Thymus Decussatus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The thymus is a specialized primary
File:Thymus.JPG, Micrograph showing a lobule of the thymus. The cortex (deeper purple area) surrounds a less dense and lighter medulla.
File:Thymic corpuscle.jpg, Micrograph showing a Hassall's corpuscle, found within the medulla of the thymus.
 The thymocytes and the epithelium of the thymus have different developmental origins. The epithelium of the thymus develops first, appearing as two outgrowths, one on either side, of the third pharyngeal pouch. It sometimes also involves the fourth pharyngeal pouch. These extend outward and backward into the surrounding
The thymocytes and the epithelium of the thymus have different developmental origins. The epithelium of the thymus develops first, appearing as two outgrowths, one on either side, of the third pharyngeal pouch. It sometimes also involves the fourth pharyngeal pouch. These extend outward and backward into the surrounding
File:Thoracic cavity of foetus 2.JPG, Thymus of a fetus
File:Radiology 1300566 Nevit.jpg, On
T cell development in the thymus.
Video by Janice Yau, describing stromal signaling and tolerance. Department of Immunology and Biomedical Communications, University of Toronto. Master's Research Project, Master of Science in Biomedical Communications. 2011. {{Authority control Immune system Lymphatic system Lymphatics of the torso Lymphoid organ Mammal anatomy Organs (anatomy)
lymphoid organ
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or '' T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.
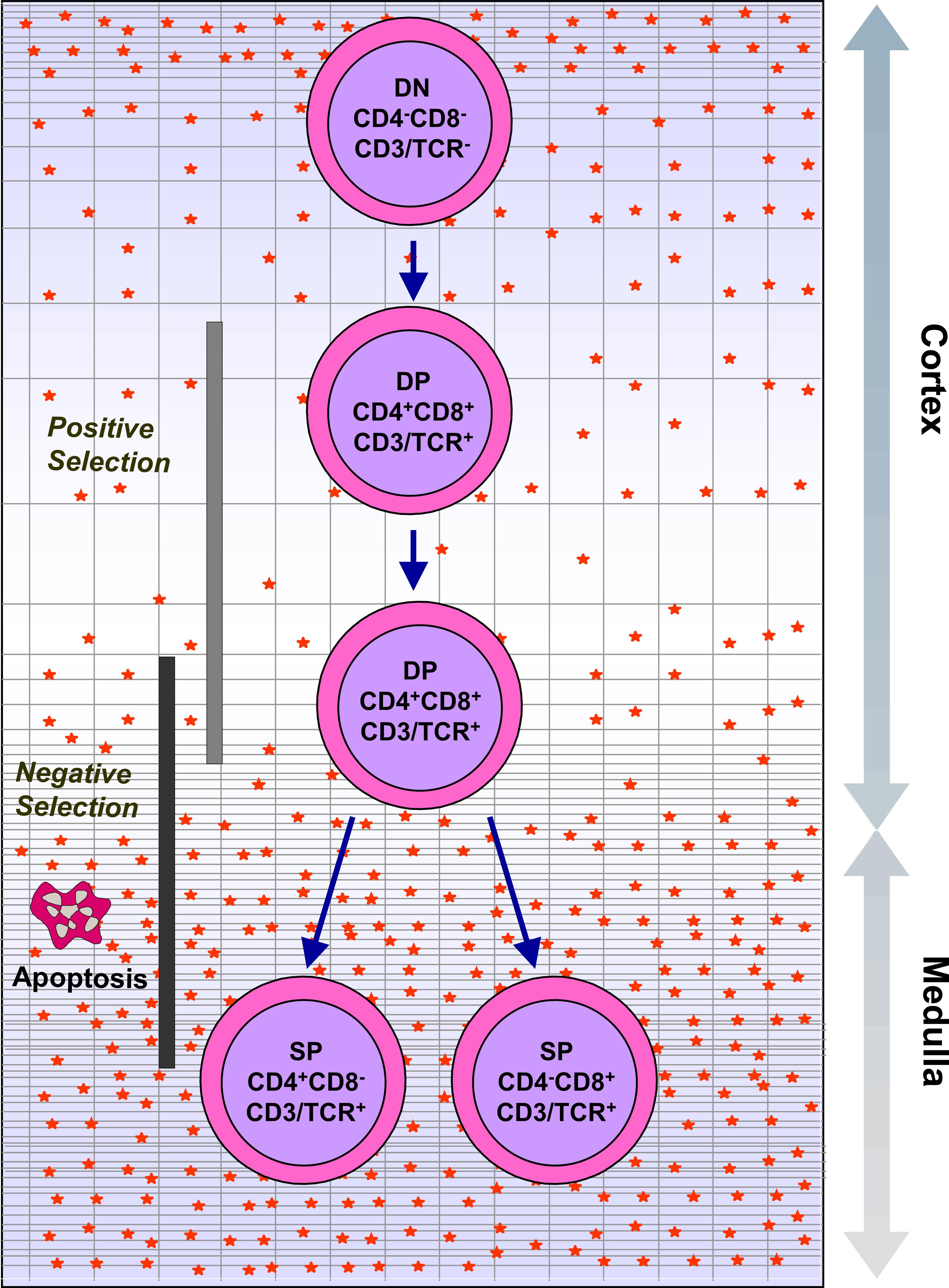
The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to decrease in size and activity and the tissue of the thymus is gradually replaced by fatty tissue. Nevertheless, some T cell development continues throughout adult life.
Abnormalities of the thymus can result in a decreased number of T cells and autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 and myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, dro ...
. These are often associated with cancer of the tissue of the thymus, called thymoma, or tissues arising from immature lymphocytes such as T cells, called lymphoma. Removal of the thymus is called thymectomy
A thymectomy is an operation to remove the thymus. It usually results in remission of myasthenia gravis with the help of medication including steroids. However, this remission may not be permanent. Thymectomy is indicated when thymoma are present ...
. Although the thymus has been identified as a part of the body since the time of the Ancient Greeks, it is only since the 1960s that the function of the thymus in the immune system has become clearer.
Structure
The thymus is an organ that sits beneath the sternum in the upper front part of the chest, stretching upwards towards the neck. In children, the thymus is pinkish-gray, soft, and lobulated on its surfaces. At birth it is about 4–6 cm long, 2.5–5 cm wide, and about 1 cm thick. It increases in size until puberty, where it may have a size of about 40–50 g, following which it decreases in size in a process known as involution. The thymus is located in theanterior mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
. It is made up of two lobes that meet in the upper midline, and stretch from below the thyroid in the neck to as low as the cartilage of the fourth rib. The lobes are covered by a capsule. The thymus lies beneath the sternum, rests on the pericardium, and is separated from the aortic arch and great vessels by a layer of fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. ...
. The left brachiocephalic vein may even be embedded within the thymus. In the neck, it lies on the front and sides of the trachea, behind the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles.
Microanatomy
The thymus consists of two lobes, merged in the middle, surrounded by a capsule that extends with blood vessels into the interior. The lobes consist of an outer rich with cells and an inner less dense . The lobes are divided into smaller lobules 0.5-2mm diameter, between which extrude radiating insertions from the capsule along . The cortex is mainly made up of thymocytes and epithelial cells. The thymocytes, immature T cells, are supported by a network of the finely-branchedepithelial reticular cells
Thymic epithelial cells (TECs) are specialized cells with high degree of anatomic, phenotypic and functional heterogeneity that are located in the outer layer (epithelium) of the thymic stroma. The thymus, as a primary lymphoid organ, mediates T ce ...
, which is continuous with a similar network in the medulla. This network forms an adventitia to the blood vessels, which enter the cortex via septa near the junction with the medulla. Other cells are also present in the thymus, including macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s, dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s, and a small amount of B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
s, neutrophils and eosinophils.
In the medulla, the network of epithelial cells is coarser than in the cortex, and the lymphoid cells are relatively fewer in number. Concentric, nest-like bodies called Hassall's corpuscles (also called ''thymic corpuscles'') are formed by aggregations of the medullary epithelial cells. These are concentric, layered whorls of epithelial cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
s that increase in number throughout life. They are the remains of the epithelial tubes, which grow out from the third pharyngeal pouches of the embryo to form the thymus.
Blood and nerve supply
The arteries supplying the thymus are branches of the internal thoracic, andinferior thyroid arteries
The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and als ...
, with branches from the superior thyroid artery
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.
Structure
From its origin under the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid the sup ...
sometimes seen. The branches reach the thymus and travel with the septa of the capsule into the area between the cortex and medulla, where they enter the thymus itself; or alternatively directly enter the capsule.
The veins of the thymus end in the left brachiocephalic vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of each corresponding internal jugular vein and subclavian vein. This is at the level of the sternoclavicular jo ...
, internal thoracic vein
In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein (previously known as the internal mammary vein) is a vessel that drains the chest wall and breasts.
Structure
Bilaterally, the internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein, an ...
, and in the inferior thyroid vein
The inferior thyroid veins appear two, frequently three or four, in number, and arise in the venous plexus on the thyroid gland, communicating with the middle and superior thyroid veins. While the superior and middle thyroid veins serve as direct ...
s. Sometimes the veins end directly in the superior vena cava.
Lymphatic vessels travel only away from the thymus, accompanying the arteries and veins. These drain into the brachiocephalic, tracheobronchial and parasternal lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s.
The nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
s supplying the thymus arise from the vagus nerve and the cervical sympathetic chain
The sympathetic trunks (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) are a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies j ...
. Branches from the phrenic nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In ...
s reach the capsule of the thymus, but do not enter into the thymus itself.
Variation
The two lobes differ slightly in size, with the left lobe usually higher than the right. Thymic tissue may be found scattered on or around the gland, and occasionally within the thyroid. The thymus in children stretches variably upwards, at times to as high as the thyroid gland.Development
 The thymocytes and the epithelium of the thymus have different developmental origins. The epithelium of the thymus develops first, appearing as two outgrowths, one on either side, of the third pharyngeal pouch. It sometimes also involves the fourth pharyngeal pouch. These extend outward and backward into the surrounding
The thymocytes and the epithelium of the thymus have different developmental origins. The epithelium of the thymus develops first, appearing as two outgrowths, one on either side, of the third pharyngeal pouch. It sometimes also involves the fourth pharyngeal pouch. These extend outward and backward into the surrounding mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
and neural crest-derived mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every o ...
in front of the ventral aorta. Here the thymocytes and epithelium meet and join with connective tissue. The pharyngeal opening of each diverticulum is soon obliterated, but the neck of the flask persists for some time as a cellular cord. By further proliferation of the cells lining the flask, buds of cells are formed, which become surrounded and isolated by the invading mesoderm.
The epithelium forms fine lobules, and develops into a sponge-like structure. During this stage, hematopoietic
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. ...
bone-marrow precursors migrate into the thymus. Normal development is dependent on the interaction between the epithelium and the hematopoietic thymocytes. Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
is also necessary for thymus development and activity.
Involution
The thymus continues to grow after birth reaching the relative maximum size by puberty. It is most active in fetal and neonatal life. It increases to a mass of 20 to 50 grams by puberty. It then begins to decrease in size and activity in a process called thymic involution. After the first year of life the amount of T cells produced begins to fall. Fat and connective tissue fills a part of the thymic volume. During involution, the thymus decreases in size and activity. Fat cells are present at birth, but increase in size and number markedly after puberty, invading the gland from the walls between the lobules first, then into the cortex and medulla. This process continues into old age, where whether with a microscope or with the human eye, the thymus may be difficult to detect, although typically weighs 5–15 grams. Additionally, there is an increasing body of evidence showing that age-related thymic involution is found in most, if not all, vertebrate species with a thymus, suggesting that this is an evolutionary process that has been conserved. 0/sup> The atrophy is due to the increased circulating level of sex hormones, and chemical or physical castration of an adult results in the thymus increasing in size and activity. Severe illness or human immunodeficiency virus infection may also result in involution.Function
T cell maturation
The thymus facilitates the maturation of T cells, an important part of the immune system providing cell-mediated immunity. T cells begin as hematopoietic precursors from the bone-marrow, and migrate to the thymus, where they are referred to as thymocytes. In the thymus they undergo a process of maturation, which involves ensuring the cells react against antigens ("positive selection"), but that they do not react against antigens found on body tissue ("negative selection"). Once mature, T cells emigrate from the thymus to provide vital functions in the immune system. Each T cell has a distinct T cell receptor, suited to a specific substance, called an antigen. Most T cell receptors bind to themajor histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are calle ...
on cells of the body. The MHC presents an antigen to the T cell receptor, which becomes active if this matches the specific T cell receptor. In order to be properly functional, a mature T cell needs to be able to bind to the MHC molecule ("positive selection"), and not to react against antigens that are actually from the tissues of body ("negative selection"). Positive selection occurs in the cortex and negative selection occurs in the medulla of the thymus. After this process T cells that have survived leave the thymus, regulated by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Further maturation occurs in the peripheral circulation. Some of this is because of hormones and cytokines secreted by cells within the thymus, including thymulin
Thymulin (also known as thymic factor or its old name facteur thymique serique) is a nonapeptide produced by two distinct epithelial populations in the thymus first described by Bach in 1977. It requires zinc for biological activity. Its peptide ...
, thymopoietin, and thymosin
Thymosins are small proteins present in many animal tissues. They are named thymosins because they were originally isolated from the thymus, but most are now known to be present in many other tissues. Thymosins have diverse biological activities, ...
s.
Positive selection
T cells have distinct T cell receptors. These distinct receptors are formed by process of V(D)J recombination gene rearrangement stimulated by RAG1 and RAG2 genes. This process is error-prone, and some thymocytes fail to make functional T-cell receptors, whereas other thymocytes make T-cell receptors that are autoreactive. If a functional T cell receptor is formed, the thymocyte will begin to express simultaneously the cell surface proteinsCD4
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ...
and CD8.
The survival and nature of the T cell then depends on its interaction with surrounding thymic epithelial cells. Here, the T cell receptor interacts with the MHC molecules on the surface of epithelial cells. A T cell with a receptor that doesn't react, or reacts weakly will die by apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
. A T cell that does react will survive and proliferate. A mature T cell expresses only CD4 or CD8, but not both. This depends on the strength of binding between the TCR and MHC class 1 or class 2. A T cell receptor that binds mostly to MHC class I tends to produce a mature "cytotoxic" CD8 positive T cell; a T cell receptor that binds mostly to MHC class II tends to produce a CD4 positive T cell.
Negative selection
T cells that attack the body's own proteins are eliminated in the thymus, called "negative selection". Epithelial cells in the medulla and dendritic cells in the thymus express major proteins from elsewhere in the body. The gene that stimulates this is AIRE. Thymocytes that react strongly to self antigens do not survive, and die by apoptosis. Some CD4 positive T cells exposed to self antigens persist asT regulatory cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosu ...
s.
Clinical significance
Immunodeficiency
As the thymus is where T cells develop, congenital problems with the development of the thymus can lead toimmunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
, whether because of a problem with the development of the thymus gland, or a problem specific to thymocyte development. Immunodeficiency can be profound. Loss of the thymus at an early age through genetic mutation (as in DiGeorge syndrome, CHARGE syndrome
CHARGE syndrome (formerly known as CHARGE association) is a rare syndrome caused by a genetic disorder. First described in 1979, the acronym "CHARGE" came into use for newborn children with the congenital features of coloboma of the eye, heart ...
, or a very rare "nude" thymus causing absence of hair and the thymus) results in severe immunodeficiency and subsequent high susceptibility to infection by viruses, protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
, and fungi. Nude mice with the very rare "nude" deficiency as a result of FOXN1
Forkhead box protein N1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FOXN1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ...
mutation are a strain of research mice as a model of T cell deficiency.
The most common congenital cause of thymus-related immune deficiency results from the deletion of the 22nd chromosome, called DiGeorge syndrome. This results in a failure of development of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches, resulting in failure of development of the thymus, and variable other associated problems, such as congenital heart disease, and abnormalities of mouth (such as cleft palate and cleft lip), failure of development of the parathyroid glands
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes pa ...
, and the presence of a fistula between the trachea and the oesophagus. Very low numbers of circulating T cells are seen. The condition is diagnosed by fluorescent in situ hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed ...
and treated with thymus transplantation
Thymus transplantation is a form of organ transplantation where the thymus is moved from one body to another. It is used in certain immunodeficiencies.
Indications
Thymus transplantation is used to treat infants with DiGeorge syndrome, which r ...
.
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) are group of rare congenital genetic diseases that can result in combined T, B, and NK cell deficiencies. These syndromes are caused by mutations that affect the maturation of the hematopoietic progenitor cells, which are the precursors of both B and T cells. A number of genetic defects can cause SCID, including IL-2 receptor gene loss of function, and mutation resulting in deficiency of the enzyme adenine deaminase
In enzymology, an adenine deaminase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the chemical reaction
:adenine + H2O \rightleftharpoons hypoxanthine + NH3
Thus, the two substrate (biochemistry), substrates of this enzyme are adenine and water, H2O, ...
.
Autoimmune disease
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1, is a rare genetic autoimmune syndrome that results from a genetic defect of the thymus tissues. Specifically, the disease results from defects in the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene, which stimulates expression of self antigens in the epithelial cells within the medulla of the thymus. Because of defects in this condition, self antigens are not expressed, resulting in T cells that are not conditioned to tolerate tissues of the body, and may treat them as foreign, stimulating an immune response and resulting in autoimmunity. People with APECED develop an autoimmune disease that affects multipleendocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
tissues, with the commonly affected organs being hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
of the thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobe (anatomy), lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of Connective tissue, tissue cal ...
, Addison's disease of the adrenal glands, and candida infection
Candidiasis is a Fungal infection in animals, fungal infection due to any type of ''Candida (genus), Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it Oral candidiasis, affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms in ...
of body surfaces including the inner lining of the mouth and of the nails due to dysfunction of TH17 cells
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg different ...
, and symptoms often beginning in childhood. Many other autoimmune diseases may also occur. Treatment is directed at the affected organs.
Thymoma-associated multiorgan autoimmunity
Thymoma-associated multiorgan autoimmunity can occur in people with thymoma. In this condition, the T cells developed in the thymus are directed against the tissues of the body. This is because the malignant thymus is incapable of appropriately educating developing thymocytes to eliminate self-reactive T cells. The condition is virtually indistinguishable from graft versus host disease.Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, dro ...
is an autoimmune disease most often due to antibodies that block acetylcholine receptors, involved in signalling between nerves and muscles. It is often associated with thymic hyperplasia or thymoma, with antibodies produced probably because of T cells that develop abnormally. Myasthenia gravis most often develops between young and middle age, causing easy fatiguing of muscle movements. Investigations include demonstrating antibodies (such as against acetylcholine receptors or muscle-specific kinase), and CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
to detect thymoma or thymectomy. With regard to the thymus, removal of the thymus, called thymectomy
A thymectomy is an operation to remove the thymus. It usually results in remission of myasthenia gravis with the help of medication including steroids. However, this remission may not be permanent. Thymectomy is indicated when thymoma are present ...
may be considered as a treatment, particularly if a thymoma is found. Other treatments include increasing the duration of acetylcholine action at nerve synapses by decreasing the rate of breakdown. This is done by acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as pyridostigmine.
Cancer
Thymomas
Tumours originating from the thymic epithelial cells are calledthymomas
A thymoma is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that is considered a rare malignancy. Thymomas are frequently associated with neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis; thymoma is found in 20% of patients with mya ...
. They most often occur in adults older than 40. Tumours are generally detected when they cause symptoms, such as a neck mass
A neck mass or neck lump is an ambiguous mass found in the neck area. There are many different possible causes, including congenital conditions like branchial anomalies and thyroglossal duct cysts.
Workup
Workup of a neck mass includes a medical ...
or affecting nearby structures such as the superior vena cava; detected because of screening in patients with myasthenia gravis, which has a strong association with thymomas and hyperplasia; and detected as an incidental finding Incidental medical findings are previously undiagnosed medical or psychiatric conditions that are discovered unintentionally and during evaluation for a medical or psychiatric condition. Such findings may occur in a variety of settings, including ro ...
on imaging such as chest x-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
s. Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferati ...
and tumours originating form the thymus are associated with other autoimmune diseases – such as hypogammaglobulinemia, Graves disease, pure red cell aplasia, pernicious anaemia and dermatomyositis, likely because of defects in negative selection in proliferating T cells.
Thymomas can be benign; benign but by virtue of expansion, invading beyond the capsule of the thymus ("invasive thyoma"), or malignant (a carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal ...
). This classification is based on the appearance of the cells. A WHO classification also exists but is not used as part of standard clinical practice. Benign tumours confined to the thymus are most common; followed by locally invasive tumours, and then by carcinomas. There is variation in reporting, with some sources reporting malignant tumours as more common. Invasive tumours, although not technically malignant, can still spread () to other areas of the body. Even though thymomas occur of epithelial cells, they can also contain thymocytes. Treatment of thymomas often requires surgery to remove the entire thymus. This may also result in temporary remission of any associated autoimmune conditions.
Lymphomas
Tumours originating from T cells of the thymus form a subset of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL). These are similar in symptoms, investigation approach and management to other forms of ALL. Symptoms that develop, like other forms of ALL, relate to deficiency of platelets, resulting in bruising or bleeding; immunosuppression resulting in infections; or infiltration by cells into parts of the body, resulting in an enlarged liver, spleen, lymph nodes or other sites. Blood test might reveal a large amount of white blood cells or lymphoblasts, and deficiency in other cell lines – such as low platelets or anaemia.Immunophenotyping Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspension, ...
will reveal cells that are CD3, a protein found on T cells, and help further distinguish the maturity of the T cells. Genetic analysis including karyotyping may reveal specific abnormalities that may influence prognosis or treatment, such as the Philadelphia translocation
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells (particularly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells). This chromosome is defective and unusually short becaus ...
. Management can include multiple courses of chemotherapy, stem cell transplant, and management of associated problems, such as treatment of infections with antibiotics, and blood transfusions. Very high white cell counts may also require cytoreduction with apheresis.
Tumours originating from the small population of B cells present in the thymus lead to primary mediastinal (thymic) large B cell lymphomas. These are a rare subtype of Non-Hodgkins lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. ...
, although by the activity of genes and occasionally microscopic shape, unusually they also have the characteristics of Hodgkins lymphomas. that occur most commonly in young and middle-aged, more prominent in females. Most often, when symptoms occur it is because of compression of structures near the thymus, such as the superior vena cava or the upper respiratory tract; when lymph nodes are affected it is often in the mediastinum and neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In ...
groups. Such tumours are often detected with a biopsy that is subject to immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to an ...
. This will show the presence of clusters of differentiation, cell surface proteins – namely CD30, with CD19
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, also known as CD19 molecule ( Cluster of Differentiation 19), B-Lymphocyte Surface Antigen B4, T-Cell Surface Antigen Leu-12 and CVID3 is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the gene ''CD19''. In humans, ...
, CD20 and CD22
CD22, or cluster of differentiation-22, is a molecule belonging to the SIGLEC family of lectins. It is found on the surface of mature B cells and to a lesser extent on some immature B cells. Generally speaking, CD22 is a regulatory molecule that ...
, and with the absence of CD15. Other markers may also be used to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment usually includes the typical regimens of CHOP
Chop, CHOP, Chops, or CHOPS may refer to:
Art
*Embouchure, in music, a synonym for chops (and later, more broadly, musical skill or ability)
*CHOPS, an Asian-American hip hop producer, rapper and member of rap group Mountain Brothers
* ''Chops'' ...
or EPOCH or other regimens; regimens generally including cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
, an anthracycline, prednisone, and other chemotherapeutics; and potentially also a stem cell transplant.
Thymic cysts
The thymus may contain cysts, usually less than 4 cm in diameter. Thymic cysts are usually detected incidentally and do not generally cause symptoms. Thymic cysts can occur along the neck or in the chest (mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
). Cysts usually just contain fluid and are lined by either many layers of flat cells or column-shaped cells. Despite this, the presence of a cyst can cause problems similar to those of thymomas, by compressing nearby structures, and some may contact internal walls () and be difficult to distinguish from tumours. When cysts are found, investigation may include a workup for tumours, which may include CT or MRI scan of the area the cyst is suspected to be in.
Surgical removal
Thymectomy
A thymectomy is an operation to remove the thymus. It usually results in remission of myasthenia gravis with the help of medication including steroids. However, this remission may not be permanent. Thymectomy is indicated when thymoma are present ...
is the surgical removal of the thymus. The usual reason for removal is to gain access to the heart for surgery to correct congenital heart defects in the neonatal period. Other indications for thymectomy include the removal of thymomas and the treatment of myasthenia gravis. In neonates the relative size of the thymus obstructs surgical access to the heart and its surrounding vessels. Removal of the thymus in infancy results in often fatal immunodeficiency, because functional T cells have not developed. In older children and adults, which have a functioning lymphatic system with mature T cells also situated in other lymphoid organs, the effect is reduced, and limited to failure to mount immune responses against new antigens.
Society and culture
When used as food for humans, the thymus of animals is known as one of the kinds of sweetbread.History
The thymus was known to the ancient Greeks, and its name comes from the Greek word θυμός (''thumos''), meaning "anger", or in Ancient Greek, "heart, soul, desire, life", possibly because of its location in the chest, near where emotions are subjectively felt; or else the name comes from the herb ''thyme'' (also in Greek ''θύμος'' or ''θυμάρι''), which became the name for a "warty excrescence", possibly due to its resemblance to a bunch of thyme. Galen was the first to note that the size of the organ changed over the duration of a person's life. In the nineteenth century, a condition was identified as ''status thymicolymphaticus'' defined by an increase in lymphoid tissue and an enlarged thymus. It was thought to be a cause of sudden infant death syndrome but is now an obsolete term. The importance of the thymus in the immune system was discovered in 1961 by Jacques Miller, by surgically removing the thymus from one-day-old mice, and observing the subsequent deficiency in a lymphocyte population, subsequently named T cells after the organ of their origin. Until the discovery of its immunological role, the thymus had been dismissed as a "evolutionary accident", without functional importance. The role the thymus played in ensuring mature T cells tolerated the tissues of the body was uncovered in 1962, with the finding that T cells of a transplanted thymus in mice demonstrated tolerance towards tissues of the donor mouse. B cells and T cells were identified as different types of lymphocytes in 1968, and the fact that T cells required maturation in the thymus was understood. The subtypes of T cells (CD8 and CD4) were identified by 1975. The way that these subclasses of T cells matured – positive selection of cells that functionally bound to MHC receptors – was known by the 1990s. The important role of the AIRE gene, and the role of negative selection in preventing autoreactive T cells from maturing, was understood by 1994. Recently, advances in immunology have allowed the function of the thymus in T-cell maturation to be more fully understood.Other animals
The thymus is present in alljawed vertebrates
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living ...
, where it undergoes the same shrinkage with age and plays the same immunological function as in other vertebrates. Recently, in 2011, a discrete thymus-like lympho-epithelial structure, termed the ''thymoid'', was discovered in the gills of larval lampreys. Hagfish possess a protothymus associated with the pharyngeal velar muscles, which is responsible for a variety of immune responses.
The thymus is also present in most other vertebrates with similar structure and function as the human thymus. A second thymus in the neck has been reported sometimes to occur in the mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
As in humans, the guinea pig's thymus naturally atrophies as the animal reaches adulthood, but the athymic hairless guinea pig
The Skinny pig or skinny is an almost hairless strain of guinea pig. Skinny pigs typically have hair on their muzzles, feet, and legs, but are hairless over the remainder of their bodies. Some of them have a thin covering of fuzzy hair on their ...
(which arose from a spontaneous laboratory mutation) possesses no thymic tissue whatsoever, and the organ cavity is replaced with cystic spaces.
Additional images
chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
, the thymus appears as a radiodense (brighter in this image) mass by the upper lobe of the child's right (left in image) lung.
References
Books
* *External links
T cell development in the thymus.
Video by Janice Yau, describing stromal signaling and tolerance. Department of Immunology and Biomedical Communications, University of Toronto. Master's Research Project, Master of Science in Biomedical Communications. 2011. {{Authority control Immune system Lymphatic system Lymphatics of the torso Lymphoid organ Mammal anatomy Organs (anatomy)