The United States dollar (
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
:
$;
code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communication ...
: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from
other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official
currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general def ...
of the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and
several other countries. The
Coinage Act of 1792
The Coinage Act of 1792 (also known as the Mint Act; officially: ''An act establishing a mint, and regulating the Coins of the United States''), passed by the United States Congress on April 2, 1792, created the United States dollar as the countr ...
introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the
Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100
cents, and authorized the minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of
Federal Reserve Note
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
s, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color.
The
monetary policy of the United States
Monetary policy of The United States concerns those policies related to the minting & printing of money, policies governing the legal exchange of currency, demand deposits, the money supply, etc. In the United States, the central bank, The Fed ...
is conducted by the
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
, which acts as the nation's
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ba ...
.
The U.S. dollar was originally defined under a
bimetallic standard
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange betwee ...
of (0.7735 troy ounces) fine silver or, from 1837, fine gold, or $20.67 per
troy ounce
Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight (24 grains), the troy ounce (20 pennyweights), and the ...
. The
Gold Standard Act
The Gold Standard Act was an Law_of_the_United_States#Federal_law, Act of the United States Congress, signed by President William McKinley and effective on March 14, 1900, defining the United States dollar by gold weight and requiring the United ...
of 1900 linked the dollar solely to gold. From 1934, its equivalence to gold was revised to $35 per
troy ounce
Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight (24 grains), the troy ounce (20 pennyweights), and the ...
. Since 1971, all links to gold have been repealed.
The U.S. dollar became an important international
reserve currency
A reserve currency (or anchor currency) is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international tran ...
after the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and displaced the
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
as the world's primary reserve currency by the
Bretton Woods Agreement
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
towards the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The dollar is the
most widely used currency in
international transactions, and a
free-floating currency. It is also the
official currency in several countries and the
''de facto'' currency in many others, with
Federal Reserve Notes
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
(and, in a few cases, U.S. coins) used in circulation.
As of February 10, 2021, currency in circulation amounted to , of which is in Federal Reserve Notes (the remaining is in the form of
coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
and older-style
United States Note
A United States Note, also known as a Legal Tender Note, is a type of paper money that was issued from 1862 to 1971 in the U.S. Having been current for 109 years, they were issued for longer than any other form of U.S. paper money. They were k ...
s).
Overview
In the Constitution
Article I,
Section 8 of the
U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
provides that
Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
has the power "
coin money." Laws implementing this power are currently codified in
Title 31 of the
U.S. Code
In the law of the United States, the Code of Laws of the United States of America (variously abbreviated to Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, U.S.C., or USC) is the official compilation and codification of the ...
, under Section 5112, which prescribes the forms in which the United States dollars should be issued.
[''Denominations, specifications, and design of coins''. .] These coins are both designated in the section as "
legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which when offered ("tendered") in pa ...
" in payment of debts.
The
Sacagawea dollar
The Sacagawea dollar (also known as the "golden dollar") is a United States dollar coin introduced in 2000, although not minted for general circulation between 2002 to 2008 and again from 2012 onward because of its general unpopularity with th ...
is one example of the
copper alloy
Copper alloys are metal alloys that have copper as their principal component. They have high resistance against corrosion. The best known traditional types are bronze, where tin is a significant addition, and brass, using zinc instead. Both of t ...
dollar, in contrast to the
American Silver Eagle
The American Silver Eagle is the official silver bullion coin of the United States.
It was first released by the United States Mint on November 24, 1986. It is struck only in the one-troy ounce, which has a nominal face value of one dollar and ...
which is pure
silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
. Section 5112 also provides for the
minting
Minting is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The village is situated south from the A158 road. The population (including Gautby) at the 2011 census was 286.
Minting Priory was located here.
Mi ...
and
issuance
Securitization is the financial practice of pooling various types of contractual debt such as residential mortgages, commercial mortgages, auto loans or credit card debt obligations (or other non-debt assets which generate receivables) and selling ...
of other coins, which have values ranging from
one cent (
U.S. Penny
The cent, the United States one-cent coin (symbol: Cent_(currency)#Symbol, ¢), often called the "penny", is a unit of currency equaling one one-hundredth of a United States dollar. It has been the lowest face-value physical unit of U.S. currenc ...
) to 100 dollars.
These other coins are more fully described in
Coins of the United States dollar
Coins of the United States dollar (aside from those of the earlier Continental currency) were first minted in 1792. New coins have been produced annually and they make up a valuable aspect of the United States currency system. Today, circulating ...
.
Article I, Section 9 of the Constitution provides that "a regular Statement and Account of the Receipts and Expenditures of all public Money shall be published from time to time," which is further specified by Section 331 of Title 31 of the U.S. Code. The sums of money reported in the "Statements" are currently expressed in U.S. dollars, thus the U.S. dollar may be described as the
unit of account
In economics, unit of account is one of the money functions. A unit of account is a standard numerical monetary unit of measurement of the market value of goods, services, and other transactions. Also known as a "measure" or "standard" of rela ...
of the United States. "Dollar" is one of the first words of Section 9, in which the term refers to the
Spanish milled dollar, or the coin worth eight
Spanish real
The ''real'' (English: /ɹeɪˈɑl/ Spanish: /reˈal/) (meaning: "royal", plural: ''reales'') was a unit of currency in Spain for several centuries after the mid-14th century. It underwent several changes in value relative to other units throu ...
es.
The Coinage Act
In 1792, the
U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
passed the
Coinage Act
Coinage Act is a stock short title used for legislation in the United Kingdom and the United States related to coinage.
List United Kingdom
* Coinage Act 1816, defined the value of pound sterling relative to gold
* Coinage Offences Act 1861 (see ...
, of which Section 9 authorized the production of various coins, including:
U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
. 1792.
Coinage Act of 1792
'. 2nd Congress, 1st Session. Sec. 9, ch. 16. Retrieved June 6, 2020.Section 20 of the Act designates the United States dollar as the
unit of currency of the United States:
Decimal units
Unlike the Spanish milled dollar, the
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
and the Coinage Act prescribed a
decimal system of units to go with the unit dollar, as follows:
the mill, or one-thousandth of a dollar; the cent, or one-hundredth of a dollar; the dime, or one-tenth of a dollar; and the eagle, or ten dollars. The current relevance of these units:
* Only the
cent (¢) is used as everyday division of the dollar.
* The
dime is used solely as the name of the
coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
with the value of 10 cents.
* The
mill (₥) is relatively unknown, but before the mid-20th century was familiarly used in matters of
sales taxes
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
, as well as
gasoline prices
The usage and pricing of gasoline (or ''petrol'') results from factors such as crude oil prices, processing and distribution costs, local demand, the strength of local currencies, local taxation, and the availability of local sources of gas ...
, which are usually in the form of $ΧΧ.ΧΧ9 per
gallon
The gallon is a unit of volume in imperial units and United States customary units. Three different versions are in current use:
*the imperial gallon (imp gal), defined as , which is or was used in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Canada, Austral ...
(e.g., $3.599, commonly written as $).
* The
eagle is also largely unknown to the general public.
This term was used in the ''Coinage Act of 1792'' for the denomination of ten dollars, and subsequently was used in naming gold coins.
The
Spanish peso or dollar was historically divided into eight
reales (colloquially, ''bits'') – hence ''pieces of eight''. Americans also learned counting in non-decimal ''bits'' of cents before 1857 when Mexican ''bits'' were more frequently encountered than American cents; in fact this practice survived in
New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed c ...
quotations until 2001.
In 1854,
Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
James Guthrie proposed creating $100, $50, and $25 gold coins, to be referred to as a ''
union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
'', ''
half union
The half union (separate varieties known as J-1546 through J-1549) was a United States pattern coin with a face value of fifty U.S. Dollars. It is often thought of as one of the most significant and well-known patterns in the history of the U.S. M ...
'', and ''quarter union'', respectively, thus implying a denomination of 1 Union = $100. However, no such coins were ever struck, and only patterns for the $50 half union exist.
When currently issued in circulating form, denominations less than or equal to a dollar are emitted as
U.S. coins, while denominations greater than or equal to a dollar are emitted as
Federal Reserve Note
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
s, disregarding these special cases:
* Gold coins issued for
circulation until the 1930s, up to the value of $20 (known as the ''
double eagle
A double eagle is a gold coin of the United States with a denomination of $20. (Its gold content of 0.9675 troy oz (30.0926 grams) was worth $20 at the 1849 official price of $20.67/oz.) The coins are 34 mm x 2 mm and are made from ...
'')
* Bullion or commemorative
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
,
silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
,
platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Platinu ...
, and
palladium coins valued up to $100 as legal tender (though worth far more as
bullion
Bullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes from t ...
).
* Civil War paper currency issue in denominations below $1, i.e. fractional currency, sometimes pejoratively referred to as ''
shinplaster
Shinplaster was paper money of low denomination, typically less than one dollar, circulating widely in the economies of the 19th century where there was a shortage of circulating coinage. The shortage of circulating coins was primarily due t ...
s''.
Etymology
In the 16th century, Count
Hieronymus Schlick
Hieronymus Schlick was a Bohemian count who authorised the minting of ''joachimstalers ,''after Joachimstal, the valley in which the silver was mined. Joachimstalers was later shortened to taler, the origin of the word "dollar
Dollar is the ...
of
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
began minting coins known as ''joachimstalers'', named for
Joachimstal, the valley in which the silver was mined. In turn, the valley's name is titled after
Saint Joachim
Joachim (; ''Yəhōyāqīm'', "he whom Yahweh has set up"; ; ) was, according to Christian tradition, the husband of Saint Anne and the father of Mary, the mother of Jesus. The story of Joachim and Anne first appears in the Biblical apocryphal ...
, whereby ''thal'' or ''tal'', a cognate of the English word , is
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
for 'valley.'
["Ask US." '']National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
''. June 2002. p. 1. The ''joachimstaler'' was later shortened to the German ''
taler'', a word that eventually found its way into many languages, including:
''tolar'' (
Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
*Czech, ...
,
Slovak and
Slovenian
Slovene or Slovenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Slovenia, a country in Central Europe
* Slovene language, a South Slavic language mainly spoken in Slovenia
* Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Sloven ...
); ''daler'' (
Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
and
Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
);
''dalar'' and ''daler'' (
Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
*Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
*Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including the ...
); ''daler'' or ''daalder'' (
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
);
''
talari'' (
Ethiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
);
''tallér'' (
Hungarian);
''tallero'' (
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
);
''دولار'' (
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
); and ''
dollar
Dollar is the name of more than 20 currencies. They include the Australian dollar, Brunei dollar, Canadian dollar, Hong Kong dollar, Jamaican dollar, Liberian dollar, Namibian dollar, New Taiwan dollar, New Zealand dollar, Singapore dollar, U ...
'' (
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
).
Though the
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
pioneered in modern-day
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
in the 17th century the use and the counting of money in silver dollars in the form of German-Dutch ''
reichsthaler
The ''Reichsthaler'' (; modern spelling Reichstaler), or more specifically the ''Reichsthaler specie'', was a standard thaler silver coin introduced by the Holy Roman Empire in 1566 for use in all German states, minted in various versions for th ...
s'' and native Dutch ''
leeuwendaalder
A thaler (; also taler, from german: Taler) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter o ...
s'' ('lion dollars'), it was the ubiquitous
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' Spanish Empire, imperial era between 15th century, 15th ...
n
eight-real coin which became exclusively known as the ''dollar'' since the 18th century.
Nicknames
The
colloquialism
Colloquialism (), also called colloquial language, everyday language or general parlance, is the style (sociolinguistics), linguistic style used for casual (informal) communication. It is the most common functional style of speech, the idiom norm ...
''
buck(s)'' (much like the British ''quid'' for the
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
) is often used to refer to dollars of various nations, including the U.S. dollar. This term, dating to the 18th century, may have originated with the colonial
leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
trade, or it may also have originated from a
poker
Poker is a family of comparing card games in which players wager over which hand is best according to that specific game's rules. It is played worldwide, however in some places the rules may vary. While the earliest known form of the game w ...
term.
''Greenback'' is another nickname, originally applied specifically to the 19th-century
Demand Note
A Demand Note is a type of United States paper money that was issued between August 1861 and April 1862 during the American Civil War in denominations of 5, 10, and 20 . Demand Notes were the first issue of paper money by the United States ...
dollars, which were printed black and green on the backside, created by
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
to finance the
North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
for the
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. It is still used to refer to the U.S. dollar (but not to the dollars of other countries). The term ''greenback'' is also used by the financial press in other countries, such as
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
,
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
,
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
,
and
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
.
Other well-known names of the dollar as a whole in denominations include ''greenmail'', ''green'', and ''dead presidents'', the latter of which referring to the deceased presidents pictured on most bills. Dollars in general have also been known as ''bones'' (e.g. "twenty bones" = $20). The newer designs, with portraits displayed in the main body of the obverse (rather than in
cameo insets), upon paper color-coded by denomination, are sometimes referred to as ''bigface'' notes or ''
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situati ...
money''.
''
Piastre
The piastre or piaster () is any of a number of units of currency. The term originates from the Italian for "thin metal plate". The name was applied to Spanish and Hispanic American pieces of eight, or pesos, by Venice, Venetian traders in the ...
'' was the original French word for the U.S. dollar, used for example in the French text of the
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
. Though the U.S. dollar is called ''dollar'' in Modern French, the term ''piastre'' is still used among the speakers of
Cajun French
Louisiana French ( frc, français de la Louisiane; lou, françé la lwizyàn) is an umbrella term for the dialects and varieties of the French language spoken traditionally by French Louisianians in colonial Lower Louisiana. As of today Louisia ...
and
New England French
New England French (french: français de Nouvelle-Angleterre) is a variety of French spoken in the New England region of the United States. It descends from Canadian French because it originally came from French Canadians who immigrated to New Eng ...
, as well as speakers in
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
and other
French-speaking Caribbean islands.
Nicknames specific to denomination:
* The
quarter dollar
The term "quarter dollar" refers to a quarter-unit of several currencies that are named "dollar". One dollar ( $1) is normally divided into subsidiary currency of 100 cents, so a quarter dollar is equal to 25 cents. These quarter dollars (aka qu ...
coin is known as ''two bits'', betraying the dollar's origins as the "piece of eight" (bits or ''reales'').
* The
$1 bill is nicknamed ''buck'' or ''single''.
* The infrequently-used
$2 bill is sometimes called ''deuce'', ''Tom'', or ''Jefferson'' (after
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
).
* The
$5 bill is sometimes called ''Lincoln'', ''fin'', ''fiver'', or ''five-spot''.
* The
$10 bill is sometimes called ''sawbuck'', ''ten-spot'', or ''Hamilton'' (after
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
).
* The
$20 bill is sometimes called ''double sawbuck'', ''Jackson'' (after
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
), or ''
double eagle
A double eagle is a gold coin of the United States with a denomination of $20. (Its gold content of 0.9675 troy oz (30.0926 grams) was worth $20 at the 1849 official price of $20.67/oz.) The coins are 34 mm x 2 mm and are made from ...
''.
* The
$50 bill is sometimes called a ''yardstick'', or a ''grant'', after President
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
.
* The
$100 bill is called ''Benjamin'', ''Benji'', ''Ben'', or ''Franklin'', referring to its portrait of
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
. Other nicknames include ''C-note'' (C being the
Roman numeral
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
for 100), ''century note'', or ''bill'' (e.g. ''two bills'' = $200).
* Amounts or multiples of $1,000 are sometimes called ''
grand
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and commu ...
'' in colloquial speech, abbreviated in written form to ''G'', ''K'', or ''k'' (from
''kilo''; e.g. $10k = $10,000). Likewise, a ''large'' or ''stack'' can also refer to a multiple of $1,000 (e.g. "fifty large" = $50,000).
Dollar sign

The symbol , usually written before the numerical amount, is used for the U.S. dollar (as well as for many other currencies). The sign was the result of a late 18th-century evolution of the
scribal abbreviation
Scribal abbreviations or sigla (grammatical number, singular: siglum) are abbreviations used by ancient and medieval scribes writing in various languages, including Latin, Greek language, Greek, Old English and Old Norse. In modern manuscrip ...
''p
s'' for the
peso
The peso is the monetary unit of several countries in the Americas, and the Philippines. Originating in the Spanish Empire, the word translates to "weight". In most countries the peso uses the Dollar sign, same sign, "$", as many currencies na ...
, the common name for the
Spanish dollars
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
that were in wide circulation in the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The ''p'' and the ''s'' eventually came to be written over each other giving rise to ''$''.
Another popular explanation is that it is derived from the
Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
on the
Spanish Coat of arms
The coat of arms of Spain represents Spain and the Spanish nation, including its national sovereignty and the country's form of government, a constitutional monarchy. It appears on the flag of Spain and it is used by the Government of Spain, the Co ...
of the
Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
. These
Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
on the silver Spanish dollar coins take the form of two vertical bars (, , ) and a swinging cloth band in the shape of an ''S''.
Yet another explanation suggests that the dollar sign was formed from the capital letters ''U'' and ''S'' written or printed one on top of the other. This theory, popularized by novelist
Ayn Rand
Alice O'Connor (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum;, . Most sources transliterate her given name as either ''Alisa'' or ''Alissa''. , 1905 – March 6, 1982), better known by her pen name Ayn Rand (), was a Russian-born American writer and p ...
in ''
Atlas Shrugged
''Atlas Shrugged'' is a 1957 novel by Ayn Rand. It was her longest novel, the fourth and final one published during her lifetime, and the one she considered her '' magnum opus'' in the realm of fiction writing. ''Atlas Shrugged'' includes eleme ...
'', does not consider the fact that the symbol was already in use before the formation of the United States.
History
Origins: the Spanish dollar
The U.S. dollar was introduced at par with the Spanish-American
silver dollar (or ''Spanish peso'', ''Spanish milled dollar'', ''eight-real coin'', ''piece-of-eight''). The latter was produced from the rich silver mine output of
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' Spanish Empire, imperial era between 15th century, 15th ...
; minted in
Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
,
Potosí
Potosí, known as Villa Imperial de Potosí in the colonial period, is the capital city and a municipality of the Department of Potosí in Bolivia. It is one of the highest cities in the world at a nominal . For centuries, it was the location o ...
(Bolivia),
Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of t ...
(Peru) and elsewhere; and was in wide circulation throughout the Americas, Asia and Europe from the 16th to 19th centuries. The minting of machine-milled Spanish dollars since 1732 boosted its worldwide reputation as a trade coin and positioned it to be model for the new currency of the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
.
Even after the
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
commenced issuing coins in 1792, locally minted ''dollars'' and ''cents'' were less abundant in circulation than
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' Spanish Empire, imperial era between 15th century, 15th ...
n ''pesos'' and ''reales''; hence Spanish, Mexican and American dollars all remained legal tender in the United States until the
Coinage Act of 1857
The Coinage Act of 1857 (Act of Feb. 21, 1857, Chap. 56, 34th Cong., Sess. III, 11 Stat. 163) was an act of the United States Congress which ended the status of foreign coins as legal tender, repealing all acts "authorizing the currency of foreign ...
. In particular, Colonists' familiarity with the Spanish two-''real quarter peso'' was the reason for issuing a quasi-decimal
25-cent quarter dollar coin rather than a 20-cent coin.
For the relationship between the
Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
and the individual state colonial currencies, see
Connecticut pound
The pound was the currency of Connecticut until 1793. Initially, sterling coin circulated along with foreign currencies. This was supplemented by local paper money from 1709. Although the local currency was denominated in £sd, it was worth less ...
,
Delaware pound
The pound was the currency of Delaware until 1793. Initially, sterling coin circulated along with foreign currencies. This was supplemented by local paper money from 1723. Although the local currency was denominated in £sd, it was worth less tha ...
,
Georgia pound
The pound was the currency of Georgia until 1793. Initially, sterling coin circulated. This was supplemented from 1735 with local paper money denominated in £sd, with 1 pound = 20 shillings = 240 pence.
The State of Georgia issued Continenta ...
,
Maryland pound
The pound (later dollar) was the currency of Maryland from 1733 until its gradual replacement with the Continental currency and later the United States dollar between the American Revolution and the early 1800s. Initially, sterling coin circulat ...
,
Massachusetts pound
The pound was the currency of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and its colonial predecessors until 1793. The Massachusetts pound used the £sd currency system of 1 pound divided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence. Initially, sterling coin and ...
,
New Hampshire pound
The pound was the currency of New Hampshire until 1793. Initially, sterling coin circulated, supplemented from 1709 by local paper money. These notes were denominated in £sd but were worth less than sterling, with 1 New Hampshire shilling = 9 pen ...
,
New Jersey pound
The pound was the currency of New Jersey until 1793. Initially, sterling coin and some foreign currencies circulated, supplemented from 1709 by local paper money. Although the notes were denominated in £sd, they were worth less than sterling. A ...
,
New York pound
The pound was the currency of the province and state of New York until 1793. Initially, sterling coin circulated along with foreign currencies. This was supplemented by local paper money from 1709. Although these were denominated in £sd, they we ...
,
North Carolina pound
The pound (symbol: £) was the currency of North Carolina until 1793. Initially, sterling coin circulated, supplemented from 1709 by the introduction of colonial currency denominated in pounds, shillings and pence in 1712. The North Carolina ...
,
Pennsylvania pound
The pound was the currency of Pennsylvania until 1793. It was created as a response to the global economic downturn caused by the collapse of the South Sea Company. Initially, Pound sterling, sterling and certain foreign coins circulated, suppleme ...
,
Rhode Island pound
The pound was the currency of Rhode Island until 1793. Initially, sterling coin and foreign coins circulated, supplemented by local paper money from 1710.Newman, 2008, p. 371. These notes were denominated in £sd, but they were worth less than ...
,
South Carolina pound, and
Virginia pound
The pound was the currency of Virginia until 1793. Initially, Pound sterling, sterling coin circulated along with foreign currencies, supplemented from 1755 by local paper money.Newman, 2008, p. 437. Although these notes were denominated in £sd ...
.
Coinage Act of 1792

On July 6, 1785, the
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
resolved that the money unit of the United States, the dollar, would contain 375.64
grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legume ...
of fine silver; on August 8, 1786, the Continental Congress continued that definition and further resolved that the money of account, corresponding with the division of coins, would proceed in a
decimal ratio, with the sub-units being mills at 0.001 of a dollar, cents at 0.010 of a dollar, and dimes at 0.100 of a dollar.
After the adoption of the
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
, the U.S. dollar was defined by the
Coinage Act of 1792
The Coinage Act of 1792 (also known as the Mint Act; officially: ''An act establishing a mint, and regulating the Coins of the United States''), passed by the United States Congress on April 2, 1792, created the United States dollar as the countr ...
. It specified a "dollar" based on the
Spanish milled dollar to contain
grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
s of fine silver, or of "standard silver" of fineness 371.25/416 = 89.24%; as well as an "eagle" to contain grains of fine gold, or of 22
karat
The fineness of a precious metal object (coin, bar, jewelry, etc.) represents the weight of ''fine metal'' therein, in proportion to the total weight which includes alloying base metals and any impurities. Alloy metals are added to increase hardn ...
or 91.67% fine gold.
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
arrived at these numbers based on a treasury assay of the average fine silver content of a selection of worn
Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
s, which came out to be 371 grains. Combined with the prevailing gold-silver ratio of 15, the standard for gold was calculated at 371/15 = 24.73 grains fine gold or 26.98 grains 22K gold. Rounding the latter to 27.0 grains finalized the dollar's standard to 24.75 grains of fine gold or 24.75*15 = 371.25 grains = 24.0566 grams = 0.7735 troy ounces of fine silver.
The same coinage act also set the value of an eagle at 10 dollars, and the dollar at eagle. It called for silver coins in denominations of 1, , , , and dollar, as well as gold coins in denominations of 1, and eagle. The value of gold or silver contained in the dollar was then converted into relative value in the economy for the buying and selling of goods. This allowed the value of things to remain fairly constant over time, except for the influx and outflux of gold and silver in the nation's economy.
Though a
Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
freshly minted after 1772 theoretically contained 417.7 grains of silver of fineness 130/144 (or 377.1 grains fine silver), reliable assays of the period in fact confirmed a fine silver content of for the average Spanish dollar in circulation.
The new U.S. silver dollar of therefore compared favorably and was received at par with the Spanish dollar for foreign payments, and after 1803 the
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
had to suspend making this coin out of its limited resources since it failed to stay in domestic circulation. It was only after Mexican independence in 1821 when their peso's fine silver content of 377.1 grains was firmly upheld, which the U.S. later had to compete with using a heavier
Trade dollar coin.
Design
The early currency of the United States did not exhibit faces of presidents, as is the custom now; although today, by law, only the portrait of a deceased individual may appear on United States currency. In fact, the newly formed government was against having portraits of leaders on the currency, a practice compared to the policies of European monarchs. The currency as we know it today did not get the faces they currently have until after the early 20th century; before that "heads" side of coinage used profile faces and striding, seated, and standing figures from Greek and Roman mythology and composite Native Americans. The last coins to be converted to profiles of historic Americans were the dime (1946) and the Dollar (1971).
Continental currency

After the
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
, the
thirteen colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
became
independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
. Freed from British monetary regulations, they each issued
£sd
£sd (occasionally written Lsd, spoken as "pounds, shillings and pence" or pronounced ) is the popular name for the pre-decimal currencies once common throughout Europe, especially in the British Isles and hence in several countries of the B ...
paper money to pay for military expenses. The
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
also began issuing "Continental Currency" denominated in Spanish dollars. For its value relative to states' currencies, see
Early American currency
Early American currency went through several stages of development during the colonial and post-Revolutionary history of the United States. John Hull was authorized by the Massachusetts legislature to make the earliest coinage of the colony (the ...
.
Continental currency depreciation (currency), depreciated badly during the war, giving rise to the famous phrase "not worth a continental". A primary problem was that monetary policy was not coordinated between Congress and the states, which continued to issue bills of credit. Additionally, neither Congress nor the governments of the several states had the will or the means to retire the bills from circulation through taxation or the sale of bonds. The currency was ultimately replaced by the silver dollar at the rate of 1 silver dollar to 1000 continental dollars. It gave rise to the phrase "not worth a continental", and was responsible for the clause in Article One of the United States Constitution#Section 10: Limits on the States, article 1, section 10 of the
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
which reads: "No state shall... make anything but gold and silver coin a tender in payment of debts".
Silver and gold standards, 19th century
From implementation of the 1792 Mint Act to the 1900 implementation of the gold standard the dollar was on a bimetallism, bimetallic silver-and-gold standard, defined as either 371.25 grain (unit), grains (24.056 g) of fine silver or 24.75 grains of fine gold (gold-silver ratio 15).
Subsequent to the Coinage Act of 1834 the dollar's fine gold equivalent was revised to 23.2 grains; it was slightly adjusted to in 1837 (gold-silver ratio ~16). The same act also resolved the difficulty in minting the "standard silver" of 89.24% fineness by revising the dollar's alloy to 412.5 grains, 90% silver, still containing 371.25 grains fine silver. Gold was also revised to 90% fineness: 25.8 grains gross, 23.22 grains fine gold.
Following the rise in the price of silver during the California Gold Rush and the disappearance of circulating silver coins, the Coinage Act of 1853 reduced the standard for silver coins less than $1 from 412.5 grains to , 90% silver per 100 cents (slightly revised to 25.0 g, 90% silver in 1873). The Act also limited the free silver right of individuals to convert
bullion
Bullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes from t ...
into only one coin, the silver dollar of 412.5 grains; smaller coins of lower standard can only be produced by the
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
using its own bullion.
Summary and Coins of the United States dollar, links to coins issued in the 19th century:
* In base metal: Half cent (United States coin), 1/2 cent, Penny (United States coin), 1 cent, Nickel (United States coin), 5 cents.
* In silver: half dime, Dime (United States coin), dime,
quarter dollar
The term "quarter dollar" refers to a quarter-unit of several currencies that are named "dollar". One dollar ( $1) is normally divided into subsidiary currency of 100 cents, so a quarter dollar is equal to 25 cents. These quarter dollars (aka qu ...
, Half dollar (United States coin), half dollar, Dollar coin (United States), silver dollar.
* In gold: Gold dollar, gold $1, Quarter eagle, $2.50 quarter eagle, Half eagle, $5 half eagle, Eagle (United States coin), $10 eagle, Double eagle, $20 double eagle
* Less common denominations: Two-cent piece (United States coin), bronze 2 cents, Three-cent nickel, nickel 3 cents, Three-cent silver, silver 3 cents, Twenty-cent piece (United States coin), silver 20 cents, Three-dollar piece, gold $3.
Note issues, 19th century

In order to finance the War of 1812, Congress authorized the issuance of Treasury Note (19th century), Treasury Notes, interest-bearing short-term debt that could be used to pay public dues. While they were intended to serve as debt, they did function "to a limited extent" as money. Treasury Notes were again printed to help resolve the reduction in public revenues resulting from the Panic of 1837 and the Panic of 1857, as well as to help finance the Mexican–American War and the
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.
Paper money was issued again in 1862 without the backing of precious metals due to the
Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. In addition to Treasury Notes, Congress in 1861 authorized the Treasury to borrow $50 million in the form of Demand Notes, which did not bear interest but could be redeemed on demand for precious metals. However, by December 1861, the Union (American Civil War), Union government's supply of specie was outstripped by demand for redemption and they were forced to suspend redemption temporarily. In February 1862 Congress passed the Legal Tender Cases, ''Legal Tender Act of 1862'', issuing United States Notes, which were not redeemable on demand and bore no interest, but were
legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which when offered ("tendered") in pa ...
, meaning that creditors had to accept them at face value for any payment except for public debts and import tariffs. However, silver and gold coins continued to be issued, resulting in the depreciation of the newly printed notes through Gresham's Law. In 1869, Supreme Court ruled in Hepburn v. Griswold that Congress could not require creditors to accept United States Notes, but overturned that ruling the next year in the Legal Tender Cases. In 1875, Congress passed the ''Specie Payment Resumption Act'', requiring the Treasury to allow U.S. Notes to be redeemed for gold after January 1, 1879.
Gold standard, 20th century

Though the dollar came under the gold standard ''de jure'' only after 1900, the bimetallism, bimetallic era was ended ''de facto'' when the Coinage Act of 1873 suspended the minting of the standard Dollar coin (United States), silver dollar of 412.5 grains (26.73 g = 0.8595 oz t), the only fully legal tender coin that individuals could convert bullion into in unlimited (or Free silver) quantities, and right at the onset of the silver rush from the Comstock Lode in the 1870s. This was the so-called "Crime of '73".
The ''
Gold Standard Act
The Gold Standard Act was an Law_of_the_United_States#Federal_law, Act of the United States Congress, signed by President William McKinley and effective on March 14, 1900, defining the United States dollar by gold weight and requiring the United ...
'' of 1900 repealed the U.S. dollar's historic link to silver and defined it solely as of fine gold (or $20.67 per
troy ounce
Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight (24 grains), the troy ounce (20 pennyweights), and the ...
of 480 grains). In 1933, gold coins were confiscated by Executive Order 6102 under Franklin D. Roosevelt, and in 1934 the standard was changed to $35 per troy ounce fine gold, or per dollar.
After 1968 a series of revisions to the gold peg was implemented, culminating in the Nixon Shock of August 15, 1971, which suddenly ended the convertibility of dollars to gold. The U.S. dollar has since floated freely on the foreign exchange markets.
Federal Reserve Notes, 20th century to present
Congress continued to issue paper money after the Civil War, the latest of which is the
Federal Reserve Note
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
that was authorized by the Federal Reserve Act of 1913. Since the discontinuation of all other types of notes (Gold Certificates in 1933, Silver Certificates in 1963, and United States Notes in 1971), U.S. dollar notes have since been issued exclusively as
Federal Reserve Note
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
s.
Emergence as reserve currency

The U.S. dollar first emerged as an important international
reserve currency
A reserve currency (or anchor currency) is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international tran ...
in the 1920s, displacing the British
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
as it emerged from the First World War relatively unscathed and since the United States was a significant recipient of wartime gold inflows. After the United States emerged as an even stronger global superpower during the Second World War, the
Bretton Woods Agreement
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
of 1944 established the U.S. dollar as the world's primary reserve currency and the only post-war currency linked to gold. Despite all links to gold being severed in 1971, the dollar continues to be the world's foremost reserve currency for international trade to this day.
The Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 also defined the post-World War II monetary order and relations among modern-day United Nations, independent states, by setting up a system of rules, institutions, and procedures to regulate the international monetary system. The agreement founded the International Monetary Fund and other institutions of the modern-day World Bank Group, establishing the infrastructure for conducting international payments and accessing the global capital markets using the U.S. dollar.
The
monetary policy of the United States
Monetary policy of The United States concerns those policies related to the minting & printing of money, policies governing the legal exchange of currency, demand deposits, the money supply, etc. In the United States, the central bank, The Fed ...
is conducted by the
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
, which acts as the nation's
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ba ...
. It was founded in 1913 under the Federal Reserve Act in order to furnish an elastic currency for the United States and to supervise its banking system, particularly in the aftermath of the Panic of 1907.
For most of the post-war period, the U.S. government has financed its own spending by borrowing heavily from the dollar-lubricated global capital markets, in debts denominated in its own currency and at minimal interest rates. This ability to borrow heavily without facing a significant balance of payments crisis has been described as the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
's exorbitant privilege.
Coins
The
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
has issued legal tender coins every year from 1792 to the present. From 1934 to the present, the only denominations produced for circulation have been the familiar penny, nickel, dime, quarter, half dollar, and dollar.
Gold and silver coins have been previously minted for general circulation from the 18th to the 20th centuries. The last gold coins were minted in 1933. The last 90% silver coins were minted in 1964, and the last 40% silver half dollar was minted in 1970.
The
United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; tha ...
currently produces circulating coins at the Philadelphia Mint, Philadelphia and Denver Mints, and commemorative and proof coins for collectors at the San Francisco Mint, San Francisco and West Point Mints. Mint mark conventions for these and for past mint branches are discussed in ''Coins of the United States dollar#Mint marks''.
The Dollar coin (United States), one-dollar coin has never been in popular circulation from 1794 to present, despite several attempts to increase their usage since the 1970s, the most important reason of which is the continued production and popularity of the United States one-dollar bill, one-dollar bill. Half dollar (United States coin), Half dollar coins were commonly used currency since inception in 1794, but has fallen out of use from the mid-1960s when all silver half dollars began to be hoarded.
The nickel (United States coin), nickel is the only coin whose size and composition (5 grams, 75% copper, and 25% nickel) is still in use from 1865 to today, except for wartime 1942-1945 Jefferson nickels which contained silver.
Due to the penny's low value, some Efforts to eliminate the penny in the United States, efforts have been made to eliminate the penny as circulating coinage.
For a discussion of other discontinued and canceled denominations, see ''Obsolete denominations of United States currency#Coinage'' and ''Canceled denominations of United States currency#Coinage''.
Collector coins
Collector coins are technically legal tender at face value but are usually worth far more due to their numismatic value or for their precious metal content. These include:
* American Eagle bullion coins
**
American Silver Eagle
The American Silver Eagle is the official silver bullion coin of the United States.
It was first released by the United States Mint on November 24, 1986. It is struck only in the one-troy ounce, which has a nominal face value of one dollar and ...
$1 (1 troy ounce, troy oz) Silver bullion coin 1986–present
**American Gold Eagle $5 ( troy oz), $10 ( troy oz), $25 ( troy oz), and $50 (1 troy oz) Gold bullion coin 1986–present
**American Platinum Eagle $10 ( troy oz), $25 ( troy oz), $50 ( troy oz), and $100 (1 troy oz) Platinum bullion coin 1997–present
**American Palladium Eagle $25 (1 troy oz) Palladium bullion coin 2017–present
* United States commemorative coins—special issue coins, among these:
**Half union, $50.00 (Half Union) minted for the Panama-Pacific International Exposition (1915)
**Silver proof sets minted since 1992 with dimes, quarters and half-dollars made of silver rather than the standard copper-nickel
**Presidential dollar coins proof sets minted since 2007
Banknotes
The Constitution of the United States, U.S. Constitution provides that Congress shall have the power to "borrow money on the credit of the United States." Congress has exercised that power by authorizing Federal Reserve Banks to issue
Federal Reserve Notes
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
. Those notes are "obligations of the United States" and "shall be redeemed in lawful money on demand at the Treasury Department of the United States, in the city of Washington, District of Columbia, or at any Federal Reserve bank". Federal Reserve Notes are designated by law as "
legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which when offered ("tendered") in pa ...
" for the payment of debts. Congress has also authorized the issuance of Federal Reserve Note, more than 10 other types of banknotes, including the
United States Note
A United States Note, also known as a Legal Tender Note, is a type of paper money that was issued from 1862 to 1971 in the U.S. Having been current for 109 years, they were issued for longer than any other form of U.S. paper money. They were k ...
and the Federal Reserve Bank Note. The Federal Reserve Note is the only type that remains in circulation since the 1970s.

Federal Reserve Notes
Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 ...
are printed by the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and are made from Cotton paper, cotton fiber paper (as opposed to Wood fibre, wood fiber used to make common paper). The "large-sized notes" issued before 1928 measured , while small-sized notes introduced that year measure . The dimensions of the modern (small-size) U.S. currency is identical to the size of Philippine peso banknotes issued under United States administration after 1903, which had proven highly successful. The American large-note bills became known as "horse blankets" or "saddle blankets."

Currently printed denominations are United States one-dollar bill, $1, United States two-dollar bill, $2, United States five-dollar bill, $5, United States ten-dollar bill, $10, United States twenty-dollar bill, $20, United States fifty-dollar bill, $50, and United States one hundred-dollar bill, $100. Notes above the $100 denomination stopped being printed in 1946 and were officially withdrawn from circulation in 1969. These notes were used primarily in inter-bank transactions or by organized crime; it was the latter usage that prompted President Richard Nixon to issue an executive order in 1969 halting their use. With the advent of electronic banking, they became less necessary. Notes in denominations of $500, $1,000, $5,000, $10,000, and $100,000 were all produced at one time; see large denomination bills in U.S. currency for details. With the exception of the $100,000 bill (which was only issued as a Series 1934 Gold Certificate and was never publicly circulated; thus it is illegal to own), these notes are now collectors' items and are worth more than their face value to collectors.
Though still predominantly green, the post-2004 series incorporate other colors to better distinguish different denominations. As a result of a 2008 decision in an accessibility lawsuit filed by the American Council of the Blind, the Bureau of Engraving and Printing is planning to implement a raised tactile feature in the next redesign of each note, except the $1 and the current version of the $100 bill. It also plans larger, higher-contrast numerals, more color differences, and distribution of currency readers to assist the visually impaired during the transition period.
Countries that use US dollar
Formal
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Informal
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Monetary policy

The Federal Reserve Act created the
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
in 1913 as the
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ba ...
of the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. Its primary task is
to conduct the nation's monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the U.S. economy. It is also tasked to promote the stability of the financial system and regulate financial institutions, and to act as lender of last resort.
The Monetary policy of the United States is conducted by the Federal Open Market Committee, which is composed of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors and 5 out of the 12 Federal Reserve Bank presidents, and is implemented by all twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks.
Monetary policy refers to actions made by central banks that determine the size and growth rate of the money supply available in the economy, and which would result in desired objectives like low inflation, low unemployment, and stable financial systems. The economy's aggregate money supply is the total of
* M0 money, or Monetary Base - "dollars" in currency and bank money balances credited to the central bank's depositors, which are backed by the central bank's assets,
* plus M1, M2, M3 money - "dollars" in the form of bank money balances credited to banks' depositors, which are backed by the bank's assets and investments.
The FOMC influences the level of money available to the economy by the following means:
* Reserve requirements - specifies a required minimum percentage of deposits in a commercial bank that should be held as a reserve (i.e. as deposits with the Federal Reserve), with the rest available to loan or invest. Higher requirements mean less money loaned or invested, helping keep inflation in check. Raising the federal funds rate earned on those reserves also helps achieve this objective.
* Open market operations - the Federal Reserve buys or sells United States Treasury security, US Treasury bonds and other securities held by banks in exchange for reserves; more reserves increase a bank's capacity to loan or invest elsewhere.
* Discount window lending - banks can borrow from the Federal Reserve.
Monetary policy directly affects interest rates; it indirectly affects stock prices, wealth, and currency exchange rates. Through these channels, monetary policy influences spending, investment, production, employment, and inflation in the United States. Effective monetary policy complements fiscal policy to support economic growth.
The adjusted monetary base has increased from approximately $400 billion in 1994, to $800 billion in 2005, and to over $3 trillion in 2013.
When the Federal Reserve makes a purchase, it credits the seller's reserve account (with the Federal Reserve). This money is not transferred from any existing funds—it is at this point that the Federal Reserve has created new high-powered money. Commercial banks then decide how much money to keep in deposit with the Federal Reserve and how much to hold as physical currency. In the latter case, the Federal Reserve places an order for printed money from the U.S. Treasury Department. The Treasury Department, in turn, sends these requests to the Bureau of Engraving and Printing (to print new Federal Reserve notes, dollar bills) and the Bureau of the Mint (to stamp the coins).
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy objectives to keep prices stable and unemployment low is often called the ''dual mandate''. This replaces past practices under a gold standard where the main concern is the gold equivalent of the local currency, or under a gold exchange standard where the concern is fixing the exchange rate versus another gold-convertible currency (previously practiced worldwide under the
Bretton Woods Agreement
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
of 1944 via fixed exchange rates to the U.S. dollar).
International use as reserve currency

Ascendancy
The primary currency used for global trade between Europe, Asia, and the Americas has historically been the Spanish-American
silver dollar, which created a global silver standard system from the 16th to 19th centuries, due to abundant silver supplies in
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' Spanish Empire, imperial era between 15th century, 15th ...
.
The U.S. dollar itself was derived from this coin. The
Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
was later displaced by the British
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
in the advent of the international gold standard in the last quarter of the 19th century.
The U.S. dollar began to displace the
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
as international
reserve currency
A reserve currency (or anchor currency) is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international tran ...
from the 1920s since it emerged from the First World War relatively unscathed and since the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
was a significant recipient of wartime gold inflows.
After the U.S. emerged as an even stronger global superpower during the Second World War, the
Bretton Woods Agreement
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
of 1944 established the post-war international monetary system, with the U.S. dollar ascending to become the world's primary
reserve currency
A reserve currency (or anchor currency) is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international tran ...
for international trade, and the only post-war currency linked to gold at $35 per
troy ounce
Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight (24 grains), the troy ounce (20 pennyweights), and the ...
.
As international reserve currency
The U.S. dollar is joined by the world's other major currencies - the euro,
pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
, Japanese yen and Chinese renminbi - in the currency basket of the special drawing rights of the International Monetary Fund. Central banks worldwide have huge reserves of U.S. dollars in their holdings and are significant buyers of United States Treasury security, U.S. treasury bills and notes.
Foreign companies, entities, and private individuals hold U.S. dollars in foreign deposit accounts called eurodollars (not to be confused with the euro), which are outside the jurisdiction of the
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
. Private individuals also hold dollars outside the banking system mostly in the form of United States one-hundred-dollar bill, US$100 bills, of which 80% of its supply is held overseas.
The United States Department of the Treasury exercises considerable oversight over the SWIFT, SWIFT financial transfers network, and consequently has a huge sway on the global financial transactions systems, with the ability to impose sanctions on foreign entities and individuals.
In the global markets
The U.S. dollar is predominantly the standard currency unit in which goods are quoted and traded, and with which payments are settled in, in the global commodity markets. The U.S. Dollar Index is an important indicator of the dollar's strength or weakness versus a basket of six foreign currencies.
The United States Government is capable of borrowing trillions of dollars from the global capital markets in U.S. dollars issued by the Federal Reserve System, Federal Reserve, which is itself under U.S. government purview, at minimal interest rates, and with virtually zero default risk. In contrast, foreign governments and corporations incapable of raising money in their own local currencies are forced to issue debt denominated in U.S. dollars, along with its consequent higher interest rates and risks of default.
The United States's ability to borrow in its own currency without facing a significant balance of payments crisis has been frequently described as its exorbitant privilege.
A frequent topic of debate is whether the strong dollar policy of the United States is indeed in America's own best interests, as well as in the best interest of the United Nations, international community.
Currencies fixed to the U.S. dollar
For a more exhaustive discussion of countries using the U.S. dollar as official or customary currency, or using currencies which are pegged to the U.S. dollar, see ''International use of the U.S. dollar#Dollarization and fixed exchange rates'' and ''Currency substitution#US dollar''.
Countries using the U.S. dollar as their official currency include:
* In the Americas: Panamanian balboa, Panama, Ecuadorian centavo coins, Ecuador, El Salvador, British Virgin Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the Caribbean Netherlands.
* The constituent states of the former Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands: Palau, the Federated States of Micronesia, and the Marshall Islands.
* Others: East Timor centavo coins, East Timor.
Among the countries using the U.S. dollar together with other foreign currencies and their local currency are Cambodian riel, Cambodia and Zimbabwe.
Currencies pegged to the U.S. dollar include:
* In the Caribbean: the Bahamian dollar, Barbadian dollar, Belize dollar, Bermudan dollar, Cayman Islands dollar, East Caribbean dollar, Netherlands Antillean guilder and the Aruban florin.
* The currencies of five oil-producing Arab countries: the Saudi riyal, United Arab Emirates dirham, Omani rial, Qatari riyal and the Bahraini dinar.
* Others: the Hong Kong dollar, Macanese pataca, Jordanian dinar, Lebanese pound.
Value
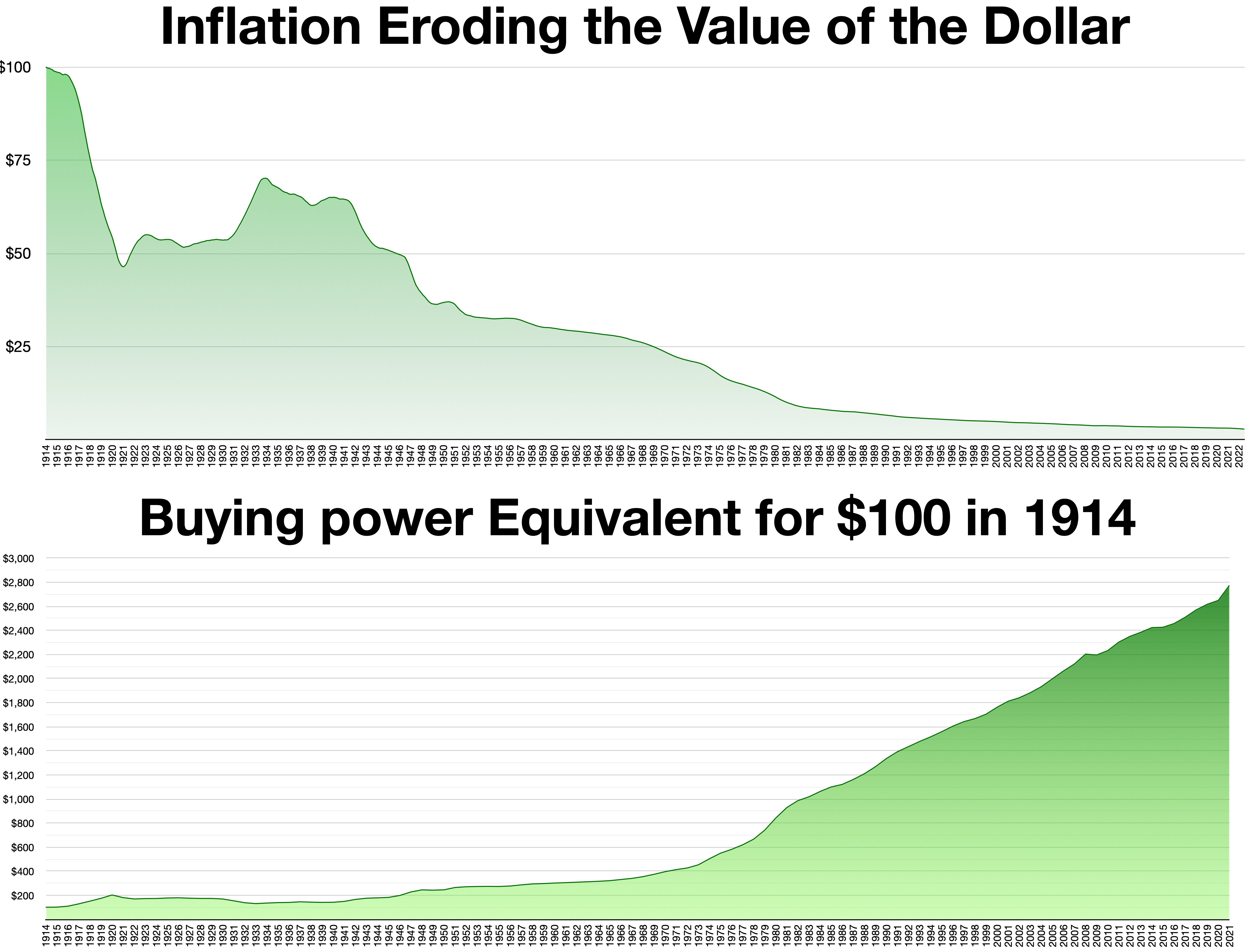
The 6th paragraph of Coinage clause, Section 8 of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that the U.S. Congress shall have the power to "coin money" and to "regulate the value" of domestic and foreign coins. Congress exercised those powers when it enacted the
Coinage Act of 1792
The Coinage Act of 1792 (also known as the Mint Act; officially: ''An act establishing a mint, and regulating the Coins of the United States''), passed by the United States Congress on April 2, 1792, created the United States dollar as the countr ...
. That Act provided for the minting of the Flowing Hair Dollar, first U.S. dollar and it declared that the U.S. dollar shall have "the value of a Spanish milled dollar as the same is now current".
The table above shows the equivalent amount of goods that, in a particular year, could be purchased with $1. The table shows that from 1774 through 2012 the U.S. dollar has lost about 97.0% of its buying power.
The decline in the value of the U.S. dollar corresponds to price inflation, which is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. A consumer price index (CPI) is a measure estimating the average price of consumer goods and services purchased by households. The United States Consumer Price Index, published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, is a measure estimating the average price of consumer goods and services in the United States. It reflects inflation as experienced by consumers in their day-to-day living expenses. A graph showing the U.S. CPI relative to 1982–1984 and the annual year-over-year change in CPI is shown at right.
The value of the U.S. dollar declined significantly during wartime, especially during the American Civil War, World War I, and World War II. The Federal Reserve, which was established in 1913, was designed to furnish an "elastic" currency subject to "substantial changes of quantity over short periods", which differed significantly from previous forms of high-powered money such as gold, national banknotes, and silver coins. Over the very long run, the prior gold standard kept prices stable—for instance, the price level and the value of the U.S. dollar in 1914 were not very different from the price level in the 1880s. The Federal Reserve initially succeeded in maintaining the value of the U.S. dollar and price stability, reversing the inflation caused by the First World War and stabilizing the value of the dollar during the 1920s, before presiding over a 30% deflation in U.S. prices in the 1930s.
Under the Bretton Woods system established after World War II, the value of gold was fixed to $35 per ounce, and the value of the U.S. dollar was thus anchored to the value of gold. Rising government spending in the 1960s, however, led to doubts about the ability of the United States to maintain this convertibility, gold stocks dwindled as banks and international investors began to convert dollars to gold, and as a result, the value of the dollar began to decline. Facing an emerging currency crisis and the imminent danger that the United States would no longer be able to redeem dollars for gold, gold convertibility was finally terminated in 1971 by Richard Nixon, President Nixon, resulting in the "Nixon shock".
The value of the U.S. dollar was therefore no longer anchored to gold, and it fell upon the Federal Reserve to maintain the value of the U.S. currency. The Federal Reserve, however, continued to increase the money supply, resulting in stagflation and a rapidly declining value of the U.S. dollar in the 1970s. This was largely due to the prevailing economic view at the time that inflation and real economic growth were linked (the Phillips curve), and so inflation was regarded as relatively benign.
Between 1965 and 1981, the U.S. dollar lost two thirds of its value.
In 1979, Jimmy Carter, President Carter appointed Paul Volcker Chairman of the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve tightened the money supply and inflation was substantially lower in the 1980s, and hence the value of the U.S. dollar stabilized.
Over the thirty-year period from 1981 to 2009, the U.S. dollar lost over half its value.
This is because the Federal Reserve has targeted not zero inflation, but a low, stable rate of inflation—between 1987 and 1997, the rate of inflation was approximately 3.5%, and between 1997 and 2007 it was approximately 2%. The so-called "Great Moderation" of economic conditions since the 1970s is credited to monetary policy targeting price stability.
There is an ongoing debate about whether central banks should target zero inflation (which would mean a constant value for the U.S. dollar over time) or low, stable inflation (which would mean a continuously but slowly declining value of the dollar over time, as is the case now). Although some economists are in favor of a zero inflation policy and therefore a constant value for the U.S. dollar,
others contend that such a policy limits the ability of the central bank to control interest rates and stimulate the economy when needed.
Pegged currencies
* Aruban florin
* Bahamian dollar (at par)
* Bahraini dinar (higher value)
* Barbadian dollar
* Belarusian ruble (alongside Euro and Russian Ruble in currency basket)
* Belize dollar
* Bermudian dollar (at par)
* Cayman Islands dollar (higher value)
* Costa Rican colon
* Cuban peso
*

East Caribbean Dollar
* East Timor centavo coins (at par)
* Ecuadorian centavo coins (at par)
* Salvadoran colon
* Eritrean nakfa
* Guatemalan quetzal
* Haitian gourde
* Honduran lempira
* Hong Kong dollar (narrow band)
* Iraqi dinar
* Jordanian dinar (higher value)
* Kuwaiti dinar (higher value)
* Lebanese pound
* Antillean guilder
* Nicaraguan cordoba
* Nigerian naira
* Omani rial (higher value)
* Panamanian balboa (at par)
* Qatari riyal
* Saudi riyal
* Sierra Leonean leone
* Trinidad and Tobago dollar
* United Arab Emirates dirham
* Yemeni rial (lower value)
* Zimbabwean bond coins and Zimbabwean bond notes, bond notes (at par)
Exchange rates

Historical exchange rates
Current exchange rates
See also
* Counterfeit United States currency
* Dedollarisation
* International use of the U.S. dollar
* List of the largest trading partners of the United States
* Monetary policy of the United States
* Petrodollar recycling
* Strong dollar policy
* U.S. Dollar Index
Notes
References
Further reading
*
External links
U.S. Bureau of Engraving and Printing
American Currency Exhibit at the San Francisco Federal Reserve BankRelative values of the U.S. dollar, from 1774 to presentSummary of BEP Production Statistics
Images of U.S. currency and coins
U.S. Currency Education Program page with images of all current banknotesU.S. Mint: Image Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:United States Dollar
United States dollar,
Currencies introduced in 1792
Currencies of British Overseas Territories
Currencies of East Timor
Currencies of Ecuador, Dollar
Currencies of El Salvador
Currencies of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Currencies of the United States, Dollar
Currencies of Zimbabwe
Historical currencies of the United States
1792 establishments in the United States
 The symbol , usually written before the numerical amount, is used for the U.S. dollar (as well as for many other currencies). The sign was the result of a late 18th-century evolution of the
The symbol , usually written before the numerical amount, is used for the U.S. dollar (as well as for many other currencies). The sign was the result of a late 18th-century evolution of the  On July 6, 1785, the
On July 6, 1785, the  After the
After the  In order to finance the War of 1812, Congress authorized the issuance of Treasury Note (19th century), Treasury Notes, interest-bearing short-term debt that could be used to pay public dues. While they were intended to serve as debt, they did function "to a limited extent" as money. Treasury Notes were again printed to help resolve the reduction in public revenues resulting from the Panic of 1837 and the Panic of 1857, as well as to help finance the Mexican–American War and the
In order to finance the War of 1812, Congress authorized the issuance of Treasury Note (19th century), Treasury Notes, interest-bearing short-term debt that could be used to pay public dues. While they were intended to serve as debt, they did function "to a limited extent" as money. Treasury Notes were again printed to help resolve the reduction in public revenues resulting from the Panic of 1837 and the Panic of 1857, as well as to help finance the Mexican–American War and the  Though the dollar came under the gold standard ''de jure'' only after 1900, the bimetallism, bimetallic era was ended ''de facto'' when the Coinage Act of 1873 suspended the minting of the standard Dollar coin (United States), silver dollar of 412.5 grains (26.73 g = 0.8595 oz t), the only fully legal tender coin that individuals could convert bullion into in unlimited (or Free silver) quantities, and right at the onset of the silver rush from the Comstock Lode in the 1870s. This was the so-called "Crime of '73".
The ''
Though the dollar came under the gold standard ''de jure'' only after 1900, the bimetallism, bimetallic era was ended ''de facto'' when the Coinage Act of 1873 suspended the minting of the standard Dollar coin (United States), silver dollar of 412.5 grains (26.73 g = 0.8595 oz t), the only fully legal tender coin that individuals could convert bullion into in unlimited (or Free silver) quantities, and right at the onset of the silver rush from the Comstock Lode in the 1870s. This was the so-called "Crime of '73".
The '' The U.S. dollar first emerged as an important international
The U.S. dollar first emerged as an important international 
 Currently printed denominations are United States one-dollar bill, $1, United States two-dollar bill, $2, United States five-dollar bill, $5, United States ten-dollar bill, $10, United States twenty-dollar bill, $20, United States fifty-dollar bill, $50, and United States one hundred-dollar bill, $100. Notes above the $100 denomination stopped being printed in 1946 and were officially withdrawn from circulation in 1969. These notes were used primarily in inter-bank transactions or by organized crime; it was the latter usage that prompted President Richard Nixon to issue an executive order in 1969 halting their use. With the advent of electronic banking, they became less necessary. Notes in denominations of $500, $1,000, $5,000, $10,000, and $100,000 were all produced at one time; see large denomination bills in U.S. currency for details. With the exception of the $100,000 bill (which was only issued as a Series 1934 Gold Certificate and was never publicly circulated; thus it is illegal to own), these notes are now collectors' items and are worth more than their face value to collectors.
Though still predominantly green, the post-2004 series incorporate other colors to better distinguish different denominations. As a result of a 2008 decision in an accessibility lawsuit filed by the American Council of the Blind, the Bureau of Engraving and Printing is planning to implement a raised tactile feature in the next redesign of each note, except the $1 and the current version of the $100 bill. It also plans larger, higher-contrast numerals, more color differences, and distribution of currency readers to assist the visually impaired during the transition period.
Currently printed denominations are United States one-dollar bill, $1, United States two-dollar bill, $2, United States five-dollar bill, $5, United States ten-dollar bill, $10, United States twenty-dollar bill, $20, United States fifty-dollar bill, $50, and United States one hundred-dollar bill, $100. Notes above the $100 denomination stopped being printed in 1946 and were officially withdrawn from circulation in 1969. These notes were used primarily in inter-bank transactions or by organized crime; it was the latter usage that prompted President Richard Nixon to issue an executive order in 1969 halting their use. With the advent of electronic banking, they became less necessary. Notes in denominations of $500, $1,000, $5,000, $10,000, and $100,000 were all produced at one time; see large denomination bills in U.S. currency for details. With the exception of the $100,000 bill (which was only issued as a Series 1934 Gold Certificate and was never publicly circulated; thus it is illegal to own), these notes are now collectors' items and are worth more than their face value to collectors.
Though still predominantly green, the post-2004 series incorporate other colors to better distinguish different denominations. As a result of a 2008 decision in an accessibility lawsuit filed by the American Council of the Blind, the Bureau of Engraving and Printing is planning to implement a raised tactile feature in the next redesign of each note, except the $1 and the current version of the $100 bill. It also plans larger, higher-contrast numerals, more color differences, and distribution of currency readers to assist the visually impaired during the transition period.
 The Federal Reserve Act created the
The Federal Reserve Act created the  The 6th paragraph of Coinage clause, Section 8 of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that the U.S. Congress shall have the power to "coin money" and to "regulate the value" of domestic and foreign coins. Congress exercised those powers when it enacted the
The 6th paragraph of Coinage clause, Section 8 of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that the U.S. Congress shall have the power to "coin money" and to "regulate the value" of domestic and foreign coins. Congress exercised those powers when it enacted the 