|
Alnulin
Taraxasterol (anthesterin) is a triterpene derived from the mevalonate pathway and is found in dandelions. Biosynthesis The precursor for the biosynthesis of taraxasterol is squalene. In the first step of this formation squalene is cyclized with molecular oxygen, FAD, and NADPH via the enzyme squalene epoxidase a flavoprotein to yield (2''S'')-2,3-oxidosqualene. In the second step if the oxidosqualene is folded in the chair conformation in the enzyme a cascade of cyclizations will occur that results in the formation of the dammarenyl cation. The dammarenyl cation is then subjected to an alkyl shift to create a six-membered ring and relieving ring strain to form the baccharenyl cation. This allows the baccharenyl double bond to attack the secondary positive charge and forms a pentacyclic ring system to yield the tertiary lupanyl cation. A Wagner-Meerwein 1,2-alykl shift will occur to form the hexacyclic ring system and the secondary oleanyl cation. This is followed by a Wagner- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triterpene
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids. Structures Triterpenes exist in a great variety of structures. Nearly 200 different skeletons have been identified. These skeletons may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. In general pentacyclic structures (5 rings) tend to dominate. Squalene is biosynthesized through the head-to-head condensation of two farnesyl pyrophosphate units. This coupling converts a pair of C15 components into a C30 product. Squalene serves as precursor for the formation of many triterpenoids, including bacterial hopanoids and eukaryotic sterols. Triterpenoids By definition triterpenoids are triterpenes that possess heteroatoms, usually oxygen. The terms ''triterpene'' and ''triterpenoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
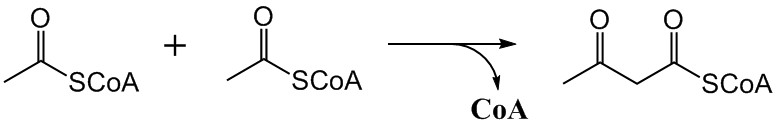
Mevalonate Pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dandelions
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and North America, but the two most commonplace species worldwide, '' T. officinale'' (the common dandelion) and '' T. erythrospermum'' (the red-seeded dandelion), were introduced from Europe into North America, where they now propagate as wildflowers. Both species are edible in their entirety. The common name ''dandelion'' ( , from French , meaning 'lion's tooth') is also given to specific members of the genus. Like other members of the family Asteraceae, they have very small flowers collected together into a composite flower head. Each single flower in a head is called a ''floret''. In part due to their abundance, along with being a generalist species, dandelions are one of the most vital early spring nectar sources for a wide host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). All plants and animals produce squalene as a biochemical intermediate to sterol biosynthesis. An estimated 12% of bodily squalene in humans is found in sebum. Squalene has a role in topical skin lubrication and protection. Squalene is a precursor for synthesis of all plant and animal sterols, including cholesterol and steroid hormones in the human body. Squalene is an important ingredient in some vaccine adjuvants: The Novartis and GlaxoSmithKline adjuvants are called MF59 and AS03, respectively. Role in steroid synthesis Squalene is the biochemical precursor to steroids. The squalene conversion begins with oxidation (via squalene monooxygenase) of one of its terminal double bonds, resulting in 2,3-oxidosqualene. It then undergoes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). It is used by all forms of cellular life. NADPH is the reduced form of NADP. NADP differs from NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate group. ADP-ribosyl cyclase allows for synthesis from nicotinamide in the salvage pathway, and NADP+ phosphatase can convert NADPH back to NADH to maintain a balance. Some forms of the NAD+ kina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squalene Epoxidase
Squalene monooxygenase (also called squalene epoxidase) is a eukaryotic enzyme that uses NADPH and diatomic oxygen to oxidize squalene to 2,3-oxidosqualene (squalene epoxide). Squalene epoxidase catalyzes the first oxygenation step in sterol biosynthesis and is thought to be one of the rate-limiting enzymes in this pathway. In humans, squalene epoxidase is encoded by the ''SQLE'' gene. Several eukaryote genomes lack a squalene monooxygenase encoding gene, but instead encode an alternative squalene epoxidase that performs the same task. Mechanism The canonical squalene monooxygenase is a flavoprotein monooxygenase. Flavoprotein monooxygenase form flavin hydroperoxides at the enzyme active site, which then transfer the terminal oxygen atom of the hydroperoxide to the substrate. Squalene monooxygenase differs from other flavin monooxygenases in that the oxygen is inserted into the substrate as an epoxide rather than as a hydroxyl group. This enzyme contains a loosely bound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavoprotein
Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin. Flavoproteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, and DNA repair. The flavoproteins are some of the most-studied families of enzymes. Flavoproteins have either FMN or FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) as a prosthetic group or as a cofactor. The flavin is generally tightly bound (as in adrenodoxin reductase, wherein the FAD is buried deeply). About 5-10% of flavoproteins have a covalently linked FAD. Based on the available structural data, FAD-binding sites can be divided into more than 200 different types. 90 flavoproteins are encoded in the human genome; about 84% require FAD, and around 16% require FMN, whereas 5 proteins require both. Flavoproteins are mainly located in the mitochondria. Of all flavoproteins, 90% perform redox reactions and the other 10% are transferases, lyases, isomerases, liga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E2 Reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. The numbers refer not to the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather to the kinetics of the reaction: E2 is bimolecular (second-order) while E1 is unimolecular (first-order). In cases where the molecule is able to stabilize an anion but possesses a poor leaving group, a third type of reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the Ei mechanism. E2 mechanism The E2 mechanism, where E2 stands for bimolecular elimination, involves a one-step mechanism in which ''carbon-hydrogen'' and ''carbon-halogen'' bonds break to form a double bond (''C=C Pi bond''). The specifics of the reaction are as follows: * E2 is a single step elimination, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triterpenes
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids. Structures Triterpenes exist in a great variety of structures. Nearly 200 different skeletons have been identified. These skeletons may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. In general pentacyclic structures (5 rings) tend to dominate. Squalene is biosynthesized through the head-to-head condensation of two farnesyl pyrophosphate units. This coupling converts a pair of C15 components into a C30 product. Squalene serves as precursor for the formation of many triterpenoids, including bacterial hopanoids and eukaryotic sterols. Triterpenoids By definition triterpenoids are triterpenes that possess heteroatoms, usually oxygen. The terms ''triterpene'' and ''triterpenoid'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |