Ulmus Laevis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Ulmus laevis'' Pall., variously known as the European white elm, fluttering elm, spreading elm, stately elm and, in the United States, the Russian elm, is a large
/ref> NB: The epithet 'white' elm commonly used by British foresters alluded to the ''timber'' of the Ulmus glabra, wych elm.Edlin, H. L. (1947). ''British Woodland Trees'', p.26. 3rd. edition. London: B. T. Batsford Ltd. The species was first identified, as ''Ulmus laevis'', by
/ref> The species differs from its closest relative, the
/ref>
File:Wych elm flower.jpg, ''U. laevis'' flowers; note long stems
File:Ulmus laevis flowers - Keila.jpg, Flowers and bud
File:Ulmus laevis samarae 1.jpg, Samarae, April; note ciliate margins
File:HW laevis leaf.jpg, ''Ulmus laevis'' leaf
File:U laevis leaf underside.jpg, Leaf underside; note undivided venation beyond lobe
File:Бял бряст - листа (есен).jpg, ''U. laevis'' autumn colour
File:Ulmus laevis bark Ada Ciganlija.jpg, Bark in early maturity
File:Ulmus laevis bark Eibergen.jpg, Bark at maturity (age 100)
File:Fladderiep te Heure bij Borculo.jpg, Bole of old tree
File:Ulmus laevis. Inverleith Park (opposite Inverleith Place), Edinburgh (1).jpg, Typical epicormic shoots and dense branching
File:Ulmus laevis, incipient buttressing.jpg, Incipient buttressing, 20-year-old tree
File:Ulmus laevis bole, Sutton Veny, UK.jpg, Bole of ancient tree, showing buttressing and epicormic brush
File:UlmusBrettwurzel.jpg, ''U. laevis'' buttresses
File:Ulmus laevis root structure.jpg, Surface root structure exposed by bank erosion
/ref> which he had never found on any other elm in Britain, an affliction confirmed many years later by Richard Hook Richens, Richens, who discovered the specimens of ''U. laevis'' grown at
Spanish trees were found to be
File:Ulmus laevis (haaksbergseweg eibergen) 080211a.jpg, ''U. laevis'' 'Helena' as street trees, Eibergen, Netherlands
File:Seattle - Roanoke Park Ulmis laevis 01.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Roanoke Park, Capitol Hill, Seattle, US (planted 1910)
File:Ulmen sachsenplatz dresden 2019-05-07 -5.jpg, Trimmed ''U. laevis'', Sachsenplatz, Dresden (2019)
File:Windblown laevis on chalk of Salisbury Plain, UK, 2km from Stonehenge.jpg, Windblown ''laevis'' on chalk, Salisbury Plain, UK
File:WP U. laevis on chalk.jpg, ''U. laevis'' slow growth on chalk, 4 m in 15 years
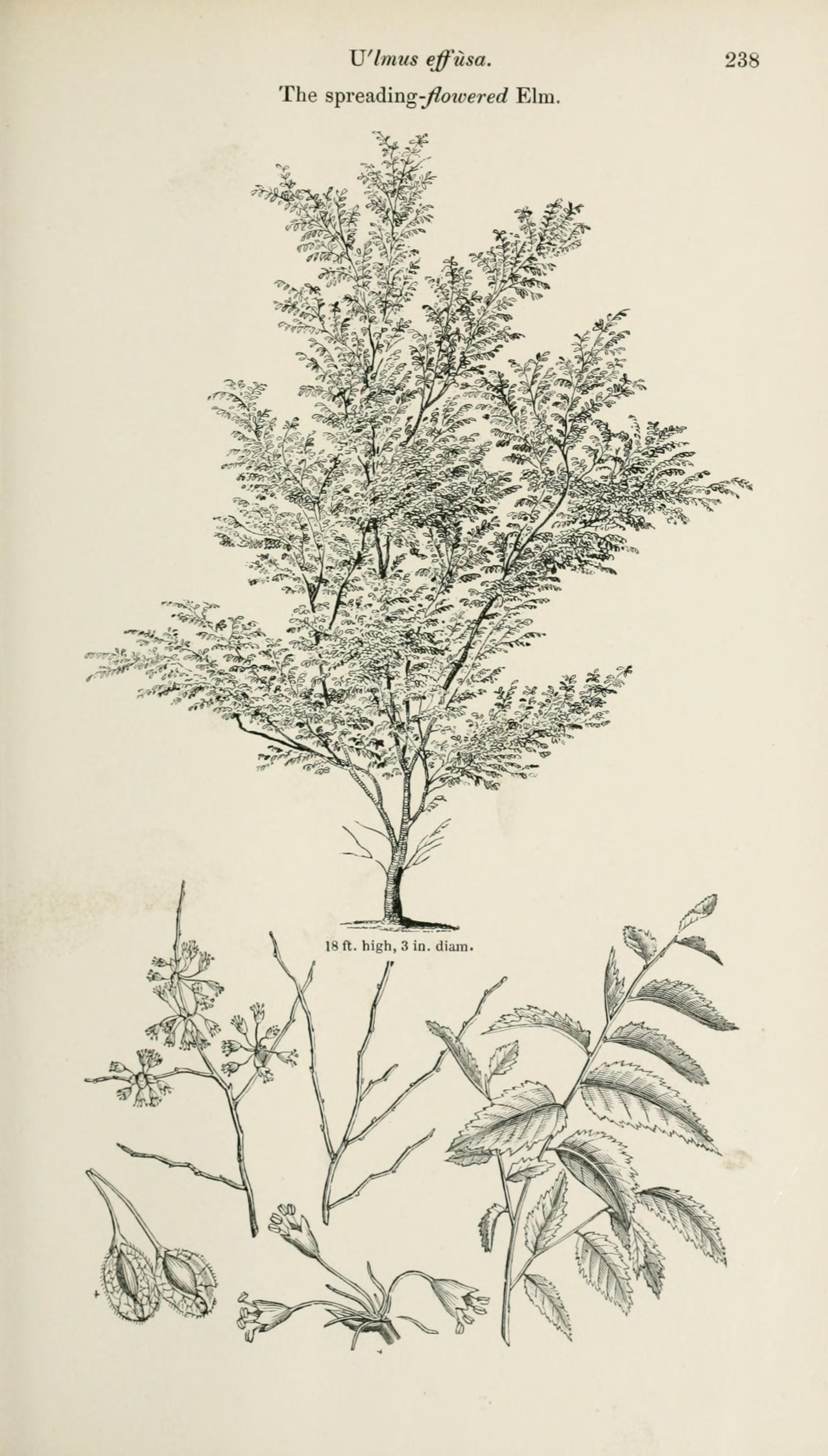 ''U. laevis'' is probably not native to the United Kingdom despite its random occurrence in the countryside, although the date and circumstances of its introduction have not survived. The earliest published references to the tree (as ''U. effusa'', citing
''U. laevis'' is probably not native to the United Kingdom despite its random occurrence in the countryside, although the date and circumstances of its introduction have not survived. The earliest published references to the tree (as ''U. effusa'', citing
''The Gardener's and Botanist's Dictionary''
Revised by Thomas Martyn, Regius Professor of Botany, University of Cambridge. The first specimen to be reported in cultivation, in 1838, was at
the tree measured in height, suggesting it had been planted at the end of the 18th century. However, the authenticity of the Whiteknights tree is a matter of contention; it flowered but did not set fertile seed, which suggested to Loudon that it might be ''U. campestris'' ( Ulmus minor 'Atinia', ''U. minor'' 'Atinia'), or, on account of it not producing suckers, possibly ''U. montana'' (: ''U. glabra''). Moreover, Whiteknights was supplied by the
/ref> It is possible the tree's distribution was associated with Capability Brown (1716–1783), known to have favoured ''U. laevis'', which he listed among his preferred "native" (sic) trees.Ignatieva, M. E. and Stewart, G. H. 'Homogeneity of urban biotopes and similarity of landscape design language in former colonial cities', in: McDonnell, M., Hahs, A., & Breuste, J. (eds.) (2009). ''Ecology of Cities and Towns: A comparative approach.'' Part III, 23, p. 409. Cambridge. This could explain the existence of the seven old specimens discovered by Elwes in 1908 on Mount Pleasant within Ugbrooke Park, Devon, designed by Brown in 1761.Stroud, D. (1950). ''Capability Brown''. New edition 1984, Faber & Faber, London. Ugbrooke is four miles from
''Beauties of England & Wales''
Vol. 4, Devon & Cornwall, Devonshire, p 99. Various publishers. Ball's introductions were known to have been marketed by his head gardener
/ref>
File:Ulmus laevis at Ugbrooke.jpg, ''U. laevis'',
File:Ulmus laevis JPG1b.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Casteau, Belgium
File:Bole of ancient Ulmus laevis in hedgerow near Over Wallop, England.jpg, Bole of coppiced ''U. laevis'', girth 410 cm, Over Wallop, UK
File:Бял бряст (стар).JPG, Burrs and epicormic shoots on old ''U. laevis''
File:Kopeci szil 2011.11.28..jpg, ''U. laevis'', Căpeni, Romania (2011)
Image:Ulmus laevis seedlings.jpg, ''U. laevis'' seedlings
Image:White Elm rooted cutting.jpg, A rooted cutting of European white elm
File:Barjols2013 007.jpg, Columnar form, Entraygues, France
* Lorenz von Ehren, Hamburg, Germany
* Noordplant, Glimmen, Netherlands * Pan-Global Plants, Frampton-on-Severn, Gloucestershire, UK * UmbraFlor, Spello, Italy *Van Den Berk (UK) Ltd.
London, UK
''Ulmus laevis''
- distribution map, genetic conservation units and related resources. European Forest Genetic Resources Programme (EUFORGEN) {{Authority control Ulmus, laevis Ornamental trees Trees of Europe Flora of France Flora of Finland Flora of Russia Flora of Ukraine Garden plants of Europe Ulmus articles with images Elm species and varieties Plants described in 1784
deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
native to Europe, from France northeast to southern Finland, east beyond the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
into Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan, and southeast to Bulgaria and the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
; there are also disjunct populations in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
and Spain, the latter now considered a relict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.
Biology
A relict (or relic) is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas.
Geology and geomorphology
In geology, a r ...
population rather than an introduction by man, and possibly the origin of the European population.Fuentes-Utrilla, P., Squirrell, J., Hollingsworth, P. M. & Gil, L. (2006). ''Ulmus laevis (Pallas) in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
. An introduced or relict tree species? New data from cpDNA
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nuc ...
analysis.'' Genetics Society, Ecological Genetics Group conference, University of Wales Aberystwyth 2006. ''U. laevis'' is rare in the UK, although its random distribution, together with the absence of any record of its introduction, has led at least one British authority to consider it native.Medhurst, J. (2013). ''Archive for the tree detail text Category'', p30/ref> NB: The epithet 'white' elm commonly used by British foresters alluded to the ''timber'' of the Ulmus glabra, wych elm.Edlin, H. L. (1947). ''British Woodland Trees'', p.26. 3rd. edition. London: B. T. Batsford Ltd. The species was first identified, as ''Ulmus laevis'', by
Pallas
Pallas may refer to:
Astronomy
* 2 Pallas asteroid
** Pallas family, a group of asteroids that includes 2 Pallas
* Pallas (crater), a crater on Earth's moon
Mythology
* Pallas (Giant), a son of Uranus and Gaia, killed and flayed by Athena
* Pa ...
, in his ''Flora Rossica'' published in 1784.Pallas, P. S. (1784). ''Flora Rossica''. i.75, t.48, f.F. The tree is allogamous and is most closely related to the American elm '' U. americana''.
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
to alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. All ...
forest, ''U. laevis'' is rarely encountered at elevations above 400 m.Girard, S. (2007). Dossier: L'orme: nouveaux espoirs? ''Forêt entreprise'' No. 175, Juillet 2007, Institut pour le developpement forestier, Paris. Most commonly found along rivers such as the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
, it is one of very few elms tolerant of prolonged waterlogged, anoxic
The term anoxia means a total depletion in the level of oxygen, an extreme form of hypoxia or "low oxygen". The terms anoxia and hypoxia are used in various contexts:
* Anoxic waters, sea water, fresh water or groundwater that are depleted of diss ...
ground conditions. The species is threatened by habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
and disturbance in some countries, notably Spain. Flood control schemes are particularly harmful, as seed dispersion is reliant on floods, while abstraction from aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
lowering ground water levels has compromised the development of the trees.
Although not possessed of an innate genetic resistance to Dutch elm disease, the species is rarely infected in western Europe.
Description
''Ulmus laevis'' is similar in stature to thewych elm
''Ulmus glabra'' Hudson, the wych elm or Scots elm, has the widest range of the European elm species, from Ireland eastwards to the Urals, and from the Arctic Circle south to the mountains of the Peloponnese and Sicily, where the species reaches i ...
, if rather less symmetric, with a looser, untidy, branch structure and less neatly rounded crown. The tree typically reaches a height and breadth of > 30 m, with a trunk < 2 m d.b.h. The extensive shallow root system ultimately forms distinctive high buttresses around the base of the trunk. The bark is smooth at first, then in early maturity breaks into thin grey scales, which separate with age into a network of grey-brown scales and reddish-brown underbark, and finally is deeply fissured in old age like other elms. The leaves are deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
, alternate, simple ovate
Ovate may refer to:
* Ovate (egg-shaped) leaves, tepals, or other botanical parts
*Ovate, a type of prehistoric stone hand axe
*Ovates, one of three ranks of membership in the Welsh Gorsedd
*Vates
In modern English, the nouns vates () and ova ...
with a markedly asymmetric base, < 10 cm long and < 7 cm broad, comparatively thin, often almost papery in texture and very translucent, smooth above with a downy underside. Significantly, the leaf veins do not divide from the central vein to the leaf margin. The leaves are shed earlier in autumn than other species of European elm.
The tree is most reliably distinguished from other European elms by its long flower stems, averaging 20 mm. Moreover, the apetalous
Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corolla''. Petals are usually ...
wind-pollinated flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechani ...
s are distinctively cream-coloured, appearing before the leaves in early spring in clusters of 15-30; they are 3–4 mm across. The fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
is a winged samara < 15 mm long by 10 mm broad with a ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a differen ...
margin, the single round 5 mm seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
maturing in late spring. The seeds have a generally high rate of germination, 45–60% for Serbian trees examined by Stilinović.Stilinović, S. (1985): ''Semenarstvo šumskog i ukrasnog drveća i žbunja''. Univerzitet u Beogradu - Šumarski fakultet, Beograd: 1-399/Seed science of forest and decorative trees and bushes, University of Belgrade– Faculty of Forestry, Belgrade: 1-399/
Although the species is protandrous
Sequential hermaphroditism (called dichogamy in botany) is a type of hermaphroditism that occurs in many fish, gastropods, and plants. Sequential hermaphroditism occurs when the individual changes its sex at some point in its life. In particular, ...
, levels of self-pollination can be high The tree can grow very rapidly; where planted in persistently moist soil, trunk width of 13-year-old trees increased by 4 cm per annum at breast height (d.b.h.).Brookes, A. H. (2020). ''Disease-resistant elm cultivars''. Butterfly Conservation, Lulworth
Lulworth is the popular name for an area on the coast of Dorset, South West England notable for its castle and cove. However, there is no actual place or feature called simply "Lulworth", the villages are East and West Lulworth and the coastal f ...
, England./ref> The species differs from its closest relative, the
American elm
''Ulmus americana'', generally known as the American elm or, less commonly, as the white elm or water elm, is a species of elm native to eastern North America, naturally occurring from Nova Scotia west to Alberta and Montana, and south to F ...
, mainly in the irregular crown structure and frequent epicormic shoots
An epicormic shoot is a shoot growing from an epicormic bud, which lies underneath the bark of a trunk, stem, or branch of a plant.
Epicormic buds lie dormant beneath the bark, their growth suppressed by hormones from active shoots higher up ...
, features which also give the tree a distinctive winter silhouette. Republished 2004 Cambridge University Press, Bean, W. J. (1981). ''Trees and shrubs hardy in Great Britain'', 7th edition. Murray, London. The American elm also has less acute leaf buds, longer petioles, narrower leaves, and a deeper apical notch in the samara which reaches the seed.Chater, A. O. (1996).'Ulmus laevis naturalized in Cards, VC46'. ''BSBI News 75'' p.63. Botanical Society of Britain & Ireland/ref>
Pests and diseases
Like other Europeanelm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the flowering plant genus ''Ulmus'' in the plant family Ulmaceae. They are distributed over most of the Northern Hemisphere, inhabiting the temperate and tropical-montane regions of North ...
s, natural populations of the European white elm have little innate resistance to Dutch elm disease
Dutch elm disease (DED) is caused by a member of the sac fungi (Ascomycota) affecting elm trees, and is spread by elm bark beetles. Although believed to be originally native to Asia, the disease was accidentally introduced into Americas, America ...
. In a study in France, losses to DED amounted to 28% over a 10 year period. However, research by Irstea
The Institut national de recherche en sciences et technologies pour l'environnement et l'agriculture (IRSTEA), formerly known as Cemagref, was a public research institute in France focusing on land management issues, such as water resources and agr ...
has isolated clones able to survive injection with the causal fungus, initially losing < 70% of their foliage, but regenerating strongly the following year.Solla et al. (2005). Screening European Elms for Resistance to Ophiostoma novo-ulmi. ''Forest Science'', 134–141. 51 (2) 2005. Society of American Foresters.
The tree is not favoured by the vector bark beetles, which colonize it only when there are no other elm alternatives available,Collin, E., Bilger, I., Eriksson, G., & Turok, J. (2000). The conservation of elm genetic resources in Europe. In Dunn, C. P. (Ed.) (2000). ''The elms: breeding, conservation & disease management''. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston. an uncommon situation in western Europe. Indeed, in a study of elm in Flanders, not one example of ''U. laevis'' was found to be afflicted by Dutch elm disease.Vander Mijnsbrugge, K., Vanden Broeck, A., & Van Slycken, J. (2005). A study of Ulmus laevis in Flanders (Northern Belgium). ''Belgian Journal of Botany'', Vol. 138, No. 2 (2005), 199–204. Royal Botanical Society of Belgium. Research in Spain has indicated that it is the presence of an antifeedant triterpene
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squa ...
, alnulin
Taraxasterol (anthesterin) is a triterpene derived from the mevalonate pathway and is found in dandelions.
Biosynthesis
The precursor for the biosynthesis of taraxasterol is squalene. In the first step of this formation squalene is cyclized wi ...
, at a concentration of 200 μg/g which renders the tree unattractive to the beetles. Ergo: the tree's decline in western Europe has been chiefly owing to woodland clearance in river valleys, and river management systems eliminating flooding, not disease. However, in 2020, it was noted by the Dutch forestry commission that many ''laevis'', but only in Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
, were succumbing to Dutch elm disease for reasons unclear.Calle, J., Calle, L., Kopinga, J., Meffert, J. (2020). Nu ook iepziekte in fladderiep. ('Now also elm disease in White Elm'). ''Natuur Bos Landschap'', 164–168, October 2020.
It was noted by Jouin at Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand ...
, and a century later by Mittempergher and Santini in Italy, that ''U. laevis'' had a very low susceptibility to the elm leaf beetle ''Xanthogaleruca luteola
''Xanthogaleruca luteola'', commonly known as the elm-leaf beetle, is a beetle species in the family Chrysomelidae that is native to Europe but invasive in other parts of the world.http://cisr.ucr.edu/elm_leaf_beetle.html - Center for Invasive Sp ...
''. Research in Germany has established that the tree is also eschewed by the Zig Zag sawfly ''Aproceros leucopoda
''Aproceros'' is a genus of insects in the family Argidae
Argidae is a large family of sawflies, containing some 800 species worldwide, primarily in tropical regions. The larvae are phytophagous, and commonly can be found feeding (and often p ...
''.
Elwes observed that trees planted at Ugbrooke in Devon were infested with ''Cacopsylla ulmi
''Cacopsylla ulmi'' is an insect of the Psyllidae family. It mainly feeds on Elm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the flowering plant genus ''Ulmus'' in the plant family Ulmaceae. They are distributed over most of th ...
'',Jerinić-Prodanović, D. (2006). A new jumping louse, Cacopsylla ulmi Förster (Homoptera, Psyllidae) on elm in Serbia. ''Acta entomologica serbica''. 2006, 11 (1/2): 11–18/ref> which he had never found on any other elm in Britain, an affliction confirmed many years later by Richard Hook Richens, Richens, who discovered the specimens of ''U. laevis'' grown at
Kew
Kew () is a district in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames. Its population at the 2011 census was 11,436. Kew is the location of the Royal Botanic Gardens ("Kew Gardens"), now a World Heritage Site, which includes Kew Palace. Kew is a ...
were the only elms in the Gardens afflicted by the louse, and the aphid ''Tinocallis platani
''Tinocallis platani'' is a species of aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The gr ...
''.Richens, R. H. (1983). ''Elm''. p.64. Cambridge University Press.
The species has a slight to moderate susceptibility to elm yellows
Elm yellows is a plant disease of elm trees that is spread by leafhoppers or by root grafts."Elm Yellows." Elmcare.Com. 19 Mar. 2008 . Elm yellows, also known as elm phloem necrosis, is very aggressive, with no known cure. Elm yellows occurs in th ...
.
Cultivation
''U. laevis'' is essentially a riparian tree, able to withstand over 100 days of continual flooding,Spohn, M. (2008). ''Trees of Britain & Europe'' (Black's Nature Guides), 256 p. A & C Black, although it is intolerant of saline conditionSpanish trees were found to be
calcifuge
A calcifuge is a plant that does not tolerate alkaline (basic) soil. The word is derived from the Latin 'to flee from chalk'. These plants are also described as ericaceous, as the prototypical calcifuge is the genus '' Erica'' (heaths). It is not ...
, preferring slightly acid, siliceous soils, and also drought-intolerant, their xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from ...
vessels prone to drought-stress cavitation.Venturas, M. ''et al.'' (2013). Ulmus laevis Pall. a native elm in the Iberian peninsula: a multidisciplinary approach. ''Abstracts. 3rd International Elm Conference 2013. The elm after 100 years of Dutch elm disease.'' Florence 2013. p.48. In England, the tree failed to prosper in chalk stream valleys, where the soil was predominantly black peat, named 'Adventurers' for the Adventurers' Land SSSI in Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
, owing to dehydration in summer. Trees planted in dry ground are notoriously short-lived.Pokorny, J. (1974). ''Colour Guide to Familiar Trees, Leaves, Bark and Fruit''. Octopus, Czechoslovakia.
''U. laevis'' is comparatively weak-wooded, much more so than field elm ''Ulmus minor
''Ulmus minor'' Mill., the field elm, is by far the most polymorphic of the European species, although its taxonomy remains a matter of contention. Its natural range is predominantly south European, extending to Asia Minor and Iran; its northern ...
'', and thus an inappropriate choice for exposed locations. In trials in southern England by Butterfly Conservation, young trees of <5 m height were badly damaged by wind gusts of 40 knots
A knot is a fastening in rope or interwoven lines.
Knot may also refer to:
Places
* Knot, Nancowry, a village in India
Archaeology
* Knot of Isis (tyet), symbol of welfare/life.
* Minoan snake goddess figurines#Sacral knot
Arts, entertainme ...
(75 km/h) in midsummer storms.
The species was never widely introduced to the United States, but is represented at several arboreta. ''Ulmus effusa'', supplied by the Späth nursery The Späth (often spelt ''Spaeth'') family created one of the world's most notable plant nurseries of the 19th and early 20th centuries. The nursery had been founded in 1720 by Christoph Späth but removed to the erstwhile district of Baumschulen ...
of Berlin, was planted at the Dominion Arboretum
The Dominion Arboretum (french: Arboretum du Dominion) is an arboretum part of the Central Experimental Farm of Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Originally begun in 1889, the Arboretum covers about of rolling land ...
, Ottawa, Canada, in 1896, as ''U. pedunculata''. In the Far East, the tree has been planted in Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
province and elsewhere in northern China; planting in Tongliao
Tongliao (; mn, ''Tüŋliyou qota'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Байшинт хот) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. The area is and as of the 2020 census, its population was 2,873,168 (3,139,153 ...
City is known to have been particularly successful. White elm is also known to have been introduced to Australia.Spencer, R., Hawker, J. and Lumley, P. (1991). ''Elms in Australia'', Royal Botanic Gardens, Melbourne, Australia.
Since the beginning of the 21st century, the tree has enjoyed a small renaissance in England. A popular larval host plant of the white-letter hairstreak
The white-letter hairstreak (''Satyrium w-album'') is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae.
Appearance and behaviour
A dark little butterfly that spends the majority of its life in the tree tops, feeding on honeydew (secretion), honeydew, making ...
''Satyrium w-album'' butterfly across Europe, the elm is now being planted by Butterfly Conservation and other groups to restore local populations decimated by the effects of Dutch elm disease on native or archaeophytic elms. The Cheshire Wildlife Trust
The Cheshire Wildlife Trust (CWT) is a wildlife trust covering the county of Cheshire and parts of the counties of Greater Manchester and Merseyside, England. The trust's chairman is Bill Stothart. It manages 43 nature reserves totalling over 470 ...
, for example, planted numerous white elms on its reserves in the former Vale Royal
A vale is a type of valley.
Vale may also refer to:
Places Georgia
* Vale, Georgia, a town in the Samtskhe-Javakheti region
Norway
* Våle, a historic municipality
Portugal
* Vale (Santa Maria da Feira), a former civil parish in the municipa ...
district of the county.
Introduction to the UK and Ireland
 ''U. laevis'' is probably not native to the United Kingdom despite its random occurrence in the countryside, although the date and circumstances of its introduction have not survived. The earliest published references to the tree (as ''U. effusa'', citing
''U. laevis'' is probably not native to the United Kingdom despite its random occurrence in the countryside, although the date and circumstances of its introduction have not survived. The earliest published references to the tree (as ''U. effusa'', citing Willdenow
Carl Ludwig Willdenow (22 August 1765 – 10 July 1812) was a German botanist, pharmacist, and plant taxonomist. He is considered one of the founders of phytogeography, the study of the geographic distribution of plants. Willdenow was al ...
) were in Sibthorp's ''Flora Oxoniensis'' (1794), and (as ''U. effusa'' Willd. but without description) in Miller's posthumously revised ''Gardener's and Botanist's Dictionary'' (1807).Miller, P. (1807)''The Gardener's and Botanist's Dictionary''
Revised by Thomas Martyn, Regius Professor of Botany, University of Cambridge. The first specimen to be reported in cultivation, in 1838, was at
Whiteknights Park
Whiteknights Park, or the Whiteknights Campus of the University of Reading, is the principal campus of that university. The park covers the area of the manor of Earley Whiteknights, also known as Earley St Nicholas and Earley Regis.
Whit ...
, Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of letters, symbols, etc., especially by sight or touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process involving such areas as word recognition, orthography (spelling ...
, which featured an elm grove;Hofland, Mrs. (1819). ''A descriptive account of the mansion and gardens of White-Knights: a seat of His Grace the Duke of Marlborough'' Private publication, Londothe tree measured in height, suggesting it had been planted at the end of the 18th century. However, the authenticity of the Whiteknights tree is a matter of contention; it flowered but did not set fertile seed, which suggested to Loudon that it might be ''U. campestris'' ( Ulmus minor 'Atinia', ''U. minor'' 'Atinia'), or, on account of it not producing suckers, possibly ''U. montana'' (: ''U. glabra''). Moreover, Whiteknights was supplied by the
Lee and Kennedy
Lee and Kennedy were two families of prominent Scottish nurserymen in partnership for three generations at the Vineyard Nursery in Hammersmith, west of London. Contains biographical entries concerning the Lees and Kennedys. "For many years," wrot ...
nursery of Hammersmith, which is not known to have stocked ''U. laevis''. A tree at Syon Park
Syon Park is the garden of Syon House, the London home of the Duke of Northumberland in Isleworth in the London Borough of Hounslow. It was landscaped by Capability Brown in the 18th century, and it is Grade I listed by English Heritage under ...
identified by Elwes & Henry as ''U. laevis'' was later considered by Bean as more closely resembling ''U. americana'' by dint of its symmetrical branch arching. The species was not reported from the wild until 1943, with the discovery of a tree in a Surrey hedgerow.''Online Atlas of the British & Irish Flora''/ref> It is possible the tree's distribution was associated with Capability Brown (1716–1783), known to have favoured ''U. laevis'', which he listed among his preferred "native" (sic) trees.Ignatieva, M. E. and Stewart, G. H. 'Homogeneity of urban biotopes and similarity of landscape design language in former colonial cities', in: McDonnell, M., Hahs, A., & Breuste, J. (eds.) (2009). ''Ecology of Cities and Towns: A comparative approach.'' Part III, 23, p. 409. Cambridge. This could explain the existence of the seven old specimens discovered by Elwes in 1908 on Mount Pleasant within Ugbrooke Park, Devon, designed by Brown in 1761.Stroud, D. (1950). ''Capability Brown''. New edition 1984, Faber & Faber, London. Ugbrooke is four miles from
Mamhead Park
Mamhead is a rural village and civil parish near Dawlish and Kenton in Devon, South West England, in the Teignbridge local authority area. Current community venues includMamhead Village Halland The Church of England parish church, dedicated t ...
, which had earlier been planted with numerous exotic trees, notably holm oak, collected by its owner, merchant Thomas Ball ( d. 1749) during his commercial travels in Europe.Britton, J. & Brayley, E. W. (1803)''Beauties of England & Wales''
Vol. 4, Devon & Cornwall, Devonshire, p 99. Various publishers. Ball's introductions were known to have been marketed by his head gardener
William Lucombe
William Lucombe (before 1720 – after 1785) was a horticulturalist and nurseryman, who discovered and gave his name to the natural hybrid Lucombe Oak ('' Quercus × hispanica'' 'Lucombeana'), a semi-deciduous oak tree.
The Lucombe nursery
William ...
, who in 1720 founded the first commercial nursery in the south-west at Exeter,Harvey, J. (1975). ''Early Nurserymen''. Phillimore, Chichester, UK. though an account of trees growing at Mamhead by Pince
Pince (; in older sources also ''Pinica'', hu, Pince) is a settlement southeast of Lendava in the Prekmurje region of Slovenia. It lies close to the extreme eastern point of Slovenia, right on the border with Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyaro ...
(grandson of Lucombe) in 1835 makes no mention of ''U. laevis'' nor of any other elms. None of Lucombe's early catalogues are known to survive, and thus the introduction of ''U. laevis'' through south Devon cannot be confirmed. However, the tree does not feature in any of the surviving arboreta accessions lists, or catalogues of the larger, nationally famous, nurseries of the day, and its earliest-known mention in commerce remains in the south-west, in the catalogue of the Ford & Please nursery (as ''U. pedunculata'') at Exeter circa 1836. James Main
James Main (29 May 1886 – 29 December 1909) was a Scottish footballer, who played for Hibernian and the Scotland national football team as a right back. Main suffered fatal internal injuries while playing in a match on Christmas Day 1909, an ...
mentions the tree as 'a native of Hungary' and in 1838 only to be met in 'ornamental plantations', but by 1846 was 'becoming available in (UK) nurseries'.
''U. laevis'', obtained from the Späth nursery The Späth (often spelt ''Spaeth'') family created one of the world's most notable plant nurseries of the 19th and early 20th centuries. The nursery had been founded in 1720 by Christoph Späth but removed to the erstwhile district of Baumschulen ...
of Berlin as ''U. effusa'', was planted in Kew Gardens
Kew Gardens is a botanic garden in southwest London that houses the "largest and most diverse botanical and mycological collections in the world". Founded in 1840, from the exotic garden at Kew Park, its living collections include some of the ...
(1895), in the Ryston Hall
Ryston Hall, Ryston, Norfolk, England is a 17th-century country house built by Sir Roger Pratt for himself. The house was constructed between 1669 and 1672 in the Carolean style. In the late 18th century, John Soane made alterations to the hous ...
arboretum, Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the No ...
(1914), and, re-propagated, in Cambridge University Botanic Garden
The Cambridge University Botanic Garden is a botanical garden located in Cambridge, England, associated with the university Department of Plant Sciences (formerly Botany School). It lies between Trumpington Road to the west, Bateman Street to ...
(1909). Evidently the tree did not gain in popularity, and was overlooked or ignored by most authors of popular guides to trees in Britain during the 20th century, notably Mabey in his ''Flora Britannica''.Books on trees in Britain in the 20th century: Trimble, L. J. F. (1946) ''Trees in Britain'', Macmillan, London. Step, E. (1904). ''Wayside And Woodland Trees. A Pocket Guide To The British Sylva''. Frederick Warne & Co., London. Gurney, R. (1958). ''Trees of Britain''. Faber & Faber, London. Mabey, R. (1998) ''Flora Britannica''. Chatto & Windus, London. The tree is also omitted from Keble-Martin's comprehensive ''Flora of Devon''.Keble-Martin, W., and Fraser, G. (1939). ''Flora of Devon''. Buncle, Arbroath.
It is not known whether ''U. laevis'' was introduced to Scotland before the early 20th century. Two of the three specimens supplied by the Späth nursery The Späth (often spelt ''Spaeth'') family created one of the world's most notable plant nurseries of the 19th and early 20th centuries. The nursery had been founded in 1720 by Christoph Späth but removed to the erstwhile district of Baumschulen ...
, Berlin, to the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh
The Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (RBGE) is a scientific centre for the study of plants, their diversity and conservation, as well as a popular tourist attraction. Founded in 1670 as a physic garden to grow medicinal plants, today it occupies ...
in 1902 as ''U. effusa'' may survive in Edinburgh, as it was the practice of the garden to distribute trees about the city; the third specimen was in the garden itself. Other examples can be found in the city, notably in Fettes College grounds opposite Inverleith Allotments, and at the entrance to North Merchiston Cemetery. In Wales, two mature trees with numerous seedlings occur in a small wood at Rhydyfelin
Rhydyfelin (, ''Mill Ford'') is a large village (originally known as Rhydfelen) and part of the community of Pontypridd Town, about two miles to its south east of Pontypridd, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf. It is on the eastern ban ...
near Aberystwyth, while another grows at Llandegfan
Llandegfan (; ; meaning ''The Church of St Tegfan'') is a village on the east of island of Anglesey in Wales. It is part of the community of Cwm Cadnant.Davies (2008) p.180 Population is around 1,580.
History and description
The original villag ...
, Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
. In Ireland, the tree is represented by a line of four at the Old Rectory, Kells Road, Ardee
Ardee (; , ) is a town and townland in County Louth, Ireland. It is located at the intersection of the N2, N52, and N33 roads. The town shows evidence of development from the thirteenth century onward but as a result of the continued deve ...
, County Louth (, girth , October 2009), and in the Channel Islands, by a clump near the well at La Seigneurie
La Seigneurie is the traditional residence of the Seigneur of Sark. The Seigneur is the head of Sark in the Channel Islands.
Michael Beaumont, 22nd Seigneur of Sark
Seigneur John Michael Beaumont (20 December 1927 – 3 July 2016) was ...
(Le Manoir), Sark
Sark (french: link=no, Sercq, ; Sercquiais: or ) is a part of the Channel Islands in the southwestern English Channel, off the coast of Normandy, France. It is a royal fief, which forms part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, with its own set of ...
.Watsonia (2001). p557/ref>
Ugbrooke
Ugbrooke House is a stately home in the parish of Chudleigh, Devon, England, situated in a valley between Exeter and Newton Abbot. The home of the Clifford family, the house and grounds are available for guided tours in summer and as an event ...
, Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
, 1908
File:Lewisham Dutch Elm.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Ladywell Fields, Lewisham
Lewisham () is an area of southeast London, England, south of Charing Cross. It is the principal area of the London Borough of Lewisham, and was within the historic county of Kent until 1889. It is identified in the London Plan as one of ...
, London, 2023, locally misidentified as a 'Klemmer' Dutch elmJohnson, O. (2011). ''Champion Trees of Britain & Ireland'', Kew Publishing, Kew, London. .
File:Lewisham elm 1.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Ladywell Fields, Lewisham, London, 2018
File:Hebden U. laevis 2.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Hebden, Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales is an upland area of the Pennines in the historic county of Yorkshire, England, most of it in the Yorkshire Dales National Park created in 1954.
The Dales comprise river valleys and the hills rising from the Vale of York w ...
File:Llandegfan Elm tree.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Llandegfan
Llandegfan (; ; meaning ''The Church of St Tegfan'') is a village on the east of island of Anglesey in Wales. It is part of the community of Cwm Cadnant.Davies (2008) p.180 Population is around 1,580.
History and description
The original villag ...
, Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
File:Sutton Veny elm 3.6.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Sutton Veny, Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
File:Sutton Veny elm 4.2.jpg, ''U. laevis'', Sutton Veny, Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
Notable trees
The two largest known trees in Europe are at Gülitz in Germany (3.1 m d.b.h.), and at Komorów inPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
(2.96 m d.b.h. in 2011), known as the Witcher. Other veterans survive at Casteau, Belgium (bole-girth 5.15 m), in Rahnsdorf near Berlin (bole-girth 4.5 m) and in Ritvala, Finland (bole-girth 4.49 m).
A lane of ''Ulmus laevis'' is found at Eibergen, Netherlands (see Gallery below), while a large, mature specimen is found within the Alhambra, Granada.
''Ulmus laevis'' has very occasionally been planted as an ornamental tree in the UK, and even more randomly in countryside hedgerows. The UK Champion is at Ferry Farm, on the banks of the River Tamar, Tamar at Harewood, Cornwall, Harewood, Cornwall (27 m high, 1.8 m d.b.h. in 1997). Other examples are few and far between though sometimes of considerable age, surviving amid diseased native elm in Cornwall at Torpoint, and Pencalenick (21 m high, diameter at breast height, d.b.h. 1.75 m),''Tree Register of the British Isles''. and near Over Wallop in Hampshire (16 m high, d.b.h. 1.3 m 2016)BSBI, (2016). ''BSBI records for north Hampshire, vc. 12''. Botanical Society of Britain & Ireland, Shirehampton, Bristol. The largest-known aggregation in England is the ring of 50 trees planted circa 1950 within a ring of Tilia × europaea, common lime around a former ammunition dump on the elevated chalk of Salisbury Plain at Hexagon Wood, Larkhill, about north of Stonehenge.
In the United States, a tree of 31.4 m (103 ft) in height (2015) grows at 3331 NE Hancock Street in Portland, Oregon; its age is not known.
Uses
The timber of the white elm is of poor quality, the cross-grain causing problems when machined, and thus of little practical use, not even as firewood. The density of the timber is significantly lower than that of other Europeanelm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the flowering plant genus ''Ulmus'' in the plant family Ulmaceae. They are distributed over most of the Northern Hemisphere, inhabiting the temperate and tropical-montane regions of North ...
s. However, owing to its rapid growth, tolerance of soil compaction, air pollution and de-icing salts, the tree has long been used for amenity planting in towns and along roadsides.
Propagation
''U. laevis'' is easily grown from seed sown on ordinary compost and kept well-watered. However, viability can vary greatly from year to year, while the seed is remarkably short-lived. Germination should occur within one week even without heat, the best seedlings attaining as much as half a metre in their first year.Harris, E. (2017). The European White Elm, Ulmus laevis Pall. ''Quarterly Journal of Forestry'', Vol. 111, No. 4, October 2017. p.261. Royal Forestry Society. Softwood cuttings taken in June is also a reliable method; the cuttings strike very quickly, well within a fortnight, rapidly producing a dense matrix of roots.Subspecies and varieties
Several putative varieties have been identified. A Ulmus laevis var. celtidea, var. ''celtidea'' from Ukraine was reported by Rogowicz in the middle of the 19th century, but no examples are known to survive. Another, Ulmus laevis var. parvifolia, var. ''parvifolia'', has been reported from Serbia.Jovanović, B. & Radulović, S. (1980). Ulmus laevis var. parvifolia. ''Glasn. Prir. Muz. u Beogradu''. (''Bulletin of the Natural History Museum, Belgrade''). 35 : 32, 38 (1980). Belgrade, Serbia. A third, Ulmus laevis var. simplicidens, var. ''simplicidens'', is very rare; the only example known to survive is at the National Botanic Garden of Latvia in Salaspils. Kew Gardens, Kew had a grafted var. ''glabra'' in the early 20th century (provenance unknown), a clone of which is present at Wakehurst Place.Cultivars
Compared with the other European species of elm, ''U. laevis'' has received scant horticultural attention, there being only eight recorded cultivars: In Russia other ornamental forms are recognized: f. ''argentovariegata'', f. ''rubra'', and f. ''tiliifolia''. A pyramidal form was reported in 1888 from the Fredericksfelde cemetery in Berlin by Bolle. A line of similar monopodial trees grows (2019) on the island in the Lot (river), Lot at Entraygues, France.Hybrids
''U. laevis'' does not hybridize naturally, in common with the American elm (''U. americana'') to which it is closely related. However, in experiments at the Arnold Arboretum, it was successfully crossed with Ulmus thomasii, ''U. thomasii'' and Ulmus pumila, ''U. pumila''; no such crosses have ever been released to commerce.Accessions
Europe
* Arboretum de La Petite Loiterie, Monthodon, France. No details available * Arboretum Freiburg-Günterstal, Germany, no details available * Brighton & Hove City Council, UK, NCCPG Elm Collection. Ten trees at Hove Recreation Ground, Hove. * Copenhagen University Botanic Garden, Denmark. No details available. * ELTE Botanic Garden, Budapest, Hungary. Acc. nos. 1998-0718, 1998-0719. * Grange Farm Arboretum, Sutton St. James, Spalding, Lincolnshire, Spalding, Lincolnshire, UK. Acc. no. 502. * Great Fontley '' Butterfly Conservation'' Elm Trials plantation, UK. Two planted 2003, grown from cuttings of specimen at RBG Wakehurst Place. * Hortus Botanicus Nationalis, Salaspils, Latvia. Acc. nos. 18136, 18140. * Linnaean Garden, Linnaean Gardens of Uppsala, Sweden. Acc. no. 1930-1014. *Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh
The Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (RBGE) is a scientific centre for the study of plants, their diversity and conservation, as well as a popular tourist attraction. Founded in 1670 as a physic garden to grow medicinal plants, today it occupies ...
, UK. Acc. no. 20070643, from seed wild collected in Val d'Allier, France.
* Royal Botanic Gardens Kew, UK. Acc. nos. 1969-17302, 1973-11712.
* Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Royal Botanic Gardens, Wakehurst Place, UK. Acc. no. 1973-21048.
* Sir Harold Hillier Gardens, Romsey, Hampshire. UK. Acc. no. 2016.0385
* Tallinn Botanic Garden, Estonia. No accession details available.
* Thenford House arboretum, Northamptonshire, UK. No details available.
* 'The Leys', University Parks, Oxford, UK. Acc. no. 02678.
* Westonbirt Arboretum, UK. Tetbury, Gloucestershire, Glos., UK. Acc. no. 1995/322
* Wijdemeren City Council, Netherlands. Elm Collection. Planted 1990 Tjalk, Loosdrecht; 2007 Hinderdam, Nederhorst den Berg; elm lane De Kwakel, Kortenhoef in 2009.
North America
* Arnold Arboretum, US. Acc. nos. 17910, 637-79, 6951, 753-80. * Brenton Arboretum, Dallas Center, Iowa, US. No details available. * Brooklyn Botanic Garden, New York City, US. Acc. no. X02589. *Dominion Arboretum
The Dominion Arboretum (french: Arboretum du Dominion) is an arboretum part of the Central Experimental Farm of Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Originally begun in 1889, the Arboretum covers about of rolling land ...
, Canada. No details available
* Longwood Gardens, US. Acc. nos. 1964-0568, 1964-1119.
* Morton Arboretum, Illinois, US. Acc. nos. 1302-27, 446-48, 492-64, 27-98.
Nurseries
* Arboretum Waasland, Nieuwkerken-Waas, Belgium * Boomkwekerij Oirschot, Oirschot, Netherlands * Landford Trees, Salisbury, U* Lorenz von Ehren, Hamburg, Germany
* Noordplant, Glimmen, Netherlands * Pan-Global Plants, Frampton-on-Severn, Gloucestershire, UK * UmbraFlor, Spello, Italy *Van Den Berk (UK) Ltd.
London, UK
References
External links
''Ulmus laevis''
- distribution map, genetic conservation units and related resources. European Forest Genetic Resources Programme (EUFORGEN) {{Authority control Ulmus, laevis Ornamental trees Trees of Europe Flora of France Flora of Finland Flora of Russia Flora of Ukraine Garden plants of Europe Ulmus articles with images Elm species and varieties Plants described in 1784