Touch Kimchay on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position ( proprioception), and
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position ( proprioception), and
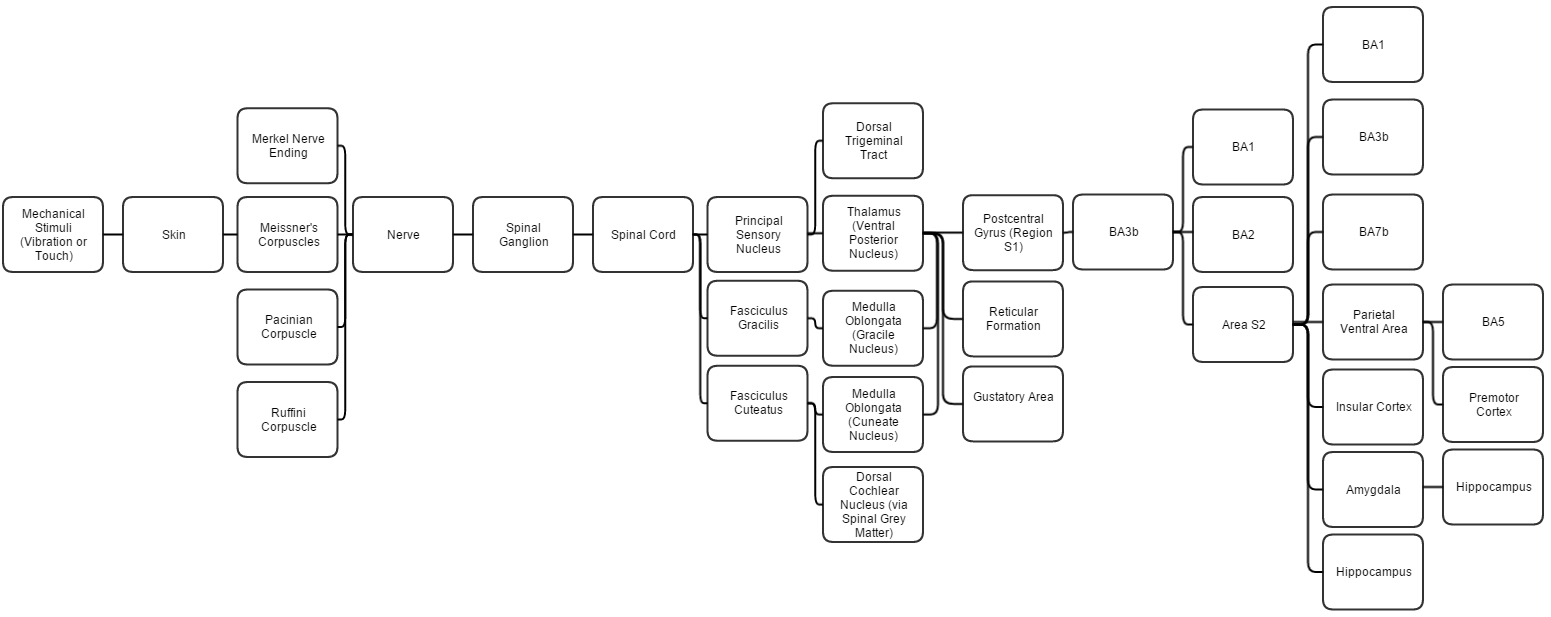
 The postcentral gyrus includes the primary somatosensory cortex ( Brodmann areas 3, 2 and 1) collectively referred to as S1.
BA3 receives the densest projections from the thalamus. BA3a is involved with the sense of relative position of neighboring body parts and amount of effort being used during movement. BA3b is responsible for distributing somatosensory information, it projects texture information to BA1 and shape and size information to BA2.
Region S2 ( secondary somatosensory cortex) divides into Area S2 and parietal ventral area. Area S2 is involved with specific touch perception and is thus integrally linked with the amygdala and hippocampus to encode and reinforce memories.
Parietal ventral area is the somatosensory relay to the premotor cortex and somatosensory memory hub, BA5.
The postcentral gyrus includes the primary somatosensory cortex ( Brodmann areas 3, 2 and 1) collectively referred to as S1.
BA3 receives the densest projections from the thalamus. BA3a is involved with the sense of relative position of neighboring body parts and amount of effort being used during movement. BA3b is responsible for distributing somatosensory information, it projects texture information to BA1 and shape and size information to BA2.
Region S2 ( secondary somatosensory cortex) divides into Area S2 and parietal ventral area. Area S2 is involved with specific touch perception and is thus integrally linked with the amygdala and hippocampus to encode and reinforce memories.
Parietal ventral area is the somatosensory relay to the premotor cortex and somatosensory memory hub, BA5.
 Photoreceptors, similar to those found in the retina of the
Photoreceptors, similar to those found in the retina of the
 Fine touch (or discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows a subject to sense and localize touch. The form of touch where localization is not possible is known as crude touch. The posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway is the pathway responsible for the sending of fine touch information to the cerebral cortex of the brain.
Crude touch (or non-discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows the subject to sense that something has touched them, without being able to localize where they were touched (contrasting "fine touch"). Its fibres are carried in the spinothalamic tract, unlike the fine touch, which is carried in the dorsal column.
As fine touch normally works in parallel to crude touch, a person will be able to localize touch until fibres carrying fine touch ( Posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway) have been disrupted. Then the subject will feel the touch, but be unable to identify where they were touched.
Fine touch (or discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows a subject to sense and localize touch. The form of touch where localization is not possible is known as crude touch. The posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway is the pathway responsible for the sending of fine touch information to the cerebral cortex of the brain.
Crude touch (or non-discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows the subject to sense that something has touched them, without being able to localize where they were touched (contrasting "fine touch"). Its fibres are carried in the spinothalamic tract, unlike the fine touch, which is carried in the dorsal column.
As fine touch normally works in parallel to crude touch, a person will be able to localize touch until fibres carrying fine touch ( Posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway) have been disrupted. Then the subject will feel the touch, but be unable to identify where they were touched.
Neurobiology: Feeling bumps and holes
News and Views, Nature, 2001 July 26;412(6845):389-91. * * * * * Grunwald, M. (Ed.) ''Human Haptic Perception – Basics and Applications.'' Boston/Basel/Berlin: Birkhäuser, 2008,
Encyclopedia of Touch
Scholarpedia Expert articles
Anatomy of Touch
Factual documentary series by BBC Radio 4. {{DEFAULTSORT:Somatosensory System
 In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position ( proprioception), and
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position ( proprioception), and pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
, and gustatory stimuli.
Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, co ...
). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through peripheral sensory neurons in the cranial nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and ...
s, such as the trigeminal nerve.
The neural pathways that go to the brain are structured such that information about the location of the physical stimulus is preserved. In this way, neighboring neurons in the somatosensory cerebral cortex in the brain represent nearby locations on the skin or in the body, creating a map, also called a cortical homunculus.
System overview

Sensory receptors
The fourmechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, ...
s in the skin each respond to different stimuli for short or long periods.
Merkel cell nerve endings are found in the basal epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
and hair follicles
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
; they react to low vibrations (5–15 Hz) and deep static touch such as shapes and edges. Due to having a small receptive field (extremely detailed information), they are used in areas like fingertips the most; they are not covered (shelled) and thus respond to pressures over long periods.
Tactile corpuscles react to moderate vibration (10–50 Hz) and light touch. They are located in the dermal papillae; due to their reactivity, they are primarily located in fingertips and lips. They respond in quick action potentials, unlike Merkel nerve endings. They are responsible for the ability to read Braille and feel gentle stimuli.
Pacinian corpuscles determine gross touch and distinguish rough and soft substances. They react in quick action potentials, especially to vibrations around 250 Hz (even up to centimeters away). They are the most sensitive to vibrations and have large receptor fields. Pacinian corpuscles react only to sudden stimuli so pressures like clothes that are always compressing their shape are quickly ignored. They have also been implicated in detecting the location of touch sensations on handheld tools.
Bulbous corpuscles react slowly and respond to sustained skin stretch. They are responsible for the feeling of object slippage and play a major role in the kinesthetic sense and control of finger position and movement. Merkel and bulbous cells - slow-response - are myelinated; the rest - fast-response - are not. All of these receptors are activated upon pressures that squish their shape causing an action potential.
Somatosensory cortex
 The postcentral gyrus includes the primary somatosensory cortex ( Brodmann areas 3, 2 and 1) collectively referred to as S1.
BA3 receives the densest projections from the thalamus. BA3a is involved with the sense of relative position of neighboring body parts and amount of effort being used during movement. BA3b is responsible for distributing somatosensory information, it projects texture information to BA1 and shape and size information to BA2.
Region S2 ( secondary somatosensory cortex) divides into Area S2 and parietal ventral area. Area S2 is involved with specific touch perception and is thus integrally linked with the amygdala and hippocampus to encode and reinforce memories.
Parietal ventral area is the somatosensory relay to the premotor cortex and somatosensory memory hub, BA5.
The postcentral gyrus includes the primary somatosensory cortex ( Brodmann areas 3, 2 and 1) collectively referred to as S1.
BA3 receives the densest projections from the thalamus. BA3a is involved with the sense of relative position of neighboring body parts and amount of effort being used during movement. BA3b is responsible for distributing somatosensory information, it projects texture information to BA1 and shape and size information to BA2.
Region S2 ( secondary somatosensory cortex) divides into Area S2 and parietal ventral area. Area S2 is involved with specific touch perception and is thus integrally linked with the amygdala and hippocampus to encode and reinforce memories.
Parietal ventral area is the somatosensory relay to the premotor cortex and somatosensory memory hub, BA5.
BA5
The BA postcode area, also known as the Bath postcode area,Royal Mail, ''Address Management Guide'', (2004) is a group of nineteen postcode districts in South West England, within sixteen post towns. These cover east Somerset (including Bath, Y ...
is the topographically organized somato memory field and association area.
BA1 processes texture info while BA2 processes size and shape information.
Area S2 processes light touch, pain, visceral sensation, and tactile attention.
S1 processes the remaining info (crude touch, pain, temperature).
BA7 integrates visual and proprioceptive info to locate objects in space.
The insular cortex (insula) plays a role in the sense of bodily-ownership, bodily self-awareness, and perception. Insula also plays a role in conveying info about sensual touch, pain, temperature, itch, and local oxygen status. Insula is a highly connected relay and thus is involved in numerous functions.
Structure
The somatosensory system is spread through all major parts of the vertebrate body. It consists both ofsensory receptor
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell ...
s and sensory neurons in the periphery (skin, muscle and organs for example), to deeper neurons within the central nervous system.
General somatosensory pathway
All afferent touch/vibration info ascends the spinal cord via the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway via gracilis (T7 and below) or cuneatus (T6 and above). Cuneatus sends signals to the cochlear nucleus indirectly via spinal grey matter, this info is used in determining if a perceived sound is just villi noise/irritation. All fibers cross (left becomes right) in the medulla. A somatosensory pathway will typically have three neurons: first-order, second-order, and third-order. # The first-order neuron is a type of pseudounipolar neuron and always has itscell body
The soma (pl. ''somata'' or ''somas''), perikaryon (pl. ''perikarya''), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek '' σῶμ ...
in the dorsal root ganglion
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsa ...
of the spinal nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into th ...
with a peripheral axon innervating touch mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, ...
s and a central axon synapsing on the second-order neuron. If the somatosensory pathway is in parts of the head or neck not covered by the cervical nerves, the first-order neuron will be the trigeminal nerve ganglia or the ganglia of other sensory cranial nerves).
# The second-order neuron has its cell body
The soma (pl. ''somata'' or ''somas''), perikaryon (pl. ''perikarya''), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek '' σῶμ ...
either in the spinal cord or in the brainstem. This neuron's ascending axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, th ...
will cross (decussate
Decussation is used in biological contexts to describe a crossing (due to the shape of the Roman numeral for ten, an uppercase 'X' (), ). In Latin anatomical terms, the form is used, e.g. .
Similarly, the anatomical term chiasma is named aft ...
) to the opposite side either in the spinal cord or in the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
.
# In the case of touch and certain types of pain, the third-order neuron has its cell body
The soma (pl. ''somata'' or ''somas''), perikaryon (pl. ''perikarya''), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek '' σῶμ ...
in the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus and ends in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe in the primary somatosensory cortex (or S1).
 Photoreceptors, similar to those found in the retina of the
Photoreceptors, similar to those found in the retina of the eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
, detect potentially damaging ultraviolet radiation ( ultraviolet A specifically), inducing increased production of melanin by melanocytes
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and heart.
...
. Thus tanning potentially offers the skin rapid protection from DNA damage and sunburn caused by ultraviolet radiation (DNA damage caused by ultraviolet B). However, whether this offers protection is debatable, because the amount of melanin released by this process is modest in comparison to the amounts released in response to DNA damage caused by ultraviolet B radiation.
Tactile feedback
The tactile feedback from proprioception is derived from the proprioceptors in the skin, muscles, and joints.Balance
The receptor for the sense of balance resides in thevestibular system
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes ...
in the ear (for the three-dimensional orientation of the head, and by inference, the rest of the body). Balance is also mediated by the kinesthetic reflex fed by proprioception (which senses the relative location of the rest of the body to the head). In addition, proprioception estimates the location of objects which are sensed by the visual system (which provides confirmation of the place of those objects relative to the body), as input to the mechanical reflexes of the body.
Fine touch and crude touch
 Fine touch (or discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows a subject to sense and localize touch. The form of touch where localization is not possible is known as crude touch. The posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway is the pathway responsible for the sending of fine touch information to the cerebral cortex of the brain.
Crude touch (or non-discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows the subject to sense that something has touched them, without being able to localize where they were touched (contrasting "fine touch"). Its fibres are carried in the spinothalamic tract, unlike the fine touch, which is carried in the dorsal column.
As fine touch normally works in parallel to crude touch, a person will be able to localize touch until fibres carrying fine touch ( Posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway) have been disrupted. Then the subject will feel the touch, but be unable to identify where they were touched.
Fine touch (or discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows a subject to sense and localize touch. The form of touch where localization is not possible is known as crude touch. The posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway is the pathway responsible for the sending of fine touch information to the cerebral cortex of the brain.
Crude touch (or non-discriminative touch) is a sensory modality that allows the subject to sense that something has touched them, without being able to localize where they were touched (contrasting "fine touch"). Its fibres are carried in the spinothalamic tract, unlike the fine touch, which is carried in the dorsal column.
As fine touch normally works in parallel to crude touch, a person will be able to localize touch until fibres carrying fine touch ( Posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway) have been disrupted. Then the subject will feel the touch, but be unable to identify where they were touched.
Neural processing of social touch
The somatosensory cortex encodes incoming sensory information from receptors all over the body. Affective touch is a type of sensory information that elicits an emotional reaction and is usually social in nature, such as a physical human touch. This type of information is actually coded differently than other sensory information. Intensity of affective touch is still encoded in the primary somatosensory cortex and is processed in a similar way to emotions invoked by sight and sound, as exemplified by the increase of adrenaline caused by the social touch of a loved one, as opposed to the physical inability to touch someone you don't love. Meanwhile, the feeling of pleasantness associated with affective touch activates the anterior cingulate cortex more than the primary somatosensory cortex.Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
(fMRI) data shows that increased blood-oxygen-level contrast (BOLD) signal in the anterior cingulate cortex as well as the prefrontal cortex is highly correlated with pleasantness scores of an affective touch. Inhibitory transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the primary somatosensory cortex inhibits the perception of affective touch intensity, but not affective touch pleasantness. Therefore, the S1 is not directly involved in processing socially affective touch pleasantness, but still plays a role in discriminating touch location and intensity.
Tactile interaction is important amongst most animals. Usually, tactile contact between two animals occurs through stroking, licking, or grooming. These behaviours are essential for the individual’s social healthcare, as in the hypothalamus they induce the release of oxytocin, a hormone that decreases stress and anxiety and increases social bonding between animals.
More precisely, the consistency of oxytocin neuron activation in rats stroked by humans has been observed, especially in the caudal paraventricular nucleus. It was found that this affiliative relationship induced by tactile contact is common no matter the relationship between the two individuals (mother-infant, male-female, human-animal). It has also been discovered that the level of oxytocin release through this behaviour correlates with the time course of social interaction as longer stroking induced a greater release of the hormone.
The importance of somatosensory stimulation in social animals such as primates has also been observed. Grooming is part of the social interaction primates exert on their conspecifics. This interaction is required between individuals to maintain the affiliative relationship within the group, avoid internal conflict and increase group bonding. However, such social interaction requires the recognition of every member in the group. As such, it has been observed that the size of the neocortex is positively correlated with the size of the group, reflecting a limit to the number of recognizable members amongst which grooming can occur. Furthermore, the time course of grooming is related to vulnerability due to predation to which animals are exposed to whilst performing such social interaction. The relationship between tactile interaction, stress reduction and social bonding depends on the evaluation of risks that occur during conducting such behaviours in the wild life, and further research is required to unveil the connection between tactile caring and fitness level.
Individual variation
A variety of studies have measured and investigated the causes for differences between individuals in the sense of fine touch. One well-studied area is passive tactile spatial acuity, the ability to resolve the fine spatial details of an object pressed against the stationary skin. A variety of methods have been used to measure passive tactile spatial acuity, perhaps the most rigorous being the grating orientation task. In this task subjects identify the orientation of a grooved surface presented in two different orientations, which can be applied manually or with automated equipment. Many studies have shown a decline in passive tactile spatial acuity with age; the reasons for this decline are unknown, but may include loss of tactile receptors during normal aging. Remarkably, index finger passive tactile spatial acuity is better among adults with smaller index fingertips; this effect of finger size has been shown to underlie the better passive tactile spatial acuity of women, on average, compared to men. The density of tactile corpuscles, a type of mechanoreceptor that detects low-frequency vibrations, is greater in smaller fingers; the same may hold for Merkel cells, which detect the static indentations important for fine spatial acuity. Among children of the same age, those with smaller fingers also tend to have better tactile acuity. Many studies have shown that passive tactile spatial acuity is enhanced among blind individuals compared to sighted individuals of the same age, possibly because of cross modal plasticity in the cerebral cortex of blind individuals. Perhaps also due to cortical plasticity, individuals who have been blind since birth reportedly consolidate tactile information more rapidly than sighted people.Clinical significance
A somatosensory deficiency may be caused by a peripheral neuropathy involving peripheral nerves of the somatosensory system. This may present as numbness orparesthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
.
Society and culture
Haptic technology can provide touch sensation in virtual and real environments. In the field ofspeech therapy
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
, tactile feedback can be used to treat speech disorders.
Affectionate touch is present in everyday life and can take multiple forms. These actions, however, seem to carry specific functions even though the evolutionary benefit from such a wide range of behaviours is not entirely understood. Researchers investigated the expression patterns and characteristics of 8 different affectionate touch actions - embracing, holding, kissing, leaning, petting, squeezing, stroking, and tickling - in a self-report study. It was found that the affectionate touch has distinct target areas on the body, different associated affect, comfort-value, and expression frequency based on the type of touch action that is performed.
Besides the rather obvious sensory consequences of touch, it can also affect higher-level aspects of cognition such as social judgements and decision-making. This effect might arise due to a physical-to-mental scaffolding process in early development, whereby sensorimotor experiences are linked to the emergence of conceptual knowledge. Such links might be maintained throughout life, and so touching an object may cue the physical sensation to its related conceptual processing. Indeed, it was found that different physical properties - weight, texture, and hardness - of a touched object can influence social judgement and decision-making. For example, participants described a passage of a social interaction to be harsher when they touched a hard wooden block instead of a soft blanket prior to the task. Building on these findings, the ability of touch to have an unconscious influence on such higher-order thoughts may provide a novel tool for marketing and communication strategies.
See also
* Allochiria *Cell signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
* Golgi tendon organ
* Haptic communication
* Haptic perception
* Muscle spindle
* Molecular cellular cognition Molecular cellular cognition (MCC) is a branch of neuroscience that involves the study of cognitive processes with approaches that integrate molecular, cellular and behavioral mechanisms. Key goals of MCC studies include the derivation of molecular ...
* Phantom limb
* Physical intimacy
* Sensory maps
* Special senses
* Supramarginal gyrus
* Tactile illusion A tactile illusion is an illusion that affects the sense of touch. Some tactile illusions require active touch (e.g., movement of the fingers or hands), whereas others can be evoked passively (e.g., with external stimuli that press against the skin ...
* Vibratese, method of communication through touch
* Tactile imaging
Notes
References
Further reading
* * Flanagan, J.R., Lederman, S.JNeurobiology: Feeling bumps and holes
News and Views, Nature, 2001 July 26;412(6845):389-91. * * * * * Grunwald, M. (Ed.) ''Human Haptic Perception – Basics and Applications.'' Boston/Basel/Berlin: Birkhäuser, 2008,
Encyclopedia of Touch
Scholarpedia Expert articles
External links
*Anatomy of Touch
Factual documentary series by BBC Radio 4. {{DEFAULTSORT:Somatosensory System