|
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
In internal combustion engines, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a nitrogen oxide () emissions reduction technique used in petrol/gasoline, diesel engines and some hydrogen engines. EGR works by recirculating a portion of an engine's exhaust gas back to the engine cylinders. The exhaust gas displaces atmospheric air and reduces in the combustion chamber. Reducing the amount of oxygen reduces the amount of fuel that can burn in the cylinder thereby reducing peak in-cylinder temperatures. The actual amount of recirculated exhaust gas varies with the engine operating parameters. In the combustion cylinder, is produced by high-temperature mixtures of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen, and this usually occurs at cylinder peak pressure. In a spark-ignition engine, an ancillary benefit of recirculating exhaust gases via an external EGR valve is an increase in efficiency, as charge dilution allows a larger throttle position and reduces associated pumping losses. Mazda's turbocharge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle
A hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicle (HICEV) is a type of hydrogen vehicle using an internal combustion engine. Hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicles are different from hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (which use electrochemical use of hydrogen rather than combustion). Instead, the hydrogen internal combustion engine is simply a modified version of the traditional gasoline-powered internal combustion engine. The absence of carbon means that no is produced, which eliminates the main greenhouse gas emission of a conventional petroleum engine. As pure hydrogen does not contain carbon, there are no carbon-based pollutants, such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (), and hydrocarbons (HC), in the exhaust. As hydrogen combustion occurs in an atmosphere containing nitrogen and oxygen, however, it can produce oxides of nitrogen known as . In this way, the combustion process is much like other high temperature combustion fuels, such as kerosene, gasoline, diesel or na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backpressure
Back pressure (or backpressure) is a resistance or force opposing the desired flow of fluid through pipes, leading to friction loss and pressure drop. The term ''back pressure'' is a misnomer, as pressure is a scalar quantity, so it has a magnitude but no direction. The fluid is what is directed, tending to flow away from high-pressure regions and toward low-pressure regions. If the low-pressure space is more high-pressure than intended (e.g. due to obstructions or tight bends in an exhaust pipe) or the high-pressure space is more low-pressure than intended, this opposes the desired flow and reduces the discharge. Similarly, bending or other operations on a pipe (such as a stock car exhaust system with a particularly high number of twists and bends) can reduce flow rate. Explanation A common example of backpressure is that caused by the exhaust system (consisting of the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler and connecting pipes) of an automotive four-stroke engine, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Ring
A piston ring is a metallic split ring that is attached to the outer diameter of a piston in an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The main functions of piston rings in engines are: # Sealing the combustion chamber so that there is minimal loss of gases to the crank case. # Improving heat transfer from the piston to the cylinder wall. # Maintaining the proper quantity of the oil between the piston and the cylinder wall # Regulating engine oil consumption by scraping oil from the cylinder walls back to the sump. Most piston rings are made from cast iron or steel. Design Piston rings are designed to seal the gap between the piston and the cylinder wall. If this gap were too small, thermal expansion of the piston could mean the piston seizes in the cylinder, causing serious damage to the engine. On the other hand, a large gap would cause insufficient sealing of the piston rings against the cylinder walls, resulting in excessive blow-by (combustion gases entering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particulates
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The term '' aerosol'' commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health, in ways additional to direct inhalation. Types of atmospheric particles include suspended particulate matter; thoracic and respirable particles; inhalable coarse particles, designated PM, which are coarse particles with a diameter of 10 micrometers (μm) or less; fine particles, designated PM, with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less; ultrafine particles, with a diameter of 100 nm or less; and soot. The IARC and WHO designate airborne particulates as a Group 1 carcinogen. Particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
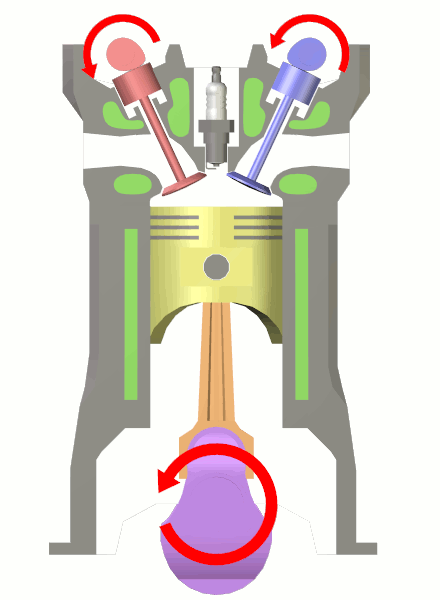
Spark-ignition Engine
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, typically diesel engines, where the heat generated from compression together with the injection of fuel is enough to initiate the combustion process, without needing any external spark. Fuels Spark-ignition engines are commonly referred to as "gasoline engines" in North America, and "petrol engines" in Britain and the rest of the world. Spark-ignition engines can (and increasingly are) run on fuels other than petrol/gasoline, such as autogas ( LPG), methanol, ethanol, bioethanol, compressed natural gas (CNG), hydrogen, and (in drag racing) nitromethane. Working cycle The working cycle of both spark-ignition and compression-ignition engines may be either two-stroke or four-stroke. A four-stroke spark-ignition engine is an Otto cycle engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement Image:Heat_exc_1-1.svg, Fig. 1: Shell and tube heat exchanger, single pass (1–1 parallel f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
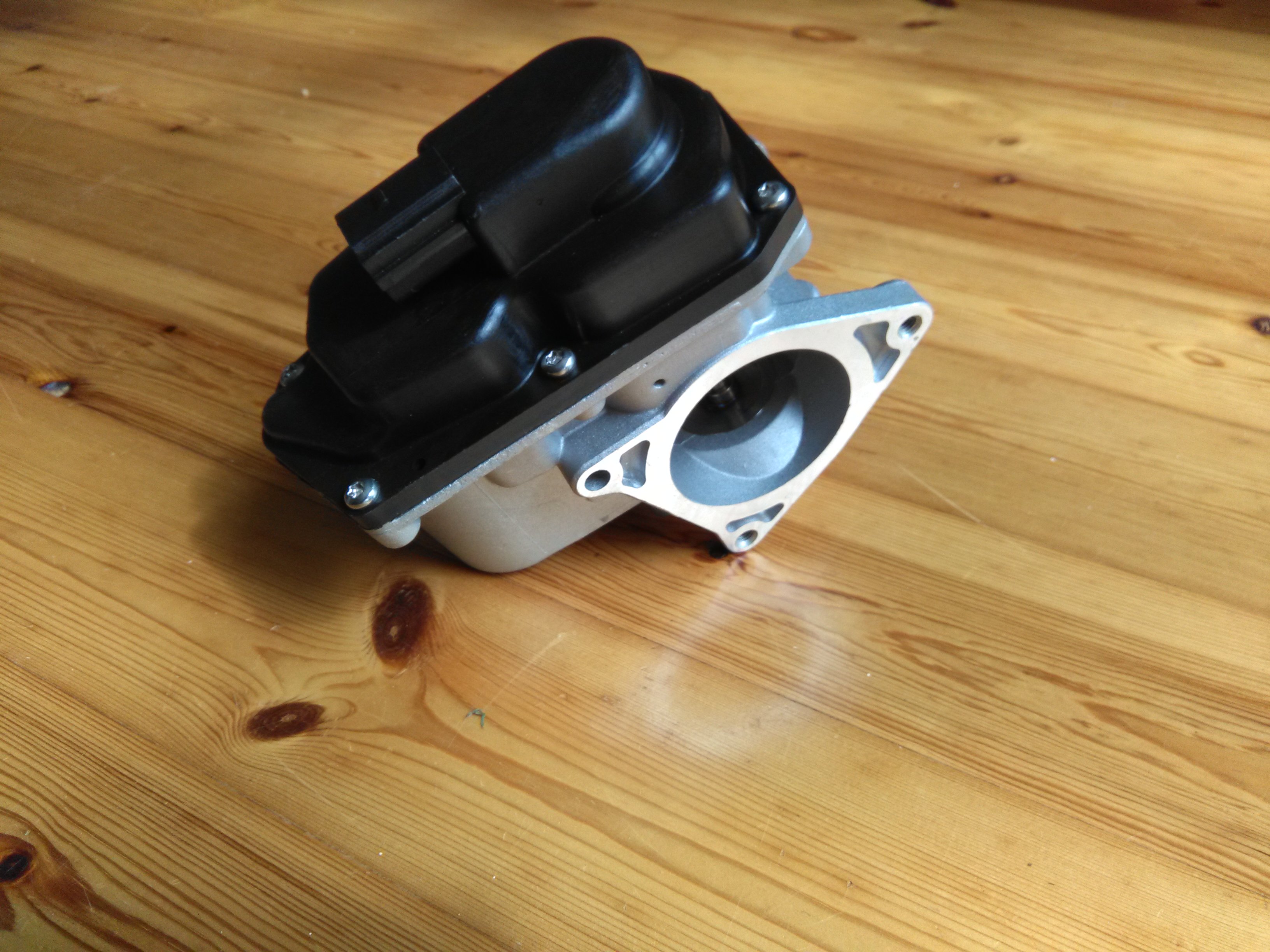
Skoda BNM EGR
Škoda means ''pity'' in the Czech and Slovak language Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by appro ...s. It may also refer to: Czech brands and enterprises * Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav ** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Škoda Auto responsible for motorsport activities * Škoda Transportation, engineering company that manufactures rail vehicles, based in Plzeň * Škoda Works, engineering company, predecessor of Škoda Transportation * Doosan Škoda Power, subsidiary of the Doosan Group, based in Plzeň People * Škoda (surname) * Skoda (Portuguese footballer) (born 1960) Art * ''Škoda lásky'', the original Czech title of the "Beer Barrel Polka" Other * British Rail Class 90, an electric locomotive nicknamed Skoda * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Centre (engineering)
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throttle Plate
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction. An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' has come to refer, informally, to any mechanism by which the power or speed of an engine is regulated, such as a car's accelerator pedal. What is often termed a ''throttle'' (in an aviation context) is also called a thrust lever, particularly for jet engine powered aircraft. For a steam locomotive, the valve which controls the steam is known as the regulator. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the throttle is a means of controlling an engine's power by regulating the amount of fuel or air entering the engine. In a motor vehicle the control used by the driver to regulate power is sometimes called the throttle, accelerator, or gas pedal. For a gasoline engine, the throttle most commonly regulates the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spark Ignition Engine
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, typically diesel engines, where the heat generated from compression together with the injection of fuel is enough to initiate the combustion process, without needing any external spark. Fuels Spark-ignition engines are commonly referred to as "gasoline engines" in North America, and "petrol engines" in Britain and the rest of the world. Spark-ignition engines can (and increasingly are) run on fuels other than petrol/gasoline, such as autogas ( LPG), methanol, ethanol, bioethanol, compressed natural gas (CNG), hydrogen, and (in drag racing) nitromethane. Working cycle The working cycle of both spark-ignition and compression-ignition engines may be either two-stroke or four-stroke. A four-stroke spark-ignition engine is an Otto cycle engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |