Volcanoes Of Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as
 According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth's
According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth's
 The most common perception of a volcano is of a
The most common perception of a volcano is of a
 Cinder cones result from eruptions of mostly small pieces of
Cinder cones result from eruptions of mostly small pieces of
 Stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes) are tall conical mountains composed of lava flows and
Stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes) are tall conical mountains composed of lava flows and
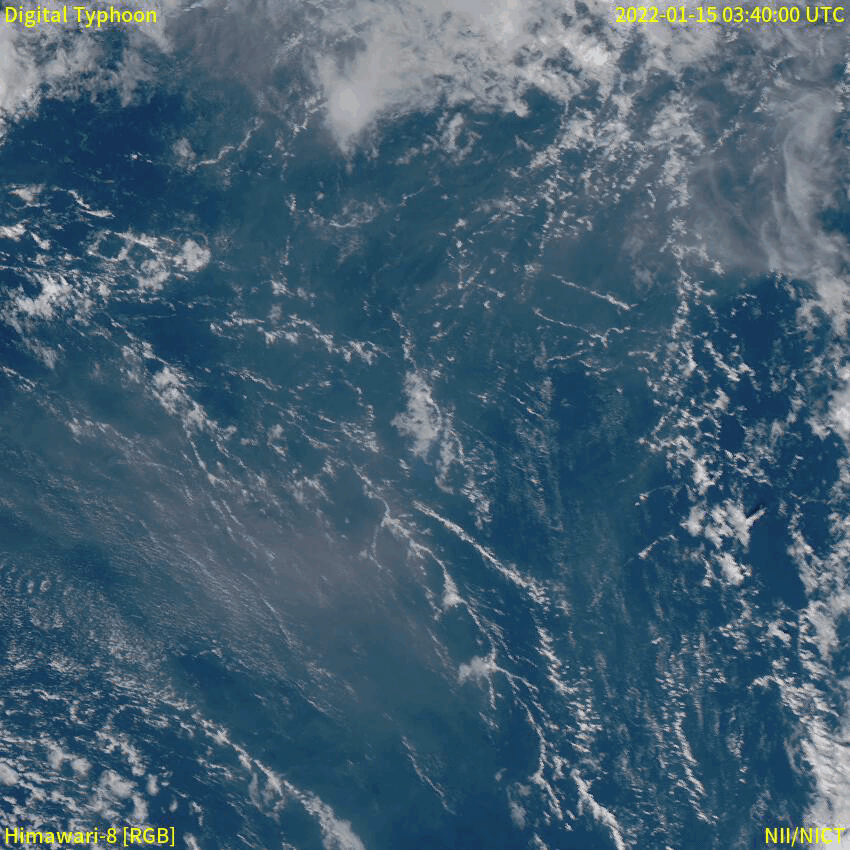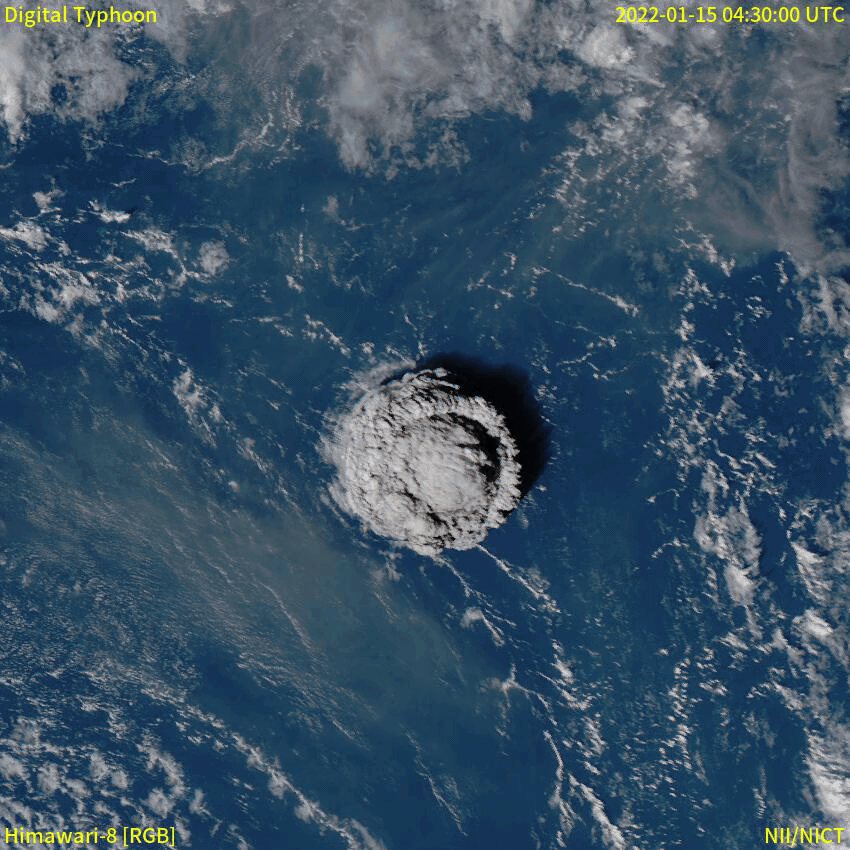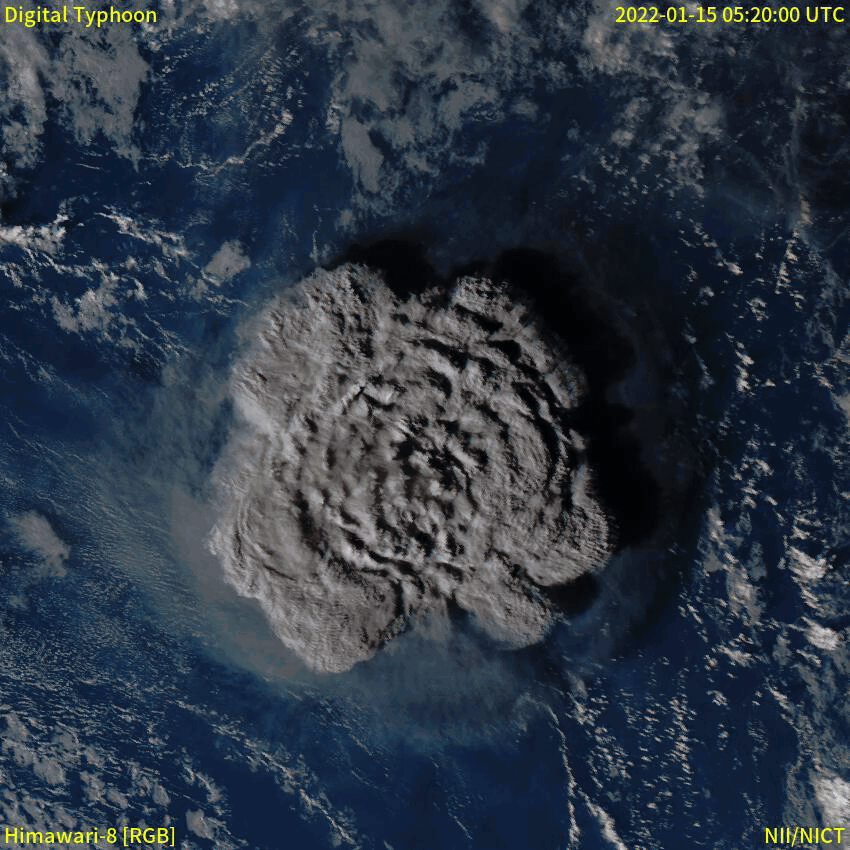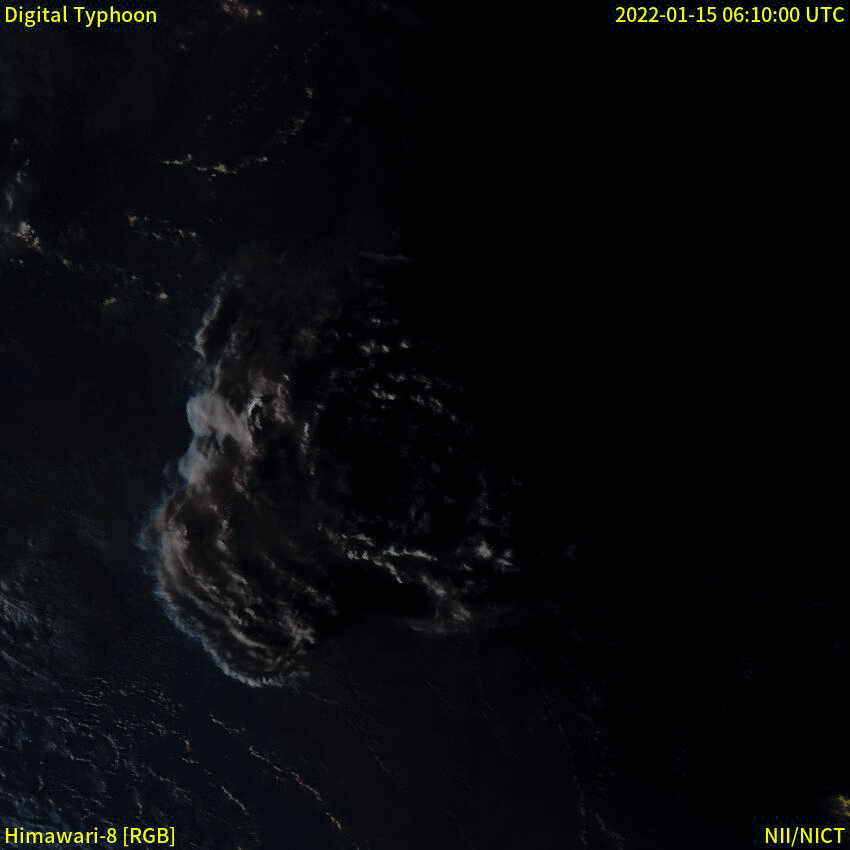 Submarine volcanoes are common features of the ocean floor. Volcanic activity during the
Submarine volcanoes are common features of the ocean floor. Volcanic activity during the

 The material that is expelled in a
The material that is expelled in a
 The form and style of eruption of a volcano is largely determined by the composition of the lava it erupts. The viscosity (how fluid the lava is) and the amount of dissolved gas are the most important characteristics of magma, and both are largely determined by the amount of silica in the magma. Magma rich in silica is much more viscous than silica-poor magma, and silica-rich magma also tends to contain more dissolved gases.
Lava can be broadly classified into four different compositions:
* If the erupted
The form and style of eruption of a volcano is largely determined by the composition of the lava it erupts. The viscosity (how fluid the lava is) and the amount of dissolved gas are the most important characteristics of magma, and both are largely determined by the amount of silica in the magma. Magma rich in silica is much more viscous than silica-poor magma, and silica-rich magma also tends to contain more dissolved gases.
Lava can be broadly classified into four different compositions:
* If the erupted
 Tephra is made when magma inside the volcano is blown apart by the rapid expansion of hot volcanic gases. Magma commonly explodes as the gas dissolved in it comes out of solution as the pressure decreases when it flows to the surface. These violent explosions produce particles of material that can then fly from the volcano. Solid particles smaller than 2 mm in diameter ( sand-sized or smaller) are called volcanic ash.
Tephra and other
Tephra is made when magma inside the volcano is blown apart by the rapid expansion of hot volcanic gases. Magma commonly explodes as the gas dissolved in it comes out of solution as the pressure decreases when it flows to the surface. These violent explosions produce particles of material that can then fly from the volcano. Solid particles smaller than 2 mm in diameter ( sand-sized or smaller) are called volcanic ash.
Tephra and other
 Eruption styles are broadly divided into magmatic, phreatomagmatic, and phreatic eruptions. The intensity of explosive volcanism is expressed using the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI), which ranges from 0 for Hawaiian-type eruptions to 8 for supervolcanic eruptions.
* Magmatic eruptions are driven primarily by gas release due to decompression. Low-viscosity magma with little dissolved gas produces relatively gentle effusive eruptions. High-viscosity magma with a high content of dissolved gas produces violent
Eruption styles are broadly divided into magmatic, phreatomagmatic, and phreatic eruptions. The intensity of explosive volcanism is expressed using the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI), which ranges from 0 for Hawaiian-type eruptions to 8 for supervolcanic eruptions.
* Magmatic eruptions are driven primarily by gas release due to decompression. Low-viscosity magma with little dissolved gas produces relatively gentle effusive eruptions. High-viscosity magma with a high content of dissolved gas produces violent
 Volcanoes vary greatly in their level of activity, with individual volcanic systems having an ''eruption recurrence'' ranging from several times a year to once in tens of thousands of years. Volcanoes are informally described as erupting, active, dormant, or extinct, but the definitions of these terms are not entirely uniform amongst volcanologists. The level of activity of most volcanoes falls upon a graduated spectrum, with much overlap between categories, and does not always fit neatly into only one of these three separate categories.
Volcanoes vary greatly in their level of activity, with individual volcanic systems having an ''eruption recurrence'' ranging from several times a year to once in tens of thousands of years. Volcanoes are informally described as erupting, active, dormant, or extinct, but the definitions of these terms are not entirely uniform amongst volcanologists. The level of activity of most volcanoes falls upon a graduated spectrum, with much overlap between categories, and does not always fit neatly into only one of these three separate categories.
Wired. 15 August 2015. By Erik Klimetti. Downloaded 24 July 2022.
 The USGS defines a "dormant volcano" as ''Any volcano that is not showing any signs of unrest such as earthquake swarms, ground swelling, or excessive noxious gas emissions, but which shows signs that it could yet become active again.'' Many dormant volcanoes have not erupted for thousands of years, but have still shown signs that they may be likely to erupt again in the future.
In an article justifying the re-classification of Alaska's Mount Edgecumbe volcano from "dormant" to "active", volcanologists at the
The USGS defines a "dormant volcano" as ''Any volcano that is not showing any signs of unrest such as earthquake swarms, ground swelling, or excessive noxious gas emissions, but which shows signs that it could yet become active again.'' Many dormant volcanoes have not erupted for thousands of years, but have still shown signs that they may be likely to erupt again in the future.
In an article justifying the re-classification of Alaska's Mount Edgecumbe volcano from "dormant" to "active", volcanologists at the
 Extinct volcanoes are those that scientists consider unlikely to erupt again because the volcano no longer has a magma supply. Examples of extinct volcanoes are many volcanoes on the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain in the Pacific Ocean (although some volcanoes at the eastern end of the chain are active), Hohentwiel in Germany, Shiprock in
Extinct volcanoes are those that scientists consider unlikely to erupt again because the volcano no longer has a magma supply. Examples of extinct volcanoes are many volcanoes on the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain in the Pacific Ocean (although some volcanoes at the eastern end of the chain are active), Hohentwiel in Germany, Shiprock in
 The Decade Volcanoes are 16 volcanoes identified by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior (IAVCEI) as being worthy of particular study in light of their history of large, destructive eruptions and proximity to populated areas. They are named Decade Volcanoes because the project was initiated as part of the United Nations-sponsored International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (the 1990s). The 16 current Decade Volcanoes are:
* Avachinsky-Koryaksky (grouped together), Kamchatka Peninsula, Kamchatka, Russia
* Colima (volcano), Nevado de Colima, Jalisco and Colima, Mexico
* Mount Etna, Sicily, Italy
* Galeras, Nariño, Colombia
*
The Decade Volcanoes are 16 volcanoes identified by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior (IAVCEI) as being worthy of particular study in light of their history of large, destructive eruptions and proximity to populated areas. They are named Decade Volcanoes because the project was initiated as part of the United Nations-sponsored International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (the 1990s). The 16 current Decade Volcanoes are:
* Avachinsky-Koryaksky (grouped together), Kamchatka Peninsula, Kamchatka, Russia
* Colima (volcano), Nevado de Colima, Jalisco and Colima, Mexico
* Mount Etna, Sicily, Italy
* Galeras, Nariño, Colombia
*

 Volcanic eruptions pose a significant threat to human civilization. However, volcanic activity has also provided humans with important resources.
Volcanic eruptions pose a significant threat to human civilization. However, volcanic activity has also provided humans with important resources.
 A
A
"Making Moai: Reconsidering Concepts of Risk in the Construction of Megalithic Architecture in Rapa Nui (Easter Island)"
. ''Rapa Nui–Easter Island: Cultural and Historical Perspectives'', pp.150-151 Volcanic ash and weathered basalt produce some of the most fertile soil in the world, rich in nutrients such as iron, magnesium, potassium, calcium, and phosphorus. Volcanic activity is responsible for emplacing valuable mineral resources, such as metal ores. It is accompanied by high rates of heat flow from the Earth's interior. These can be tapped as geothermal power.
 The Earth's Moon has no large volcanoes and no current volcanic activity, although recent evidence suggests it may still possess a partially molten core. However, the Moon does have many volcanic features such as lunar mare, maria (the darker patches seen on the Moon), rilles and lunar dome, domes.
The planet Venus has a surface that is 90%
The Earth's Moon has no large volcanoes and no current volcanic activity, although recent evidence suggests it may still possess a partially molten core. However, the Moon does have many volcanic features such as lunar mare, maria (the darker patches seen on the Moon), rilles and lunar dome, domes.
The planet Venus has a surface that is 90%  There are several extinct volcanoes on Mars, four of which are vast shield volcanoes far bigger than any on Earth. They include Arsia Mons, Ascraeus Mons, Hecates Tholus, Olympus Mons, and Pavonis Mons. These volcanoes have been extinct for many millions of years, but the European ''Mars Express'' spacecraft has found evidence that volcanic activity may have occurred on Mars in the recent past as well.
There are several extinct volcanoes on Mars, four of which are vast shield volcanoes far bigger than any on Earth. They include Arsia Mons, Ascraeus Mons, Hecates Tholus, Olympus Mons, and Pavonis Mons. These volcanoes have been extinct for many millions of years, but the European ''Mars Express'' spacecraft has found evidence that volcanic activity may have occurred on Mars in the recent past as well.
U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency Volcano advice
Volcano World
{{Authority control Volcanoes, * Geological hazards Volcanism Plate tectonics Volcanic landforms Volcanoes by status, * Volcanic rocks, * Volcanology Articles containing video clips
 A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
, that allows hot lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
, volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
, and gases
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
to escape from a magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it up ...
below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North A ...
, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring ...
has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of ...
and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Carib ...
and Rio Grande rift
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihuahu ...
in North America. Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–T ...
s from the core–mantle boundary
The core–mantle boundary (CMB) of Earth lies between the planet's silicate mantle and its liquid iron-nickel outer core. This boundary is located at approximately 2,891 km (1,796 miles) depth beneath Earth's surface. The boundary is observed ...
, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tr ...
, of which the Hawaiian hotspot
The Hawaii hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii plume is responsible for the creation of the ...
is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.
Large eruptions can affect atmospheric temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
obscure the Sun and cool the Earth's troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. Fro ...
. Historically, large volcanic eruptions have been followed by volcanic winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by volcanic ash and droplets of sulfuric acid and water obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, particularly explosiv ...
s which have caused catastrophic famines.
Other planets besides Earth have volcanoes. For example, Mercury has pyroclastic
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroc ...
deposits formed by explosive volcanic activity.
Etymology
The word ''volcano'' is derived from the name ofVulcano
Vulcano ( scn, Vurcanu) or Vulcan is a small volcanic island belonging to Italy in the Tyrrhenian Sea, about north of Sicily and located at the southernmost end of the seven Aeolian Islands. The island is known for its volcanic activity and ...
, a volcanic island in the Aeolian Islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; it, Isole Eolie ; scn, Ìsuli Eoli), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named afte ...
of Italy whose name in turn comes from Vulcan, the god of fire in Roman mythology
Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, ''Roman mythology'' may also refer to the modern study of these representa ...
. The study of volcanoes is called volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word '' vulcan''. Vulcan was the an ...
, sometimes spelled ''vulcanology''.
Plate tectonics
lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years ...
, its rigid outer shell, is broken into sixteen larger and several smaller plates. These are in slow motion, due to convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
in the underlying ductile mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
, and most volcanic activity on Earth takes place along plate boundaries, where plates are converging (and lithosphere is being destroyed) or are diverging (and new lithosphere is being created).
Divergent plate boundaries
At themid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
s, two tectonic plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
diverge from one another as hot mantle rock creeps upwards beneath the thinned oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic ...
. The decrease of pressure in the rising mantle rock leads to adiabatic expansion and the partial melting
Partial melting occurs when only a portion of a solid is melted. For mixed substances, such as a rock containing several different minerals or a mineral that displays solid solution, this melt can be different from the bulk composition of the soli ...
of the rock, causing volcanism and creating new oceanic crust. Most divergent plate boundaries are at the bottom of the oceans, and so most volcanic activity on the Earth is submarine, forming new seafloor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth an ...
. Black smoker
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s (also known as deep sea vents) are evidence of this kind of volcanic activity. Where the mid-oceanic ridge is above sea level, volcanic islands are formed, such as Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
.
Convergent plate boundaries
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
zones are places where two plates, usually an oceanic plate and a continental plate, collide. The oceanic plate subducts (dives beneath the continental plate), forming a deep ocean trench just offshore. In a process called flux melting, water released from the subducting plate lowers the melting temperature of the overlying mantle wedge, thus creating magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
. This magma tends to be extremely viscous
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the in ...
because of its high silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
content, so it often does not reach the surface but cools and solidifies at depth. When it does reach the surface, however, a volcano is formed. Thus subduction zones are bordered by chains of volcanoes called volcanic arcs. Typical examples are the volcanoes in the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring ...
, such as the Cascade Volcanoes
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern ...
or the Japanese Archipelago
The Japanese archipelago (Japanese: 日本列島, ''Nihon rettō'') is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan, as well as the Russian island of Sakhalin. It extends over from the Sea of Okhotsk in the northeast to the East Chin ...
, or the eastern islands of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
.
Hotspots
Hotspots
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tra ...
are volcanic areas thought to be formed by mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
s, which are hypothesized to be columns of hot material rising from the core-mantle boundary. As with mid-ocean ridges, the rising mantle rock experiences decompression melting which generates large volumes of magma. Because tectonic plates move across mantle plumes, each volcano becomes inactive as it drifts off the plume, and new volcanoes are created where the plate advances over the plume. The Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
are thought to have been formed in such a manner, as has the Snake River Plain
The Snake River cutting through the plain leaves many canyons and Canyon#List of gorges">gorges, such as this one near Twin Falls, Idaho
The Snake River Plain is a geologic feature located primarily within the U.S. state of Idaho. It stre ...
, with the Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corn ...
being the part of the North American plate currently above the Yellowstone hotspot
The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake Riv ...
. However, the mantle plume hypothesis has been questioned.
Continental rifting
Sustained upwelling of hot mantle rock can develop under the interior of a continent and lead to rifting. Early stages of rifting are characterized byflood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s and may progress to the point where a tectonic plate is completely split. A divergent plate boundary then develops between the two halves of the split plate. However, rifting often fails to completely split the continental lithosphere (such as in an aulacogen
An aulacogen is a failed arm of a triple junction. Aulacogens are a part of plate tectonics where oceanic and continental crust is continuously being created, destroyed, and rearranged on the Earth’s surface. Specifically, aulacogens are a ri ...
), and failed rifts are characterized by volcanoes that erupt unusual alkali lava or carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive or extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geochemical verification.
Carbonati ...
s. Examples include the volcanoes of the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of ...
.
Volcanic features
 The most common perception of a volcano is of a
The most common perception of a volcano is of a conical
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines c ...
mountain, spewing lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
and poisonous gases
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
from a crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
* Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
* Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surf ...
at its summit; however, this describes just one of the many types of volcano. The features of volcanoes are much more complicated and their structure and behavior depends on a number of factors. Some volcanoes have rugged peaks formed by lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions ...
s rather than a summit crater while others have landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the ...
features such as massive plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
s. Vents that issue volcanic material (including lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
and ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non-gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
) and gases (mainly steam and magmatic gases) can develop anywhere on the landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
and may give rise to smaller cones such as Puu Ōō on a flank of Kīlauea
Kīlauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. His ...
in Hawaii.
Other types of volcano include cryovolcano
A cryovolcano (sometimes informally called an ice volcano) is a type of volcano that erupts volatiles such as water, ammonia or methane into an extremely cold environment that is at or below their freezing point. The process of formation is known ...
es (or ice volcanoes), particularly on some moons of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
; and mud volcano
A mud volcano or mud dome is a landform created by the eruption of mud or slurries, water and gases. Several geological processes may cause the formation of mud volcanoes. Mud volcanoes are not true igneous volcanoes as they do not produce ...
es, which are formations often not associated with known magmatic activity. Active mud volcanoes tend to involve temperatures much lower than those of igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
volcanoes except when the mud volcano is actually a vent of an igneous volcano.
Fissure vents
Volcanic fissure vents are flat, linear fractures through whichlava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
emerges.
Shield volcanoes
Shield volcanoes, so named for their broad, shield-like profiles, are formed by the eruption of low-viscosity lava that can flow a great distance from a vent. They generally do not explode catastrophically, but are characterized by relatively gentleeffusive eruption
An effusive eruption is a type of volcanic eruption in which lava steadily flows out of a volcano onto the ground.
Overview
There are two major groupings of eruptions: effusive and explosive. Effusive eruption differs from explosive eruption ...
s. Since low-viscosity magma is typically low in silica, shield volcanoes are more common in oceanic than continental settings. The Hawaiian volcanic chain is a series of shield cones, and they are common in Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, as well.
Lava domes
Lava domes are built by slow eruptions of highly viscous lava. They are sometimes formed within the crater of a previous volcanic eruption, as in the case of Mount St. Helens, but can also form independently, as in the case ofLassen Peak
Lassen Peak ( ), commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is a lava dome volcano and the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range of the Western United States. Located in the Shasta Cascade region of Northern California, it is part of the ...
. Like stratovolcanoes, they can produce violent, explosive eruptions, but the lava generally does not flow far from the originating vent.
Cryptodomes
Cryptodomes are formed when viscous lava is forced upward causing the surface to bulge. The 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens was an example; lava beneath the surface of the mountain created an upward bulge, which later collapsed down the north side of the mountain.Cinder cones
 Cinder cones result from eruptions of mostly small pieces of
Cinder cones result from eruptions of mostly small pieces of scoria
Scoria is a pyroclastic, highly vesicular, dark-colored volcanic rock that was ejected from a volcano as a molten blob and cooled in the air to form discrete grains or clasts.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) '' ...
and pyroclastics
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyrocl ...
(both resemble cinders, hence the name of this volcano type) that build up around the vent. These can be relatively short-lived eruptions that produce a cone-shaped hill perhaps high. Most cinder cones erupt only once
Once means a one-time occurrence.
Once may refer to:
Music
* ''Once'' (Pearl Jam song), a 1991 song from the album ''Ten''
* ''Once'' (Roy Harper album), a 1990 album by Roy Harper
* ''Once'' (The Tyde album), a 2001 debut album by The Tyd ...
. Cinder cones may form as flank vents on larger volcanoes, or occur on their own. Parícutin
Parícutin (or Volcán de Parícutin, also accented Paricutín) is a cinder cone volcano located in the Mexican state of Michoacán, near the city of Uruapan and about west of Mexico City. The volcano surged suddenly from the cornfield of loca ...
in Mexico and Sunset Crater in Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
are examples of cinder cones. In New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, Caja del Rio
Caja del Rio (Spanish: " box of the river") is a dissected plateau, of volcanic origin, which covers approximately 84,000 acres of land in northern Santa Fe County, New Mexico, United States. The region is also known as the Caja, Caja del Rio Pl ...
is a volcanic field
A volcanic field is an area of Earth's crust that is prone to localized volcanic activity. The type and number of volcanoes required to be called a "field" is not well-defined. Volcanic fields usually consist of clusters of up to 100 volcanoes ...
of over 60 cinder cones.
Based on satellite images, it was suggested that cinder cones might occur on other terrestrial bodies in the Solar system too; on the surface of Mars and the Moon.
Stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes)
tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they r ...
in alternate layers, the strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum ( : strata) is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as e ...
that gives rise to the name. They are also known as composite volcanoes because they are created from multiple structures during different kinds of eruptions. Classic examples include Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest ...
in Japan, Mayon Volcano
Mayon ( bcl, Bulkan Mayon; tl, Bulkang Mayon, ), also known as Mount Mayon and Mayon Volcano ( es, Monte Mayón, Volcán Mayón), is an active stratovolcano in the province of Albay in Bicol, Philippines. A popular tourist spot, it is renow ...
in the Philippines, and Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of ...
and Stromboli
Stromboli ( , ; scn, Struògnuli ) is an island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, off the north coast of Sicily, containing Mount Stromboli, one of the four active volcanoes in Italy. It is one of the eight Aeolian Islands, a volcanic arc north of Si ...
in Italy.
Ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non-gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
produced by the explosive eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma su ...
of stratovolcanoes has historically
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
posed the greatest volcanic hazard to civilizations. The lavas of stratovolcanoes are higher in silica, and therefore much more viscous, than lavas from shield volcanoes. High-silica lavas also tend to contain more dissolved gas. The combination is deadly, promoting explosive eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma su ...
s that produce great quantities of ash, as well as pyroclastic surge
A pyroclastic surge is a fluidised mass of turbulent gas and rock fragments that is ejected during some volcanic eruptions. It is similar to a pyroclastic flow but it has a lower density or contains a much higher ratio of gas to rock, which makes ...
s like the one that destroyed the city of Saint-Pierre in Martinique in 1902. They are also steeper than shield volcanoes, with slopes of 30–35° compared to slopes of generally 5–10°, and their loose tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they r ...
are material for dangerous lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extr ...
s. Large pieces of tephra are called volcanic bomb
A volcanic bomb or lava bomb is a mass of partially molten rock (tephra) larger than 64 mm (2.5 inches) in diameter, formed when a volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during an eruption. Because volcanic bombs cool after they l ...
s. Big bombs can measure more than 4 feet (1.2 meters) across and weigh several tons.
Supervolcanoes
A supervolcano is a volcano that has experienced one or more eruptions that produced over of volcanic deposits in a single explosive event. Such eruptions occur when a very large magma chamber full of gas-rich, silicic magma is emptied in a catastrophiccaldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
-forming eruption. Ash flow tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
s emplaced by such eruptions are the only volcanic product with volumes rivaling those of flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s.
A supervolcano can produce devastation on a continental scale. Such volcanoes are able to severely cool global temperatures for many years after the eruption due to the huge volumes of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
and ash released into the atmosphere. They are the most dangerous type of volcano. Examples include Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corn ...
in Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
and Valles Caldera
Valles Caldera (or Jemez Caldera) is a wide volcanic caldera in the Jemez Mountains of northern New Mexico. Hot springs, streams, fumaroles, natural gas seeps and volcanic domes dot the caldera floor landscape. The highest point in the calde ...
in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
(both western United States); Lake Taupō
Lake Taupō (also spelled Taupo; mi, Taupō-nui-a-Tia or ) is a large crater lake in New Zealand's North Island, located in the caldera of the Taupō Volcano. The lake is the namesake of the town of Taupō, which sits on a bay in the lake's n ...
in New Zealand; Lake Toba in Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Indonesia; and Ngorongoro Crater in Tanzania. Fortunately, supervolcano eruptions are very rare events, though because of the enormous area they cover, and subsequent concealment under vegetation and glacial deposits, supervolcanoes can be difficult to identify in the geologic record without careful geologic map
A geologic map or geological map is a special-purpose map made to show various geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by color or symbols. Bedding planes and structural features such as faults, folds, are shown with s ...
ping.
Submarine volcanoes
 Submarine volcanoes are common features of the ocean floor. Volcanic activity during the
Submarine volcanoes are common features of the ocean floor. Volcanic activity during the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
Epoch has been documented at only 119 submarine volcanoes, but there may be more than one million geologically young submarine volcanoes on the ocean floor. In shallow water, active volcanoes disclose their presence by blasting steam and rocky debris high above the ocean's surface. In the deep ocean basins, the tremendous weight of the water prevents the explosive release of steam and gases; however, submarine eruptions can be detected by hydrophone
A hydrophone ( grc, ὕδωρ + φωνή, , water + sound) is a microphone designed to be used underwater for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones are based on a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potenti ...
s and by the discoloration of water because of volcanic gas
Volcanic gases are gases given off by active (or, at times, by dormant) volcanoes. These include gases trapped in cavities (vesicles) in volcanic rocks, dissolved or dissociated gases in magma and lava, or gases emanating from lava, from volcani ...
es. Pillow lava
Pillow lavas are lavas that contain characteristic pillow-shaped structures that are attributed to the extrusion of the lava underwater, or ''subaqueous extrusion''. Pillow lavas in volcanic rock are characterized by thick sequences of discont ...
is a common eruptive product of submarine volcanoes and is characterized by thick sequences of discontinuous pillow-shaped masses which form under water. Even large submarine eruptions may not disturb the ocean surface, due to the rapid cooling effect and increased buoyancy in water (as compared to air), which often causes volcanic vents to form steep pillars on the ocean floor. Hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspo ...
s are common near these volcanoes, and some support peculiar ecosystems based on chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic (chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic ( chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototr ...
s feeding on dissolved minerals. Over time, the formations created by submarine volcanoes may become so large that they break the ocean surface as new islands or floating pumice raft
A pumice raft is a floating raft of pumice created by some eruptions of submarine volcanoes or coastal subaerial volcanoes.
Biologists suggest that animals and plants have migrated from island to island on pumice rafts.
Pumice rafts have uniqu ...
s.
In May and June 2018, a multitude of seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
signals were detected by earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
monitoring agencies all over the world. They took the form of unusual humming sounds, and some of the signals detected in November of that year had a duration of up to 20 minutes. An oceanographic
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
research campaign in May 2019 showed that the previously mysterious humming noises were caused by the formation of a submarine volcano off the coast of Mayotte
Mayotte (; french: Mayotte, ; Shimaore: ''Maore'', ; Kibushi: ''Maori'', ), officially the Department of Mayotte (french: Département de Mayotte), is an overseas department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is loca ...
.
Subglacial volcanoes
Subglacial volcanoes develop underneath icecaps. They are made up of lava plateaus capping extensive pillow lavas andpalagonite
Palagonite is an alteration product from the interaction of water with volcanic glass of chemical composition similar to basalt. Palagonite can also result from the interaction between water and basalt melt. The water flashes to steam on contact ...
. These volcanoes are also called table mountains, tuya
A tuya is a flat-topped, steep-sided volcano formed when lava erupts through a thick glacier or ice sheet. They are rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were covered by glaciers and had active volcanism during the same period.
As lava ...
s, or (in Iceland) mobergs. Very good examples of this type of volcano can be seen in Iceland and in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
. The origin of the term comes from Tuya Butte
Tuya Butte is a tuya in the Tuya Range of north-central British Columbia, Canada. It is a bit less isolated from other ranges than neighbouring Mount Josephine. Some of the other volcanoes in the area include South Tuya, Ash Mountain, and M ...
, which is one of the several tuyas in the area of the Tuya River
The Tuya River is a major tributary of the Stikine River in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. From its source at High Tuya Lake in Tuya Mountains Provincial Park just south of Ash Mountain, the highest peak of the ...
and Tuya Range
The Tuya Range is a mountain range in the Stikine Ranges of the Cassiar Mountains in the far north of the Canadian province of British Columbia, near its border with the Yukon Territory and to the southwest of Watson Lake, Yukon, which is the ne ...
in northern British Columbia. Tuya Butte was the first such landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
analyzed and so its name has entered the geological literature for this kind of volcanic formation. The Tuya Mountains Provincial Park
Tuya Mountains Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, protecting the Tuya Range, a volcanic region at the head of the Tuya River. The park is located on the north side of Tuya Lake
Tuya Lake, located in northweste ...
was recently established to protect this unusual landscape, which lies north of Tuya Lake
Tuya Lake, located in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, presumably derives its name from the presence of nearby steep-sided, flat-topped volcanoes, known as tuyas. The lake is situated just south of Tuya Butte at a latitude of about 59 d ...
and south of the Jennings River
The Jennings River is a river in far northern British Columbia, Canada. It is approximately long. The river was named for William T. Jennings (1846-1906), a civil engineer who, in 1897, assessed various road and railroad routes from the Pacifi ...
near the boundary with the Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
.
Mud volcanoes
Mud volcanoes (mud domes) are formations created by geo-excreted liquids and gases, although there are several processes which may cause such activity. The largest structures are 10 kilometers in diameter and reach 700 meters high.Erupted material
 The material that is expelled in a
The material that is expelled in a volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are oft ...
can be classified into three types:
#Volcanic gas
Volcanic gases are gases given off by active (or, at times, by dormant) volcanoes. These include gases trapped in cavities (vesicles) in volcanic rocks, dissolved or dissociated gases in magma and lava, or gases emanating from lava, from volcani ...
es, a mixture made mostly of steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporizatio ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, and a sulfur compound (either sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic a ...
, SO2, or hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
, H2S, depending on the temperature)
#Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
, the name of magma when it emerges and flows over the surface
#Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they r ...
, particles of solid material of all shapes and sizes ejected and thrown through the air
Volcanic gases
The concentrations of differentvolcanic gas
Volcanic gases are gases given off by active (or, at times, by dormant) volcanoes. These include gases trapped in cavities (vesicles) in volcanic rocks, dissolved or dissociated gases in magma and lava, or gases emanating from lava, from volcani ...
es can vary considerably from one volcano to the next. Water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
is typically the most abundant volcanic gas, followed by carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
and sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic a ...
. Other principal volcanic gases include hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
, hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chlorid ...
, and hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock ...
. A large number of minor and trace gases are also found in volcanic emissions, for example hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
, halocarbon
Halocarbon compounds are chemicals in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine – ) resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlor ...
s, organic compounds, and volatile metal chlorides.
Lava flows
 The form and style of eruption of a volcano is largely determined by the composition of the lava it erupts. The viscosity (how fluid the lava is) and the amount of dissolved gas are the most important characteristics of magma, and both are largely determined by the amount of silica in the magma. Magma rich in silica is much more viscous than silica-poor magma, and silica-rich magma also tends to contain more dissolved gases.
Lava can be broadly classified into four different compositions:
* If the erupted
The form and style of eruption of a volcano is largely determined by the composition of the lava it erupts. The viscosity (how fluid the lava is) and the amount of dissolved gas are the most important characteristics of magma, and both are largely determined by the amount of silica in the magma. Magma rich in silica is much more viscous than silica-poor magma, and silica-rich magma also tends to contain more dissolved gases.
Lava can be broadly classified into four different compositions:
* If the erupted magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
contains a high percentage (>63%) of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, the lava is described as ''felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, wh ...
''. Felsic lavas (dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained ( aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyo ...
s or rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The miner ...
s) are highly viscous
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the in ...
and are erupted as domes or short, stubby flows. Lassen Peak
Lassen Peak ( ), commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is a lava dome volcano and the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range of the Western United States. Located in the Shasta Cascade region of Northern California, it is part of the ...
in California is an example of a volcano formed from felsic lava and is actually a large lava dome.
:Because felsic magmas are so viscous, they tend to trap volatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.
On planet Earth, the term ...
(gases) that are present, which leads to explosive volcanism. Pyroclastic flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of b ...
s (ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surro ...
s) are highly hazardous products of such volcanoes, since they hug the volcano's slopes and travel far from their vents during large eruptions. Temperatures as high as are known to occur in pyroclastic flows, which will incinerate everything flammable in their path, and thick layers of hot pyroclastic flow deposits can be laid down, often many meters thick. Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U ...
's Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes
The Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes is a valley within Katmai National Park and Preserve in Alaska which is filled with ash flow from the eruption of Novarupta on June 6–8, 1912.
Following the eruption, thousands of fumaroles vented steam fro ...
, formed by the eruption of Novarupta
Novarupta (meaning "newly erupted" in Latin) is a volcano that was formed in 1912, located on the Alaska Peninsula on a slope of Trident Volcano in Katmai National Park and Preserve, about southwest of Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage. Formed durin ...
near Katmai in 1912, is an example of a thick pyroclastic flow or ignimbrite deposit. Volcanic ash that is light enough to be erupted high into the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
as an eruption column
An eruption column or eruption plume is a cloud of super-heated ash and tephra suspended in gases emitted during an explosive volcanic eruption. The volcanic materials form a vertical column or plume that may rise many kilometers into the ai ...
may travel hundreds of kilometers before it falls back to ground as a fallout tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
. Volcanic gases may remain in the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air h ...
for years.
:Felsic magmas are formed within the crust, usually through melting of crust rock from the heat of underlying mafic magmas. The lighter felsic magma floats on the mafic magma without significant mixing. Less commonly, felsic magmas are produced by extreme fractional crystallization of more mafic magmas. This is a process in which mafic minerals crystallize out of the slowly cooling magma, which enriches the remaining liquid in silica.
* If the erupted magma contains 52–63% silica, the lava is of ''intermediate composition In igneous petrology, an intermediate composition refers to the chemical composition of a rock that has 5263 wt% SiO2 being an intermediate between felsic and mafic compositions. Typical intermediate rocks include andesite, dacite, and trachyan ...
'' or ''andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomin ...
''. Intermediate magmas are characteristic of stratovolcanoes. They are most commonly formed at convergent boundaries
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a ...
between tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
s, by several processes. One process is hydration melting of mantle peridotite followed by fractional crystallization. Water from a subducting slab
Slab or SLAB may refer to:
Physical materials
* Concrete slab, a flat concrete plate used in construction
* Stone slab, a flat stone used in construction
* Slab (casting), a length of metal
* Slab (geology), that portion of a tectonic plate tha ...
rises into the overlying mantle, lowering its melting point, particularly for the more silica-rich minerals. Fractional crystallization further enriches the magma in silica. It has also been suggested that intermediate magmas are produced by melting of sediments carried downwards by the subducted slab. Another process is magma mixing between felsic rhyolitic and mafic basaltic magmas in an intermediate reservoir prior to emplacement or lava flow.
* If the erupted magma contains <52% and >45% silica, the lava is called ''mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks in ...
'' (because it contains higher percentages of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
(Mg) and iron (Fe)) or basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic. These lavas are usually hotter and much less viscous than felsic lavas. Mafic magmas are formed by partial melting of dry mantle, with limited fractional crystallization and assimilation of crustal material.
:Mafic lavas occur in a wide range of settings. These include mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
s; Shield volcanoes (such the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
, including Mauna Loa
Mauna Loa ( or ; Hawaiian: ; en, Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano (as opposed to subaqueous volcanoes) in both mass and ...
and Kilauea), on both oceanic and continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' be ...
; and as continental flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s.
* Some erupted magmas contain ≤45% silica and produce ''ultramafic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
'' lava. Ultramafic flows, also known as komatiite
Komatiite () is a type of ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rock defined as having crystallised from a lava of at least 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon, potassium and aluminium, and high to extremely high magnesium content. Komatiite w ...
s, are very rare; indeed, very few have been erupted at the Earth's surface since the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided i ...
, when the planet's heat flow was higher. They are (or were) the hottest lavas, and were probably more fluid than common mafic lavas, with a viscosity less than a tenth that of hot basalt magma.
Mafic lava flows show two varieties of surface texture: Aa (pronounced ) and pāhoehoe
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
(), both Hawaiian words. Aa is characterized by a rough, clinkery surface and is the typical texture of cooler basalt lava flows. Pāhoehoe is characterized by its smooth and often ropey or wrinkly surface and is generally formed from more fluid lava flows. Pāhoehoe flows are sometimes observed to transition to aa flows as they move away from the vent, but never the reverse.
More silicic lava flows take the form of block lava, where the flow is covered with angular, vesicle-poor blocks. Rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The ...
flows typically consist largely of obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.
Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements such as silicon ...
.
Tephra
 Tephra is made when magma inside the volcano is blown apart by the rapid expansion of hot volcanic gases. Magma commonly explodes as the gas dissolved in it comes out of solution as the pressure decreases when it flows to the surface. These violent explosions produce particles of material that can then fly from the volcano. Solid particles smaller than 2 mm in diameter ( sand-sized or smaller) are called volcanic ash.
Tephra and other
Tephra is made when magma inside the volcano is blown apart by the rapid expansion of hot volcanic gases. Magma commonly explodes as the gas dissolved in it comes out of solution as the pressure decreases when it flows to the surface. These violent explosions produce particles of material that can then fly from the volcano. Solid particles smaller than 2 mm in diameter ( sand-sized or smaller) are called volcanic ash.
Tephra and other volcaniclastics
Volcaniclastics are geologic materials composed of broken fragments ( clasts) of volcanic rock. These encompass all clastic volcanic materials, regardless of what process fragmented the rock, how it was subsequently transported, what environment it ...
(shattered volcanic material) make up more of the volume of many volcanoes than do lava flows. Volcaniclastics may have contributed as much as a third of all sedimentation in the geologic record. The production of large volumes of tephra is characteristic of explosive volcanism.
Types of volcanic eruptions
explosive eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma su ...
s. The range of observed eruption styles is expressed from historical examples.
* Hawaiian eruptions are typical of volcanoes that erupt mafic lava with a relatively low gas content. These are almost entirely effusive, producing local fire fountains and highly fluid lava flows but relatively little tephra. They are named after the Hawaiian volcanoes.
* Strombolian eruptions are characterized by moderate viscosities and dissolved gas levels. They are characterized by frequent but short-lived eruptions that can produce eruptive columns hundreds of meters high. Their primary product is scoria
Scoria is a pyroclastic, highly vesicular, dark-colored volcanic rock that was ejected from a volcano as a molten blob and cooled in the air to form discrete grains or clasts.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) '' ...
. They are named after Stromboli
Stromboli ( , ; scn, Struògnuli ) is an island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, off the north coast of Sicily, containing Mount Stromboli, one of the four active volcanoes in Italy. It is one of the eight Aeolian Islands, a volcanic arc north of Si ...
.
* Vulcanian eruptions are characterized by yet higher viscosities and partial crystallization of magma, which is often intermediate in composition. Eruptions take the form of short-lived explosions over the course of several hours, which destroy a central dome and eject large lava blocks and bombs. This is followed by an effusive phase that rebuilds the central dome. Vulcanian eruptions are named after Vulcano
Vulcano ( scn, Vurcanu) or Vulcan is a small volcanic island belonging to Italy in the Tyrrhenian Sea, about north of Sicily and located at the southernmost end of the seven Aeolian Islands. The island is known for its volcanic activity and ...
.
* Peléan eruptions are more violent still, being characterized by dome growth and collapse that produces various kinds of pyroclastic flows. They are named after Mount Pelée
Mount Pelée or Mont Pelée ( ; french: Montagne Pelée, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Montann Pèlé, meaning "bald mountain" or "peeled mountain") is an active volcano at the northern end of Martinique, an island and French overseas departmen ...
.
* Plinian eruptions are the most violent of all volcanic eruptions. They are characterized by sustained huge eruption columns whose collapse produces catastrophic pyroclastic flows. They are named after Pliny the Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo (61 – c. 113), better known as Pliny the Younger (), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate ...
, who chronicled the Plinian eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79
Of the many eruptions of Mount Vesuvius, a major stratovolcano in southern Italy, the best-known is its eruption in 79 AD, which was one of the deadliest in European history. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD is one of the best-known in h ...
AD.
* Phreatomagmatic eruptions are characterized by interaction of rising magma with groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
. They are driven by the resulting rapid buildup of pressure in the superheated groundwater.
* Phreatic eruptions are characterized by superheating of groundwater that comes in contact with hot rock or magma. They are distinguished from phreatomagmatic eruptions because the erupted material is all country rock
Country rock is a genre of music which fuses rock and country. It was developed by rock musicians who began to record country-flavored records in the late 1960s and early 1970s. These musicians recorded rock records using country themes, vocal ...
; no magma is erupted.
Volcanic activity
 Volcanoes vary greatly in their level of activity, with individual volcanic systems having an ''eruption recurrence'' ranging from several times a year to once in tens of thousands of years. Volcanoes are informally described as erupting, active, dormant, or extinct, but the definitions of these terms are not entirely uniform amongst volcanologists. The level of activity of most volcanoes falls upon a graduated spectrum, with much overlap between categories, and does not always fit neatly into only one of these three separate categories.
Volcanoes vary greatly in their level of activity, with individual volcanic systems having an ''eruption recurrence'' ranging from several times a year to once in tens of thousands of years. Volcanoes are informally described as erupting, active, dormant, or extinct, but the definitions of these terms are not entirely uniform amongst volcanologists. The level of activity of most volcanoes falls upon a graduated spectrum, with much overlap between categories, and does not always fit neatly into only one of these three separate categories.
Erupting
The USGS defines a volcano as "erupting" whenever the ejection of magma from any point on the volcano is visible, including visible magma still contained within the walls of the summit crater.Active
While there is no international consensus among volcanologists on how to define an "active" volcano, the USGS defines a volcano as "active" whenever subterranean indicators, such as earthquake swarms, ground inflation, or unusually high levels of carbon dioxide and/or sulfur dioxide are present.How We Tell if a Volcano Is Active, Dormant, or ExtinctWired. 15 August 2015. By Erik Klimetti. Downloaded 24 July 2022.
Dormant and reactivated
 The USGS defines a "dormant volcano" as ''Any volcano that is not showing any signs of unrest such as earthquake swarms, ground swelling, or excessive noxious gas emissions, but which shows signs that it could yet become active again.'' Many dormant volcanoes have not erupted for thousands of years, but have still shown signs that they may be likely to erupt again in the future.
In an article justifying the re-classification of Alaska's Mount Edgecumbe volcano from "dormant" to "active", volcanologists at the
The USGS defines a "dormant volcano" as ''Any volcano that is not showing any signs of unrest such as earthquake swarms, ground swelling, or excessive noxious gas emissions, but which shows signs that it could yet become active again.'' Many dormant volcanoes have not erupted for thousands of years, but have still shown signs that they may be likely to erupt again in the future.
In an article justifying the re-classification of Alaska's Mount Edgecumbe volcano from "dormant" to "active", volcanologists at the Alaska Volcano Observatory
The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) is a joint program of the United States Geological Survey, the Geophysical Institute of the University of Alaska Fairbanks, and the State of Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys (ADGGS). AVO ...
pointed out that the term "dormant" in reference to volcanoes has been deprecated over the past few decades and that "[t]he term "dormant volcano" is so little used and undefined in modern volcanology that the Encyclopedia of Volcanoes (2000) does not contain it in the glossaries or index," however the USGS still widely employs the term.
Previously a volcano was often considered to be extinct if there were no written records of its activity. With modern volcanic activity monitoring techniques, it is now understood that volcanoes may remain dormant for a long period of time, and then become unexpectedly active again. For example, Yellowstone Caldera, Yellowstone has a repose/recharge period of around 700,000 years, and Toba Lake, Toba of around 380,000 years. Vesuvius was described by Roman writers as having been covered with gardens and vineyards before its Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79, eruption of 79 CE, which destroyed the towns of Herculaneum and Pompeii.
It can sometimes be difficult to distinguish between an extinct volcano and a dormant (inactive) one. Mount Pinatubo, Pinatubo was an inconspicuous volcano, unknown to most people in the surrounding areas, and initially not seismically monitored before its unanticipated and catastrophic eruption of 1991. Two other examples of volcanoes which were once thought to be extinct, before springing back into eruptive activity were the long-dormant Soufrière Hills volcano on the island of Montserrat, thought to be extinct until activity resumed in 1995 (turning its capital Plymouth, Montserrat, Plymouth into a ghost town) and Fourpeaked Mountain in Alaska, which, before its September 2006 eruption, had not erupted since before 8000 BCE.
Extinct
 Extinct volcanoes are those that scientists consider unlikely to erupt again because the volcano no longer has a magma supply. Examples of extinct volcanoes are many volcanoes on the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain in the Pacific Ocean (although some volcanoes at the eastern end of the chain are active), Hohentwiel in Germany, Shiprock in
Extinct volcanoes are those that scientists consider unlikely to erupt again because the volcano no longer has a magma supply. Examples of extinct volcanoes are many volcanoes on the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain in the Pacific Ocean (although some volcanoes at the eastern end of the chain are active), Hohentwiel in Germany, Shiprock in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, United States, US, Capulin Volcano National Monument, Capulin in New Mexico, US, Zuidwal volcano in the Netherlands, and many volcanoes in Italy such as Monte Vulture. Edinburgh Castle in Scotland is located atop an extinct volcano, which forms Castle Rock (Edinburgh), Castle Rock. Whether a volcano is truly extinct is often difficult to determine. Since "supervolcano" caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
s can have eruptive lifespans sometimes measured in millions of years, a caldera that has not produced an eruption in tens of thousands of years may be considered dormant instead of extinct.
Volcanic-alert level
The three common popular classifications of volcanoes can be subjective and some volcanoes thought to have been extinct have erupted again. To help prevent people from falsely believing they are not at risk when living on or near a volcano, countries have adopted new classifications to describe the various levels and stages of volcanic activity. Some alert systems use different numbers or colors to designate the different stages. Other systems use colors and words. Some systems use a combination of both.Decade volcanoes
 The Decade Volcanoes are 16 volcanoes identified by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior (IAVCEI) as being worthy of particular study in light of their history of large, destructive eruptions and proximity to populated areas. They are named Decade Volcanoes because the project was initiated as part of the United Nations-sponsored International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (the 1990s). The 16 current Decade Volcanoes are:
* Avachinsky-Koryaksky (grouped together), Kamchatka Peninsula, Kamchatka, Russia
* Colima (volcano), Nevado de Colima, Jalisco and Colima, Mexico
* Mount Etna, Sicily, Italy
* Galeras, Nariño, Colombia
*
The Decade Volcanoes are 16 volcanoes identified by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior (IAVCEI) as being worthy of particular study in light of their history of large, destructive eruptions and proximity to populated areas. They are named Decade Volcanoes because the project was initiated as part of the United Nations-sponsored International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (the 1990s). The 16 current Decade Volcanoes are:
* Avachinsky-Koryaksky (grouped together), Kamchatka Peninsula, Kamchatka, Russia
* Colima (volcano), Nevado de Colima, Jalisco and Colima, Mexico
* Mount Etna, Sicily, Italy
* Galeras, Nariño, Colombia
* Mauna Loa
Mauna Loa ( or ; Hawaiian: ; en, Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano (as opposed to subaqueous volcanoes) in both mass and ...
, Hawaii, US
* Mount Merapi, Central Java, Indonesia
* Mount Nyiragongo, Democratic Republic of the Congo
* Mount Rainier, Washington (state), Washington, US
* Sakurajima, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan
* Santa María (volcano), Santa Maria/Santiaguito, Guatemala
* Santorini, Cyclades, Greece
* Taal Volcano, Luzon, Philippines
* Teide, Canary Islands, Spain
* Ulawun, New Britain, Papua New Guinea
* Mount Unzen, Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan
* Vesuvius, Province of Naples, Naples, Italy
The Deep Earth Carbon Degassing Project, an initiative of the Deep Carbon Observatory, monitors nine volcanoes, two of which are Decade volcanoes. The focus of the Deep Earth Carbon Degassing Project is to use Multi-Component Gas Analyzer System instruments to measure CO2/SO2 ratios in real-time and in high-resolution to allow detection of the pre-eruptive degassing of rising magmas, improving prediction of volcanic activity.
Volcanoes and humans

 Volcanic eruptions pose a significant threat to human civilization. However, volcanic activity has also provided humans with important resources.
Volcanic eruptions pose a significant threat to human civilization. However, volcanic activity has also provided humans with important resources.
Hazards
There are many different types of volcanic eruptions and associated activity: phreatic eruptions (steam-generated eruptions), explosive eruption of high-silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
lava (e.g., rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The miner ...
), effusive eruption of low-silica lava (e.g., basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
), pyroclastic flows, lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extr ...
s (debris flow) and Greenhouse gas emissions, carbon dioxide emission. All of these activities can pose a hazard to humans. Earthquakes, hot springs, fumaroles, mud pots and geysers often accompany volcanic activity.
Volcanic gases can reach the stratosphere, where they form sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
aerosols that can reflect solar radiation and lower surface temperatures significantly. Sulfur dioxide from the eruption of Huaynaputina may have caused the Russian famine of 1601–1603. Chemical reactions of sulfate aerosols in the stratosphere can also damage the ozone layer, and acids such as hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chlorid ...
(HCl) and hydrogen fluoride (HF) can fall to the ground as acid rain. Explosive eruption, Explosive volcanic eruptions release the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
and thus provide a deep source of carbon for biogeochemical cycles.
Ash thrown into the air by eruptions can present a hazard to aircraft, especially jet aircraft where the particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. This can cause major disruptions to air travel.
 A
A volcanic winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by volcanic ash and droplets of sulfuric acid and water obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, particularly explosiv ...
is thought to have taken place around 70,000 years ago after the supervolcano, supereruption of Lake Toba on Sumatra island in Indonesia, This may have created a Toba catastrophe theory, population bottleneck that affected the genetic inheritance of all humans today. Volcanic eruptions may have contributed to major extinction events, such as the Ordovician-Silurian extinction events, End-Ordovician, Permian-Triassic extinction event, Permian-Triassic, and Late Devonian extinction, Late Devonian mass extinctions.
The 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora created global climate anomalies that became known as the "Year Without a Summer" because of the effect on North American and European weather. The freezing winter of 1740–41, which led to widespread Irish Famine (1740–1741), famine in northern Europe, may also owe its origins to a volcanic eruption.
Benefits
Although volcanic eruptions pose considerable hazards to humans, past volcanic activity has created important economic resources. Tuff formed from volcanic ash is a relatively soft rock, and it has been used for construction since ancient times.Marcari, G., G. Fabbrocino, and G. Manfredi. "Shear seismic capacity of tuff masonry panels in heritage constructions." Structural Studies, Repairs and Maintenance of Heritage Architecture X 95 (2007): 73. The Romans often used tuff, which is abundant in Italy, for construction. The Rapa Nui people used tuff to make most of the ''moai'' statues in Easter Island.Richards, Colin. 2016"Making Moai: Reconsidering Concepts of Risk in the Construction of Megalithic Architecture in Rapa Nui (Easter Island)"
. ''Rapa Nui–Easter Island: Cultural and Historical Perspectives'', pp.150-151 Volcanic ash and weathered basalt produce some of the most fertile soil in the world, rich in nutrients such as iron, magnesium, potassium, calcium, and phosphorus. Volcanic activity is responsible for emplacing valuable mineral resources, such as metal ores. It is accompanied by high rates of heat flow from the Earth's interior. These can be tapped as geothermal power.
Safety considerations
Many volcanoes near human settlements are heavily monitored with the aim of providing adequate advance warnings of imminent eruptions to nearby populations. Also, a better modern-day understanding of volcanology has led to some better informed governmental responses to unanticipated volcanic activities. While the science of volcanology may not yet be capable of predicting the exact times and dates of eruptions far into the future, on suitably monitored volcanoes the monitoring of ongoing volcanic indicators is generally capable of predicting imminent eruptions with advance warnings minimally of hours, and usually of days prior to any imminent eruptions. Thus in many cases, while volcanic eruptions may still cause major property destruction, the periodic large-scale loss of human life that was once associated with many volcanic eruptions has recently been significantly reduced in areas where volcanoes are adequately monitored. This life-saving ability is derived via such volcanic-activity monitoring programs, through the greater abilities of local officials to facilitate timely evacuations based upon the greater modern-day knowledge of volcanism that is now available, and upon improved communications technologies such as cell phones. Such operations tend to provide enough time for humans to escape at least with their lives prior to a pending eruption. One example of such a recent successful volcanic evacuation was the Mount Pinatubo evacuation of 1991. This evacuation is believed to have saved 20,000 lives. Citizens who may be concerned about their own exposure to risk from nearby volcanic activity should familiarize themselves with the types of, and quality of, volcano monitoring and public notification procedures being employed by governmental authorities in their areas.Volcanoes on other celestial bodies
 The Earth's Moon has no large volcanoes and no current volcanic activity, although recent evidence suggests it may still possess a partially molten core. However, the Moon does have many volcanic features such as lunar mare, maria (the darker patches seen on the Moon), rilles and lunar dome, domes.
The planet Venus has a surface that is 90%
The Earth's Moon has no large volcanoes and no current volcanic activity, although recent evidence suggests it may still possess a partially molten core. However, the Moon does have many volcanic features such as lunar mare, maria (the darker patches seen on the Moon), rilles and lunar dome, domes.
The planet Venus has a surface that is 90% basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
, indicating that volcanism played a major role in shaping its surface. The planet may have had a major global resurfacing event about 500 million years ago, from what scientists can tell from the density of impact craters on the surface. Lava, Lava flows are widespread and forms of volcanism not present on Earth occur as well. Changes in the planet's atmosphere and observations of lightning have been attributed to ongoing volcanic eruptions, although there is no confirmation of whether or not Venus is still volcanically active. However, radar sounding by the Magellan probe revealed evidence for comparatively recent volcanic activity at Venus's highest volcano Maat Mons, in the form of ash flows near the summit and on the northern flank. However, the interpretation of the flows as ash flows has been questioned.
 There are several extinct volcanoes on Mars, four of which are vast shield volcanoes far bigger than any on Earth. They include Arsia Mons, Ascraeus Mons, Hecates Tholus, Olympus Mons, and Pavonis Mons. These volcanoes have been extinct for many millions of years, but the European ''Mars Express'' spacecraft has found evidence that volcanic activity may have occurred on Mars in the recent past as well.
There are several extinct volcanoes on Mars, four of which are vast shield volcanoes far bigger than any on Earth. They include Arsia Mons, Ascraeus Mons, Hecates Tholus, Olympus Mons, and Pavonis Mons. These volcanoes have been extinct for many millions of years, but the European ''Mars Express'' spacecraft has found evidence that volcanic activity may have occurred on Mars in the recent past as well.
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
's Natural satellite, moon Io (moon), Io is the most volcanically active object in the Solar System because of tides, tidal interaction with Jupiter. It is covered with volcanoes that erupt sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic a ...
and silicate rock, and as a result, Io (moon), Io is constantly being resurfaced. Its lavas are the hottest known anywhere in the Solar System, with temperatures exceeding 1,800 K (1,500 °C). In February 2001, the largest recorded volcanic eruptions in the Solar System occurred on Io. Europa (moon), Europa, the smallest of Jupiter's Galilean moons, also appears to have an active volcanic system, except that its volcanic activity is entirely in the form of water, which freezes into ice on the frigid surface. This process is known as cryovolcanism, and is apparently most common on the moons of the outer planets of the Solar System.
In 1989, the ''Voyager 2'' spacecraft observed cryovolcano
A cryovolcano (sometimes informally called an ice volcano) is a type of volcano that erupts volatiles such as water, ammonia or methane into an extremely cold environment that is at or below their freezing point. The process of formation is known ...
es (ice volcanoes) on Triton (moon), Triton, a Natural satellite, moon of Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
, and in 2005 the ''Cassini–Huygens'' probe photographed Enceladus (moon)#Cryovolcanism, fountains of frozen particles erupting from Enceladus, a moon of Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
. The ejecta may be composed of water, liquid nitrogen, ammonia, dust, or methane compounds. ''Cassini–Huygens'' also found evidence of a methane-spewing cryovolcano on the Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
ian moon Titan (moon), Titan, which is believed to be a significant source of the methane found in its atmosphere. It is theorized that cryovolcanism may also be present on the Kuiper Belt Object 50000 Quaoar, Quaoar.
A 2010 study of the exoplanet COROT-7b, which was detected by transit method, transit in 2009, suggested that tidal heating from the host star very close to the planet and neighboring planets could generate intense volcanic activity similar to that found on Io.
History of volcanology
Many ancient accounts ascribe volcanic eruptions to supernatural causes, such as the actions of deity, gods or demigods. To the ancient Greeks, volcanoes' capricious power could only be explained as acts of the gods, while 16th/17th-century German astronomer Johannes Kepler believed they were ducts for the Earth's tears. One early idea counter to this was proposed by Society of Jesus, Jesuit Athanasius Kircher (1602–1680), who witnessed eruptions of Mount Etna andStromboli
Stromboli ( , ; scn, Struògnuli ) is an island in the Tyrrhenian Sea, off the north coast of Sicily, containing Mount Stromboli, one of the four active volcanoes in Italy. It is one of the eight Aeolian Islands, a volcanic arc north of Si ...
, then visited the crater of Vesuvius and published his view of an Earth with a central fire connected to numerous others caused by the burning of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, bitumen and coal.
Various explanations were proposed for volcano behavior before the modern understanding of the Earth's mantle (geology), mantle structure as a semisolid material was developed. For decades after awareness that compression and radioactive materials may be heat sources, their contributions were specifically discounted. Volcanic action was often attributed to chemical reactions and a thin layer of molten rock near the surface.
See also
* * List of volcanic eruptions by death toll * * * * *References
Further reading
* * * * This is a reference aimed at geologists, but many articles are accessible to non-professionals.External links
*U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency Volcano advice
Volcano World
{{Authority control Volcanoes, * Geological hazards Volcanism Plate tectonics Volcanic landforms Volcanoes by status, * Volcanic rocks, * Volcanology Articles containing video clips