Time (Rick Bryant Album) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Time is the continued
 Generally speaking, methods of temporal measurement, or
Generally speaking, methods of temporal measurement, or

 A large variety of devices have been invented to measure time. The study of these devices is called horology.
An Egyptian device that dates to c. 1500 BC, similar in shape to a bent T-square, measured the passage of time from the shadow cast by its crossbar on a nonlinear rule. The T was oriented eastward in the mornings. At noon, the device was turned around so that it could cast its shadow in the evening direction.
A
A large variety of devices have been invented to measure time. The study of these devices is called horology.
An Egyptian device that dates to c. 1500 BC, similar in shape to a bent T-square, measured the passage of time from the shadow cast by its crossbar on a nonlinear rule. The T was oriented eastward in the mornings. At noon, the device was turned around so that it could cast its shadow in the evening direction.
A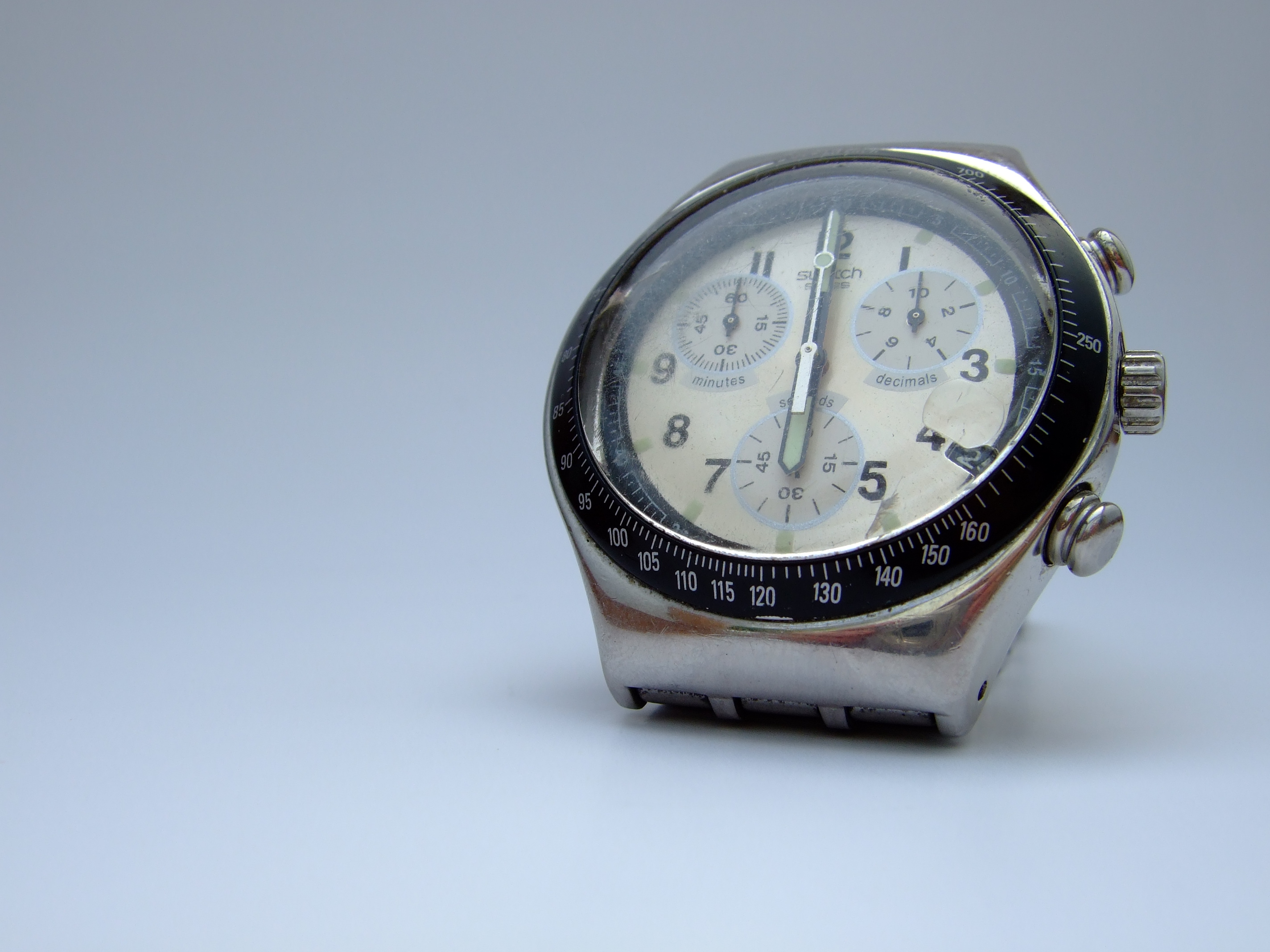  The
The  Clocks can range from watches to more exotic varieties such as the
Clocks can range from watches to more exotic varieties such as the

 Two contrasting viewpoints on time divide prominent philosophers. One view is that time is part of the fundamental structure of the
Two contrasting viewpoints on time divide prominent philosophers. One view is that time is part of the fundamental structure of the
The Function of Conscious Experience: An Analogical Paradigm of Perception and Behavior
, ''Consciousness and Cognition''. In Philosophy, time was questioned throughout the centuries; what time is and if it is real or not. Ancient Greek philosophers asked if time was linear or cyclical and if time was endless or finite. These


 The animations visualise the different treatments of time in the Newtonian and the relativistic descriptions. At the heart of these differences are the
The animations visualise the different treatments of time in the Newtonian and the relativistic descriptions. At the heart of these differences are the
 The specious present refers to the time duration wherein one's
The specious present refers to the time duration wherein one's
Different systems of measuring time
*
Time
in the ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'', by Bradley Dowden. * {{Authority control Time, Main topic articles Concepts in aesthetics Concepts in epistemology Concepts in metaphysics Concepts in the philosophy of mind Concepts in the philosophy of science Metaphysical theories Ontology Perception Philosophy of time Physical phenomena Qualia Reality Scalar physical quantities SI base quantities Spacetime
sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present
The present (or here'' and ''now) is the time that is associated with the events perception, perceived directly and in the first time, not as a recollection (perceived more than once) or a speculation (predicted, hypothesis, uncertain). It is ...
, into the future
The future is the time after the past and present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the apparent nature of reality and the unavoidability of the future, everything that currently ...
. It is a component quantity of various measurement
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events.
In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared ...
s used to sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities
Quantity or amount is a property that can exist as a multitude or magnitude, which illustrate discontinuity and continuity. Quantities can be compared in terms of "more", "less", or "equal", or by assigning a numerical value multiple of a unit ...
in material reality or in the conscious
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
experience
Experience refers to conscious events in general, more specifically to perceptions, or to the practical knowledge and familiarity that is produced by these conscious processes. Understood as a conscious event in the widest sense, experience involv ...
. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a Space (mathematics), mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any Point (geometry), point within it. Thus, a Line (geometry), lin ...
, along with three spatial dimensions.
Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars.
Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts
The performing arts are arts such as music, dance, and drama which are performed for an audience. They are different from the visual arts, which are the use of paint, canvas or various materials to create physical or static art objects. Perform ...
all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems.
108 pages.
Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
reads".
The physical nature of time is addressed by general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
with respect to events in spacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
. Examples of events are the collision of two particles, the explosion of a supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
, or the arrival of a rocket ship. Every event can be assigned four numbers representing its time and position (the event's coordinates). However, the numerical values are different for different observers. In general relativity, the question of what time it is now only has meaning relative to a particular observer. Distance and time are intimately related, and the time required for light to travel a specific distance is the same for all observers, as first publicly demonstrated by Michelson and Morley. General relativity does not address the nature of time for extremely small intervals where quantum mechanics holds. At this time, there is no generally accepted theory of quantum general relativity.
Time is one of the seven fundamental physical quantities
A physical quantity is a physical property of a material or system that can be quantified by measurement. A physical quantity can be expressed as a ''value'', which is the algebraic multiplication of a ' Numerical value ' and a ' Unit '. For examp ...
in both the International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
(SI) and International System of Quantities. The SI base unit of time is the second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
, which is defined by measuring the electronic transition frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
of caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
atoms. Time is used to define other quantities, such as velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity is a ...
, so defining time in terms of such quantities would result in circularity of definition.Duff, Okun, Veneziano, ''ibid''. p. 3. "There is no well established terminology for the fundamental constants of Nature. ... The absence of accurately defined terms or the uses (i.e., actually misuses) of ill-defined terms lead to confusion and proliferation of wrong statements."
An operational definition
An operational definition specifies concrete, replicable procedures designed to represent a construct. In the words of American psychologist S.S. Stevens (1935), "An operation is the performance which we execute in order to make known a concept." F ...
of time, wherein one says that observing a certain number of repetitions of one or another standard cyclical event (such as the passage of a free-swinging pendulum) constitutes one standard unit such as the second, is highly useful in the conduct of both advanced experiments and everyday affairs of life. To describe observations of an event, a location (position in space) and time are typically noted.
The operational definition of time does not address what the fundamental nature of it is. It does not address why events can happen forward and backward in space, whereas events only happen in the forward progress of time. Investigations into the relationship between space and time led physicists to define the spacetime continuum. General relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
is the primary framework for understanding how spacetime works. Through advances in both theoretical and experimental investigations of spacetime, it has been shown that time can be distorted and dilated, particularly at the edges of black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
s.
Temporal measurement has occupied scientists and technologists and was a prime motivation in navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
and astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
. Periodic events and periodic motion have long served as standards for units of time. Examples include the apparent motion of the sun across the sky, the phases of the moon, and the swing of a pendulum. Time is also of significant social importance, having economic value (" time is money") as well as personal value, due to an awareness
Awareness is the state of being conscious of something. More specifically, it is the ability to directly know and perceive, to feel, or to be cognizant of events. Another definition describes it as a state wherein a subject is aware of some inform ...
of the limited time in each day and in human life spans.
There are many systems for determining what time it is, including the Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
, other satellite systems, Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used ...
and mean solar time
Solar time is a calculation of the passage of time based on the position of the Sun in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day, based on the synodic rotation period. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time (sundial ti ...
. In general, the numbers obtained from different time systems differ from one another.
Measurement
 Generally speaking, methods of temporal measurement, or
Generally speaking, methods of temporal measurement, or chronometry
Chronometry (from Ancient Greek, Greek χρόνος ''chronos'', "time" and μέτρον ''metron'', "measure") is the science of the measurement of time, or timekeeping. Chronometry provides a standard of measurement for time, and therefore serv ...
, take two distinct forms: the calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physi ...
, a mathematical tool for organising intervals of time,
and the clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
, a physical mechanism that counts the passage of time. In day-to-day life, the clock is consulted for periods less than a day, whereas the calendar is consulted for periods longer than a day. Increasingly, personal electronic devices display both calendars and clocks simultaneously. The number (as on a clock dial or calendar) that marks the occurrence of a specified event as to hour or date is obtained by counting from a fiducial epoch – a central reference point.
History of the calendar
Artifacts from thePaleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
suggest that the moon was used to reckon time as early as 6,000 years ago.
Lunar calendar
A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon's phases (synodic months, lunations), in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based only directly on the solar year. The most commonly used calendar, the Gre ...
s were among the first to appear, with years of either 12 or 13 lunar month
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month.
Variations
In Shona, Middle Eastern, and Europ ...
s (either 354 or 384 days). Without intercalation
Intercalation may refer to:
* Intercalation (chemistry), insertion of a molecule (or ion) into layered solids such as graphite
*Intercalation (timekeeping), insertion of a leap day, week or month into some calendar years to make the calendar foll ...
to add days or months to some years, season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
s quickly drift in a calendar based solely on twelve lunar months. Lunisolar calendar
A lunisolar calendar is a calendar in many cultures, combining lunar calendars and solar calendars. The date of Lunisolar calendars therefore indicates both the Moon phase and the time of the solar year, that is the position of the Sun in the Ea ...
s have a thirteenth month added to some years to make up for the difference between a full year (now known to be about 365.24 days) and a year of just twelve lunar months. The numbers twelve and thirteen came to feature prominently in many cultures, at least partly due to this relationship of months to years. Other early forms of calendars originated in Mesoamerica, particularly in ancient Mayan civilization. These calendars were religiously and astronomically based, with 18 months in a year and 20 days in a month, plus five epagomenal
The intercalary month or epagomenal days. of the ancient Egyptian, Coptic, and Ethiopian calendars are a period of five days in common years and six days in leap years in addition to those calendars' 12 standard months, sometimes reckoned as thei ...
days at the end of the year.
The reforms of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
in 45 BC put the Roman world
The culture of ancient Rome existed throughout the almost 1200-year history of the civilization of Ancient Rome. The term refers to the culture of the Roman Republic, later the Roman Empire, which at its peak covered an area from present-day Lo ...
on a solar calendar
A solar calendar is a calendar whose dates indicate the season or almost equivalently the apparent position of the Sun relative to the stars. The Gregorian calendar, widely accepted as a standard in the world, is an example of a solar calendar.
T ...
. This Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
was faulty in that its intercalation still allowed the astronomical solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
s and equinoxes to advance against it by about 11 minutes per year. Pope Gregory XIII introduced a correction in 1582; the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ...
was only slowly adopted by different nations over a period of centuries, but it is now by far the most commonly used calendar around the world.
During the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, a new clock and calendar were invented in an attempt to de-Christianize time and create a more rational system in order to replace the Gregorian calendar. The French Republican Calendar's days consisted of ten hours of a hundred minutes of a hundred seconds, which marked a deviation from the base 12 (duodecimal
The duodecimal system (also known as base 12, dozenal, or, rarely, uncial) is a positional notation numeral system using twelve as its base. The number twelve (that is, the number written as "12" in the decimal numerical system) is instead wri ...
) system used in many other devices by many cultures. The system was abolished in 1806.
History of other devices

 A large variety of devices have been invented to measure time. The study of these devices is called horology.
An Egyptian device that dates to c. 1500 BC, similar in shape to a bent T-square, measured the passage of time from the shadow cast by its crossbar on a nonlinear rule. The T was oriented eastward in the mornings. At noon, the device was turned around so that it could cast its shadow in the evening direction.
A
A large variety of devices have been invented to measure time. The study of these devices is called horology.
An Egyptian device that dates to c. 1500 BC, similar in shape to a bent T-square, measured the passage of time from the shadow cast by its crossbar on a nonlinear rule. The T was oriented eastward in the mornings. At noon, the device was turned around so that it could cast its shadow in the evening direction.
A sundial
A sundial is a horological device that tells the time of day (referred to as civil time in modern usage) when direct sunlight shines by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a flat ...
uses a gnomon
A gnomon (; ) is the part of a sundial that casts a shadow. The term is used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields.
History
A painted stick dating from 2300 BC that was excavated at the astronomical site of Taosi is the ol ...
to cast a shadow on a set of markings calibrated to the hour. The position of the shadow marks the hour in local time. The idea to separate the day into smaller parts is credited to Egyptians because of their sundials, which operated on a duodecimal system. The importance of the number 12 is due to the number of lunar cycles in a year and the number of stars used to count the passage of night.
The most precise timekeeping device of the ancient world was the water clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured.
Water clocks are one of the oldest time-m ...
, or ''clepsydra'', one of which was found in the tomb of Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep I. They could be used to measure the hours even at night but required manual upkeep to replenish the flow of water. The ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
and the people from Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
(southeastern Mesopotamia) regularly maintained timekeeping records as an essential part of their astronomical observations. Arab inventors and engineers, in particular, made improvements on the use of water clocks up to the Middle Ages. In the 11th century, Chinese inventors and engineers
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limit ...
invented the first mechanical clocks driven by an escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to ...
mechanism.
 The
The hourglass
An hourglass (or sandglass, sand timer, sand clock or egg timer) is a device used to measure the passage of time. It comprises two glass bulbs connected vertically by a narrow neck that allows a regulated flow of a substance (historically sand) ...
uses the flow of sand to measure the flow of time. They were used in navigation. Ferdinand Magellan used 18 glasses on each ship for his circumnavigation of the globe (1522).
Incense sticks and candles were, and are, commonly used to measure time in temples and churches across the globe. Waterclocks, and later, mechanical clocks, were used to mark the events of the abbeys and monasteries of the Middle Ages. Richard of Wallingford (1292–1336), abbot of St. Alban's abbey, famously built a mechanical clock as an astronomical orrery about 1330.
Great advances in accurate time-keeping were made by Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
and especially Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists of ...
with the invention of pendulum-driven clocks along with the invention of the minute hand by Jost Burgi."History of Clocks." About.com Inventors. About.com, n.d. Web. 21 February 2016.
The English word clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
probably comes from the Middle Dutch word ''klocke'' which, in turn, derives from the medieval Latin word ''clocca'', which ultimately derives from Celtic and is cognate with French, Latin, and German words that mean bell. The passage of the hours at sea was marked by bells and denoted the time (see ship's bell
A ship's bell is a bell on a ship that is used for the indication of time as well as other traditional functions. The bell itself is usually made of brass or bronze, and normally has the ship's name engraved or cast on it.
Strikes Timing of s ...
). The hours were marked by bells in abbeys as well as at sea.
 Clocks can range from watches to more exotic varieties such as the
Clocks can range from watches to more exotic varieties such as the Clock of the Long Now
The Clock of the Long Now, also called the 10,000-year clock, is a mechanical clock under construction that is designed to keep time for 10,000 years. It is being built by the Long Now Foundation. A two-meter prototype is on display at the Sci ...
. They can be driven by a variety of means, including gravity, springs, and various forms of electrical power, and regulated by a variety of means such as a pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the ...
.
Alarm clocks first appeared in ancient Greece around 250 BC with a water clock that would set off a whistle. This idea was later mechanized by Levi Hutchins and Seth E. Thomas.
A chronometer
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...
is a portable timekeeper that meets certain precision standards. Initially, the term was used to refer to the marine chronometer
A marine chronometer is a precision timepiece that is carried on a ship and employed in the determination of the ship's position by celestial navigation. It is used to determine longitude by comparing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), or in the modern ...
, a timepiece used to determine longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter l ...
by means of celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of ...
, a precision firstly achieved by John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was a self-educated English Carpentry, carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the History of longitude, problem of calculating longitude while at s ...
. More recently, the term has also been applied to the chronometer watch, a watch that meets precision standards set by the Swiss agency COSC.
The most accurate timekeeping devices are atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwee ...
s, which are accurate to seconds in many millions of years, and are used to calibrate other clocks and timekeeping instruments.
Atomic clocks use the frequency of electronic transitions in certain atoms to measure the second. One of the atoms used is caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
, most modern atomic clocks probe caesium with microwaves to determine the frequency of these electron vibrations. Since 1967, the International System of Measurements bases its unit of time, the second, on the properties of caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
atoms. SI defines the second as 9,192,631,770 cycles of the radiation that corresponds to the transition between two electron spin energy levels of the ground state of the 133Cs atom.
Today, the Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
in coordination with the Network Time Protocol
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable- latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in c ...
can be used to synchronize timekeeping systems across the globe.
In medieval philosophical writings, the atom was a unit of time referred to as the smallest possible division of time. The earliest known occurrence in English is in Byrhtferth's ''Enchiridion'' (a science text) of 1010–1012, where it was defined as 1/564 of a ''momentum'' (1 minutes), and thus equal to 15/94 of a second. It was used in the ''computus
As a moveable feast, the date of Easter is determined in each year through a calculation known as (). Easter is celebrated on the first Sunday after the Paschal full moon, which is the first full moon on or after 21 March (a fixed approxi ...
'', the process of calculating the date of Easter.
, the smallest time interval uncertainty in direct measurements is on the order of 12 attosecond
An attosecond (symbol as) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 1×10−18 of a second (one quintillionth of a second). For comparison, an attosecond is to a second what a second is to about 31.71 billion years.
s (1.2 × 10−17 seconds), about 3.7 × 1026 Planck times.
Units
Thesecond
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
(s) is the SI base unit. A minute
The minute is a unit of time usually equal to (the first sexagesimal fraction) of an hour, or 60 seconds. In the UTC time standard, a minute on rare occasions has 61 seconds, a consequence of leap seconds (there is a provision to insert a nega ...
(min) is 60 seconds in length, and an hour
An hour (symbol: h; also abbreviated hr) is a unit of time conventionally reckoned as of a day and scientifically reckoned between 3,599 and 3,601 seconds, depending on the speed of Earth's rotation. There are 60 minutes in an hour, and 24 ho ...
is 60 minutes or 3600 seconds in length. A day is usually 24 hours or 86,400 seconds in length; however, the duration of a calendar day can vary due to Daylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time (United States, Canada, and Australia), and summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks (typicall ...
and Leap second
A leap second is a one-second adjustment that is occasionally applied to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), to accommodate the difference between precise time (International Atomic Time (TAI), as measured by atomic clocks) and imprecise observe ...
s.
Definitions and standards
A time standard is a specification for measuring time: assigning a number orcalendar date
A calendar date is a reference to a particular day represented within a calendar system. The calendar date allows the specific day to be identified. The number of days between two dates may be calculated. For example, "25 " is ten days after " ...
to an instant
In physics and the philosophy of science, instant refers to an infinitesimal interval in time, whose passage is instantaneous. In ordinary speech, an instant has been defined as "a point or very short space of time," a notion deriving from its ety ...
(point in time), quantifying the duration of a time interval, and establishing a chronology
Chronology (from Latin ''chronologia'', from Ancient Greek , ''chrónos'', "time"; and , '' -logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. I ...
(ordering of events). In modern times, several time specifications have been officially recognized as standards, where formerly they were matters of custom and practice. The invention in 1955 of the caesium atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwee ...
has led to the replacement of older and purely astronomical time standards such as sidereal time
Sidereal time (as a unit also sidereal day or sidereal rotation period) (sidereal ) is a timekeeping system that astronomers use to locate celestial objects. Using sidereal time, it is possible to easily point a telescope to the proper coord ...
and ephemeris time, for most practical purposes, by newer time standards based wholly or partly on atomic time using the SI second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
.
International Atomic Time (TAI) is the primary international time standard from which other time standards are calculated. Universal Time
Universal Time (UT or UT1) is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. While originally it was mean solar time at 0° longitude, precise measurements of the Sun are difficult. Therefore, UT1 is computed from a measure of the Earth's angle with ...
(UT1) is mean solar time at 0° longitude, computed from astronomical observations. It varies from TAI because of the irregularities in Earth's rotation. Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used ...
(UTC) is an atomic time scale designed to approximate Universal Time. UTC differs from TAI by an integral number of seconds. UTC is kept within 0.9 second of UT1 by the introduction of one-second steps to UTC, the "leap second". The Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
broadcasts a very precise time signal based on UTC time.
The surface of the Earth is split up into a number of time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
s. Standard time or civil time in a time zone deviates a fixed, round amount, usually a whole number of hours, from some form of Universal Time, usually UTC. Most time zones are exactly one hour apart, and by convention compute their local time as an offset from UTC. For example, time zones at sea are based on UTC. In many locations (but not at sea) these offsets vary twice yearly due to daylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time (United States, Canada, and Australia), and summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks (typicall ...
transitions.
Some other time standards are used mainly for scientific work. Terrestrial Time
Terrestrial Time (TT) is a modern astronomical time standard defined by the International Astronomical Union, primarily for time-measurements of astronomical observations made from the surface of Earth.
For example, the Astronomical Almanac uses T ...
is a theoretical ideal scale realized by TAI. Geocentric Coordinate Time
Geocentric Coordinate Time (TCG - Temps-coordonnée géocentrique) is a coordinate time standard intended to be used as the independent variable of time for all calculations pertaining to precession, nutation, the Moon, and artificial satellites ...
and Barycentric Coordinate Time
Barycentric Coordinate Time (TCB, from the French Temps-coordonnée barycentrique) is a coordinate time standard intended to be used as the independent variable of time for all calculations pertaining to orbits of planets, asteroids, comets, and ...
are scales defined as coordinate time
In the theory of relativity, it is convenient to express results in terms of a spacetime coordinate system relative to an implied observer. In many (but not all) coordinate systems, an event is specified by one time coordinate and three spatial ...
s in the context of the general theory of relativity. Barycentric Dynamical Time is an older relativistic scale that is still in use.
Philosophy
Religion
Linear and cyclical
Ancient cultures such as Incan,Mayan
Mayan most commonly refers to:
* Maya peoples, various indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Maya civilization, pre-Columbian culture of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Mayan languages, language family spoken ...
, Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
, and other Native American Tribes – plus the Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
ns, ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cultu ...
, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current ...
, and others – have a concept of a wheel of time: they regard time as cyclical
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to:
Anthropology and social sciences
* Cyclic history, a theory of history
* Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr.
* Social cycle, various cycles in soc ...
and quantic
Quantic may refer to:
* Quantic, an older name for a homogeneous polynomial.
* Quantic Dream, a video game developer studio
* Will Holland, musician and producer with stage name ''Quantic''
* Quantic School of Business and Technology, an online ...
, consisting of repeating ages that happen to every being of the Universe between birth and extinction.
In general, the Islamic and Judeo-Christian
The term Judeo-Christian is used to group Christianity and Judaism together, either in reference to Christianity's derivation from Judaism, Christianity's borrowing of Jewish Scripture to constitute the "Old Testament" of the Christian Bible, or ...
world-view regards time as linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear r ...
and directional,
beginning with the act of creation
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
* Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
* Creationism, the belief tha ...
by God. The traditional Christian view sees time ending, teleologically,
with the eschatological end of the present order of things, the "end time
The end time (also called end times, end of time, end of days, last days, final days, doomsday, or eschaton) refers to:
* Eschatology in various religions—beliefs concerning the final events of history or the destiny of humanity
End Time, En ...
".
In the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
book Ecclesiastes
Ecclesiastes (; hbo, קֹהֶלֶת, Qōheleṯ, grc, Ἐκκλησιαστής, Ekklēsiastēs) is one of the Ketuvim ("Writings") of the Hebrew Bible and part of the Wisdom literature of the Christian Old Testament. The title commonly use ...
, traditionally ascribed to Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
(970–928 BC), time (as the Hebrew word עידן, זמן ''iddan (age, as in "Ice age") zĕman(time)'' is often translated) was traditionally regarded as a medium for the passage of predestined
Predestination, in theology, is the doctrine that all events have been willed by God, usually with reference to the eventual fate of the individual soul. Explanations of predestination often seek to address the paradox of free will, whereby Go ...
events. (Another word, زمان" זמן" ''zamān'', meant ''time fit for an event'', and is used as the modern Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, and Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
equivalent to the English word "time".)
Time in Greek mythology
The Greek language denotes two distinct principles,Chronos
Chronos (; grc-gre, Χρόνος, , "time"), also spelled Khronos or Chronus, is a personification of time in pre-Socratic philosophy and later literature.
Chronos is frequently confused with, or perhaps consciously identified with, the Tit ...
and Kairos
Kairos ( grc, καιρός) is an ancient Greek word meaning 'the right, critical, or opportune moment'. In modern Greek, ''kairos'' also means 'weather' or 'time'.
It is one of two words that the ancient Greeks had for 'time'; the other bei ...
. The former refers to numeric, or chronological, time. The latter, literally "the right or opportune moment", relates specifically to metaphysical or Divine time. In theology, Kairos is qualitative, as opposed to quantitative.
In Greek mythology, Chronos (ancient Greek: Χρόνος) is identified as the Personification of Time. His name in Greek means "time" and is alternatively spelled Chronus (Latin spelling) or Khronos. Chronos is usually portrayed as an old, wise man with a long, gray beard, such as "Father Time". Some English words whose etymological root is khronos/chronos include ''chronology'', ''chronometer'', ''chronic'', ''anachronism
An anachronism (from the Ancient Greek, Greek , 'against' and , 'time') is a chronology, chronological inconsistency in some arrangement, especially a juxtaposition of people, events, objects, language terms and customs from different time per ...
'', ''synchronise'', and ''chronicle''.
Time in Kabbalah
According toKabbalists
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The defin ...
, "time" is a paradox and an illusion. Both the future and the past are recognised to be combined and simultaneously present.
In Western philosophy
universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
– a dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a Space (mathematics), mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any Point (geometry), point within it. Thus, a Line (geometry), lin ...
independent of events, in which events occur in sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
. Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
subscribed to this realist view, and hence it is sometimes referred to as Newtonian time.
The opposing view is that ''time'' does not refer to any kind of "container" that events and objects "move through", nor to any entity that "flows", but that it is instead part of a fundamental intellectual structure (together with space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
and number) within which humans sequence and compare events. This second view, in the tradition of Gottfried Leibniz
and Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (, , ; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and ...
,
holds that ''time'' is neither an event nor a thing, and thus is not itself measurable nor can it be travelled.
Furthermore, it may be that there is a subjective component to time, but whether or not time itself is "felt", as a sensation, or is a judgment, is a matter of debate.*
*
*
*
* *
*
*
Lehar, Steve. (2000)The Function of Conscious Experience: An Analogical Paradigm of Perception and Behavior
, ''Consciousness and Cognition''. In Philosophy, time was questioned throughout the centuries; what time is and if it is real or not. Ancient Greek philosophers asked if time was linear or cyclical and if time was endless or finite. These
philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
s had different ways of explaining time; for instance, ancient Indian philosophers had something called the Wheel of Time. It is believed that there was repeating ages over the lifespan of the universe. This led to beliefs like cycles of rebirth and reincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the philosophical or religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new life in a different physical form or body after biological death. Resurrection is a ...
. The Greek philosophers believe that the universe was infinite, and was an illusion to humans. Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
believed that time was made by the Creator at the same instant as the heavens. He also says that time is a period of motion of the heavenly bodies
"Heavenly Bodies" is a song written by Elaine Lifton, Gloria Nissenson and Lee Ritenour, and recorded by American country music artist Earl Thomas Conley. It was released in May 1982 as the first single from the album '' Somewhere Between Right ...
. Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
believed that time correlated to movement, that time did not exist on its own but was relative to motion of objects. he also believed that time was related to the motion of celestial bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
; the reason that humans can tell time was because of orbital periods and therefore there was a duration on time.
The ''Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
'', the earliest texts on Indian philosophy
Indian philosophy refers to philosophical traditions of the Indian subcontinent. A traditional Hindu classification divides āstika and nāstika schools of philosophy, depending on one of three alternate criteria: whether it believes the Veda ...
and Hindu philosophy
Hindu philosophy encompasses the philosophies, world views and teachings of Hinduism that emerged in Ancient India which include six systems ('' shad-darśana'') – Samkhya, Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Mimamsa and Vedanta.Andrew Nicholson (20 ...
dating back to the late 2nd millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC.
In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.
The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era:
The first half of the mil ...
, describe ancient Hindu cosmology
Hindu cosmology is the description of the universe and its states of matter, cycles within time, physical structure, and effects on living entities according to Hindu texts. Hindu cosmology is also intertwined with the idea of a creator who allo ...
, in which the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
goes through repeated cycles of creation, destruction and rebirth, with each cycle lasting 4,320 million years.
Ancient Greek philosophers, including Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; grc-gre, Παρμενίδης ὁ Ἐλεάτης; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Elea in Magna Graecia.
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Elea, from a wealthy and illustrious family. His dates a ...
and Heraclitus
Heraclitus of Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἡράκλειτος , "Glory of Hera"; ) was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire.
Little is known of Heraclitus's life. He wrote ...
, wrote essays on the nature of time.
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, in the ''Timaeus'', identified time with the period of motion of the heavenly bodies. Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, in Book IV of his ''Physica'' defined time as 'number of movement in respect of the before and after'.
In Book 11 of his '' Confessions'', St. Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Af ...
ruminates on the nature of time, asking, "What then is time? If no one asks me, I know: if I wish to explain it to one that asketh, I know not." He begins to define time by what it is not rather than what it is,
an approach similar to that taken in other negative definitions. However, Augustine ends up calling time a "distention" of the mind (Confessions 11.26) by which we simultaneously grasp the past in memory, the present by attention, and the future by expectation.
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
believed in absolute space and absolute time; Leibniz believed that time and space are relational.
The differences between Leibniz's and Newton's interpretations came to a head in the famous Leibniz–Clarke correspondence
The Leibniz–Clarke correspondence was a scientific, theological and philosophical debate conducted in an exchange of letters between the German thinker Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz and Samuel Clarke, an English supporter of Isaac Newton during the ...
.
Philosophers in the 17th and 18th century questioned if time was real and absolute, or if it was an intellectual concept that humans use to understand and sequence events. These questions lead to realism vs anti-realism; the realists believed that time is a fundamental part of the universe, and be perceived by events happening in a sequence, in a dimension. Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
said that we are merely occupying time, he also says that humans can only understand relative time
In physics, the relativity of simultaneity is the concept that ''distant simultaneity'' – whether two spatially separated events occur at the same time – is not absolute, but depends on the observer's reference frame. This possib ...
. Relative time is a measurement of objects in motion. The anti-realists believed that time is merely a convenient intellectual concept for humans to understand events. This means that time was useless unless there were objects that it could interact with, this was called relational time. René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathem ...
, John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism ...
, and David Hume
David Hume (; born David Home; 7 May 1711 NS (26 April 1711 OS) – 25 August 1776) Cranston, Maurice, and Thomas Edmund Jessop. 2020 999br>David Hume" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved 18 May 2020. was a Scottish Enlightenment philo ...
said that one's mind needs to acknowledge time, in order to understand what time is. Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (, , ; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and ...
believed that we can not know what something is unless we experience it first hand.
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (, , ; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and ...
, in the '' Critique of Pure Reason'', described time as an ''a priori
("from the earlier") and ("from the later") are Latin phrases used in philosophy to distinguish types of knowledge, justification, or argument by their reliance on empirical evidence or experience. knowledge is independent from current ex ...
'' intuition that allows us (together with the other ''a priori'' intuition, space) to comprehend sense experience
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences an ...
.
translated by J.M.D. Meiklejohn, eBooks@Adelaide, 2004
With Kant, neither space nor time are conceived as substances, but rather both are elements of a systematic mental framework that necessarily structures the experiences of any rational agent, or observing subject. Kant thought of time as a fundamental part of an abstract conceptual framework, together with space and number, within which we sequence events, quantify their duration, and compare the motions of objects. In this view, ''time'' does not refer to any kind of entity that "flows," that objects "move through," or that is a "container" for events. Spatial measurement
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events.
In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared ...
s are used to quantify the extent of and distances between objects
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ...
, and temporal measurements are used to quantify the durations of and between events. Time was designated by Kant as the purest possible schema
The word schema comes from the Greek word ('), which means ''shape'', or more generally, ''plan''. The plural is ('). In English, both ''schemas'' and ''schemata'' are used as plural forms.
Schema may refer to:
Science and technology
* SCHEMA ...
of a pure concept or category.
Henri Bergson
Henri-Louis Bergson (; 18 October 1859 – 4 January 1941) was a French philosopherHenri Bergson. 2014. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 13 August 2014, from https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/61856/Henri-Bergson
believed that time was neither a real homogeneous medium nor a mental construct, but possesses what he referred to as ''Duration
Duration may refer to:
* The amount of time elapsed between two events
* Duration (music) – an amount of time or a particular time interval, often cited as one of the fundamental aspects of music
* Duration (philosophy) – a theory of time and ...
''. Duration, in Bergson's view, was creativity and memory as an essential component of reality.
According to Martin Heidegger
Martin Heidegger (; ; 26 September 188926 May 1976) was a German philosopher who is best known for contributions to phenomenology, hermeneutics, and existentialism. He is among the most important and influential philosophers of the 20th centur ...
we do not exist inside time, we ''are'' time. Hence, the relationship to the past is a present awareness of ''having been'', which allows the past to exist in the present. The relationship to the future is the state of anticipating a potential possibility, task, or engagement. It is related to the human propensity for caring and being concerned, which causes "being ahead of oneself" when thinking of a pending occurrence. Therefore, this concern for a potential occurrence also allows the future to exist in the present. The present becomes an experience, which is qualitative instead of quantitative. Heidegger seems to think this is the way that a linear relationship with time, or temporal existence, is broken or transcended.
We are not stuck in sequential time. We are able to remember the past and project into the future – we have a kind of random access to our representation of temporal existence; we can, in our thoughts, step out of (ecstasis) sequential time.
Modern era
An era is a span of time defined for the purposes of chronology or historiography, as in the regnal eras in the history of a given monarchy, a calendar era used for a given calendar, or the geological eras defined for the history of Earth.
Compa ...
philosophers asked: is time real or unreal, is time happening all at once or a duration, is time tensed or tenseless, and is there a future to be? There is a theory called the tenseless or B-theory; this theory says that any tensed terminology can be replaced with tenseless terminology. For example, "we will win the game" can be replaced with "we do win the game", taking out the future tense. On the other hand, there is a theory called the tense or A-theory; this theory says that our language has tense verbs for a reason and that the future can not be determined. There is also something called imaginary time, this was from Stephen Hawking, he says that space and imaginary time are finite but have no boundaries. Imaginary time
Imaginary time is a mathematical representation of time which appears in some approaches to special relativity and quantum mechanics. It finds uses in connecting quantum mechanics with statistical mechanics and in certain cosmological theories.
...
is not real or unreal, it is something that is hard to visualize. Philosophers can agree that physical time exists outside of the human mind and is objective, and psychological time is mind-dependent and subjective.
Unreality
In 5th century BCGreece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, Antiphon the Sophist, in a fragment preserved from his chief work ''On Truth'', held that: "Time is not a reality (hypostasis), but a concept (noêma) or a measure (metron)." Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; grc-gre, Παρμενίδης ὁ Ἐλεάτης; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Elea in Magna Graecia.
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Elea, from a wealthy and illustrious family. His dates a ...
went further, maintaining that time, motion, and change were illusions, leading to the paradoxes of his follower Zeno
Zeno ( grc, Ζήνων) may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 BC), ...
. Time as an illusion is also a common theme in Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
thought.
J. M. E. McTaggart
John McTaggart Ellis McTaggart (3 September 1866 – 18 January 1925) was an English idealist metaphysician. For most of his life McTaggart was a fellow and lecturer in philosophy at Trinity College, Cambridge. He was an exponent of the philo ...
's 1908 ''The Unreality of Time
''The Unreality of Time'' is the best-known philosophical work of the Cambridge idealist J. M. E. McTaggart (1866–1925). In the argument, first published as a journal article in '' Mind'' in 1908, McTaggart argues that time is unreal b ...
'' argues that, since every event has the characteristic of being both present and not present (i.e., future or past), that time is a self-contradictory idea (see also The flow of time).
These arguments often center on what it means for something to be ''unreal''. Modern physicists generally believe that time is as ''real'' as space – though others, such as Julian Barbour in his book '' The End of Time'', argue that quantum equations of the universe take their true form when expressed in the timeless realm
A realm is a community or territory over which a sovereign rules. The term is commonly used to describe a monarchical or dynastic state. A realm may also be a subdivision within an empire, if it has its own monarch, e.g. the German Empire.
Etym ...
containing every possible ''now'' or momentary configuration of the universe, called "platonia
''Platonia insignis'', the sole species of the genus ''Platonia'', is a tree of the family (biology), family Clusiaceae native to South America in the humid forests of Brazil, Paraguay, parts of Colombia and northeast to Guyana; especially in ...
" by Barbour.
A modern philosophical theory called presentism views the past and the future as human-mind interpretations of movement instead of real parts of time (or "dimensions") which coexist with the present. This theory rejects the existence of all direct interaction with the past or the future, holding only the present as tangible. This is one of the philosophical arguments against time travel. This contrasts with eternalism (all time: present, past and future, is real) and the growing block theory (the present and the past are real, but the future is not).
Physical definition
Until Einstein's reinterpretation of the physical concepts associated with time and space in 1907, time was considered to be the same everywhere in the universe, with all observers measuring the same time interval for any event. Non-relativisticclassical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical ...
is based on this Newtonian idea of time.
Einstein, in his special theory of relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two Postulates of ...
,
postulated the constancy and finiteness of the speed of light for all observers. He showed that this postulate, together with a reasonable definition for what it means for two events to be simultaneous, requires that distances appear compressed and time intervals appear lengthened for events associated with objects in motion relative to an inertial observer.
The theory of special relativity finds a convenient formulation in Minkowski spacetime, a mathematical structure that combines three dimensions of space with a single dimension of time. In this formalism, distances in space can be measured by how long light takes to travel that distance, e.g., a light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
is a measure of distance, and a meter is now defined in terms of how far light travels in a certain amount of time. Two events in Minkowski spacetime are separated by an ''invariant interval
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differ ...
'', which can be either space-like
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
, light-like
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
, or time-like
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why differen ...
. Events that have a time-like separation cannot be simultaneous in any frame of reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin, orientation, and scale are specified by a set of reference points― geometric points whose position is identified both mathema ...
, there must be a temporal component (and possibly a spatial one) to their separation. Events that have a space-like separation will be simultaneous in some frame of reference, and there is no frame of reference in which they do not have a spatial separation. Different observers may calculate different distances and different time intervals between two events, but the ''invariant interval'' between the events is independent of the observer (and his or her velocity).
Classical mechanics
In non-relativisticclassical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical ...
, Newton's concept of "relative, apparent, and common time" can be used in the formulation of a prescription for the synchronization of clocks. Events seen by two different observers in motion relative to each other produce a mathematical concept of time that works sufficiently well for describing the everyday phenomena of most people's experience. In the late nineteenth century, physicists encountered problems with the classical understanding of time, in connection with the behavior of electricity and magnetism. Einstein resolved these problems by invoking a method of synchronizing clocks using the constant, finite speed of light as the maximum signal velocity. This led directly to the conclusion that observers in motion relative to one another measure different elapsed times for the same event.
Spacetime
Time has historically been closely related with space, the two together merging into spacetime in Einstein'sspecial relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The laws o ...
and general relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
. According to these theories, the concept of time depends on the spatial reference frame of the observer, and the human perception, as well as the measurement by instruments such as clocks, are different for observers in relative motion. For example, if a spaceship carrying a clock flies through space at (very nearly) the speed of light, its crew does not notice a change in the speed of time on board their vessel because everything traveling at the same speed slows down at the same rate (including the clock, the crew's thought processes, and the functions of their bodies). However, to a stationary observer watching the spaceship fly by, the spaceship appears flattened in the direction it is traveling and the clock on board the spaceship appears to move very slowly.
On the other hand, the crew on board the spaceship also perceives the observer as slowed down and flattened along the spaceship's direction of travel, because both are moving at very nearly the speed of light relative to each other. Because the outside universe appears flattened to the spaceship, the crew perceives themselves as quickly traveling between regions of space that (to the stationary observer) are many light years apart. This is reconciled by the fact that the crew's perception of time is different from the stationary observer's; what seems like seconds to the crew might be hundreds of years to the stationary observer. In either case, however, causality remains unchanged: the past is the set of events that can send light signals to an entity and the future
The future is the time after the past and present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the apparent nature of reality and the unavoidability of the future, everything that currently ...
is the set of events to which an entity can send light signals.
Dilation
Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
showed in his thought experiments that people travelling at different speeds, while agreeing on cause and effect
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cau ...
, measure different time separations between events, and can even observe different chronological orderings between non-causally related events. Though these effects are typically minute in the human experience, the effect becomes much more pronounced for objects moving at speeds approaching the speed of light. Subatomic particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a pr ...
s exist for a well-known average fraction of a second in a lab relatively at rest, but when travelling close to the speed of light they are measured to travel farther and exist for much longer than when at rest. According to the special theory of relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two Postulates of ...
, in the high-speed particle's frame of reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin, orientation, and scale are specified by a set of reference points― geometric points whose position is identified both mathema ...
, it exists, on the average, for a standard amount of time known as its mean lifetime
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and ...
, and the distance it travels in that time is zero, because its velocity is zero. Relative to a frame of reference at rest, time seems to "slow down" for the particle. Relative to the high-speed particle, distances seem to shorten. Einstein showed how both temporal and spatial dimensions can be altered (or "warped") by high-speed motion.
Einstein (''The Meaning of Relativity
''The Meaning of Relativity: Four Lectures Delivered at Princeton University, May 1921'' is a book published by Princeton University Press in 1922 that compiled the 1921 Stafford Little Lectures at Princeton University, given by Albert Einstein. ...
''): "Two events taking place at the points A and B of a system K are simultaneous if they appear at the same instant when observed from the middle point, M, of the interval AB. Time is then defined as the ensemble of the indications of similar clocks, at rest relative to K, which register the same simultaneously."
Einstein wrote in his book, ''Relativity'', that simultaneity is also relative, i.e., two events that appear simultaneous to an observer in a particular inertial reference frame need not be judged as simultaneous by a second observer in a different inertial frame of reference.
Relativistic versus Newtonian
 The animations visualise the different treatments of time in the Newtonian and the relativistic descriptions. At the heart of these differences are the
The animations visualise the different treatments of time in the Newtonian and the relativistic descriptions. At the heart of these differences are the Galilean
Generically, a Galilean (; he, גלילי; grc, Γαλιλαίων; la, Galilaeos) is an inhabitant of Galilee, a region of Israel surrounding the Sea of Galilee (Kinneret). The New Testament notes that the Apostle Peter's accent gave him a ...
and Lorentz transformations applicable in the Newtonian and relativistic theories, respectively.
In the figures, the vertical direction indicates time. The horizontal direction indicates distance (only one spatial dimension is taken into account), and the thick dashed curve is the spacetime trajectory ("world line
The world line (or worldline) of an object is the path that an object traces in 4-dimensional spacetime. It is an important concept in modern physics, and particularly theoretical physics.
The concept of a "world line" is distinguished from con ...
") of the observer. The small dots indicate specific (past and future) events in spacetime.
The slope of the world line (deviation from being vertical) gives the relative velocity to the observer. Note how in both pictures the view of spacetime changes when the observer accelerates.
In the Newtonian description these changes are such that ''time'' is absolute: the movements of the observer do not influence whether an event occurs in the 'now' (i.e., whether an event passes the horizontal line through the observer).
However, in the relativistic description the ''observability of events'' is absolute: the movements of the observer do not influence whether an event passes the " light cone" of the observer. Notice that with the change from a Newtonian to a relativistic description, the concept of ''absolute time'' is no longer applicable: events move up and down in the figure depending on the acceleration of the observer.
Arrow
Time appears to have a direction – the past lies behind, fixed and immutable, while the future lies ahead and is not necessarily fixed. Yet for the most part, the laws of physics do not specify an arrow of time, and allow any process to proceed both forward and in reverse. This is generally a consequence of time being modelled by a parameter in the system being analysed, where there is no "proper time": the direction of the arrow of time is sometimes arbitrary. Examples of this include the cosmological arrow of time, which points away from theBig Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
, CPT symmetry
Charge, parity, and time reversal symmetry is a fundamental symmetry of physical laws under the simultaneous transformations of charge conjugation (C), parity transformation (P), and time reversal (T). CPT is the only combination of C, P, and T ...
, and the radiative arrow of time, caused by light only travelling forwards in time (see light cone). In particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
, the violation of CP symmetry implies that there should be a small counterbalancing time asymmetry to preserve CPT symmetry
Charge, parity, and time reversal symmetry is a fundamental symmetry of physical laws under the simultaneous transformations of charge conjugation (C), parity transformation (P), and time reversal (T). CPT is the only combination of C, P, and T ...
as stated above. The standard description of measurement
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events.
In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared ...
in quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
is also time asymmetric (see Measurement in quantum mechanics). The second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ( ...
states that entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
must increase over time (see Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
). This can be in either direction – Brian Greene
Brian Randolph Greene (born February 9, 1963) is a American theoretical physicist, mathematician, and string theorist. Greene was a physics professor at Cornell University from 19901995, and has been a professor at Columbia University since 1 ...
theorizes that, according to the equations, the change in entropy occurs symmetrically whether going forward or backward in time. So entropy tends to increase in either direction, and our current low-entropy universe is a statistical aberration, in a similar manner as tossing a coin often enough that eventually heads will result ten times in a row. However, this theory is not supported empirically in local experiment.
Quantization
Time quantization is a hypothetical concept. In the modern established physical theories (theStandard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying a ...
of Particles and Interactions and General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics ...
) time is not quantized.
Planck time (~ 5.4 × 10−44 seconds) is the unit of time in the system of natural units known as Planck units. Current established physical theories are believed to fail at this time scale, and many physicists expect that the Planck time might be the smallest unit of time that could ever be measured, even in principle. Tentative physical theories that describe this time scale exist; see for instance loop quantum gravity
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is a theory of quantum gravity, which aims to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity, incorporating matter of the Standard Model into the framework established for the pure quantum gravity case. It is an attem ...
.
Travel
Time travel is the concept of moving backwards or forwards to different points in time, in a manner analogous to moving through space, and different from the normal "flow" of time to an earthbound observer. In this view, all points in time (including future times) "persist" in some way. Time travel has been a plot device in fiction since the 19th century. Travelling backwards or forwards in time has never been verified as a process, and doing so presents many theoretical problems and contradictive logic which to date have not been overcome. Any technological device, whether fictional or hypothetical, that is used to achieve time travel is known as atime machine
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a w ...
.
A central problem with time travel to the past is the violation of causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cau ...
; should an effect precede its cause, it would give rise to the possibility of a temporal paradox. Some interpretations of time travel resolve this by accepting the possibility of travel between branch points
In the mathematical field of complex analysis, a branch point of a multi-valued function (usually referred to as a "multifunction" in the context of complex analysis) is a point such that if the function is n-valued (has n values) at that point, ...
, parallel realities
''Parallel Realities'' is an album by drummer Jack DeJohnette with guitarist Pat Metheny and pianist Herbie Hancock recorded in 1990 and released on the MCA label. The Allmusic review by Ron Wynn states, "An overlooked session with Pat Metheny ...
, or universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
s.
Another solution to the problem of causality-based temporal paradoxes is that such paradoxes cannot arise simply because they have not arisen. As illustrated in numerous works of fiction, free will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded.
Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actio ...
either ceases to exist in the past or the outcomes of such decisions are predetermined. As such, it would not be possible to enact the grandfather paradox because it is a historical fact that one's grandfather was not killed before his child (one's parent) was conceived. This view does not simply hold that history is an unchangeable constant, but that any change made by a hypothetical future time traveller would already have happened in his or her past, resulting in the reality that the traveller moves from. More elaboration on this view can be found in the Novikov self-consistency principle
The Novikov self-consistency principle, also known as the Novikov self-consistency conjecture and Larry Niven's law of conservation of history, is a principle developed by Russian physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov in the mid-1980s. Novikov inten ...
.
Perception
 The specious present refers to the time duration wherein one's
The specious present refers to the time duration wherein one's perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
s are considered to be in the present. The experienced present is said to be 'specious' in that, unlike the objective present, it is an interval and not a durationless instant. The term ''specious present'' was first introduced by the psychologist E.R. Clay, and later developed by William James
William James (January 11, 1842 – August 26, 1910) was an American philosopher, historian, and psychologist, and the first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States.
James is considered to be a leading thinker of the lat ...
.
Biopsychology
The brain's judgment of time is known to be a highly distributed system, including at least the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and basal ganglia as its components. One particular component, the suprachiasmatic nucleus, suprachiasmatic nuclei, is responsible for the circadian rhythm, circadian (or daily) rhythm, while other cell clusters appear capable of shorter-range (ultradian) timekeeping. Psychoactive drugs can impair the judgment of time. Stimulants can lead both humans and rats to overestimate time intervals, while depressants can have the opposite effect. The level of activity in the brain of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine may be the reason for this. Such chemicals will either excite or inhibit the firing of neurons in the brain, with a greater firing rate allowing the brain to register the occurrence of more events within a given interval (speed up time) and a decreased firing rate reducing the brain's capacity to distinguish events occurring within a given interval (slow down time). Mental chronometry is the use of response time in perceptual-motor tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of cognitive operations.Early childhood education
Children's expanding cognitive abilities allow them to understand time more clearly. Two- and three-year-olds' understanding of time is mainly limited to "now and not now". Five- and six-year-olds can grasp the ideas of past, present, and future. Seven- to ten-year-olds can use clocks and calendars.Alterations
In addition to psychoactive drugs, judgments of time can be altered by temporal illusions (like the kappa effect),Wada Y, Masuda T, Noguchi K, 2005, "Temporal illusion called 'kappa effect' in event perception" Perception 34 ECVP Abstract Supplement age, and hypnosis. The sense of time is impaired in some people with neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease and attention deficit disorder. Psychologists assert that time seems to go faster with age, but the literature on this age-related perception of time remains controversial. Those who support this notion argue that young people, having more excitatory neurotransmitters, are able to cope with faster external events.Spatial conceptualization
Although time is regarded as an abstract concept, there is increasing evidence that time is Conceptual metaphor, conceptualized in the mind in terms of space. That is, instead of thinking about time in a general, abstract way, humans think about time in a spatial way and mentally organize it as such. Using space to think about time allows humans to mentally organize temporal events in a specific way. This spatial representation of time is often represented in the mind as a Mental Time Line (MTL). Using space to think about time allows humans to mentally organize temporal order. These origins are shaped by many environmental factors––for example, literacy appears to play a large role in the different types of MTLs, as reading/Writing system, writing direction provides an everyday temporal orientation that differs from culture to culture. In western cultures, the MTL may unfold rightward (with the past on the left and the future on the right) since people read and write from left to right. Western calendars also continue this trend by placing the past on the left with the future progressing toward the right. Conversely, Arabic, Farsi, Urdu and Israeli Hebrew language, Israeli-Hebrew speakers read from right to left, and their MTLs unfold leftward (past on the right with future on the left), and evidence suggests these speakers organize time events in their minds like this as well. This linguistic evidence that abstract concepts are based in spatial concepts also reveals that the way humans mentally organize time events varies across cultures––that is, a certain specific mental organization system is not universal. So, although Western cultures typically associate past events with the left and future events with the right according to a certain MTL, this kind of horizontal, egocentric MTL is not the spatial organization of all cultures. Although most developed nations use an egocentric spatial system, there is recent evidence that some cultures use an allocentric spatialization, often based on environmental features. A recent study of the indigenous Yupno people of Papua New Guinea focused on the directional gestures used when individuals used time-related words. When speaking of the past (such as "last year" or "past times"), individuals gestured downhill, where the river of the valley flowed into the ocean. When speaking of the future, they gestured uphill, toward the source of the river. This was common regardless of which direction the person faced, revealing that the Yupno people may use an allocentric MTL, in which time flows uphill. A similar study of the Pormpuraawans, an Aboriginal groupings of Western Australia, aboriginal group in Australia, revealed a similar distinction in which when asked to organize photos of a man aging "in order," individuals consistently placed the youngest photos to the east and the oldest photos to the west, regardless of which direction they faced. This directly clashed with an American group that consistently organized the photos from left to right. Therefore, this group also appears to have an allocentric MTL, but based on the cardinal directions instead of geographical features. The wide array of distinctions in the way different groups think about time leads to the broader question that different groups may also think about other abstract concepts in different ways as well, such as causality and number.Use
In sociology and anthropology, time discipline is the general name given to society, social and economic rules, conventions, customs, and expectations governing the measurement of time, the social currency and awareness of time measurements, and people's expectations concerning the observance of these customs by others. Arlie Russell Hochschild and Norbert Elias have written on the use of time from a sociological perspective. The use of time is an important issue in understanding human behavior, education, and travel behavior. Time-use research is a developing field of study. The question concerns how time is allocated across a number of activities (such as time spent at home, at work, shopping, etc.). Time use changes with technology, as the television or the Internet created new opportunities to use time in different ways. However, some aspects of time use are relatively stable over long periods of time, such as the amount of time spent traveling to work, which despite major changes in transport, has been observed to be about 20–30 minutes one-way for a large number of cities over a long period. Time management is the organization of tasks or events by first estimating how much time a task requires and when it must be completed, and adjusting events that would interfere with its completion so it is done in the appropriate amount of time. Calendars and day planners are common examples of time management tools.Sequence of events
A sequence of events, or series of events, is asequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
of items, facts, events, actions, changes, or procedural steps, arranged in time order (chronological order), often with causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cau ...
relationships among the items.
Because of causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cau ...
, cause precedes result, effect, or cause and effect may appear together in a single item, but effect never precedes cause. A sequence of events can be presented in text, Table (information), tables, charts, or timelines. The description of the items or events may include a timestamp. A sequence of events that includes the time along with place or location information to describe a sequential path may be referred to as a world line
The world line (or worldline) of an object is the path that an object traces in 4-dimensional spacetime. It is an important concept in modern physics, and particularly theoretical physics.
The concept of a "world line" is distinguished from con ...
.
Uses of a sequence of events include stories,
historical events (chronology
Chronology (from Latin ''chronologia'', from Ancient Greek , ''chrónos'', "time"; and , '' -logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. I ...
), directions and steps in procedures,
and timetables for scheduling activities. A sequence of events may also be used to help describe Process (engineering), processes in science, technology, and medicine. A sequence of events may be focused on past events (e.g., stories, history, chronology), on future events that must be in a predetermined order (e.g., plans, schedule (project management), schedules, procedures, timetables), or focused on the observation of past events with the expectation that the events will occur in the future (e.g., processes, projections). The use of a sequence of events occurs in fields as diverse as machines (cam timer), documentaries (''Seconds From Disaster''), law (Choice of law#Sequence of events in conflict cases, choice of law), finance (directional-change intrinsic time), computer simulation (discrete event simulation), and electric power transmission
(sequence of events recorder). A specific example of a sequence of events is the timeline of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
See also
* List of UTC timing centers * Time metrologyOrganizations
* Antiquarian Horological Society – AHS (United Kingdom) * Chronometrophilia (Switzerland) * Deutsche Gesellschaft für Chronometrie – DGC (Germany) * National Association of Watch and Clock Collectors – NAWCC (United States)Miscellaneous arts and sciences
* Date and time representation by country * List of cycles * Nonlinear narrative * Philosophy of physics * Rate (mathematics)Miscellaneous units
* Fiscal year * Half-life * Hexadecimal time * Tithi * Unix epochReferences
Further reading
*
* Craig Callendar, ''Introducing Time'', Icon Books, 2010,
* – Research bibliography
*
*
*
* Benjamin Gal-Or, ''Cosmology, Physics and Philosophy'', Springer Verlag, 1981, 1983, 1987, .
* Charlie Gere, (2005) ''Art, Time and Technology: Histories of the Disappearing Body'', Berg
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Bernard Stiegler, Stiegler, Bernard, ''Technics and Time, 1: The Fault of Epimetheus''
* Roberto Mangabeira Unger and Lee Smolin, ''The Singular Universe and the Reality of Time'', Cambridge University Press, 2014, .
*
*
*
External links
Different systems of measuring time
*
Time
in the ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'', by Bradley Dowden. * {{Authority control Time, Main topic articles Concepts in aesthetics Concepts in epistemology Concepts in metaphysics Concepts in the philosophy of mind Concepts in the philosophy of science Metaphysical theories Ontology Perception Philosophy of time Physical phenomena Qualia Reality Scalar physical quantities SI base quantities Spacetime