|
Leap Second
A leap second is a one- second adjustment that is occasionally applied to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), to accommodate the difference between precise time (International Atomic Time (TAI), as measured by atomic clocks) and imprecise observed solar time ( UT1), which varies due to irregularities and long-term slowdown in the Earth's rotation. The UTC time standard, widely used for international timekeeping and as the reference for civil time in most countries, uses TAI and consequently would run ahead of observed solar time unless it is reset to UT1 as needed. The leap second facility exists to provide this adjustment. The leap second was introduced in 1972 and since then 27 leap seconds have been added to UTC. Because the Earth's rotation speed varies in response to climatic and geological events, UTC leap seconds are irregularly spaced and unpredictable. Insertion of each UTC leap second is usually decided about six months in advance by the International Earth Rotation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leapsecond2016
A leap second is a one-second adjustment that is occasionally applied to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), to accommodate the difference between precise time (International Atomic Time (TAI), as measured by atomic clocks) and imprecise observed solar time (UT1), which varies due to irregularities and long-term slowdown in the Earth's rotation. The UTC time standard, widely used for international timekeeping and as the reference for civil time in most countries, uses TAI and consequently would run ahead of observed solar time unless it is reset to UT1 as needed. The leap second facility exists to provide this adjustment. The leap second was introduced in 1972 and since then 27 leap seconds have been added to UTC. Because the Earth's rotation speed varies in response to climatic and geological events, UTC leap seconds are irregularly spaced and unpredictable. Insertion of each UTC leap second is usually decided about six months in advance by the International Earth Rotation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leapsecond
A leap second is a one- second adjustment that is occasionally applied to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), to accommodate the difference between precise time (International Atomic Time (TAI), as measured by atomic clocks) and imprecise observed solar time ( UT1), which varies due to irregularities and long-term slowdown in the Earth's rotation. The UTC time standard, widely used for international timekeeping and as the reference for civil time in most countries, uses TAI and consequently would run ahead of observed solar time unless it is reset to UT1 as needed. The leap second facility exists to provide this adjustment. The leap second was introduced in 1972 and since then 27 leap seconds have been added to UTC. Because the Earth's rotation speed varies in response to climatic and geological events, UTC leap seconds are irregularly spaced and unpredictable. Insertion of each UTC leap second is usually decided about six months in advance by the International Earth Rotation a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee For Weights And Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (GCWM; french: Conférence générale des poids et mesures, CGPM) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established in 1875 under the terms of the Metre Convention through which member states act together on matters related to measurement science and measurement standards. The CGPM is made up of delegates of the governments of the member states and observers from the Associates of the CGPM. Under its authority, the International Committee for Weights and Measures (ICWM; ) executes an exclusive direction and supervision of the BIPM. Initially the Metre Convention was only concerned with the kilogram and the metre, but in 1921 the scope of the treaty was extended to accommodate all physical measurements and hence all aspects of the metric system. In 1960 the 11th CGPM approved the International System of Units, usually known as "SI". The General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Tropical Year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky of a celestial body of the Solar System such as the Earth, completing a full cycle of seasons; for example, the time from vernal equinox to vernal equinox, or from summer solstice to summer solstice. It is the type of year used by tropical solar calendars. The solar year is one type of astronomical year and particular orbital period. Another type is the sidereal year (or sidereal orbital period), which is the time it takes Earth to complete one full orbit around the Sun as measured with respect to the fixed stars, resulting in a duration of 20 minutes longer than the tropical year, because of the precession of the equinoxes. Since antiquity, astronomers have progressively refined the definition of the tropical year. The entry for "year, tropical" in the '' Astronomical Almanac Online Glossary'' states: An equivalent, more descriptive, definition is "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky of a celestial body of the Solar System such as the Earth, completing a full cycle of seasons; for example, the time from vernal equinox to vernal equinox, or from summer solstice to summer solstice. It is the type of year used by tropical solar calendars. The solar year is one type of astronomical year and particular orbital period. Another type is the sidereal year (or sidereal orbital period), which is the time it takes Earth to complete one full orbit around the Sun as measured with respect to the fixed stars, resulting in a duration of 20 minutes longer than the tropical year, because of the precession of the equinoxes. Since antiquity, astronomers have progressively refined the definition of the tropical year. The entry for "year, tropical" in the '' Astronomical Almanac Online Glossary'' states: An equivalent, more descriptive, definition i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereal Year
A sidereal year (, ; ), also called a sidereal orbital period, is the time that Earth or another planetary body takes to orbit the Sun once with respect to the fixed stars. Hence, for Earth, it is also the time taken for the Sun to return to the same position relative to Earth with respect to the fixed stars after apparently travelling once around the ecliptic. It equals for the J2000.0 epoch. The sidereal year differs from the solar year, "the period of time required for the ecliptic longitude of the Sun to increase 360 degrees", due to the precession of the equinoxes. The sidereal year is 20 min 24.5 s longer than the mean tropical year at J2000.0 . At present, the rate of axial precession corresponds to a period of 25,772 years, so sidereal year is longer than tropical year by 1,224.5 seconds (20 min 24.5 s, ~365.24219*86400/25772). Before the discovery of the precession of the equinoxes by Hipparchus in the Hellenistic period, the difference between sidereal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Newcomb
Simon Newcomb (March 12, 1835 – July 11, 1909) was a Canadian– American astronomer, applied mathematician, and autodidactic polymath. He served as Professor of Mathematics in the United States Navy and at Johns Hopkins University. Born in Nova Scotia, at the age of 19 Newcomb left an apprenticeship to join his father in Massachusetts, where the latter was teaching. Though Newcomb had little conventional schooling, he completed a BSc at Harvard in 1858. He later made important contributions to timekeeping, as well as to other fields in applied mathematics, such as economics and statistics. Fluent in several languages, he also wrote and published several popular science books and a science fiction novel. Biography Early life Simon Newcomb was born in the town of Wallace, Nova Scotia. His parents were John Burton Newcomb and his wife Miriam Steeves. His father was an itinerant school teacher, and frequently moved in order to teach in different parts of Canada, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
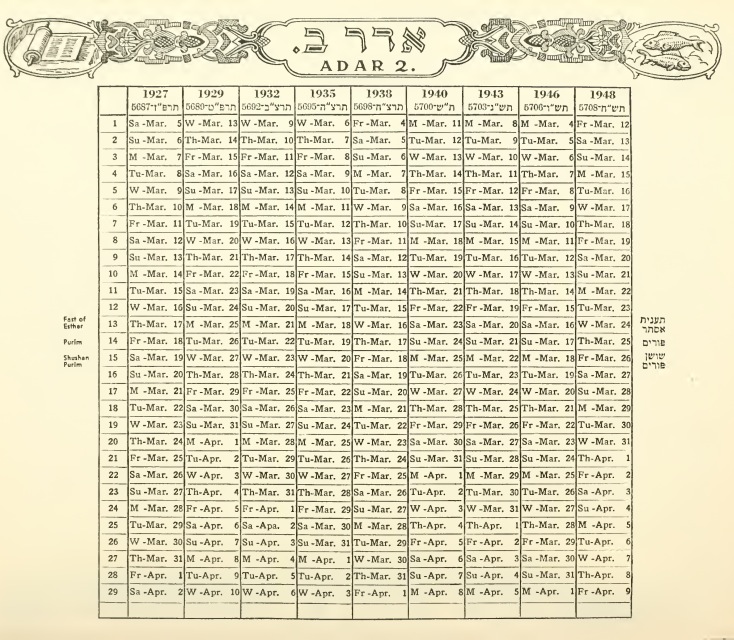
Hebrew Calendar
The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate Torah reading, public reading of Weekly Torah portion, Torah portions, ''yahrzeits'' (dates to commemorate the death of a relative), and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official calendar for civil holidays, alongside the Gregorian calendar. The present Hebrew calendar is the result of a process of development, including a Babylonian calendar, Babylonian influence. Until the Tannaitic period (approximately 10–220 Common Era, CE), the calendar employed a new lunar phase, crescent moon, with an Intercalation (timekeeping), additional month normally added every two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Comparative Religion", "Father of modern geodesy", and the first anthropologist. Al-Biruni was well versed in physics, mathematics, astronomy, and natural sciences, and also distinguished himself as a historian, chronologist, and linguist. He studied almost all the sciences of his day and was rewarded abundantly for his tireless research in many fields of knowledge. Royalty and other powerful elements in society funded Al-Biruni's research and sought him out with specific projects in mind. Influential in his own right, Al-Biruni was himself influenced by the scholars of other nations, such as the Greeks, from whom he took inspiration when he turned to the study of philosophy. A gifted linguist, he was conversant in Khwarezmian, Persian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |