of the World Wide Web whose contents are not indexed by standard web search-engine programs. This is in contrast to the " surface web", which is accessible to anyone using the Internet. Co ...<br></span></div>. A 2002 survey of 2,024 million web pages determined that by far the most web content was in the English language: 56.4%; next were pages in German (7.7%), French (5.6%), and Japanese (4.9%). A more recent study, which used web searches in 75 different languages to sample the Web, determined that there were over 11.5 billion web pages in the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/S/Surface_Web.html" ;"title="Surface Web">publicly indexable web</a> as of the end of January 2005. , the indexable web contains at least 25.21 billion pages. On 25 July 2008, Google software engineers Jesse Alpert and Nissan Hajaj announced that <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/G/Google_Search.html" "title="Google Search">Google Search</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Google Search (also known simply as Google) is a search engine provided by Google. Handling more than 3.5 billion searches per day, it has a 92% share of the global search engine market. It is also the most-visited website in the world.
The ...<br></span></div> had discovered one trillion unique URLs.<ref></ref> , over 109.5 million domains operated.<ref name=NI></ref> Of these, 74% were commercial or other domains operating in the <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/g/generic_top-level_domain.html" ;"title="generic top-level domain">generic top-level domain</a> ''com''.<ref name=NI /> Statistics measuring a website's popularity, such as the <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/A/Alexa_Internet.html" "title="Alexa Internet">Alexa Internet</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Alexa Internet, Inc. was an American web traffic analysis company based in San Francisco. It was a wholly-owned subsidiary of Amazon.
Alexa was founded as an independent company in 1996 and acquired by Amazon in 1999 for $250 million in stock. ...<br></span></div> rankings, are usually based either on the number of <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/p/page_view.html" ;"title="page view">page view</a>s or on associated server "<div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/h/hit_(internet).html" "title="hit (internet)">hits</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Hits or H.I.T.S. may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''H.I.T.S.'', 1991 album by New Kids on the Block
* ''...Hits'' (Phil Collins album), 1998
* ''Hits'' (compilation series), 1984–2006; 2014 - a British compilation album se ...<br></span></div>" (file requests) that it receives.-->
<h1><br><p> See also </h1></p>
* <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/E/Electronic_publishing.html" "title="Electronic publishing">Electronic publishing</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Electronic publishing (also referred to as publishing, digital publishing, or online publishing) includes the digital publication of e-books, Online magazine, digital magazines, and the development of digital library, digital libraries and catalo ...<br></span></div>
* <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_metaphors.html" "title="Internet metaphors">Internet metaphors</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Internet metaphors provide users and researchers of the Internet a structure for understanding and communicating its various functions, uses, and experiences. An advantage of employing metaphors is that they permit individuals to visualize an abst ...<br></span></div>
* <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/I/Internet_security.html" ;"title="Internet security">Internet security</a>
* <a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/L/Lists_of_websites.html" ;"title="Lists of websites">Lists of websites</a>
* <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/S/Streaming_media.html" "title="Streaming media">Streaming media</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content it ...<br></span></div>
* <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_development_tools.html" "title="Web development tools">Web development tools</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Web development tools (often called devtools or inspect element) allow web developers to test and debug their code. They are different from website builders and integrated development environments (IDEs) in that they do not assist in the direct c ...<br></span></div>
* <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/W/Web_literacy.html" "title="Web literacy">Web literacy</a><span class="linkinfotext">
Web literacy comprises the skills and competencies needed for reading, writing and participating on the web. It has been described as "both content and activity" – i.e., web users should not just learn about the web but also about how to make t ...<br></span></div>
<h1><br><p> References </h1></p>
<h1><br><p> Further reading </h1></p>
*
*
* Brügger, Niels, ed, ''Web25: Histories from the first 25 years of the World Wide Web'' (Peter Lang, 2017).
*
* Niels Brügger, ed. ''Web History'' (2010) 362 pages; Historical perspective on the World Wide Web, including issues of culture, content, and preservation.
*
* Skau, H.O. (March 1990). "The World Wide Web and Health Information". ''New Devices''.
<h1><br><p> External links </h1></p>
<br><a href="http://info.cern.ch/hypertext/WWW/TheProject.html" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="The first website">The first website</a><br><br><a href="http://www.w3.org/History/19921103-hypertext/hypertext/WWW/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="Early archive of the first Web site">Early archive of the first Web site</a><br><br><a href="https://www.mit.edu/people/mkgray/net/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="Internet Statistics: Growth and Usage of the Web and the Internet">Internet Statistics: Growth and Usage of the Web and the Internet</a><br><br><a href="ttp://www.livinginternet.com/w/w" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title=""></a><br>A comprehensive history of the Internet, including the World Wide Web
*
<br><a href="http://www.w3.org/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)">World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)</a><br><br><a href="ttp://www.w3.org/Protocols/NL-PerfNote" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title=""></a><br><br><a href="http://www.worldwidewebsize.com/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="World Wide Web Size">World Wide Web Size</a><br>Daily estimated size of the World Wide Web
<br><a href="https://web.archive.org/web/20110501162838/http://cle.ens-lyon.fr/40528325/0/fiche___pagelibre/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="Antonio A. Casilli, Some Elements for a Sociology of Online Interactions">Antonio A. Casilli, Some Elements for a Sociology of Online Interactions</a><br><br><a href="http://web-graph.org/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="The Erdős Webgraph Server">The Erdős Webgraph Server</a><br> offers weekly updated graph representation of a constantly increasing fraction of the WWW
<br><a href="http://techchange.org/work/u-s-global-development-lab-25th-anniversary-of-the-world-wide-web/" target="_blank" class="mw-redirect" title="The 25th Anniversary of the World Wide Web">The 25th Anniversary of the World Wide Web</a><br> is an animated video produced by <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/U/USAID.html" "title="USAID">USAID</a><span class="linkinfotext">
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 bi ...<br></span></div> and <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/T/TechChange.html" "title="TechChange">TechChange</a><span class="linkinfotext">
TechChange is a US social enterprise which provides courses on the use of technology in addressing social and global challenges. Their e-learning platform "has been used by more than 600 students from more than 70 countries." It is a registered ...<br></span></div> which explores the role of the WWW in addressing extreme <div class="linkinfo_desc"><a class = "desc_only" href="/html/ALL/l/p/poverty.html" "title="poverty">poverty</a><span class="linkinfotext">
<!-- This SD is < 40 characters & mirrors the SD for Wealth -->
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...<br></span></div>
{{Authority control
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/World_Wide_Web.html" ;"title="World Wide Web"> </a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Computer-related_introductions_in_1989.html" ;"title="Computer-related introductions in 1989">Computer-related introductions in 1989</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/English_inventions.html" ;"title="English inventions">English inventions</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/British_inventions.html" ;"title="British inventions">British inventions</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Human–computer_interaction.html" ;"title="Human–computer interaction">Human–computer interaction</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Information_Age.html" ;"title="Information Age">Information Age</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/CERN.html" ;"title="CERN">CERN</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Tim_Berners-Lee.html" ;"title="Tim Berners-Lee">Tim Berners-Lee</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/Web_technology.html" ;"title="Web technology">Web technology</a>
<a class="link_plain"; href="/html/ALL/l/C/20th-century_inventions.html" ;"title="20th-century inventions">20th-century inventions</a>
</div>
<div id="AdvertBottom1">
</div>
<center>
<script src="/js/AdvertBottom1.js">
</script>
</center>
<footer>
<div>
<br><br>
<br><br>
<center>
<br><a target="_top" href="../index.html"> HOME </a><br>
<br>Content is Copyleft<br>Website design, code, and AI is Copyrighted (c) 2014-2017 by Stephen Payne<br><br>
<a target="_top" href="https://donate.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=Special:LandingPage&country=US&uselang=en&utm_medium=sidebar&utm_source=donate&utm_campaign=C13_en.wikipedia.org"> Consider donating to Wikimedia </a><br>
<br>
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases
<br>
</center>
</div>
</footer>
<div id="AddedByJS">
</div>
<script src="/js/site.js">
</script>
<!--#include file="inc/summary_footer.html" -->
</body></html>
information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people ...
enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web server
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiate ...
s and can be accessed by programs such as web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...
s. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locator
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifi ...
s (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup language supports plain text, images, embedded video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) syste ...
and audio
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to:
Sound
*Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound
*Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum
*Digital audio, representation of sound ...
contents, and scripts
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of handw ...
(short programs) that implement complex user interaction. The HTML language also supports hyperlink
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text wit ...
s (embedded URLs) which provide immediate access to other web resources. Web navigation, or web surfing, is the common practice of following such hyperlinks across multiple websites. Web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...
s are web pages that function as application software
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a c ...
. The information in the Web is transferred across the Internet using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
(HTTP).
Multiple web resources with a common theme and usually a common domain name make up a website
A website (also written as a web site) is a collection of web pages and related content that is identified by a common domain name and published on at least one web server. Examples of notable websites are Google Search, Google, Facebook, Amaz ...
. A single web server may provide multiple websites, while some websites, especially the most popular ones, may be provided by multiple servers. Website content is provided by a myriad of companies, organizations, government agencies, and individual users; and comprises an enormous amount of educational, entertainment, commercial, and government information.
The World Wide Web has become the world's dominant software platform. It is the primary tool billions of people worldwide use to interact with the Internet.
The Web was originally conceived as a document management system. It was invented by Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. He is a Professorial Fellow of Computer Science at the University of Oxford and a profess ...
at CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gene ...
in 1989 and opened to the public in 1991.
History
 The Web was invented by English computer scientist
The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. He is a Professorial Fellow of Computer Science at the University of Oxford and a profess ...
at CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gene ...
, and originally conceived as a document management system. The first proposal was written in 1989, and a working system implemented by the end of 1990 including the WorldWideWeb browser and an HTTP server. The technology was released outside CERN to other research institutions starting in January 1991, and then to the general public on 23 August 1991. The Web was a success at CERN, and began to spread to other scientific and academic institutions. Within the next two years, there were 50 websites created.
CERN made the Web protocol and code available royalty free in 1993, enabling its widespread use. After the NCSA released Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
later that year, the Web became very popular with thousands of websites springing up in less than a year. Mosaic was a graphical browser that could display inline images and submit forms, and HTTPd
HTTPd is a software program that usually runs in the background, as a process, and plays the role of a server in a client–server model using the HTTP and/or HTTPS network protocol(s).
The process waits for the incoming client requests and for ...
, a server that could process forms (see CGI). Marc Andreessen
Marc Lowell Andreessen ( ; born July 9, 1971) is an American entrepreneur, investor, and software engineer. He is the co-author of Mosaic, the first widely used web browser; co-founder of Netscape; and co-founder and general partner of Silicon ...
and Jim Clark
James Clark Jr. OBE (4 March 1936 – 7 April 1968) was a British Formula One racing driver from Scotland, who won two World Championships, in 1963 and 1965. A versatile driver, he competed in sports cars, touring cars and in the Indianapol ...
founded Netscape
Netscape Communications Corporation (originally Mosaic Communications Corporation) was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was onc ...
the following year and released Navigator
A navigator is the person on board a ship or aircraft responsible for its navigation.Grierson, MikeAviation History—Demise of the Flight Navigator FrancoFlyers.org website, October 14, 2008. Retrieved August 31, 2014. The navigator's primar ...
, which introduced Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
and JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
to the Web. It quickly became the dominant browser. Netscape became a public company in 1995 which triggered a frenzy for the Web and started the dot-com bubble
The dot-com bubble (dot-com boom, tech bubble, or the Internet bubble) was a stock market bubble in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet.
Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Compo ...
. Microsoft responded by developing its own browser, Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated IE or MSIE) is a series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft which was used in the Microsoft Wind ...
. By bundling it with Windows, it became the dominant browser for 14 years.
Tim Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web Consortium
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web. Founded in 1994 and led by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations that maintain full-time staff working to ...
(W3C) which created XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. T ...
in 1996 and recommended replacing HTML with stricter XHTML
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
While HTML, prior ...
. In the meantime, developers began exploiting an IE feature called XMLHttpRequest
XMLHttpRequest (XHR) is an API in the form of an object whose methods transfer data between a web browser and a web server. The object is provided by the browser's JavaScript environment. Particularly, retrieval of data from XHR for the purpose o ...
to make Ajax applications and launched the Web 2.0 revolution. Mozilla
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, wi ...
, Opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
, and Apple rejected XHTML and created the WHATWG which developed HTML5. In 2009, the W3C conceded and abandoned XHTML and in 2019, ceded control of the HTML specification to the WHATWG.
The World Wide Web has been central to the development of the Information Age
The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during ...
and is the primary tool billions of people use to interact on the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
.
Function
 The terms ''Internet'' and ''World Wide Web'' are often used without much distinction. However, the two terms do not mean the same thing. The Internet is a global system of
The terms ''Internet'' and ''World Wide Web'' are often used without much distinction. However, the two terms do not mean the same thing. The Internet is a global system of computer network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are ...
s interconnected through telecommunications and optical networking. In contrast, the World Wide Web is a global collection of documents and other resources, linked by hyperlinks and URIs. Web resources are accessed using HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
or HTTPS, which are application-level Internet protocols that use the Internet's transport protocols.
Viewing a web page on the World Wide Web normally begins either by typing the URL
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifie ...
of the page into a web browser or by following a hyperlink to that page or resource. The web browser then initiates a series of background communication messages to fetch and display the requested page. In the 1990s, using a browser to view web pages—and to move from one web page to another through hyperlinks—came to be known as 'browsing,' 'web surfing' (after channel surfing
Channel surfing (also known as channel hopping or zapping) is the practice of quickly scanning through different television channels or radio frequencies to find something interesting to watch or listen to. Modern viewers, who may have cable or ...
), or 'navigating the Web'. Early studies of this new behavior investigated user patterns in using web browsers. One study, for example, found five user patterns: exploratory surfing, window surfing, evolved surfing, bounded navigation and targeted navigation.
The following example demonstrates the functioning of a web browser when accessing a page at the URL . The browser resolves the server name of the URL () into an Internet Protocol address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.. Updated by . An IP address serves two main functions: network interface ident ...
using the globally distributed Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned to ...
(DNS). This lookup returns an IP address such as ''203.0.113.4'' or ''2001:db8:2e::7334''. The browser then requests the resource by sending an HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
request across the Internet to the computer at that address. It requests service from a specific TCP port number that is well known for the HTTP service so that the receiving host can distinguish an HTTP request from other network protocols it may be servicing. HTTP normally uses port number 80 and for HTTPS it normally uses port number 443. The content of the HTTP request can be as simple as two lines of text:
HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...
) for a basic web page might look like this:
The World Wide Web, abbreviated as WWW and commonly known ...