|
Parasagittal
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts ( mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal). The term ''sagittal'' was coined by Gerard of Cremona. Variations in terminology Examples of sagittal planes include: * The terms ''median plane'' or ''mid-sagittal plane'' are sometimes used to describe the sagittal plane running through the midline. This plane cuts the body into halves (assuming bilateral symmetry), passing through midline structures such as the navel and spine. It is one of the planes which, combined with the Umbilical plane, defines the four quadrants of the human abdomen. * The term ''parasagittal'' is used to describe any plane parallel or adjacent to a given sagittal plane. Specific named parasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal Plane
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts ( mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal). The term ''sagittal'' was coined by Gerard of Cremona. Variations in terminology Examples of sagittal planes include: * The terms ''median plane'' or ''mid-sagittal plane'' are sometimes used to describe the sagittal plane running through the midline. This plane cuts the body into halves (assuming bilateral symmetry), passing through midline structures such as the navel and spine. It is one of the planes which, combined with the Umbilical plane, defines the four quadrants of the human abdomen. * The term ''parasagittal'' is used to describe any plane parallel or adjacent to a given sagittal plane. Specific named parasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human and animal anatomy, three principal planes are used: * The sagittal plane or lateral plane (''longitudinal, anteroposterior'') is a plane parallel to the sagittal suture. It divides the body into left and right. * The coronal plane or frontal plane (''vertical'') divides the body into dorsal and ventral (back and front, or posterior and anterior) portions. * The transverse plane or axial plane (''horizontal'') divides the body into cranial and caudal (head and tail) portions. Terminology There could be any number of sagittal planes; however, there is only one cardinal sagittal plane. The term ''cardinal'' refers to the one plane that divides the body into equal segments, with exactly one half of the body on either side of the cardinal plane. The term ''cardinal plane'' appears in some texts as the ''principal plane''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Plane
The transumbilical plane or umbilical plane, one of the transverse planes in human anatomy, is a horizontal line that passes through the abdomen at the level of the navel (or umbilicus). In physical examination, clinicians use the transumbilical plane and its intersection with the median plane The median plane also called a mid-sagittal plane is used to describe the sagittal plane as it bisects the body vertically through the midline marked by the navel, dividing the body exactly in left and right side. The term parasagittal plane is u ... to divide the abdomen into four quadrants.Regions of the abdomen. Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/regions-of-the-abdomen. Accessed 30 January 2021. Animal anatomy {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Plane
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a longitudinal plane. For a human, the mid-coronal plane would transect a standing body into two halves (front and back, or anterior and posterior) in an imaginary line that cuts through both shoulders. The description of the coronal plane applies to most animals as well as humans even though humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in the vertical orientation. The sternal plane (''planum sternale'') is a coronal plane which transects the front of the sternum. Etymology The term is derived from Latin ''corona'' ('garland, crown'), from Ancient Greek κορώνη (''korōnē'', 'garland, wreath'). The coronal plane is so-called because it lies in the direction of Coronal suture. Additional images File:Coronal plane CT scan of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Plane
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a longitudinal plane. For a human, the mid-coronal plane would transect a standing body into two halves (front and back, or anterior and posterior) in an imaginary line that cuts through both shoulders. The description of the coronal plane applies to most animals as well as humans even though humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in the vertical orientation. The sternal plane (''planum sternale'') is a coronal plane which transects the front of the sternum. Etymology The term is derived from Latin ''corona'' ('garland, crown'), from Ancient Greek κορώνη (''korōnē'', 'garland, wreath'). The coronal plane is so-called because it lies in the direction of Coronal suture. Additional images File:Coronal plane CT scan of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-sagittal Plane
The median plane also called a mid-sagittal plane is used to describe the sagittal plane as it bisects the body vertically through the midline marked by the navel, dividing the body exactly in left and right side. The term parasagittal plane is used to refer to any plane parallel to the sagittal and median plane. It is one of the lines used to define the right upper quadrant of the human abdomen. The midsternal line can be interpreted as a segment of the median plane. File:Sagittal brain MRI.jpg, Median plane magnetic resonance imaging of the head. File:Median plane CT scan of a pregnancy of 37 weeks of gestational age.jpg, Median plane CT scan of a pregnant woman. The fetus (exposed in the coronal plane) is 37 weeks of gestational age In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Plane
The median plane also called a mid-sagittal plane is used to describe the sagittal plane as it bisects the body vertically through the midline marked by the navel, dividing the body exactly in left and right side. The term parasagittal plane is used to refer to any plane parallel to the sagittal and median plane. It is one of the lines used to define the right upper quadrant of the human abdomen. The midsternal line can be interpreted as a segment of the median plane. File:Sagittal brain MRI.jpg, Median plane magnetic resonance imaging of the head. File:Median plane CT scan of a pregnancy of 37 weeks of gestational age.jpg, Median plane CT scan of a pregnant woman. The fetus (exposed in the coronal plane) is 37 weeks of gestational age In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambdoidal Suture
The lambdoid suture (or lambdoidal suture) is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture. Structure The lambdoid suture is between the paired parietal bones and the occipital bone of the skull. It runs from the asterion on each side. Nerve supply The lambdoid suture may be supplied by a branch of the supraorbital nerve, a branch of the frontal branch of the trigeminal nerve. Clinical significance At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. If certain bones of the skull grow too fast, then craniosynostosis (premature closure of the sutures) may occur. This can result in skull deformities. If the lambdoid suture closes too soon on one side, the skull will appear twisted and asymmetrical, a condition called "plagiocephaly". Plagiocephaly refers to the shape and not the condition. The condition is craniosynostosis. The lambdoid sutu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
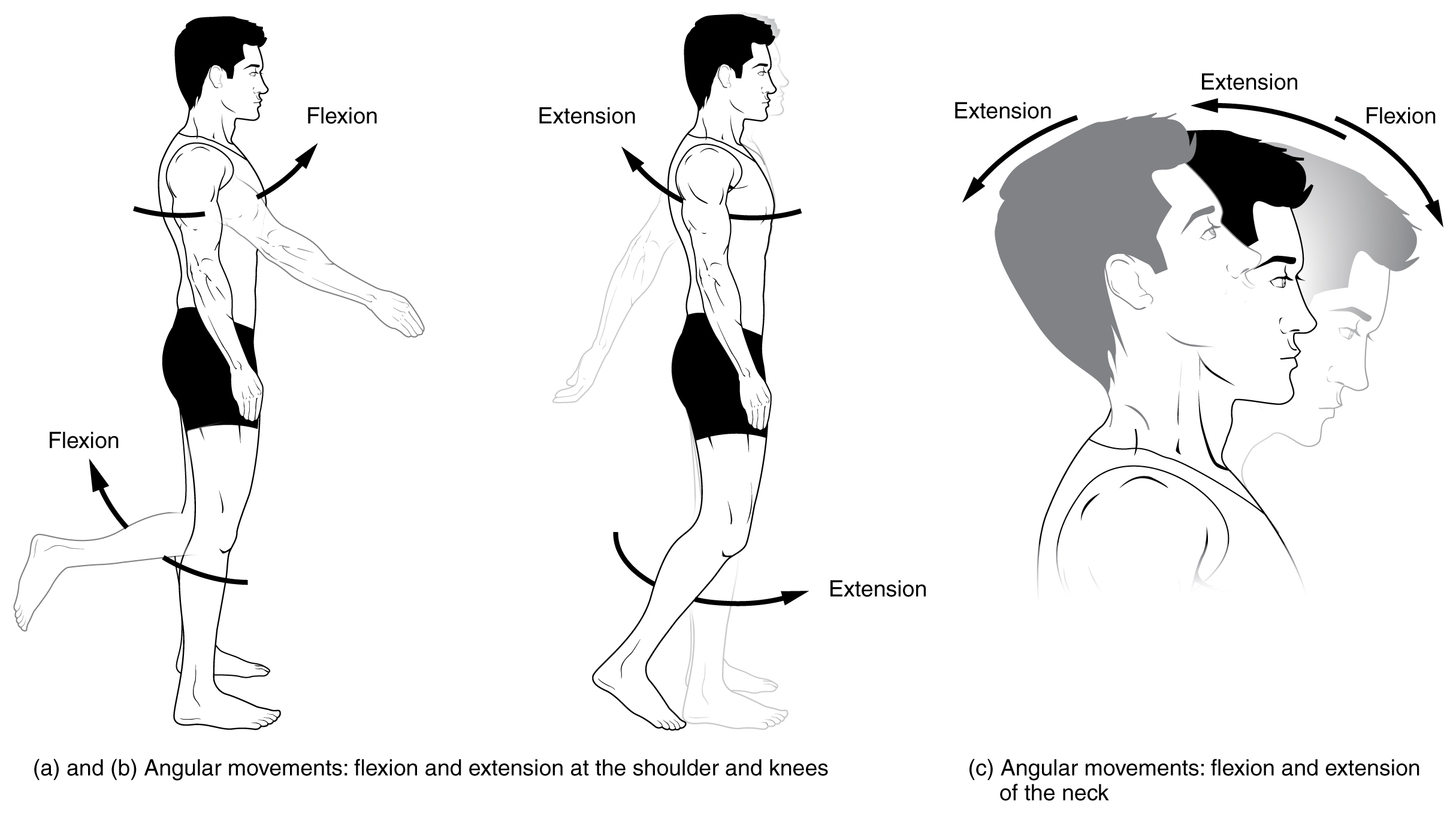
Extension (kinesiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abduction (kinesiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |