|
French West Indies
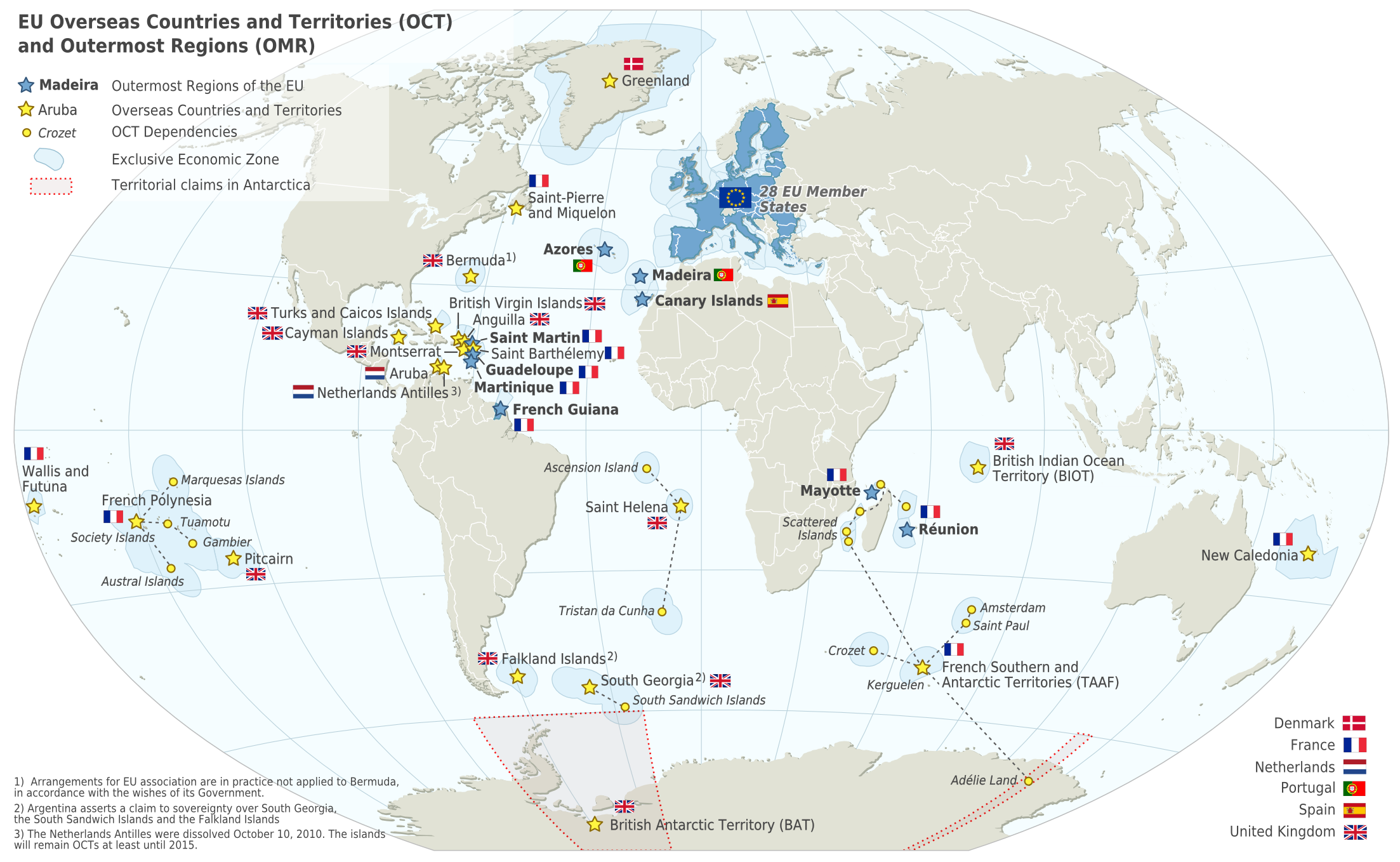
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean: * The two overseas departments of: ** Guadeloupe, including the islands of Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Les Saintes, Marie-Galante, and La Désirade. ** Martinique * The two overseas collectivities of: ** Saint Martin, the northern half of the island with the same name, the southern half is Sint Maarten, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. ** Saint Barthélemy History Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc was a French trader and adventurer in the Caribbean, who established the first permanent French colony, Saint-Pierre, on the island of Martinique in 1635. Belain sailed to the Caribbean in 1625, hoping to establish a French settlement on the island of St. Christopher (St. Kitts). In 1626 he returned to France, where he won the support of Cardinal Richelieu to establish Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Franc
The franc (, ; sign: F or Fr), also commonly distinguished as the (FF), was a currency of France. Between 1360 and 1641, it was the name of coins worth 1 livre tournois and it remained in common parlance as a term for this amount of money. It was reintroduced (in decimal form) in 1795. After two centuries of inflation, it was redenominated in 1960, with each (NF) being worth 100 old francs. The NF designation was continued for a few years before the currency returned to being simply the franc. Many French residents, though, continued to quote prices of especially expensive items in terms of the old franc (equivalent to the new centime), up to and even after the introduction of the euro (for coins and banknotes) in 2002. The French franc was a commonly held international reserve currency of reference in the 19th and 20th centuries. Between 1998 and 2002, the conversion of francs to euros was carried out at a rate of 6.55957 francs to 1 euro. History The French Franc tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Collectivity Of France
The French overseas collectivities (''collectivité d'outre-mer'' or ''COM'') are first-order administrative divisions of France, like the French regions, but have a semi-autonomous status. The COMs include some former French overseas colonies and other French overseas entities with a particular status, all of which became COMs by constitutional reform on 28 March 2003. The COMs differ from overseas regions and overseas departments, which have the same status as metropolitan France but are located outside Europe. As integral parts of France, overseas collectivities are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council. Though some are outside the European Union, all can vote to elect members of the European Parliament (MEPs). (All of France became one multi-member EU constituency in 2019.) The Pacific COMs use the CFP franc, a currency pegged to the euro, whereas the Atlantic COMs use the euro itself. As of 31 March 2011, there were five COMs: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
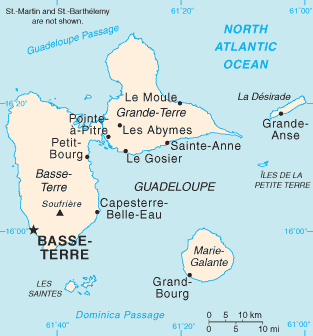
La Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France. History Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian population lived on La Désirade from the 3rd to the 16th centuries. Spanish colonization Deseada was the first island sighted by Christopher Columbus in 1493. When he landed there during his second voyage to America, he took possession of the island on behalf of the Spanish crown, followed by the island of Marie-Galante. Like other Antillean islands, it served as a hideout for pirates or corsairs who attacked Spanish overseas possessions. Some sources indicate that the island owes its name to the relief of the members of Columbus crew who saw the first dry land since leaving the Canary Islands of Spain. They cried out: "Oh, desired island" The French name ''La Désirade'' is an adaptation of its historical name in Spanish (''La Deseada'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie-Galante
Marie-Galante ( gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Mawigalant) is one of the islands that form Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of . It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 the total was officially estimated to be 10,655, with a population density of . Administration Marie-Galante is divided into three communes (with populations at 1 January 2013): * Grand-Bourg (5,564 residents), * Capesterre-de-Marie-Galante (3,389) and * Saint-Louis (2,575). These three communes formed an intercommunal entity in 1994: the Community of Communes of Marie-Galante (french: communauté de communes de Marie-Galante). This is the oldest intercommunal structure of the overseas regions of France. History The Huecoids are the oldest known civilizations to have occupied Marie-Galante, followed by Arawaks, and then by the Island Caribs circa 850. The island was called ''Aichi'' by the Caribs and ''Touloukaera'' by the Arawak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grande-Terre
Grande-Terre Island (french: île de Grande-Terre / île de la Grande-Terre; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwantè) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe island, Basse-Terre, by a narrow sea channel called ''Rivière Salée'' (in English Salt River). Pointe de la Grande Vigie, in Grande-Terre, is the northernmost point of Guadeloupe island. To the east lies La Désirade, to the south lies Marie Galante Despite its name, Grande-Terre (literally "Large Land" in French) is smaller than Basse-Terre Island. It was called like that, in contrast with the much smaller Petite Terre Islands ("Small Land" Islands), two very small islands located about 10 km south-east of the Grande-Terre (see map to the left). Grande-Terre's indented coastline is surrounded by coral reefs and the island itself is a limestone plateau. Its surface is a series of rolling hills, white sand beaches and cliffs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basse-Terre Island
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the two inhabited Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat, north of the Commonwealth of Dominica. The region's capital city is Basse-Terre, located on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; however, the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both located on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 384,239 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 971 Guadeloupe INSEE Like the other overseas departments, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Department And Region Of France
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainland France's regions and departments. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations (France's civil code, penal code, administrative law, social laws, tax laws, etc.) apply to French overseas regions the same as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas regions cannot themselves pass new laws. As integral parts of France and the European Union, overseas departments are represented in the National Assembly, Senate, and Economic and Social Council, vote to elect members of the European Parliament (MEP), and also use the euro as their currency. The overseas departments and regions are not the same as the overs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean) and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America. Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: The Greater Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago on the north and the Lesser Antilles and the on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (the Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands), which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antilles
The Antilles (; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy; es, Antillas; french: Antilles; nl, Antillen; ht, Antiy; pap, Antias; Jamaican Patois: ''Antiliiz'') is an archipelago bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the south and west, the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north and east. The Antillean islands are divided into two smaller groupings: the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. The Greater Antilles includes the larger islands of the Cayman Islands, Cuba, Hispaniola (subdivided into the nations of the Dominican Republic and Haiti), Jamaica, and Puerto Rico. The Lesser Antilles contains the northerly Leeward Islands and the southeasterly Windward Islands as well as the Leeward Antilles just north of Venezuela. The Lucayan Archipelago (consisting of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands), though a part of the West Indies, is generally not included among the Antillean islands. Geographically, the Antillean islands are generally consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antillean Creole
Antillean Creole (Antillean French Creole, Kreyol, Kwéyòl, Patois) is a French-based creole that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles. Its grammar and vocabulary include elements of Carib, English, and African languages. Antillean Creole is related to Haitian Creole but has a number of distinctive features. Antillean Creole is spoken natively, to varying degrees, in Dominica, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Îles des Saintes, Martinique, Saint-Barthélemy (St. Barts), Saint Lucia, French Guiana, Trinidad and Tobago, and Venezuela (mainly in Macuro, Güiria and El Callao Municipality). It is also spoken in various Creole-speaking immigrant communities in the United States Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, and the Collectivity of Saint Martin. Antillean Creole has approximately 1 million speakers and is a means of communication for migrant populations traveling between neighbouring English- and French-speaking territories. In a number of countries (including Dominica, Grena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)