|
Partial Melting
Partial melting occurs when only a portion of a solid is melted. For mixed substances, such as a rock containing several different minerals or a mineral that displays solid solution, this melt can be different from the bulk composition of the solid. Partial melting occurs where the solidus and liquidus temperatures are different. For single minerals this can happen when they exhibit solid solution, for example in olivines between iron and magnesium. In rocks made up of several different minerals, some will melt at lower temperatures than others. Partial melting of the mantle Melting in the mantle requires one of three possible events to occur: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or the addition of volatiles to the system (a change in composition). Temperature In the case of raising the temperature, mantle melting will only occur if the mantle is heated past the normal geotherm. It is believed that heat flux from the core and lower mantle is responsible for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabatic Process
In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process (Greek: ''adiábatos'', "impassable") is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat or mass between the thermodynamic system and its environment. Unlike an isothermal process, an adiabatic process transfers energy to the surroundings only as work.. A translation may be founhere. Also a mostly reliabltranslation is to be foundin As a key concept in thermodynamics, the adiabatic process supports the theory that explains the first law of thermodynamics. Some chemical and physical processes occur too rapidly for energy to enter or leave the system as heat, allowing a convenient "adiabatic approximation".Bailyn, M. (1994), pp. 52–53. For example, the adiabatic flame temperature uses this approximation to calculate the upper limit of flame temperature by assuming combustion loses no heat to its surroundings. In meteorology and oceanography, adiabatic cooling produces condensation of moisture or salinity, overs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (geology)
The matrix or groundmass of a rock is the finer-grained mass of material in which larger grains, crystals, or clasts are embedded. The matrix of an igneous rock consists of finer-grained, often microscopic, crystals in which larger crystals, called phenocrysts, are embedded. This porphyritic texture is indicative of multi-stage cooling of magma. For example, porphyritic andesite will have large phenocrysts of plagioclase in a fine-grained matrix. Also in South Africa, diamonds are often mined from a matrix of weathered clay-like rock ( kimberlite) called "yellow ground". The matrix of sedimentary rocks is finer-grained sedimentary material, such as clay or silt, in which larger grains or clasts are embedded. It is also used to describe the rock material in which a fossil is embedded. Cementation All sediments are at first in an incoherent condition (e.g. sands, clays and gravels, beds of shells), and they may remain in this state for an indefinite period. Millions of ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incompatible Element
In petrology and geochemistry, an incompatible element is one that is unsuitable in size and/or charge to the cation sites of the minerals of which it is included. It is defined by the partition coefficient between rock-forming minerals and melt being much smaller than 1. During the fractional crystallization of magma and magma generation by the partial melting of the Earth's mantle and crust, elements that have difficulty in entering cation sites of the minerals are concentrated in the melt phase of magma (liquid phase). Two groups of incompatible elements that have difficulty entering the solid phase are known by acronyms. One group includes elements having large ionic radius, such as potassium, rubidium, caesium, strontium, barium (called LILE, or large-ion lithophile elements), and the other group includes elements of large ionic valences (or high charges), such as zirconium, niobium, hafnium, rare-earth elements (REE), thorium, uranium and tantalum Tantalum is a chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the uppermost mantle. The lithosphere is underlain by the asthenosphere which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle failure, while the asthenosphere deforms viscously and accommodates strain through plastic deformation. The thickness of the lithosphere is thus considered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the Earth#Surface, surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust (geology), crust or Mantle (geology), mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock (geology), rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
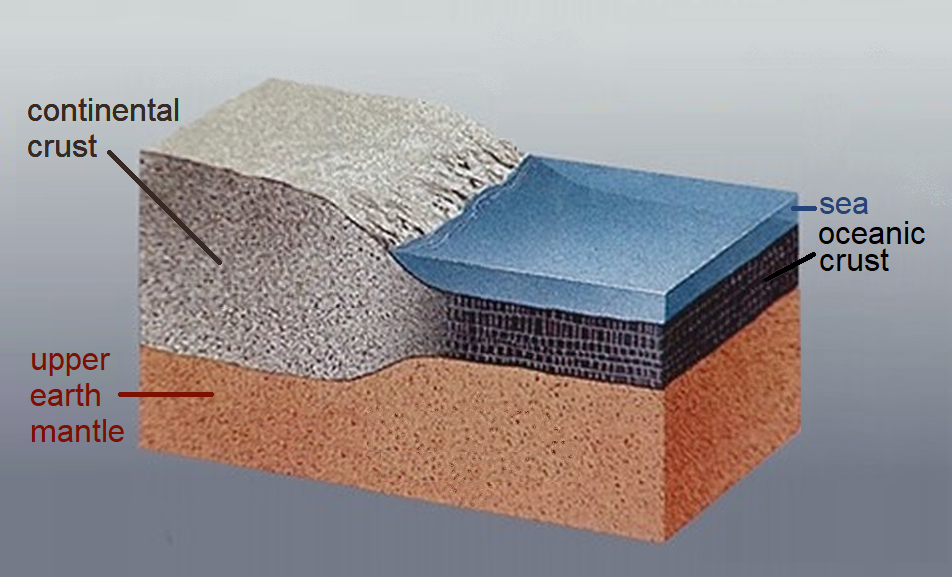
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Zones
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
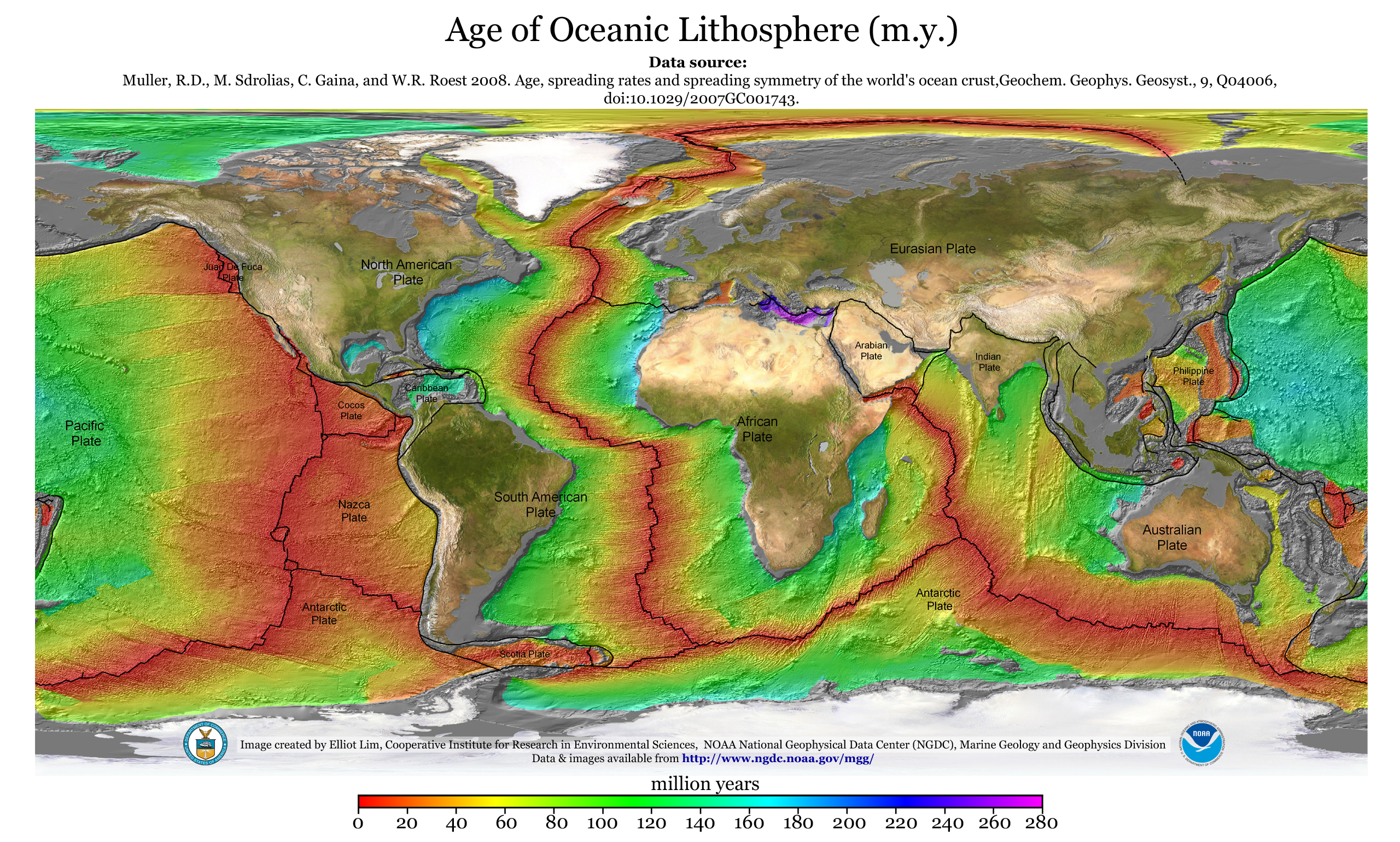
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. It is usually distinguished from the underlying mantle by its chemical makeup; however, in the case of icy satellites, it may be distinguished based on its phase (solid crust vs. liquid mantle). The crusts of Earth, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, the Moon and other planetary bodies formed via igneous processes and were later modified by erosion, impact cratering, volcanism, and sedimentation. Most terrestrial planets have fairly uniform crusts. Earth, however, has two distinct types: continental crust and oceanic crust. These two types have different chemical compositions and physical properties and were formed by different geological processes. Types of crust Planetary geologists divide crust into three categories based on how and when it formed. Primary crust / primordial crust This is a planet's "original" crust. It forms from solidification of a magma ocean. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |