Tracheal Intubation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as

 The vast majority of tracheal intubations involve the use of a
The vast majority of tracheal intubations involve the use of a
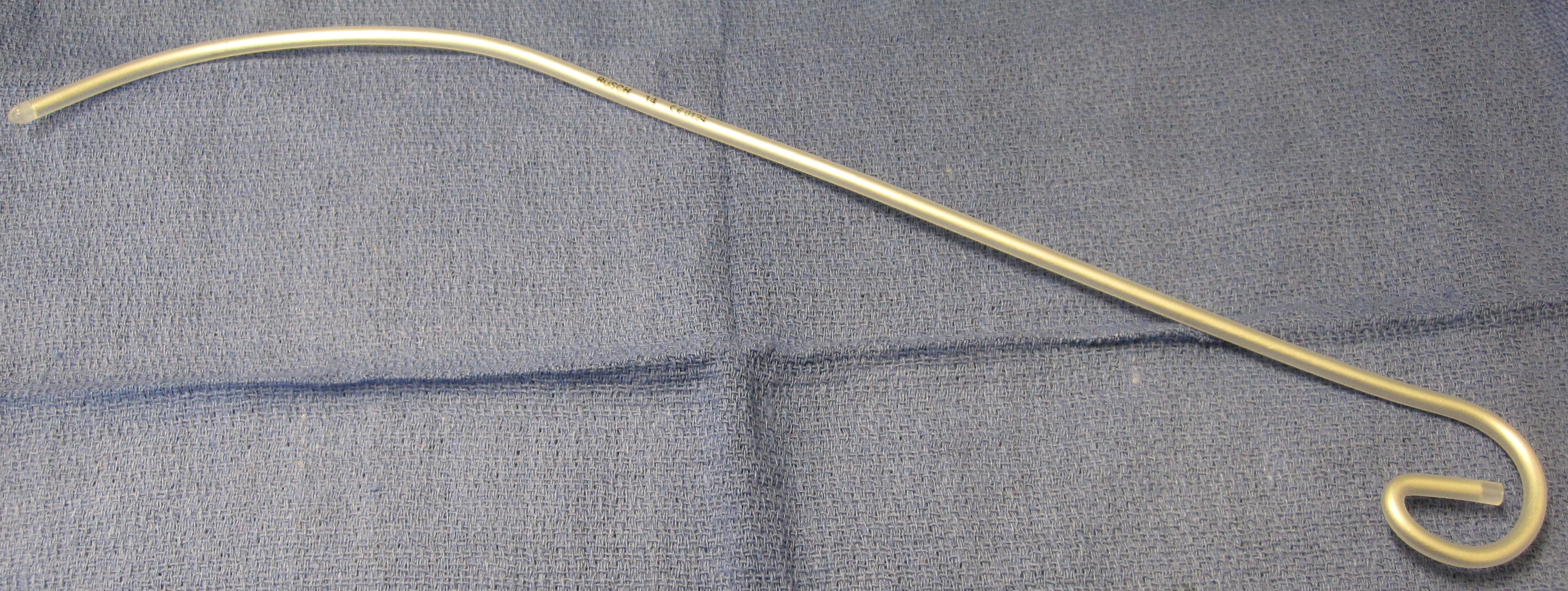 An intubating stylet is a malleable metal wire designed to be inserted into the endotracheal tube to make the tube conform better to the upper airway anatomy of the specific individual. This aid is commonly used with a difficult laryngoscopy. Just as with laryngoscope blades, there are also several types of available stylets, such as the Verathon Stylet, which is specifically designed to follow the 60° blade angle of the GlideScope video laryngoscope.
The Eschmann tracheal tube introducer (also referred to as a "gum elastic bougie") is specialized type of stylet used to facilitate difficult intubation. This flexible device is in length, 15 French (5 mm diameter) with a small "hockey-stick" angle at the far end. Unlike a traditional intubating stylet, the Eschmann tracheal tube introducer is typically inserted directly into the trachea and then used as a guide over which the endotracheal tube can be passed (in a manner analogous to the
An intubating stylet is a malleable metal wire designed to be inserted into the endotracheal tube to make the tube conform better to the upper airway anatomy of the specific individual. This aid is commonly used with a difficult laryngoscopy. Just as with laryngoscope blades, there are also several types of available stylets, such as the Verathon Stylet, which is specifically designed to follow the 60° blade angle of the GlideScope video laryngoscope.
The Eschmann tracheal tube introducer (also referred to as a "gum elastic bougie") is specialized type of stylet used to facilitate difficult intubation. This flexible device is in length, 15 French (5 mm diameter) with a small "hockey-stick" angle at the far end. Unlike a traditional intubating stylet, the Eschmann tracheal tube introducer is typically inserted directly into the trachea and then used as a guide over which the endotracheal tube can be passed (in a manner analogous to the
 A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent (open and unobstructed) airway. Tracheal tubes are frequently used for
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent (open and unobstructed) airway. Tracheal tubes are frequently used for

 No single method for confirming tracheal tube placement has been shown to be 100% reliable. Accordingly, the use of multiple methods for confirmation of correct tube placement is now widely considered to be the
No single method for confirming tracheal tube placement has been shown to be 100% reliable. Accordingly, the use of multiple methods for confirmation of correct tube placement is now widely considered to be the
 A cricothyrotomy is an incision made through the skin and
A cricothyrotomy is an incision made through the skin and
 There are significant differences in airway anatomy and respiratory physiology between children and adults, and these are taken into careful consideration before performing tracheal intubation of any
There are significant differences in airway anatomy and respiratory physiology between children and adults, and these are taken into careful consideration before performing tracheal intubation of any
 Tracheal intubation is not a simple procedure and the consequences of failure are grave. Therefore, the patient is carefully evaluated for potential difficulty or complications beforehand. This involves taking the
Tracheal intubation is not a simple procedure and the consequences of failure are grave. Therefore, the patient is carefully evaluated for potential difficulty or complications beforehand. This involves taking the
 In 1854, a Spanish
In 1854, a Spanish
Video of endotracheal intubation using C-MAC D-blade and bougie used as introducer.
Videos of direct laryngoscopy recorded with the Airway Cam (TM) imaging system
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110619231642/http://www.equipmentexplained.com/physics/airway/ett/endotracheal_tubes.html Free image rich resource explaining various types of endotracheal tubes
Tracheal intubation live case 2022
{{Good article Airway management Anesthesia Emergency medical procedures First aid Intensive care medicine Medical equipment Oral and maxillofacial surgery Otorhinolaryngology Respiratory system procedures Respiratory therapy Medical treatments
intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blakemo ...
, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube
Tube or tubes may refer to:
* ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film
* ''The Tube'' (TV series), a music related TV series by Channel 4 in the United Kingdom
* "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM television show
* Tube (band), a ...
into the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
(windpipe) to maintain an open airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to th ...
or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill, or anesthetized patients to facilitate ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Ventilator, a m ...
of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air ...
, and to prevent the possibility of asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can i ...
tion or airway obstruction.
The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an endotracheal tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the Vertebrate trachea, trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate Gas exchange, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Many diffe ...
is passed through the mouth and vocal apparatus
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articula ...
into the trachea. In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Other methods of intubation involve surgery and include the cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, or ...
(used almost exclusively in emergency circumstances) and the tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The ...
, used primarily in situations where a prolonged need for airway support is anticipated.
Because it is an invasive and uncomfortable medical procedure
A medical procedure is a course of action intended to achieve a result in the delivery of healthcare.
A medical procedure with the intention of determining, measuring, or diagnosing a patient condition or parameter is also called a medical test. ...
, intubation is usually performed after administration of general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
and a neuromuscular-blocking drug
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors.
In cl ...
. It can, however, be performed in the awake patient with local
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
* Local government, a form of public administration, usually the lowest tier of administrat ...
or topical anesthesia A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topi ...
or in an emergency without any anesthesia at all. Intubation is normally facilitated by using a conventional laryngoscope
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ge ...
, flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope, or video laryngoscope to identify the vocal cords
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech ...
and pass the tube between them into the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
instead of into the esophagus. Other devices and techniques may be used alternatively.
After the trachea has been intubated, a balloon cuff is typically inflated just above the far end of the tube to help secure it in place, to prevent leakage of respiratory gases, and to protect the tracheobronchial tree
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
from receiving undesirable material such as stomach acid. The tube is then secured to the face or neck and connected to a T-piece, anesthesia breathing circuit, bag valve mask
A bag valve mask (BVM), sometimes known by the proprietary name Ambu bag or generically as a manual resuscitator or "self-inflating bag", is a hand-held device commonly used to provide positive pressure ventilation to patients who are not breathi ...
device, or a mechanical ventilator
A ventilator is a piece of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators ...
. Once there is no longer a need for ventilatory assistance or protection of the airway, the tracheal tube is removed; this is referred to as extubation of the trachea (or decannulation, in the case of a surgical airway such as a cricothyrotomy or a tracheotomy).
For centuries, tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The ...
was considered the only reliable method for intubation of the trachea. However, because only a minority of patients survived the operation, physicians undertook tracheotomy only as a last resort, on patients who were nearly dead. It was not until the late 19th century, however, that advances in understanding of anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
, as well an appreciation of the germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade h ...
, had improved the outcome of this operation to the point that it could be considered an acceptable treatment option. Also at that time, advances in endoscopic
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
instrumentation had improved to such a degree that direct laryngoscopy had become a viable means to secure the airway by the non-surgical orotracheal route. By the mid-20th century, the tracheotomy as well as endoscopy and non-surgical tracheal intubation had evolved from rarely employed procedures to becoming essential components of the practices of anesthesiology
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, ...
, critical care medicine
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
, emergency medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for unsche ...
, and laryngology
Laryngology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders, diseases and injuries of the larynx, colloquially known as the voice box. Laryngologists treat disorders of the larynx, including diseases that affects the voice, swallowing, or upper a ...
.
Tracheal intubation can be associated with complications such as broken teeth or lacerations of the tissues of the upper airway. It can also be associated with potentially fatal complications such as pulmonary aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material such as pharyngeal secretions, food or drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the larynx (voice box) and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respira ...
of stomach contents which can result in a severe and sometimes fatal chemical aspiration pneumonitis, or unrecognized intubation of the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
which can lead to potentially fatal anoxia. Because of this, the potential for difficulty or complications due to the presence of unusual airway anatomy or other uncontrolled variables is carefully evaluated before undertaking tracheal intubation. Alternative strategies for securing the airway must always be readily available.
Indications
Tracheal intubation isindicated
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. There can be multiple indications to use a procedure or medication. An indication can commonly be confused with the term diagnosis. A diagnosis ...
in a variety of situations when illness or a medical procedure prevents a person from maintaining a clear airway, breathing, and oxygenating the blood. In these circumstances, oxygen supplementation using a simple face mask
The simple face mask (SFM) is a basic disposable mask, made of clear plastic, to provide oxygen therapy for patients who are experiencing conditions such as chest pain (possible heart attacks), dizziness, and minor hemorrhages. This mask is onl ...
is inadequate.
Depressed level of consciousness
Perhaps the most common indication for tracheal intubation is for the placement of a conduit through whichnitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a ...
or volatile anesthetics
An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vapor ...
may be administered. General anesthetic agents, opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid us ...
s, and neuromuscular-blocking drugs may diminish or even abolish the respiratory drive
The control of ventilation refers to the physiological mechanisms involved in the control of breathing, which is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Ventilation facilitates respiration. Respiration refers to the utilization of oxygen a ...
. Although it is not the only means to maintain a patent airway during general anesthesia, intubation of the trachea provides the most reliable means of oxygenation and ventilation
Ventilation may refer to:
* Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation
** Mechanical ventilation, in medicine, using artificial methods to assist breathing
*** Ventilator, a m ...
and the greatest degree of protection against regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration.
Damage to the brain (such as from a massive stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
, non-penetrating head injury, intoxication
Intoxication — or poisoning, especially by an alcoholic or narcotic substance — may refer to:
* Substance intoxication:
** Alcohol intoxication
** LSD intoxication
** Toxidrome
** Tobacco intoxication
** Cannabis intoxication
** Cocaine i ...
or poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
ing) may result in a depressed level of consciousness. When this becomes severe to the point of stupor or coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
(defined as a score on the Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury.
The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These thre ...
of less than 8), dynamic collapse of the extrinsic muscles of the airway can obstruct the airway, impeding the free flow of air into the lungs. Furthermore, protective airway reflexes such as cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three pha ...
ing and swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing i ...
may be diminished or absent. Tracheal intubation is often required to restore patency (the relative absence of blockage) of the airway and protect the tracheobronchial tree from pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents.
Hypoxemia
Intubation may be necessary for a patient with decreased oxygen content andoxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It ca ...
of the blood caused when their breathing is inadequate (hypoventilation
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia ...
), suspended (apnea
Apnea, BrE: apnoea, is the temporal cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the airways are ( patency), there ...
), or when the lungs are unable to sufficiently transfer gasses to the blood. Such patients, who may be awake and alert, are typically critically ill with a multisystem disease or multiple severe injuries. Examples of such conditions include cervical spine injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cor ...
, multiple rib fractures, severe pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
, acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
(ARDS), or near-drowning
Drowning is a type of suffocation induced by the submersion of the mouth and nose in a liquid. Most instances of fatal drowning occur alone or in situations where others present are either unaware of the victim's situation or unable to offer a ...
. Specifically, intubation is considered if the arterial
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pul ...
partial pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas ...
of oxygen (PaO2) is less than 60 millimeters of mercury
A millimetre of mercury is a manometric unit of pressure, formerly defined as the extra pressure generated by a column of mercury one millimetre high, and currently defined as exactly pascals. It is denoted mmHg or mm Hg.
Although not an S ...
(mm Hg) while breathing an inspired O2 concentration ( FIO2) of 50% or greater. In patients with elevated arterial carbon dioxide, an arterial partial pressure of CO2 (PaCO2) greater than 45 mm Hg in the setting of acidemia
Acidosis is a process causing increased acidity in the blood and other body tissues (i.e., an increase in hydrogen ion concentration). If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma.
The term ''acidemia'' describes t ...
would prompt intubation, especially if a series of measurements demonstrate a worsening respiratory acidosis
Respiratory acidosis is a state in which decreased ventilation (hypoventilation) increases the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood and decreases the blood's pH (a condition generally called acidosis).
Carbon dioxide is produced continuou ...
. Regardless of the laboratory values, these guidelines are always interpreted in the clinical context.
Airway obstruction
Actual or impending airway obstruction is a common indication for intubation of the trachea. Life-threatening airway obstruction may occur when aforeign body
A foreign body (FB) is any object originating outside the body of an organism. In machinery, it can mean any unwanted intruding object.
Most references to foreign bodies involve propulsion through natural orifices into hollow organs.
Foreign bo ...
becomes lodged in the airway; this is especially common in infants and toddlers. Severe blunt
Blunt may refer to:
* Blunt (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name)
* Blunt (cigar), a term used in the cigar industry to designate blunt-tipped, usually factory-rolled cigars
* Blunt (cannabis), a slang term used in cannabis cult ...
or penetrating injury to the face or neck may be accompanied by swelling and an expanding hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillary, capillaries. A he ...
, or injury to the larynx, trachea or bronchi. Airway obstruction is also common in people who have suffered smoke inhalation
Smoke inhalation is the breathing in of harmful fumes (produced as by-products of combusting substances) through the respiratory tract. This can cause smoke inhalation injury (subtype of acute inhalation injury) which is damage to the respirator ...
or burns within or near the airway or epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is the inflammation of the epiglottis—the flap at the base of the tongue that prevents food entering the trachea (windpipe). Symptoms are usually rapid in onset and include trouble swallowing which can result in drooling, changes t ...
. Sustained generalized seizure activity and angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling ( edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which ...
are other common causes of life-threatening airway obstruction which may require tracheal intubation to secure the airway.
Manipulation of the airway
Diagnostic or therapeutic manipulation of the airway (such as bronchoscopy,laser therapy
Laser medicine consists in the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery.
Lasers
Lasers used in medicine include in principle any type of laser, but ...
or stent
In medicine, a stent is a metal or plastic tube inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open, and stenting is the placement of a stent. A wide variety of stents are used for different purposes, from expandab ...
ing of the bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
) may intermittently interfere with the ability to breathe; intubation may be necessary in such situations.
Newborns
Syndromes such as respiratory distress syndrome,congenital heart disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular ...
, pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve ...
, and shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emergen ...
may lead to breathing problems in newborn infants that require endotracheal intubation and mechanically assisted breathing (mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air ...
). Newborn infants may also require endotracheal intubation during surgery while under general anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
.
Equipment
Laryngoscopes
 The vast majority of tracheal intubations involve the use of a
The vast majority of tracheal intubations involve the use of a viewing instrument
A viewing instrument is a type of optical instrument that is used to assist viewing or visually examining an object or scenery
Types
* binoculars
* contact lenses
* cystoscope
* electrotachyscope
* endoscope
* eyeglasses
* fibrescope
* findersc ...
of one type or another. The modern conventional laryngoscope consists of a handle containing batteries that power a light and a set of interchangeable blade
A blade is the portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with an edge that is designed to puncture, chop, slice or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are to be used on. Historic ...
s, which are either straight or curved. This device is designed to allow the laryngoscopist to directly view the larynx. Due to the widespread availability of such devices, the technique of blind intubation of the trachea is rarely practiced today, although it may still be useful in certain emergency situations, such as natural or man-made disasters. In the prehospital emergency setting, digital intubation may be necessitated if the patient is in a position that makes direct laryngoscopy impossible. For example, digital intubation may be used by a paramedic if the patient is entrapped in an inverted position in a vehicle after a motor vehicle collision with a prolonged extrication time.
The decision to use a straight or curved laryngoscope blade depends partly on the specific anatomical features of the airway, and partly on the personal experience and preference of the laryngoscopist. The Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and ...
blade is the most widely used curved laryngoscope blade, while the Miller blade is the most popular style of straight blade. Both Miller and Macintosh laryngoscope blades are available in sizes 0 (infant) through 4 (large adult). There are many other styles of straight and curved blades, with accessories such as mirrors for enlarging the field of view and even ports for the administration of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
. These specialty blades are primarily designed for use by anesthetists and otolaryngologists
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical a ...
, most commonly in the operating room
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
.
Fiberoptic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
laryngoscopes have become increasingly available since the 1990s. In contrast to the conventional laryngoscope, these devices allow the laryngoscopist to indirectly view the larynx. This provides a significant advantage in situations where the operator needs to see around an acute bend in order to visualize the glottis, and deal with otherwise difficult intubations. Video laryngoscopes are specialized fiberoptic laryngoscopes that use a digital video camera sensor to allow the operator to view the glottis and larynx on a video monitor. Other "noninvasive" devices which can be employed to assist in tracheal intubation are the laryngeal mask airway
A laryngeal mask airway (LMA), also known as laryngeal mask, is a medical device that keeps a patient's airway open during anaesthesia or while they are unconscious. It is a type of supraglottic airway device. They are most commonly used by anae ...
(used as a conduit for endotracheal tube placement) and the Airtraq
Airtraq is a fibreoptic intubation device used for indirect (video or optic assisted) tracheal intubation in difficult airway situations. It is designed to enable a view of the glottic opening without aligning the oral with the pharyngeal, and ...
.
Stylets
Seldinger technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organs. It is named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Swedish radiologist who introduced th ...
). As the Eschmann tracheal tube introducer is considerably less rigid than a conventional stylet, this technique is considered to be a relatively atraumatic means of tracheal intubation.
The tracheal tube exchanger is a hollow catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cath ...
, in length, that can be used for removal and replacement of tracheal tubes without the need for laryngoscopy. The Cook Airway Exchange Catheter (CAEC) is another example of this type of catheter; this device has a central lumen (hollow channel) through which oxygen can be administered. Airway exchange catheters are long hollow catheters which often have connectors for jet ventilation, manual ventilation, or oxygen insufflation. It is also possible to connect the catheter to a capnograph to perform respiratory monitoring.
The lighted stylet is a device that employs the principle of transillumination
Transillumination is the technique of sample illumination by transmission of light through the sample. Transillumination is used in a variety of methods of imaging.
Microscopy
In microscopy transillumination refers to the illumination of a sample ...
to facilitate blind orotracheal intubation (an intubation technique in which the laryngoscopist does not view the glottis).
Tracheal tubes
 A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent (open and unobstructed) airway. Tracheal tubes are frequently used for
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent (open and unobstructed) airway. Tracheal tubes are frequently used for airway management
Airway management includes a set of maneuvers and medical procedures performed to prevent and relieve airway obstruction. This ensures an open pathway for gas exchange between a patient's lungs and the atmosphere. This is accomplished by either cl ...
in the settings of general anesthesia, critical care, mechanical ventilation, and emergency medicine. Many different types of tracheal tubes are available, suited for different specific applications. An endotracheal tube is a specific type of tracheal tube that is nearly always inserted through the mouth (orotracheal) or nose (nasotracheal). It is a breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular ...
conduit designed to be placed into the airway of critically injured, ill or anesthetized patients in order to perform mechanical positive pressure ventilation
Modes of mechanical ventilation are one of the most important aspects of the usage of mechanical ventilation. The mode refers to the method of inspiratory support. In general, mode selection is based on clinician familiarity and institutional pref ...
of the lungs and to prevent the possibility of aspiration or airway obstruction. The endotracheal tube has a fitting designed to be connected to a source of pressurized gas such as oxygen. At the other end is an orifice through which such gases are directed into the lungs and may also include a balloon (referred to as a cuff). The tip of the endotracheal tube is positioned above the carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Osečina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
(before the trachea divides to each lung) and sealed within the trachea so that the lungs can be ventilated equally. A tracheostomy tube is another type of tracheal tube; this curved metal or plastic tube is inserted into a tracheostomy stoma
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bor ...
or a cricothyrotomy incision.
Tracheal tubes can be used to ensure the adequate exchange
Exchange may refer to:
Physics
*Gas exchange is the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Places United States
* Exchange, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* ...
of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
, to deliver oxygen in higher concentrations than found in air, or to administer other gases such as helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
, nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its che ...
, nitrous oxide, xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
, or certain volatile anesthetic agents such as desflurane
Desflurane (1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a highly fluorinated methyl ethyl ether used for maintenance of general anesthesia. Like halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, it is a racemic mixture of (''R'') and (''S'') optical i ...
, isoflurane
Isoflurane, sold under the brand name Forane among others, is a general anesthetic. It can be used to start or maintain anesthesia; however, other medications are often used to start anesthesia rather than isoflurane, due to airway irritation w ...
, or sevoflurane
Sevoflurane, sold under the brand name Sevorane, among others, is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflura ...
. They may also be used as a route for administration of certain medications such as bronchodilator
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lun ...
s, inhaled corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
, and drugs used in treating cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
such as atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given i ...
, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
, lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidoca ...
and vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
.
Originally made from latex rubber
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosper ...
, most modern endotracheal tubes today are constructed of polyvinyl chloride. Tubes constructed of silicone rubber Silicone rubber is an elastomer (rubber-like material) composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations ...
, wire-reinforced silicone rubber or stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ...
are also available for special applications. For human use, tubes range in size from in internal diameter. The size is chosen based on the patient's body size, with the smaller sizes being used for infants and children. Most endotracheal tubes have an inflatable cuff to seal the tracheobronchial tree against leakage of respiratory gases and pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents, blood, secretions, and other fluids. Uncuffed tubes are also available, though their use is limited mostly to children (in small children, the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
is the narrowest portion of the airway and usually provides an adequate seal for mechanical ventilation).
In addition to cuffed or uncuffed, preformed endotracheal tubes are also available. The oral and nasal RAE tubes (named after the inventors Ring, Adair and Elwyn) are the most widely used of the preformed tubes.
There are a number of different types of double-lumen endo-bronchial tube
A double-lumen endotracheal tube (also called double-lumen endobronchial tube or DLT) is a type of endotracheal tube which is used in tracheal intubation during thoracic surgery and other medical conditions to achieve selective, one-sided ventilat ...
s that have endobronchial as well as endotracheal channels (Carlens, White and Robertshaw tubes). These tubes are typically coaxial
In geometry, coaxial means that several three-dimensional linear or planar forms share a common axis. The two-dimensional analog is ''concentric''.
Common examples:
A coaxial cable is a three-dimensional linear structure. It has a wire conduc ...
, with two separate channels and two separate openings. They incorporate an endotracheal lumen which terminates in the trachea and an endobronchial lumen, the distal tip of which is positioned 1–2 cm into the right or left mainstem bronchus. There is also the Univent tube, which has a single tracheal lumen and an integrated endobronchial blocker. These tubes enable one to ventilate both lungs, or either lung independently. Single-lung ventilation (allowing the lung on the operative side to collapse) can be useful during thoracic surgery
Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart (heart disease), lungs (lung disease), and other pleural or mediastinal stru ...
, as it can facilitate the surgeon's view and access to other relevant structures within the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
.
The "armored" endotracheal tubes are cuffed, wire-reinforced silicone rubber tubes. They are much more flexible than polyvinyl chloride tubes, yet they are difficult to compress or kink. This can make them useful for situations in which the trachea is anticipated to remain intubated for a prolonged duration, or if the neck is to remain flexed during surgery. Most armored tubes have a Magill curve, but preformed armored RAE tubes are also available. Another type of endotracheal tube has four small openings just above the inflatable cuff, which can be used for suction of the trachea or administration of intratracheal medications if necessary. Other tubes (such as the Bivona Fome-Cuf tube) are designed specifically for use in laser surgery in and around the airway.
Methods to confirm tube placement

 No single method for confirming tracheal tube placement has been shown to be 100% reliable. Accordingly, the use of multiple methods for confirmation of correct tube placement is now widely considered to be the
No single method for confirming tracheal tube placement has been shown to be 100% reliable. Accordingly, the use of multiple methods for confirmation of correct tube placement is now widely considered to be the standard of care
In tort law, the standard of care is the only degree of prudence and caution required of an individual who is under a duty of care.
The requirements of the standard are closely dependent on circumstances. Whether the standard of care has been b ...
. Such methods include direct visualization as the tip of the tube passes through the glottis, or indirect visualization of the tracheal tube within the trachea using a device such as a bronchoscope. With a properly positioned tracheal tube, equal bilateral breath sounds
Respiratory sounds, also known as lung sounds or breath sounds, refer to the specific sounds generated by the movement of air through the respiratory system. These may be easily audible or identified through auscultation of the respiratory system ...
will be heard upon listening to the chest with a stethoscope, and no sound upon listening to the area over the stomach. Equal bilateral rise and fall of the chest wall will be evident with ventilatory excursions. A small amount of water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
will also be evident within the lumen of the tube with each exhalation and there will be no gastric contents in the tracheal tube at any time.
Ideally, at least one of the methods utilized for confirming tracheal tube placement will be a measuring instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Establ ...
. Waveform capnography
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide () in the respiratory gases. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care. It is usually presented as a ...
has emerged as the gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
for the confirmation of tube placement within the trachea. Other methods relying on instruments include the use of a colorimetric
Colorimetry is "the science and technology used to quantify and describe physically the human color perception".
It is similar to spectrophotometry, but is distinguished by its interest in reducing spectra to the physical correlates of color ...
end-tidal carbon dioxide detector, a self-inflating esophageal bulb, or an esophageal detection device. The distal tip of a properly positioned tracheal tube will be located in the mid-trachea, roughly above the bifurcation of the carina; this can be confirmed by chest x-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
. If it is inserted too far into the trachea (beyond the carina), the tip of the tracheal tube is likely to be within the right main bronchus
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts Atmosphere of Earth, air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the Carina of trachea, carina are the right ma ...
—a situation often referred to as a "right mainstem intubation". In this situation, the left lung may be unable to participate in ventilation, which can lead to decreased oxygen content due to ventilation/perfusion mismatch.
Special situations
Emergencies
Tracheal intubation in the emergency setting can be difficult with the fiberoptic bronchoscope due to blood, vomit, orsecretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical ...
s in the airway and poor patient cooperation. Because of this, patients with massive facial injury, complete upper airway obstruction, severely diminished ventilation, or profuse upper airway bleeding are poor candidates for fiberoptic intubation. Fiberoptic intubation under general anesthesia typically requires two skilled individuals. Success rates of only 83–87% have been reported using fiberoptic techniques in the emergency department, with significant nasal bleeding occurring in up to 22% of patients. These drawbacks limit the use of fiberoptic bronchoscopy somewhat in urgent and emergency situations.
Personnel experienced in direct laryngoscopy are not always immediately available in certain settings that require emergency tracheal intubation. For this reason, specialized devices have been designed to act as bridges to a definitive airway. Such devices include the laryngeal mask airway, cuffed oropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
airway and the esophageal-tracheal combitube (Combitube
The Combitube—also known as the esophageal tracheal airway or esophageal tracheal double-lumen airway—is a blind insertion airway device (BIAD) used in the pre-hospital and emergency setting.Jorge E. Zamora and Tarit K. Saha,Combitube rescue f ...
). Other devices such as rigid stylets, the lightwand (a blind technique) and indirect fiberoptic rigid stylets, such as the Bullard scope, Upsher scope and the WuScope can also be used as alternatives to direct laryngoscopy. Each of these devices have its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks, and none of them is effective under all circumstances.
Rapid-sequence induction and intubation
Rapid sequence induction and intubation (RSI) is a particular method of induction of general anesthesia, commonly employed in emergency operations and other situations where patients are assumed to have a full stomach. The objective of RSI is to minimize the possibility of regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents during the induction of general anesthesia and subsequent tracheal intubation. RSI traditionally involves preoxygenating the lungs with a tightly fitting oxygen mask, followed by the sequential administration of an intravenous sleep-inducing agent and a rapidly acting neuromuscular-blocking drug, such asrocuronium
Rocuronium bromide (brand names Zemuron, Esmeron) is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker or muscle relaxant used in modern anaesthesia to facilitate tracheal intubation by providing skeletal muscle relaxation, most commonly ...
, succinylcholine
Suxamethonium chloride, also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux by medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or ele ...
, or cisatracurium besilate, before intubation of the trachea.
One important difference between RSI and routine tracheal intubation is that the practitioner does not manually assist the ventilation of the lungs after the onset of general anesthesia and cessation of breathing, until the trachea has been intubated and the cuff has been inflated. Another key feature of RSI is the application of manual 'cricoid pressure Cricoid pressure, also known as the Sellick manoeuvre or Sellick maneuver, is a technique used in endotracheal intubation to try to reduce the risk of regurgitation. The technique involves the application of pressure to the cricoid cartilage at the ...
' to the cricoid cartilage, often referred to as the "Sellick maneuver", prior to instrumentation of the airway and intubation of the trachea.
Named for British anesthetist Brian Arthur Sellick (1918–1996) who first described the procedure in 1961, the goal of cricoid pressure is to minimize the possibility of regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents. Cricoid pressure has been widely used during RSI for nearly fifty years, despite a lack of compelling evidence to support this practice. The initial article by Sellick was based on a small sample size at a time when high tidal volume
Tidal volume (symbol VT or TV) is the volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during a normal breath. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 ml per inspiration or 7 ml/kg of body mass.
Mechanical vent ...
s, head-down positioning and barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as we ...
anesthesia were the rule. Beginning around 2000, a significant body of evidence has accumulated which questions the effectiveness of cricoid pressure. The application of cricoid pressure may in fact displace the esophagus laterally instead of compressing it as described by Sellick. Cricoid pressure may also compress the glottis, which can obstruct the view of the laryngoscopist and actually cause a delay in securing the airway.
Cricoid pressure is often confused with the "BURP" (Backwards Upwards Rightwards Pressure) maneuver. While both of these involve digital pressure to the anterior aspect (front) of the laryngeal apparatus, the purpose of the latter is to improve the view of the glottis during laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, rather than to prevent regurgitation. Both cricoid pressure and the BURP maneuver have the potential to worsen laryngoscopy.
RSI may also be used in prehospital emergency situations when a patient is conscious but respiratory failure is imminent (such as in extreme trauma). This procedure is commonly performed by flight paramedics. Flight paramedics often use RSI to intubate before transport because intubation in a moving fixed-wing or rotary-wing aircraft is extremely difficult to perform due to environmental factors. The patient will be paralyzed and intubated on the ground before transport by aircraft.
Cricothyrotomy
cricothyroid membrane
The cricothyroid ligament (also known as the cricothyroid membrane or cricovocal membrane) is a ligament in the neck. It connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. It prevents these cartilages from moving too far apart. It is cut dur ...
to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, or massive facial trauma. A cricothyrotomy is nearly always performed as a last resort in cases where orotracheal and nasotracheal intubation are impossible or contraindicated. Cricothyrotomy is easier and quicker to perform than tracheotomy, does not require manipulation of the cervical spine and is associated with fewer complications.
The easiest method to perform this technique is the needle cricothyrotomy (also referred to as a percutaneous {{More citations needed, date=January 2021
In surgery, a percutaneous procedurei.e. Granger et al., 2012 is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using ...
dilational cricothyrotomy), in which a large-bore (12–14 gauge
Gauge ( or ) may refer to:
Measurement
* Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments
* Gauge (firearms)
* Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire
** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, es ...
) intravenous catheter is used to puncture the cricothyroid membrane. Oxygen can then be administered through this catheter via jet insufflation. However, while needle cricothyrotomy may be life-saving in extreme circumstances, this technique is only intended to be a temporizing measure until a definitive airway can be established. While needle cricothyrotomy can provide adequate oxygenation, the small diameter of the cricothyrotomy catheter is insufficient for elimination of carbon dioxide (ventilation). After one hour of apneic oxygenation through a needle cricothyrotomy, one can expect a PaCO2 of greater than 250 mm Hg and an arterial pH of less than 6.72, despite an oxygen saturation of 98% or greater. A more definitive airway can be established by performing a surgical cricothyrotomy, in which a endotracheal tube or tracheostomy tube can be inserted through a larger incision.
Several manufacturers market prepackaged cricothyrotomy kits, which enable one to use either a wire-guided percutaneous dilational (Seldinger) technique, or the classic surgical technique to insert a polyvinylchloride catheter through the cricothyroid membrane. The kits may be stocked in hospital emergency departments and operating suites, as well as ambulances and other selected pre-hospital
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services or paramedic services, are emergency services that provide urgent pre-hospital treatment and stabilisation for serious illness and injuries and transport to definitive care. ...
settings.
Tracheotomy
Tracheotomy consists of making an incision on the front of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea. The resultingopening
Opening may refer to:
* Al-Fatiha, "The Opening", the first chapter of the Qur'an
* The Opening (album), live album by Mal Waldron
* Backgammon opening
* Chess opening
* A title sequence or opening credits
* , a term from contract bridge
* , ...
can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheostomy tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of his nose or mouth. The opening may be made by a scalpel or a needle (referred to as surgical and percutaneous techniques respectively) and both techniques are widely used in current practice. In order to limit the risk of damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and ...
s (the nerves that control the voice box), the tracheotomy is performed as high in the trachea as possible. If only one of these nerves is damaged, the patient's voice may be impaired (dysphonia
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice, can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
); if both of the nerves are damaged, the patient will be unable to speak ( aphonia). In the acute setting, indications for tracheotomy are similar to those for cricothyrotomy. In the chronic setting, indications for tracheotomy include the need for long-term mechanical ventilation and removal of tracheal secretions (e.g., comatose patients, or extensive surgery involving the head and neck).
Children
 There are significant differences in airway anatomy and respiratory physiology between children and adults, and these are taken into careful consideration before performing tracheal intubation of any
There are significant differences in airway anatomy and respiratory physiology between children and adults, and these are taken into careful consideration before performing tracheal intubation of any pediatric
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
patient. The differences, which are quite significant in infants, gradually disappear as the human body approaches a mature age and body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and he ...
.
For infants and young children, orotracheal intubation is easier than the nasotracheal route. Nasotracheal intubation carries a risk of dislodgement of adenoids
In anatomy, the adenoid, also known as the pharyngeal tonsil or nasopharyngeal tonsil, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphatic tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx, where the nose blend ...
and nasal bleeding. Despite the greater difficulty, nasotracheal intubation route is preferable to orotracheal intubation in children undergoing intensive care and requiring prolonged intubation because this route allows a more secure fixation of the tube. As with adults, there are a number of devices specially designed for assistance with difficult tracheal intubation in children. Confirmation of proper position of the tracheal tube is accomplished as with adult patients.
Because the airway of a child is narrow, a small amount of glottic or tracheal swelling can produce critical obstruction. Inserting a tube that is too large relative to the diameter of the trachea can cause swelling. Conversely, inserting a tube that is too small can result in inability to achieve effective positive pressure ventilation due to retrograde escape of gas through the glottis and out the mouth and nose (often referred to as a "leak" around the tube). An excessive leak can usually be corrected by inserting a larger tube or a cuffed tube.
The tip of a correctly positioned tracheal tube will be in the mid-trachea, between the collarbones on an anteroposterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
chest radiograph. The correct diameter of the tube is that which results in a small leak at a pressure of about of water. The appropriate inner diameter for the endotracheal tube is estimated to be roughly the same diameter as the child's little finger. The appropriate length for the endotracheal tube can be estimated by doubling the distance from the corner of the child's mouth to the ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
Struc ...
. For premature infants internal diameter is an appropriate size for the tracheal tube. For infants of normal gestational age
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Su ...
, internal diameter is an appropriate size. For normally nourished children 1 year of age and older, two formulae are used to estimate the appropriate diameter and depth for tracheal intubation. The internal diameter of the tube in mm is (patient's age in years + 16) / 4, while the appropriate depth of insertion in cm is 12 + (patient's age in years / 2).
Newborn infants
Endotrachael suctioning is often used during intubation in newborn infants to reduce the risk of a blocked tube due to secretions, a collapsed lung, and to reduce pain. Suctioning is sometimes used at specifically scheduled intervals, "as needed", and less frequently. Further research is necessary to determine the most effective suctioning schedule or frequency of suctioning in intubated infants. In newborns free flowoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
used to be recommended during intubation however as there is no evidence of benefit the 2011 NRP guidelines no longer do.
Predicting difficulty
 Tracheal intubation is not a simple procedure and the consequences of failure are grave. Therefore, the patient is carefully evaluated for potential difficulty or complications beforehand. This involves taking the
Tracheal intubation is not a simple procedure and the consequences of failure are grave. Therefore, the patient is carefully evaluated for potential difficulty or complications beforehand. This involves taking the medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other peo ...
of the patient and performing a physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patien ...
, the results of which can be scored against one of several classification systems. The proposed surgical procedure (e.g., surgery involving the head and neck, or bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery (or weight loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. Long term weight loss through the standard of care procedures ( Roux en-Y bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion ...
) may lead one to anticipate difficulties with intubation. Many individuals have unusual airway anatomy, such as those who have limited movement of their neck or jaw, or those who have tumors, deep swelling due to injury or to allergy, developmental abnormalities of the jaw, or excess fatty tissue of the face and neck. Using conventional laryngoscopic techniques, intubation of the trachea can be difficult or even impossible in such patients. This is why all persons performing tracheal intubation must be familiar with alternative techniques of securing the airway. Use of the flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope and similar devices has become among the preferred techniques in the management of such cases. However, these devices require a different skill set than that employed for conventional laryngoscopy and are expensive to purchase, maintain and repair.
When taking the patient's medical history, the subject is questioned about any significant signs or symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
s, such as difficulty in speaking or difficulty in breathing. These may suggest obstructing lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
s in various locations within the upper airway, larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
, or tracheobronchial tree. A history of previous surgery (e.g., previous cervical fusion), injury, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
, or tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s involving the head, neck and upper chest can also provide clues to a potentially difficult intubation. Previous experiences with tracheal intubation, especially difficult intubation, intubation for prolonged duration (e.g., intensive care unit) or prior tracheotomy are also noted.
A detailed physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patien ...
of the airway is important, particularly:
*the range of motion of the cervical spine
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sau ...
: the subject should be able to tilt the head back and then forward so that the chin touches the chest.
*the range of motion of the jaw (the temporomandibular joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that it ...
): three of the subject's fingers should be able to fit between the upper and lower incisors.
*the size and shape of the upper jaw
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
and lower jaw
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
, looking especially for problems such as maxillary hypoplasia
Maxillary hypoplasia, or maxillary deficiency, is an underdevelopment of the bones of the upper jaw. It is associated with Crouzon syndrome, Angelman syndrome, as well as Fetal alcohol syndrome. It can also be associated with Cleft lip and clef ...
(an underdeveloped upper jaw), micrognathia
Micrognathism is a condition where the jaw is undersized. It is also sometimes called mandibular hypoplasia. It is common in infants, but is usually self-corrected during growth, due to the jaws' increasing in size. It may be a cause of abnorm ...
(an abnormally small jaw), or retrognathia
Retrognathia is a type of malocclusion which refers to an abnormal posterior positioning of the maxilla or mandible, particularly the mandible, relative to the facial skeleton and soft tissues.
A retrognathic mandible is commonly referred to as a ...
(misalignment of the upper and lower jaw).
*the thyromental distance Thyromental distance (TMD) measurement is a method commonly used to predict the difficulty of Tracheal intubation, intubation and is measured from the Superior thyroid notch, thyroid notch to the tip of the jaw with the head extended. If it is less ...
: three of the subject's fingers should be able to fit between the Adam's apple and the chin.
*the size and shape of the tongue and palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sepa ...
relative to the size of the mouth.
*the teeth, especially noting the presence of prominent maxillary incisors, any loose or damaged teeth, or crowns
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
.
Many classification systems have been developed in an effort to predict difficulty of tracheal intubation, including the Cormack-Lehane classification system, the Intubation Difficulty Scale (IDS), and the Mallampati score
In anesthesia, the Mallampati score or Mallampati classification, named after the Indian anaesthesiologist Seshagiri Mallampati, is used to predict the ease of endotracheal intubation. The test comprises a visual assessment of the distance fro ...
. The Mallampati score is drawn from the observation that the size of the base of the tongue influences the difficulty of intubation. It is determined by looking at the anatomy of the mouth, and in particular the visibility of the base of palatine uvula
The palatine uvula, usually referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also conta ...
, faucial pillars
The fauces, isthmus of fauces, or the oropharyngeal isthmus, is the opening at the back of the mouth into the throat. It is a narrow passage between the velum and the base of the tongue.
The fauces is a part of the oropharynx directly behind the ...
and the soft palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. ...
. Although such medical scoring systems may aid in the evaluation of patients, no single score or combination of scores can be trusted to specifically detect all and only those patients who are difficult to intubate. Furthermore, one study of experienced anesthesiologists, on the widely used Cormack–Lehane classification system, found they did not score the same patients consistently over time, and that only 25% could correctly define all four grades of the widely used Cormack–Lehane classification system. Under certain emergency circumstances (e.g., severe head trauma or suspected cervical spine injury), it may be impossible to fully utilize these the physical examination and the various classification systems to predict the difficulty of tracheal intubation. A recent Cochrane systematic review examined the sensitivity and specificity of various bedside tests commonly used for predicting difficulty in airway management. In such cases, alternative techniques of securing the airway must be readily available.
Complications
Tracheal intubation is generally considered the best method for airway management under a wide variety of circumstances, as it provides the most reliable means of oxygenation and ventilation and the greatest degree of protection against regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration. However, tracheal intubation requires a great deal of clinical experience to master and serious complications may result even when properly performed. Four anatomic features must be present for orotracheal intubation to be straightforward: adequate mouth opening (full range of motion of the temporomandibular joint), sufficient pharyngeal space (determined by examining the back of the mouth), sufficient submandibular space (distance between the thyroid cartilage and the chin, the space into which the tongue must be displaced in order for the larygoscopist to view the glottis), and adequate extension of the cervical spine at the atlanto-occipital joint. If any of these variables is in any way compromised, intubation should be expected to be difficult. Minor complications are common after laryngoscopy and insertion of an orotracheal tube. These are typically of short duration, such as sore throat, lacerations of the lips orgums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue linin ...
or other structures within the upper airway, chipped, fractured or dislodged teeth, and nasal injury. Other complications which are common but potentially more serious include accelerated or irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, elevated intracranial
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull minus the mandible is called the ''cranium''. The cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in ...
and introcular pressure, and bronchospasm
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release (degranulation) of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylatoxins. It causes di ...
.
More serious complications include laryngospasm
Laryngospasm is an uncontrolled or involuntary muscular contraction (spasm) of the vocal folds. The condition typically lasts less than 60 seconds, but in cases partial blocking it may last 20 to 30 minutes and hinder inspiration, while exhala ...
, perforation of the trachea or esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
, pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents or other foreign bodies, fracture or dislocation of the cervical spine, temporomandibular joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that it ...
or arytenoid cartilage
The arytenoid cartilages () are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoid ...
s, decreased oxygen content, elevated arterial carbon dioxide, and vocal cord weakness. In addition to these complications, tracheal intubation via the nasal route carries a risk of dislodgement of adenoids and potentially severe nasal bleeding. Newer technologies such as flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy have fared better in reducing the incidence of some of these complications, though the most frequent cause of intubation trauma remains a lack of skill on the part of the laryngoscopist.
Complications may also be severe and long-lasting or permanent, such as vocal cord damage, esophageal perforation and retropharyngeal abscess
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA) is an abscess located in the tissues in the back of the throat behind the posterior pharyngeal wall (the retropharyngeal space). Because RPAs typically occur in deep tissue, they are difficult to diagnose by physical ...
, bronchial intubation, or nerve injury. They may even be immediately life-threatening, such as laryngospasm and negative pressure pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
(fluid in the lungs), aspiration, unrecognized esophageal intubation, or accidental disconnection or dislodgement of the tracheal tube. Potentially fatal complications more often associated with prolonged intubation or tracheotomy include abnormal communication between the trachea and nearby structures such as the innominate artery
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.
It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachio ...
(tracheoinnominate fistula
A fistula (plural: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") in anatomy is an abnormal connection between two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow or ...
) or esophagus (tracheoesophageal fistula
A tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF, or TOF; see spelling differences) is an abnormal connection (fistula) between the esophagus and the trachea. TEF is a common congenital abnormality, but when occurring late in life is usually the sequela of surgic ...
). Other significant complications include airway obstruction due to loss of tracheal rigidity, ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of lung infection that occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation breathing machines in hospitals. As such, VAP typically affects critically ill persons that are in an intensive care unit (I ...
and narrowing of the glottis or trachea. The cuff pressure is monitored carefully in order to avoid complications from over-inflation, many of which can be traced to excessive cuff pressure restricting the blood supply to the tracheal mucosa. A 2000 Spanish study of bedside percutaneous tracheotomy reported overall complication rates of 10–15% and procedural mortality of 0%, which is comparable to those of other series reported in the literature from the Netherlands and the United States.
Inability to secure the airway, with subsequent failure of oxygenation and ventilation is a life-threatening complication which if not immediately corrected leads to decreased oxygen content, brain damage, cardiovascular collapse
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thi ...
, and death. When performed improperly, the associated complications (e.g., unrecognized esophageal intubation) may be rapidly fatal. Without adequate training and experience, the incidence of such complications is high. The case of Andrew Davis Hughes, from Emerald Isle, NC is a widely known case in which the patient was improperly intubated and, due to the lack of oxygen, sustained severe brain damage and died. For example, among paramedic
A paramedic is a registered healthcare professional who works autonomously across a range of health and care settings and may specialise in clinical practice, as well as in education, leadership, and research.
Not all ambulance personnel are p ...
s in several United States urban communities, unrecognized esophageal or hypopharyngeal intubation has been reported to be 6% to 25%. Although not common, where basic emergency medical technician
An emergency medical technician (EMT), also known as an ambulance technician, is a health professional that provides emergency medical services. EMTs are most commonly found working in ambulances. In English-speaking countries, paramedics are ...
s are permitted to intubate, reported success rates are as low as 51%. In one study, nearly half of patients with misplaced tracheal tubes died in the emergency room. Because of this, recent editions of the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
's ''Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation'' have de-emphasized the role of tracheal intubation in favor of other airway management techniques such as bag-valve-mask ventilation, the laryngeal mask airway and the Combitube. However, recent higher quality studies have shown no survival or neurological benefit with endotracheal intubation over supraglottic airway devices (Laryngeal mask or Combitube).
One complication—unintentional and unrecognized intubation of the esophagus—is both common (as frequent as 25% in the hands of inexperienced personnel) and likely to result in a deleterious or even fatal outcome. In such cases, oxygen is inadvertently administered to the stomach, from where it cannot be taken up by the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, instead of the lungs. If this situation is not immediately identified and corrected, death will ensue from cerebral and cardiac anoxia.
Of 4,460 claims in the American Society of Anesthesiologists
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) is an educational, research and scientific association of physicians organized to raise the standards of the medical practice of anesthesiology and to improve patient care.
As of 2021, the organizat ...
(ASA) Closed Claims Project database, 266 (approximately 6%) were for airway injury. Of these 266 cases, 87% of the injuries were temporary, 5% were permanent or disabling, and 8% resulted in death. Difficult intubation, age older than 60 years, and female gender were associated with claims for perforation of the esophagus or pharynx. Early signs of perforation were present in only 51% of perforation claims, whereas late sequelae
A sequela (, ; usually used in the plural, sequelae ) is a pathological condition resulting from a disease, injury, therapy, or other trauma. Derived from the Latin word, meaning “sequel”, it is used in the medical field to mean a complication ...
occurred in 65%.
During the SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''sever ...
and COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
s, tracheal intubation has been used with a ventilator
A ventilator is a piece of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators ...
in severe cases where the patient struggles to breathe. Performing the procedure carries a risk of the caregiver becoming infected.
Alternatives
Although it offers the greatest degree of protection against regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration, tracheal intubation is not the only means to maintain a patent airway. Alternative techniques for airway management and delivery of oxygen, volatile anesthetics or otherbreathing gas
A breathing gas is a mixture of gaseous chemical elements and compounds used for respiration. Air is the most common and only natural breathing gas, but other mixtures of gases, or pure oxygen, are also used in breathing equipment and enclosed h ...
es include the laryngeal mask airway
A laryngeal mask airway (LMA), also known as laryngeal mask, is a medical device that keeps a patient's airway open during anaesthesia or while they are unconscious. It is a type of supraglottic airway device. They are most commonly used by anae ...
, i-gel, cuffed oropharyngeal airway, continuous positive airway pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The ap ...
(CPAP mask), nasal BiPAP
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alter ...
mask, simple face mask, and nasal cannula.
General anesthesia is often administered without tracheal intubation in selected cases where the procedure is brief in duration, or procedures where the depth of anesthesia is not sufficient to cause significant compromise in ventilatory function. Even for longer duration or more invasive procedures, a general anesthetic may be administered without intubating the trachea, provided that patients are carefully selected, and the risk-benefit ratio is favorable (i.e., the risks associated with an unprotected airway are believed to be less than the risks of intubating the trachea).
Airway management can be classified into closed or open techniques depending on the system of ventilation used. Tracheal intubation is a typical example of a closed technique as ventilation occurs using a closed circuit. Several open techniques exist, such as spontaneous ventilation, apnoeic ventilation or jet ventilation. Each has its own specific advantages and disadvantages which determine when it should be used.
Spontaneous ventilation has been traditionally performed with an inhalational agent (i.e. gas induction or inhalational induction using halothane or sevoflurane) however it can also be performed using intravenous anaesthesia (e.g. propofol, ketamine or dexmedetomidine). SponTaneous Respiration using IntraVEnous anaesthesia and High-flow nasal oxygen (STRIVE Hi) is an open airway technique that uses an upwards titration of propofol which maintains ventilation at deep levels of anaesthesia. It has been used in airway surgery as an alternative to tracheal intubation.
History
;Tracheotomy The earliest known depiction of a tracheotomy is found on two Egyptian tablets dating back to around 3600 BC. The 110-page Ebers Papyrus, an Egyptian medical papyrus which dates to roughly 1550 BC, also makes reference to the tracheotomy. Tracheotomy was described in theRigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Sh ...
, a Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
text of ayurvedic medicine
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
written around 2000 BC in ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
. The Sushruta Samhita
The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (सुश्रुतसंहिता, IAST: ''Suśrutasaṃhitā'', literally "Suśruta's Compendium") is an ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and surgery, and one of the most important such treatises on this subj ...
from around 400 BC is another text from the Indian subcontinent on ayurvedic medicine and surgery that mentions tracheotomy. Asclepiades of Bithynia (–40 BC) is often credited as being the first physician to perform a non-emergency tracheotomy. Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a ...
(AD 129–199) clarified the anatomy of the trachea and was the first to demonstrate that the larynx generates the voice. In one of his experiments, Galen used bellows to inflate the lungs of a dead animal. Ibn Sīnā
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic ...
(980–1037) described the use of tracheal intubation to facilitate breathing in 1025 in his 14-volume medical encyclopedia, ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
''. In the 12th century medical textbook ''Al-Taisir'', Ibn Zuhr
Abū Marwān ‘Abd al-Malik ibn Zuhr ( ar, أبو مروان عبد الملك بن زهر), traditionally known by his Latinized name Avenzoar (; 1094–1162), was an Arab physician, surgeon, and poet. He was born at Seville in medieval And ...
(1092–1162)—also known as Avenzoar—of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, ...
provided a correct description of the tracheotomy operation.
The first detailed descriptions of tracheal intubation and subsequent artificial respiration of animals were from Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' '' ...
(1514–1564) of Brussels. In his landmark book published in 1543, ''De humani corporis fabrica
''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (Latin, lit. "On the fabric of the human body in seven books") is a set of books on human anatomy written by Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) and published in 1543. It was a major advance in the history ...
'', he described an experiment in which he passed a reed
Reed or Reeds may refer to:
Science, technology, biology, and medicine
* Reed bird (disambiguation)
* Reed pen, writing implement in use since ancient times
* Reed (plant), one of several tall, grass-like wetland plants of the order Poales
* ...
into the trachea of a dying animal whose thorax had been opened and maintained ventilation by blowing into the reed intermittently. Antonio Musa Brassavola
Antonio Musa Brassavola (variously spelled Brasavoli, Brasavola, or Brasavoli; 16 January 1500 – 1555) was an Italian physician and one of the most famous of his time. He studied under Niccolò Leoniceno and Giovanni Manardo. He was the friend an ...
(1490–1554) of Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream ...
successfully treated a patient with peritonsillar abscess
Peritonsillar abscess (PTA), also known as quinsy, is an accumulation of pus due to an infection behind the tonsil. Symptoms include fever, throat pain, trouble opening the mouth, and a change to the voice. Pain is usually worse on one side. Com ...
by tracheotomy. Brassavola published his account in 1546; this operation has been identified as the first recorded successful tracheotomy, despite the many previous references to this operation. Towards the end of the 16th century, Hieronymus Fabricius
Girolamo Fabrici d'Acquapendente, also known as Girolamo Fabrizio or Hieronymus Fabricius (20 May 1533 – 21 May 1619), was a pioneering anatomist and surgeon known in medical science as "The Father of Embryology."
Life and accomplishments ...
(1533–1619) described a useful technique for tracheotomy in his writings, although he had never actually performed the operation himself. In 1620 the French surgeon Nicholas Habicot (1550–1624) published a report of four successful tracheotomies. In 1714, anatomist Georg Detharding (1671–1747) of the University of Rostock
The University of Rostock (german: link=no, Universität Rostock) is a public university located in Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. Founded in 1419, it is the third-oldest university in Germany. It is the oldest university in continen ...
performed a tracheotomy on a drowning victim.
Despite the many recorded instances of its use since antiquity, it was not until the early 19th century that the tracheotomy finally began to be recognized as a legitimate means of treating severe airway obstruction. In 1852, French physician Armand Trousseau
Armand Trousseau (14 October 1801 – 23 June 1867) was a French internist. His contributions to medicine include Trousseau sign of malignancy, Trousseau sign of latent tetany, Trousseau–Lallemand bodies (an archaic synonym for Bence Jones ...
(1801–1867) presented a series of 169 tracheotomies to the Académie Impériale de Médecine. 158 of these were performed for the treatment of croup
Croup, also known as laryngotracheobronchitis, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms o ...
, and 11 were performed for "chronic maladies of the larynx". Between 1830 and 1855, more than 350 tracheotomies were performed in Paris, most of them at the Hôpital des Enfants Malades, a public hospital
A public hospital, or government hospital, is a hospital which is government owned and is fully funded by the government and operates solely off the money that is collected from taxpayers to fund healthcare initiatives. In some countries, this typ ...
, with an overall survival rate of only 20–25%. This compares with 58% of the 24 patients in Trousseau's private practice, who fared better due to greater postoperative care.
In 1871, the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg
Friedrich Trendelenburg (; 24 May 184415 December 1924) was a German surgeon. He was son of the philosophy, philosopher Friedrich Adolf Trendelenburg, father of the pharmacology, pharmacologist Paul Trendelenburg and grandfather of the pharmaco ...
(1844–1924) published a paper describing the first successful elective human tracheotomy to be performed for the purpose of administration of general anesthesia. In 1888, Sir Morell Mackenzie
Sir Morell Mackenzie (7 July 1837 – 3 February 1892) was a British physician, one of the pioneers of laryngology in the United Kingdom.
Biography
Morell Mackenzie was born at Leytonstone, Essex, England on 7 July 1837. He was the eldest of ni ...
(1837–1892) published a book discussing the indications for tracheotomy. In the early 20th century, tracheotomy became a life-saving treatment for patients affected with paralytic poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe sym ...
who required mechanical ventilation. In 1909, Philadelphia laryngologist Chevalier Jackson
Chevalier Quixote Jackson (November 4, 1865 – August 16, 1958) was an American pioneer in laryngology. He is sometimes known as the "father of endoscopy", although Philipp Bozzini (1773–1809) is also often given this sobriquet. Chevalier Q. J ...
(1865–1958) described a technique for tracheotomy that is used to this day.
;Laryngoscopy and non-surgical techniques
 In 1854, a Spanish
In 1854, a Spanish singing teacher
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how proper singing technique is accomplished.
Vocal pedagogy covers a ...
named Manuel García (1805–1906) became the first man to view the functioning glottis in a living human. In 1858, French pediatrician Eugène Bouchut (1818–1891) developed a new technique for non-surgical orotracheal intubation to bypass laryngeal obstruction resulting from a diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
-related pseudomembrane. In 1880, Scottish surgeon William Macewen
Sir William Macewen, (; 22 June 1848 – 22 March 1924) was a Scottish surgeon. He was a pioneer in modern brain surgery, considered the ''father of neurosurgery'' and contributed to the development of bone graft surgery, the surgical treat ...
(1848–1924) reported on his use of orotracheal intubation as an alternative to tracheotomy to allow a patient with glottic edema to breathe, as well as in the setting of general anesthesia with chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to ...
. In 1895, Alfred Kirstein
Alfred may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*'' Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series
* ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne
* ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák
*"Alfred (Interl ...
(1863–1922) of Berlin first described direct visualization of the vocal cords, using an esophagoscope he had modified for this purpose; he called this device an autoscope.
In 1913, Chevalier Jackson was the first to report a high rate of success for the use of direct laryngoscopy as a means to intubate the trachea. Jackson introduced a new laryngoscope blade that incorporated a component that the operator could slide out to allow room for passage of an endotracheal tube or bronchoscope. Also in 1913, New York surgeon Henry H. Janeway (1873–1921) published results he had achieved using a laryngoscope he had recently developed. Another pioneer in this field was Sir Ivan Whiteside Magill (1888–1986), who developed the technique of awake blind nasotracheal intubation, the Magill forceps, the Magill laryngoscope blade, and several apparati for the administration of volatile anesthetic agents. The Magill curve of an endotracheal tube is also named for Magill. Sir Robert Macintosh
Sir Robert Reynolds Macintosh (17 October 1897, Timaru, New Zealand – 28 August 1989, Oxford, England) was a New Zealand-born British anaesthetist. He was the first professor of anaesthetics outside the United States.
Early life
Macintosh w ...
(1897–1989) introduced a curved laryngoscope blade in 1943; the Macintosh blade remains to this day the most widely used laryngoscope blade for orotracheal intubation.
Between 1945 and 1952, optical engineers
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
built upon the earlier work of Rudolph Schindler (1888–1968), developing the first gastrocamera. In 1964, optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
technology was applied to one of these early gastrocameras to produce the first flexible fiberoptic endoscope. Initially used in upper GI endoscopy, this device was first used for laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation by Peter Murphy, an English anesthetist, in 1967. The concept of using a stylet for replacing or exchanging orotracheal tubes was introduced by Finucane and Kupshik in 1978, using a central venous catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more central ...
.
By the mid-1980s, the flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope had become an indispensable instrument within the pulmonology and anesthesia communities. The digital revolution of the 21st century has brought newer technology to the art and science of tracheal intubation. Several manufacturers have developed video laryngoscopes which employ digital technology Digital technology may refer to:
* Application of digital electronics
* Any significant piece of knowledge from information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange a ...
such as the CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFE ...
active pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effec ...
(CMOS APS) to generate a view of the glottis so that the trachea may be intubated.
See also
*Intratracheal instillation
Intratracheal instillation is the introduction of a substance directly into the trachea. It is widely used to test the respiratory toxicity of a substance as an alternative to inhalation in animal testing. Intratracheal instillation was reporte ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Video of endotracheal intubation using C-MAC D-blade and bougie used as introducer.
Videos of direct laryngoscopy recorded with the Airway Cam (TM) imaging system
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110619231642/http://www.equipmentexplained.com/physics/airway/ett/endotracheal_tubes.html Free image rich resource explaining various types of endotracheal tubes
Tracheal intubation live case 2022
{{Good article Airway management Anesthesia Emergency medical procedures First aid Intensive care medicine Medical equipment Oral and maxillofacial surgery Otorhinolaryngology Respiratory system procedures Respiratory therapy Medical treatments