Ulegyria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ulegyria is a 
 The physical features of ulegyria consist of small radial scars which occupy the cortical
The physical features of ulegyria consist of small radial scars which occupy the cortical
 Ulegyria develops as a result of a brain injury called
Ulegyria develops as a result of a brain injury called
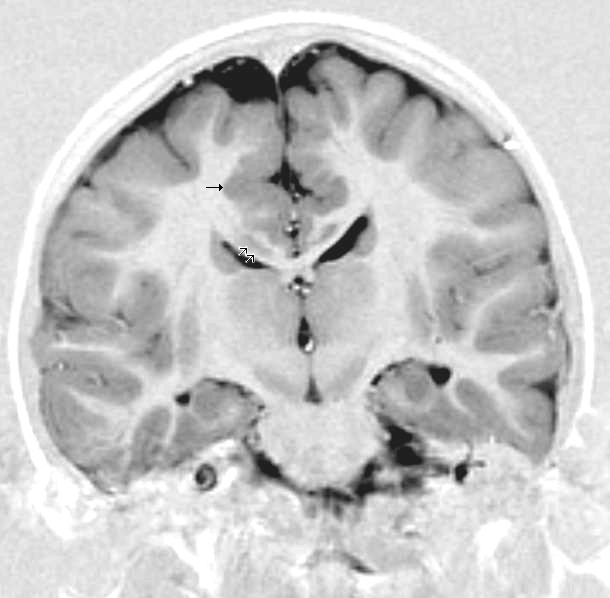 Ulegyria is often confused with a similar distortion of the
Ulegyria is often confused with a similar distortion of the
diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
used to describe a specific type of cortical scarring in the deep regions of the sulcus that leads to distortion of the gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ma ...
. Ulegyria is identified by its characteristic "mushroom-shaped" gyri, in which scarring causes shrinkage and atrophy in the deep sulcal regions while the surface gyri are spared. This condition is most often caused by hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the perinatal period
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal deve ...
. The effects of ulegyria can range in severity, although it is most commonly associated with cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensa ...
, mental retardation
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signific ...
and epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical ...
. N.C. Bresler was the first to view ulegyria in 1899 and described this abnormal morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
in the brain as “mushroom-gyri." Although ulegyria was first identified in 1899, there is still limited information known or reported about the condition.

Anatomy
 The physical features of ulegyria consist of small radial scars which occupy the cortical
The physical features of ulegyria consist of small radial scars which occupy the cortical sulci
Sulci or Sulki (in Greek , Steph. B., Ptol.; , Strabo; , Paus.), was one of the most considerable cities of ancient Sardinia, situated in the southwest corner of the island, on a small island, now called Isola di Sant'Antioco, which is, howev ...
. Overall, the physical structure of affected areas in the brain is described as a “mushroom”-like shape in which the gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ma ...
are unusually large and the sulci become wider deeper in the cortex. N.C. Bresler, the first person to view a brain with ulegyria in 1899, coined the phrase mushroom gyri. He also named the disorder, basing it off the Latin root ''ule'', meaning scar. This mushroom-like structure is the result of the lower parts of the ulegyria-affected area being more prone to deterioration, while the upper gyri are usually spared. However, the entire affected area shrinks and presents brown coloration as a result of ulegyria. In addition, “islands” of neurons that are relatively unaffected can exist between ulegyria affected neurons. Ulegyria can develop bilaterally or unilaterally, though the former is more commonly diagnosed.
Ulegyria can affect many parts of the brain including the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of ...
, parasagittal
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divid ...
areas and posterior regions of the brain, such as the parietal and occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
s. These areas are situated either near artery rich regions or near a major cerebral artery
The cerebral arteries describe three main pairs of arteries and their branches, which perfuse the cerebrum of the brain.
The three main arteries are the:
* ''Anterior cerebral artery'' (ACA)
* ''Middle cerebral artery'' (MCA)
* ''Posterior cereb ...
. For instance, specifically in neonatal
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
children, ulegyria-affected areas are found near the posterior cerebral artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifur ...
or near the artery rich region between the middle and posterior regions of the brain, often referred to as watershed regions.
Neurons affected by ulegyria exhibit properties that differ from normally functioning neurons. For instance, ulegyria affected neurons experience gliosis
Gliosis is a nonspecific reactive change of glial cells in response to damage to the central nervous system (CNS). In most cases, gliosis involves the proliferation or hypertrophy of several different types of glial cells, including astrocytes, ...
in which glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form mye ...
, specifically astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
, build up near and around neurons. Ulegyria affected neurons also display decreases in their white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution ...
content, showing signs of sclerosis, which is characterized by the deterioration of myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
in neurons. However, in regions of grey matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distingui ...
, large dense aggregates of myelin are present. Ulegyria affected neurons also display metabolic disorders which could be linked to the disease phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also resu ...
and disruptions in the urea cycle
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). Animals that use this cycle, mainly amphibians and mammals, are called ureotelic.
The urea cycle converts highl ...
. Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
and hypoxia
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of the specific environment
* Hypoxia (medical), abnormally low level of oxygen in the tis ...
are also thought to accompany the symptoms of ulegyria-affected neurons as well.
Causes
 Ulegyria develops as a result of a brain injury called
Ulegyria develops as a result of a brain injury called cerebral ischemia
Brain ischemia is a condition in which there is insufficient bloodflow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia and thus leads to the death of brain tissue or cerebral infarction/ischemic stroke. ...
surrounding the time of an infant's birth. Oftentimes, fetal hypoxic-ischemic brain injuries occur as a result of a pregnancy complications such as placental abruption, cord accident, or cardiovascular stress due to a difficult delivery. A lack of oxygen to the brain contributes to the formation of lesions
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
usually near the three main cerebral arteries
The cerebral arteries describe three main pairs of arteries and their branches, which perfuse the cerebrum of the brain.
The three main arteries are the:
* ''Anterior cerebral artery'' (ACA)
* ''Middle cerebral artery'' (MCA)
* ''Posterior cereb ...
, located near the parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integrates sensory informa ...
and occipital lobes
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the v ...
of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
. The cause of perinatal brain injuries includes:
:1. cerebral ischemia
Brain ischemia is a condition in which there is insufficient bloodflow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia and thus leads to the death of brain tissue or cerebral infarction/ischemic stroke. ...
:2. cerebral hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as cerebral bleed, intraparenchymal bleed, and hemorrhagic stroke, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain, into its ventricles, or into both. It is one kind of bleed ...
:3. ascending intrauterine infections
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It ...
.
Some risk factors for perinatal brain injuries include: low birth weight, preterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 we ...
, poor perinatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
cardiorespiratory fitness
Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) refers to the ability of the circulatory and respiratory systems to supply oxygen to skeletal muscles during sustained physical activity. Scientists and researchers use CRF to assess the functional capacity of the re ...
, and artificial ventilation
Artificial ventilation (also called artificial respiration) is a means of assisting or stimulating respiration, a metabolic process referring to the overall exchange of gases in the body by pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, and interna ...
.
Cerebral ischemia
Cerebral ischemia occurs when the brain is not receiving adequate oxygen to continue normal functions. When this occurs, the body makes restoring oxygenated blood flow to life-sustaining organs a priority. The brain alters the diameter of major blood vessels to redistribute blood to key organs such as the brain,heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
, and adrenal glands
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
. If sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of th ...
activation does not produce any improvement, oxygen levels will continue to fall and disruptions to metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, other cellular processes, and overall functioning will ensue.
Another serious result of inefficient blood flow is that cells do not receive adequate amounts of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
. An immediate effect of low intracellular glucose is reduced ATP production in the cell. This effectively inactivates the Na-K pump, leading to the uptake of calcium ions by the cell. Continued influx of calcium serves to constitutively activate downstream effectors, including lipases
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
, proteases
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the for ...
, and endonucleases
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonucleases ...
, whose actions eventually destroy the cell skeleton. Intracellular calcium concentrations are increased further due to the opening of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
-regulated ion channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
. Ischemia causes anoxic
The term anoxia means a total depletion in the level of oxygen, an extreme form of hypoxia or "low oxygen". The terms anoxia and hypoxia are used in various contexts:
* Anoxic waters, sea water, fresh water or groundwater that are depleted of diss ...
cell depolarizations and it is this increase in membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges ...
at the presynaptic cell
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in neuromuscular junction, muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form biological neural ...
that triggers the release of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
, an excitatory neurotransmitter.
Glucose deprivation in the brain for any amount of time has the potential to pose serious consequences, and the amount of time the brain spends under these anoxic conditions is directly related to accumulation of irreversible damage to protein biosynthesis pathways. Protein synthesis all over the body is severely inhibited and essentially comes to a standstill while the brain is suffering from acute oxygen deprivation
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can i ...
. Once oxygen sufficiently saturates the tissues again, protein biosynthesis returns to normal in non-vulnerable areas but remains at below normal levels in other areas. Insufficient protein synthesis in the brain is especially troubling in the fetal brain given the amount of growth and development that normally occurs. Areas particularly vulnerable to the damaging effects of hypoxic episodes include: the superior brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
, the cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
, white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution ...
and subcortical structures supplied by the branches of deep and superficial penetrating blood vessels. Vulnerable areas where protein synthesis is interrupted usually indicate impending cell death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as dis ...
in neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
. When oxygen levels return, oxygen radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron.
With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spont ...
, nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its che ...
and an imbalance of neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neur ...
cause further damage and lead to cellular death through apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
. Neuron cell death is responsible for gliosis
Gliosis is a nonspecific reactive change of glial cells in response to damage to the central nervous system (CNS). In most cases, gliosis involves the proliferation or hypertrophy of several different types of glial cells, including astrocytes, ...
and results in the mushroom appearance of areas and is characteristic of ulegyria.
Cerebral hemorrhage
Acerebral hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as cerebral bleed, intraparenchymal bleed, and hemorrhagic stroke, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain, into its ventricles, or into both. It is one kind of bleed ...
is the result of immature blood vessels of a brain lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
bursting. The germinal matrix In anatomy, the germinal matrix is a highly cellular and highly vascularized region in the brain out from which cells migrate during brain development. The germinal matrix is the source of both neurons and glial cells and is most active between 8 an ...
is a part of the brain that normally disappears as the fetal brain develops but during this process it is not unusual for changes in vessel volume to cause a vessel to burst. According to recent microscopic studies, the most common location for a cerebral hemorrhage is where the medullary veins drain to the terminal vein in the sub- ependymal region. It has been hypothesized that because pre-term babies don't have fully developed sympathetic nervous systems, they cannot react as well to low oxygen saturation levels caused by the cerebral hemorrhage. Although babies born at full-term are still susceptible to this, they are likely to respond better and thus, tend to have better outcomes in response to low-oxygen events.
Ascending intrauterine infections
Recent research has found a connection betweenintrauterine infections
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It ...
and inflammation in the mother and an increased likelihood of perinatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
brain damage in the fetus. This study suggested that intrauterine infections in the mother could affect glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form mye ...
and toll-like receptors
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize st ...
(TLRs) which are important in moderating the inflammatory response in the fetal brain. When glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form mye ...
and TLRs are negatively affected they are not able to react to developing inflammation in the brain as well. The connection between ascending intrauterine infections and perinatal brain damage is a developing research theory but a more detailed explanation of the connection is not yet known.
Signs and symptoms
Ulegyria was found in about 1/3 of patients with defects caused by circulatory disease in theperinatal period
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal deve ...
. Most clinical observations of the condition report mental retardation, cerebral palsy, and seizures as the main defects. However, milder cases have been reported in which patients that exhibit ulegyria develop relatively normally. The main movement disorders associated with ulegyria that are classified as cerebral palsy are choreoathetosis
Choreoathetosis is the occurrence of involuntary movements in a combination of chorea (irregular migrating contractions) and athetosis (twisting and writhing).
It is caused by many different diseases and agents. It is a symptom of several diseases ...
, dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological hyperkinetic movement disorder in which sustained or repetitive muscle contractions result in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed postures. The movements may resemble a tremor. Dystonia is often inten ...
, and ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
. It is suspected that ulegyria leads to epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical ...
because malformation of the cortex obstructs the differentiation of neurons, glial cells, and synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
. Parietal-occipital
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cereb ...
lobe epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical ...
, which is often synonymous with posterior cortex Posterior cortex usually means the posterior (back) part of the complete cerebral cortex and includes the occipital, parietal, and temporal cortices. In other words, the posterior cortex includes all the cerebral cortex without the frontal cortex. ...
epilepsy (PCE), is the form of the disease seen in most cases involving ulegyria. This type of epilepsy is very rare, making up about 5% of all reports of epilepsy. This form of the disease involves symptoms that would be expected from damage to the parietal and occipital lobes: seizures with visual hallucinations, visuospatial dysfunction, tingling, numbness, pain, and a burning sensation. In addition to ulegyria, tumors and cortical dysplasia
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is a congenital abnormality of brain development where the neurons in an area of the brain failed to migrate in the proper formation in utero. ''Focal'' means that it is limited to a focal zone in any lobe. Focal co ...
constitute the major causes of PCE. Most of the epilepsy seen in conjunction with ulegyria is classified as medically refractory, meaning it is not responsive to treatment. Patients usually present symptoms of epilepsy at an early age. The severity of epilepsy has been shown to depend on this age of onset as well as the quantity of cortical lesions; earlier onset of epilepsy and a larger extent of lesions tends to mean more severe seizures.
Similar conditions
cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
known as polymicrogyria
Polymicrogyria (PMG) is a condition that affects the development of the human brain by multiple small gyri ( microgyri) creating excessive folding of the brain leading to an abnormally thick cortex. This abnormality can affect either one region of ...
. Polymicrogyria is characterized by excessive folding of the surface gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ma ...
and a thickening of the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of ...
, rather than the sulcal scarring that is typical of ulegyria. In addition to morphological differences, the period in which polmicrogyria and ulegyria emerge is also different. Polymicrogyria typically forms while the embryo's central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
is maturing. Ulegyria is acquired later in development during the perinatal period
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal deve ...
after neuronal migration
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The fiel ...
has already occurred. It is also suspected that polymicrogyra is genetically linked, whereas ulegyria is caused by environmental factors—namely lack of oxygen.
Polymicrogyria can lead to similar conditions that are linked to ulegyria such as mental retardation
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signific ...
, cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensa ...
, and epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical ...
. It has been observed that patients with polymicrogyria are not receptive to epilepsy surgery
Epilepsy surgery involves a neurosurgery, neurosurgical procedure where an area of the brain involved in seizures is either resected, ablative brain surgery, ablated, disconnected or stimulated. The goal is to eliminate seizures or significantly ...
. However, responses of patients with ulegyria to similar surgeries are still not fully known, which makes distinction of these two disorders significant. In vivo neuroimaging techniques, namely MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
, have been instrumental in making this distinction. An MRI image of ulegyria is identified by mushroom shaped gyri, deformities in white matter, and localization mainly in the posterior cerebral region. Polymicrogyria is typically recognized by a scalloped appearance at the bordering region between grey and white matter. Although these distinctions have been made with many patients, there is still some difficulty in defining distinct boundaries between these two similar conditions.
Detection
Primarily, the main method of detecting ulegyria is through the use ofMRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
screening for epilepsy. Normally an MRI of an ulegyria affected region will reveal groups of deteriorated neurons with gliosis present. In addition, unaffected gyri are also present in especially bilateral watershed regions indicating delayed effects of perinatal hypoxic damage. However, there are three main criteria for diagnosing ulegyria using MRI in addition to the features mentioned above:
:1.The presence of a poorly demarcated lesion
:2. Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply t ...
and thinning of the cortex resulting in the characteristic “mushroom” like shape of ulegyria.
:3. Presence of white matter signal abnormalities as a result of FLAIR signaling (fluid attenuated inversion recovery).
Another sign of ulegyria that is visible on an MRI scan is the presence of a widened subarachnoid space
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in th ...
, signifying cortex atrophy. FLAIR signaling can help visualize the depths of the parietal-occipital sulci, which also allows ulegyria-affected gyri to be identified. Though there is still confusion in differentiating ulegyria and polymicrogyria in patients, MRI allows for the proper identification in the majority of the cases. In addition, most of the current research regarding ulegyria is focused on improving this identification. Furthermore, MRI can diagnose whether ulegyria presence is unilateral or bilateral. Electroencephalography, EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
, can also be used to screen for ulegyria, though MRI is still preferred. This is mainly done for epilepsy patients as abnormalities in EEG recordings indicate the presence of ulegyria in the area of the brain being tested. For example, when EEG tests in epileptic patients show deviations in the frontal and central-parietal regions, ulegyria can be considered to be present in that area.
Treatment
Presently, there is no well-defined treatment for ulegyria mainly because of the irreversibleischaemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
damage done to neurons of an affected area. However, conditions associated with ulegyria, such as epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical ...
and cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensa ...
, can be treated using the appropriate treatment. For instance, seizures caused by epilepsy, due to the presence of ulegyria in the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
, can be controlled using antiepileptic
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
drugs in some patients. In other patients, such as those who suffer from ulegyria in the posterior cortex Posterior cortex usually means the posterior (back) part of the complete cerebral cortex and includes the occipital, parietal, and temporal cortices. In other words, the posterior cortex includes all the cerebral cortex without the frontal cortex. ...
, drugs are not effective and surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
of the area causing epilepsy is needed. These treatments treat only the conditions but have no effect on the condition of ulegyria itself.
References
{{Reflist, colwidth=35em Cerebrum Neuropathology