Variant Call Format on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Variant Call Format or VCF is a standard text file format used in
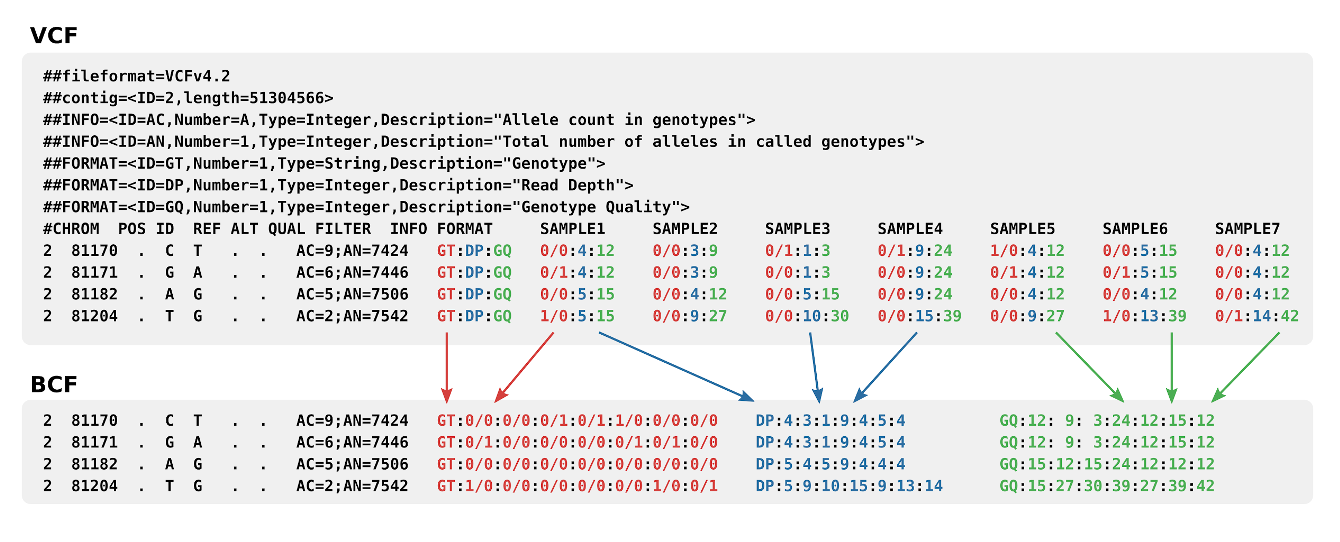
An explanation of the format in picture form
{{Bioinformatics Biological sequence format
bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, ...
for storing gene sequence
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
or DNA sequence variations. The format was developed in 2010 for the 1000 Genomes Project
The 1000 Genomes Project (1KGP), taken place from January 2008 to 2015, was an international research effort to establish the most detailed catalogue of human genetic variation at the time. Scientists planned to sequence the genomes of at least o ...
and has since been used by other large-scale genotyping Genotyping is the process of determining differences in the genetic make-up (genotype) of an individual by examining the individual's DNA sequence using bioassay, biological assays and comparing it to another individual's sequence or a reference seq ...
and DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
projects. VCF is a common output format for variant calling programs due to its relative simplicity and scalability. Many tools have been developed for editing and manipulating VCF files, including VCFtools, which was released in conjunction with the VCF format in 2011, and BCFtools, which was included as part of SAMtools
SAMtools is a set of utilities for interacting with and post-processing short DNA sequence read alignments in the SAM (Sequence Alignment/Map), BAM (Binary Alignment/Map) and CRAM formats, written by Heng Li. These files are generated as output ...
until being split into an independent package in 2014.
The standard is currently in version 4.5, although the 1000 Genomes Project
The 1000 Genomes Project (1KGP), taken place from January 2008 to 2015, was an international research effort to establish the most detailed catalogue of human genetic variation at the time. Scientists planned to sequence the genomes of at least o ...
has developed its own specification for structural variations such as duplications, which are not easily accommodated into the existing schema.
Additional file formats have been developed based on VCF, including genomic VCF (gVCF). gVCF is an extended format which includes additional information about "blocks" that match the reference and their qualities.
Example
##fileformat=VCFv4.3
##fileDate=20090805
##source=myImputationProgramV3.1
##reference=file:///seq/references/1000GenomesPilot-NCBI36.fasta
##contig=
##phasing=partial
##INFO=
##INFO=
##INFO=
##INFO=
##INFO=
##INFO=
##FILTER=
##FILTER=
##FORMAT=
##FORMAT=
##FORMAT=
##FORMAT=
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT NA00001 NA00002 NA00003
20 14370 rs6054257 G A 29 PASS NS=3;DP=14;AF=0.5;DB;H2 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0, 0:48:1:51,51 1, 0:48:8:51,51 1/1:43:5:.,.
20 17330 . T A 3 q10 NS=3;DP=11;AF=0.017 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0, 0:49:3:58,50 0, 1:3:5:65,3 0/0:41:3
20 1110696 rs6040355 A G,T 67 PASS NS=2;DP=10;AF=0.333,0.667;AA=T;DB GT:GQ:DP:HQ 1, 2:21:6:23,27 2, 1:2:0:18,2 2/2:35:4
20 1230237 . T . 47 PASS NS=3;DP=13;AA=T GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0, 0:54:7:56,60 0, 0:48:4:51,51 0/0:61:2
20 1234567 microsat1 GTC G,GTCT 50 PASS NS=3;DP=9;AA=G GT:GQ:DP 0/1:35:4 0/2:17:2 1/1:40:3

The VCF header
The header begins the file and providesmetadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
describing the body of the file. Header lines are denoted as starting with . Special keywords in the header are denoted with . Recommended keywords include , and .
The header contains keywords that optionally semantically and syntactically describe the fields used in the body of the file, notably INFO, FILTER, and FORMAT (see below).
The columns of a VCF
The body of VCF follows the header, and is tab separated into 8 mandatory columns and an unlimited number of optional columns that may be used to record other information about the sample(s). When additional columns are used, the first optional column is used to describe the format of the data in the columns that follow.Common INFO fields
Arbitrary keys are permitted, although the following sub-fields are reserved (albeit optional): Any other info fields are defined in the .vcf header.Common FORMAT fields
Any other format fields are defined in the .vcf header.Binary VCF
Binary VCF or BCF files are binary, BGZF compressed variation of VCF files. BCF files allow fast and efficient indexed queries through tools like Tabix once an index file has been created.See also
* TheFASTA
FASTA is a DNA and protein sequence alignment software package first described by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985. Its legacy is the FASTA format which is now ubiquitous in bioinformatics.
History
The original FASTA program ...
format, used to represent genome sequences.
* The FASTQ
FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both a biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence) and its corresponding quality scores. Both the sequence letter and quality score are each encoded with a single ASCII character for brevity.
...
format, used to represent DNA sequencer reads along with quality scores.
* The SAM format, used to represent genome sequencer reads that have been aligned to genome sequences.
* The GVF format (Genome Variation Format), an extension based on the GFF3 format.
* Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH), the group leading the management and expansion of the VCF format. The VCF specification is no longer maintained by the 1000 Genomes Project.
* Human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These ar ...
* Human genetic variation
Human genetic variation is the genetic differences in and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (alleles), a situation called polymorphism.
No two humans are genetically identical. Even ...
* Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in ...
(SNP)
References
External links
An explanation of the format in picture form
{{Bioinformatics Biological sequence format