Upper Swabia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
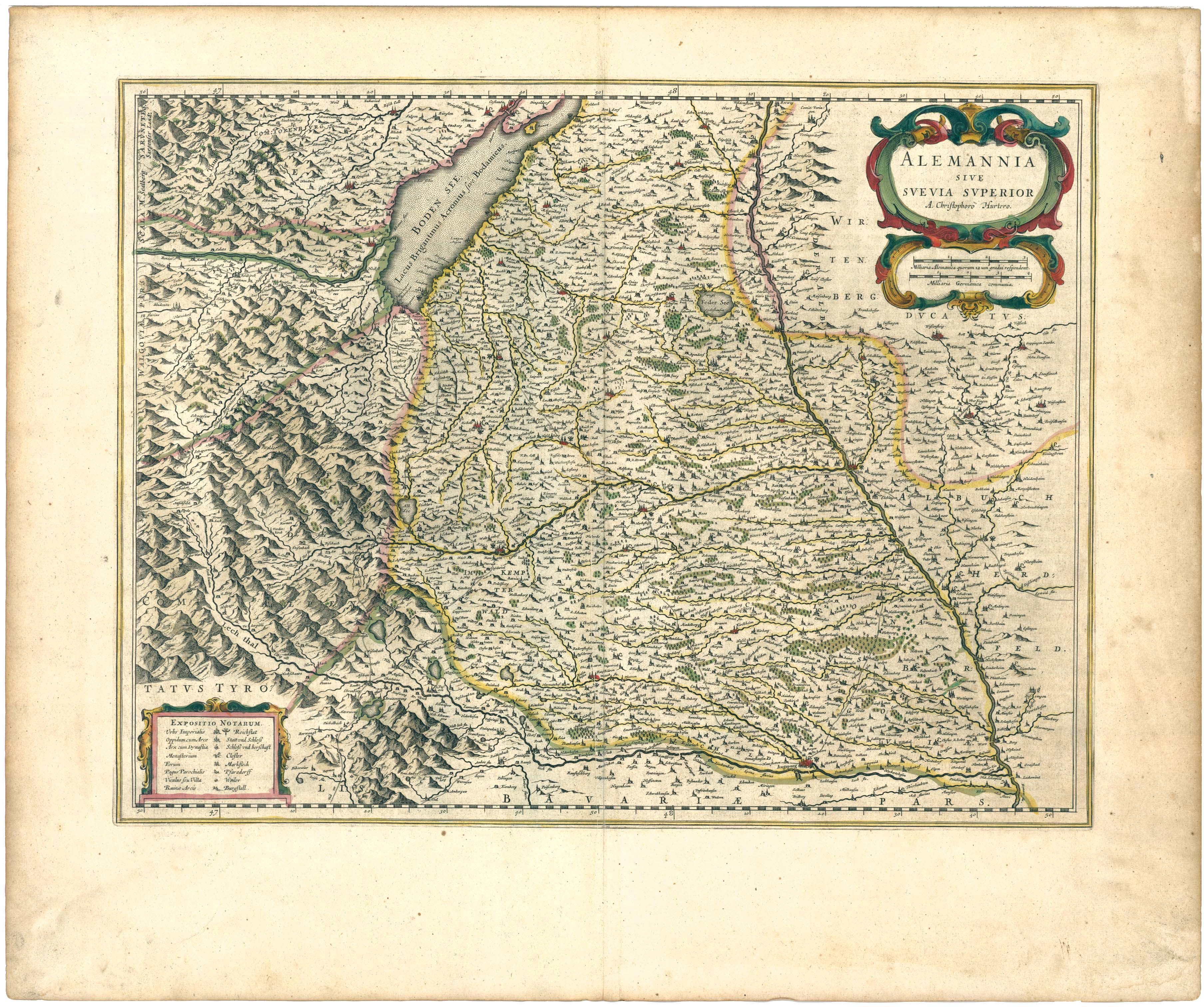


















 Upper Swabia (german: Oberschwaben or ) is a region in
Upper Swabia (german: Oberschwaben or ) is a region in
Webpage of the Upper Swabian Tourist Office
German webpage of the Upper Swabian Baroque Route
German webpage of the Swabian Spa Route
German webpage of the German Half-Timbered Buildings Route
German webpage of the Upper Swabian Mill Route
{{Authority control Regions of Baden-Württemberg

















 Upper Swabia (german: Oberschwaben or ) is a region in
Upper Swabia (german: Oberschwaben or ) is a region in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
in the federal states of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
and Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
.''Brockhaus Enzyklopädie.'' 19. Auflage. Band 16, 1991, p. 72. The name refers to the area between the Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of ...
, Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Lak ...
and the Lech. Its counterpart is Lower Swabia (''Niederschwaben''), the region around Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state.
From the late Middle Ages, it developed into an important trading centre. A ...
.
Geography
The region of Upper Swabia is situated in the central south of Germany consisting of the south-east of Baden-Württemberg and the south-west bavarian Swabia region and lies on the Iller-Lech Plateau, also known as the Upper Swabian Plain, one of thenatural regions of Germany
This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Poli ...
. The landscape of Upper Swabia was formed by retreating glaciers after the Riss glaciation
The Riss glaciation, Riss Glaciation, Riss ice age, Riss Ice Age, Riss glacial or Riss Glacial (german: Riß-Kaltzeit, ', ' or (obsolete) ') is the second youngest glaciation of the Pleistocene epoch in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classi ...
, leaving behind a large number of shallows which quickly filled up with water. This led to the large quantity of lakes in Upper Swabia. The landscape of Upper Swabia is quite hilly rising from approximately 458 metres above sea level in the valley of the river Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
to a maximum of 833 metres above sea level in the south-west of Upper Swabia only to drop again to 395 meters above sea level at Lake Constance. The European watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
also passes through the region, with some rivers emptying into the Danube (ultimately flowing into the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
) and others emptying into Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Lak ...
(ultimately ending in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
).
Due to Upper Swabia's altitude and hilly terrain, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
consists mainly of dairy farming, the exception being the basin of the river Schussen, where the predominant produce is hops and fruits.
Upper Swabia is still a very rural area dominated by villages. The urban population is concentrated in the cities of Friedrichshafen
Friedrichshafen ( or ; Low Alemannic: ''Hafe'' or ''Fridrichshafe'') is a city on the northern shoreline of Lake Constance (the ''Bodensee'') in Southern Germany, near the borders of both Switzerland and Austria. It is the district capital (''K ...
, Ravensburg
Ravensburg ( Swabian: ''Raveschburg'') is a city in Upper Swabia in Southern Germany, capital of the district of Ravensburg, Baden-Württemberg.
Ravensburg was first mentioned in 1088. In the Middle Ages, it was an Imperial Free City and an im ...
& Weingarten Weingarten may refer to:
Places
* Weingarten, Württemberg, Germany
** Weingarten Abbey
* Weingarten (Baden), Germany
* Weingarten, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
* Weingarten, Thuringia, Germany
* Weingarten, Switzerland
* Weingarten, Missouri ...
and Biberach an der Riß
Biberach an der Riß ( Swabian: ''Bibra''), often referred to as simply Biberach (), is a town in southern Germany. It is the capital of Biberach district, in the Upper Swabia region of the German state (Land) of Baden-Württemberg. It is calle ...
as well as Memmingen
Memmingen (; Swabian: ''Memmenge'') is a town in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is the economic, educational and administrative centre of the Danube-Iller region. To the west the town is flanked by the Iller, the river that marks the Baden-Wür ...
and Günzburg.
The eastern border of Upper Swabia has been disputed for some time. Historically, the river Lech marks the border between Swabia and Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
. However, this would mean that large parts of Bavarian Swabia would have to be incorporated into Upper Swabia. As a result, these days the river Iller marks the eastern border of Upper Swabia.
The inhabitants of the former Free Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
Ulm and those that belonged to the former Imperial Abbey
Princely abbeys (german: Fürstabtei, ''Fürststift'') and Imperial abbeys (german: Reichsabtei, ''Reichskloster'', ''Reichsstift'', ''Reichsgotthaus'') were religious establishments within the Holy Roman Empire which enjoyed the status of impe ...
of Zwiefalten
Zwiefalten is a municipality in the district of Reutlingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany located halfway between Stuttgart and Lake Constance. The former Zwiefalten Abbey dominates the town. The former monastery is considered one of the finest exam ...
do not consider themselves as being part of Upper Swabia. Yet, in spite of their location close to the Swabian Alb
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of ...
, geographically, historically and culturally, they have always been closely connected to Upper Swabia.
Administration
Upper Swabia is part of theTübingen
Tübingen (, , Swabian: ''Dibenga'') is a traditional university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer rivers. about one in thre ...
, a being a sub-division of a federal state.
The following districts are wholly or partially part of Upper Swabia:
* Alb-Donau
* Biberach
* Bodenseekreis
Bodenseekreis ("Lake Constance district") is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the south-east of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from west, clockwise) Konstanz, Sigmaringen and Ravensburg, and in Bavaria, Lindau district. T ...
(''Lake Constance'')
* Ravensburg
Ravensburg ( Swabian: ''Raveschburg'') is a city in Upper Swabia in Southern Germany, capital of the district of Ravensburg, Baden-Württemberg.
Ravensburg was first mentioned in 1088. In the Middle Ages, it was an Imperial Free City and an im ...
* Reutlingen
Reutlingen (; Swabian: ''Reitlenga'') is a city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is the capital of the eponymous district of Reutlingen. As of June 2018, it has a population of 115,818.
Reutlingen has a university of applied sciences, which ...
* Sigmaringen
Sigmaringen ( Swabian: ''Semmerenga'') is a town in southern Germany, in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Situated on the upper Danube, it is the capital of the Sigmaringen district.
Sigmaringen is renowned for its castle, Schloss Sigmaringen, ...
* Ulm
History
Upper Swabia has been populated at least since theNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
age. Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscape ...
evidence confirming this was discovered around the Federsee
Federsee is a lake located just north of Bad Buchau in the region of Upper Swabia in Southern Germany. It is surrounded by moorland, partially overgrown with reeds. With a size of 33 km2 (8,155 acres), the area is one of the largest, grou ...
, a lake near Bad Buchau
Bad Buchau () (formerly Buchau; Swabian: ''Buacha'') is a small town in the district of Biberach, Baden-Württemberg, Germany with about 4,000 inhabitants. It is situated near Lake Federsee, which is separated from the town by a wide reed belt. ...
.
Until around the year 260 CE, the region that was to become Upper Swabia, was part of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west w ...
, after which the Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pr ...
invaded the Agri Decumates and settling there.
During the Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
period, Upper Swabia came under the rule of the Frankish kings. It was part of the Duchy of the Alamanni. During the same period, the Christianization of the region began.
During the Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
, Ottonian and Salian
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125).
After the death of the la ...
period, Upper Swabia was part of the Duchy of Swabia.
From the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD ...
onwards, Upper Swabia became fragmented into a large number of small independent political units: Free Imperial Cities
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
, principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall und ...
, counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
, seigneuries, Imperial Abbeys
Princely abbeys (german: Fürstabtei, ''Fürststift'') and Imperial abbeys (german: Reichsabtei, ''Reichskloster'', ''Reichsstift'', ''Reichsgotthaus'') were religious establishments within the Holy Roman Empire which enjoyed the status of imp ...
and other clerical territories.
During the German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
of 1524–1525, Upper Swabia was a centre of the revolt. The peasants formed three armed groups, called '' Haufen'' (or ''Haufe''): the Allgäuer Haufen, active in the Allgäu and eastern Upper Swabia, the Seehaufen, centred on the region north of Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Lak ...
, and the Baltringer Haufen, named after the village of Baltringen
Baltringen is a once autonomous village in Baden-Württemberg in the region of Upper Swabia, situated approximately 17 km north of Biberach. Administratively, Baltringen is part of the municipality of Mietingen. Baltringen lies on the rive ...
, a few kilometres south of Laupheim in northern Upper Swabia.
During the revolt, numerous castles and monasteries in Upper Swabia were destroyed by the peasants. By July 1525, however, the rising had been utterly suppressed in Upper Swabia, with countless peasants losing their lives either due to battles or due to punitive measures inflicted upon them afterwards by their lords. Economically and socially, the consequences were dramatic: whole communities were bankrupt and unable to pay proper taxes for a long time, the legal position of peasants was not to be altered for another 300 years, and due to the large number of outlawed peasants trying to survive by illegal means, such as robbery, commerce was severely hindered.
This instability was one of the factors that lead to Upper Swabia's becoming a plaything of marauding armies during the Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
1618 - 1648. Military actions followed by disease, such as the plague, led to a severe depopulation of Upper Swabia.
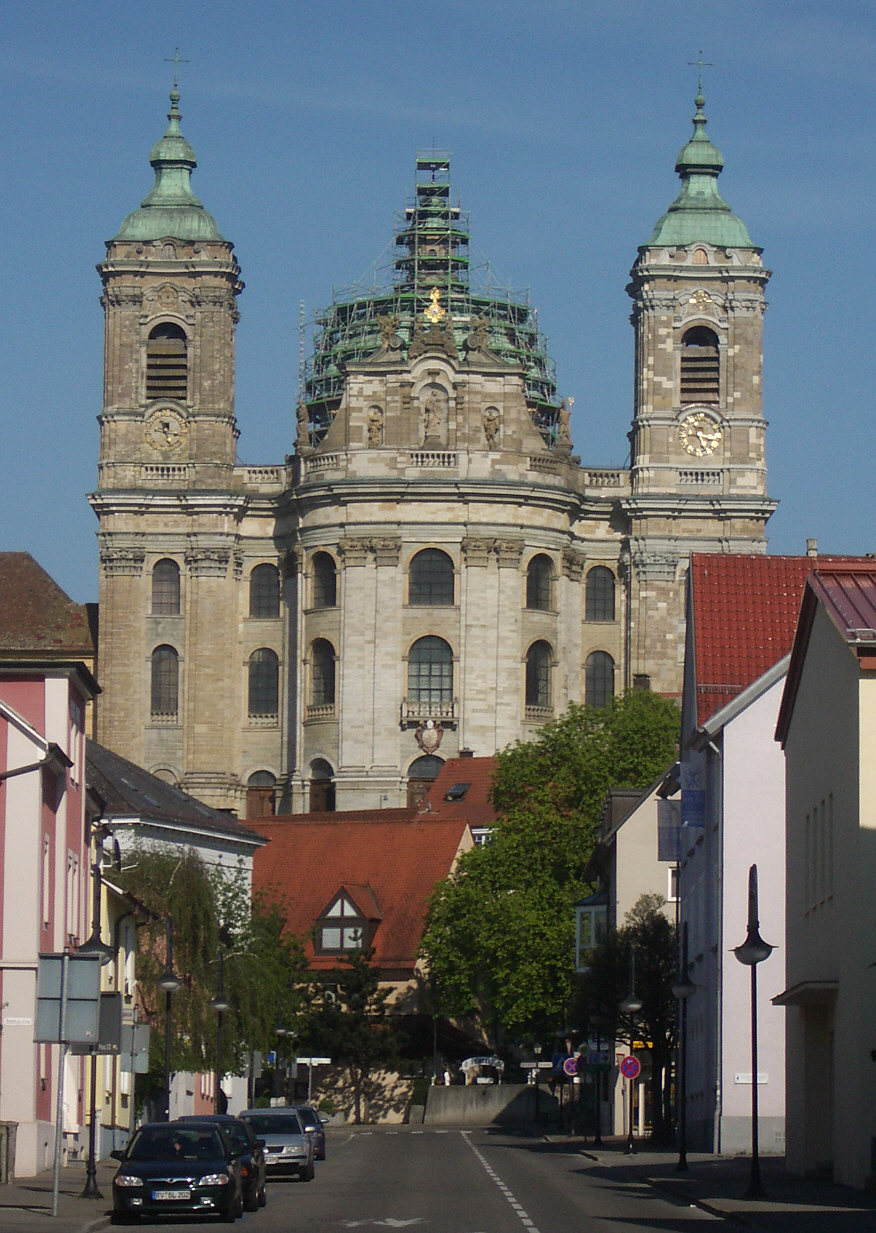
After the end of the war, the Catholic Church intensified its efforts to regain ground from the Protestants. These efforts are known as the Counter-Reformation. The local lords, secular and clerical, tried to attract immigrants to areas affected by the ravages of war and to re-populate these areas. This led to an economic upturn within the region. The efforts of the Counter-Reformation and the newly acquired financial ability of both secular and clerical lords enabled them to restore, extend and enhance the already existing seigneurial buildings in Baroque-style. The result of this is today called Upper Swabian Baroque.
During the secularization
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses t ...
and mediatization in 1803, almost all monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whic ...
were dissolved and the Free Imperial Cities lost their independence. With the end of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
in 1806, marked by the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss
The ' (formally the ', or "Principal Conclusion of the Extraordinary Imperial Delegation"), sometimes referred to in English as the Final Recess or the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the ' (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Em ...
, catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
Upper Swabia was incorporated into the protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Kingdom of Württemberg
The Kingdom of Württemberg (german: Königreich Württemberg ) was a German state that existed from 1805 to 1918, located within the area that is now Baden-Württemberg. The kingdom was a continuation of the Duchy of Württemberg, which exist ...
. This annexation was finalized during the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815.
The aristocratic dynasties that ruled Upper Swabia for centuries still have considerable political and economic influence and power.
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and the end of the Kingdom of Württemberg
The Kingdom of Württemberg (german: Königreich Württemberg ) was a German state that existed from 1805 to 1918, located within the area that is now Baden-Württemberg. The kingdom was a continuation of the Duchy of Württemberg, which exist ...
, Upper Swabia became part of the new federal state Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Wür ...
.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the northernmost areas of Upper Swabia became part of the American occupation zone, while the larger, southern area became part of the French occupation zone
The French occupation zone in Germany (, ) was one of the Allied-occupied areas in Germany after World War II.
Background
In the aftermath of the Second World War, Winston Churchill, Franklin D. Roosevelt and Joseph Stalin met at the Yalta ...
. In 1946, the Allied authorities founded the states of Württemberg-Baden
Württemberg-Baden was a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was created in 1945 by the United States occupation forces, after the previous states of Baden and Württemberg had been split up between the US and French occupation zones. ...
and Württemberg-Hohenzollern
Württemberg-Hohenzollern (french: Wurtemberg-Hohenzollern ) was a West German state created in 1945 as part of the French post-World War II occupation zone. Its capital was Tübingen. In 1952, it was merged into the newly founded state of Bade ...
, the borders of which ran along the borders of the occupation zones. As a consequence, the northern areas of Upper Swabia became part of the state of Württemberg-Baden
Württemberg-Baden was a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was created in 1945 by the United States occupation forces, after the previous states of Baden and Württemberg had been split up between the US and French occupation zones. ...
and the southern areas became part of the state of Württemberg-Hohenzollern. Both states joined the Federal Republic of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south ...
on its founding in 1949. This situation lasted until 1952, when, following a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
the previous year, Württemberg-Baden
Württemberg-Baden was a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was created in 1945 by the United States occupation forces, after the previous states of Baden and Württemberg had been split up between the US and French occupation zones. ...
and Württemberg-Hohenzollern
Württemberg-Hohenzollern (french: Wurtemberg-Hohenzollern ) was a West German state created in 1945 as part of the French post-World War II occupation zone. Its capital was Tübingen. In 1952, it was merged into the newly founded state of Bade ...
together with Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden ...
created the new federal state of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
.
Tourism
Theme routes
* The Upper Swabian Baroque Route has several branches, leading from Ulm to Lake Constance and back again. During the age of Counter-Reformation in the 17th and 18th century, a large number of churches,abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns.
The conce ...
s and secular buildings were built inBaroque-style.
* The Swabian Spa Route
Swabian or Schwabian, or ''variation'', may refer to:
* the German region of Swabia (German: "''Schwaben''")
* Swabian German, a dialect spoken in Baden-Württemberg in south-west Germany and adjoining areas (German:"''Schwäbisch''")
* Danube Sw ...
connects various spa towns, recognizable by the designation ''Bad''.
* The eastern leg of the German Half-Timbered Buildings Route leads from Bad Urach
Bad Urach () is a town in the district of Reutlingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated 14 km east of Reutlingen, at the foot of the Swabian ''Alb'' (or Swabian Alps in English), and is known for its spa and therapeutic bath.
Ne ...
to Lake Constance, passing through Biberach an der Riß, Riedlingen
Riedlingen () is a town in the district (''Kreis'') of Biberach, Baden-Württemberg, in the south-west of Germany. It is one of the destinations of the Upper Swabian Baroque Route. Riedlingen has approximately 10,000 inhabitants.
Geography ...
, Pfullendorf and Meersburg
Meersburg () is a town in Baden-Württemberg in the southwest of Germany. It is on Lake Constance.
It is known for its medieval city. The lower town ("Unterstadt") and upper town ("Oberstadt") are reserved for pedestrians only, and connected by t ...
.
* The Upper Swabian Mill Route
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
was established in 2005 and passes along more than 100 grinding mills in the region.
Vantage points
In spite of this, the touristic development of Upper Swabia has been rather slow during the last decennia. The bordering regions of Allgäu, Swabian Alb,Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is ...
and particularly the area around Lake Constance have been more prosperous. Even politicians
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, reject and create laws that govern the land and by an extension of its people. Broadly speaking, a ...
remarked in the 1990s that Upper Swabia was more an industrial region, albeit only in a few centres, than a tourist destination. However, during recent years, amends have been made in order to attract more tourism. This has been supported by the state government which provided subsidies
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
, particularly to improve rural infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
.
Regional media
Print media
* ' (Swabian Newspaper), based in Leutkirch im Allgäu; most read daily . * ' (South-Western Press)), based in Ulm, mostly read in northern Upper Swabia, and its counterpart for the region around Lake Constance the ' ('Southern Courier') based inKonstanz
Konstanz (, , locally: ; also written as Constance in English) is a university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the south of Germany. The city houses the University of Konstanz and was ...
.
* ' (Weekly Paper), free weekly newspaper, based in Biberach an der Riß.
* ' (Weekly Paper), free weekly newspaper, based in Memmingen
Radio and television
* ('Southwest Broadcasting') have local and regional studios for radio and television broadcasts in Ulm and Friedrichshafen. * REGIO TV Euro 3, regional television channel for southern Upper Swabia. * Radio 7, commercial radio station, based in Ulm with several local studios throughout the region. * Donau 3 FM, local commercial radio station, based in Ulm, for the surrounding region. * RT1-Südschwaben, local commercial radio station, based in Memmingen, for the surrounding region between Memmingen,Mindelheim
Mindelheim (; Swabian: ''Mindelhoi'') is a town in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. The town is the capital of the Unterallgäu district. At various points in history it was the chief settlement of an eponymous state.
Geography
Mindelheim is loc ...
and Illertissen
Infrastructure
Railways
Upper Swabia is criss-crossed by several railway lines: * (Wurttembergian Southern Railway), the most important railway line, linking Ulm with Friedrichshafen on Lake Constance. At Laupheim-West station arailway line
Rail terminology is a form of technical terminology. The difference between the American term ''railroad'' and the international term ''railway'' (used by the International Union of Railways and English-speaking countries outside the United Sta ...
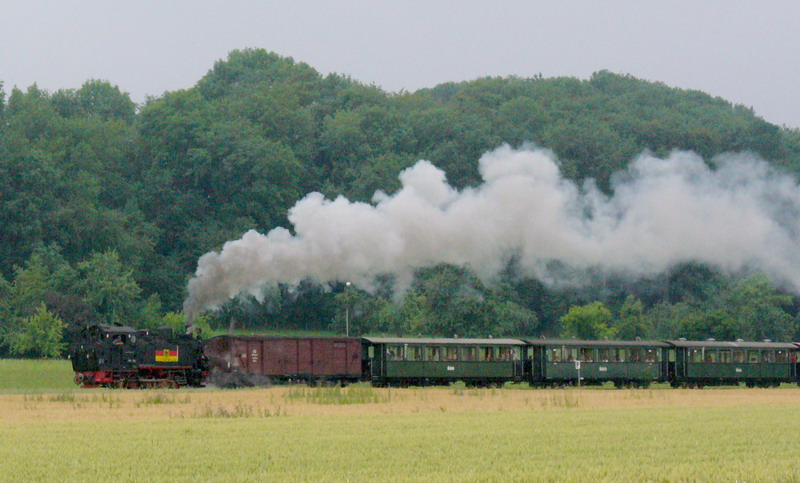
branches off, connecting the city of Laupheim with the main artery of the Wurttembergian Southern Railway. Originally this railway line extended as far as the municipality of Schwendi. In Warthausen, the so-called '' Öchsle,'' a narrow-gauge railway
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structur ...
line to Ochsenhausen, branches off. These days, the is only used as a museum railway line. From May to October, it runs every weekend and on public holidays too, from July until September also on Thursdays. Additionally, there are extra tours during the winter months.
* (Wurttembergian Allgäu Railway), connecting Aulendorf with Memmingen
Memmingen (; Swabian: ''Memmenge'') is a town in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is the economic, educational and administrative centre of the Danube-Iller region. To the west the town is flanked by the Iller, the river that marks the Baden-Wür ...
* (Danube Valley Railway), leading from Ulm via Sigmaringen
Sigmaringen ( Swabian: ''Semmerenga'') is a town in southern Germany, in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Situated on the upper Danube, it is the capital of the Sigmaringen district.
Sigmaringen is renowned for its castle, Schloss Sigmaringen, ...
to Donaueschingen
Donaueschingen (; Low Alemannic: ''Eschinge'') is a German town in the Black Forest in the southwest of the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in the Schwarzwald-Baar '' Kreis''. It stands near the confluence of the two sources of the river ...
in Baden. Finally
* (Zollern Alb Railway), which on its stretch from Aulendorf to Sigmaringen
Sigmaringen ( Swabian: ''Semmerenga'') is a town in southern Germany, in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Situated on the upper Danube, it is the capital of the Sigmaringen district.
Sigmaringen is renowned for its castle, Schloss Sigmaringen, ...
passes through Upper Swabia, before leading on to Tübingen
Tübingen (, , Swabian: ''Dibenga'') is a traditional university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer rivers. about one in thre ...
across the Swabian Alb mountain range, passing the ancestral home of the dynasty of the Hohenzollern, hence the name of the railway line.
Roads
There are nomotorways
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
() in Upper Swabia. However, several federal highways () traverse the region:
* Bundesstraße 31
The Bundesstraße 31 (B 31) is a federal highway or ''Bundesstraße'' running from east to west in South Germany. It runs from Breisach on the border with France to the Sigmarszell junction on the Bundesautobahn 96 (A 96) near Lindau. B ...
, along the northern shore of Lake Constance.
* Bundesstraße 311, from Ulm to Sigmaringen.
* Bundesstraße 30, from Ulm to Friedrichshafen.
* Bundesstraße 32
''Bundesstraße'' (German for "federal highway"), abbreviated ''B'', is the denotation for German and Austrian national highways.
Germany
Germany's ''Bundesstraßen'' network has a total length of about 40,000 km.
German ''Bundesstraßen'' ...
, from Sigmaringen to Wangen.
* Bundesstraße 33
''Bundesstraße'' (German for "federal highway"), abbreviated ''B'', is the denotation for German and Austrian national highways.
Germany
Germany's ''Bundesstraßen'' network has a total length of about 40,000 km.
German ''Bundesstraßen'' ...
, from Ravensburg to Meersburg.
* Bundesstraße 312, from Riedlingen to Memmingen.
* Bundesstraße 465, from Ehingen to Leutkirch im Allgäu.
* Bundesstraße 467
''Bundesstraße'' (German for "federal highway"), abbreviated ''B'', is the denotation for German and Austrian national highways.
Germany
Germany's ''Bundesstraßen'' network has a total length of about 40,000 km.
German ''Bundesstraßen ...
, from Ravensburg to Kressbronn
Kressbronn am Bodensee is a municipality and a village in the district of Bodensee in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It lies on Lake Constance.
Between 1919 and 2011, Kressbronn was the site of the Bodan-Werft shipyard, which built many of the ...
.
* Bundesautobahn 7
* Bundesautobahn 96
is a motorway in southern Germany, leading from the Austrian border ( A14) near Lindau ( Lake Constance) through Memmingen, Landsberg am Lech to Munich. Two European routes lead through the autobahn: E 43 and E 54.
It was first p ...
Airports
* Bodensee-Airport Friedrichshafen is serviced by several airlines and also caters for charter flights to popular holiday destinations. * Memmingen Airport is serviced by several airlines and also caters for charter flights to popular holiday destinations.See also
*Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
* Swabia region
* Upper Swabian Baroque Route
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Webpage of the Upper Swabian Tourist Office
German webpage of the Upper Swabian Baroque Route
German webpage of the Swabian Spa Route
German webpage of the German Half-Timbered Buildings Route
German webpage of the Upper Swabian Mill Route
{{Authority control Regions of Baden-Württemberg