Utoronto Coa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a
 On March 15, 1827, a
On March 15, 1827, a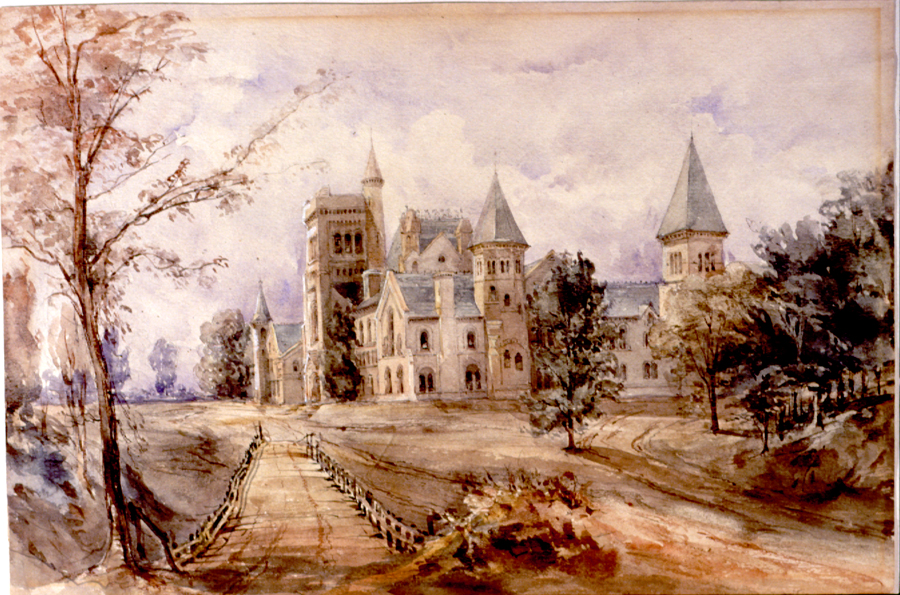  Established in 1878, the School of Practical Science was the precursor to the Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, which has been nicknamed ''Skule'' since its earliest days. While the Faculty of Medicine opened in 1843, medical teaching was conducted by proprietary schools from 1853 until 1887 when the faculty absorbed the Toronto School of Medicine. Meanwhile, the university continued to set examinations and confer medical degrees. The university opened the Faculty of Law in 1887, followed by the Faculty of Dentistry in 1888 when the
Established in 1878, the School of Practical Science was the precursor to the Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, which has been nicknamed ''Skule'' since its earliest days. While the Faculty of Medicine opened in 1843, medical teaching was conducted by proprietary schools from 1853 until 1887 when the faculty absorbed the Toronto School of Medicine. Meanwhile, the university continued to set examinations and confer medical degrees. The university opened the Faculty of Law in 1887, followed by the Faculty of Dentistry in 1888 when the
 The
The
 The university grounds lie about north of the
The university grounds lie about north of the  A lawn at the northeast is anchored by Hart House, a Gothic-revival student centre complex. Among its many common rooms, the building's Great Hall is noted for large stained-glass windows and a long quotation from John Milton's ''
A lawn at the northeast is anchored by Hart House, a Gothic-revival student centre complex. Among its many common rooms, the building's Great Hall is noted for large stained-glass windows and a long quotation from John Milton's ''
 The University of Toronto has traditionally been a
The University of Toronto has traditionally been a
 The Faculty of Arts and Science is the university's main
The Faculty of Arts and Science is the university's main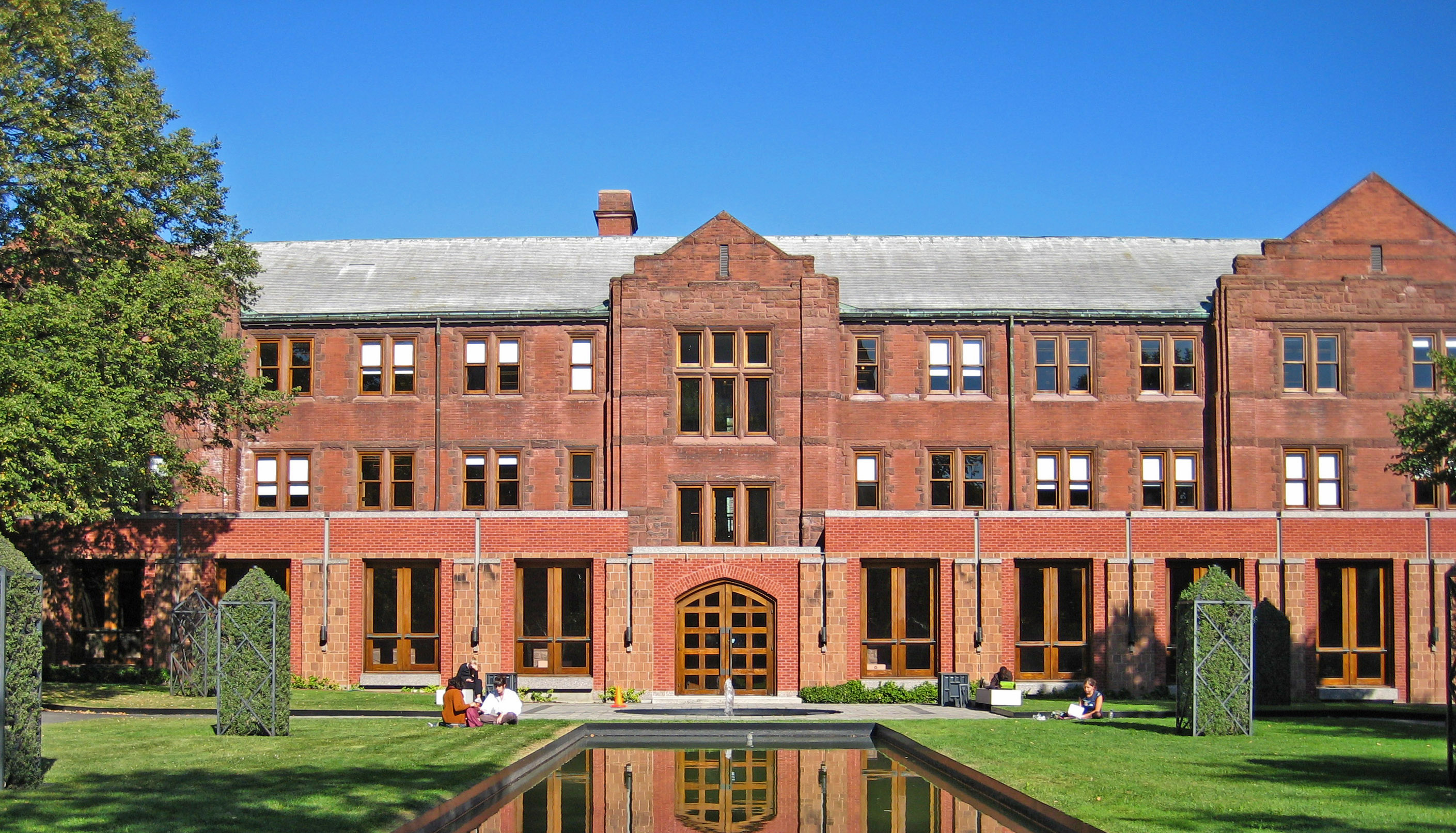  The
The  The Temerty Faculty of Medicine is affiliated with a network of ten
The Temerty Faculty of Medicine is affiliated with a network of ten
 The
The
 Since 1926, the University of Toronto has been a member of the
Since 1926, the University of Toronto has been a member of the  The discovery of insulin at the University of Toronto in 1921 is considered among the most significant events in the
The discovery of insulin at the University of Toronto in 1921 is considered among the most significant events in the  The University of Toronto is the primary research presence that supports one of the world's largest concentrations of
The University of Toronto is the primary research presence that supports one of the world's largest concentrations of
 In the heart of social, cultural and recreational life at the University of Toronto lies Hart House, the sprawling
In the heart of social, cultural and recreational life at the University of Toronto lies Hart House, the sprawling

 ''The Varsity (newspaper), The Varsity'' is one of Canada's oldest student-run newspapers in publication since 1880. The paper was originally a daily broadsheet, but has since adopted a compact format and is now weekly during the Fall and Winter semesters. It publishes online in the summer. ''Hart House Review'', a literary magazine, publishes prose, poetry, and visual art from emerging Canadian writers and artists. ''The Newspaper'' is an independent student-run community newspaper, published weekly since 1978. CIUT-FM is the university's campus radio station, while the University of Toronto Television broadcasts student-produced content. Students at each college and academic faculty also produce their own set of journals and news publications. University College's ''The Gargoyle (newspaper), The Gargoyle'' was an early training ground for such notables as journalist Naomi Klein and musician/comedian Paul Shaffer. Victoria University's ''Acta Victoriana'' is the oldest active literary journal in Canada, and provided first publication credits to such literary figures as Margaret Atwood and
''The Varsity (newspaper), The Varsity'' is one of Canada's oldest student-run newspapers in publication since 1880. The paper was originally a daily broadsheet, but has since adopted a compact format and is now weekly during the Fall and Winter semesters. It publishes online in the summer. ''Hart House Review'', a literary magazine, publishes prose, poetry, and visual art from emerging Canadian writers and artists. ''The Newspaper'' is an independent student-run community newspaper, published weekly since 1978. CIUT-FM is the university's campus radio station, while the University of Toronto Television broadcasts student-produced content. Students at each college and academic faculty also produce their own set of journals and news publications. University College's ''The Gargoyle (newspaper), The Gargoyle'' was an early training ground for such notables as journalist Naomi Klein and musician/comedian Paul Shaffer. Victoria University's ''Acta Victoriana'' is the oldest active literary journal in Canada, and provided first publication credits to such literary figures as Margaret Atwood and
 Each college at the University of Toronto operates its own set of residence halls and Cafeteria, dining halls clustered in a different area of the campus. Innis, New, St. Michael's, Trinity, University, Victoria, and Woodsworth colleges reserve most of their dormitories for their undergraduate students within the Faculty of Arts and Science while setting a portion available to students from the professional and postgraduate faculties.
Each college at the University of Toronto operates its own set of residence halls and Cafeteria, dining halls clustered in a different area of the campus. Innis, New, St. Michael's, Trinity, University, Victoria, and Woodsworth colleges reserve most of their dormitories for their undergraduate students within the Faculty of Arts and Science while setting a portion available to students from the professional and postgraduate faculties.
 The 44 sports teams of the Varsity Blues represent the university in intercollegiate competitions. The two main leagues in which the Blues participate are
The 44 sports teams of the Varsity Blues represent the university in intercollegiate competitions. The two main leagues in which the Blues participate are  Formed in 1891, the storied Toronto Varsity Blues men's ice hockey, Varsity Blues men's ice hockey team has left many legacies on the national, professional and international hockey scenes. Conn Smythe played for the Blues as a centre (ice hockey), centre during his undergraduate years, and was a Blues coach from 1923 to 1926. When Smythe took over the Toronto Maple Leafs in 1927, his new team adopted the Varsity Blues' familiar blue-and-white sweater design. Blues hockey competed at the Ice hockey at the 1928 Winter Olympics, 1928 Winter Olympics and captured the gold medal for Canada at the 1928 Winter Olympics, Canada. At the 1980 Winter Olympics, Blues coach Tom Watt (ice hockey), Tom Watt served as co-coach of the Canadian hockey team in which six players were Varsity grads. In all, the Blues have won the David Johnston University Cup, U Sports University Cup national hockey title ten times, last in 1984.
Formed in 1891, the storied Toronto Varsity Blues men's ice hockey, Varsity Blues men's ice hockey team has left many legacies on the national, professional and international hockey scenes. Conn Smythe played for the Blues as a centre (ice hockey), centre during his undergraduate years, and was a Blues coach from 1923 to 1926. When Smythe took over the Toronto Maple Leafs in 1927, his new team adopted the Varsity Blues' familiar blue-and-white sweater design. Blues hockey competed at the Ice hockey at the 1928 Winter Olympics, 1928 Winter Olympics and captured the gold medal for Canada at the 1928 Winter Olympics, Canada. At the 1980 Winter Olympics, Blues coach Tom Watt (ice hockey), Tom Watt served as co-coach of the Canadian hockey team in which six players were Varsity grads. In all, the Blues have won the David Johnston University Cup, U Sports University Cup national hockey title ten times, last in 1984.
File:King60th.jpg, William Lyon Mackenzie King, the longest-serving Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister in Canadian history with over 21 years in office, BA, MA
File:Lester B. Pearson with a pencil.jpg, Lester B. Pearson, Canadian Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister and winner of the Nobel Peace Prize in 1957, BA
File:Paul martin 2004.jpg, Paul Martin, List of prime ministers of Canada, 21st Canadian Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister, LLB
File:John Kenneth Galbraith 1982.jpg, John Kenneth Galbraith, noted economist and a leading proponent of 20th-century Modern liberalism in the United States, American liberalism, B.Sc.(Agr.)
File:John charles fields.jpg, John Charles Fields, mathematician and the founder of the prestigious Fields Medal
File:Harold Innis public-domain library archives-canada.jpg,
In addition to Eric A. Havelock, Havelock, Harold Innis, Innis, Northrop Frye, Frye, Edmund Snow Carpenter, Carpenter and Marshall McLuhan, McLuhan, former professors of the 20th century include Frederick Banting, Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter, Robertson Davies, John Charles Fields, Leopold Infeld and C. B. Macpherson. Twelve List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates studied or taught at the University of Toronto. As of 2006, University of Toronto academics accounted for 15 of 23 Canadian members in the American Academy of Arts and Sciences (65%) and 20 of 72 Canadian fellows in the American Association for the Advancement of Science (28%). Among honorees from Canada between 1980 and 2006, University of Toronto faculty made up 11 of 21 Canada Gairdner International Award recipients (52%), 44 of 101 Guggenheim Fellowship, Guggenheim Fellows (44%), 16 of 38 Royal Society fellows (42%), 10 of 28 members in the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, United States National Academies (36%) and 23 of 77 Sloan Research Fellowship, Sloan Research Fellows (30%).
Alumni of the University of Toronto's colleges, faculties and professional schools have assumed notable roles in a wide range of fields and specialties. In government, Governor General of Canada, Governors General
The University of Toronto: A History
'. University of Toronto Press. . * Levi, Charles Morden. (2003).
Comings and Goings
'. McGill-Queen's University Press. . * A. B. McKillop, McKillop, A. Brian. (1994). ''Matters of Mind''. University of Toronto Press. . * Slater, John G. (2005).
Minerva's Aviary: Philosophy at Toronto
'. University of Toronto Press. . * Wallace, W. Stewart. ''A History of the University of Toronto, 1827–1927.'' University of Toronto Press, 1927.
public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichk ...
research university
A research university or a research-intensive university is a university that is committed to research as a central part of its mission. They are the most important sites at which knowledge production occurs, along with "intergenerational kn ...
in Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of th ...
. Originally controlled by the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
, the university assumed its present name in 1850 upon becoming a secular institution. As a collegiate university
A collegiate university is a university in which functions are divided between a central administration and a number of constituent colleges. Historically, the first collegiate university was the University of Paris and its first college was the C ...
, it comprises eleven college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offerin ...
s each with substantial autonomy on financial and institutional affairs and significant differences in character and history. The university maintains three campuses, the oldest of which, St. George, is located in downtown Toronto
Downtown Toronto is the main central business district of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Located entirely within the district of Old Toronto, it is approximately 16.6 square kilometres in area, bounded by Bloor Street to the northeast and Dupont Str ...
. The other two satellite campus
A satellite campus or branch campus or regional campus is a campus of a university or college that is physically at a distance from the original university or college area. This branch campus may be located in a different city, state, or coun ...
es are located in Scarborough Scarborough or Scarboro may refer to:
People
* Scarborough (surname)
* Earl of Scarbrough
Places Australia
* Scarborough, Western Australia, suburb of Perth
* Scarborough, New South Wales, suburb of Wollongong
* Scarborough, Queensland, su ...
and Mississauga.
The University of Toronto offers over 700 undergraduate and 200 graduate programs. In all major rankings, the university consistently ranks in the top ten public universities in the world and as the top university in the country. It receives the most annual scientific research funding and endowment of any Canadian university and is one of two members of the Association of American Universities
The Association of American Universities (AAU) is an organization of American research universities devoted to maintaining a strong system of academic research and education. Founded in 1900, it consists of 63 universities in the United States ( ...
outside the United States, the other being McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous ...
in Montreal.
Academically, the University of Toronto is noted for influential movements and curricula in literary criticism and communication theory, known collectively as the Toronto School. The university was the birthplace of insulin and stem cell research, the first artificial cardiac pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart ei ...
, and the site of the first successful lung transplant
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. ...
and nerve transplant. The university was also home to the first electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, the development of deep learning, neural network, multi-touch technology, the identification of the first black hole Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a galactic X-ray source in the constellation Cygnus and was the first such source widely accepted to be a black hole. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the ...
, and the development of the theory of NP-completeness
In computational complexity theory, a problem is NP-complete when:
# it is a problem for which the correctness of each solution can be verified quickly (namely, in polynomial time) and a brute-force search algorithm can find a solution by trying ...
.
The Varsity Blues are the athletic teams that represent the university in intercollegiate league matches, primarily within U Sports
U Sports (stylized as U SPORTS) is the national sport governing body of university sport in Canada, comprising the majority of degree-granting universities in the country. Its equivalent body for organized sports at colleges in Canada is the C ...
, with ties to gridiron football, rowing and ice hockey. The earliest recorded instance of gridiron football occurred at University of Toronto's University College
In a number of countries, a university college is a college institution that provides tertiary education but does not have full or independent university status. A university college is often part of a larger university. The precise usage varies ...
in November 1861. The university's Hart House is an early example of the North American student centre, simultaneously serving cultural, intellectual, and recreational interests within its large Gothic-revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
complex.
University of Toronto alumni include three Governors General of Canada, five Prime Ministers of Canada, nine foreign leaders, and seventeen justices of the Supreme Court of Canada
A judge is a person who presides over court proceedings, either alone or as a part of a panel of judges. A judge hears all the witnesses and any other evidence presented by the barristers or solicitors of the case, assesses the credibility an ...
. , twelve Nobel laureates, six Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in comput ...
winners, 94 Rhodes Scholars, and one Fields Medalist have been affiliated with the university.
History
Early history
The founding of a colonial college had long been the desire ofJohn Graves Simcoe
John Graves Simcoe (25 February 1752 – 26 October 1806) was a British Army general and the first lieutenant governor of Upper Canada from 1791 until 1796 in southern Ontario and the watersheds of Georgian Bay and Lake Superior. He founded Yor ...
, the first Lieutenant-Governor of Upper Canada
The following is a list of lieutenant governors of Ontario and the lieutenant governors of the former colony of Upper Canada. The office of Lieutenant Governor of Ontario was created in 1867, when the Province of Ontario was created upon Confed ...
and founder of York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, the colonial capital. As an Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
-educated military commander who had fought in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, Simcoe believed a college was needed to counter the spread of republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It ...
from the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. The Upper Canada Executive Committee recommended in 1798 that a college be established in York.
 On March 15, 1827, a
On March 15, 1827, a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
was formally issued by King George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten ye ...
, proclaiming "from this time one College, with the style and privileges of a University ... for the education of youth in the principles of the Christian Religion, and for their instruction in the various branches of Science and Literature ... to continue for ever, to be called King's College." The granting of the charter was largely the result of intense lobbying by John Strachan
John Strachan (; 12 April 1778 – 1 November 1867) was a notable figure in Upper Canada and the first Anglican Bishop of Toronto. He is best known as a political bishop who held many government positions and promoted education from common sc ...
, the influential Anglican Bishop of Toronto who took office as the college's first president. The original three-storey Greek Revival
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but a ...
school building was built on the present site of Queen's Park.
Under Strachan's stewardship, King's College was a religious institution closely aligned with the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
and the British colonial elite, known as the Family Compact
The Family Compact was a small closed group of men who exercised most of the political, economic and judicial power in Upper Canada (today’s Ontario) from the 1810s to the 1840s. It was the Upper Canadian equivalent of the Château Clique in ...
. Reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can ...
politicians opposed the clergy's control over colonial institutions and fought to have the college secularized
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
. In 1849, after a lengthy and heated debate, the newly elected responsible government of the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on th ...
voted to rename King's College as the University of Toronto and severed the school's ties with the church. Having anticipated this decision, the enraged Strachan had resigned a year earlier to open Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
as a private Anglican seminary. University College
In a number of countries, a university college is a college institution that provides tertiary education but does not have full or independent university status. A university college is often part of a larger university. The precise usage varies ...
was created as the nondenominational teaching branch of the University of Toronto. During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
, the threat of Union blockade
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of of Atlanti ...
on British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
prompted the creation of the University Rifle Corps, which saw battle in resisting the Fenian raids on the Niagara border in 1866. The Corps was part of the Reserve Militia led by Professor Henry Croft.
 Established in 1878, the School of Practical Science was the precursor to the Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, which has been nicknamed ''Skule'' since its earliest days. While the Faculty of Medicine opened in 1843, medical teaching was conducted by proprietary schools from 1853 until 1887 when the faculty absorbed the Toronto School of Medicine. Meanwhile, the university continued to set examinations and confer medical degrees. The university opened the Faculty of Law in 1887, followed by the Faculty of Dentistry in 1888 when the
Established in 1878, the School of Practical Science was the precursor to the Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, which has been nicknamed ''Skule'' since its earliest days. While the Faculty of Medicine opened in 1843, medical teaching was conducted by proprietary schools from 1853 until 1887 when the faculty absorbed the Toronto School of Medicine. Meanwhile, the university continued to set examinations and confer medical degrees. The university opened the Faculty of Law in 1887, followed by the Faculty of Dentistry in 1888 when the Royal College of Dental Surgeons
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a ci ...
became an affiliate. Women were first admitted to the university in 1884.
A devastating fire in 1890 gutted the interior of University College and destroyed 33,000 volumes from the library, but the university restored the building and replenished its library within two years. Over the next two decades, a collegiate system
A collegiate university is a university in which functions are divided between a central administration and a number of constituent colleges. Historically, the first collegiate university was the University of Paris and its first college was the ...
took shape as the university arranged federation with several ecclesiastical colleges, including Strachan's Trinity College in 1904. The university operated the Royal Conservatory of Music
The Royal Conservatory of Music (RCM), branded as The Royal Conservatory, is a non-profit music education institution and performance venue headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was founded in 1886 by Edward Fisher as The Toronto Con ...
from 1896 to 1991 and the Royal Ontario Museum from 1912 to 1968; both still retain close ties with the university as independent institutions. The University of Toronto Press
The University of Toronto Press is a Canadian university press founded in 1901. Although it was founded in 1901, the press did not actually publish any books until 1911.
The press originally printed only examination books and the university cale ...
was founded in 1901 as Canada's first academic publishing house. The Faculty of Forestry, founded in 1907 with Bernhard Fernow
Bernhard Eduard Fernow ( ; January 7, 1851 – February 6, 1923) was the third chief of the USDA's Division of Forestry of the United States from 1886 to 1898, preceding Gifford Pinchot in that position, and laying much of the groundwork for the e ...
as dean, was Canada's first university faculty devoted to forest science. In 1910, the Faculty of Education opened its laboratory school
A laboratory school or demonstration school is an elementary or secondary school operated in association with a university, college, or other teacher education institution and used for the training of future teachers, educational experimentation, ...
, the University of Toronto Schools
University of Toronto Schools (UTS) is an independent secondary day school affiliated with the University of Toronto in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The school follows a specialized academic curriculum, and admission is determined by competitive ex ...
.
World wars and post-war years
 The
The First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second World Wars
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
curtailed some university activities as undergraduate and graduate men eagerly enlisted. Intercollegiate athletic competitions and the Hart House Debates were suspended, although exhibition and interfaculty games were still held. The David Dunlap Observatory
The David Dunlap Observatory (DDO) is an astronomical observatory site in Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada. Established in 1935, it was owned and operated by the University of Toronto until 2008. It was then acquired by the city of Richmond Hill, ...
in Richmond Hill opened in 1935, followed by the University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies in 1949. The university opened suburban campuses in Scarborough Scarborough or Scarboro may refer to:
People
* Scarborough (surname)
* Earl of Scarbrough
Places Australia
* Scarborough, Western Australia, suburb of Perth
* Scarborough, New South Wales, suburb of Wollongong
* Scarborough, Queensland, su ...
in 1964 and in Mississauga in 1967. The university's former affiliated schools at the Ontario Agricultural College
The Ontario Agricultural College (OAC) originated at the agricultural laboratories of the Toronto Normal School, and was officially founded in 1874 as an associate agricultural college of the University of Toronto. Since 1964, it has become affili ...
and Glendon Hall
Glendon College is a public liberal arts college in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Formally the federated bilingual campus of York University, it is one of the school's nine colleges and 11 faculties with 100 full-time faculty members and a student p ...
became fully independent of the University of Toronto and became part of University of Guelph
, mottoeng = "to learn the reasons of realities"
, established = May 8, 1964 ()As constituents: OAC: (1874) Macdonald Institute: (1903) OVC: (1922)
, type = Public university
, chancellor ...
in 1964 and York University
York University (french: Université York), also known as YorkU or simply YU, is a public university, public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is Canada's fourth-largest university, and it has approximately 55,700 students, 7,0 ...
in 1965, respectively. Beginning in the 1980s, reductions in government funding prompted more rigorous fundraising efforts.
Since 2000
In 2000, geophysicist Kin-Yip Chun was reinstated as a professor of the university, after he launched an unsuccessful lawsuit against the university alleging racial discrimination. In 2017, a human rights application was filed against the University by one of its students for allegedly delaying the investigation of sexual assault and being dismissive of their concerns. In 2018, the university cleared one of its professors of allegations of discrimination andantisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
in an internal investigation, after a complaint was filed by one of its students.
The University of Toronto was the first Canadian university to amass a financial endowment greater than billion in 2007. On September 24, 2020, the university announced a $250 million gift to the Faculty of Medicine from businessman and philanthropist James C. Temerty, the largest single philanthropic donation in Canadian history. This broke the previous record for the school set in 2019 when Gerry Schwartz
Gerald W. Schwartz, OC (born 1941) is the founder, chairman and CEO of Onex Corporation. Schwartz has a net worth of US$1.5 billion, according to Forbes.
Early life and career
Schwartz was born in Winnipeg, Manitoba. He graduated from Kelvin H ...
and Heather Reisman
Heather Maxine Reisman (born August 28, 1948) is a Canadian businesswoman and philanthropist. Reisman is the founder and chief executive of the Canadian retail chain Indigo Books and Music. She is the co-founder and past Chair of Kobo, and was ...
jointly donated $100 million for the creation of a innovation and artificial intelligence centre.
Grounds
 The university grounds lie about north of the
The university grounds lie about north of the Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
in Downtown Toronto
Downtown Toronto is the main central business district of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Located entirely within the district of Old Toronto, it is approximately 16.6 square kilometres in area, bounded by Bloor Street to the northeast and Dupont Str ...
, immediately north of Chinatown and the Discovery District, and immediately south of the neighbourhoods of Yorkville and The Annex
The Annex is a neighbourhood in Downtown Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The traditional boundaries of the neighbourhood are north to Dupont Street, south to Bloor Street, west to Bathurst Street and east to Avenue Road. The City of Toronto recognizes ...
. The site encompasses bounded mostly by Bay Street
Bay Street is a major thoroughfare in Downtown Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is the centre of Toronto's Financial District and is often used by metonymy to refer to Canada's financial services industry since succeeding Montreal's St. James Stre ...
to the east, Bloor Street
Bloor Street is a major east–west residential and commercial thoroughfare in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Bloor Street runs from the Prince Edward Viaduct, which spans the Don River Valley, westward into Mississauga where it ends at Central Park ...
to the north, Spadina Avenue
Spadina Avenue (, less commonly ) is one of the most prominent streets in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Running through the western section of downtown, the road has a very different character in different neighbourhoods.
Spadina Avenue runs south ...
to the west and College Street to the south. An enclave surrounded by university grounds, Queen's Park, contains the Ontario Legislative Building
The Ontario Legislative Building (french: L'édifice de l'Assemblée législative de l'Ontario) is a structure in central Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It houses the Legislative Assembly of Ontario, and the viceregal suite of the Lieutenant Governor ...
and several historic monuments. With its green spaces and many interlocking courtyards, the university forms a distinct region of urban park
An urban park or metropolitan park, also known as a municipal park (North America) or a public park, public open space, or municipal gardens ( UK), is a park in cities and other incorporated places that offer recreation and green space to r ...
land in the city's downtown core. The namesake University Avenue
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, th ...
is a ceremonial boulevard
A boulevard is a type of broad avenue planted with rows of trees, or in parts of North America, any urban highway.
Boulevards were originally circumferential roads following the line of former city walls.
In American usage, boulevards may ...
and arterial thoroughfare that runs through downtown between Queen's Park and Front Street. The , , , , and stations of the Toronto subway
The Toronto subway is a rapid transit system serving Toronto and the neighbouring city of Vaughan in Ontario, Canada, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC). It is a multimodal rail network consisting of three heavy-capacity rail ...
system are nearby.
The architecture is epitomized by a combination of Romanesque and Gothic Revival buildings spread across the eastern and central portions of campus, most dating between 1858 and 1929. The traditional heart of the university, known as Front Campus, is near the campus centre in an oval lawn enclosed by King's College Circle. The centrepiece is the main building of University College
In a number of countries, a university college is a college institution that provides tertiary education but does not have full or independent university status. A university college is often part of a larger university. The precise usage varies ...
, built in 1857 with an eclectic blend of Richardsonian Romanesque and Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
architectural elements. The dramatic effect of this blended design by architect Frederick William Cumberland
:''See also Cumberland (disambiguation), Cumberland (surname).''
Frederick William Cumberland (10 April 1821 – 5 August 1881) was a Canadian engineer, architect and politician. He represented the riding of Algoma in the 1st and 2nd Ontar ...
drew praise from European visitors of the time: "Until I reached Toronto," remarked Lord Dufferin
Frederick Temple Hamilton-Temple-Blackwood, 1st Marquess of Dufferin and Ava (21 June 182612 February 1902) was a British public servant and prominent member of Victorian society. In his youth he was a popular figure in the court of Queen Vict ...
during his visit in 1872, "I confess I was not aware that so magnificent a specimen of architecture existed upon the American continent." The building was declared a National Historic Site of Canada
National Historic Sites of Canada (french: Lieux historiques nationaux du Canada) are places that have been designated by the federal Minister of the Environment on the advice of the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada (HSMBC), as being ...
in 1968. Built in 1907, Convocation Hall
Convocation Hall is a domed rotunda (architecture), rotunda on the grounds of the University of Toronto in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Designed by Darling and Pearson and completed in 1907, its radially planned interior has been compared to the gran ...
is recognizable for its domed roof and Ionic-pillared rotunda. Although its foremost function is hosting the annual convocation ceremonies, the building is a venue for academic and social events throughout the year. The sandstone buildings of Knox College epitomizes the North American collegiate Gothic design, with its characteristic cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against a ...
s surrounding a secluded courtyard.
 A lawn at the northeast is anchored by Hart House, a Gothic-revival student centre complex. Among its many common rooms, the building's Great Hall is noted for large stained-glass windows and a long quotation from John Milton's ''
A lawn at the northeast is anchored by Hart House, a Gothic-revival student centre complex. Among its many common rooms, the building's Great Hall is noted for large stained-glass windows and a long quotation from John Milton's ''Areopagitica
''Areopagitica; A speech of Mr. John Milton for the Liberty of Unlicenc'd Printing, to the Parlament of England'' is a 1644 prose polemic by the English poet, scholar, and polemical author John Milton opposing licensing and censorship. ''Are ...
'' inscribed around the walls. The adjacent Soldiers' Tower stands tall as the most prominent structure in the vicinity, its stone arches etched with the names of university members lost to the battlefields of the two World Wars. The tower houses a 51-bell carillon played on special occasions such as Remembrance Day
Remembrance Day (also known as Poppy Day owing to the tradition of wearing a remembrance poppy) is a memorial day observed in Commonwealth member states since the end of the First World War to honour armed forces members who have died in t ...
and convocation. North of University College, the main building of Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
displays Jacobethan Tudor architecture
The Tudor architectural style is the final development of Medieval architecture in England and Wales, during the Tudor period (1485–1603) and even beyond, and also the tentative introduction of Renaissance architecture to Britain. It fo ...
, while its chapel was built in the Perpendicular Gothic style of Giles Gilbert Scott
Sir Giles Gilbert Scott (9 November 1880 – 8 February 1960) was a British architect known for his work on the New Bodleian Library, Cambridge University Library, Lady Margaret Hall, Oxford, Battersea Power Station, Liverpool Cathedral, and ...
. The chapel features exterior walls of sandstone and interiors of Indiana Limestone
Indiana limestone — also known as Bedford limestone in the building trade — has long been an economically important building material, particularly for monumental public structures. Indiana limestone is a more common term for Salem Limestone, ...
and was built by Italian stonemasons using ancient building methods. Philosopher's Walk
The is a pedestrian path that follows a cherry-tree-lined canal in Kyoto, Japan between Ginkaku-ji and Nanzen-ji. First opened in 1890 and extended again in 1912, the path follows the course of a shallow irrigation channel bringing water fro ...
is a scenic footpath that follows a meandering, wooded ravine
A ravine is a landform that is narrower than a canyon and is often the product of streambank erosion.Taddle Creek
Taddle Creek is a buried stream in Toronto, Ontario, Canada that flowed a southeasterly course about six kilometres long, from St. Clair Avenue west of Bathurst Street through the present site of Wychwood Park, through the University of Toronto ...
, linking with Trinity College, Varsity Arena
Varsity Arena, located at 299 Bloor Street West, Toronto, Ontarioretrieved from http://rrs.osm.utoronto.ca 2007-10-22 is an indoor arena that opened on December 17, 1926, and is primarily home to the ice hockey teams of the University of Toronto, ...
and the Faculty of Law. Victoria College is on the eastern side of Queen's Park, centred on a Romanesque main building made of contrasting red sandstone and grey limestone.
Developed after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the western section of the campus consists mainly of modernist
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
and internationalist
Internationalist may refer to:
* Internationalism (politics), a movement to increase cooperation across national borders
* Liberal internationalism, a doctrine in international relations
* Internationalist/Defencist Schism, socialists opposed to ...
structures that house laboratories and faculty offices. The most significant example of Brutalist architecture
Brutalist architecture is an architectural style that emerged during the 1950s in the United Kingdom, among the reconstruction projects of the post-war era. Brutalist buildings are characterised by minimalist constructions that showcase the ba ...
is the massive Robarts Library
The John P. Robarts Research Library, commonly referred to as Robarts Library, is the main humanities and social sciences library of the University of Toronto Libraries and the largest individual library in the university. Opened in 1973 and n ...
complex, built in 1972 and opened a year later in 1973. It features raised podia, extensive use of triangular geometric designs and a towering fourteen-storey concrete structure that cantilevers above a field of open space and mature trees. Sidney Smith Hall
The Faculty of Arts & Science is a division of the University of Toronto (U of T) which offers arts and science teaching and research institutions. With almost 27,000 undergraduate and 3,000 graduate students, Arts & Science represents over half ...
is the home to the Faculty of Arts and Science, as well as a few departments within the faculty. The Leslie L. Dan Pharmacy Building, completed in 2006, exhibits the high-tech architectural style of glass and steel by British architect Norman Foster
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Nor ...
.
Governance and colleges
 The University of Toronto has traditionally been a
The University of Toronto has traditionally been a decentralized
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those regarding planning and decision making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group.
Conce ...
institution, with governing authority shared among its central administration, academic faculties and colleges. The Governing Council is the unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
legislative organ of the central administration, overseeing general academic, business and institutional affairs. Before 1971, the university was governed under a bicameral system composed of the board of governors and the university senate. The chancellor, usually a former governor general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
, lieutenant governor, premier or diplomat, is the ceremonial head of the university. The president is appointed by the council as the chief executive.
Unlike most North American institutions, the University of Toronto is a collegiate university
A collegiate university is a university in which functions are divided between a central administration and a number of constituent colleges. Historically, the first collegiate university was the University of Paris and its first college was the C ...
with a model that resembles those of the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
and the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
in Britain. The colleges hold substantial autonomy over admissions, scholarships, programs and other academic and financial affairs, in addition to the housing and social duties of typical residential college
A residential college is a division of a university that places academic activity in a community setting of students and faculty, usually at a residence and with shared meals, the college having a degree of autonomy and a federated relationship wi ...
s. The system emerged in the 19th century, as ecclesiastical colleges considered various forms of union with the University of Toronto to ensure their viability. The desire to preserve religious traditions in a secular institution resulted in the federative collegiate model that came to characterize the university.
University College
In a number of countries, a university college is a college institution that provides tertiary education but does not have full or independent university status. A university college is often part of a larger university. The precise usage varies ...
was the founding nondenominational college, created in 1853 after the university was secularized. Knox College, a Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
institution, and Wycliffe College
Wycliffe College () is an evangelical graduate school of theology at the University of Toronto. Founded in 1877 as an evangelical seminary in the Anglican tradition, Wycliffe College today attracts students from many Christian denominations from ...
, a low church seminary, both encouraged their students to study for non-divinity degrees at University College. In 1885, they entered a formal affiliation with the University of Toronto, and became federated school An affiliated school (also affiliated college, federated school, federated college or federated university) is an educational institution that operates independently, but also has a formal collaborative agreement with another, usually larger institu ...
s in 1890. The idea of federation initially met strong opposition at Victoria University, a Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
school in Cobourg, but a financial incentive in 1890 convinced the school to join. Decades after the death of John Strachan, the Anglican seminary Trinity College Trinity College may refer to:
Australia
* Trinity Anglican College, an Anglican coeducational primary and secondary school in , New South Wales
* Trinity Catholic College, Auburn, a coeducational school in the inner-western suburbs of Sydney, New ...
entered federation in 1904, followed in 1910 by St. Michael's College, a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
college founded by the Basilian Fathers
, image = Basilian_Fathers.png
, image_size = 150px
, abbreviation = CSB
, nickname = Basilians
, formation =
, founding_location = Annonay, France
, founders =
, type ...
. Among the institutions that had considered federation but ultimately remained independent were McMaster University
McMaster University (McMaster or Mac) is a public research university in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. The main McMaster campus is on of land near the residential neighbourhoods of Ainslie Wood and Westdale, adjacent to the Royal Botanical Ga ...
, a Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
school that later moved to Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilt ...
, and Queen's College, a Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
school in Kingston that later became Queen's University.
The post-war era saw the creation of New College in 1962, Innis College
Innis College is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Toronto. It is one of the University of Toronto's smallest colleges in terms of size and the second smallest college in terms of population with approximately 2000 registered ...
in 1964 and Woodsworth College
Woodsworth College, named after politician and clergyman James Shaver Woodsworth (1874–1942), is a college within the University of Toronto in Canada. It is one of the largest colleges in the Faculty of Arts and Science at the St. George Camp ...
in 1974, all of them nondenominational. Along with University College, they comprise the university's constituent colleges, which are established and funded by the central administration and are therefore financially dependent. Massey College
Massey College is a graduate residential college at the University of Toronto that was established, built and partially endowed in 1962 by the Massey Foundation and officially opened in 1963, though women were not admitted until 1974. It was mo ...
was established in 1963 by the Massey Foundation
The Massey Foundation was incorporated in 1918. It is responsible for the construction of many Toronto landmarks. It was the first trust of its kind in Canada.
History
In 1896, Hart Massey, an industrialist who built the Massey-Harris farm equi ...
as a college exclusively for graduate students. Regis College, a Jesuit seminary, entered federation with the university in 1979.
In contrast with the constituent colleges, the colleges of Knox, Massey, Regis, St. Michael's, Trinity, Victoria and Wycliffe continue to exist as legally distinct entities, each possessing a separate financial endowment. While St. Michael's, Trinity and Victoria continue to recognize their religious affiliations and heritage, they have since adopted secular policies of enrolment and teaching in non-divinity subjects. Some colleges have, or once had, collegiate structures of their own: Emmanuel College is a college of Victoria and St. Hilda's College is part of Trinity; St. Joseph's College had existed as a college within St. Michael's until it was dissolved in 2006. Ewart College
Ewart College was a historical women's college located in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, affiliated with the Presbyterian Church in Canada. In September 1991, it merged with Knox College, University of Toronto.
Founded on October 11, 1897, it was then ...
existed as an affiliated college until 1991, when it was merged into Knox College. Postgraduate theology degrees are conferred by the colleges of Knox, Regis and Wycliffe, along with the divinity faculties within Emmanuel, St. Michael's and Trinity, including joint degrees with the university through the Toronto School of Theology.
Academics
 The Faculty of Arts and Science is the university's main
The Faculty of Arts and Science is the university's main undergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, in the United States, an entry-le ...
faculty, and administers most of the courses in the college system. While the colleges are not entirely responsible for teaching duties, most of them house specialized academic programs and lecture series. Among other subjects, Trinity College is associated with programs in international relations
International relations (IR), sometimes referred to as international studies and international affairs, is the scientific study of interactions between sovereign states. In a broader sense, it concerns all activities between states—such a ...
, as are University College with Canadian studies Canadian studies is an interdisciplinary field of undergraduate- and postgraduate-level study of Canadian culture and society, the languages of Canada, Canadian literature, media and communications, Quebec, Acadians, agriculture in Canada, natu ...
, Victoria College with Renaissance studies
Renaissance studies (also ''Renaissance and Early Modern Studies'') is the interdisciplinary study of the Renaissance and early modern period. The field of study often incorporates knowledge from history, art history, literature, music, architectu ...
, Innis College with film studies
Film studies is an academic discipline that deals with various theoretical, historical, and critical approaches to cinema as an art form and a medium. It is sometimes subsumed within media studies and is often compared to television studies.
...
and urban studies
Urban studies is based on the study of the urban development of cities. This includes studying the history of city development from an architectural point of view, to the impact of urban design on community development efforts. The core theoretica ...
, New College with gender studies
Gender studies is an interdisciplinary academic field devoted to analysing gender identity and gendered representation. Gender studies originated in the field of women's studies, concerning women, feminism, gender, and politics. The field ...
, Woodsworth College with industrial relations
Industrial relations or employment relations is the multidisciplinary academic field that studies the employment relationship; that is, the complex interrelations between employers and employees, labor/trade
unions, employer organizations, ...
and St. Michael's College with Medievalism
Medievalism is a system of belief and practice inspired by the Middle Ages of Europe, or by devotion to elements of that period, which have been expressed in areas such as architecture, literature, music, art, philosophy, scholarship, and variou ...
. The faculty teaches undergraduate commerce in collaboration with the Rotman School of Management
The Joseph L. Rotman School of Management (commonly known as the Rotman School of Management, the Rotman School or just Rotman) is the University of Toronto's graduate business school, located in Downtown Toronto. The University of Toronto has b ...
. The Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering is the other major direct-entry undergraduate faculty.
The University of Toronto is the birthplace of an influential school of thought
A school of thought, or intellectual tradition, is the perspective of a group of people who share common characteristics of opinion or outlook of a philosophy, discipline, belief, social movement, economics, cultural movement, or art movement.
...
on communication theory and literary criticism known as the Toronto School. Described as "the theory of the primacy of communication in the structuring of human cultures and the structuring of the human mind", the school is rooted in the works of Eric A. Havelock
Eric Alfred Havelock (; 3 June 1903 – 4 April 1988) was a British classicist who spent most of his life in Canada and the United States. He was a professor at the University of Toronto and was active in the Canadian socialist movement du ...
and Harold Innis
Harold Adams Innis (November 5, 1894 – November 9, 1952) was a Canadian professor of political economy at the University of Toronto and the author of seminal works on media, communication theory, and Canadian economic history. He helped deve ...
and the subsequent contributions of Edmund Snow Carpenter
Edmund "Ted" Snow Carpenter (September 2, 1922 – July 1, 2011) was an American anthropologist best known for his work on tribal art and visual media.
Early life
Born in Rochester, New York to the artist and educator Fletcher Hawthorne Carpe ...
, Northrop Frye
Herman Northrop Frye (July 14, 1912 – January 23, 1991) was a Canadian literary critic and literary theorist, considered one of the most influential of the 20th century.
Frye gained international fame with his first book, '' Fearful Symm ...
and Marshall McLuhan. Since 1963, the McLuhan Program in Culture and Technology of the Faculty of Information
Faculty may refer to:
* Faculty (academic staff), the academic staff of a university (North American usage)
* Faculty (division), a division within a university (usage outside of the United States)
* Faculty (instrument), an instrument or warrant ...
has carried the mandate for teaching and advancing the Toronto School.
Several notable works in arts and humanities are based at the university, including the ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography
The ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' (''DCB''; french: Dictionnaire biographique du Canada) is a dictionary of biographical entries for individuals who have contributed to the history of Canada. The ''DCB'', which was initiated in 1959, is a ...
'' since 1959 and the ''Collected Works of Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (; ; English: Erasmus of Rotterdam or Erasmus;''Erasmus'' was his baptismal name, given after St. Erasmus of Formiae. ''Desiderius'' was an adopted additional name, which he used from 1496. The ''Roterodamus'' w ...
'' since 1969. The ''Records of Early English Drama The Records of Early English Drama (REED) is a performance history research project, based at the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was founded in 1976 by a group of international scholars interested in understanding “the native tradition ...
'' collects and edits the surviving documentary evidence of dramatic arts in pre-Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
England, while the '' Dictionary of Old English'' compiles the early vocabulary of the English language from the Anglo-Saxon period.
Munk School of Global Affairs
The Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy at the University of Toronto is an interdisciplinary academic centre with various research and educational programs committed to the field of globalization. Located in Toronto, Ontario, it offers ...
encompasses the university's various programs and curricula in international affairs and foreign policy. As the Cold War heightened, Toronto's Slavic studies program evolved into an important institution on Soviet politics and economics, financed by the Rockefeller Rockefeller is a German surname, originally given to people from the village of Rockenfeld near Neuwied in the Rhineland and commonly referring to subjects associated with the Rockefeller family. It may refer to:
People with the name Rockefeller f ...
, Ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
and Mellon foundations. The Munk School is also home to the G20 Research Group
John James Kirton (born 1948) is professor emeritus of political science and the director and founder of the G7 Research Group, director and founder of the G20 Research Group, founder and co-director (with James Orbinski) of the Global Health Dip ...
, which conducts independent monitoring and analysis on the Group of Twenty
The G20 or Group of Twenty is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 countries and the European Union (EU). It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigatio ...
, and the Citizen Lab
The Citizen Lab is an interdisciplinary laboratory based at the Munk School of Global Affairs at the University of Toronto, Canada. It was founded by Ronald Deibert in 2001. The laboratory studies information controls that impact the openness ...
, which conducts research on Internet censorship
Internet censorship is the legal control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet. Censorship is most often applied to specific internet domains (such as Wikipedia.org) but exceptionally may extend to all Int ...
as a joint founder of the OpenNet Initiative
The OpenNet Initiative (ONI) was a joint project whose goal was to monitor and report on internet filtering and surveillance practices by nations. The project employed a number of technical means, as well as an international network of investigato ...
. The university operates international offices in Berlin, Hong Kong and Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centur ...
.
The Dalla Lana School of Public Health
Dalla Lana School of Public Health is the school of public health at the University of Toronto. It was founded in 1927, and was home for 50 years to Connaught Laboratories, a manufacturer of vaccines, insulin, and many other pharmaceutical produc ...
is a Faculty of the University of Toronto that began as one of the Schools of Hygiene begun by the Rockefeller Foundation in 1927. The School went through a dramatic renaissance after the 2003 SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''seve ...
crisis, and it is now Canada's largest public health school, with more than 750 faculty, 800 students, and research and training partnerships with institutions throughout Toronto and the world. With more than $39 million in research funding per year, the School supports discovery in global health, tobacco impacts on health, occupational disease and disability, air pollution, inner city, circumpolar health, and many other pressing issues in population health.
 The Temerty Faculty of Medicine is affiliated with a network of ten
The Temerty Faculty of Medicine is affiliated with a network of ten teaching hospital
A teaching hospital is a hospital or medical centre that provides medical education and training to future and current health professionals. Teaching hospitals are almost always affiliated with one or more universities and are often co-located ...
s, providing medical treatment, research and advisory services to patients and clients from Canada and abroad. A core member of the network is University Health Network
University Health Network (UHN) is a public research and teaching hospital network in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is the largest health research organization in Canada and ranks first in Canada for total research funding. It was named Canada's ...
, itself a specialized federation of Toronto General Hospital
The Toronto General Hospital (TGH) is a major teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and the flagship campus of University Health Network (UHN). It is located in the Discovery District of Downtown Toronto along University Avenue's Hospital ...
, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
The Princess Margaret Cancer Centre (previously, ''Princess Margaret Hospital'') is a scientific research centre and a teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, affiliated with the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine as part of the Univ ...
, Toronto Western Hospital
The Toronto Western Hospital (TWH) is a major research and teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is part of the University Health Network (UHN). It has 256 beds, with 46,000 visits to its emergency department annually. It is known for ...
, and Toronto Rehabilitation Institute
Toronto Rehabilitation Institute (TRI or commonly Toronto Rehab) is the largest rehabilitation hospital in Canada. Owned and operated by the University Health Network (UHN), Toronto Rehab provides patients with rehabilitation care, helping people ...
. Physicians in the medical institutes have cross-appointments to faculty and supervisory positions in university departments. The Rotman School of Management
The Joseph L. Rotman School of Management (commonly known as the Rotman School of Management, the Rotman School or just Rotman) is the University of Toronto's graduate business school, located in Downtown Toronto. The University of Toronto has b ...
developed the discipline and methodology of integrative thinking
Integrative thinking is a field which was developed by Graham Douglas in 1986. He describes integrative thinking as the process of integrating intuition, reason and imagination in a human mind with the objective of developing a holistic continuum o ...
, upon which the school bases its curriculum. Founded in 1887, the Faculty of Law's emphasis on formal teachings of liberal arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin "free" and "art or principled practice") is the traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term '' art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically th ...
and legal theory
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning ...
was then considered unconventional, but gradually helped shift the country's legal education system away from the apprenticeship model that prevailed until the mid-20th century. The Ontario Institute for Studies in Education
The Ontario Institute for Studies in Education of the University of Toronto (OISE/UT) is Canada's only all-graduate institute of teaching, learning and research, located in Toronto, Ontario. It is located directly above the St. George subway st ...
is the teachers college
A normal school or normal college is an institution created to train teachers by educating them in the norms of pedagogy and curriculum. In the 19th century in the United States, instruction in normal schools was at the high school level, turni ...
of the university, affiliated with its two laboratory school
A laboratory school or demonstration school is an elementary or secondary school operated in association with a university, college, or other teacher education institution and used for the training of future teachers, educational experimentation, ...
s, the Institute of Child Study and the University of Toronto Schools
University of Toronto Schools (UTS) is an independent secondary day school affiliated with the University of Toronto in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The school follows a specialized academic curriculum, and admission is determined by competitive ex ...
(a private high school run by the university). Autonomous institutes at the university include the Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, the Pontifical Institute of Mediaeval Studies
The Pontifical Institute of Mediaeval Studies (PIMS) is a research institute in the University of Toronto that is dedicated to advanced studies in the culture of the Middle Ages.
Governance
The Roman Catholic Archbishop of Toronto, currently Th ...
and the Fields Institute
The Fields Institute for Research in Mathematical Sciences, commonly known simply as the Fields Institute, is an international centre for scientific research in mathematical sciences. It is an independent non-profit with strong ties to 20 Ontar ...
.
Within the Faculty of Arts and Science, notable departments include the Department of Mathematics
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
.
Library and collections
 The
The University of Toronto Libraries
The University of Toronto Libraries system is the largest academic library in Canada and is ranked third among peer institutions in North America, behind only Harvard and Yale. The system consists of 39 libraries located on University of Toronto' ...
is the third-largest academic library system in North America, following those of Harvard and Yale
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wor ...
, measured by number of volumes held. Its collections include more than 12 million print books, 1.9 million digital books, over 160,000 journal titles, and close to 30,000 metres of archival materials. The largest of the libraries, Robarts Library
The John P. Robarts Research Library, commonly referred to as Robarts Library, is the main humanities and social sciences library of the University of Toronto Libraries and the largest individual library in the university. Opened in 1973 and n ...
, holds about five million bound volumes that form the main collection for humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at the t ...
and social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of so ...
s. The Thomas Fisher Rare Book Library
The Thomas Fisher Rare Book Library is a library in the University of Toronto, constituting the largest repository of publicly accessible rare books and manuscripts in Canada. The library is also home to the university archives which, in addit ...
constitutes one of the largest repositories of publicly accessible rare books
Book collecting is the collecting of books, including seeking, locating, acquiring, organizing, cataloging, displaying, storing, and maintaining whatever books are of interest to a given collector. The love of books is ''bibliophilia'', and someo ...
and manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in ...
s. Its collections range from ancient Egyptian papyri to incunabula and libretti
A libretto (Italian for "booklet") is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to the text of major l ...
; the subjects of focus include British, Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Canadian literature
Canadian literature is the literature of a multicultural country, written in languages including Canadian English, Canadian French, Indigenous languages, and many others such as Canadian Gaelic. Influences on Canadian writers are broad both g ...
, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
, Darwin, the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
, the history of science and medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
, Canadiana
Canadiana is a term used to describe things (e.g., books, historical documents, and artifacts), ideas, or activities that concern or are distinctive of Canada, its people, and/or its culture, especially works of literature and other cultural pro ...
and the history of books. The Cheng Yu Tung East Asian Library
The Cheng Yu Tung East Asian Library (Chinese language, Chinese: 鄭裕彤東亞圖書館) is a Canadian library and a part of the University of Toronto Libraries system. Located on the 8th floor of the Robarts Library at the University of Toronto' ...
has a rare 40,000-volume Chinese collection from the Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
(960–1279) to the Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
(1644–1911) that was originally held by scholar Mu Xuexun (1880–1929). The Richard Charles Lee Canada-Hong Kong Library
The Richard Charles Lee Canada-Hong Kong Library ( zh, 利銘澤典宬) is part of the University of Toronto Libraries system. It features a unique research collection on Canada-Hong Kong studies. Located inside Robarts Library at the University o ...
has the largest research collection for Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
and Canada–Hong Kong studies outside of Hong Kong. The rest of the library collections are dispersed at departmental and faculty libraries in addition to about 1.3 million bound volumes the colleges hold. The university has collaborated with the Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
since 2005 to digitize
DigitizationTech Target. (2011, April). Definition: digitization. ''WhatIs.com''. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/digitization is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer- ...
some of its library holdings.
Housed within University College, the University of Toronto Art Centre contains three major art collections. The Malcove Collection is primarily represented by Early Christian and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
sculptures, bronzeware, furniture, icons and liturgical items. It also includes glassware and stone reliefs from the Greco-Roman period, and the painting ''Adam and Eve'' by Lucas Cranach the Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder (german: Lucas Cranach der Ältere ; – 16 October 1553) was a German Renaissance painter and printmaker in woodcut and engraving. He was court painter to the Electors of Saxony for most of his career, and is kno ...
, dated from 1538. The University of Toronto Collection features Canadian contemporary art
Canadian art refers to the visual arts, visual (including painting, photography, and printmaking) as well as plastic arts (such as sculpture) originating from the geographical area of contemporary Canada. Art in Canada is marked by thousands of ...
, while the University College Art Collection holds significant works by the Group of Seven
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated member". It is officiall ...
and 19th century landscape artists
Landscape painting, also known as landscape art, is the depiction of natural scenery such as mountains, valleys, trees, rivers, and forests, especially where the main subject is a wide view—with its elements arranged into a coherent composi ...
.
Reputation
In the 2022 '' Academic Ranking of World Universities'' (also known as the Shanghai Ranking), the university ranked 22nd in the world and first in Canada. The 2023 ''QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
'' ranked the university 34th in the world, and second in Canada. In 2019, it ranked 11th among the universities around the world by ''SCImago Institutions Rankings
The SCImago Institutions Rankings (SIR) since 2009 has published its international ranking of worldwide research institutions, the SIR World Report. The SIR World Report is the work of the SCImago Research Group,Times Higher Education World University Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'' (often referred to as the THE Rankings) is an annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli ...
'' ranked the university 18th in the world, and first in Canada. In the Times' 2020 reputational ranking, the publication placed the university 19th in the world. In the 2022–23 '' U.S. News & World Report Best Global University Ranking'', the university ranked 18th in the world, and first in Canada. The Canadian-based ''Maclean's
''Maclean's'', founded in 1905, is a Canadian news magazine reporting on Canadian issues such as politics, pop culture, and current events. Its founder, publisher John Bayne Maclean, established the magazine to provide a uniquely Canadian persp ...
'' magazine ranked the University of Toronto second in their 2022-2023 Medical Doctoral university category. ''Maclean's'' 2023 university rankings also ranked the University of Toronto first in its reputation survey. The university was ranked in spite of having opted out — along with several other universities in Canada — of participating in ''Maclean's'' graduate survey since 2006.
The university's research performance has been noted in several bibliometric
Bibliometrics is the use of statistical methods to analyse books, articles and other publications, especially in regard with scientific contents. Bibliometric methods are frequently used in the field of library and information science. Biblio ...
university rankings, which use citation analysis
Citation analysis is the examination of the frequency, patterns, and graphs of citations in documents. It uses the directed graph of citations — links from one document to another document — to reveal properties of the documents. A t ...
to evaluate the impact
Impact may refer to:
* Impact (mechanics), a high force or shock (mechanics) over a short time period
* Impact, Texas, a town in Taylor County, Texas, US
Science and technology
* Impact crater, a meteor crater caused by an impact event
* Impac ...
a university has on academic publications. In 2019, the Performance Ranking of Scientific Papers for World Universities
The Performance Ranking of Scientific Papers for World Universities or NTU Ranking is a ranking system of world universities by scientific paper volume, impact, and performance output. The ranking was originally published from 2007 to 2011 by the ...
ranked the university fourth in the world, and first in Canada. The University Ranking by Academic Performance
The University Ranking by Academic Performance (URAP) is a College and university rankings, university ranking developed by the Informatics Institute of Middle East Technical University. Since 2010, it has been publishing annual national and glob ...
2019–2020 rankings placed the university second in the world, and first in Canada.
Along with academic and research-based rankings, the university has also been ranked by publications that evaluate the employment prospects of its graduates. In the ''Times Higher Education's'' 2022 global employability ranking, the university ranked 11th in the world, and first in Canada. In ''QS's'' 2022 graduate employability ranking, the university ranked 21st in the world, and first in Canada. In a 2013 employment survey conducted by the ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', the University of Toronto was ranked 14th in the world.
In 2018, the University of Toronto Entrepreneurship was ranked the fourth best university-based incubator
An incubator is anything that performs or facilitates various forms of incubation, and may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Incubator (culture), a device used to grow and maintain microbiological cultures or cell cultures
* Incubator (egg), a de ...
in the world by UBI Global in the "World Top Business Incubator – Managed by a University" category.
Research
 Since 1926, the University of Toronto has been a member of the
Since 1926, the University of Toronto has been a member of the Association of American Universities
The Association of American Universities (AAU) is an organization of American research universities devoted to maintaining a strong system of academic research and education. Founded in 1900, it consists of 63 universities in the United States ( ...
, a consortium of the leading North American research universities. The university manages by far the largest annual research budget of any university in Canada with sponsored direct-cost expenditures of $878 million in 2010. In 2018, the University of Toronto was named the top research university in Canada by Research Infosource, with a sponsored research income (external sources of funding) of $1,147.584 million in 2017. In the same year, the university's faculty averaged a sponsored research income of $428,200, while graduate students averaged a sponsored research income of $63,700. The federal government was the largest source of funding, with grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR; french: Instituts de recherche en santé du Canada; IRSC) is a federal agency responsible for funding health and medical research in Canada. Comprising 13 institutes, it is the successor to the M ...
, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council
The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC; french: Conseil de recherches en sciences naturelles et en génie du Canada, CRSNG) is the major federal agency responsible for funding natural sciences and engineering rese ...
and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council
The Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC; french: Conseil de recherches en sciences humaines du Canada, CRSH) is a Canadian federal research-funding agency that promotes and supports post-secondary research and traini ...
amounting to about one-third of the research budget. About eight percent of research funding came from corporations, mostly in the healthcare industry
The healthcare industry (also called the medical industry or health economy) is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, ...
.
The first practical electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
was built by the physics department in 1938. During World War II, the university developed the G-suit
A g-suit, or anti-''g'' suit, is a flight suit worn by aviators and astronauts who are subject to high levels of acceleration force ( g). It is designed to prevent a black-out and g-LOC (g-induced loss of consciousness) caused by the blood pool ...
, a life-saving garment worn by Allied fighter plane pilots, later adopted for use by astronauts. Development of the infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
chemiluminescence technique improved analyses of energy behaviours in chemical reactions. In 1963, the asteroid 2104 Toronto
2104 Toronto, provisional designation , is a metallic background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 36 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 15 August 1963, by Karl Walter Kamper, Karl Kamper at the David D ...
is discovered in the David Dunlap Observatory
The David Dunlap Observatory (DDO) is an astronomical observatory site in Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada. Established in 1935, it was owned and operated by the University of Toronto until 2008. It was then acquired by the city of Richmond Hill, ...
in Richmond Hill and is named after the university. In 1972, studies on Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a galactic X-ray source in the constellation Cygnus and was the first such source widely accepted to be a black hole. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the ...
led to the publication of the first observational evidence proving the existence of black holes. Toronto astronomers have also discovered the Uranian
Uranian may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Sexuality
*Uranian (sexology), a historical term for homosexual men
* Uranians, a group of male homosexual poets
Astronomy
*Uranian, of or pertaining to the planet Uranus
* Uranian system, refers to the 27 moons ...
moons of Caliban
Caliban ( ), son of the witch Sycorax, is an important character in William Shakespeare's play '' The Tempest''.
His character is one of the few Shakespearean figures to take on a life of its own "outside" Shakespeare's own work: as Russell H ...
and Sycorax, the dwarf galaxies
A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is so ...
of Andromeda I, II and III, and the supernova SN 1987A
SN 1987A was a type II supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It occurred approximately from Earth and was the closest observed supernova since Kepler's Supernova. 1987A's light reached Earth on ...
. A pioneer in computing technology, the university designed and built UTEC
UTEC (University of Toronto Electronic Computer Mark I) was a computer built at the University of Toronto (UofT) in the early 1950s. It was the first computer in Canada, one of the first working computers in the world, although only built in a pro ...
, one of the world's first operational computers, and later purchased ''Ferut'', the second commercial computer after UNIVAC I
The UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer I) was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer design for business application produced in the United States. It was designed principally by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, the inven ...
. Multi-touch technology was developed at Toronto, with applications ranging from handheld devices
A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physical ...
to high-end drawing monitors to collaboration walls. The AeroVelo Atlas
The AeroVelo Atlas is a human-powered helicopter (HPH) that was built for AHS International's Igor I. Sikorsky Human Powered Helicopter Competition. On 13 June 2013, it became the first aircraft to achieve the goals of the competition and thus w ...
, which won the Igor I. Sikorsky Human Powered Helicopter Competition
The Igor I. Sikorsky Human Powered Helicopter Competition was established in 1980 by the American Helicopter Society (AHS) International. The award, the AHS Sikorsky Prize, was given for the first human powered helicopter (HPH) to meet a set of e ...
in 2013, was developed by the university's team of students and graduates and was tested in Vaughan
Vaughan () (2021 population 323,103) is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located in the Regional Municipality of York, just north of Toronto. Vaughan was the fastest-growing municipality in Canada between 1996 and 2006 with its population increas ...
.
history of medicine
The history of medicine is both a study of medicine throughout history as well as a multidisciplinary field of study that seeks to explore and understand medical practices, both past and present, throughout human societies.
More than just histo ...
. The stem cell was discovered at the university in 1963, forming the basis for bone marrow transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce ...
and all subsequent research on adult and embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre- implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist ...
s. This was the first of many findings at Toronto relating to stem cells, including the identification of pancreatic
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocr ...
and retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
l stem cells. The cancer stem cell was first identified in 1997 by Toronto researchers, who have since found stem cell associations in leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
, brain tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seconda ...
s and colorectal cancer. Medical inventions developed at Toronto include the glycaemic index, the infant cereal Pablum
Pablum is a processed cereal for infants originally marketed and co-created by the Mead Johnson Company in 1931. The product was developed at The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Ontario, to combat infant malnutrition.
The trademar ...
, the use of protective hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
in open heart surgery
Cardiac surgery, or cardiovascular surgery, is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. It is often used to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, with coronary artery bypass grafting); to c ...
and the first artificial cardiac pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart ei ...
. The first successful single-lung transplant was performed at Toronto in 1981, followed by the first nerve transplant in 1988, and the first double-lung transplant in 1989. Researchers identified the maturation promoting factor
Maturation-promoting factor (abbreviated MPF, also called mitosis-promoting factor or M-Phase-promoting factor) is the cyclin-Cdk complex that was discovered first in frog eggs. It stimulates the mitotic and meiotic phases of the cell cycle. MPF ...
that regulates cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
, and discovered the T-cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
, which triggers responses of the immune system. The university is credited with isolating the genes that cause Fanconi anemia
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of no ...
, cystic fibrosis and early-onset Alzheimer's disease
Early-onset Alzheimer's disease, also called younger-onset Alzheimer's, is Alzheimer's disease diagnosed before the age of 65. It is an uncommon form of Alzheimer's, accounting for only 5–10% of all Alzheimer's cases. About 60% have a positive ...
, among numerous other diseases. Between 1914 and 1972, the university operated the Connaught Medical Research Laboratories, now part of the pharmaceutical corporation Sanofi-Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
. Among the research conducted at the laboratory was the development of gel electrophoresis.
 The University of Toronto is the primary research presence that supports one of the world's largest concentrations of
The University of Toronto is the primary research presence that supports one of the world's largest concentrations of biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
firms. More than 5,000 principal investigator
In many countries, the term principal investigator (PI) refers to the holder of an independent grant and the lead researcher for the grant project, usually in the sciences, such as a laboratory study or a clinical trial. The phrase is also often us ...
s reside within from the university grounds in Toronto's Discovery District
The Discovery District is one of the commercial districts in Downtown Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It has a high concentration of hospitals and research institutions, particularly those related to biotechnology. The district is roughly bounded by B ...
, conducting $1 billion of medical research annually. MaRS Discovery District
MaRS Discovery District is a not-for-profit corporation founded in Toronto, Ontario, Canada in 2000. Its stated goal is to commercialize publicly funded medical research and other technologies with the help of local private enterprises and as such ...
is a research park
The following is a list of science park, technology parks and biomedical parks of the world, organized by continent.
Asia
ASEAN Economic Community
Report listing all the Economic Zones in the ASEAN Economic Community froUNIDO Viet Nam China ...
that serves commercial enterprises and the university's technology transfer
Technology transfer (TT), also called transfer of technology (TOT), is the process of transferring (disseminating) technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, in an attempt to transform invent ...
ventures. In 2008, the university disclosed 159 inventions and had 114 active start-up companies. Its SciNet Consortium
SciNet is a consortium of the University of Toronto and affiliated Ontario hospitals. It has received funding from both the federal and provincial government, Faculties at the University of Toronto, and affiliated hospitals.
It is one of seve ...
operates the most powerful supercomputer in Canada.
Culture and student life
 In the heart of social, cultural and recreational life at the University of Toronto lies Hart House, the sprawling
In the heart of social, cultural and recreational life at the University of Toronto lies Hart House, the sprawling neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
student activity centre that was conceived by alumnus-benefactor Vincent Massey
Charles Vincent Massey (February 20, 1887December 30, 1967) was a Canadian lawyer and diplomat who served as Governor General of Canada, the 18th since Confederation. Massey was the first governor general of Canada who was born in Canada after ...
and named for his grandfather Hart
Hart often refers to:
* Hart (deer)
Hart may also refer to:
Organizations
* Hart Racing Engines, a former Formula One engine manufacturer
* Hart Skis, US ski manufacturer
* Hart Stores, a Canadian chain of department stores
* Hart's Reptile Wo ...
. Opened in 1919, the complex established a communitarian spirit in the university and its students, who at the time kept largely within their own colleges under the decentralized collegiate system. At Hart House, a student can read in the library, dine casually or, formally, have a haircut
A hairstyle, hairdo, haircut or coiffure refers to the styling of hair, usually on the human scalp. Sometimes, this could also mean an editing of facial or body hair. The fashioning of hair can be considered an aspect of personal grooming ...
, visit the art gallery, watch a play in the theatre, listen to a concert, observe or join in debates, play billiards
Cue sports are a wide variety of games of skill played with a cue, which is used to strike billiard balls and thereby cause them to move around a cloth-covered table bounded by elastic bumpers known as .
There are three major subdivisions ...
, or go for a swim and find a place to study, all under the same roof and within the span of a day. The confluence of assorted functions is the result of a deliberate effort to create a holistic educational experience, a goal summarized in the Founders' Prayer. The Hart House model was influential in the planning of student centres at other universities, notably Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to tea ...
's Willard Straight Hall
Willard Straight Hall is the student union building on the central campus of Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. It is located on Campus Road, adjacent to the Ho Plaza and Cornell Health.
Background
The construction of Willard Straight Hall ...
.
Hart House resembles some traditional aspects of student representation through its financial support of student clubs, and its standing committees and board of stewards that are composed mostly of undergraduate students. However, the main students' unions on administrative and policy issues are the University of Toronto Students' Union
The University of Toronto Students' Union (UTSU), legally known as the Students' Administrative Council of the University of Toronto, Inc., is the representative student government of full-time undergraduate students at the University of Toronto ...
, Association of Part-time Undergraduate Students and the Graduate Students' Union. Student representative bodies also exist at the various colleges, academic faculties and departments.
The Hart House Debating Club
Hart House is a student activity centre at the University of Toronto. Established in 1919, it is one of the earliest North American student centres, being the location of student debates and conferences since its construction. Hart House was in ...
employs a debating
Debate is a process that involves formal discourse on a particular topic, often including a moderator and audience. In a debate, arguments are put forward for often opposing viewpoints. Debates have historically occurred in public meetings, a ...
style that combines the American emphasis on analysis
Analysis ( : analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (3 ...
and the British use of wit. Smaller debating societies at Trinity, University and Victoria College have served as initial training grounds for debaters who later progress to Hart House. The club won the World Universities Debating Championship
The World Universities Debating Championship (WUDC) is the world's largest debating tournament and one of the largest annual international student events in the world. WUDC is held in the British Parliamentary Debate format (involving four team ...
in 1981 and 2006. The North American Model United Nations (NAMUN) hosts an annual Model United Nations
Model United Nations, also known as Model UN or MUN, is an educational simulation in which students can learn about diplomacy, international relations, and the United Nations. At a MUN conference, students work as the representative of a count ...
conference on campus, while the United Nations Society participates in various North American and international conferences. The Toronto chess team has captured the top title six times at the Pan American Intercollegiate Team Chess Championship The Pan-American Intercollegiate Team Chess Championship is the foremost intercollegiate team chess championship in the Americas. Hosted in part by the United States Chess Federation, the Pan-Am Intercollegiate is open to any team comprising four p ...
. The Formula SAE
Formula SAE is a student design competition organized by SAE International (previously known as the Society of Automotive Engineers, SAE). The competition was started in 1980 by the SAE student branch at the University of Texas at Austin after ...
Racing Team won the Formula Student European Championships in 2003, 2005 and 2006.
Greek life
The University of Toronto is home to the first collegiate fraternity in Canada,Zeta Psi
Zeta Psi () is a collegiate fraternity. It was founded in June 1, 1847 at New York University. The organization now comprises fifty-three active chapters and thirty-four inactive chapters, encompassing roughly fifty thousand members, and is a ...
, whose Toronto chapter has been active since 1879. Other fraternity chapters at the University of Toronto include Alpha Delta Phi, Alpha Epsilon Pi
Alpha Epsilon Pi (), commonly known as AEPi, is a college fraternity founded at New York University in 1913 by Charles C. Moskowitz and ten other men. The fraternity has more than 150 active chapters across the United States, Canada, United K ...
, Delta Kappa Epsilon
Delta Kappa Epsilon (), commonly known as ''DKE'' or ''Deke'', is one of the oldest fraternities in the United States, with fifty-six active chapters and five active colonies across North America. It was founded at Yale College in 1844 by fiftee ...
, Sigma Chi
Sigma Chi () International Fraternity is one of the largest North American fraternal literary societies. The fraternity has 244 active (undergraduate) chapters and 152 alumni chapters across the United States and Canada and has initiated more t ...
, Delta Upsilon
Delta Upsilon (), commonly known as DU, is a collegiate men's fraternity founded on November 4, 1834 at Williams College in Williamstown, Massachusetts. It is the sixth-oldest, all-male, college Greek Letter Organizations#Greek letters, Greek-let ...
, Phi Delta Theta, Phi Kappa Sigma
Phi Kappa Sigma () is an international all-male college secret society and social fraternity. While nicknames differ from institution to institution, the most common nicknames for the fraternity are Skulls, Skullhouse, Phi Kap, and PKS (the fi ...
, Phi Gamma Delta, Psi Upsilon
Psi Upsilon (), commonly known as Psi U, is a North American fraternity,''Psi Upsilon Tablet'' founded at Union College on November 24, 1833. The fraternity reports 50 chapters at colleges and universities throughout North America, some of which ...
, Beta Theta Pi, Phi Kappa Pi
Phi Kappa Pi () is a Canadian national fraternity. Founded on , as Canada's only national fraternity, Phi Kappa Pi has active chapters in Burnaby, Halifax, Toronto, and Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most pop ...
, Kappa Sigma, Lambda Phi Epsilon
Lambda Phi Epsilon (, also known as LPhiE and LFE) is the largest Asian-American-Interest fraternity in North America. Lambda Phi Epsilon is affiliated with the National APIDA Panhellenic Association, and is a former member of the North American ...
, Sigma Nu, Theta Delta Chi
Theta Delta Chi () is a social fraternity that was founded in 1847 at Union College, New York, United States. While nicknames differ from institution to institution, the most common nicknames for the fraternity are TDX, Thete, Theta Delt, and Thump ...
, Alpha Kappa Nu
Alpha Kappa Nu () was one of the first documented African-American collegiate fraternal organizations in the United States. Formed in 1903 at Indiana University and lasting until around 1905, it had a membership of 10, which included all th ...
, Alpha Omicron Pi, Delta Delta Delta
Delta Delta Delta (), also known as Tri Delta, is an international women's fraternity founded on November 27, 1888 at Boston University by Sarah Ida Shaw, Eleanor Dorcas Pond, Isabel Morgan Breed, and Florence Isabelle Stewart.
Tri Delta part ...
, Pi Beta Phi
Pi Beta Phi (), often known simply as Pi Phi, is an international women's fraternity founded at Monmouth College, in Monmouth, Illinois on April 28, 1867 as I. C. Sorosis, the first national secret college society of women to be modeled after ...
and Lambda Chi Alpha
Lambda Chi Alpha (), commonly known as Lambda Chi, is a college fraternity in North America which was founded at Boston University in 1909. It is one of the largest social fraternities in North America, with more than 300,000 lifetime members a ...
. Other Greek-letter societies include Alpha Gamma Delta
Alpha Gamma Delta (), also known as Alpha Gam, is an international women's fraternity and social organization. It was founded on May 30, 1904, by eleven female students at Syracuse University in Syracuse, New York, making it the youngest member ...
, Alpha Phi
Alpha Phi International Women's Fraternity (, also known as APhi) is an international sorority with 172 active chapters and over 250,000 initiated members.
Founded at Syracuse University in Syracuse, New York on September 18, 1872, it is the fo ...
, Alpha Sigma Nu
Alpha Sigma Nu () is the honor society of Jesuit colleges and universities. ΑΣΝ is a member of the Association of College Honor Societies. Founded in 1915 at Marquette University as Alpha Sigma Tau, it adopted the current name in 1930. The s ...
, Delta Phi Nu, Gamma Phi Beta
Gamma Phi Beta (, also known as GPhi or Gamma Phi) is an international college sorority. It was founded in Syracuse University in 1874, and was the first of the Greek organizations to call itself a sorority. The main archive URL iThe Baird's Man ...
, Kappa Alpha Society
The Kappa Alpha Society (), founded in 1825, was the progenitor of the modern fraternity system in North America. It is considered to be the oldest national, secret, Greek-letter social fraternity and was the first of the fraternities which would ...
, Delta Psi Delta, Gamma Delta Nu, Kappa Phi Xi, Delta Pi, Chi Sigma Xi, Zeta Beta Omega, Kappa Kappa Gamma, and alpha Kappa Delta Phi
alpha Kappa Delta Phi (), also known as aKDPhi, Kappa Delta Phi, KDPhi, is an international Asian-interest sorority founded at the University of California, Berkeley. alpha Kappa Delta Phi has 63 chapters located at numerous universities acros ...
. A secret society known as ''Episkopon
The Episkopon (Greek: ΕΠΙΣΚΟΠΩΝ, "bishop") is a secret society at Trinity College in the University of Toronto, which has been active since 1858 when its male branch was founded. The 225th reading of its original male branch was held in 2 ...
'' has operated from Trinity College since 1858.
Theatre and music

Hart House Theatre
Hart House Theatre is a 454-seat theatre in Toronto, Ontario located on the campus of the University of Toronto in the Hart House Student Centre. The theatre serves the university and the Toronto community at large.
Hart House Theatre opened i ...
is the university's student amateur theatre
Amateur theatre, also known as amateur dramatics, is theatre performed by amateur actors and singers. Amateur theatre groups may stage plays, revues, musicals, light opera, pantomime or variety shows, and do so for the social activity as well as f ...
, generally producing four major plays every season. As old as Hart House itself, the theatre is considered a pioneer in Canadian theatre
Canada's contemporary theatre reflects a rich diversity of regional and cultural identities. Since the late 1960s, there has been a concerted effort to develop the voice of the 'Canadian playwright', which is reflected in the nationally focused ...
for introducing the Little Theatre Movement As the new medium of cinema was beginning to replace theater as a source of large-scale spectacle, the Little Theatre Movement developed in the United States around 1912. The Little Theatre Movement served to provide experimental centers for the dr ...
from Europe. It has cultivated numerous performing-arts talents, including Donald Sutherland, Lorne Michaels, Wayne and Shuster and William Hutt (actor), William Hutt. Three members of the Group of Seven
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated member". It is officiall ...
painters (Lawren Harris, Harris, Arthur Lismer, Lismer and J. E. H. MacDonald, MacDonald) have been set designers at the theatre, and composer Healey Willan was director of music for fourteen productions. The theatre also hosts annual variety shows run by several student theatrical companies at the colleges and academic faculties, the most prominent of which are ''U.C. Follies'' of University College, ''Skule Nite'' of the Faculty of Engineering, and ''Daffydil'' of the Faculty of Medicine, the latter in its hundredth year of production in 2010–2011.
The main musical ensembles at Hart House are the orchestra, the chamber strings, the chorus, the jazz choir, the jazz ensemble and the symphonic band. The ''Jazz at Oscar's'' concert series performs big band and vocal jazz on Friday nights at the period lounge and bar of the Hart House Arbor Room. ''Open Stage'' is the monthly open mic event featuring singers, comics, poets and storytellers. The Sunday Concert is the oldest musical series at Hart House; since 1922, the series has performed more than 600 classical music concerts in the Great Hall, freely attended by the university community and general audiences. The public may also screen midday events held at noon, when concerts are recited prior to formal debut.
Student media
Northrop Frye
Herman Northrop Frye (July 14, 1912 – January 23, 1991) was a Canadian literary critic and literary theorist, considered one of the most influential of the 20th century.
Frye gained international fame with his first book, '' Fearful Symm ...
. ''Juxtaposition Magazine, Juxtaposition Global Health Magazine'' is another peer-reviewed student publication at the campus. The magazine focuses on global health and international development, and is published in association with the university's Centre for International Health.
Members of the student press have contributed to activist causes on several notable occasions. At the height of debate on coeducation in 1880, ''The Varsity'' published an article in its inaugural issue voicing in favour of admitting women. In 1895, the university suspended the editor of ''The Varsity'' for breach of collegiality, after he published a letter that harshly criticized the provincial government's dismissal of a professor and involvement in academic affairs. University College students then approved a motion by ''Varsity'' staff member and future Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King and boycotted lectures for a week. After Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau LGBT rights in Canada, decriminalized homosexuality throughout Canada in 1969, a medical research assistant placed an advertisement in ''The Varsity'' seeking volunteers to establish the first university homophile association in Canada.
Student social media
Several Facebook pages that posts memes about student life at the university were created in the 2010s, particularly True , and has impacted the student culture of the institution.Residences
Massey College
Massey College is a graduate residential college at the University of Toronto that was established, built and partially endowed in 1962 by the Massey Foundation and officially opened in 1963, though women were not admitted until 1974. It was mo ...
is exclusively for graduate students, while Knox and Wycliffe Colleges mainly house graduate theology students. Annesley Hall of Victoria College, a National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site, was the first university residence for women in Canada. After St. Hilda's College became coeducational in 2005, Annesley Hall and Loretto College of St. Michael's College are the last remaining women's halls at the university.
As campus residences accommodate just 6,400 students in all, the university guarantees housing only for undergraduates in their first year of study, while most upper-year and graduate students reside off-campus. Traditionally, the adjacent neighbourhoods of The Annex
The Annex is a neighbourhood in Downtown Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The traditional boundaries of the neighbourhood are north to Dupont Street, south to Bloor Street, west to Bathurst Street and east to Avenue Road. The City of Toronto recognizes ...
and Harbord Village are popular settling grounds for University of Toronto students, forming a distinct student quarter enclave, though Chinatown and Kensington Market are increasingly populated by students. In 2004, the university purchased and converted a nearby hotel in the district that would later become First Chinatown, Toronto, Little Japan to the south into the Chestnut Residence, which houses students from all colleges and faculties. There are also numerous fraternity houses and student housing cooperatives, where boarders pay reduced rent for assuming housekeeping duties.
Demographics
The University of Toronto is known for having a high enrolment of international students. In 2016–17, 19.7 percent of students were international. The University plans to grow its international enrolment to 20.1 percent by 2021–22. In 2017, the University of Toronto had more international students enrolled than all other Canadian post-secondary institutions. In 2011, 78 percent of incoming first-year students identified as a visible minority. In 2001–02, the overall gender ratio was about 57.1 percent female to 42.9 percent male for enrolled students, or about 15 males for every 20 females. This gender gap has improved slightly in recent years to 55.8% female and 44.2% male, or about 16 males for every 20 females in 2014–15 (non-binary genders were not reported). This gap is more pronounced for graduation rates, with 59% of degrees conferred on females. Gender ratios also depend on undergraduate versus graduate enrolment, and department. The overall average of high school grades for first-year students was about 86% for fall 2014. The retention rate was 92.1%. In 2011–12, 40.3% of the students were enrolled in the Social Science and Humanities departments, 23.9% were enrolled in Biology, Engineering, and Mathematics & Physical Sciences. General education accounted for 14.7% enrolment (all undergraduates). Health Professions was 12.7%, Education 5.8%, and Fine Arts 2.6%.Campus suicides
The University of Toronto has faced significant criticism of its handling of student suicides and students' mental health problems. From 2017 to 2019, four students committed suicide at the school, three of them in the Bahen Centre for Information Technology. Student advocacy groups have said that the university contributed to the suicides by failing to provide mental health resources, with computer science student Shahin Imtiaz saying in an interview that "the university has turned into a pressure-cooker of intense demands, without the resources to meet the student needs to back it up." While the university does not generally acknowledge student deaths as suicides, the university responded to the deaths by adding additional safety barriers to the Bahen Centre and by promising additional support, adding close to three million dollars in funding for student wellbeing.Athletics
U Sports
U Sports (stylized as U SPORTS) is the national sport governing body of university sport in Canada, comprising the majority of degree-granting universities in the country. Its equivalent body for organized sports at colleges in Canada is the C ...
(formerly known as Canadian Interuniversity Sport (CIS)) for national competitions and the auxiliary Ontario University Athletics (OUA) conference at the provincial level. The athletic nickname of Varsity Blues was not consistently used until the 1930s; previously, references such as "Varsity", "The Big Blue", "The Blue and White", "The Varsity Blue" and simply "The Blues" also appeared interchangeably. ''The Blue and White'' is commonly played and sung in athletic games as a fight song.
Gridiron football, North American (gridiron) football traces its very origin to the University of Toronto with the first documented football game played at University College on November 9, 1861. The Blues played their first College football, intercollegiate football match in 1877 against the University of Michigan in a game that ended with a scoreless draw. Since intercollegiate seasons began in 1898, the Blues have won four Grey Cup, two Vanier Cup and 25 Yates Cup championships, including the inaugural championships for all three trophies. However, the football team has hit a rough patch following its last championship in 1993. From 2001 until 2008, the Blues suffered the longest losing streak in Canadian collegiate history, recording 49 consecutive winless games. This was preceded by a single victory in 2001 that ended a run of 18 straight losses. The site of Varsity Stadium has served as the primary playing grounds of the Varsity Blues football and soccer programs since 1898. It also served as the venue for Archery at the 2015 Pan American Games, archery during the 2015 Pan American Games.
 Formed in 1891, the storied Toronto Varsity Blues men's ice hockey, Varsity Blues men's ice hockey team has left many legacies on the national, professional and international hockey scenes. Conn Smythe played for the Blues as a centre (ice hockey), centre during his undergraduate years, and was a Blues coach from 1923 to 1926. When Smythe took over the Toronto Maple Leafs in 1927, his new team adopted the Varsity Blues' familiar blue-and-white sweater design. Blues hockey competed at the Ice hockey at the 1928 Winter Olympics, 1928 Winter Olympics and captured the gold medal for Canada at the 1928 Winter Olympics, Canada. At the 1980 Winter Olympics, Blues coach Tom Watt (ice hockey), Tom Watt served as co-coach of the Canadian hockey team in which six players were Varsity grads. In all, the Blues have won the David Johnston University Cup, U Sports University Cup national hockey title ten times, last in 1984.
Formed in 1891, the storied Toronto Varsity Blues men's ice hockey, Varsity Blues men's ice hockey team has left many legacies on the national, professional and international hockey scenes. Conn Smythe played for the Blues as a centre (ice hockey), centre during his undergraduate years, and was a Blues coach from 1923 to 1926. When Smythe took over the Toronto Maple Leafs in 1927, his new team adopted the Varsity Blues' familiar blue-and-white sweater design. Blues hockey competed at the Ice hockey at the 1928 Winter Olympics, 1928 Winter Olympics and captured the gold medal for Canada at the 1928 Winter Olympics, Canada. At the 1980 Winter Olympics, Blues coach Tom Watt (ice hockey), Tom Watt served as co-coach of the Canadian hockey team in which six players were Varsity grads. In all, the Blues have won the David Johnston University Cup, U Sports University Cup national hockey title ten times, last in 1984. Varsity Arena
Varsity Arena, located at 299 Bloor Street West, Toronto, Ontarioretrieved from http://rrs.osm.utoronto.ca 2007-10-22 is an indoor arena that opened on December 17, 1926, and is primarily home to the ice hockey teams of the University of Toronto, ...
has been the permanent home of the Blues ice hockey programs since it opened in 1926. In men's basketball, the Varsity Blues have won 14 conference titles, including the inaugural championship in 1909, but have not won a national title. In swimming, the men's team has claimed the national crown 16 times since 1964, while the women's team has claimed the crown 14 times since 1970. Established in 1897, the University of Toronto Rowing Club is Canada's oldest collegiate rowing club. It earned a silver medal for the country in the 1924 Summer Olympics, finishing second to Yale's crew.
Back Campus Fields, The back campus of University College was used for Field hockey at the 2015 Pan American Games, field hockey during the 2015 Pan American Games and the field was renamed Pan Am / Parapan Am Fields for the duration of the Pan American Games.
Notable people
Harold Innis
Harold Adams Innis (November 5, 1894 – November 9, 1952) was a Canadian professor of political economy at the University of Toronto and the author of seminal works on media, communication theory, and Canadian economic history. He helped deve ...
, professor of political economy, helped develop the staples thesis and the Toronto School of communication theory
File:Frederick Banting 3.jpg, Frederick Banting, Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Laureate in Medicine and the first person to use insulin on humans, MD
File:Roberta Bondar NASA.jpg, Roberta Bondar, Canadian Space Agency, CSA astronaut and the first Canadian female in space, PhD
File:Julie Payette 2017.jpg, Julie Payette, CSA astronaut and the List of governors general of Canada, 29th Governor General of Canada, MASc
File:Smillie portrait.jpg, Jennie Smillie Robertson, First female surgeon in Canada, MD
Vincent Massey
Charles Vincent Massey (February 20, 1887December 30, 1967) was a Canadian lawyer and diplomat who served as Governor General of Canada, the 18th since Confederation. Massey was the first governor general of Canada who was born in Canada after ...
, Adrienne Clarkson, and Julie Payette, Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Ministers William Lyon Mackenzie King, Arthur Meighen, Lester B. Pearson, Paul Martin and Stephen Harper, and 17 List of Justices of the Supreme Court of Canada, Justices of the Supreme Court have all graduated from the university, while world leaders include President of Latvia Vaira Vīķe-Freiberga, Premier of the Republic of China Liu Chao-shiuan, President of Trinidad and Tobago Noor Hassanali, and List of spouses and partners of Icelandic presidents, First Lady of Iceland Eliza Reid. Economist John Kenneth Galbraith, political scientist David Easton, historian Margaret MacMillan, philosophers David Gauthier and Ted Honderich, anthropologist Davidson Black, social activist Ellen Pence, sociologist Erving Goffman, psychologists Endel Tulving, Daniel Schacter, and Lisa Feldman Barrett, physicians Norman Bethune and Charles Best (medical scientist), Charles Best, geologists Joseph Tyrrell and John Tuzo Wilson, mathematicians Irving Kaplansky and William Kahan, physicists Arthur Leonard Schawlow and Bertram Brockhouse, religion scholar Amir Hussain, architect James Strutt, engineer Gerald Bull, computer scientists Alfred Aho and Brian Kernighan, and astronauts Roberta Bondar and Julie Payette are also some of the most well-known academic figures from the university.
In business, University of Toronto alumni include Rogers Communications' Edward S. Rogers Jr., Ted Rogers, Toronto-Dominion Bank's W. Edmund Clark, Bank of Montreal's Bill Downe, Scotiabank's Peter Godsoe, Barrick Gold's Peter Munk, BlackBerry Limited, BlackBerry's Jim Balsillie, eBay's Jeffrey Skoll, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, Fiat S.p.A.'s Sergio Marchionne, and Apotex's Barry Sherman, Bernard Sherman. In literature and media, the university has produced writers Stephen Leacock, John McCrae, Rohinton Mistry, Margaret Atwood and Michael Ondaatje, film directors Arthur Hiller, Norman Jewison, David Cronenberg and Atom Egoyan, actor Donald Sutherland, screenwriter David Shore, television producer and writer Hart Hanson, musician Paul Shaffer, and journalists Malcolm Gladwell, Naomi Klein and Barbara Amiel.
The University of Toronto alumni-founded companies generate roughly equivalent to one quarter of the Canadian GDP according to a survey published in 2021.
See also
* Education in Toronto * Higher education in Ontario * List of universities in Ontario * University of Toronto Campus SafetyNotes
References
Further reading
* Claude Bissell, Bissell, Claude T. (1974). ''Halfway up Parnassus: A Personal Account of the University of Toronto''. University of Toronto Press. . * Ford, Ann Rochon. (1985). ''A Path Not Strewn with Roses''. University of Toronto Press. . * Martin Friedland, Friedland, Martin L. (2002).The University of Toronto: A History
'. University of Toronto Press. . * Levi, Charles Morden. (2003).
Comings and Goings
'. McGill-Queen's University Press. . * A. B. McKillop, McKillop, A. Brian. (1994). ''Matters of Mind''. University of Toronto Press. . * Slater, John G. (2005).
Minerva's Aviary: Philosophy at Toronto
'. University of Toronto Press. . * Wallace, W. Stewart. ''A History of the University of Toronto, 1827–1927.'' University of Toronto Press, 1927.
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:University Of Toronto University of Toronto, Universities in Canada Organizations based in Canada with royal patronage, Toronto, University Educational institutions established in 1827, Toronto, University Forestry education 1827 establishments in Upper Canada Universities in Ontario U15 Group of Canadian Research Universities, Toronto