|
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial–mesenchymal Transition
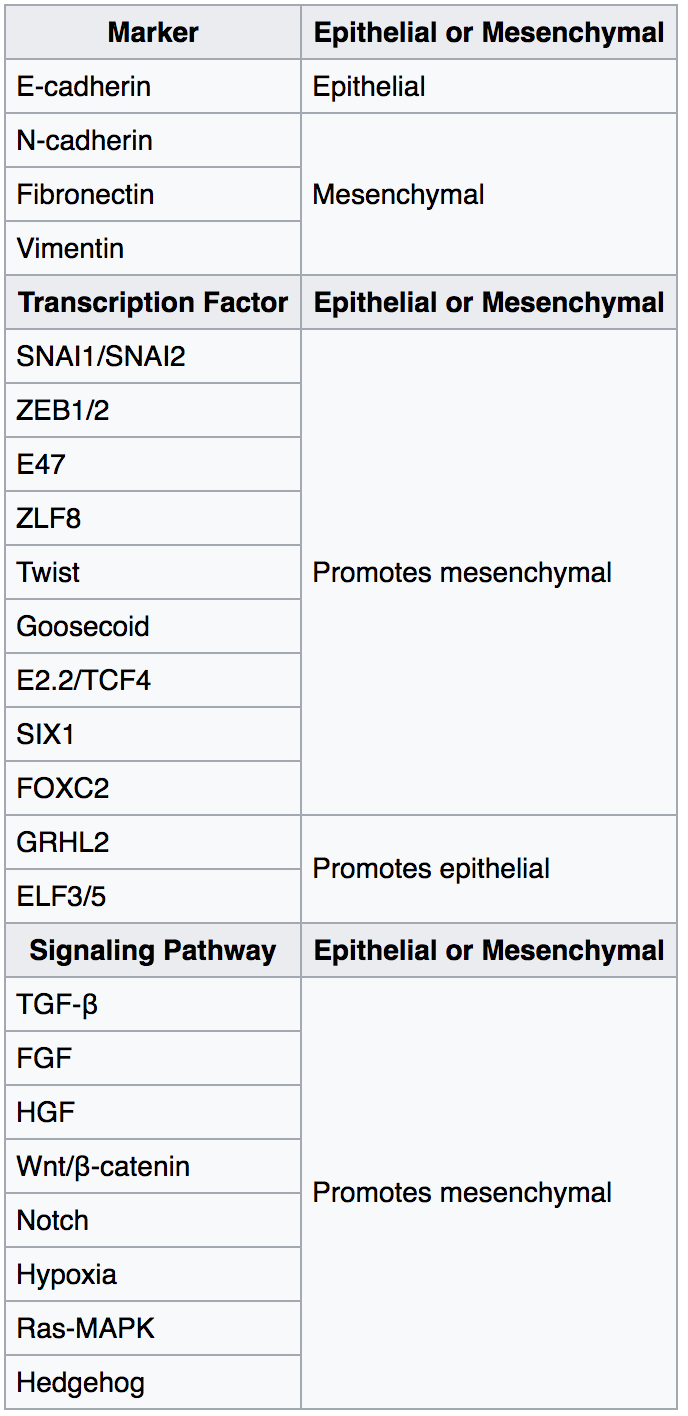
The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell–cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. EMT is essential for numerous developmental processes including mesoderm formation and neural tube formation. EMT has also been shown to occur in wound healing, in organ fibrosis and in the initiation of metastasis in cancer progression. Introduction Epithelial–mesenchymal transition was first recognized as a feature of embryogenesis by Betty Hay in the 1980s. EMT, and its reverse process, MET ( mesenchymal-epithelial transition) are critical for development of many tissues and organs in the developing embryo, and numerous embryonic events such as gastrulation, neural crest formation, heart valve formation, secondary palate development, and myogenesis. Epithelial and mesenchym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splanchnopleuric Mesenchyme
In the anatomy of an embryo, the splanchnopleuric mesenchyme is a structure created during embryogenesis when the lateral mesodermal germ layer splits into two layers. The inner (or splanchnic) layer adheres to the endoderm, and with it forms the splanchnopleure (mesoderm external to the coelom plus the endoderm). See also Post development the somato and splanchnopleuric junction lies at the duodeno-jejunal flexure. * somatopleure * mesenchyme References External links * * Overviewat Kennesaw State University Kennesaw State University (KSU) is a public research university located in the state of Georgia with two different campuses in the Atlanta metropolitan area, one in Kennesaw and the other in Marietta on a combined of land. The school was fo ... Embryology {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Before gastrulation, the embryo is a continuous epithelial sheet of cells; by the end of gastrulation, the embryo has begun differentiation to establish distinct cell lineages, set up the basic axes of the body (e.g. dorsal-ventral, anterior-posterior), and internalized one or more cell types including the prospective gut. In triploblastic organisms, the gastrula is trilaminar (three-layered). These three germ layers are the ectoderm (outer layer), mesoderm (middle layer), and endoderm (inner layer).Mundlos 2009p. 422/ref>McGeady, 2004: p. 34 In diploblastic organisms, such as Cnidaria and Ctenophora, the gastrula has only ectoderm and endoderm. The two layers are also sometimes referred to as the ''hypoblast'' and ''epiblast' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadherin-1
Cadherin-1 or Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin), (not to be confused with the APC/C activator protein CDH1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDH1'' gene. Mutations are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid, and ovarian cancers. CDH1 has also been designated as CD324 (cluster of differentiation 324). It is a tumor suppressor gene. History The discovery of cadherin cell-cell adhesion proteins is attributed to Masatoshi Takeichi, whose experience with adhering epithelial cells began in 1966. His work originally began by studying lens differentiation in chicken embryos at Nagoya University, where he explored how retinal cells regulate lens fiber differentiation. To do this, Takeichi initially collected media that had previously cultured neural retina cells (CM) and suspended lens epithelial cells in it. He observed that cells suspended in the CM media had delayed attachment compared to cells in his regular medium. His interest in cell adherence was spark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramembranous Ossification
Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created. Intramembranous ossification is also an essential process during the natural healing of bone fractures and the rudimentary formation of bones of the head. Unlike endochondral ossification, which is the other process by which bone tissue is created during fetal development, cartilage is not present during intramembranous ossification. Formation of woven bone Mesenchymal stem cells within mesenchyme or the medullary cavity of a bone fracture initiate the process of intramembranous ossification. A mesenchymal stem cell, or MSC, is an unspecialized cell that can develop into an osteoblast. Before it begins to develop, the morphological characteristics of a MSC are: A small cell body with a few cell processes that are long and thin; a large, round nucleus with a promin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal (connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Sarcomas are ''primary'' connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to ''secondary'' (or "metastatic") connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body (such as the lungs, breast tissue or prostate) spreads to the connective tissue. The word ''sarcoma'' is derived from the Greek σάρκωμα ''sarkōma'' "fleshy excrescence or substance", itself from σάρξ ''sarx'' meaning "flesh". Classification Sarcomas are typically divided into two major groups: bone sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchymal Stem Cell
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) also known as mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (bone cells), chondrocytes (cartilage cells), myocytes (muscle cells) and adipocytes (fat cells which give rise to marrow adipose tissue). Structure Definition While the terms ''mesenchymal stem cell'' (MSC) and ''marrow stromal cell'' have been used interchangeably for many years, neither term is sufficiently descriptive: * Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue that is derived from the mesoderm and that differentiates into hematopoietic and connective tissue, whereas MSCs do not differentiate into hematopoietic cells. * Stromal cells are connective tissue cells that form the supportive structure in which the functional cells of the tissue reside. While this is an accurate description for one function of MSCs, the term fails to convey the relatively recently discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |