Treaty Of Sèvres on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the
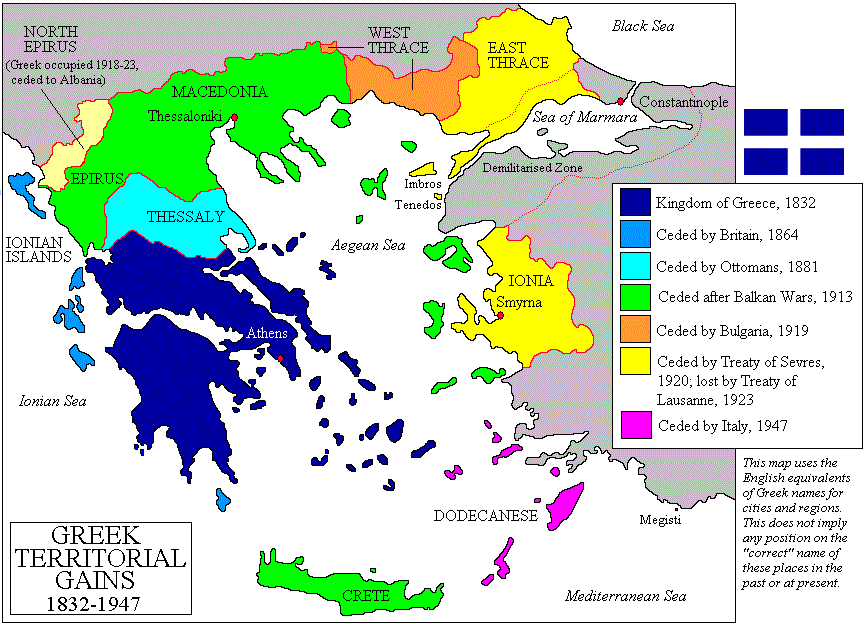 The Greek government administered the occupation of Smyrna from 21 May 1919. A
The Greek government administered the occupation of Smyrna from 21 May 1919. A
 A Zone of the Straits was proposed to include the
A Zone of the Straits was proposed to include the
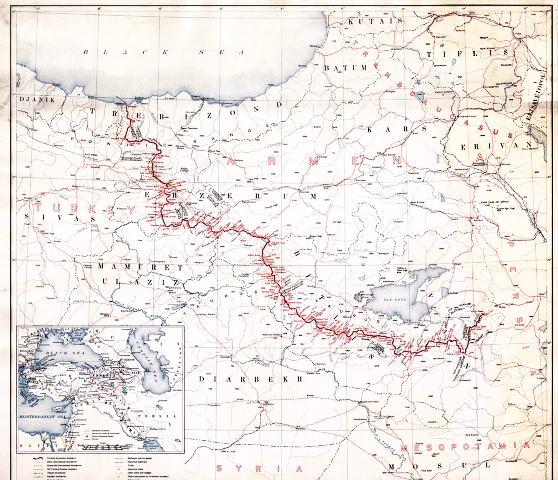 Armenia was recognised as a "free and independent" state in Section VI "Armenia", Articles 88-93. By Article 89, "Turkey and Armenia, as well as the other High Contracting Parties agree to submit to the arbitration of the President of the United States of America the question of the frontier to be fixed between Turkey and Armenia in the vilayets of Erzerum, Trebizond, Van and Bitlis, and to accept his decision thereupon, as well as any stipulations he may prescribe as to access for Armenia to the sea, and as to the demilitarisation of any portion of Turkish territory adjacent to the said frontier".
The treaty specified that the frontiers between Armenia and Azerbaijan and Georgia were to be determined by direct negotiation between those states, with the Principle Allied Powers making the decision if those states fail to agree.
Armenia was recognised as a "free and independent" state in Section VI "Armenia", Articles 88-93. By Article 89, "Turkey and Armenia, as well as the other High Contracting Parties agree to submit to the arbitration of the President of the United States of America the question of the frontier to be fixed between Turkey and Armenia in the vilayets of Erzerum, Trebizond, Van and Bitlis, and to accept his decision thereupon, as well as any stipulations he may prescribe as to access for Armenia to the sea, and as to the demilitarisation of any portion of Turkish territory adjacent to the said frontier".
The treaty specified that the frontiers between Armenia and Azerbaijan and Georgia were to be determined by direct negotiation between those states, with the Principle Allied Powers making the decision if those states fail to agree.
Treaty of Peace between the British Empire and Allied Powers and Turkey
UK Treaty Series No. 11 of 1920;
online
* Karčić, Hamza. "Sèvres at 100: The Peace Treaty that Partitioned the Ottoman Empire." ''Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs'' (Sept 2020) 40#3 pp 470-479. https://doi.org/10.1080/13602004.2020.1813988 * Macfie, A. L. “The British Decision Regarding the Future of Constantinople, November 1918-January 1920.” ''Historical Journal'' 18#2 (1975), pp. 391–400
online
* Montgomery, A. E. "The Making of the Treaty of Sevres of 10 August 1920." ''Historical Journal'' 15#4 (1972): 775-87
online
* Sion, Abraham. "To Whom Was the Promised Land Promised?" (Mazo, 2020) * Toynbee, A. J. ''The Western Question in Greece and Turkey'' (London, 1922
online
440pp
Text of the Treaty of Sèvres
!
->
Treaty text and mapsTreaty of Sevres bordersTripartite Agreement between the British Empire, France and Italy Respecting Anatolia 10 August, 1920
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Treaty of Sevres 1920 in Armenia 1920 in France 1920 in the Ottoman Empire Adana vilayet Adrianople vilayet Aftermath of World War I in Turkey Aidin Vilayet Aleppo vilayet Bitlis vilayet Eleftherios Venizelos David Lloyd George Woodrow Wilson Erzurum vilayet Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922) History of Kurdistan Modern history of Turkey History of Palestine (region) Hüdavendigâr vilayet Konya vilayet Mamuret-ul-Aziz vilayet Ottoman Empire–United Kingdom relations Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920) Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sivas vilayet Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Trebizond vilayet Sevres Van vilayet Sevres
 The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman E ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well as creating large occupation zones within the Ottoman Empire. It was one of a series of treaties that the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
signed with the Allied Powers after their defeat in World War I. Hostilities had already ended with the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by ...
.
The treaty was signed on 10 August 1920 in an exhibition room at the Manufacture nationale de Sèvres porcelain factory in Sèvres, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
.
The Treaty of Sèvres marked the beginning of the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire. The treaty's stipulations included the renunciation of most territory not inhabited by Turkish people
The Turkish people, or simply the Turks ( tr, Türkler), are the world's largest Turkic ethnic group; they speak various dialects of the Turkish language and form a majority in Turkey and Northern Cyprus. In addition, centuries-old ethnic Tu ...
and their cession to the Allied administration.
The ceding of Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to comm ...
lands saw the introduction of novel polities, including the British Mandate for Palestine
The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British administration of the territories of Palestine and Transjordan, both of which had been conceded by the Ottoman Empire following the end of World War I in 1918. The mandat ...
and the French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon.
The terms stirred hostility and Turkish nationalism. The treaty's signatories were stripped of their citizenship by the Grand National Assembly, led by Mustafa Kemal Pasha, which ignited the Turkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
. Atatürk led the Turkish nationalists in the war, but fear of British reinforcements arriving at Chanak led him to accept an Allied invitation to negotiate a peace at Mudanya with the signatories of the Treaty of Sèvres. The 1923 Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conf ...
, which superseded the Treaty of Sèvres, ended the conflict and saw the establishment of the Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula i ...
.
Summary
Parties
George Dixon Grahame
Sir George Dixon Grahame (28 April 1873 – 9 July 1940) was a British diplomat.
Life
Grahame was the only son of Richard Grahame of Alderley Edge, and was educated at Charterhouse, in Hodgsonite House, between summer 1887 and autumn 1888.
...
signed for the United Kingdom, Alexandre Millerand for France and Count Lelio Longare for Italy. One Allied power, Greece, did not accept the borders as drawn, mainly because of the political change after the 1920 Greek legislative election and so never ratified the treaty. There were three signatories for the Ottoman Empire:
# Ex-Ambassador Hadi Pasha,
# Ex-Minister of Education Rıza Tevfik Bölükbaşı,
# Second secretary of the Ottoman embassy in Bern, Reşad Halis.
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
was not a party to the treaty because it had negotiated the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
with the Ottoman Empire in 1918.
The Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
was signed with the German Empire before the Treaty of Sèvres and annulled German concessions in the Ottoman sphere, including economic rights and enterprises.
Also, France, Britain, and Italy signed a Tripartite Agreement on the same date. It confirmed Britain's oil and commercial concessions and turned the former German enterprises in the Ottoman Empire over to a tripartite corporation.
The United States, having refused in the Senate to assume a League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for adminis ...
over Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
, decided not to participate in the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire. The US wanted a permanent peace as quickly as possible, with financial compensation for its military expenditure. However, after the Senate rejected the Armenian mandate, the only US hope was its inclusion in the treaty by the influential Greek Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos ( el, Ελευθέριος Κυριάκου Βενιζέλος, translit=Elefthérios Kyriákou Venizélos, ; – 18 March 1936) was a Greeks, Greek statesman and a prominent leader of the Greek national liberati ...
.
Provisions
upright=1.4, Original map from 1920 illustrating the Treaty of Sèvres region (not depicting the zones of influences) The treaty imposed a number of territorial losses on Turkey and had a number of provisions that applied to the territory recognised as belonging to Turkey.Non-territorial
Financial restrictions
The Allies were to control the Ottoman Empire's finances, such as approving and supervising the national budget, implementing financial laws and regulations and totally controlling the Ottoman Bank. The Ottoman Public Debt Administration, instituted in 1881, was redesigned to include only British, French, and Italian bondholders. The Ottoman debt problem had dated back to the time of theCrimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included t ...
(1854–1856) during which the Ottoman Empire had borrowed money from abroad, mainly from France. Also the capitulations of the Ottoman Empire
Capitulations of the Ottoman Empire were contracts between the Ottoman Empire and other powers in Europe, particularly France. Turkish capitulations, or Ahidnâmes were generally bilateral acts whereby definite arrangements were entered into ...
, which had been abolished in 1914 by Talaat Pasha
Mehmed Talaat (1 September 187415 March 1921), commonly known as Talaat Pasha or Talat Pasha,; tr, Talat Paşa, links=no was an Ottoman politician and convicted war criminal of the late Ottoman Empire who served as its leader from 1913 t ...
, were restored.
The empire was required to grant freedom of transit to people, goods, vessels etc. passing through its territory, and goods in transit were to be free of all customs duties. Future changes to the tax system, the customs system, internal and external loans, import and export duties and concessions would need the consent of the financial commission of the Allied Powers to be implemented. To forestall the economic repenetration of Germany, Austria, Hungary or Bulgaria, the treaty demanded the empire to liquidate the property of citizens of those countries living within its territories. The public liquidation was to be organized by the Reparations Commission. Property rights of the Baghdad Railway
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesipho ...
were to pass from German control.
Military restrictions
TheOttoman Army
The military of the Ottoman Empire ( tr, Osmanlı İmparatorluğu'nun silahlı kuvvetleri) was the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire.
Army
The military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the ...
was to be restricted to 50,700 men, and the Ottoman Navy could maintain only seven sloops
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular ...
and six torpedo boats. The Ottoman Empire was prohibited from creating an air force. The treaty included an interallied commission of control and organisation to supervise the execution of the military clauses.
International trials
The treaty required determination of those responsible for theArmenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
. Article 230 of the Treaty of Sèvres required the Ottoman Empire to "hand over to the Allied Powers the persons whose surrender may be required by the latter as being responsible for the massacres committed during the continuance of the state of war on territory which formed part of the Ottoman Empire on August 1, 1914". However, the inter-allied tribunal attempt After World War I, the effort to prosecute Ottoman war criminals was taken up by the Paris Peace Conference (1919) and ultimately included in the Treaty of Sèvres (1920) with the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman government organized a series of courts ...
to prosecute war criminals as demanded by the Treaty of Sèvres was eventually suspended, and the men who orchestrated the genocide escaped prosecution and traveled relatively freely throughout Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
. Power, Samantha. '' A Problem from Hell'', p. 16–17. Basic Books, 2002.
Foreign zones of influence
France
Within the territory retained by Turkey under the treaty, France received Syria and neighbouring parts of southeasternAnatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
, including Antep, Urfa
Urfa, officially known as Şanlıurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features e ...
and Mardin
Mardin ( ku, Mêrdîn; ar, ماردين; syr, ܡܪܕܝܢ, Merdīn; hy, Մարդին) is a city in southeastern Turkey. The capital of Mardin Province, it is known for the Artuqid architecture of its old city, and for its strategic location ...
. Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian language, Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from th ...
, including Adana
Adana (; ; ) is a major city in southern Turkey. It is situated on the Seyhan River, inland from the Mediterranean Sea. The administrative seat of Adana province, it has a population of 2.26 million.
Adana lies in the heart of Cilicia, ...
, Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır (; ; ; ) is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.
Situated around a high plateau by the banks of the Tigris river on which stands the historic Diyarbakır Fortress, ...
and large portions of east-central Anatolia all the way north to Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
and Tokat
Tokat is the capital city of Tokat Province of Turkey in the mid-Black Sea region of Anatolia. It is located at the confluence of the Tokat River (Tokat Suyu) with the Yeşilırmak. In the 2018 census, the city of Tokat had a population of 155,0 ...
, were declared a zone of French influence.
Greece
 The Greek government administered the occupation of Smyrna from 21 May 1919. A
The Greek government administered the occupation of Smyrna from 21 May 1919. A protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inte ...
was established on 30 July 1922. The treaty transferred "the exercise of her rights of sovereignty to a local parliament" but left the region within the Ottoman Empire. The treaty had Smyrna to be administered by a local parliament, with a plebiscite overseen by the League of Nations after five years to decide if Smyrna's citizens wished to join Greece or to remain in the Ottoman Empire. The treaty accepted Greek administration of the Smyrna enclave, but the area remained under Turkish sovereignty. To protect the Christian population from attacks by the Turkish irregulars, the Greek army expanded its jurisdiction also to nearby cities creating the so-called "Smyrna Zone".
Italy
Italy was formally given possession of the Dodecanese Islands, which had been under Italian occupation since the Italo-Turkish War of 1911–1912 despite the Treaty of Ouchy according to which Italy should have returned the islands to the Ottoman Empire. Large portions of southern and west-centralAnatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
, including the port city of Antalya
Antalya () is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey as well as the capital of Antalya Province. Located on Anatolia's southwest coast bordered by the Taurus Mountains, Antalya is the largest Turkish city on the Mediterranean coast outside the Ae ...
and the historic Seljuk capital of Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
, were declared to be an Italian zone of influence. Antalya Province had been promised by the Triple Entente to Italy in the Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
, and the Italian colonial authorities wished the zone to become an Italian colony under the name of Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is t ...
.
Territorial provisions
Zone of the Straits
 A Zone of the Straits was proposed to include the
A Zone of the Straits was proposed to include the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
, the Dardanelles and the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the ...
. Navigation would be open in the Dardanelles in times of peace and war alike to all vessels of commerce and war, regardless of flag. That would effectively lead to the internationalisation of the waters, which were not to be subject to blockade, and no act of war could be committed there except to enforce decisions of the League of Nations.
Free zones
Certain ports were to be declared to be of international importance. The League of Nations insisted on the complete freedom and the absolute equality in treatment at such ports, particularly regarding charges and facilities, to ensure that economic provisions in commercially-strategic places were carried out. The regions were to be called "free zones". The ports wereConstantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
from San Stefano to Dolmabahçe, Haidar-Pasha, Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to promi ...
, Alexandretta, Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropoli ...
, Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
, Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
and Batum.
Thrace
Eastern Thrace (up to the Chatalja line), the islands ofImbros
Imbros or İmroz Adası, officially Gökçeada (lit. ''Heavenly Island'') since 29 July 1970,Alexis Alexandris, "The Identity Issue of The Minorities in Greece And Turkey", in Hirschon, Renée (ed.), ''Crossing the Aegean: An Appraisal of the 1 ...
and Tenedos
Tenedos (, ''Tenedhos'', ), or Bozcaada in Turkish, is an island of Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively, the island constitutes the Bozcaada district of Çanakkale Province. With an area of it is the third lar ...
and the islands of the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the ...
were ceded to Greece. The waters surrounding the islands were declared international territory and left to the administration of the "Zone of the Straits".
Kurdistan
TheKurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages ...
region, including Mosul Province, was scheduled to have a referendum to decide its fate.
There was no general agreement among Kurds on what the borders of Kurdistan should be because of the disparity between the areas of Kurdish settlement and the political and administrative boundaries of the region. The outlines of Kurdistan as an entity had been proposed in 1919 by Şerif Pasha
Mehmet Şerif Pasha (1865, Üsküdar, Istanbul - December 22, 1951; Catanzaro, Italy), a founding member of Kurd Society for Cooperation and Progress and representative of the Society for the Elevation of Kurdistan to the Paris Peace Conference (1 ...
, who represented the Society for the Elevation of Kurdistan (''Kürdistan Teali Cemiyeti'') at the Paris Peace Conference Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include:
Listed by name
Paris Accords
may refer to:
* Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germ ...
. He defined the region's boundaries as follows:
The frontiers of Turkish Kurdistan, from an ethnographical point of view, begin in the north at Ziven, on the Caucasian frontier, and continue westwards toThat caused controversy among other Kurdish nationalists, as it excluded the Van Region (possibly as a sop toErzurum Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010. The city uses t ..., Erzincan, Kemah, Arapgir,Besni Besni ( ku, Bêsnî) is a town and district of Adıyaman Province of Turkey, 44 km west of the city of Adıyaman. History The city was historically known as Bahasna. It was controlled by the Byzantines until it was captured by the Umayyad arm ...and Divick ( Divrik?); in the south they follow the line fromHarran Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, Kάρραι, Kárrhai), is a rural town and district of the Şanlıurfa Province in southeastern Turkey, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa and 20 kilometers from the border cr ..., Sinjar Mountains, Tel Asfar,Erbil Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000. H ..., Süleymaniye, Akk-el-man, Sinne; in the east, Ravandiz, Başkale, Vezirkale, that is to say the frontier ofPersia Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...as far asMount Ararat Mount Ararat or , ''Ararat''; or is a snow-capped and dormant compound volcano in the extreme east of Turkey. It consists of two major volcanic cones: Greater Ararat and Little Ararat. Greater Ararat is the highest peak in Turkey and the ....
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
claims to that region). Emin Ali Bedir Khan proposed an alternative map that included Van and an outlet to the sea via what is now Turkey's Hatay Province
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of ...
. Amid a joint declaration by Kurdish and Armenian delegations, Kurdish claims concerning Erzurum vilayet and Sassoun ( Sason) were dropped, but arguments for sovereignty over Ağrı and Muş remained.
Neither proposal was endorsed by the treaty of Sèvres, which outlined a truncated Kurdistan on what is now Turkish territory (leaving out the Kurds of Iran, British-controlled Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and French-controlled Syria). The current Iraqi–Turkish border was agreed upon in July 1926.
Article 63 explicitly granted the full safeguard and protection to the Assyro-Chaldean minority, but that provision was dropped in the Treaty of Lausanne.
Armenia
 Armenia was recognised as a "free and independent" state in Section VI "Armenia", Articles 88-93. By Article 89, "Turkey and Armenia, as well as the other High Contracting Parties agree to submit to the arbitration of the President of the United States of America the question of the frontier to be fixed between Turkey and Armenia in the vilayets of Erzerum, Trebizond, Van and Bitlis, and to accept his decision thereupon, as well as any stipulations he may prescribe as to access for Armenia to the sea, and as to the demilitarisation of any portion of Turkish territory adjacent to the said frontier".
The treaty specified that the frontiers between Armenia and Azerbaijan and Georgia were to be determined by direct negotiation between those states, with the Principle Allied Powers making the decision if those states fail to agree.
Armenia was recognised as a "free and independent" state in Section VI "Armenia", Articles 88-93. By Article 89, "Turkey and Armenia, as well as the other High Contracting Parties agree to submit to the arbitration of the President of the United States of America the question of the frontier to be fixed between Turkey and Armenia in the vilayets of Erzerum, Trebizond, Van and Bitlis, and to accept his decision thereupon, as well as any stipulations he may prescribe as to access for Armenia to the sea, and as to the demilitarisation of any portion of Turkish territory adjacent to the said frontier".
The treaty specified that the frontiers between Armenia and Azerbaijan and Georgia were to be determined by direct negotiation between those states, with the Principle Allied Powers making the decision if those states fail to agree.
British Mandate for Iraq
The details in the treaty regarding the British Mandate for Iraq were completed on 25 April 1920 at the San Remo Conference. The oil concession in the region was given to the British-controlledTurkish Petroleum Company
The Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC), formerly known as the Turkish Petroleum Company (TPC), is an oil company that had a virtual monopoly on all oil exploration and production in Iraq between 1925 and 1961. It is jointly owned by some of the world's ...
(TPC), which had held concessionary rights to Mosul Province. British and Iraqi negotiators held acrimonious discussions over the new oil concession. The League of Nations voted on the disposition of Mosul, and the Iraqis feared that without British support, Iraq would lose the area. In March 1925, the TPC was renamed the " Iraq Petroleum Company" (IPC) and granted a full and complete concession for 75 years.
British Mandate for Palestine
The three principles of the BritishBalfour Declaration
The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing its support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, then an Ottoman regio ...
regarding Palestine were adopted in the Treaty of Sèvres:
:Article 95: The High Contracting Parties agree to entrust, by application of the provisions of Article 22, the administration of Palestine, within such boundaries as may be determined by the Principal Allied Powers, to a Mandatory to be selected by the said Powers. The Mandatory will be responsible for putting into effect the declaration originally made on 2 November 1917 by the British Government, and adopted by the other Allied Powers, in favour of the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people, it being clearly understood that nothing shall be done which may prejudice the civil and religious rights of existing non-Jewish communities in Palestine, or the rights and political status enjoyed by Jews in any other country.
French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon
The French Mandate was settled at the San Remo Conference and comprised the region between the Euphrates River and theSyrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ar, بادية الشام ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert and steppe covering of the Middle East, including parts of so ...
on the east and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
on the west, and it extended from the Nur Mountains in the north to Egypt in the south, an area of about with a population of about 3,000,000, including the Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
and an enlarged Syria, both of which were later reassigned under a League of Nations Mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for adminis ...
. The region was divided under the French into four governments as follows: Government of Aleppo, from the Euphrates region to the Mediterranean; Great Lebanon, extending from Tripoli to Palestine; Damascus, including Damascus, Hama, Hems and the Hauran; and the country of Mount Arisarieh. Faisal ibn Husayn, who had been proclaimed king of Syria by a Syrian National Congress in Damascus in March 1920, was ejected by the French in July the same year. The next year, he became king of Iraq.
Kingdom of Hejaz
The Kingdom of Hejaz, on the Arabian Peninsula, was granted international recognition and had an estimated area of and a population of about 750,000. The main cities were the Holy Places of Makka, with a population of 80,000, and Medina, with a population of 40,000. Under the Ottomans, it had been the vilayet of Hejaz, but during the war, it became an independent kingdom under British influence.Abandonment
The Treaty of Sèvres imposed terms on the Ottoman Empire that were far more severe than those imposed on the German Empire by the Treaty of Versailles. France, Italy and Britain had secretly begun planning the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire as early as 1915. The open negotiations covered a period of more than 15 months, started at theParis Peace Conference of 1919
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, continued at the Conference of London of February 1920 and took definite shape only after the San Remo Conference in April 1920. The delay occurred because the powers could not come to an agreement, which, in turn, hinged on the outcome of the Turkish National Movement
The Turkish National Movement ( tr, Türk Ulusal Hareketi) encompasses the political and military activities of the Turkish revolutionaries that resulted in the creation and shaping of the modern Republic of Turkey, as a consequence of the defe ...
. The Treaty of Sèvres was never ratified, and after the Turkish War of Independence, most of the Treaty of Sèvres's signatories signed and ratified the Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conf ...
in 1923 and 1924.
While the Treaty of Sèvres was still under discussion, the Turkish national movement under Mustafa Kemal Pasha split with the monarchy, based in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, and set up a Turkish Grand National Assembly
The Grand National Assembly of Turkey ( tr, ), usually referred to simply as the TBMM or Parliament ( tr, or ''Parlamento''), is the unicameral Turkish legislature. It is the sole body given the legislative prerogatives by the Turkish Consti ...
in Ankara in April 1920. He demanded for the Turks to fight against the Greeks, who were trying to take the land that had been held by the Ottoman Empire and given to Greece in the treaty. That started the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
The Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922, ota, گرب جابهاسی, Garb Cebhesi) in Turkey, and the Asia Minor Campaign ( el, Μικρασιατική Εκστρατεία, Mikrasiatikí Ekstrateía) or the Asia Minor Catastrophe ( el, Μικ ...
, which resulted in a Turkish victory.
On 18 October, the government of Damat Ferid Pasha was replaced by a provisional one under Ahmed Tevfik Pasha
Ahmet Tevfik Pasha ( ota, احمد توفیق پاشا; 11 February 1845 – 8 October 1936), later Ahmet Tevfik Okday after the Turkish Surname Law of 1934, was an Ottoman statesman of Crimean Tatar origin. He was the last Grand vizie ...
as Grand Vizier, who announced an intention to convene the Senate to ratify the Treaty of Sèvres if national unity was achieved. That required seeking the co-operation of Mustafa Kemal, who expressed disdain for the treaty and started a military assault. As a result, the Turkish government issued a note to the Entente that the ratification of the treaty was impossible at the time.
Eventually, Mustafa Kemal succeeded in his War of Independence and forced most of the former wartime Allies to return to the negotiating table.
Aside from Mustafa Kemal's armed opposition to the treaty in Anatolia, Arabs in Syria were unwilling to accept French rule, the Turks around Mosul attacked the British and Arabs were up in arms against British rule in Baghdad. There was also disorder in Egypt.
Subsequent treaties
During theTurkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
, the Turkish Army successfully fought Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
and French forces and secured the independence of a territory similar to that of present-day Turkey, as was aimed at by the Misak-ı Milli.
The Turkish national movement developed its own international relations with the Treaty of Moscow with Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
on 16 March 1921, the Accord of Ankara with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
putting an end to the Franco-Turkish War, the Treaty of Alexandropol
The Treaty of Alexandropol ( hy, Ալեքսանդրապոլի պայմանագիր; tr, Gümrü Anlaşması) was a peace treaty between the First Republic of Armenia and the Grand National Assembly of Turkey. The treaty ended the Turkish-Armenian ...
with the Armenians and the Treaty of Kars
The Treaty of Kars ( tr, Kars Antlaşması, rus, Карсский договор, Karskii dogovor, ka, ყარსის ხელშეკრულება, hy, Կարսի պայմանագիր, az, Qars müqaviləsi) was a treaty that est ...
to fix the eastern borders.
Hostilities with Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
over the neutral zone of the Straits were narrowly avoided in the Chanak Crisis of September 1922, when the Armistice of Mudanya was concluded on 11 October, leading the former Allies of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman E ...
to return to the negotiating table with the Turks in November 1922. That culminated in 1923 in the Treaty of Lausanne, which replaced the Treaty of Sèvres and restored a large territory in Anatolia and Thrace to the Turks. Under the Treaty of Lausanne, France and Italy had only areas of economic interaction, rather than zones of influence. Constantinople was not made an international city, and a demilitarised zone between Turkey and Bulgaria was established.Bendeck, Whitney. "Pyrrhic Victory Achieved." Lecture, Europe in the Total Age of War, Florida State University, Tallahassee, October 11, 2016.
See also
* Sèvres syndrome *Paris Peace Conference Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include:
Listed by name
Paris Accords
may refer to:
* Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germ ...
* Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
* Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye
* Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine (french: Traité de Neuilly-sur-Seine) required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly ...
* Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formal ...
* Minority Treaties
The Minority Treaties are treaties, League of Nations mandates, and unilateral declarations made by countries applying for membership in the League of Nations that conferred basic rights on all the inhabitants of the country without distinction ...
References
Treaty of Peace between the British Empire and Allied Powers and Turkey
UK Treaty Series No. 11 of 1920;
Command paper
A command paper is a document issued by the Government of the United Kingdom, UK Government and presented to Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament.
White papers, green papers, treaty, treaties, government responses, draft bills, reports fr ...
Cmd.964
Notes
Further reading
* Darwin, John, and Beverley Nielsen. ''Britain, Egypt and the Middle East: Imperial policy in the aftermath of war 1918–1922'' (Springer, 1981). * * Helmreich, Paul C. ''From Paris to Sèvres: the partition of the Ottoman Empire at the Peace Conference of 1919-1920'' (Ohio State UP, 1974). * Howard, Harry N. ''The Partition of Turkey'' (U of Oklahoma Press, I93ionline
* Karčić, Hamza. "Sèvres at 100: The Peace Treaty that Partitioned the Ottoman Empire." ''Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs'' (Sept 2020) 40#3 pp 470-479. https://doi.org/10.1080/13602004.2020.1813988 * Macfie, A. L. “The British Decision Regarding the Future of Constantinople, November 1918-January 1920.” ''Historical Journal'' 18#2 (1975), pp. 391–400
online
* Montgomery, A. E. "The Making of the Treaty of Sevres of 10 August 1920." ''Historical Journal'' 15#4 (1972): 775-87
online
* Sion, Abraham. "To Whom Was the Promised Land Promised?" (Mazo, 2020) * Toynbee, A. J. ''The Western Question in Greece and Turkey'' (London, 1922
online
440pp
External links
Text of the Treaty of Sèvres
!
->
Treaty text and maps
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Treaty of Sevres 1920 in Armenia 1920 in France 1920 in the Ottoman Empire Adana vilayet Adrianople vilayet Aftermath of World War I in Turkey Aidin Vilayet Aleppo vilayet Bitlis vilayet Eleftherios Venizelos David Lloyd George Woodrow Wilson Erzurum vilayet Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922) History of Kurdistan Modern history of Turkey History of Palestine (region) Hüdavendigâr vilayet Konya vilayet Mamuret-ul-Aziz vilayet Ottoman Empire–United Kingdom relations Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920) Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sivas vilayet Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Sevres Trebizond vilayet Sevres Van vilayet Sevres