
The
spark-ignition
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, ty ...
petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as ' ...
s listed below operate on the
four-stroke cycle
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directi ...
, and unless stated otherwise, use a
wet sump
Within piston engines, a wet sump is part of a lubrication system whereby the crankcase sump is used as an integral oil reservoir. An alternative system is the dry sump, whereby oil is pumped from a shallow sump into an external reservoir.Wet sum ...
lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology.
Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubric ...
system, and are
water-cooled
Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant
Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and n ...
.
ETKA
ETKA is the official electronic parts catalogue for Volkswagen Group motor vehicles. Launched in 1989, ETKA superseded the older parts books and microfilm-based catalogues. ETKA is an abbreviation from the german: Elektronischer Teilekatalog. It ...
official factory data
Since the Volkswagen Group is German, official
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
performance ratings are published using the
International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. ...
(commonly abbreviated "SI"), a modern form of the
metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the Intern ...
of figures. Motor vehicle engines will have been tested by a
Deutsches Institut für Normung
' (DIN; in English, the German Institute for Standardisation Registered Association) is the German national organization for standardization and is the German ISO member body. DIN is a German Registered Association ('' e.V.'') headquartered ...
(DIN) accredited testing facility, to either the original ''
80/1269/EEC
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lis ...
'', or the later ''1999/99/
EC'' standards. The standard initial measuring unit for establishing the rated motive
power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
output is the
kilowatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
(kW); and in their official literature, the power rating may be published in either the kW, or the
metric horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the ...
(often abbreviated "PS" for the German word ''Pferdestärke''), or both, and may also include conversions to imperial units such as the
horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are t ...
(hp) or
brake horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the ...
(bhp). (
Conversions: one PS = 735.5
watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
s (W); ˜ 0.98632 hp (SAE)). In case of conflict, the metric power figure of kilowatts (kW) will be stated as the primary figure of reference. For the turning force generated by the engine, the
Newton metre
The newton-metre (also newton metre or newton meter; symbol N⋅m or N m) is the unit of torque (also called ) in the International System of Units (SI). One newton-metre is equal to the torque resulting from a force of one newton applie ...
(Nm) will be the reference figure of
torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
. Furthermore, in accordance with European automotive traditions, engines shall be listed in the following ''ascending'' order of preference:
#Number of cylinders,
#Engine displacement (in
litre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3 ...
s),
#Engine configuration, and
#Rated
motive
Motive(s) or The Motive(s) may refer to:
* Motive (law)
Film and television
* ''Motives'' (film), a 2004 thriller
* ''The Motive'' (film), 2017
* ''Motive'' (TV series), a 2013 Canadian TV series
* ''The Motive'' (TV series), a 2020 Israeli T ...
power output (in kilowatts).
The petrol engines which Volkswagen Group previously manufactured and installed are in the ''
list of discontinued Volkswagen Group petrol engines
The spark-ignition petrol (gasoline) engines listed below were formerly used by various marques of automobiles and commercial vehicles of the German automotive concern, Volkswagen Group,ETKA official factory data and also in Volkswagen Industria ...
'' article.
EA111
The EA111 series of internal combustion engines was initially developed by Audi under Ludwig Kraus's leadership and introduced in 1974 in the
Audi 50
The Audi 50 (known internally as the ''Typ'' 86) is a supermini economy car produced by German automaker Audi from 1974 to 1978, and sold only in Europe. Introduced two or three years after the Italian Fiat 127 and the French Renault 5, the model ...
and shortly after, in the original
Volkswagen Polo
The Volkswagen Polo is a supermini car ( B-segment) produced by the German car manufacturer Volkswagen since 1975. It is sold in Europe and other markets worldwide in hatchback, saloon, and estate variants throughout its production run.
Histor ...
. It is a series of water-cooled
inline three- and
inline four-cylinder petrol and
diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-cal ...
s, in a variety of displacement sizes. This
overhead camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion cha ...
engine features a
crossflow cylinder head
A crossflow cylinder head is a cylinder head that features the intake and exhaust ports on opposite sides. The gases can be thought to flow across the head. This is in contrast to reverse-flow cylinder head designs that have the ports on the same ...
design. The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft, this belt also provides the drive for coolant pump. The oil pump is directly driven by crankshaft, petrol pump and distributor are driven by camshaft. Other "V" belt-driven accessories are the alternator and (if fitted) power steering, and air-conditioning pump. In transverse mount configuration, the exhaust side is towards the vehicle firewall, in longitudinal configuration, the exhaust side is to the right as you face front in either left or right-hand drive vehicles.
EA211
The EA211 engines are a completely new four-cylinder turbocharged and direct-injection TSI engines. Compared to its predecessor, the EA211 series is significantly more compact, with installation length shorter, thus offering more interior space. The installation position of the engines has also been optimised. Just as in the diesels, the petrol engines are now mounted with the exhaust side facing backwards and tilted at an angle of 12 degrees. The weight of these petrol engines made of die-cast aluminium is only for the 1.2 TSI and for the 1.4 TSI. The crankshaft alone became lighter by 20 per cent; the connecting rods lost 30 per cent of their weight. In addition the connecting rod bearing journals are now hollow-drilled and pistons now come with flat bottoms, all of them optimized for lower weight.
Regarding thermal management, the EA211 petrol engine is equipped with a modern dual-circuit cooling system. That means that a high temperature circuit with a mechanically driven cooling pump cools the basic engine, while a low temperature circuit flows through the intercooler and the turbo-charger casing. The cylinder-head circuit heats the cabin's interior. The exhaust manifold is integrated into the cylinder head, enabling the engine to warm up more quickly, in turn making heat available quickly for the passenger cabin. At high loads, the exhaust is cooled by the coolant, lowering fuel consumption.
EA 824, EA 825
EA 824 and EA 825 are families of twin turbo 90 degrees V8 spark ignition engines.
Audi uses the EA 824, while Porsche uses EA 825 for Panamera Turbo.
EA 825 uses two twin-scroll turbochargers, iron coating on the cylinder linings, fuel injector at centre of combustion chamber, cylinder deactivation at 950-3500rpm with a torque limit.
EA 839
EA 839 is a family of turbocharged 90 degrees V6 spark ignition engines. It includes steel cylinder liners, balancer shaft located within the vee, maximum compression ratio of 11.2:1, bore and stroke of .
EA888
The EA888 engines are a family of three and four-cylinder engines that are currently in use across the Volkswagen Group. An EA888 family is a corporate VAG designed unit that is an evolution of the earlier EA827/113 units. It features some of the latest engine technology such as direct fuel injection, sintered camshaft lobes, thin-walled engine block, variable valve timing and lift for intake and exhaust valves, downstream oxygen sensors, exhaust manifold integrated into the cylinder head,
exhaust gas recirculation
In internal combustion engines, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a nitrogen oxide () emissions reduction technique used in petrol/gasoline, diesel engines and some hydrogen engines. EGR works by recirculating a portion of an engine's exhaust ...
and cooling, distributors coil-on-plug ignition, lightweight engine internals, slide valve thermostat (some variants), and the addition of port fuel injection to aid low load fuel consumption and cold start emissions. The port fuel injection also aids in reducing the potential carbon deposits that can occur in direct-injected engines. As of 2016, the 'dual injection' system has not been offered in North American markets. Still, VAG has made numerous enhancements to their engine designs such as the positive crankcase ventilation, repositioning injectors and more to lessen the potential that carbon deposits accumulate on intake valves. Currently, the EA888 engine is available in two sizes: 1.8T and 2.0T. Engine output ranges from to over . A concept car based on the Volkswagen Golf R, dubbed R400, produced 395 hp from 2 litres of displacement. Furthermore, the R400 would be able to accelerate from 0–100 km/h in just 3.8 seconds, thanks to a
haldex
Haldex AB (originally Halda Fickurfabrik AB, then Svenska AB Bromsregulatorer, SAB), also known as Haldex Group, is a Swedish public company operating in the commercial vehicle industry. It is listed on the OMX Stockholm Stock Exchange (Mid Cap), ...
4-wheel drive system, and a 6 or 7-speed DSG gearbox.
Three-cylinder petrols
1.0 R3 12v (EA211)
The new fuel-saving engine presented at the 2012
Geneva Motor Show
The Geneva International Motor Show is an annual auto show held in March in the Swiss city of Geneva. The show is hosted at the Palexpo, a convention centre located next to the Geneva Cointrin International Airport. The Salon is organised by t ...
;identification:parts code prefix: 04E, ID code: CHYA, CHYB, CHZD, CSEB, DHSB
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline three engine (R3/I3); bore x stroke: , bore spacing: ,
stroke ratio
In a reciprocating piston engine, the stroke ratio, defined by either bore/stroke ratio or stroke/bore ratio, is a term to describe the ratio between cylinder bore diameter and piston stroke length. This can be used for either an internal comb ...
: 0.99:1 – '
square engine', cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy; four main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 12 valves total, double overhead camshaft (DOHC)
;aspiration: natural and turbocharged
;fuel system: multi-point electronic indirect fuel injection with three intake manifold-sited fuel injectors
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
: at 5,000–6,000 rpm; at 3,000–4,300 rpm (CHYA)
: at 6,200 rpm; at 3,000–4,300 rpm (CHYB)
: at 6,350 rpm; at 3,000 rpm with Ethanol (CSEB)
: at 5,000–5,500 rpm; at 1500–3,500 rpm (CHZB)
: at 5,000–5,500 rpm; at 2000–3,500 rpm (CHZD)
: at 5,500 rpm; at 2,000-3,500 rpm with Ethanol (DHSB)
;application:
Volkswagen up!
The Volkswagen Up (stylized as Volkswagen up!) is a city car, part of the Volkswagen Group New Small Family (NSF) series of models, unveiled at the 2011 International Motor Show Germany (IAA). Production of the Up started in December 2011 at th ...
,
Skoda Citigo
The Volkswagen Up (stylized as Volkswagen up!) is a city car, part of the Volkswagen Group New Small Family (NSF) series of models, unveiled at the 2011 International Motor Show Germany (IAA). Production of the Up started in December 2011 at t ...
, Skoda Fabia III,
Seat Mii
The Volkswagen Up (stylized as Volkswagen up!) is a city car, part of the Volkswagen Group New Small Family (NSF) series of models, unveiled at the 2011 International Motor Show Germany (IAA). Production of the Up started in December 2011 at t ...
, Seat Ibiza, Seat Arona,
Volkswagen Golf VII
The Volkswagen Golf (Mk7) is a small family car (C-segment) produced by German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, as the seventh generation of the Golf and the successor to the Golf Mk6. It was introduced in Berlin on 4 September 2012, before ...
,
Volkswagen Polo
The Volkswagen Polo is a supermini car ( B-segment) produced by the German car manufacturer Volkswagen since 1975. It is sold in Europe and other markets worldwide in hatchback, saloon, and estate variants throughout its production run.
Histor ...
,
Volkswagen T-Roc
The Volkswagen T-Roc is a subcompact crossover SUV (B-segment) manufactured by German automaker Volkswagen since 2017. It is based on the Volkswagen Group MQB A1 platform, and positioned between the Tiguan and the slightly smaller T-Cross.
Ov ...
,
Volkswagen T-Cross
The Volkswagen T-Cross is a subcompact crossover SUV (B-segment) manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen. It is based on the MQB A0 platform shared with the Polo Mk6, and was officially launched in April 2019. Positioned below the T-Roc ...
,
Audi A1 (GB),
SEAT León (4th Gen)
1.2 R3 (EA111)
This all-aluminium alloy engine is manufactured at the
Škoda Auto
Škoda Auto a.s. (), often shortened to Škoda, is a Czech automobile manufacturer established in 1925 as the successor to Laurin & Klement and headquartered in Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic. Škoda Works became state owned in 1948. After ...
plant in
Mladá Boleslav
Mladá Boleslav (; german: Jungbunzlau) is a city in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 42,000 inhabitants.
Mladá Boleslav is the second most populated city in the region and a major centre of the Czech automotive ind ...
.
;parts code prefix: 03E
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline three engine (R3/I3); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.88:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 399.4 cc per cylinder
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy; four main bearings, die-forged steel
crossplane
The crossplane or cross-plane is a crankshaft design for piston engines with a 90° angle (phase in crank rotation) between the crank throws. The crossplane crankshaft is the most popular configuration used in V8 road cars.
Aside from the V8 alr ...
crankshaft with 120 degree crankpins, gear-driven contra-rotating
balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
T ...
, simplex chain-driven oil pump
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, simplex roller chain-driven overhead camshaft
:6v: two valves per cylinder, 6 valves total, single overhead camshaft (SOHC), compression ratio: 10.3:1
:12v: four valves per cylinder, 12 valves total, double overhead camshaft (DOHC), compression ratio: 10.5:1
;aspiration: plastic intake manifold
;fuel system, ignition system & management:
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection (MPI) with three intake manifold-sited fuel injectors; three individual spark coils;
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
SIMOS 91 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), EU4 compliant
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes – 6v
: at 4,750 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — AWY, BMD
: at 5,000 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — BBM
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes – 12v
: at 5,200 rpm; at 2,000 rpm — CGPB
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — AZQ, BME
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — BZG, CEV, CGPA
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,750 rpm — CGPC
;applications:
Volkswagen Fox
The Volkswagen Fox is a subcompact car produced and designed by Volkswagen of Brazil and sold in Latin America from 2003 until 2021 and in Europe from 2005 until 2011, where it was sold as the city car offering. The Fox was produced as a 3-do ...
(BMD: 04/05->),
Volkswagen Polo Mk4
The Volkswagen Polo Mk4 is the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Polo supermini car produced by the German manufacturer Volkswagen. It was marketed from early 2002 to 2009 in most countries except Argentina and the USA. It was manufactured in So ...
(9N, PQ24 – AZQ: 11/01-05/04, AWY: 01/02-05/04, BMD: 05/04-05/07, BME: 11/04-07/07, BBM/BZG: 05/07->),
Škoda Fabia
The Škoda Fabia is a supermini car produced by Czech manufacturer Škoda Auto since 1999. It is the successor of the Škoda Felicia, which was discontinued in 2001. The Fabia was available in hatchback, estate (named Fabia Combi) and saloon ...
(AWY: 07/01-05/04, BMD: 05/04-12/07, BME: 12/04-12/07, BBM: 12/06-05/09, BZG: 01/07-05/09, CEV: 01/08->),
Škoda Roomster
The Škoda Roomster (''Type'' 5J) is a five-door, five passenger, front-engine, front-wheel drive high-roof vehicle manufactured and marketed by Škoda Auto from 2006–2015 over a single generation with a single intermediate facelift — and ...
(BME: 05/06-01/07, BZG: 01/07-03/09, CGPA: 03/09->),
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
(BBM: 06/07-05/08, AZQ: 01/02->, BME: 11/04->, BZG: 03/08->),
SEAT Cordoba
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair, a chair equ ...
(AZQ: 10/02->, BME: 11/04->),
Volkswagen Jetta Konig
Four-cylinder EA827/EA113/EA111/EA211 petrols
The EA827 family of internal combustion engines was initially developed by Audi under Ludwig Kraus leadership and introduced in 1972 in the
Audi 80
The Audi 80 is a compact executive car produced by the Audi subdivision of the Volkswagen Group across four generations from 1966 to 1996. It shared its platform with the Volkswagen Passat from 1973 to 1986 and was available as a saloon, and s ...
, and was eventually superseded by the EA113 evolution introduced in 1993. Both share the same cylinder spacing. The latter EA113 was updated with
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) direct injection, to be topped by the 2.0 TFSI used in the
Audi TTS. Forty million engines have been produced. This range will eventually be superseded by the evolved version with heavy changes
EA888
The spark-ignition petrol engines listed below operate on the four-stroke cycle, and unless stated otherwise, use a wet sump lubrication system, and are water-cooled.ETKA official factory data
Since the Volkswagen Group is German, official ...
project, introduced with the
1.8 TSI/TFSI below, but the EA113 still remains in production.
1.2 TSI/TFSI (EA111)
This engine is manufactured at the
Škoda Auto
Škoda Auto a.s. (), often shortened to Škoda, is a Czech automobile manufacturer established in 1925 as the successor to Laurin & Klement and headquartered in Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic. Škoda Works became state owned in 1948. After ...
plant in
Mladá Boleslav
Mladá Boleslav (; german: Jungbunzlau) is a city in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 42,000 inhabitants.
Mladá Boleslav is the second most populated city in the region and a major centre of the Czech automotive ind ...
;identification: parts code prefix: 03F, ID codes: CBZA, CBZB, CBZC
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.94:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 299.3 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1, peak pressures
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy, five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation
:two valves per cylinder, 8 valves total, roller chain-driven single overhead camshaft (SOHC)
;aspiration: hot-film
air mass meter, cast alloy
throttle body
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
with
electronically controlled Bosch "E-Gas"
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valve;
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
with maximum pressure , water-cooled
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
integrated into intake manifold
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; – fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): camshaft-driven single-piston high-pressure injection pump supplying up to fuel pressure in
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel rail, four combustion chamber sited
direct injection sequential fuel injectors, mounted on the intake side between the intake port and cylinder head gasket level, homogeneous mixing, stratified lean-burn operation with excess air at part load; 95
RON ultra-low sulphur unleaded petrol (ULSP)
;ignition system & engine management: centrally positioned longlife spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with four individual direct-acting
single spark coils; electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU),
knock control via a single knock sensor, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control, EU5 compliant
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
: at 4,800 rpm; at 1,500–3,500 rpm — CBZA;
Volkswagen Golf Mk6
The Volkswagen Golf Mk6 (code named ''Typ 5K'') is a compact car, the sixth generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk5. It was unveiled at the Paris Motor Show in October 2008 for the 2009 model year. Volkswag ...
(05/10->),
Audi A1
The Audi A1 (internally designated ''Typ 8X'') is a supermini car launched by Audi at the 2010 Geneva Motor Show. Sales of the initial three-door A1 model started in Germany in August 2010, with the United Kingdom following in November 2010. A f ...
: at 4,500 rpm; at 1,500–3,500 rpm — CBZC;
Volkswagen Polo
The Volkswagen Polo is a supermini car ( B-segment) produced by the German car manufacturer Volkswagen since 1975. It is sold in Europe and other markets worldwide in hatchback, saloon, and estate variants throughout its production run.
Histor ...
(05/11->)
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,550–4,100 rpm — CBZB;
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
;applications:
Volkswagen Beetle (A5),
Volkswagen Polo Mk5
The Volkswagen Polo Mk5 is the fifth generation of the Polo, a supermini-class car manufactured by Volkswagen since 2009. The vehicle unveiled at the 2009 Geneva Motor Show in March 2009, while the three-door version was unveiled at the 2009 Fr ...
,
Volkswagen Golf Mk6
The Volkswagen Golf Mk6 (code named ''Typ 5K'') is a compact car, the sixth generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk5. It was unveiled at the Paris Motor Show in October 2008 for the 2009 model year. Volkswag ...
,
Volkswagen Caddy
The Volkswagen Caddy is a panel van and leisure activity vehicle (M-segment) produced by the German automaker Volkswagen Group since 1980. It is sold in Europe and in other markets around the world. The Volkswagen Caddy was first introduced in Nor ...
(05/09->),
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
,
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
(1P),
SEAT Altea
The SEAT Altea is an automobile produced by the Spanish automaker SEAT from 2004 to 2015 being previewed by the Salsa Emoción concept. As a compact multi-purpose vehicle (MPV), the car was designed by the Italian Walter de Silva, and was launc ...
,
SEAT Altea XL
The SEAT Altea is an automobile produced by the Spanish automaker SEAT from 2004 to 2015 being previewed by the Salsa Emoción concept. As a compact multi-purpose vehicle (MPV), the car was designed by the Italian Walter de Silva, and was launc ...
,
SEAT Toledo (2012) (KG)
Škoda Octavia
The Škoda Octavia is a small family car produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since the end of 1996. It shares its name with an earlier model produced between 1959 and 1971. Four generations of the modern-era Octavia model hav ...
(02/10->),
Škoda Yeti
The Škoda Yeti (codenamed ''Typ'' 5L)ETKA, accessed 27 January 2010 is a compact crossover SUV produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto and introduced at the 2009 Geneva Motor Show, as the carmaker's first entry into the SUV market. In ...
,
Škoda Fabia
The Škoda Fabia is a supermini car produced by Czech manufacturer Škoda Auto since 1999. It is the successor of the Škoda Felicia, which was discontinued in 2001. The Fabia was available in hatchback, estate (named Fabia Combi) and saloon ...
(02/10->),
Audi A1
The Audi A1 (internally designated ''Typ 8X'') is a supermini car launched by Audi at the 2010 Geneva Motor Show. Sales of the initial three-door A1 model started in Germany in August 2010, with the United Kingdom following in November 2010. A f ...
,
Škoda Rapid (2012)
The Škoda Rapid (NH) is range of small family car models produced by the Czech manufacturer Škoda Auto. It consists of three body styles: a 5-door liftback, a 5-door hatchback marketed as "Spaceback" and a 4-door sedan sold in China. The model ...
(NH)
;references:
auto-motor-sport.de and the Volkswagen press releases to the new Polo 2009
1.2 TSI (EA211)
Main article - Volkswagen_EA211_engine
These newly developed generation of modern petrol engines are manufactured at the
Škoda Auto
Škoda Auto a.s. (), often shortened to Škoda, is a Czech automobile manufacturer established in 1925 as the successor to Laurin & Klement and headquartered in Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic. Škoda Works became state owned in 1948. After ...
plant in
Mladá Boleslav
Mladá Boleslav (; german: Jungbunzlau) is a city in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 42,000 inhabitants.
Mladá Boleslav is the second most populated city in the region and a major centre of the Czech automotive ind ...
.
;identification: EA211 engine family. Turbocharged and direct-injection TSI engines with a four-cylinder, four-valve layout and belt driven camshafts.
;1.2 TSI 66 kW:The entry-level petrol engine. Turbocharging produces a maximum torque of 160 Nm (at 1,400 to 3,500 rpm).
;1.2 TSI 77 kW:The improved performance version of the 1.2 TSI Green tec, which includes a start/stop system and brake energy recuperation, manages an output of 77 kW (105 hp). This TSI engine provides a maximum torque of 175 Nm at between 1,400 and 4,000 rpm.
1.4 R4 16v TSI/TFSI
Based on the EA111, this new engine was announced at the 2005
Frankfurt Motor Show
The International Motor Show Germany or International Mobility Show Germany, in German known as the ''Internationale Automobil-Ausstellung'' (''IAA'' – International Automobile Exhibition), is one of the world's largest mobility shows. It cons ...
, to be first used in the
Mk5 Golf GT, the 125 kW 1.4-litre TSI engine is a "
Twincharger
A twincharger refers to a compound forced induction system used on some internal combustion engines. It is a combination of an exhaust-driven turbocharger and a mechanically driven supercharger, each mitigating the weaknesses of the other.
Twinch ...
", and uses both a
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
and a
supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induct ...
. Its
displacement downsizing leads to improved fuel economy, with 14% more power than the 2.0 FSI, but consuming 5% less fuel. The mechanical supercharger compressor, driven at 5 times the speed of the crankshaft, mainly operates at low engine speeds from idle up to 2,400 revolutions per minute (rpm) to increase low-end torque. At engine speeds just above idle, the belt-driven supercharger provides a boost pressure of . The turbocharger assumes full effectiveness at middle revs, and the engine map disengages the clutch-controlled supercharger at a maximum upper limit of 3,500 rpm; the supercharger will then be bypassed once the turbocharger spools up and reaches sufficient speed to provide adequate boost in the upper rev-ranges. This engine is made at Volkswagen-Motorenfertigung,
Chemnitz
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the German state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany a ...
.
In 2007, Volkswagen announced the 90 kW model which will replace the 1.6 FSI engine. This engine differs from the 103 kW and 125 kW models in several ways. It uses only one method of forced induction – a turbocharger (and not a supercharger), and has water-cooled intercooler. The engine has reduced frictional losses, optimised camshafts, new intake ports, and new high-pressure injector valves. It is also lighter than the 125 kW model, in order to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions.
;identification: parts code prefix: 03C, ID codes: BLG, BMY, CAXC
;engine displacement & engine configuration: inline-four engine (R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 1.01:1 – 'square engine', 347.5 cc per cylinder, peak pressures, compression ratio: 10.0:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; cylinder spacing, five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft, roller chain-driven oil pump
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 16 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, roller chain driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC), continuous adjusting
variable intake valve timing
;aspiration: hot-film air mass meter, cast alloy throttle body with
electronically controlled Bosch "E-Gas"
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valve
:90 to 96 kW variants — two-part plastic intake manifold,
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
incorporated in exhaust manifold with maximum boost pressure , water-cooled
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
integrated into intake manifold
:103 to 125 kW variants — multi-ribbed belt-driven fifth-generation
Eaton Roots
A root is the part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors the plant body, and absorbs and stores water and nutrients.
Root or roots may also refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''The Root'' (magazine), an online magazine focusing ...
-type positive displacement
supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induct ...
operated by a magnetic clutch integrated in a module inside the water pump, internal step-down ratio on the input end of the synchronisation gear pair, and KKK turbocharger with integrated wastegate connected in series, administrated by a control flap, pressure at 1,500 rpm, front-mounted intercooler (FMIC)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; – fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): camshaft-driven single-piston high-pressure injection pump supplying up to fuel pressure in
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel rail integrated into the inlet manifold, four combustion chamber sited
direct injection sequential solenoid-controlled six-hole fuel injectors, mounted on the intake side between the intake port and cylinder head , homogeneous mixing, stratified lean-burn operation with excess air at part load,
:90 to 103 kW variants — 95
RON ultra-low sulphur unleaded petrol (ULSP)
:110 to 125 kW variants — 98 RON 'Super Unleaded' ultra-low sulphur unleaded petrol (ULSP) – 95 RON may be used, but will result in lower power output
;ignition system & engine management: centrally positioned
NGK longlife spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with four individual direct-acting
single spark coils;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
ME electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU),
knock control via a single knock sensor, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control
;exhaust system: cast iron exhaust manifold (with integrated turbocharger), one
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
, two heated
oxygen sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or sond, is an electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed.
It was ...
s monitoring pre- and post catalyst exhaust gases
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
:; at 1,500–4,000 rpm — Passat (2009 on)
:; at 1,500–3,500 rpm — CAXA; Golf Mk5 (2007 on), Tiguan (08/10->), Škoda Octavia Mk2, Scirocco Mk3, Audi A1, Audi A3 Mk3
:; at 1,500–4,000 rpm — CAXC; Audi A3, SEAT Leon
:; at 1,750–3,500 rpm — CFBA; Golf Mk6, VW Jetta V, Passat B6, Škoda Octavia Mk2, LAVIDA(SAIC-VW), Bora
:; — BMY; Touran from early 2006, Golf Mk5, Jetta
: at 5,800 rpm; at 1,250–4,500 rpm — CAVF/CTHF; SEAT Ibiza FR
: at 5,800 rpm; at 1,750–4,000 rpm — BWK/CAVA; VW Tiguan; VW Sharan Mk2
: at 5,800 rpm; at 1,750–4,000 rpm — CDGA; Touran, Passat B7 EcoFuel
: at 5,800 rpm; at 1,750–4,500 rpm — CAVD/CTHD; Golf Mk5, Golf Mk6, Scirocco Mk3, VW Jetta TSI Sport
: at 6,000 rpm; (MEP 21.7 bar) at 1,750–4,500 rpm ( at 1,250–6,000 rpm), rev limit: 7,000 rpm — BLG; Golf Mk5 GT, Jetta, Golf Plus, Touran
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,000 – 4,500 rpm — CAVE/CTHE; SEAT Ibiza Cupra, Polo GTI, Fabia RS
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,000 – 4,500 rpm — CAVG/CTHG; Audi A1
;applications: 2005
VW Golf Mk5, 2006
VW Touran, 2008
Audi A3
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
, 2008
VW Scirocco
The Volkswagen Scirocco is a three-door, Front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout, front-engine, front-wheel-drive, sport compact hatchback manufactured and marketed by Volkswagen in two generations from 1974 to 1992 and a third generation from 2008 ...
, possibly in the 2008
VW Concept R, 2007
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
, 2008
Škoda Octavia
The Škoda Octavia is a small family car produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since the end of 1996. It shares its name with an earlier model produced between 1959 and 1971. Four generations of the modern-era Octavia model hav ...
, 2009
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
, 2009
VW Golf Mk6
;references:
Awards
:Was winner of the "Best New Engine" category in the 2006 annual competition for
International Engine of the Year.
:Was winner of the "1.0-litre 1.4-litre" category for six consecutive years in the 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010 and 2011 annual competition for
International Engine of the Year.
:Was winner of the "Green Engine of the Year" category in the 2009 annual competition for
International Engine of the Year.
:Was outright overall winner of the 2009 and 2010
International Engine of the Year annual competition.
1.4 TSI (EA211)
For 2012, these newly developed generation of modern petrol engines are manufactured at the
Škoda Auto
Škoda Auto a.s. (), often shortened to Škoda, is a Czech automobile manufacturer established in 1925 as the successor to Laurin & Klement and headquartered in Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic. Škoda Works became state owned in 1948. After ...
plant in
Mladá Boleslav
Mladá Boleslav (; german: Jungbunzlau) is a city in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 42,000 inhabitants.
Mladá Boleslav is the second most populated city in the region and a major centre of the Czech automotive ind ...
.
;identification:parts code prefix: 04E
;description:1.4 TFSI Green tec engine with 110 kW (140 hp). This engine achieves its maximum torque of 250 Nm at 1,500 to 3,500 rpm.
In North American market it is referred to as CZTA type engine (150 hp).
In Chilean market it is referred to as CHPA type engine (140 hp) or CZDA type engine (150 hp).
New lightweight aluminum construction, an integrated (into the head) exhaust manifold, and a toothed-belt drive for its double overhead
camshaft valvetrain that incorporates variable intake and exhaust timing. The only aspect to be carried over from the EA111 engine that
preceded it is the 82 mm cylinder spacing. The cylinder bore was decreased by 2 mm (to 74.5mm) while the stroke was increased to 80mm, a
change which helps compactness, increases torque, and is ideal for adding boost.
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,500-4,000 rpm — CMBA, CPVA
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,500-4,000 rpm — CZCA, CPVB
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,500-4,000 rpm — CHPA, CPTA (CPTA engine is a CHPA engine with automatic #2 and #3 cylinders deactivation system known as ACT - Active Cylinder Technology)
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,500-4,000 rpm — CZDA, CZEA, CZTA
1.5 TSI (EA211 Evo)
;identification:parts code prefix: 05E
;description:1.5 TFSI Green tece engine
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,400-3,500 rpm — DACA
: at 5,000 rpm; at 1,500-3,500 rpm — DADA, DPCA
1.6 R4 16v
;identification: parts code prefix: 036
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.88:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 399.4 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1 (China), 11.5:1 (ATN, AUS, AZD, BCB), 12.1:1 (AUS)
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 16 valves total, double overhead camshaft (DOHC)
;fuel system & engine management
: electronic multipoint injection;
Bosch MD 7; Magneti Marelli 4MV (ATN, AUS), 4LV (AZD, BCB), 7GV
: electronic injection
Total Flex
Total may refer to:
Mathematics
* Total, the summation of a set of numbers
* Total order, a partial order without incomparable pairs
* Total relation, which may also mean
** connected relation (a binary relation in which any two elements are comp ...
gasoline or ethanol (Brazil)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 5,700 rpm; at 4,500 rpm — AUS, AZD, ATN, BCB (discontinued)
: at 5,600 rpm; at 3,800 rpm — BTS, CFNA, CLSA
: at 5,200 rpm; at 3,750 rpm — CFNB
: at 5,800 rpm; at 4,200 rpm — (China)
;applications:
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
Mk3, Mk4 & Mk5,
SEAT Córdoba
The SEAT Córdoba is the saloon, estate and coupé version of the SEAT Ibiza supermini car, built by the Spanish automaker SEAT. It was manufactured between 1993 and 2010, and was related with the second and third generations of the Ibiza.
F ...
Mk2,
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
Mk1,
SEAT Toledo
The SEAT Toledo is a small family car produced by the Spanish manufacturer SEAT, part of Volkswagen Group. The Toledo name was first introduced to the SEAT line up in May 1991 being named after a Spanish city with the same name, with the fourt ...
Mk2, Mk4,
Škoda Fabia
The Škoda Fabia is a supermini car produced by Czech manufacturer Škoda Auto since 1999. It is the successor of the Škoda Felicia, which was discontinued in 2001. The Fabia was available in hatchback, estate (named Fabia Combi) and saloon ...
Mk2,
Škoda Rapid,
Škoda Roomster
The Škoda Roomster (''Type'' 5J) is a five-door, five passenger, front-engine, front-wheel drive high-roof vehicle manufactured and marketed by Škoda Auto from 2006–2015 over a single generation with a single intermediate facelift — and ...
(BTS: 05/06->),
Škoda Octavia
The Škoda Octavia is a small family car produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since the end of 1996. It shares its name with an earlier model produced between 1959 and 1971. Four generations of the modern-era Octavia model hav ...
,
Volkswagen Polo Mk4
The Volkswagen Polo Mk4 is the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Polo supermini car produced by the German manufacturer Volkswagen. It was marketed from early 2002 to 2009 in most countries except Argentina and the USA. It was manufactured in So ...
,
Volkswagen Golf Mk4
The Volkswagen Golf Mk4 (or VW ''Type 1J'') is a compact car, the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk3. Launched in October 1997 for the 1998 model year, it was the best selling car in Europe in ...
,
Volkswagen Bora
The Volkswagen Bora is a small family car, the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Jetta, and the successor to the Volkswagen Vento. Production of the car began in July 1999. Carrying on the wind nomenclature from previous generations, the car wa ...
,
VW Jetta Mk4 (China),
Volkswagen Polo sedan
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
1.8 R4
;identification:parts code prefix: ???, ID code: ADF
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.94:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 445.2 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 9.0:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; two valves per cylinder, 8 valves total, hydraulic bucket tappets, timing belt-driven single overhead camshaft (SOHC)
;fuel system:
Pierburg 1B3 downdraft carburettor
;dimensions: length: , width , height , dry mass:
;
EWG-rated motive power & torque output
: at 4,000 rpm; at 2,100 rpm
;application:
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
(04/94->)
;reference:
1.8 R4
;identification:parts code prefix: ???, ID codes: HT, RD, RV, PB, GZ, GX, PF, FP, ABS, ADZ, ACC
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.94:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 445.2 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 8.5–10.8:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; two valves per cylinder, 8 valves total, single overhead camshaft (SOHC)
;fuel system & engine management
: Bosch CIS continuous single-point fuel injection system, with or without knock control and electronic timing advance
: multi-point electronic indirect fuel injection with four intake manifold-sited fuel injectors;
Magneti Marelli
Magneti Marelli S.p.A. () is an Italian developer and manufacturer of components for the automotive industry. The firm is headquartered in Corbetta, Italy, and includes 86 manufacturing plants, 12 R&D centres, and 26 application centers in 19 c ...
,
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
or
Digifant
: electronic injection Total Flex, Gasoline or Ethanol (BR)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes, applications
: at 5,000 rpm; at 2,500 rpm — AAM, ANN (discontinued)
: at 5,200 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — RP (discontinued)
: at 5,500 rpm; at 2,500 rpm — ABS, ADZ, ANP:
VW Gol,
VW Golf Mk3,
VW Pointer
{{Infobox automobile
, name = Volkswagen Pointer
, image = Pwiki1.jpg
, manufacturer = Autolatina (1994–1995)Volkswagen (1996)
, production = 1994 (1993 for Logus)–1996
, predecessor =
, successor = Volkswagen Gol
, class = Small fami ...
,
SEAT Ibiza Mk2
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — 1P (discontinued)
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — VW Gol,
Volkswagen Santana
The Volkswagen Santana is a nameplate used by Volkswagen for various Sedan (automobile), sedans and station wagons since 1983. The first generation is based on the second-generation Volkswagen Passat (B2). It was introduced in 1981 while producti ...
,
VW Golf Mk1,
VW Golf Mk2,
VW Saveiro
;applications:
Audi 80
The Audi 80 is a compact executive car produced by the Audi subdivision of the Volkswagen Group across four generations from 1966 to 1996. It shared its platform with the Volkswagen Passat from 1973 to 1986 and was available as a saloon, and s ...
,
Audi 100
The Audi 100 and Audi 200 (and sometimes called Audi 5000 in North America) are primarily mid-size/executive cars manufactured and marketed by the Audi division of the Volkswagen Group. The car was made from 1968 to 1997 across four generations (C ...
,
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
Mk2,
SEAT Córdoba
The SEAT Córdoba is the saloon, estate and coupé version of the SEAT Ibiza supermini car, built by the Spanish automaker SEAT. It was manufactured between 1993 and 2010, and was related with the second and third generations of the Ibiza.
F ...
Mk1,
SEAT Toledo
The SEAT Toledo is a small family car produced by the Spanish manufacturer SEAT, part of Volkswagen Group. The Toledo name was first introduced to the SEAT line up in May 1991 being named after a Spanish city with the same name, with the fourt ...
Mk1,
Volkswagen Golf Mk2
The Volkswagen Golf Mk2 is a hatchback, the second generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk1. It was Volkswagen's highest volume seller from 1983 and ended in (German) production in late 1992, to be replaced ...
,
Volkswagen Golf Mk3
The Volkswagen Golf Mk3 is a medium-sized compact family car. The third generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk2, which was produced by Volkswagen from August 1991 (for the 1992 model year) to 2002 (for Cab ...
,
Volkswagen Golf Mk3 Cabriolet,
Volkswagen Golf Mk3 Variant,
Volkswagen Vento Volkswagen Vento can refer to:
* Volkswagen Vento (A3) (1992–1999), the third generation Jetta was badged as the Volkswagen Vento outside of North America.
* Volkswagen Jetta (A5) (2005–2011), the fifth generation Jetta was rebadged as the Volk ...
,
Volkswagen Jetta Mk2,
Volkswagen Jetta Mk3,
Volkswagen Passat B2,
Volkswagen Passat B3
The third-generation Volkswagen Passat, known as Volkswagen Passat B3 or Volkswagen Passat 35i, was introduced in March 1988 in Europe, 1989 in North America, and 1995 in South America; it was also briefly available in Australia in 1991, when a t ...
,
Volkswagen Passat B4
1.8 R4 16v
;identification: parts code prefix: PL, 9A, KR (1.8 & 2.0 versions)
;engine displacement & engine configuration: inline-four engine (R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.94:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 445.2 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.0:1, longitudinally mounted
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 16 valves total, double overhead camshaft (DOHC)
;fuel system & engine management: multi-point electronic sequential indirect fuel injection with four intake manifold-sited fuel injectors;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque output: at ?,??? rpm; at ?,??? rpm:
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
GTI
1.8 R4 20vT (EA113/EA827)
Wholly created and developed by
AUDI AG
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The o ...
, this version is a 1.8-
litre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3 ...
20-valve turbocharged
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
engine built in
Wolfsburg
Wolfsburg (; Eastphalian: ''Wulfsborg'') is the fifth largest city in the German state of Lower Saxony, located on the river Aller. It lies about east of Hanover and west of Berlin.
Wolfsburg is famous as the location of Volkswagen AG's hea ...
, Germany;
Győr
Győr ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names of European cities in different languages: E-H#G, names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Győr-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia, Western Transdanubia ...
, Hungary; and
Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
, Mexico. Output varies based on internal component selection, turbocharger, and
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU) software. This ubiquitous power plant has been extensively used in all four mainstream
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
marques, along with
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
applications.
This engine is also used in a very high state of tune in the one-make
Formula Palmer Audi
Formula Palmer Audi, officially abbreviated to FPA, and sometimes informally abbreviated to Palmer Audi, was a one-make class of open wheel Formula racing founded in 1998 by former Formula One driver, Jonathan Palmer. It was based in the United ...
(FPA)
open-wheeled auto racing
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competition.
Auto racing has existed since the invention of the automobile. Races of various sorts were organise ...
series. It develops , with an extra available from a driver operated 'push-to-pass' turbo boost button. Based entirely on road-car production engines and prepared and built by
Mountune Racing
Mountune Racing is a specialist automotive engineering company. It was formed in 1980 in Maldon, Essex by David Mountain to provide Mini race engines.
In the late 1980s, Mountune started preparing Cosworth YB engines for numerous motorsport cham ...
, it only differs by utilising a
Pi Research
The number (; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number appears in many formulas across mathematics and physics. It is an irrat ...
Pectel electronic fuel injection and a water-cooled
Garrett T34 turbocharger with closed-loop boost control.
Furthermore, an even higher 'step up' version of this engine is used in the later
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an-based
FIA Formula Two Championship
The FIA Formula 2 Championship is a second-tier single-seater championship organised by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). Held on road racing, racing circuits, the championship was introduced in 2017, following the rebrandi ...
. Developed as a pure race engine and again built by Mountune Racing, this variant includes many all-new lightweight components, and has been converted to a
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conve ...
lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology.
Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubric ...
system. For its initial
2009 season, it produced a continuous maximum power of at 8,250 revolutions per minute (rpm), and includes a limited duration 'overboost' to , aided by an all-new Garrett GT35 turbocharger and a Pi Research Pectel MQ12 ECU. From the
2010 season, base power is increased to , and with overboost to .
;identification: parts code prefix: 058, 06A, 06B
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.94:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 445.2 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 9.0–9.5:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft, fracture-split forged steel connecting rods,
Mahle forged aluminium alloy pistons
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy;
five valves per cylinder, 20 valves total, hydraulic bucket tappets, timing belt-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC) with
variable inlet valve timing
;aspiration: cast aluminium alloy intake manifold, turbocharger, intercooler
;fuel system, ignition system & engine management: multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection with four intake manifold-sited fuel injectors; mapped direct ignition with four individual direct-acting
single spark coils;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
ME 7.5 (MBE 975F on Industrial variants) electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), red line: 6,500 rpm, rev limit 6,800 rpm
Mass
149 kg ('BAM' engine, dry)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes, applications
: at 5,800 rpm; at 1,750–4,600 rpm — AEB, AGU, AJH, APH, ARX, ARZ, ATW, AUM, AWC, AWD, AWL, AWT, AWV, AWW, BJX, BKF, BKV
::
VW Polo GTI
The Volkswagen Polo is a supermini car (B-segment) produced by the German car manufacturer Volkswagen since 1975. It is sold in Europe and other markets worldwide in hatchback, saloon, and estate variants throughout its production run.
History
...
,
VW Golf Mk4 GTI,
VW Bora,
VW New Beetle,
VW Passat B5 and
VW Sagitar.
VW Sharan . Also on the
Audi TT Mk1 (8N),
Audi A3
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
(first gen.),
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
,
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
,
Škoda Octavia
The Škoda Octavia is a small family car produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since the end of 1996. It shares its name with an earlier model produced between 1959 and 1971. Four generations of the modern-era Octavia model hav ...
,
Škoda Superb
The Škoda Superb is a large family car that has been produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since 2001.
The first generation of the modern Superb, produced from 2001 to 2008, was based on the VW B5 PL45+ platform. The second gener ...
(first gen.) and
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
.
: at 5,700 rpm; at 1,800 rpm — EU5 rated: CFMA
::
SEAT Exeo
The SEAT Exeo () is a large family car and flagship model, that was built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT, subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
Previously codenamed ''Bolero'', (though not to be confused with SEAT's earlier concept car bea ...
(CFMA: 12/08-on)
: — AQX, AYP
::
SEAT Ibiza Mk3 Cupra, Cupra R,
SEAT Cordoba Cupra
: at 5,700 rpm; at 1,950–4,700 rpm — BFB, BKB, BVP
::replaced the 110 kW version in 2003 on most models;
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
,
Audi TT
: at 5,900 rpm; at 1,950–5,000 rpm —
AMB, AWM
::
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
,
VW Passat. This version only exists in
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n and emerging markets.
: at 5,500 rpm; at 1,950–5,000 rpm — AJQ, APP, ARY, ATC, AUQ, AWP, BEK, BNU (North America only), AJL, BBU (UK)
::
Volkswagen Golf Mk4
The Volkswagen Golf Mk4 (or VW ''Type 1J'') is a compact car, the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk3. Launched in October 1997 for the 1998 model year, it was the best selling car in Europe in ...
GTI,
VW Bora/Jetta,
New Beetle
The Volkswagen New Beetle is a compact car, introduced by Volkswagen in 1997, drawing heavy inspiration from the exterior design of the original Beetle. Unlike the original Beetle, the New Beetle has its engine in the front, driving the fron ...
,
Audi A3
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
,
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
Quattro Sport,
Audi TT Mk1 (8N),
Škoda Octavia vRS
Škoda means ''pity'' in the Czech and Slovak languages. It may also refer to:
Czech brands and enterprises
* Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav
** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Škoda Auto respons ...
,
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
,
SEAT Toledo
The SEAT Toledo is a small family car produced by the Spanish manufacturer SEAT, part of Volkswagen Group. The Toledo name was first introduced to the SEAT line up in May 1991 being named after a Spanish city with the same name, with the fourt ...
,
VW Polo GTI
The Volkswagen Polo is a supermini car (B-segment) produced by the German car manufacturer Volkswagen since 1975. It is sold in Europe and other markets worldwide in hatchback, saloon, and estate variants throughout its production run.
History
...
.
: at 5,700 rpm; at 1,950–4,700 rpm — BEX, BVR
::
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
(BEX: 11/02-12/04),
Audi TT Mk1 (8N) (BVR: 09/05-06/06)
:; — APY, AUL, AMK
::
Audi S3 (8L) (APY: 11/98-08/00, AUL: 09/99-04/01, AMK: 09/00-04/02),
SEAT León Mk1 (1M) Cupra R (05/02-05/03)
: at 5,900 rpm; at 2,200–5,500 rpm — AMU, BEA (North America only), APX, BAM
::
Audi TT Mk1 (8N),
Audi S3 (8L),
SEAT León Mk1 (1M) Cupra R (05/03-06/06). This version is built in Győr.
: at 5,700 rpm; at 2,300–5,000 rpm —
::2005
Audi TT quattro Sport, (9:1 compression ratio) — BFV
;EWG-rated motive power & torque outputs, applications
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,500 rpm —
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
, Stage1
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,500 rpm —
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
, Stage2
: at 6,000 rpm; at 4,000–5,500 rpm —
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
, Stage3
;references:
awards
:Was placed in the 1997, 1998, 2001, 2002 and 2003 annual list of
Ward's 10 Best Engines 10 of the World's best engines is an annual list of the ten ''"''best''"'' automobile engines available in the U.S. market, that are selected by ''Ward's AutoWorld'' magazine. The list was started in 1994 for Model Year 1995, and has been drawn eve ...
2.0 R4 (EA827)
;identification:parts code prefix: ???
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.89:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 496.1 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.0–10.5:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: CG25 grey cast iron; five main bearings; die-forged steel crankshaft, forged steel connecting rods
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; two valves per cylinder, 8 valves total, hydraulic bucket tappets, timing belt-driven one-piece cast single overhead camshaft (SOHC)
;aspiration: cast aluminium alloy intake manifold
;engine management:
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
or
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
Simos electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU)
;EWG-rated motive power & torque outputs, application, ID codes
: at 2,800 rpm; at 2,100–2,400 rpm —
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
multi-fuel (
petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
/
LPG /
CNG
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in cy ...
) – CBS (08/06->)
: at 2,800 rpm; at 2,100–2,400 rpm —
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
multi-fuel (
petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
/
LPG /
CNG
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in cy ...
) – BEF (04/02->)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,500 rpm — Ecofuel (bivalent) at 2,600 rpm — ATM
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,200 rpm — AZH, AZJ
: at 5,400 rpm; at 3,500 rpm — AZM
: at 5,200 rpm; at 2,700-4,700 rpm — AXA
: at 5,600 rpm; at 2,400 rpm — ATF
: at 5,600 rpm; at 2,600 rpm — AUZ, ASU, AVA
;applications:
SEAT Ibiza
The SEAT Ibiza is a supermini car that has been manufactured by Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since 1984. It is SEAT's best-selling car. The Ibiza is named after the Spanish island of Ibiza and was the second SEAT model to be named after a Spa ...
Mk2 & Mk3,
SEAT Córdoba
The SEAT Córdoba is the saloon, estate and coupé version of the SEAT Ibiza supermini car, built by the Spanish automaker SEAT. It was manufactured between 1993 and 2010, and was related with the second and third generations of the Ibiza.
F ...
,
SEAT Toledo
The SEAT Toledo is a small family car produced by the Spanish manufacturer SEAT, part of Volkswagen Group. The Toledo name was first introduced to the SEAT line up in May 1991 being named after a Spanish city with the same name, with the fourt ...
Mk1,
SEAT Alhambra
The SEAT Alhambra is a seven-seater minivan that was built from 1996 to 2020. It was manufactured under the SEAT brand from June 1996 onwards at the Volkswagen Group's AutoEuropa plant in Palmela, Portugal. It shares the same platform with the Vo ...
,
Škoda Fabia Mk1 (6Y),
Škoda Octavia Mk1 (1U),
Škoda Superb Mk1 (3U),
Volkswagen Santana
The Volkswagen Santana is a nameplate used by Volkswagen for various Sedan (automobile), sedans and station wagons since 1983. The first generation is based on the second-generation Volkswagen Passat (B2). It was introduced in 1981 while producti ...
,
Volkswagen Polo Mk4
The Volkswagen Polo Mk4 is the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Polo supermini car produced by the German manufacturer Volkswagen. It was marketed from early 2002 to 2009 in most countries except Argentina and the USA. It was manufactured in So ...
,
Volkswagen Golf Mk3
The Volkswagen Golf Mk3 is a medium-sized compact family car. The third generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk2, which was produced by Volkswagen from August 1991 (for the 1992 model year) to 2002 (for Cab ...
,
Volkswagen Golf Mk4
The Volkswagen Golf Mk4 (or VW ''Type 1J'') is a compact car, the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Golf and the successor to the Volkswagen Golf Mk3. Launched in October 1997 for the 1998 model year, it was the best selling car in Europe in ...
,
Volkswagen Vento Volkswagen Vento can refer to:
* Volkswagen Vento (A3) (1992–1999), the third generation Jetta was badged as the Volkswagen Vento outside of North America.
* Volkswagen Jetta (A5) (2005–2011), the fifth generation Jetta was rebadged as the Volk ...
,
Volkswagen Bora
The Volkswagen Bora is a small family car, the fourth generation of the Volkswagen Jetta, and the successor to the Volkswagen Vento. Production of the car began in July 1999. Carrying on the wind nomenclature from previous generations, the car wa ...
,
Volkswagen Jetta
The Volkswagen Jetta () is a compact car/small family car manufactured and marketed by Volkswagen since 1979. Positioned to fill a sedan niche above the firm's Golf hatchback, it has been marketed over seven generations, variously as the Atlant ...
,
Volkswagen New Beetle
The Volkswagen New Beetle is a compact car, introduced by Volkswagen in 1997, drawing heavy inspiration from the exterior design of the original Beetle. Unlike the original Beetle, the New Beetle has its engine in the front, driving the fron ...
,
VW Passat B3,
VW Passat B4,
VW Passat B5,
Volkswagen Transporter (T5)
The Volkswagen Transporter T5 range is the fifth generation of Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles (VWCV/VWN) 'Transporter' series of medium-sized light commercial vehicles and the people mover Caravelle/Multivan range. It was launched 6 October 20 ...
,
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
;reference:
2.0 R4 16v "Turbo FSI"/TSI/TFSI (EA113)
This turbocharged EA113 engine is based on the naturally aspirated
110kW 2.0 FSI.
;identification: parts code prefix/variant: 06F.C, 06F.D
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.89:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 496.1 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: CG25 grey cast iron with liquid-blasted cylinder bore honing; cylinder spacing, five main bearings, die-forged steel crankshaft, two simplex-roller chain driven
balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
T ...
s
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; modified inlet duct geometry for high tumble values providing superior
knock resistance, four valves per cylinder (exhaust valves sodium filled for increased cooling), 16 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, belt and roller-chain driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC), continuous intake camshaft adjustment (42° variance from crankshaft)
;aspiration: hot-film air mass meter incorporated into air filter housing, cast alloy throttle body with
electronically controlled throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valve, plastic
variable length controlled intake manifold with charge movement flaps adjusted by a continuous-action pilot motor, boost water-cooled
BorgWarner
BorgWarner Inc. is an American automotive supplier headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. The company maintains production facilities and technical systems at 93 sites (as of June 6, 2022) in 22 countries worldwide and has around 49,000 emplo ...
K03
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
(K04 on 169 kW upwards) incorporated in exhaust manifold, sandwiched central front-mounted
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
(FMIC)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; – fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump,
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): inlet camshaft double-cam driven
Hitachi
() is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (''Hitachi Gurūpu'') and had formed part of the Ni ...
single-piston high-pressure injection pump maintaining a pressure between in the stainless steel
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel rail, four combustion chamber sited
direct injection sequential solenoid-controlled fuel injectors, air-guided combustion process, multi-pulse injection with homogeneous mixing, stratified lean-burn operation with excess air at part load
;ignition system & engine management: centrally positioned
Bosch longlife spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with four individual direct-acting single spark coils; Bosch
Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED 9.1 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), cylinder-selective
knock control via two knock sensors, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control
;exhaust system: Cast iron exhaust manifold (with integrated
BorgWarner
BorgWarner Inc. is an American automotive supplier headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. The company maintains production facilities and technical systems at 93 sites (as of June 6, 2022) in 22 countries worldwide and has around 49,000 emplo ...
turbocharger), one primary and one main ceramic
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s, two heated
oxygen sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or sond, is an electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed.
It was ...
s monitoring pre- and post catalyst exhaust gases
;dimensions: length: , width: , height: , mass:
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes & applications
: at 4,300 rpm; at 1,800–4,200 rpm — BPJ —
Audi A6 (C6),
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
: at 6,000 rpm; at 1,800–5,000 rpm — BWA — 2005
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
: at 5,100–6,000 rpm; at 1,700–5,000 rpm — AXX, BWA, BWE, BPY (North America) —
Audi A4 (B7),
Audi A3 (8P), 2006
Audi TT,
VW Passat (B6),
VW Golf Mk5 GTI,
VW Jetta Mk5 GLI,
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
FR Mk2,
SEAT Altea
The SEAT Altea is an automobile produced by the Spanish automaker SEAT from 2004 to 2015 being previewed by the Salsa Emoción concept. As a compact multi-purpose vehicle (MPV), the car was designed by the Italian Walter de Silva, and was launc ...
,
SEAT Toledo
The SEAT Toledo is a small family car produced by the Spanish manufacturer SEAT, part of Volkswagen Group. The Toledo name was first introduced to the SEAT line up in May 1991 being named after a Spanish city with the same name, with the fourt ...
Mk3,
SEAT Exeo
The SEAT Exeo () is a large family car and flagship model, that was built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT, subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
Previously codenamed ''Bolero'', (though not to be confused with SEAT's earlier concept car bea ...
,
Škoda Octavia (1Z) vRS
: at 5,900 rpm; at 2,200–4,800 rpm — BUL — 2005
Audi A4 (B7) DTM Edition,
Audi A4 (B7) Special Edition
: at 4,500–6,300 rpm; at 2,500–4,400 rpm — CDL — Volkswagen Polo R WRC
: at 4,200–6,000 rpm; at 1,450–4,200 rpm — CDL —
Audi A5 (B9; 40 TFSI)
: at 5,500 rpm; at 2,250–5,200 rpm — BYD —
VW Golf Mk5 GTI Edition 30,
Pirelli Edition
: at 5,500 rpm; at 2,200–5,200 rpm — CDL — Volkswagen Golf MKVI GTI Edition 35
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,200–5,500 rpm — BWJ —
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
Cupra,
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
Cupra Mk2 facelift
: at 5,000–6,000 rpm; at 1,600–4,500 rpm — CDLA —
Audi A5 (B9; 45 TFSI)
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,400–5,200 rpm — CDL —
Audi S3 (8P),
Golf R (Australia, Japan, Middle-East and North America)
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,000 rpm — BHZ —
Audi S3 (8P)
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,000 rpm — CDL —
Scirocco R
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,300–5,200 rpm — CDLA —
Audi S3 (8P),
Audi TTS,
SEAT León
The SEAT León (), also spelled Leon in some other languages (named after the city of León, which also means "Lion" in Spanish), is a hatchback compact car built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT since October 1999.ETKA
The first two Leó ...
Cupra R Mk2 facelift, VW Scirocco R
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,000 rpm — CDLF —
Golf R (Europe)
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,000 rpm — CDLB —
Audi TTS (Europe),
VW Arteon (North America)
;notes: the 162 kW
(only Polo R WRC) and higher versions have stronger pistons and
gudgeon pin
In internal combustion engines, the gudgeon pin (UK, wrist pin or piston pin US) connects the piston to the connecting rod, and provides a bearing for the connecting rod to pivot upon as the piston moves.Nunney, Malcolm James (2007) "The Reciproc ...
s, new rings, reinforced connecting rods, new bearings, reinforced cylinder block at the main bearing pedestals and cap, new lightweight
aluminium-silicon alloy cylinder head for high temperature resistance and strength, adjusted exhaust camshaft timing, increased cross-section high-pressure injectors,
(value only valid for Audi S3(8P)) boost pressure K04
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
with larger turbine and compression rotor (S3, Cupra, GTI Edition 30), of which some components are NOT shared with the lower output variants
;references:
awards
:Was winner of the "1.8-litre 2.0-litre" category for four consecutive years in the 2005, 2006, 2007 and 2008 annual competition for
International Engine of the Year,
:Was placed for four consecutive years in the 2006, 2007, 2008 and 2009 annual list of
Ward's 10 Best Engines 10 of the World's best engines is an annual list of the ten ''"''best''"'' automobile engines available in the U.S. market, that are selected by ''Ward's AutoWorld'' magazine. The list was started in 1994 for Model Year 1995, and has been drawn eve ...
Four-cylinder EA888 petrols
This latest EA888 family of
straight-four 16-valve internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
s with
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
is anticipated to be an eventual complete replacement of the
EA113 range. It was wholly designed and developed by
VAG AG. The only common feature with its predecessors is the sharing of the same cylinder spacing – which keeps the engine length relatively short, meaning it can be installed either
transversely or
longitudinally, though engineers have said that it is an evolution of the earlier EA827/113 designs due to cost concerns.
Grey
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
(GJL 250) remains the choice material for the cylinder block and crankcase, due to its inherent good acoustic dampening properties. This all-new EA888 range is notable for utilising simplex roller chains to drive the two overhead camshafts, instead of the former engines' toothed-rubber
timing belt. Like the final developments of the former EA113 engine generation, all EA888s only use the VAG AG/Bosch
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) direct injection. Furthermore, EA888 engines are also able to utilise the corporate 'valvelift' technology, which complements the existing
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
. This new family of engines is scheduled to be universally available for all markets on five continents, within all marques of the
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
. The closely related EA113 range still remains in production.
Grainger & Worrall was reported to have cast 50 CGI cylinder blocks for over 12 months as of October 2013, based on the EA888 gasoline engine.
1.8 R4 16v TSI/TFSI (EA888)
;identification: parts code prefix: 06H, 06J; ID codes: BYT
;engine displacement & engine configuration: EA888
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.98:1 – 'square engine', 449.6 cc per cylinder; compression ratio: 9.6:1, cylinder spacing
;cylinder block & crankcase: GJL 250 grey cast iron; , die-forged steel crankshaft with five diameter main bearings, two toothed chain-driven counter-rotating balance shafts suppressing second degree free inertial forces and oil pump, horizontal-baffled
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
sump
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 16 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, toothed chain-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC), continuous vane-adjustable
variable intake valve timing
;aspiration: hot-film
air mass meter, cast alloy
throttle body
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
with
electronically controlled Bosch E-Gas
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valve, plastic
variable length controlled intake manifold with charge movement flaps controlling combustion chamber air movement,
BorgWarner
BorgWarner Inc. is an American automotive supplier headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. The company maintains production facilities and technical systems at 93 sites (as of June 6, 2022) in 22 countries worldwide and has around 49,000 emplo ...
K03 water-cooled
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
incorporated into cast iron exhaust manifold, sandwiched central front-mounted
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
(FMIC)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; – fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): single-piston high-pressure injection pump driven by a four-lobe cam on the exhaust camshaft supplying up to fuel pressure in the stainless steel common rail fuel rail, four combustion chamber sited
direct injection sequential solenoid-controlled six-hole fuel injectors, air-guided combustion process, multi-pulse dual-stage injection during the induction and compression stroke with homogeneous mixing, stratified lean-burn operation with excess air at part load, 95
RON unleaded ultra-low sulphur petrol
;ignition system & engine management: centrally positioned longlife spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with four individual direct-acting single spark coils; Bosch
Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), cylinder-selective
knock control via two knock sensors, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control
;exhaust system: cast iron exhaust manifold (with integrated turbocharger), close-coupled and main
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s – both ceramic
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 4,000–6,200
rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
; at 1,500–3,650rpm — longitudinal —
Audi A4 (B8),
SEAT Exeo
The SEAT Exeo () is a large family car and flagship model, that was built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT, subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
Previously codenamed ''Bolero'', (though not to be confused with SEAT's earlier concept car bea ...
: at 4,500–6,200 rpm; at 1,500–4,500 rpm, from 1,000 rpm — transversal — CDAA
Škoda Yeti
The Škoda Yeti (codenamed ''Typ'' 5L)ETKA, accessed 27 January 2010 is a compact crossover SUV produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto and introduced at the 2009 Geneva Motor Show, as the carmaker's first entry into the SUV market. In ...
,
SEAT Leon Mk2 (1P)
: at 4,300–6,200 rpm; at 1,500–4,200 rpm, from 1,000 rpm — transversal — CDAB
Škoda Yeti
The Škoda Yeti (codenamed ''Typ'' 5L)ETKA, accessed 27 January 2010 is a compact crossover SUV produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto and introduced at the 2009 Geneva Motor Show, as the carmaker's first entry into the SUV market. In ...
: at 4,500–6,200 rpm; at 1,500–4,500 rpm — longitudinal —
Audi A4 (B8),
Audi A3 Mk2 (8P),
Audi TT Mk2 (8J),
SEAT Exeo
The SEAT Exeo () is a large family car and flagship model, that was built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT, subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
Previously codenamed ''Bolero'', (though not to be confused with SEAT's earlier concept car bea ...
— CDHB
Audi A4 (B8)
: at 4,800–6,200 rpm; at 1,750–4,750 rpm — transverse —
VW USA-Passat B7 (NMS) — CPKA, CPRA (born 2014)
: at 4,800–6,200 rpm; at 1,500–4,800 rpm — longitudinal —
Audi A5
The Audi A5 is a series of compact executive coupe cars produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi since June 2007. The A5 range additionally comprises the coupe, cabriolet, and "Sportback" (a five-door liftback with a fastback roofline) v ...
: at 3,800–6,200 rpm; at 1,400–3,700 rpm — longitudinal —
Audi A4 (B8) (2012–),
Audi A5
The Audi A5 is a series of compact executive coupe cars produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi since June 2007. The A5 range additionally comprises the coupe, cabriolet, and "Sportback" (a five-door liftback with a fastback roofline) v ...
— CJEB
: at 5,100–6,200 rpm; at 1,250–5,000 rpm — transverse —
Audi TT (FV/8S) (2014–) — CJSA (EA888-Gen3)
;applications:
Audi TT Mk2 (8J),
Audi 8P A3,
Audi B7 A4,
Audi A4 (B8),
Audi A5
The Audi A5 is a series of compact executive coupe cars produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi since June 2007. The A5 range additionally comprises the coupe, cabriolet, and "Sportback" (a five-door liftback with a fastback roofline) v ...
,
SEAT Leon Mk2 (1P),
SEAT Altea XL
The SEAT Altea is an automobile produced by the Spanish automaker SEAT from 2004 to 2015 being previewed by the Salsa Emoción concept. As a compact multi-purpose vehicle (MPV), the car was designed by the Italian Walter de Silva, and was launc ...
,
Škoda Yeti
The Škoda Yeti (codenamed ''Typ'' 5L)ETKA, accessed 27 January 2010 is a compact crossover SUV produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto and introduced at the 2009 Geneva Motor Show, as the carmaker's first entry into the SUV market. In ...
,
Škoda Octavia Mk2 (1Z, Ming Rui),
Škoda Superb Mk2 (3T),
VW Jetta Mk5/Sagitar,
VW Passat B6,
VW Passat CC
;references:
of the German technical engine publication mtz, press release 11/2006: "Der neue Audi 1.8 TFSI-Motor"Owners Manual, Passat, U.S. Edition, Model Year 2015. p. 44.
2.0 R4 16v TSI/TFSI (EA888)
Manufacturing commenced March 2008.
;identification: parts code prefix: 06H, 06J; ID codes: CAEA, CAEB, CAWA, CAWB, CBFA, CCTA, CCTB, CCZA, CCZB, CCZC, CCZD, CDNB, CDNC, CHHA, CHHB, CJXA, CJXB, CJXC, CJXD, CJXE, CJXF, CJXG, CYFB, DKFA
;engine displacement & engine configuration: EA888
inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
(R4/I4); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.89:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 496.1 cc per cylinder; compression ratio: 9.6:1 (10.3:1 A3 Cabrio 2009), cylinder spacing
;cylinder block & crankcase: GJL 250 grey cast iron; , die-forged steel crankshaft with five diameter main bearings, two chain-driven counter-rotating
balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
T ...
s suppressing second degree free inertial forces and oil pump, horizontal-baffled oil sump. The water pump bolts to the side of the block, under the intake manifold, and is driven by a toothed belt and a pulley on the back of the intake-side balance shaft.
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 16 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, toothed chain-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC), continuous vane-adjustable
variable intake valve timing, Audi variants have two-stage ''"valvelift"'' inlet valve lift variable control
;aspiration: hot-film
air mass meter, cast alloy
throttle body
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
with
electronically controlled Bosch E-Gas
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valve, plastic
variable length controlled intake manifold with charge movement flaps controlling combustion chamber air movement, IHI water-cooled
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
incorporated in exhaust manifold, sandwiched central front-mounted
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
(FMIC)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; – fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): single-piston high-pressure injection pump driven by a four-lobe cam on the exhaust camshaft supplying up to fuel pressure in the stainless steel common rail fuel rail, four combustion chamber sited direct injection sequential solenoid-controlled six-hole fuel injectors, air-guided combustion process, multi-pulse dual-stage injection during the induction and compression stroke with homogeneous mixing, stratified lean-burn operation with excess air at part load, 95
RON ultra-low sulphur unleaded petrol
;ignition system & engine management: centrally positioned longlife spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with four individual direct-acting single spark coils; Bosch
Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED 17 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), cylinder-selective
knock control via two knock sensors, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control
;exhaust system: cast iron exhaust manifold (with integrated turbocharger), close-coupled and main
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s – both ceramic
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs and applications – Non-''valvelift'' variants
: at 4,300–6,000 rpm; at 1,700–5,000 rpm — CAWA:
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
: at 4,300–6,200 rpm; at 1,700–4,200 rpm — CCZC:
Audi Q3
The Audi Q3 is a subcompact luxury crossover SUV made by Audi. The Q3 has a transverse-mounted front engine, and entered production in 2011.
__TOC__
First generation (Typ 8U; 2011)
Concept Vehicle: Audi Cross Coupé quattro (2007)
Designed ...
, engine is installed transversely,
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
: at 4,500–6,200 rpm; at 1,700–4,500 rpm — CCZD:
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
: at 5,100–6,000 rpm; at 1,800–5,000 rpm — CCTA/CBFA: 2009
VW Golf Mk5 GTI (US only),
VW Golf Mk6 GTI (US only),
Audi Q3
The Audi Q3 is a subcompact luxury crossover SUV made by Audi. The Q3 has a transverse-mounted front engine, and entered production in 2011.
__TOC__
First generation (Typ 8U; 2011)
Concept Vehicle: Audi Cross Coupé quattro (2007)
Designed ...
(US Only),
VW Jetta Mk5,
VW Jetta Mk6,
VW Passat B6,
VW CC,
Audi A3 (8P)
: at 5,100–6,000 rpm; at 1,700–5,000 rpm — CAWB:
Audi A3
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
Cabriolet,
VW Scirocco
The Volkswagen Scirocco is a three-door, Front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout, front-engine, front-wheel-drive, sport compact hatchback manufactured and marketed by Volkswagen in two generations from 1974 to 1992 and a third generation from 2008 ...
,
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
, CCZA:
Audi TT,
Škoda Superb Mk2 (3T),
Škoda Octavia
The Škoda Octavia is a small family car produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since the end of 1996. It shares its name with an earlier model produced between 1959 and 1971. Four generations of the modern-era Octavia model hav ...
: at 5,000–6,000 rpm; at 1,800–5,000 rpm — CGMA: China market only;
VW Golf Mk6 GTI,
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
,
VW Magotan (Passat)
: at 5,000–6,200 rpm; at 1,800–4,900 rpm — CPSA:
Audi Q3
The Audi Q3 is a subcompact luxury crossover SUV made by Audi. The Q3 has a transverse-mounted front engine, and entered production in 2011.
__TOC__
First generation (Typ 8U; 2011)
Concept Vehicle: Audi Cross Coupé quattro (2007)
Designed ...
, engine is installed transversely
: at 5,300–6,200 rpm; at 1,700–5,200 rpm — CCZB:
VW Golf Mk6 GTI, has larger front-mounted intercooler as found in 2010+ Audi S3/VW Mk6 Golf R CDL EA113,
VW Scirocco
The Volkswagen Scirocco is a three-door, Front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout, front-engine, front-wheel-drive, sport compact hatchback manufactured and marketed by Volkswagen in two generations from 1974 to 1992 and a third generation from 2008 ...
,
VW Passat,
VW CC,
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
, SEAT Altea Freetrack, SEAT Leon FR
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs and applications – EA888 evo2 and EA888 Gen3 with ''Valvelift'' at exhaust side
.
: at 4,200–6,000 rpm; at 1,500–4,000 rpm — CAEA/CDNB:
Audi A4 (B8),
Audi Q5
The Audi Q5 is a series of compact luxury crossover SUVs produced by the German luxury car manufacturer Audi from 2008. The original first-generation (''Typ 8R'') model was the third member of the ''B8'' family to be released after the Audi A ...
,
Škoda Kodiaq
The Škoda Kodiaq is a mid-size crossover SUV manufactured by the Czech automaker Škoda Auto since 2016. The vehicle sits in Škoda's D-SUV, above the Škoda Kamiq and Škoda Karoq. The vehicle is based on the Volkswagen Group MQB platform, shar ...
: at 4,300–6,000 rpm; at 1,500–4,200 rpm — CAEA/CAEB/CDNC:
Audi A4 (B8),
Audi A5
The Audi A5 is a series of compact executive coupe cars produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi since June 2007. The A5 range additionally comprises the coupe, cabriolet, and "Sportback" (a five-door liftback with a fastback roofline) v ...
,
Audi Q5
The Audi Q5 is a series of compact luxury crossover SUVs produced by the German luxury car manufacturer Audi from 2008. The original first-generation (''Typ 8R'') model was the third member of the ''B8'' family to be released after the Audi A ...
,
SEAT Exeo
The SEAT Exeo () is a large family car and flagship model, that was built by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT, subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
Previously codenamed ''Bolero'', (though not to be confused with SEAT's earlier concept car bea ...
: at 4,300–6,000 rpm; at 1,600–4,200 rpm — CESA:
Audi TT Mk2 (8J), engine is installed transversely
: at 4,500–6,200 rpm; at 1,500–4,400 rpm — CHHB:
Audi A3
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
,
Skoda Superb
Škoda means ''pity'' in the Czech and Slovak languages. It may also refer to:
Czech brands and enterprises
* Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav
** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Škoda Auto respons ...
,
VW Golf Mk7 GTI,
Škoda Octavia RS
Škoda means ''pity'' in the Czech language, Czech and Slovak languages. It may also refer to:
Czech brands and enterprises
* Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav
** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Šk ...
,
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
CULC:
VW Scirocco GTS
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
: at 4,500–6,250 rpm; at 1,500–4,500 rpm — CNCD:
Audi Q5
The Audi Q5 is a series of compact luxury crossover SUVs produced by the German luxury car manufacturer Audi from 2008. The original first-generation (''Typ 8R'') model was the third member of the ''B8'' family to be released after the Audi A ...
,
Audi A4 (B8)
: at 4,500–6,250 rpm; at 1,500–4,500 rpm — CUHA: China 5 emission standard
Volkswagen Phideon
The Volkswagen Phideon () is an executive sedan manufactured by the German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle. Introduced at the 2016 Geneva Motor Show, the Phideon is aimed at the marke ...
,
Audi A6L C7
: at 4,500–6,250 rpm; at 1,650–4,500 rpm — DMJA: China 6b(PN 11 without RDE) emission standard,
Volkswagen Phideon
The Volkswagen Phideon () is an executive sedan manufactured by the German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle. Introduced at the 2016 Geneva Motor Show, the Phideon is aimed at the marke ...
:165 kW (224 PS; 221 bhp) at 4,500–6,250 rpm; at 1,650–4,500 rpm — DKWB: China 6b(PN 11 without RDE) emission standard,
Audi A6L C8,
Audi Q5
The Audi Q5 is a series of compact luxury crossover SUVs produced by the German luxury car manufacturer Audi from 2008. The original first-generation (''Typ 8R'') model was the third member of the ''B8'' family to be released after the Audi A ...
L
: at 4,700–6,200 rpm; at 1,500–4,600 rpm — CHHA/DKFA:
VW Golf Mk7 GTI Performance,
Škoda Octavia RS230,
VW Jetta Mk7 GLI
: at 4,700–6,200 rpm; at 1,600–4,300 rpm — DLBA:
Škoda Octavia RS245,
VW Tiguan
The Volkswagen Tiguan () is a car produced by German manufacturer Volkswagen since 2007, sitting between the smaller T-Roc and the larger Touareg in the company's crossover SUV range. The first generation is based on the PQ46 platform, while t ...
:185 kW (224 PS; 221 bhp) at 4,500–6,250 rpm; at 1,500–4,500 rpm — DKWA: China 6b(PN 11 without RDE) emission standard,
Audi A4L,
Audi Q5L
: at 5,350–6,600 rpm; at 1,750–5,300 rpm — CJXE:
Volkswagen Golf MK7 GTI Clubsport,
SEAT Leon Cupra
: at 5,100–6,500 rpm; at 1,800–5,500 rpm — CJXA/CJXB:
SEAT Leon Cupra,
Skoda Superb
Škoda means ''pity'' in the Czech and Slovak languages. It may also refer to:
Czech brands and enterprises
* Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav
** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Škoda Auto respons ...
. (
Audi S3
S3, S-3 or S03 may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Si3'' (flim), originally titled ''S III'' and also known as ''Singam 3'', the third film in the ''Singam'' franchise
* '' Expedition to the Barrier Peaks'', code S3, a 1980 ''Dungeons & Dragons'' adv ...
and
VW Golf Mk7 R in some foreign markets)
: at 5,900–6,400 rpm; at 1,700–5,800 rpm — CJXD:
SEAT Leon Cupra
: at 5,400 rpm; at 1,800 rpm — CYFB:
VW Golf Mk7 R,
Audi S3
S3, S-3 or S03 may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Si3'' (flim), originally titled ''S III'' and also known as ''Singam 3'', the third film in the ''Singam'' franchise
* '' Expedition to the Barrier Peaks'', code S3, a 1980 ''Dungeons & Dragons'' adv ...
in North America (lacks
MPI)
: at 5,500–6,200 rpm; at 1,800–5,500 rpm — CJXC/CJXA:
Audi S3
S3, S-3 or S03 may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Si3'' (flim), originally titled ''S III'' and also known as ''Singam 3'', the third film in the ''Singam'' franchise
* '' Expedition to the Barrier Peaks'', code S3, a 1980 ''Dungeons & Dragons'' adv ...
,
VW Golf Mk7 R (
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
),
SEAT Leon Cupra
:; — CJXG:
Audi TTS,
VW Golf Mk7 R,
SEAT Leon Cupra R
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair, a chair eq ...
:235 kW (320 PS; 316 bhp; 420 N⋅m (310 lbf⋅ft) — Evo4 -
Golf Mk8 R
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs and applications – EA888 Gen3 with ''Valvelift'' at intake side known as EA888 Gen3 Bz.
: at 4,100–6,000 rpm; at 1,600–4,000 rpm — DBFA: China 5 emission standard,
Volkswagen Magotan
The Volkswagen Passat is a series of D-segment, large family cars manufactured and marketed by the Germany, German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen since 1973, and now in its eighth generation. It has been marketed variously as the Dasher, Sa ...
: at 4,100–6,000 rpm; at 1,500–4,000 rpm — DKVA: China 6b(without PN 11) emission standard,
Volkswagen Magotan
The Volkswagen Passat is a series of D-segment, large family cars manufactured and marketed by the Germany, German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen since 1973, and now in its eighth generation. It has been marketed variously as the Dasher, Sa ...
: at 4,100–6,000 rpm; at 1,500–4,000 rpm — DPLA: China 6b(PN 11 without RDE) emission standard,
Volkswagen Magotan
The Volkswagen Passat is a series of D-segment, large family cars manufactured and marketed by the Germany, German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen since 1973, and now in its eighth generation. It has been marketed variously as the Dasher, Sa ...
: at 4,200–6,000 rpm; at 1,450–4,200 rpm — CWNA: China 5 emission standard
Audi A4L
: at 4,200–6,000 rpm; at 1,450–4,200 rpm — DKUA: China 6b(without PN 11) emission standard
Audi A4L
: at 4,200–6,000 rpm; at 1,450–4,200 rpm — DTAA: China 6b(PN 11 without RDE) emission standard
Audi A4L
;reference
:
:
:
awards
:Winner of the "1.8-litre 2.0-litre" category in the 2009 annual competition for
International Engine of the Year.
Known problems
The Generation 1 EA888 suffered from higher than usual / favorable engine oil consumption in both 1.8 and 2.0 litre forms. Mainly affecting the Longitudinal Audi applications between 2008 and 2012 (most commonly the 8K / B8 A4 8T / 8F B8 A5 & 8R Q5). In rare occurrences it affects the Transverse applications in the 8P Audi A3, 8J Audi TT and in even rarer occasions would affect the MK6 Volkswagen Golf GTI and lower powered Sciroccos etc. that were not fitted with the EA113 family of engines. In even more extreme cases it would affect the Generation 3 from 2016 to present day. The rectification for this is performed after a two part oil consumption test is carried out by a main dealer, The vehicle will need to be burning more than approximately a metric litre per 1,000 KM or 600 miles, or if the top up oil warning illuminates on the instrument cluster. Only after this test is carried out and an agreement of payment by the manufacturer & customer contribution is agreed the repair can be carried out only by main dealers and manufacturer approved repairers. The rectification that is carried out is to remove the engine, replace the Piston & Connecting Rod assemblies in all four cylinders with modified units, head gasket and so forth. From late 2012, the modified internal engine components were fitted to new replacement engines and new vehicle units by the Volkswagen group engine plants.
Another common issue is camshaft timing chain tensioner failure, again in earlier generation 1 models. This was due to the design of the retaining element that after higher mileages and / or premature wear stopped the tensioner from holding the tension in the timing chain. If in the case of this component
failing, the chain would jump, allowing the pistons and valves to potentially hit each other, causing expensive and possibly terminal engine damage. Along with the earlier mentioned oil consumption issues, this was eventually addressed by the Volkswagen Group engine plants, Who fitted a modified (internally known as Version 2) tensioner that is retained by a much more reliable spring retainer instead.
The final mainstream common issue affects all EA888 generations. The cooling system is mainly a problem free system, with the exception of the plastic thermostat unit, these are very commonly known to be prone to leaks, with no specific part of the housing known to leak. On the EA888, the thermostat unit also includes the coolant pump, on the Generation 2 & 3 the coolant pump is still part of the thermostat, however is available separately. The coolant pump / thermostat unit is located under the intake manifold regardless of generation, model year or application. The thermostat side is joined by a plastic union directly to the engine oil cooler, which in turn is mounted to and is an integral part of the ancillary / alternator bracket (also includes the oil filter housing in all generations and applications). The coolant pump is driven by the intake side balance shaft, on the flywheel side of the engine. The rectification is to renew the thermostat unit with a modified unit, and if needed in later models, the coolant pump if necessary. However these newer units are still known to leak. There have currently been no further modifications to the design of this to combat the issues by Volkswagen Group.
= Turbo
=
The MQB platform suffers from early turbocharger failure. This affects models like the Audi S3, Golf 7 R/GTI and the Seat Cupra models. More so: models built prior to 2015 are more prone to failure. This can be caused because there is shaft play due to an imbalanced input shaft which can cause the turbine to collide with the teflon coating of the turbocharger, or because of the manifold sealing surface.
List of turbos
IHI IS20 - Transverse - Mid output engines, like 2.0T A3
* 06K 145 702 K
* 06K 145 702 Q
* 06K 145 702 R
* 06K 145 702 T
* 06K 145 722 G
* 06K 145 722 K
* 06K 145 722 L
IHI IS20 - Longitudinal - Mid output engines, like 2.0T A4
* 06L 145 702
* 06L 145 702 D
* 06L 145 702 F
* 06L 145 702 M
* 06L 145 702 P
* 06L 145 702 Q
* 06L 145 702 R
* 06L 145 722 B
* 06L 145 722 C
* 06L 145 722 D
* 06L 145 722 E
* 06L 145 722 F
* 06L 145 722 G
* 06L 145 722 L
* 06L 145 722 M
IHI IS38 - Transverse - High output engine, like 2.0T S3, Golf R
* 06K 145 702 J
* 06K 145 702 M
* 06K 145 702 N
* 06K 145 722 A
* 06K 145 722 H
* 06K 145 722 N
* 06K 145 722 P
* 06K 145 722 S
* 06K 145 722 T
* 06K 145 874 F
* 06K 145 874 N
= Waterpump/thermostat
=
A lot of people driving a Golf 7 R/GTI have been reporting failing thermostat housings. Most of them are being replaced under warranty by VW. This is most likely due to the plastic housing, it's recommended to install an uprated aluminium one.
Five-cylinder petrols
2.5 R5 20v TFSI udi TTRS, RS3, RSQ3 & quattro Concept(EA855 and EA855 evo)
An all-new engine designed by
AUDI AGs high-performance subsidiary
Audi Sport GmbH
Audi Sport GmbH, formerly known as quattro GmbH,[Audi-Mediacente ...](_blank)
(formerly
quattro GmbH
Audi Sport GmbH, formerly known as quattro GmbH,[Audi-Mediacente ...](_blank)
), harking back to the original turbocharged five cylinder Audi engines in the ''"Ur-"''
Audi Quattro
The Audi Quattro is a road and rally car, produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi, part of the Volkswagen Group. It was first shown at the 1980 Geneva Motor Show on 3 March. Production continued through 1991.
Background
The word ...
of the 1980s. A world first for a petrol engine, its cylinder block is constructed from
compacted vermicular graphite cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
(GJV/CGI) – first used in Audi's large displacement, high-performance
Turbocharged Direct Injection
TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) is Volkswagen Group's term for its current common rail direct injection turbodiesel engine range that have an intercooler in addition to the turbo compressor.
TDI engines are used in motor vehicles sold by th ...
(TDI)
diesel engines
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-calle ...
.
;identification: parts code prefix/variant: 07K3; ID code: CEPA, CEPB, CTSA, CZGA, CZGB, DAZA, DNWA
;engine displacement & engine configuration:
inline five engine (R5/I5); bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.89:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 496.1 cc per cylinder; cylinder spacing, 144 degree firing interval, firing order: 1-2-4-5-3, compression ratio: 10.0:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: GJV-450
compacted vermicular graphite cast iron (GJV/CGI); six main bearings, two-part cast aluminium alloy horizontal-baffled
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
sump, simplex roller chain-driven oil pump,
die
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
-forged steel crankshaft, forged steel connecting rods, cast aluminium alloy pistons (weight, each, including rings and gudgeon pin: )
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast high hot-strength aluminium alloy, modified inlet duct geometry for high tumble values providing superior
knock resistance, four valves per cylinder (exhaust valves sodium filled for increased cooling), 20 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic
valve clearance compensation, simplex roller chain-driven (relay method) lightweight double overhead camshafts (DOHC),
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
with continuous adjusting intake and exhaust camshaft timing of up to 42 degrees from the crankshaft, two-stage 'valvelift' variable lift control for inlet valves, siamesed inlet ports,
Audi "RS" 'red' plastic cam cover
;aspiration: twin charge pressure sensors; one pre-throttle plate, one intake manifold mounted, no air flow meter, cast alloy
throttle body
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
with
electronically controlled throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valve, two piece intake manifold with charge movement flaps adjusted by a continuous-action pilot motor, water-cooled
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
incorporated in exhaust manifold with diameter outlet, generating up to boost, separated central lower front-mounted
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
(FMIC)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless: fuel tank-mounted low-pressure fuel lift pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): single-piston high-pressure injection pump supplying up to fuel pressure in the stainless steel common rail fuel rail, five combustion chamber sited
direct injection sequential solenoid-controlled fuel injectors, air-guided combustion process, multi-pulse injection with homogeneous mixing, stratified lean-burn operation with excess air at part load, ultra-low sulfur unleaded petrol (ULSP)
;ignition system & engine management:
Beru longlife spark plugs centrally positioned in combustion chamber, mapped direct ignition with five individual direct-acting single spark coils;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), cylinder-selective
knock control via two knock sensors, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control
;exhaust system:
secondary air injection
Secondary air injection (commonly known as air injection) is a vehicle emissions control strategy introduced in 1966, wherein fresh air is injected into the exhaust stream to allow for a fuller secondary combustion of exhaust gases.
Development
T ...
pump for direct injection into exhaust ports to assist cold start operation, cast iron exhaust manifold (with integrated turbocharger), one primary and two secondary high-flow sports
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s, two heated
oxygen sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or sond, is an electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed.
It was ...
s monitoring pre- and post-primary catalyst exhaust gases (secondary catalysts unmonitored), vacuum-operated map-controlled flap-valve mounted in one rear exhaust
silencer tail pipe
;dimensions: length: , mass:
;DIN-rated motive power & torque output: at 5,400–6,500 rpm (specific power of per litre); at 1,600–5,300 rpm; redline: 7,100 rpm – RS Q3
: at 5,400–6,500 rpm (specific power of per litre); at 1,600–5,300 rpm; redline: 7,100 rpm – RS 3, TT RS, RS Q3 (facelift)
: at 5,400–6,500 rpm (specific power of per litre); at 1,600–5,300 rpm; redline: 7,100 rpm – TT RS plus
: at 5,400–6,500 rpm (specific power of per litre); at 1,600–5,300 rpm; redline: 7,100 rpm – RS Q3 performance, RS 3 (2015–)
: at 5,400–6,500 rpm; (specific power of per litre); at 1,600–5,300 rpm; redline: 7,100 rpm – TT RS, RS 3 (2017–), RS Q3 (2019–)
;application:
Audi quattro concept
The Audi quattro concept is a concept car produced by Audi and presented at the Paris Motor Show in 2010. It commemorates the 30th anniversary of the original Audi Quattro and the Audi quattro four wheel drive system. Based on the Audi RS5, it f ...
(2010),
Audi RS3 RS3 or RS-3 may refer to:
Vehicles Automobiles
* Audi RS3, a 2011–present German compact performance car
* Baojun RS-3, a 2019–present Chinese subcompact SUV
Other
* RS3 (sail), a windsurfing sail
* ALCO RS-3, diesel locomotive built by Am ...
(2010–2013),
Audi TT RS (07/2009 –>),
Audi RS Q3 (2013 ->),
Audi RS3 RS3 or RS-3 may refer to:
Vehicles Automobiles
* Audi RS3, a 2011–present German compact performance car
* Baojun RS-3, a 2019–present Chinese subcompact SUV
Other
* RS3 (sail), a windsurfing sail
* ALCO RS-3, diesel locomotive built by Am ...
(2015 ->),
KTM X-Bow GTX (2020 ->),
KTM X-Bow GT2 Concept (2020 ->),
Cupra Formentor
The Cupra Formentor is a compact crossover SUV (C-segment) manufactured by the Spanish car manufacturer SEAT under their Cupra performance-oriented sub-brand. Marketed as a coupé SUV, it is the first car designed specifically for the sub-brand. ...
(2021->)
;references:
awards
:was winner of the "2.0-litre 2.5-litre" category in the 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014 annual competition for
International Engine of the Year.
Six-cylinder petrols
2.5 VR6 24v TSI (EA390)
This 2.5 VR6 engine is only available for Chinese market on
Volkswagen Teramont
The Volkswagen Atlas is a mid-size crossover SUV manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen since 2017. Developed mainly for the North American and Chinese market, the vehicle is based on the Volkswagen Group MQB platform. Outside the US and ...
. It is derived from now retired 3.0 VR6 engine, which also was available in China only. This Engine is also available in the
Volkswagen Talagon
The Volkswagen Talagon () is a mid-size crossover SUV with three-row seating manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen through FAW-Volkswagen
FAW-Volkswagen Automobile Co., Ltd. is a joint venture between FAW Group and Volkswagen Group ...
;identification: parts code prefix: 03H, ID Code: DDKA, DPKA
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 10.6°
VR6
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 1:1 – square-stroke, 415.3 cc per cylinder, compression ratio is not disclosed at the moment.
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; die-forged steel crankshaft;
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four unequal-length valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, simplex roller chain-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC – one camshaft for all exhaust valves, and one for all intake valves), continuous timing adjustment
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
(52 degrees on the inlet, 22 degrees on the exhaust)
;aspiration: single turbo charger from MHI (Mitsubishi Heavy Industries), hot-film
air mass meter, electronic
drive by wire
Drive by wire, DbW, by-wire, steer-by-wire, fly-by-wire or x-by-wire technology in the automotive or aviation industry is the use of electrical or electro-mechanical systems for performing vehicle functions traditionally achieved by mechanical link ...
throttle valve, two-piece cast aluminium alloy intake manifold, two cast iron exhaust manifolds
;fuel system:
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) high-pressure direct injection with two common rails
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,750-3,500 rpm - DDKA, DPKA
;production: Volkswagen Salzgitter Plant
;applications
: DDKA:
Volkswagen Teramont
The Volkswagen Atlas is a mid-size crossover SUV manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen since 2017. Developed mainly for the North American and Chinese market, the vehicle is based on the Volkswagen Group MQB platform. Outside the US and ...
, Chinese market only, China 5 emission standard.
: DPKA:
Volkswagen Teramont X,
Volkswagen Teramont
The Volkswagen Atlas is a mid-size crossover SUV manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen since 2017. Developed mainly for the North American and Chinese market, the vehicle is based on the Volkswagen Group MQB platform. Outside the US and ...
, Chinese market only, China 6b(stage of PN11 without RDE) emission standard.
2.8 V6 30v
;identification: parts code prefix: 078, ID codes: ACK, AGE, AHA, ALG, AMX, APR, AQD, ATQ, ATX, BBG
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.95:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 461.9 cc per cylinder,
compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stati ...
: 10.1:1 (AGE, ATX, BBG); 10.3:1 (ALG, AMX), 10.6:1 (ACK, AHA, APR, AQD, ATQ)
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast steel; die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy;
five valves per cylinder, 30 valves total, hydraulic bucket tappets with automatic valve clearance compensation, belt-driven double overhead camshafts (exhaust cams are belt driven, intake cams are driven by the exhaust cams using short chains), continuously adjusting
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake camshafts
;engine management:
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU); regular premium unleaded (98 octane normally or 95 with "lower power output", according to manual)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque output, ID codes
: at 6,000 rpm; at 3,200 rpm — AGE
: at 6,000 rpm; at 3,200 rpm — ATX, BBG
: at 6,000 rpm; at 3,200 rpm — ALG, AMX
: at 6,000 rpm; at 3,200 rpm — ACK, AHA, APR, AQD, ATQ
;applications:
Volkswagen Passat
The Volkswagen Passat is a series of D-segment, large family cars manufactured and marketed by the Germany, German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen since 1973, and now in its eighth generation. It has been marketed variously as the Dasher, Sa ...
(1997–2005) including the Variant and Chinese
Škoda Superb
The Škoda Superb is a large family car that has been produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since 2001.
The first generation of the modern Superb, produced from 2001 to 2008, was based on the VW B5 PL45+ platform. The second gener ...
;
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
,
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
and
Audi A8
The Audi A8 is a full-size luxury sedan manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi since 1994. Succeeding the Audi V8, and now in its fourth generation, the A8 has been offered with both front- or permanent all-wheel drive—and in s ...
2.8 V6 24v FSI
The 2.8 V6 is a stroke-reduced version of the
3.2 V6 FSI introducing the Audi ''valvelift'' variable control of inlet valve lift.
;identification:parts code prefix: ???, ID code: BDX
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik ...
, cylinders banks offset; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 1.03:1 – oversquare/short-stroke, 462.1 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 12.0:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous monoblock low-pressure gravity die cast
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg) with a closed-deck design, mechanically stripped hard silicon crystal integral liners, honed under simulated mechanical stress; long, wide, high, ; die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, chain-driven double overhead camshaft, continuous adjusting
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts, two-stage ''valvelift'' inlet valve lift variable control
;fuel system: common rail
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) high-pressure direct injection
;dimensions:
;DIN-rated motive power & torque output
: at 5,500 rpm; at 3,000–5,000 rpm
: at 5,250 rpm; at 3,000–5,000 rpm
: at 5,500 rpm; at 3,000–5,000 rpm; 6,800 rpm max
: at 5,750 rpm; at 3,200–5,000 rpm
;applications: C6/C7
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
, C7
Audi A7
The Audi A7 is an executive luxury four-door coupé produced by Audi since 2010. A five-door liftback (also available as a three-box, four-door saloon in China since 2021), it features a sloping roofline with a steeply raked rear window and inte ...
, D3
Audi A8
The Audi A8 is a full-size luxury sedan manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi since 1994. Succeeding the Audi V8, and now in its fourth generation, the A8 has been offered with both front- or permanent all-wheel drive—and in s ...
;reference:
3.0 V6 30v
This engine unveiled in 2000 is an all-aluminium alloy, longer stroke version of the
2.8 V6.
;identification: parts code prefix: 06C
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.89:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 496.1 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy; die-forged steel crankshaft; light pistons, balancer shaft
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; five valves per cylinder, 30 valves total, hydraulic bucket tappets with automatic valve clearance compensation, belt-driven double overhead camshaft, continuous adjusting
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts
;aspiration: two-position
variable length intake manifold
In internal combustion engines, a variable-length intake manifold (VLIM),variable intake manifold (VIM), or variable intake system (VIS) is an automobile internal combustion engine manifold technology. As the name implies, VLIM/VIM/VIS can vary ...
;engine management:
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
ME 7.1.1 with electronic throttle control, EU4 compliant
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
:BBJ: for the C6 A6
:AVK: at 6,300 rpm; at 3,200 rpm
;applications: 2002–2005
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
, 2002–2004
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
, 2005
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
(some Far East markets)
;reference:
3.0 V6 24v TFSI (EA837)
;identification: parts code prefix: 06E, ID codes: CAJA, CAKA, CCBA, CMUA
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.95:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 499.7 cc per cylinder, cylinder spacing, compression ratio: 10.3:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy; die-forged steel
crossplane
The crossplane or cross-plane is a crankshaft design for piston engines with a 90° angle (phase in crank rotation) between the crank throws. The crossplane crankshaft is the most popular configuration used in V8 road cars.
Aside from the V8 alr ...
crankshaft
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, chain-driven double overhead camshaft, continuous adjusting
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts
;aspiration:
Eaton 'Twin Vortices Series' (TVS) Roots
A root is the part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors the plant body, and absorbs and stores water and nutrients.
Root or roots may also refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''The Root'' (magazine), an online magazine focusing ...
-type positive displacement
supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induct ...
compressor with 160-degree axial twist twin four-lobe rotors and two integrated water-cooled
charge air coolers (one per cylinder bank), mounted within the Vee pumping charged air directly into the inlet manifold
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): two inlet camshaft double-cam driven single-piston high-pressure injection pumps maintaining a pressure of in the two stainless steel common rail fuel distributor rails (one rail per cylinder bank), six combustion chamber sited
direct injection solenoid-controlled sequential fuel injectors, homogenous mixing, stratified-charge combustion (lean-burn) at partial load
;ignition system and engine management: mapped direct ignition with centrally mounted spark plugs and six individual direct-acting single spark coils;
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
Simos 8.xx electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU)
;exhaust system: two ceramic
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s
;dimensions: length: , width: , mass:
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
: at 4,780–6,500 rpm; at 2,150–4,780 rpm — CMUA:
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
,
Audi A5
The Audi A5 is a series of compact executive coupe cars produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi since June 2007. The A5 range additionally comprises the coupe, cabriolet, and "Sportback" (a five-door liftback with a fastback roofline) v ...
,
Audi Q5
The Audi Q5 is a series of compact luxury crossover SUVs produced by the German luxury car manufacturer Audi from 2008. The original first-generation (''Typ 8R'') model was the third member of the ''B8'' family to be released after the Audi A ...
: at 4,850–6,500 rpm; at 2,500–4,800 rpm — CAJA:
Audi A6 (C6)
: at 5,500–7,000 rpm; at 2,500–5,000 rpm — CAKA/CCBA:
Audi S4 (B8),
Audi S5
The Audi S5 is one of two high-performance variants of Audi's A5. It is also the coupé, cabriolet, and five-door fastback sedan versions of the fourth-generation (B8) Audi S4 saloon and estate models.
Like all Audi "S" cars, they are only ...
,
Audi Q7 (4M)
: at 6,000–6,500 rpm; at 4,000–4,500 rpm — CTXA:
Audi SQ5#B8(8R),
;applications:2009
Audi A8 (D3),
Audi A6 (C6),
Audi A6 (C7),
Audi A7 (C7),
Audi A4 (B8),
Audi S5
The Audi S5 is one of two high-performance variants of Audi's A5. It is also the coupé, cabriolet, and five-door fastback sedan versions of the fourth-generation (B8) Audi S4 saloon and estate models.
Like all Audi "S" cars, they are only ...
,
Audi S4 (B8), 2010
VW Touareg Hybrid (anticipated), 2011 Porsche Cayenne S Hybrid
The Porsche Cayenne is a series of mid-size luxury crossover sport utility vehicles manufactured by the German automaker Porsche since 2002 (Type 9PA or E1), with North American sales beginning in 2003. It is the first V8-engined vehicle built by ...
, 2015-2019 Audi Q7 (4M), 2013 Audi SQ5#(8R/B8), 2016 Volkswagen Phideon
The Volkswagen Phideon () is an executive sedan manufactured by the German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle. Introduced at the 2016 Geneva Motor Show, the Phideon is aimed at the marke ...
;references:
3.0/2.9 V6 24v TFSI (EA839)
The base engine is the 3.0 TFSI, available on Audi S4/S5/SQ5 models and a slightly detuned version () with 48V
mild hybrid system on various Audi models such as the A6, A7, A8, Q7 and Q8. The 2.9 TFSI engine is a shorter stroke variant with much higher output.
;identification: parts code prefix:???, ID codes: CWGD, CZSE/DR, DECA
;engine displacement & engine configuration
: 3.0 TFSI variant: 90°
V6; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.94:1 - undersquare/long-stroke, compression ratio: 11.2:1
: 2.9 TFSI variant: 90°
V6; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.98:1 - undersquare/long-stroke, compression ratio: 10.0:1 to 10.5:1 depending on models
;cylinder block & crankcase: sand-cast
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
aluminium-silicon alloy; atmospheric plasma sprayed coating on cylinder walls
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 24 valves total,
DOHC
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion c ...
,
continuous timing adjustment on both intake and exhaust camshaft(from 130 degrees up to 180 degrees), 2-stage(6mm and 10mm)
Audi Valvelift System(AVS) on the intake sides
;aspiration
: all variants feature both Otto and Miller cycles, achieved from valve timing; hot-film
air mass meter; electronic
drive by wire
Drive by wire, DbW, by-wire, steer-by-wire, fly-by-wire or x-by-wire technology in the automotive or aviation industry is the use of electrical or electro-mechanical systems for performing vehicle functions traditionally achieved by mechanical link ...
throttle valve; exhaust manifold integrated into cylinder head; hot-V configuration
: 3.0 TFSI: twin-scroll single-turbo charged
: 2.9 TFSI:
twin-turbo
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case ...
charged
;fuel system: common rail
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) high-pressure
direct injection
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
;: 3.0 TFSI variants
: at 5,400-6,400 rpm; at 1,340-4,900 rpm - unknown/Porsche variant
: at 5,000-6,400 rpm; at 1,370-4,500 rpm - CZSE(2017-2018)/DR(2019-)
: at 5,400-6,400 rpm; at 1,370-4,500 rpm - CWGD
;: 2.9 TFSI variants
: at 5,250-6,500 rpm; at 1,750-5,000 rpm - unknown/Porsche variant
: at 5,650-6,600 rpm; at 1,750-5,500 rpm - unknown/Porsche variant
: at 5,700-6,700 rpm; at 1,900-5,000 rpm - DECA
;production: Audi Hungaria Zrt. in
Győr
Győr ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names of European cities in different languages: E-H#G, names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Győr-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia, Western Transdanubia ...
;applications
: 3.0 TFSI():
Porsche Panamera/Panamera 4 (2nd gen)
: 2.9 TFSI():
Porsche Panamera 4 E-Hybrid (2nd gen)
: CZSE/DR:
Audi A6 (C8),
Audi A7 (C8/4K8),
Audi A8 (D5),
Audi Q8
The Audi Q8 is a mid-size luxury crossover SUV coupé made by Audi that was launched in 2018. It is the flagship of the Audi SUV line, and is being produced at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant.
Overview
BMW launched its coupe SUV in 2008, the B ...
,
Porsche Cayenne/Cayenne E-Hybrid (3rd gen),
Volkswagen Touareg (3rd gen)
: CWGD:
Audi S4 (B9, B9.5 excluding European models),
Audi S5 (B9/F5, B9.5 excluding European models),
Audi SQ5 (FY, excluding European facelited models)
: 2.9 TFSI():
Porsche Panemera 4S (2nd gen),
Porsche Cayenne S (3rd gen)
: DECA:
Audi RS4 (B9),
Audi RS5 (B9/F5),
Audi S6 (C8, excluding European models),
Audi S7 (C8/4K8, excluding European models)
;references
audi.deporsche.comvolkswagen.de
3.2 VR6 24v
This
VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
was often badged as a ''"V6"'' in Audi models
;identification: parts code prefix: 022, ID codes: CBRA
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 15°
VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.88:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 531.5 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 11.3:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; seven main bearings; die-forged steel crankshaft, cast aluminium alloy oil sump
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four unequal-length valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, simplex roller chain-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC – one camshaft for all exhaust valves, and one for all intake valves), continuous timing adjustment
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
(52 degrees on the inlet, 22 degrees on the exhaust)
;aspiration: hot-film
air mass meter, electronic
drive by wire
Drive by wire, DbW, by-wire, steer-by-wire, fly-by-wire or x-by-wire technology in the automotive or aviation industry is the use of electrical or electro-mechanical systems for performing vehicle functions traditionally achieved by mechanical link ...
throttle valve, one piece plastic with variable runner length switching by way of an ecu controlled valve intake manifold, two cast iron exhaust manifolds
;fuel system, ignition system, engine management: common rail multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
with six intake manifold-sited fuel injectors; mapped direct ignition with six
NGK longlife spark plugs and six individual single spark coils; electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU)
;EWG-rated motive power, ID code & application: — BMF —
Volkswagen Industrial Motor
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
(
LPG)
(05/04->)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes & applications
: at 6,200 rpm; at 3,200 rpm — BDL —
Volkswagen Transporter (T5)
The Volkswagen Transporter T5 range is the fifth generation of Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles (VWCV/VWN) 'Transporter' series of medium-sized light commercial vehicles and the people mover Caravelle/Multivan range. It was launched 6 October 20 ...
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,950 rpm — BKK —
Volkswagen Transporter (T5)
The Volkswagen Transporter T5 range is the fifth generation of Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles (VWCV/VWN) 'Transporter' series of medium-sized light commercial vehicles and the people mover Caravelle/Multivan range. It was launched 6 October 20 ...
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,500–3,000 rpm — BFH —
VW Golf Mk4 R32 (US)
: at 6,250 rpm; at 2,800–3,200 rpm — BML —
VW Golf Mk4 R32 (Australia)
: at 6,300 rpm; at 2,500–3,000 rpm — BDB, BHE, BMJ, BPF, BUB —
Audi A3
The Audi A3 is a subcompact executive/small family car (C-segment) manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi AG since September 1996, currently in its fourth generation.
The first two generations of the Audi A3 were based on the ...
(BDB: 07/03-08/04, BMJ: 09/04-10/05, BUB: 11/05-05/09),
Audi TT (BHE: 07/03-06/06, BPF: 05/04-05/06, BUB: 08/06-06/10),
VW Golf Mk5 R32,
Porsche Cayenne
The Porsche Cayenne is a series of mid-size luxury crossover sport utility vehicles manufactured by the German automaker Porsche since 2002 (Type 9PA or E1), with North American sales beginning in 2003. It is the first V8-engined vehicle built b ...
;references:
3.2 VR6 24v FSI (EA390)
;identification: parts code prefix: 03H, ID code: AXZ
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 10.6°
VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
; bore: x stroke: 90.9mm, stroke ratio: 0.95:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 531.5 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 12:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; seven main bearings; die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four unequal-length valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, simplex roller chain-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC – one camshaft for all exhaust valves, and one for all intake valves), continuous timing adjustment
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
(52 degrees on the inlet, 22 degrees on the exhaust)
;aspiration: hot-film
air mass meter, electronic
drive by wire
Drive by wire, DbW, by-wire, steer-by-wire, fly-by-wire or x-by-wire technology in the automotive or aviation industry is the use of electrical or electro-mechanical systems for performing vehicle functions traditionally achieved by mechanical link ...
throttle valve, one-piece cast aluminium alloy intake manifold, two cast iron exhaust manifolds
;fuel system:
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) high-pressure direct injection with two common rails
;ignition system: mapped direct ignition with six individual ignition coils
;DIN-rated motive power & torque output:
;application:
VW Passat B6 3.2 FSI (09/05->),
VW Phaeton
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
3.2 V6 24v FSI
;identification:parts code prefix: ???, ID codes: AUK, BKH, BYU, (191 kW – BPK)
;engine configuration: 90°
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik ...
; cylinder spacing, compression ratio: 12.5:1 (184 kW: 11.3:1)
;engine displacement etc.
:; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.91:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 520.4 cc per cylinder
:; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.92:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 532.8 cc per cylinder
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous monoblock low-pressure chill gravity die cast
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg) with a closed-deck design, mechanically stripped hard silicon crystal integral liners, honed under simulated mechanical stress; die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, chain-driven double overhead camshaft, continuous adjusting
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts
;fuel system: common rail
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) high-pressure
direct injection between
;aspiration & exhaust system: variable intake manifold, two ceramic
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s
;dimensions: length: , width: , mass:
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
: at 6,300 rpm; at 2,500–3,000 rpm
: at 6,500 rpm; at 3,250 rpm, 90% available between 1,900–5,900 rpm, 7,200 rpm max —
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
: at 6,500 rpm — Audi A8
: at 6,500 rpm; at 3,200–5,000 rpm — Audi A4, Audi A5
;applications: 2005
Audi A8
The Audi A8 is a full-size luxury sedan manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi since 1994. Succeeding the Audi V8, and now in its fourth generation, the A8 has been offered with both front- or permanent all-wheel drive—and in s ...
,
Audi A6
The Audi A6 is an executive car made by the German automaker Audi. Now in its fifth generation, the successor to the Audi 100 is manufactured in Neckarsulm, Germany, and is available in saloon and estate configurations, the latter marketed by Aud ...
,
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group.
The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first ...
,
Audi A5
The Audi A5 is a series of compact executive coupe cars produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi since June 2007. The A5 range additionally comprises the coupe, cabriolet, and "Sportback" (a five-door liftback with a fastback roofline) v ...
;references:
3.6 VR6 24v FSI (EA390)
;identification: parts code prefix: 03H
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 10.6°
VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.92:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 599.7 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 11.4–12.0:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: grey cast iron; die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder head & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four unequal-length valves per cylinder, 24 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, simplex roller chain-driven double overhead camshaft (DOHC – one camshaft for all exhaust valves, and one for all intake valves), continuous timing adjustment
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
(52 degrees on the inlet, 22 degrees on the exhaust)
;aspiration: hot-film
air mass meter, electronic
drive by wire
Drive by wire, DbW, by-wire, steer-by-wire, fly-by-wire or x-by-wire technology in the automotive or aviation industry is the use of electrical or electro-mechanical systems for performing vehicle functions traditionally achieved by mechanical link ...
throttle valve, two-piece cast aluminium alloy intake manifold, two cast iron exhaust manifolds
;fuel system:
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) high-pressure direct injection with two common rails
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,500–5000 rpm; Compression Ratio: 11.4:1 — CDVA —
Škoda Superb
The Škoda Superb is a large family car that has been produced by the Czech car manufacturer Škoda Auto since 2001.
The first generation of the modern Superb, produced from 2001 to 2008, was based on the VW B5 PL45+ platform. The second gener ...
4x4 DSG and
Volkswagen Eos
The Volkswagen Eos was a sport compact cabriolet coupé produced by the German automaker Volkswagen from 2006 to 2015. Assembled at AutoEuropa in Portugal, it was a convertible only compact coupé introduced as the successor of the Volkswagen Gol ...
3.6
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,750 rpm; — BLV —
Volkswagen Passat (B6 and B7) (North America and Middle-East only)
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,500–5000 rpm; — CDVB —
Volkswagen Passat (NMS)
The Volkswagen Passat for the North American and Chinese markets (internally designated ''Volkswagen New Midsize Sedan'', or ''NMS'' while under development) is a mid-size sedan that debuted in January 2011 at the Detroit Auto Show. It replaced ...
(North America and Middle-East only)
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,500–5000 rpm; — CDVC/CDVD —
Volkswagen Atlas
The Volkswagen Atlas is a mid-size crossover SUV manufactured by the German automaker Volkswagen since 2017. Developed mainly for the North American and Chinese market, the vehicle is based on the Volkswagen Group MQB platform. Outside the US and ...
(North America, Russia and Middle-East)
: at 6,200 rpm; at 3,500 rpm; — CHNA/CMVA —
Volkswagen Phaeton
The Volkswagen Phaeton ( ) (''Typ'' 3D) is a full-size luxury sedan/saloon manufactured by the German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle. Introduced at the 2002 Geneva Motor Show, the ...
: at 6,200 rpm; at 3,500 rpm; — CGRA/CMTA —
Volkswagen Touareg
The Volkswagen Touareg (German pronunciation: ) is a car produced by German automaker Volkswagen Group since 2002 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant. A five-seater mid-size luxury crossover SUV, the vehicle was named after the nomadic Tuareg peo ...
: at 6,600 rpm; at 2,400–5,300 rpm — BWS —
Volkswagen Passat R36 (B6) (Europe, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, Middle-East)
: at 6,600 rpm; at 2,400–5300 rpm; — CNNA —
Volkswagen CC
The Volkswagen CC, originally marketed as the Volkswagen Passat CC in its first generation, is a variant of the Volkswagen Passat that trades headroom and cargo space for a coupé-like profile and sweeping roofline. The CC debuted in January 200 ...
(North America, Russia and Middle-East)
;applications:
VW Passat B6 3.6 FSI (BLV: 09/05->, BWS: 04/07-05/07),
VW Passat CC (BLV: 06/08->, BWS: 05/08->, CNNA: 01/12->),
VW Phaeton
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-W ...
,
VW Touareg
The Volkswagen Touareg (German pronunciation: ) is a car produced by German automotive industry, automaker Volkswagen Group since 2002 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant. A five-seater Executive car, mid-size luxury crossover SUV, the vehicle was ...
,
Porsche Cayenne
The Porsche Cayenne is a series of mid-size luxury crossover sport utility vehicles manufactured by the German automaker Porsche since 2002 (Type 9PA or E1), with North American sales beginning in 2003. It is the first V8-engined vehicle built b ...
,
Audi Q7
The Audi Q7 is a mid-size luxury crossover SUV made by the German manufacturer Audi, unveiled in September 2005 at the Frankfurt Motor Show. Production of this seven-seater SUV began in the autumn of 2005 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant in ...
;references:
Eight-cylinder petrols
Of their eight-cylinder petrol engines, all ''
Volkswagen Group V8 engines'' are primarily constructed from a lightweight cast
aluminium alloy
An aluminium alloy (or aluminum alloy; see spelling differences) is an alloy in which aluminium (Al) is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin, nickel and zinc. There are two principal ...
cylinder block (crankcase) and cylinder heads. They all use
multi-valve
In automotive engineering a multi-valve or multivalve engine is one where each cylinder has more than two valves. A multi-valve engine has better breathing and may be able to operate at higher revolutions per minute (RPM) than a two-valve engine ...
technology, with the valves being operated by
two
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
overhead camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion cha ...
s per
cylinder bank
The engine configuration describes the fundamental operating principles by which internal combustion engines are categorized.
Piston engines are often categorized by their cylinder layout, valves and camshafts. Wankel engines are often categorize ...
(sometimes referred to as 'quad cam'). All functions of engine control are carried out by varying types of
Robert Bosch GmbH
Robert Bosch GmbH (; ), commonly known as Bosch and stylized as BOSCH, is a German multinational engineering and technology company headquartered in Gerlingen, Germany. The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886. Bosch is 9 ...
Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
s.
These V8 petrol engines initially were only used in cars bearing the
Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
Th ...
marque
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create an ...
, but are now also installed in
Volkswagen Passenger Cars 'premium models'. They are all
longitudinally orientated, and with the exception of the
Audi R8
The Audi R8 is a mid-engine, 2-seater sports car, which uses Audi's trademark quattro permanent all-wheel drive system. It was introduced by the German car manufacturer Audi AG in 2006.
The car is exclusively designed, developed, and manufactu ...
, are
front-mounted.
4.2 V8 FSI 32v

Based on the existing Audi 40 valve V8, this new engine is heavily revised over its predecessor, with all-new components including: crankshaft, connecting rods and pistons, cylinder heads and valvetrain, oil and cooling system, intake and exhaust system, and engine management system. It is available in two versions; a basic or 'comfort' version, first used in the Audi Q7; and a sports-focussed high-revving version, with features borrowed from motorsport, for the
B7 RS 4 quattro and the
R8. This is the first eight-cylinder road car engine to use
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI), which was successfully developed by Audi in their Le Mans winning
R8 racing car. The
5.2 V10 FSI was developed directly from this V8 engine.
;identification: parts code prefix/variant: 079.D
;displacement & configuration: 90° V8 engine;
cylinder bank
The engine configuration describes the fundamental operating principles by which internal combustion engines are categorized.
Piston engines are often categorized by their cylinder layout, valves and camshafts. Wankel engines are often categorize ...
offset; cylinder spacing; bore and stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.91:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 520.4 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 12.5:1, firing order: 1–5–4–8–6–3–7–2; water:oil lubricant cooler (RS 4/R8 utilises an additional thermostatically controlled air:oil cooler); Q7 and RS 4 utilise a
wet sump
Within piston engines, a wet sump is part of a lubrication system whereby the crankcase sump is used as an integral oil reservoir. An alternative system is the dry sump, whereby oil is pumped from a shallow sump into an external reservoir.Wet sum ...
system (RS 4 with additional longitudinal axis flapped baffles controlled by lateral g-force), R8 uses
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conve ...
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous monoblock low-pressure chill gravity die casting
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg) with a closed-deck design, mechanically stripped hard silicon crystal integral liners, honed under simulated mechanical stress; reinforced by a cast lower crankcase alloy bedplate (AlSi17Cu4Mg) mimicking a ladder-frame design, and including five GGG50 nodular cast iron press-fit main bearing caps each attached by four bolts; overall length, cylinder block height; two-stage 3/8" simplex roller chain and gear driven 'accessory drive' which includes the oil pump, water pump, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor; baffle-plate sump
;crankshaft, connecting rods and pistons: die-forged and tempered high alloy steel (42CrMoS4) 90° crankshaft with diameter and width main bearing journals and diameter and width big end bearing journals; long high strength forged cracked trapezoidal connecting rods (36MnVS4 in basic engine, ultra high strength 34CrNiMo8 in RS 4/R8 with more restrictive geometry tolerances); forged aluminium pistons with shaped piston crowns designed to impart charged volume tumbling effect for fully homogeneous air/fuel charge
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy, partition-plate horizontally divided intake ports producing a tumble effect (larger cross-section on RS 4/R8); four valves per cylinder: chrome-plated solid-stem (hollow-stem on RS 4/R8) intake valves, and chrome-plated sodium-filled hollow-stem exhaust valves, both with valve lift (longer valve lift on RS 4/R8), 32 valves total; lightweight low-friction roller finger cam followers (uprated with
peened rollers on RS 4/R8) with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, double overhead camshafts (each a hollow tube composite) on each cylinder bank, driven from the flywheel side via a two-stage chain drive using three 3/8" simplex roller chains (sleeve-type on RS 4/R8), valve opening (in crank angle degrees) 200 intake (230 for RS 4/R8) and 210 e exhaust (230 for RS 4/R8); valve overlap facilitates integral exhaust gas recirculation; continuous hydraulic vane-adjustable variable valve timing for intake and exhaust camshafts with up to 42 degrees adjustment, each controlled via information from
Hall sensor
In architecture, a hall is a relatively large space enclosed by a roof and walls. In the Iron Age and early Middle Ages in northern Europe, a mead hall was where a lord and his retainers ate and also slept. Later in the Middle Ages, the grea ...
s,
Audi "RS" 'red' plastic cam covers on RS 4, 'anthracite' plastic on R8
;aspiration: two single-entry air filters each with hot-film air mass flow meters (Q7), or triple-entry single air filter with single hot-film air mass meter (RS 4), or double-entry dual-element single air filter with two hot-film air mass flow meters (R8); single (Q7 & RS 4) or twin (R8) cast alloy
throttle body
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
electronically controlled Bosch E-Gas
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves (Bosch diameter on Q7, Pierburg diameter on RS4), two-stage four-piece gravity die-cast (Q7) (sand-cast on RS 4/R8) magnesium-aluminium alloy variable length intake manifold with electronically map-controlled silicon tipped tract-length flaps along with tumble flaps inducing a swirling movement in the drawn air (RS 4 & R8 do not use a variable tract-length intake manifold)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled, (Q7 returnless, RS 4 return to tank); fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): two inlet camshaft double-cam driven single-piston high-pressure injection pumps maintaining a pressure between in the two stainless steel
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel distributor rails, eight combustion chamber sited
direct injection solenoid-controlled 65 volt single-hole sequential fuel injectors with integrated swirl plates; 98
RON/ROZ (93
AKI) EuroSuperPlus (premium) unleaded recommended for maximum performance and fuel economy (95 RON (91 AKI) may be used, but will reduce performance and worsen fuel economy)
;ignition system & engine management: mapped direct ignition with centrally mounted longlife spark plugs and eight individual direct-acting single spark coils;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED 9.1.1 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU) (two MED 9.1 ECUs in the RS 4 and R8, working on the 'master and slave' concept due to the high revving nature of the engine), four knock sensors, EU4 emissions standard, map-controlled coolant thermostat (Q7 only), additional electric after-run coolant pump with two additional side-mounted radiators (RS 4/R8), water-cooled
alternator
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Go ...
, two map-controlled radiator fans
;exhaust system: vacuum-controlled secondary air injection to assist cold start operation; air-gap insulated exhaust manifold per cylinder bank (Q7), or 4-into-2-into-1 fan-branch exhaust manifold per cylinder bank to minimise reverse pulsation of expelled exhaust gases (RS 4), or fan branch manifold with integrated
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
per cylinder bank; two close-coupled and two main underfloor catalytic converters – ceramic on Q7, high-flow metallic on RS 4, or main catalytic converter integrated into transverse main rear silencer with quad outlets; four heated oxygen (lambda) sensors (broadband upstream, nonlinear downstream) monitoring pre- and post-catalyst exhaust gases; siamesed absorption-type middle silencer (Q7 with crossover) and siamesed rear silencer, separate rear silencers on RS 4 with vacuum-operated flap valves
;dimensions: Q7 (for auto transmission with plate-type flywheel): approx. , RS4 (for 6-speed manual with
dual-mass flywheel
A dual-mass flywheel (DMF or DMFW) is a rotating mechanical device that is used to provide continuous energy (rotational energy) in systems where the energy source is not continuous, the same way as a conventional flywheel acts, but damping any ...
): approx.
;DIN-rated power & torque outputs, ID codes, applications
: at 6,800 rpm; at 3,500 rpm, 85% available from 2,000 rpm — BAR:
Audi Q7
The Audi Q7 is a mid-size luxury crossover SUV made by the German manufacturer Audi, unveiled in September 2005 at the Frankfurt Motor Show. Production of this seven-seater SUV began in the autumn of 2005 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant in ...
(03/06-05/10),
Volkswagen Touareg
The Volkswagen Touareg (German pronunciation: ) is a car produced by German automaker Volkswagen Group since 2002 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant. A five-seater mid-size luxury crossover SUV, the vehicle was named after the nomadic Tuareg peo ...
(06/06-05/10); BVJ:
Audi C6 A6 (05/06-08/11),
Audi D3 A8 (06/06-07/10)
: at 7,000 rpm — CAU:
Audi S5
The Audi S5 is one of two high-performance variants of Audi's A5. It is also the coupé, cabriolet, and five-door fastback sedan versions of the fourth-generation (B8) Audi S4 saloon and estate models.
Like all Audi "S" cars, they are only ...
(06/07-03/12)
: at 7,800 rpm; at 5,500 rpm, 90% available between 2,250 and 7,600 rpm, 8,250 rpm
rev limiter
A rev limiter is a device fitted in modern vehicles that have internal
combustion engines. They are intended to protect an engine by restricting its maximum rotational speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
Rev limiters are pre-set by th ...
— BNS:
Audi RS 4 (B7) (09/05-06/08); BYH:
Audi R8
The Audi R8 is a mid-engine, 2-seater sports car, which uses Audi's trademark quattro permanent all-wheel drive system. It was introduced by the German car manufacturer Audi AG in 2006.
The car is exclusively designed, developed, and manufactu ...
(04/07-09/10)
;references:
Awards
:was placed in the 2005 and 2006 annual list of
Ward's 10 Best Engines 10 of the World's best engines is an annual list of the ten ''"''best''"'' automobile engines available in the U.S. market, that are selected by ''Ward's AutoWorld'' magazine. The list was started in 1994 for Model Year 1995, and has been drawn eve ...
4.2 V8 40v
;identification: parts code prefix: 079
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V8 engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V8 engine was produced by the French Antoinette company in 1904, developed and us ...
; cylinder spacing; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 1.1:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 521.5 cc per cylinder
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous
monobloc low-pressure gravity die cast
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg) with a closed-deck design, mechanically stripped hard silicon crystal integral liners, honed under simulated mechanical stress; five main bearings; die-forged steel crankshaft
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy, five valves per cylinder, 40 valves total; lightweight low-friction roller cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, roller chain-driven double overhead camshafts
;aspiration: synthetic material two-stage
variable intake manifold
;fuel system & engine management: two linked common rail fuel distributor rails, multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
with eight intake manifold-sited fuel injectors;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
ME 7.1.1. electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU); 98
RON/ROZ (93
AKI) EuroSuperPlus (premium) unleaded recommended for maximum performance and fuel economy
;exhaust system: two multi-stage
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s
;dimensions: length: , mass:
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes
: at 6,600 rpm; at 3,500 rpm, 6,800 rpm max — Audi A6, BAT, A8: BFM (BFM engine is belt driven)
: at 6,200 rpm; at 2,700–4,600 rpm, 6,500 rpm max — Audi A6 allroad: BAS
: at 7,000 rpm; at 3,500 rpm — Audi S4: BBK (03/03-03/09)
: at 7,200 rpm; at 3,000 rpm — Audi S4: BHF (03/03-03/09 – US/Korea only)
: at 6,500 rpm; at 2,800-3,700 rpm — Volkswagen Phaeton: BGH, BGJ (Belt driven)
;applications:
Audi B6 S4,
Audi B7 S4,
Audi C5 A6 allroad (BAS: 07/02-08/05),
Audi C6 A6 (BAT: 05/04-05/06),
Audi A8
The Audi A8 is a full-size luxury sedan manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi since 1994. Succeeding the Audi V8, and now in its fourth generation, the A8 has been offered with both front- or permanent all-wheel drive—and in s ...
(BFM: 10/02-07/10),
Volkswagen Phaeton
The Volkswagen Phaeton ( ) (''Typ'' 3D) is a full-size luxury sedan/saloon manufactured by the German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle. Introduced at the 2002 Geneva Motor Show, the ...
(BGJ: 05/03-07/03, BGH: 08/03-05/10)
;reference:
Awards
:was placed in the 2004 annual list of
Ward's 10 Best Engines 10 of the World's best engines is an annual list of the ten ''"''best''"'' automobile engines available in the U.S. market, that are selected by ''Ward's AutoWorld'' magazine. The list was started in 1994 for Model Year 1995, and has been drawn eve ...
4.0 TFSI
This engine is part of Audi's modular 90° V6/V8 engine family. It shares its bore and stroke, 90° V-angle, and 90mm cylinder spacing with the Audi V6. The earlier V6 engines (EA837) used an Eaton TVS Supercharger instead of turbocharger(s). In 2016, Audi and Porsche released a new turbocharged V6 engine they dubbed EA839. These 2.9L (biturbo) & 3.0L (single turbo) V6 engines share the 4.0T TFSI V8's “hot vee” design, meaning the turbo(s) are placed in the Vee of the engine (between each bank of cylinders) instead of on the outside of each cylinder bank. This allows the turbocharger(s) to produce boost pressure more quickly as the path the exhaust gases travel is much reduced. It also aids in getting the engine's emissions hardware up to temperature more quickly. As with the V6, the V8 is used in various Audi and Porsche models, but the V8 also finds use in Bentley and Lamborghini vehicles.
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V8 engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V8 engine was produced by the French Antoinette company in 1904, developed and us ...
; cylinder spacing; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.95:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 499.1 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1
;fuel system;
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): Central-Overhead Injectors
;exhaust system: two twin-scroll turbo chargers and twin air- and water-cooled intercoolers
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID codes, applications
: at 5,500 rpm; from 1,400 rpm to 5,400 rpm— CEUC:
Audi S6 C7,
S7, CEUA:
A8 D4
: at 5,800 rpm; from 1,400 rpm to 5,300 rpm— CTGA:
A8 D4,
A8 D5
: at 6,200 rpm; from 1,700 rpm to 5,500 rpm— DDTA: Audi
S8 D4 (overboost to 750 Nm), CWUC:
Audi RS7 performance(C7), Audi
RS6 performance (C7)
: at 5,700 rpm; from 1,750 rpm to 5,500 rpm— CRDB, CWUB: Audi
RS6 C7 and
RS7 C7
: at 5,500 rpm; from 1,800 rpm to 4,500 rpm— CXYA:
A8 D5,
Porsche Panamera GTS
: at 5,500 rpm; from 1,800 rpm to 4,500 rpm in
Porsche Panamera GTS (Facelifted)
: at 6,000 rpm; from 1,700 rpm to 5,400 rpm in
Bentley Continental GT V8 and
Flying Spur V8
: at 6,000 rpm; at 1,750 rpm to 5,500 rpm in
Bentley Continental GT V8 S
: at 5,500 rpm; from 2,000 rpm to 4,000 rpm in Audi
SQ7 and
SQ8
: from 5,750 rpm to 6,000 rpm; from 1,960 rpm to 4,500 rpm in
Porsche Panamera Turbo, Turbo S E-Hybrid,
Bentley Continental GT V8 (2019–) and
Flying Spur (2019-)
: at 6,000 rpm; from 2,050 rpm to 4,500 rpm in Audi
S8 D5
: from 5,750 rpm to 6,000 rpm; from 1,960 rpm to 4,500 rpm in
Porsche Panamera Turbo S E-Hybrid (Facelifted)
: from 6,000 rpm to 6,250 rpm; from 2,050 rpm to 4,500 rpm in Audi
RS6 C8 and
RS7 C8
: at 6,000 rpm; from 2,200 rpm to 4,500 rpm in Audi
RS Q8
: at 6,000 rpm; from 2,300 rpm to 4,500 rpm in Audi
RS6 Avant performance (C8) and
RS7 performance (C8)
: from 5,750 rpm to 6,000 rpm; from 1,960 rpm to 4,500 rpm in
Porsche Panamera Turbo S
: at 6,000 rpm; in
Lamborghini Urus
The Lamborghini Urus is a high performance luxury SUV manufactured by Italian automobile manufacturer Lamborghini. It was unveiled on 4 December 2017 and was put on the market for the 2018 model year. The name comes from the urus, the ancestor ...
: at 6,000 rpm; in Porsche Cayenne Coupé Turbo GT
Audi version of the engine includes electronic monitoring of the oil level, while Bentley engine includes a dipstick for oil check. In addition, the Bentley engine uses switchable hydraulic mounts instead of Audi's active electrohydraulic engine mounts.
6.75 V8 biturbo (Bentley)
This 6.75 litre V8 is a legacy engine, developed by
Rolls-Royce Limited
Rolls-Royce was a British luxury car and later an aero-engine manufacturing business established in 1904 in Manchester by the partnership of Charles Rolls and Henry Royce. Building on Royce's good reputation established with his cranes, they ...
before the takeover of
Bentley Motors Limited
Bentley Motors Limited is a British designer, manufacturer and marketer of luxury cars and SUVs. Headquartered in Crewe, England, the company was founded as Bentley Motors Limited by W. O. Bentley (1888–1971) in 1919 in Cricklewood, North ...
by the German
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
, but still used during their ownership.
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V8 engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V8 engine was produced by the French Antoinette company in 1904, developed and us ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 1.05:1 – oversquare/short-stroke, 843.5 cc per cylinder
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy, single central camshaft
;
cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas in more modern ov ...
s &
valvetrain
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) ...
: cast aluminium alloy, two valves per cylinder, 16 valves total,
overhead valve
An overhead valve (OHV) engine, sometimes called a ''pushrod engine'', is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier flathead engines, where the valves were located be ...
(OHV) with pushrods
;aspiration:
biturbo
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case ...
– one
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
per cylinder bank
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
: at 4,100 rpm; at 3,250 rpm
: at 4,200 rpm; at 3,300 rpm — R
: at ?,??? rpm; — Bentley Brooklands, Bentley Mulsanne Speed
;applications: 2005
Bentley Arnage
The Bentley Arnage is a full-size luxury car manufactured and marketed by Bentley Motors in Crewe, England, from 1998 to 2009. The Arnage and its Rolls-Royce-branded sibling, the Silver Seraph, were introduced in the spring of 1998. They were ...
, 2006
Bentley Azure
The Bentley Azure is a four-seater convertible grand tourer produced by British automobile manufacturer Bentley Motors. The first version debuted in 1995 on the Bentley Continental R platform and was made until 2003. After a three-year break, ...
, 2008
Bentley Brooklands
Bentley Brooklands is the name of two distinct models produced by British automobile manufacturer Bentley Motors. The first Brooklands was a full-size luxury saloon, launched in 1992 to replace the Bentley Mulsanne and in turn succeeded by the ...
, 2010
Bentley Mulsanne
;references:
German press release: auto katalog 2006; auto, motor und sport
Ten-cylinder petrols
5.0 V10 40v TFSI (Audi C6 RS6)
This 'Audi V10 TFSI' – a 5.0
litre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3 ...
V10
A V10 engine is a ten-cylinder piston engine where two banks of five cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V10 engines are much less common than V8 and V12 engines. Several V10 diesel engines have been pr ...
'
biturbo
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case ...
' petrol engine is one of the most powerful engines fitted into any
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
automobile. From its DIN-rated maximum power output of , this engine generates a
specific power
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
output of per litre displacement.
;identification: parts code prefix/variant: 07L.B, ID code: BUH
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V10 engine
A V10 engine is a ten-cylinder piston engine where two banks of five cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V10 engines are much less common than V8 and V12 engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder pis ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.95:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 499.1 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.5:1;
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conve ...
lubrication system, simplex roller chain and gear-driven external ancillaries including combined oil pump and
centrifugal coolant pump, two oil coolers – oil:water and
thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint.
Thermostats are used in any device or system tha ...
ically controlled oil:air, water-cooled
alternator
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Go ...
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous
monoblock
Monoblock can refer to:
*A type of air conditioner
*A monoblock LNB
* Monoblock PC, a computer workstation
*A mono (one channel) audio power amplifier
*In photography, another name for a monolight, a type of electronic flash with the electronics ...
low-pressure chill die cast
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg); reinforced by a cast alloy bedplate with six integral GGG50 grey cast iron main bearing caps each affixed by four bolts, web-reinforced inner vee; inner-vee
balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
T ...
eliminating first degree inertial forces, cylinder bore spacing, cylinder bank offset; die-forged steel
crossplane
The crossplane or cross-plane is a crankshaft design for piston engines with a 90° angle (phase in crank rotation) between the crank throws. The crossplane crankshaft is the most popular configuration used in V8 road cars.
Aside from the V8 alr ...
crankshaft with pins shared by opposing pistons (contrary to the 5.2 V10 from the S6), cast aluminium alloy oil sump
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; partition-plate horizontally divided intake ports designed to induce swirl-effect during induction stroke, four valves per cylinder, 40 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, double overhead camshaft driven from the rear
flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, ass ...
end in a relay method using four roller chains, continuous adjusting
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts, plastic-composite cam covers
;aspiration: two air filters, two hot-film
air mass meters, two cast alloy
throttle bodies each with
electronically controlled Bosch "E-Gas"
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves, three-part sand-cast
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
alloy fixed tract-length intake manifold incorporating electronically controlled vacuum-actuated two-stage tumble flaps inducing a swirling movement in the drawn air, '
biturbo
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case ...
': two parallel water-cooled (with reverse flow electric after-run pump)
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
s integrated into exhaust manifold with electronically controlled vacuum-actuated excess pressure regulation giving a maximum boost of , two side-mounted
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
s (SMICs)
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled; two fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel lift pumps,
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): two returnless single-piston high-pressure FSI injection pumps driven via roller tappet from a double cam lobe on the inlet camshaft – maintaining a maximum pressure of in the two separate stainless steel common rail fuel distributor rails (one rail per cylinder bank), ten combustion chamber sited
direct injection solenoid-controlled sequential fuel injectors
;ignition system & engine management: mapped direct ignition with centrally mounted spark plugs and ten individual direct-acting single spark coils; two
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
ME 9.1.2 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
s (ECUs) working on the master/slave concept due to the high rev limit
;exhaust system: two close-coupled and two main underfloor
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s, eight
lambda sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or sond, is an electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed.
It was de ...
s
;DIN-rated motive power & torque output:BUH: at 6,250–6,700 rpm; at 1,500–6,250 rpm
;application:
Audi C6 RS6 5.0 TFSI quattro (04/08-08/10)
;reference:
,
5.2 V10 40v FSI (C6 S6/D3 S8)
A first in
Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
Th ...
's history, this new generation high-performance
V10 engine
A V10 engine is a ten-cylinder piston engine where two banks of five cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V10 engines are much less common than V8 and V12 engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder pis ...
is based on
Audi's V8 FSI engines, and retains the same fundamental design principals of the
V8 FSI, including the crankcase, cylinder heads, valvetrain, fuel system and intake manifold. However, an all new crankshaft,
balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
T ...
, double-chambered intake manifold with dual throttle valves, exhaust manifold, and ECU—are all unique to the V10. As part of the new V10 engine development, specific emphasis was placed on 'refinement', 'comfort' and 'sportiness' – as required for installation in Audi high-performance luxury cars. As well as gaining two additional cylinders compared to the V8, it has been bored by an extra two millimetres, and also shares the 90 degree (°) cylinder bank angle of the recent Audi
V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder b ...
s. Audi continue to use the
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI) technology, originally developed in the
Audi R8 LMP endurance race cars.
This engine is often, but incorrectly, referred to as a derivative of the Gallardo's original 5.0-litre
Lamborghini V10
The Lamborghini V10 is a ninety degree (90°) V10 petrol engine which was developed for the Lamborghini Gallardo automobile, first sold in 2003.
Developed by Lamborghini, for use in the Gallardo, and the first engine developed for Automobili Lam ...
, which was also developed under the Volkswagen Group ownership. However, the subsequent
5.2 V10 FSI installed in the Gallardo LP560 and
Audi R8 V10 is fundamentally identical to this Audi unit, save for a stronger crankshaft with solid main pin design, forged pistons, dry sump oiling system, different intake and exhaust valves, and engine management systems.
;identification: parts code prefix: 07L
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V10 engine
A V10 engine is a ten-cylinder piston engine where two banks of five cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V10 engines are much less common than V8 and V12 engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder pis ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.91:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 520.4 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 12.5:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous
monoblock
Monoblock can refer to:
*A type of air conditioner
*A monoblock LNB
* Monoblock PC, a computer workstation
*A mono (one channel) audio power amplifier
*In photography, another name for a monolight, a type of electronic flash with the electronics ...
low-pressure chill die cast
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg); reinforced by a cast alloy bedplate (AlSi12Cu1) with six integral GGG50 grey cast iron main bearing caps each affixed by four bolts, long, wide, approx. in weight, inner-vee sited chain-driven contra-rotating spheroidal cast iron
balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
T ...
eliminating first degree inertial forces, cylinder bore spacing, cylinder bank offset
;crankshaft, connecting rods and pistons: die-forged steel crankshaft, with 18 degree crankpin offset to achieve a 72° crank angle even firing interval; high strength cracked trapezoidal connecting rods (36MnVS4); Kolbenschmidt cast aluminium pistons with shaped piston crowns designed to impart charged volume tumbling effect for fully homogenous air/fuel charge, skirt with iron liner
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; partition-plate horizontally divided intake ports, four valves per cylinder, intake valves and sodium-filled exhaust valves, 40 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, hollow tube composite double overhead camshafts driven from the flywheel side via a two-stage chain drive utilising three 3/8" simplex roller chains, continuous vane-adjustable
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts with up to 42 degrees adjustment
;aspiration: two air filters, two hot-film
air mass meters, two cast alloy
throttle bodies each with
electronically controlled throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves, two-stage four-piece die cast
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
alloy
variable tract-length intake manifold utilising electronically map controlled silicon tipped tract length flaps along with tumble flaps inducing a swirling movement in the drawn air
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; two fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pumps,
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): two inlet camshaft double-cam driven single-piston high-pressure injection pumps maintaining a pressure between in the two stainless steel
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel distributor rails with an over-pressure release valve set to , ten combustion chamber sited
direct injection solenoid-controlled 65 volt single-hole sequential fuel injectors with integrated swirl plates
;ignition system & engine management: mapped direct ignition with centrally mounted spark plugs and ten individual direct-acting single spark coils; two
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED 9.1 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
s (ECUs) working on the 'master and slave' concept due to the high revving nature of the engine, four knock sensors, EU4 emissions standard
;exhaust system: vacuum-controlled secondary air injection into exhaust ports to assist cold start operation, 2-1-2 branch exhaust manifold per cylinder bank ( nominal length) to minimise reverse pulsation of expelled exhaust gases, four close-coupled 600-cell ceramic
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s, eight heated oxygen (lambda) sensors monitoring pre- and post-catalyst exhaust gases
;dimensions: approx. ( less than the
BMW S85 with its bore spacing); length: , width: , height: with all components
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, applications, ID codes
:Audi S6 — BXA: at 6,800
rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
; at 3,000–4,000 rpm, (over between 2,500 and 5,500 rpm)
:Audi S8 — BSM: at 7,000 rpm; at 3,500 rpm (90% available from 2,300 rpm), 21.7
m/s maximum
piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
speed, maximum
MEP
;applications:
Audi C6 S6 (03/06-08/11),
Audi D3 S8 (06/06-07/10)
;references:
5.2 V10 40v FSI (Gallardo LP560-4/Huracán LP610-4/R8)
This is the second Lamborghini engine developed by
AUDI AG
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The o ...
, who became owners of
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. following the takeover of Lamborghini by the German
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
. It is a development of Audi's fundamentally identical
5.2 V10 40v FSI engine as used in the
Audi C6 S6 and
Audi D3 S8. This variant has been de-tuned for the
Audi R8 V10.
;identification: parts code prefix: 07L.Y
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
V10 engine
A V10 engine is a ten-cylinder piston engine where two banks of five cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V10 engines are much less common than V8 and V12 engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder pis ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.91:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 520.4 cc per cylinder; compression ratio: 12.5:1;
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conve ...
lubrication system
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy; cylinder bore spacing; die-forged steel crankshaft with shared crankpins (creating an uneven firing interval of either 54 deg or 90 deg separation)
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 40 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, chain driven double overhead camshafts, continuously
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
system both for intake and exhaust
;aspiration: two air filters, two hot-film
air mass meters, two cast alloy
throttle bodies each with
electronically controlled throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves, cast
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
alloy
variable geometry and resonance intake manifold
;fuel system: fully demand-controlled and returnless; fuel tank–mounted low-pressure fuel pump,
Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI): two inlet camshaft double-cam driven single-piston high-pressure injection pumps maintaining pressure in the two stainless steel
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel distributor rails, ten combustion chamber sited
direct injection solenoid-controlled sequential fuel injectors
;ignition system & engine management: mapped direct ignition with centrally mounted spark plugs and ten individual direct-acting single spark coils; two
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
MED 9.1 or Lamborghini LIE electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
s (ECUs) working on the 'master and slave' concept due to the high revving nature of the engine
;exhaust system: 2-1-2 branch exhaust manifold per cylinder bank to minimise reverse pulsation of expelled exhaust gases
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs, ID,
;applications
:Audi — BUJ: at 8,000
rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
; at 6,500 rpm —
Audi R8
The Audi R8 is a mid-engine, 2-seater sports car, which uses Audi's trademark quattro permanent all-wheel drive system. It was introduced by the German car manufacturer Audi AG in 2006.
The car is exclusively designed, developed, and manufactu ...
V10 (04/09-07/15)
:LP550: at 8,000 rpm; at 6,500 rpm —
Lamborghini Gallardo
The Lamborghini Gallardo (; ) is a sports car built by the Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini from 2003 to 2013. It is Lamborghini's second car released under parent company Audi, and best-selling model with 14,022 built throughout its ...
LP 550-2
:LP560: at 8,000 rpm; at 6,500 rpm — Lamborghini Gallardo LP 560-4
:LP570: at 8,000 rpm; at 6,500 rpm — Lamborghini Gallardo LP 570-4 Superleggera, Spyder Performante, Super Trofeo, Squadra Corse
:LP580: at 8,000 rpm; at 6,500 rpm —
Lamborghini Huracán
The Lamborghini Huracán (Spanish for "hurricane"; ) is a sports car manufactured by Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini replacing the previous V10 offering, the Gallardo. The Huracán was revealed online in December 2013, making its w ...
LP 580-2
:LP610: at 8,250 rpm; at 6,500 rpm — Lamborghini Huracán LP 610-4, EVO RWD,
Audi R8
The Audi R8 is a mid-engine, 2-seater sports car, which uses Audi's trademark quattro permanent all-wheel drive system. It was introduced by the German car manufacturer Audi AG in 2006.
The car is exclusively designed, developed, and manufactu ...
V10 Plus
:LP640: at 8,000 rpm; , for STO and Tecnica, at 6,500 rpm — Lamborghini Huracán LP 640-4 Performante, EVO, STO, Tecnica
;references:
Twelve-cylinder petrols
6.0 WR12 48v
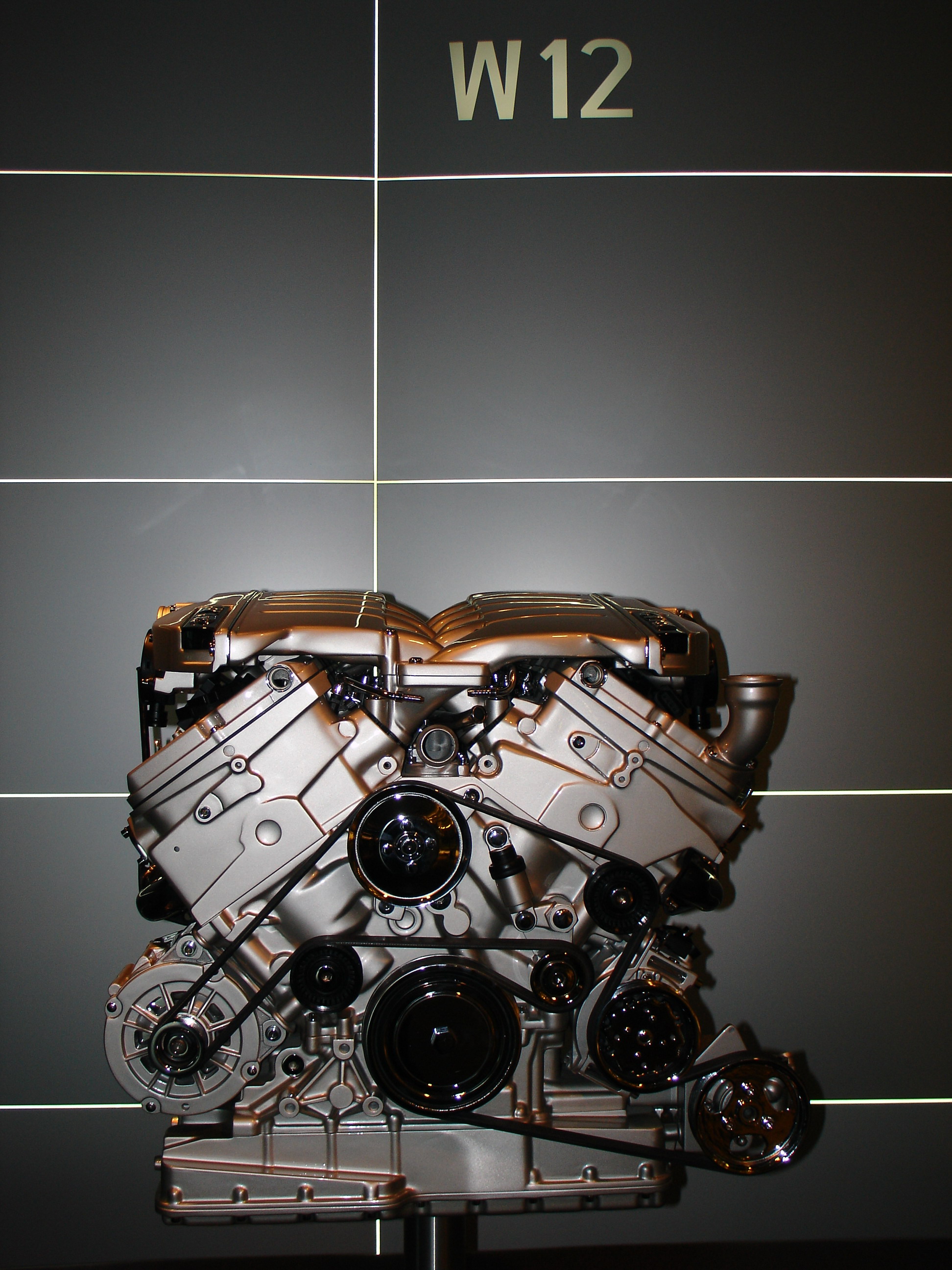
This W12 badged
W12 engine
A W12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where three banks of four cylinders are arranged in a W configuration around a common crankshaft.
W12 engines with three banks of four cylinders were used by several aircraft engines from 1917 unti ...
is a twelve cylinder
W engine
A W engine is a type of piston engine where three or four cylinder banks use the same crankshaft, resembling the letter W when viewed from the front.
W engines with three banks of cylinders are also called "broad arrow" engines, due to their shap ...
of four rows of three cylinders, formed by joining two imaginary 15°
VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
cylinder blocks, placed on a single crankshaft, with each cylinder 'double-bank' now at a 72° angle. This specific configuration is more appropriately described as a WR12 engine.
This
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
engine is also used with slight modification, and with the addition of two
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
s in the
Bentley Continental GT
The Bentley Continental GT is a grand tourer manufactured and marketed by British automaker Bentley Motors since 2003. It was the first car released by Bentley under Volkswagen AG management, after the company's acquisition in 1998, and the fir ...
and
Bentley Flying Spur. It has also been used in a form aboard the
Volkswagen W12
The Volkswagen W12 was a series of concept cars created by Volkswagen Passenger Cars in 1997. The cars have been portrayed in games, such as '' Gran Turismo'', '' Asphalt 8'', '' Asphalt 9'', '' Project Gotham Racing 3'', ''GTI Racing'', ''World ...
prototype sports car to establish a 24-hour record of in 2002 at the
Nardò Ring
The Nardò Ring, originally known as Pista di prova di Nardò della Fiat (Fiat's Nardò test track) when it was built in 1975, is a high speed test track located at more than north-west of the town of Nardò, Italy, in the southern region of Apu ...
in
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
.
;identification: parts code prefix: 07C
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 72°
W12 engine
A W12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where three banks of four cylinders are arranged in a W configuration around a common crankshaft.
W12 engines with three banks of four cylinders were used by several aircraft engines from 1917 unti ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 0.93:1 – undersquare/long-stroke, 499.9 cc per cylinder, compression ratio: 10.7:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: homogeneous
monoblock
Monoblock can refer to:
*A type of air conditioner
*A monoblock LNB
* Monoblock PC, a computer workstation
*A mono (one channel) audio power amplifier
*In photography, another name for a monolight, a type of electronic flash with the electronics ...
low-pressure chill die cast
hypereutectic
A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ...
'
Alusil
Alusil as a hypereutectic aluminium- silicon alloy (EN AC-AlSi17Cu4Mg / EN AC-48100 or A390) contains approximately 78% aluminium and 17% silicon. This alloy was theoretically conceived in 1927 by Schweizer & Fehrenbach, of the Badener Metall-War ...
'
aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
-
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
(AlSi17Cu4Mg); torsionally stiff aluminium alloy crankcase with high-resistance
cylinder liner
In a reciprocating engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels.
The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is s ...
s, simplex roller chain driven oil pump; die-forged steel 21.2 kg crankshaft, seven main bearings, crankpins offset to achieve a constant firing order as on a V6 engine
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 48 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, double overhead camshaft driven from the flywheel side via a two-stage chain drive utilising three 3/8" simplex roller chains, continuous vane-adjustable
variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
for intake and exhaust camshafts with up to 52 degrees timing range for the flow-optimised inlet ports, 22 degrees on the exhaust camshafts
;aspiration: two air filters, two hot-film
air mass meters, two
throttle bodies each with
electronically controlled Bosch 'E-Gas'
throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves, four-part two-channel cast
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
alloy
intake manifold
In automotive engineering, an inlet manifold or intake manifold (in American English) is the part of an engine that supplies the fuel/air mixture to the cylinders. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the ...
;
Bentley
Bentley Motors Limited is a British designer, manufacturer and marketer of luxury cars and SUVs. Headquartered in Crewe, England, the company was founded as Bentley Motors Limited by W. O. Bentley (1888–1971) in 1919 in Cricklewood, North ...
versions also use
twin-turbo
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case ...
s – one
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
per VR cylinder bank
;fuel system, ignition system, engine management: two linked
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel distributor rails,
multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
with twelve intake manifold-sited fuel injectors; centrally positioned
NGK longlife spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with 12 individual direct-acting
single spark coils;
Bosch Motronic
Motronic is the trade name given to a range of digital engine control units developed by Robert Bosch GmbH (commonly known as Bosch) which combined control of fuel injection and ignition in a single unit. By controlling both major systems in a si ...
ME 7.1.1 electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
(ECU), cylinder-selective
knock control via four knock sensors, permanent
lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave ri ...
control, water-cooled alternator
;exhaust system: two vacuum-controlled
secondary air injection
Secondary air injection (commonly known as air injection) is a vehicle emissions control strategy introduced in 1966, wherein fresh air is injected into the exhaust stream to allow for a fuller secondary combustion of exhaust gases.
Development
T ...
pumps for direct injection into exhaust ports to assist cold start operation, four exhaust manifolds with four integrated ceramic
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s, eight heated
oxygen sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or sond, is an electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed.
It was ...
s monitoring pre- and post catalyst exhaust gases
;dimensions: length: , height: , width: then
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs – Audi / Volkswagen, ID codes
:; — Audi A8: AZC (01/01-09/02), VW Phaeton: BAN (04/02-05/05)
: at 6,200 rpm, at 4,000 rpm, at 2,300–5,300 rpm — Audi A8: BHT, BSB, BTE (12/03-07/10)
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,750–5,000 rpm — Phaeton: BRN, BTT (05/05-03/16)
: at 6,000 rpm; at 3,300 rpm — Touareg: BJN, CFRA (08/04-05/10)
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs – Bentley twin turbo
: at 6,100 rpm; at 1,600–6,100 rpm — standard models: BWR, BEB, MTBHT
: at 6,000 rpm; at 1,700–5,600 rpm — "Speed" models: CKHC, BWRA
;applications:
Audi A8
The Audi A8 is a full-size luxury sedan manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi since 1994. Succeeding the Audi V8, and now in its fourth generation, the A8 has been offered with both front- or permanent all-wheel drive—and in s ...
(AZC: 03/01-09/02, BHT: 02/04-, BSB: 10/04-, BTE: 02/05-),
Volkswagen Phaeton
The Volkswagen Phaeton ( ) (''Typ'' 3D) is a full-size luxury sedan/saloon manufactured by the German automobile manufacturer Volkswagen, described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle. Introduced at the 2002 Geneva Motor Show, the ...
(BAN: 05/02-05/05, BRN: 05/05-10/08, BTT: 05/05-10/08),
Volkswagen Touareg
The Volkswagen Touareg (German pronunciation: ) is a car produced by German automaker Volkswagen Group since 2002 at the Volkswagen Bratislava Plant. A five-seater mid-size luxury crossover SUV, the vehicle was named after the nomadic Tuareg peo ...
sport
(BJN: 08/04-, CFRA: 02/08-),
Bentley Continental GT
The Bentley Continental GT is a grand tourer manufactured and marketed by British automaker Bentley Motors since 2003. It was the first car released by Bentley under Volkswagen AG management, after the company's acquisition in 1998, and the fir ...
,
Bentley Flying Spur
;references:
6.0 WR12 48v TFSI
This engine produces of power and of torque. It would mostly share the same technical specifications with its turbocharged 6.0-liter predecessor, other than the fact that it was modified to meet new WLTP emission standards. This new engine was promised to be made available on the
fourth generation A8, following
S8 and 60 TFSI/TDI models. However, as of August 2020, only examples of the W12 variant were press cars. It is rumoured that the W12 variant is only available as special orders in selected European dealerships.
;reference:
6.3 WR12 48v FSI (CEJA)
This engine produces of power and of torque. This new engine was promised to be made available on the
3rd generation A8 More compact dimensions than a comparable V8 engine FSI direct injection with twin high-pressure fuel pumps, twin fuel rails and six-port high pressure injectors.
;applications:
:
A8 L W12 6.3 FSI quattro (CEJA)
6.5 V12 48v (L539) (Lamborghini)
This is a new V12 engine developed for Lamborghini. The company's fourth in-house engine and their first new V12 since its founding, it made its first appearance in the
Lamborghini Aventador
The Lamborghini Aventador () is a mid-engine sportscar produced by the Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini. In keeping with Lamborghini tradition, the Aventador is named after a Spanish fighting bull that fought in Zaragoza, Aragón in ...
.
;engine configuration: 60°
V12 engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines.
The fi ...
;
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conve ...
lubrication system
;engine displacement etc.
:6.5: ; bore x stroke: , compression ratio: 11.8:1
;cylinder block & crankcase: cast aluminium alloy
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 48 valves total, double overhead camshaft
;aspiration: two air filters, four cast alloy
throttle bodies each with
Magneti Marelli
Magneti Marelli S.p.A. () is an Italian developer and manufacturer of components for the automotive industry. The firm is headquartered in Corbetta, Italy, and includes 86 manufacturing plants, 12 R&D centres, and 26 application centers in 19 c ...
electronically controlled throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves, cast
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
alloy
intake manifold
In automotive engineering, an inlet manifold or intake manifold (in American English) is the part of an engine that supplies the fuel/air mixture to the cylinders. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the ...
;fuel system & ignition system: two linked
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel distributor rails,
multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
with twelve intake manifold-sited fuel injectors; centrally positioned spark plugs, mapped direct ignition with 12 individual direct-acting
single spark coils
;exhaust system: two 3-branch exhaust manifolds per cylinder bank, connected to dual-inlet
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually ...
s, heated oxygen (lambda) sensors monitoring pre- and post-catalyst exhaust gases
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
:LP 700: at 8,250 rpm; and at 5,500 rpm
:LP 720: at 8,250 rpm; and at 5,500 rpm
:LP 740: at 8,400 rpm; and at 5,500 rpm
:LP 750: at 8,400 rpm; and at 5,500 rpm
:LP 770: at 8,500 rpm; and at 6,750 rpm
:LP 780: at 8,500 rpm; and at 6,750 rpm
;applications:
:
Lamborghini Aventador
The Lamborghini Aventador () is a mid-engine sportscar produced by the Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini. In keeping with Lamborghini tradition, the Aventador is named after a Spanish fighting bull that fought in Zaragoza, Aragón in ...
LP 700-4 (2011–)
:
Lamborghini Aventador
The Lamborghini Aventador () is a mid-engine sportscar produced by the Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini. In keeping with Lamborghini tradition, the Aventador is named after a Spanish fighting bull that fought in Zaragoza, Aragón in ...
LP 720-4 50th Anniversario (2013–)
:
Lamborghini Veneno
The Lamborghini Veneno () is a limited production high performance sports car manufactured by Italian automobile manufacturer Lamborghini. Based on the Lamborghini Aventador, the Veneno was developed to celebrate Lamborghini's 50th anniversary. ...
LP 750-4 (2013–2014)
:
Lamborghini Centenario
The Lamborghini Centenario (; ) is a limited production sports car based on the Lamborghini Aventador which was unveiled at the 2016 Geneva Motor Show to commemorate the 100th birthday of the company's founder, Ferruccio Lamborghini.
Developm ...
LP 770-4 (2016–2017)
;reference:
Sixteen-cylinder petrol
8.0 WR16 64v4T (Bugatti)

This W16 badged engine is the first and so far the only production
W16 engine
A W16 engine is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine with four banks of four cylinders in a W configuration.
W16 engines are rarely produced, with the notable exception of the Volkswagen Group 8.0 WR16 engine, which has been used since 2005 in the ...
in the world. It is a sixteen-cylinder
W engine
A W engine is a type of piston engine where three or four cylinder banks use the same crankshaft, resembling the letter W when viewed from the front.
W engines with three banks of cylinders are also called "broad arrow" engines, due to their shap ...
, of four rows of four cylinders, and is created by joining two
VR8-engined 15° cylinder banks at the crankcase, and placed on a single crankshaft, with each cylinder 'double-bank' now at a 90° V-angle. This specific configuration method means it is more appropriately described as a WR16 engine.
;engine displacement & engine configuration: 90°
W16 engine
A W16 engine is a sixteen-cylinder piston engine with four banks of four cylinders in a W configuration.
W16 engines are rarely produced, with the notable exception of the Volkswagen Group 8.0 WR16 engine, which has been used since 2005 in the ...
; bore x stroke: , stroke ratio: 1.00:1 – '
square engine', 499.56 cc per cylinder
;cylinder block & crankcase: forged aluminium alloy;
plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
-coated cylinder bores,
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conve ...
lubrication system featuring an eight-stage aluminium-geared
oil pump, die-forged steel crankshaft, lightweight
titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
connecting rods
;cylinder heads & valvetrain: cast aluminium alloy; four valves per cylinder, 64 valves total, low-friction roller finger cam followers with automatic hydraulic valve clearance compensation, double overhead camshaft
;engine cooling: two separate water cooling circuits: one of capacity utilising three front-mounted radiators, the second of for cooling the charged induction air in the two
intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
...
s
;aspiration: lightweight cast
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
alloy intake manifold with twin '
drive by wire
Drive by wire, DbW, by-wire, steer-by-wire, fly-by-wire or x-by-wire technology in the automotive or aviation industry is the use of electrical or electro-mechanical systems for performing vehicle functions traditionally achieved by mechanical link ...
'
electronically controlled throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
valves in separate
throttle bodies, four parallel
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
s with integrated excess pressure regulation valves, two water-cooled top-mounted intercoolers
;fuel system, ignition system & engine management: two linked
common rail
Common rail direct fuel injection is a direct fuel injection system built around a high-pressure (over ) fuel rail feeding solenoid valves, as opposed to a low-pressure fuel pump feeding unit injectors (or pump nozzles). High-pressure injecti ...
fuel distributor rails,
multi-point electronic sequential
indirect fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
with sixteen intake manifold-sited fuel injectors; mapped direct ignition with 16 individual direct-acting
single spark coils; two digital electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
s (ECUs), ion-current
knock control and misfire cylinder-selective detection system
;dimensions & mass: length: , mass: ˜
;DIN-rated motive power & torque outputs
: at 6,000 rpm; at 2,200–5,500 rpm; achieving a top speed of
: ; – in the
Bugatti Veyron
The Bugatti Veyron EB 16.4 is a mid-engine sports car, designed and developed in Germany by the Volkswagen Group and Bugatti and manufactured in Molsheim, France, by French automobile manufacturer Bugatti. It was named after the racing driver Pie ...
Super Sport; achieving a top speed of
;application
;references:
Petrol engines data table
The following table contains a very brief selection of current and historical
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
spark-ignition
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, ty ...
petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as ' ...
s for comparison of performance and operating characteristics:
See also
*
List of Volkswagen Group diesel engines
List of Volkswagen Group diesel engines. The compression-ignition diesel engines listed below are currently used by various marques of automobiles and commercial vehicles of the German automotive concern, Volkswagen Group,ETKA official factory ...
*
Wasserboxer
The Volkswagen wasserboxer is a four cylinder horizontally opposed pushrod overhead-valve (OHV) petrol engine developed by Volkswagen. The engine is water-cooled, and takes its name from the german: "wasserboxer" ("Water-boxer"); with "boxer" b ...
*
VR6 engine
VR6 engines are V6 piston engines with a narrow angle between the cylinder banks and a single cylinder head covering both banks of cylinders.
Volkswagen Group introduced the first VR6 engine in 1991 and VR6 engines currently remain in producti ...
*
G-Lader
The G-Lader is a scroll-type supercharger used in various Volkswagen Passenger Cars models. Its purpose is to increase the motive power output from the internal combustion engine attainable with a given engine displacement. Since it is not enoug ...
*
G60 – for detailed development info and progression of
forced induction
In an internal combustion engine, forced induction is where turbocharging or supercharging is used to increase the density of the intake air. Engines without forced induction are classified as naturally aspirated.
Operating principle Overvi ...
in
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen AG (), known internationally as the Volkswagen Group, is a German multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial ...
engines
References
*
*
External links
VolkswagenAG.com– Volkswagen Group corporate website
**[https://web.archive.org/web/20090319033446/http://www.volkswagen.com/vwcms/master_public/virtualmaster/en2/unternehmen/mobility_and_sustainability0/regionen/Europa/Kassel.html Kassel (Germany) – engine plant Mobility and Sustainability]
Salzgitter (Germany) – engine plant Mobility and Sustainability**[https://web.archive.org/web/20090316063814/http://www.volkswagen.com/vwcms/master_public/virtualmaster/en2/unternehmen/mobility_and_sustainability0/regionen/amerika/Sao_Carlos.html São Carlos (Brazil) – engine plant Mobility and Sustainability]
Shanghai (China) – engine plant Mobility and Sustainability
Golf R400 (EA888)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen Group engines, *
Gasoline engines by model
Lists of automobile engines
Slanted engines
 The
The  This W12 badged
This W12 badged  This W16 badged engine is the first and so far the only production
This W16 badged engine is the first and so far the only production