Thermal Metamorphism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Metamorphism is the transformation of existing
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing
 Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. The importance of heating in the formation of metamorphic rock was first recognized by the pioneering Scottish naturalist,
Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. The importance of heating in the formation of metamorphic rock was first recognized by the pioneering Scottish naturalist,
 Metamorphic rocks are typically more coarsely crystalline than the protolith from which they formed. Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. This is partially missing at the surface of the crystal, producing a ''
Metamorphic rocks are typically more coarsely crystalline than the protolith from which they formed. Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. This is partially missing at the surface of the crystal, producing a ''
 To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. This form of metamorphism takes place at
To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. This form of metamorphism takes place at
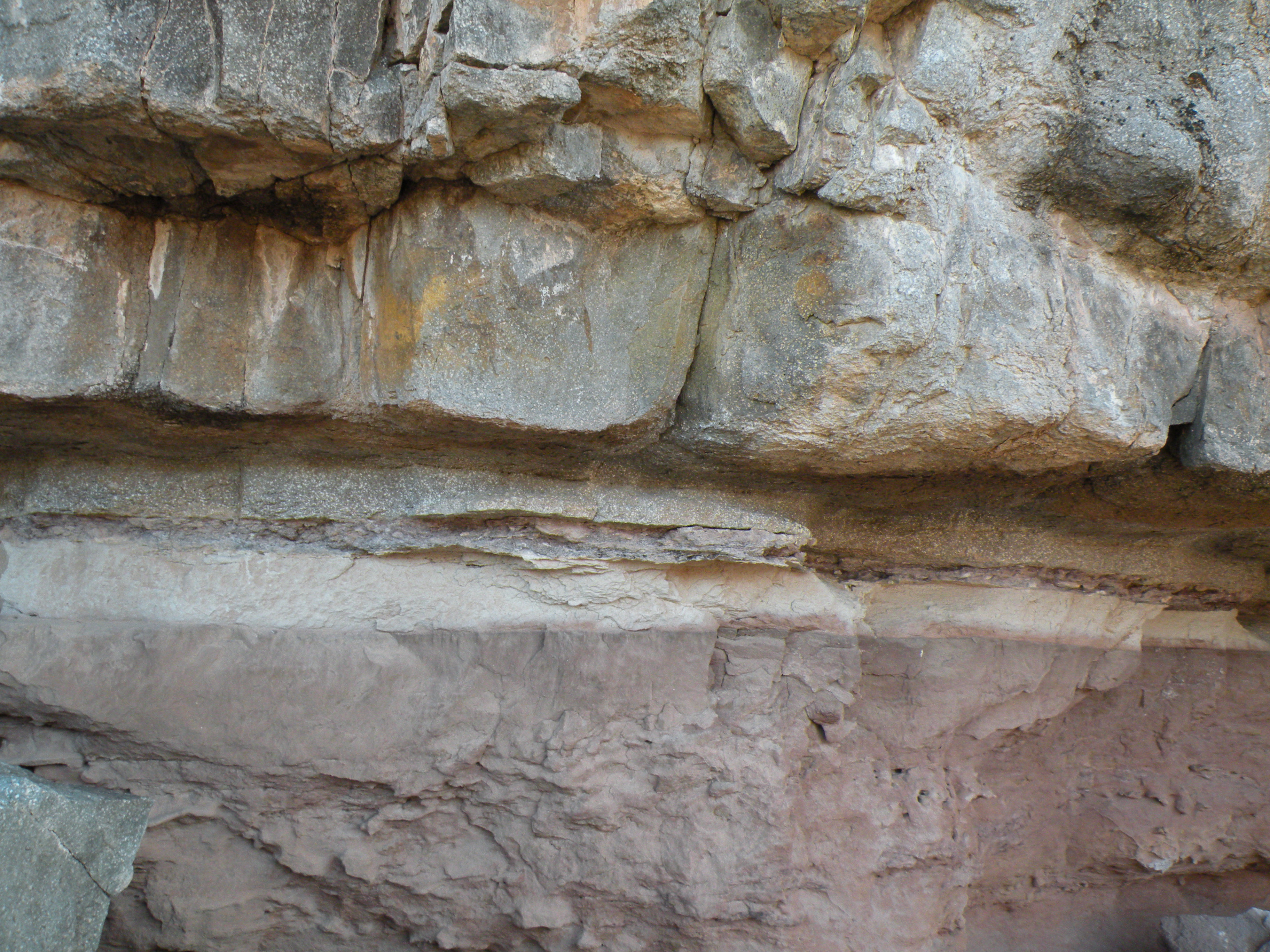 Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler
Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler
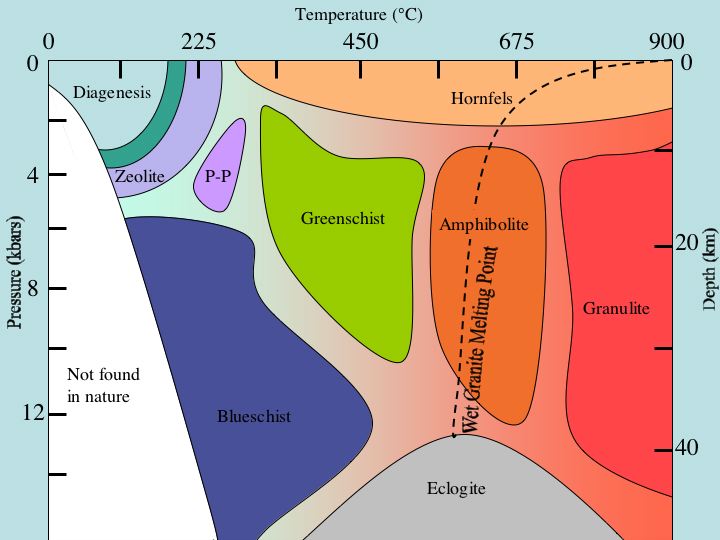 See diagram for more detail.
See diagram for more detail.

 Metamorphic processes act to bring the protolith closer to thermodynamic equilibrium, which is its state of maximum stability. For example, shear stress (nonhydrodynamic stress) is incompatible with thermodynamic equilibrium, so sheared rock will tend to deform in ways that relieve the shear stress. The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy
where:
*''U'' is the
Metamorphic processes act to bring the protolith closer to thermodynamic equilibrium, which is its state of maximum stability. For example, shear stress (nonhydrodynamic stress) is incompatible with thermodynamic equilibrium, so sheared rock will tend to deform in ways that relieve the shear stress. The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy
where:
*''U'' is the
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 1. How to Name a Metamorphic Rock
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 2. Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. Structural terms including fault rock terms
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 4. High P/T Metamorphic Rocks
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110720035915/http://metpetdb.rpi.edu/ Metamorphic Petrology Database(
 Metamorphism is the transformation of existing
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
(the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface.
Various forms of metamorphism exist, including regional, contact
Contact may refer to:
Interaction Physical interaction
* Contact (geology), a common geological feature
* Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye
* Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects
* ...
, hydrothermal, shock, and dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasing temperature and pressure characterize ''retrograde metamorphism''.
Metamorphic petrology
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together ...
is the study of metamorphism. Metamorphic petrologists rely heavily on statistical mechanics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. It does not assume or postulate any natural laws, but explains the macroscopic be ...
and experimental petrology
Experimental petrology is the field of research concerned with experimentally determining the physical and chemical behavior of rocks and their constituents. Because there is no way to directly observe or measure deep earth processes, geochemist ...
to understand metamorphic processes.
Metamorphic processes
 Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. The importance of heating in the formation of metamorphic rock was first recognized by the pioneering Scottish naturalist,
Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. The importance of heating in the formation of metamorphic rock was first recognized by the pioneering Scottish naturalist, James Hutton
James Hutton (; 3 June O.S.172614 June 1726 New Style. – 26 March 1797) was a Scottish geologist, agriculturalist, chemical manufacturer, naturalist and physician. Often referred to as the father of modern geology, he played a key role i ...
, who is often described as the father of modern geology. Hutton wrote in 1795 that some rock beds of the Scottish Highlands had originally been sedimentary rock, but had been transformed by great heat.
Hutton also speculated that pressure was important in metamorphism. This hypothesis was tested by his friend, James Hall, who sealed chalk into a makeshift pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.
Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size o ...
constructed from a cannon barrel and heated it in an iron foundry furnace. Hall found that this produced a material strongly resembling marble, rather than the usual quicklime
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ma ...
produced by heating of chalk in the open air. French geologists subsequently added metasomatism, the circulation of fluids through buried rock, to the list of processes that help bring about metamorphism. However, metamorphism can take place without metasomatism (isochemical metamorphism) or at depths of just a few hundred meters where pressures are relatively low (for example, in contact metamorphism).
Rock can be transformed without melting because heat causes atomic bonds to break, freeing the atoms to move and form new bonds with other atoms. Pore fluid present between mineral grains is an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. This permits recrystallization of existing minerals or crystallization of new minerals with different crystalline structures or chemical compositions ( neocrystallization). The transformation converts the minerals in the protolith into forms that are more stable (closer to chemical equilibrium) under the conditions of pressure and temperature at which metamorphism takes place.
Metamorphism is generally regarded to begin at temperatures of . This excludes diagenetic changes due to compaction and lithification, which result in the formation of sedimentary rocks. The upper boundary of metamorphic conditions lies at the solidus of the rock, which is the temperature at which the rock begins to melt. At this point, the process becomes an igneous process. The solidus temperature depends on the composition of the rock, the pressure, and whether the rock is saturated with water. Typical solidus temperatures range from for wet granite at a few hundred megapascals (Mpa) of pressure to about for wet basalt at atmospheric pressure. Migmatites are rocks formed at this upper limit, which contains pods and veins of material that has started to melt but has not fully segregated from the refractory residue.
The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar
The bar is a metric unit of pressure, but not part of the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as exactly equal to 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), or slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea lev ...
(1500 Mpa).
Recrystallization
The change in the grain size and orientation in the rock during the process of metamorphism is called recrystallization. For instance, the smallcalcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
crystals in the sedimentary rocks limestone and chalk change into larger crystals in the metamorphic rock marble. In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. Both high temperatures and pressures contribute to recrystallization. High temperatures allow the atoms and ions in solid crystals to migrate, thus reorganizing the crystals, while high pressures cause solution of the crystals within the rock at their points of contact ('' pressure solution'') and redeposition in pore space.
During recrystallization, the identity of the mineral does not change, only its texture. Recrystallization generally begins when temperatures reach above half the melting point of the mineral on the Kelvin scale.
Pressure solution begins during diagenesis (the process of lithification of sediments into sedimentary rock) but is completed during early stages of metamorphism. For a sandstone protolith, the dividing line between diagenesis and metamorphism can be placed at the point where strained quartz grains begin to be replaced by new, unstrained, small quartz grains, producing a ''mortar texture'' that can be identified in thin sections under a polarizing microscope. With increasing grade of metamorphism, further recrystallization produces ''foam texture'', characterized by polygonal grains meeting at triple junctions, and then ''porphyroblastic texture'', characterized by coarse, irregular grains, including some larger grains ( porphyroblasts.)
 Metamorphic rocks are typically more coarsely crystalline than the protolith from which they formed. Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. This is partially missing at the surface of the crystal, producing a ''
Metamorphic rocks are typically more coarsely crystalline than the protolith from which they formed. Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. This is partially missing at the surface of the crystal, producing a ''surface energy
In surface science, surface free energy (also interfacial free energy or surface energy) quantifies the disruption of intermolecular bonds that occurs when a surface is created. In solid-state physics, surfaces must be intrinsically less energe ...
'' that makes the surface thermodynamically unstable. Recrystallization to coarser crystals reduces the surface area and so minimizes the surface energy.
Although grain coarsening is a common result of metamorphism, rock that is intensely deformed may eliminate strain energy by recrystallizing as a fine-grained rock called '' mylonite''. Certain kinds of rock, such as those rich in quartz, carbonate minerals, or olivine, are particularly prone to form mylonites, while feldspar and garnet are resistant to mylonitization.
Phase change
Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. An example is provided by thealuminium silicate
Aluminium silicate (or aluminum silicate) is a name commonly applied to chemical compounds which are derived from aluminium oxide, Al2O3 and silicon dioxide, SiO2 which may be anhydrous or hydrated, naturally occurring as minerals or synthetic. ...
minerals, kyanite, andalusite, and sillimanite. All three have the identical composition, . Kyanite is stable at surface conditions. However, at atmospheric pressure, kyanite transforms to andalusite at a temperature of about . Andalusite, in turn, transforms to sillimanite when the temperature reaches about . At pressures above about 4 kbar (400 Mpa), kyanite transforms directly to sillimanite as the temperature increases. A similar phase change is sometimes seen between calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
and aragonite, with calcite transforming to aragonite at elevated pressure and relatively low temperature.
Neocrystallization
Neocrystallization involves the creation of new mineral crystals different from the protolith. Chemical reactions digest the minerals of the protolith which yields new minerals. This is a very slow process as it can also involve the diffusion of atoms through solid crystals. An example of a neocrystallization reaction is the reaction of fayalite with plagioclase at elevated pressure and temperature to form garnet. The reaction is: Many complex high-temperature reactions may take place between minerals without them melting, and each mineral assemblage produced provides us with a clue as to the temperatures and pressures at the time of metamorphism. These reactions are possible because of rapid diffusion of atoms at elevated temperature. Pore fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. A particularly important group of neocrystallization reactions are those that releasevolatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.
On planet Earth, the term ' ...
such as water and carbon dioxide. During metamorphism of basalt to eclogite in subduction zones
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
, hydrous minerals break down, producing copious quantities of water. The water rises into the overlying mantle, where it lowers the melting temperature of the mantle rock, generating magma via flux melting. The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. The resulting arc volcanoes tend to produce dangerous eruptions, because their high water content makes them extremely explosive.
Examples of ''dehydration reactions'' that release water include:
An example of a decarbonation reaction is:
Plastic deformation
In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. In order for this to happen temperatures must be high enough that brittle fractures do not occur, but not so high that diffusion of crystals takes place. As with pressure solution, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis.Types
Regional
''Regional metamorphism'' is a general term for metamorphism that affects entire regions of the Earth's crust. It most often refers to ''dynamothermal metamorphism'', which takes place in '' orogenic belts'' (regions wheremountain building
Mountain formation refers to the geological processes that underlie the formation of mountains. These processes are associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust (tectonic plates). Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intr ...
is taking place), but also includes ''burial metamorphism'', which results simply from rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin.
Dynamothermal
convergent plate boundaries
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a p ...
, where two continental plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
or a continental plate and an island arc collide. The collision zone becomes a belt of mountain formation called an ''orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted t ...
''. The orogenic belt is characterized by thickening of the Earth's crust, during which the deeply buried crustal rock is subjected to high temperatures and pressures and is intensely deformed. Subsequent erosion of the mountains exposes the roots of the orogenic belt as extensive outcrops of metamorphic rock, characteristic of mountain chains.
Metamorphic rock formed in these settings tends to shown well-developed foliation. Foliation develops when a rock is being shortened along one axis during metamorphism. This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is ...
and chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac ...
, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. This results in a banded, or foliated, rock, with the bands showing the colors of the minerals that formed them. Foliated rock often develops planes of cleavage. Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
is an example of a foliated metamorphic rock, originating from shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
, and it typically shows well-developed cleavage that allows slate to be split into thin plates.
The type of foliation that develops depends on the metamorphic grade. For instance, starting with a mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology. ...
, the following sequence develops with increasing temperature: The mudstone is first converted to slate, which is a very fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock, characteristic of very low grade metamorphism. Slate in turn is converted to phyllite, which is fine-grained and found in areas of low grade metamorphism. Schist is medium to coarse-grained and found in areas of medium grade metamorphism. High-grade metamorphism transforms the rock to gneiss, which is coarse to very coarse-grained.
Rocks that were subjected to uniform pressure from all sides, or those that lack minerals with distinctive growth habits, will not be foliated. Marble lacks platy minerals and is generally not foliated, which allows its use as a material for sculpture and architecture.
Collisional orogenies are preceded by subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
of oceanic crust. The conditions within the subducting slab as it plunges toward the mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
in a subduction zone produce their own distinctive regional metamorphic effects, characterized by paired metamorphic belts
Paired metamorphic belts are sets of parallel linear rock units that display contrasting Metamorphic facies, metamorphic mineral assemblages. These paired belts develop along Convergent boundary, convergent plate boundaries where subduction is acti ...
.
The pioneering work of George Barrow on regional metamorphism in the Scottish Highlands showed that some regional metamorphism produces well-defined, mappable zones of increasing metamorphic grade. This '' Barrovian metamorphism'' is the most recognized metamorphic series Metamorphic series include the Barrovian and Buchan series of metamorphic rocks. George Barrow was a geologist in Scotland who discovered the Barrovian series. These are also called metamorphic facies series. A metamorphic facies series is a seque ...
in the world. However, Barrovian metamorphism is specific to pelitic
A pelite (Greek: ''pelos'', "clay") or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, ...
rock, formed from mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology. ...
or siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, p ...
, and it is not unique even in pelitic rock. A different sequence in the northeast of Scotland defines ''Buchan metamorphism Metamorphic series include the Barrovian and Buchan series of metamorphic rocks. George Barrow (geologist), George Barrow was a geologist in Scotland who discovered the Barrovian series. These are also called metamorphic facies series. A metamorphic ...
'', which took place at lower pressure than the Barrovian.
Burial
Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. Here the rock subjected to high temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock layers above. Burial metamorphism tends to produced low-grade metamorphic rock. This shows none of the effects of deformation and folding so characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism. Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as theSioux Quartzite
The Sioux Quartzite is a Proterozoic quartzite that is found in the region around the intersection of Minnesota, South Dakota, and Iowa, and correlates with other rock units throughout the upper midwestern and southwestern United States. It was ...
, and in the Hamersley Basin
The Hamersley Range is a mountainous region of the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The range was named on 12 June 1861 by explorer Francis Thomas Gregory after Edward Hamersley (senior), Edward Hamersley, a prominent promoter of his explo ...
of Australia.
Contact (thermal)
country rock
Country rock is a genre of music which fuses rock and country. It was developed by rock musicians who began to record country-flavored records in the late 1960s and early 1970s. These musicians recorded rock records using country themes, vocal s ...
. The area surrounding the intrusion where the contact metamorphism effects are present is called the metamorphic aureole, the contact aureole, or simply the aureole. Contact metamorphic rocks are usually known as hornfels. Rocks formed by contact metamorphism may not present signs of strong deformation and are often fine-grained and extremely tough.
Contact metamorphism is greater adjacent to the intrusion and dissipates with distance from the contact. The size of the aureole depends on the heat of the intrusion, its size, and the temperature difference with the wall rocks. Dikes generally have small aureoles with minimal metamorphism, extending not more than one or two dike thicknesses into the surrounding rock, whereas the aureoles around batholiths
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, suc ...
can be up to several kilometers wide.
The metamorphic grade of an aureole is measured by the peak metamorphic mineral which forms in the aureole. This is usually related to the metamorphic temperatures of pelitic
A pelite (Greek: ''pelos'', "clay") or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, ...
or aluminosilicate rocks and the minerals they form. The metamorphic grades of aureoles at shallow depth are albite-epidote
Epidote is a calcium aluminium iron sorosilicate mineral.
Description
Well developed crystals of epidote, Ca2Al2(Fe3+;Al)(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system, are of frequent occurrence: they are commonly prismatic in habi ...
hornfels, hornblende hornfels, pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
hornfels, and sillimanite hornfels, in increasing order of temperature of formation. However, the albite-epidote hornfels is often not formed, even though it is the lowest temperature grade.
Magmatic fluids coming from the intrusive rock may also take part in the metamorphic reactions. An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks. In this case the metamorphism grades into metasomatism. If the intruded rock is rich in carbonate the result is a skarn. Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
-rich magmatic waters which leave a cooling granite may often form greisens within and adjacent to the contact of the granite. Metasomatic altered aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest.
''Fenitization'', or ''Na-metasomatism'', is a distinctive form of contact metamorphism accompanied by metasomatism. It takes place around intrusions of a rare type of magma called a '' carbonatite'' that is highly enriched in carbonates and low in silica. Cooling bodies of carbonatite magma give off highly alkaline fluids rich in sodium as they solidify, and the hot, reactive fluid replaces much of the mineral content in the aureole with sodium-rich minerals.
A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism
Pyrometamorphism is a type of metamorphism in which rocks are rapidly changed by heat, ''e.g.'' coming from a rapidly emplaced extrusive or intrusive igneous rock or from a fossil fuel fire. The rocks produced by pyrometamorphism include buchite, ...
.
Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal metamorphism is the result of the interaction of a rock with a high-temperature fluid of variable composition. The difference in composition between an existing rock and the invading fluid triggers a set of metamorphic and metasomatic reactions. The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Convective circulation of hydrothermal fluids in the ocean floor basalts produces extensive hydrothermal metamorphism adjacent to spreading centers and other submarine volcanic areas. The fluids eventually escape through vents on the ocean floor known asblack smokers
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
. The patterns of this hydrothermal alteration are used as a guide in the search for deposits of valuable metal ores.
Shock
Shock metamorphism occurs when an extraterrestrial object (ameteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the ...
for instance) collides with the Earth's surface. Impact metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature. The resulting minerals (such as SiO2 polymorphs coesite and stishovite
Stishovite is an extremely hard, dense tetragonal form (Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph) of silicon dioxide. It is very rare on the Earth's surface; however, it may be a predominant form of silicon dioxide in the Earth, especially in ...
) and textures are characteristic of these conditions.
Dynamic
Dynamic metamorphism is associated with zones of high strain such as fault zones. In these environments, mechanical deformation is more important than chemical reactions in transforming the rock. The minerals present in the rock often do not reflect conditions of chemical equilibrium, and the textures produced by dynamic metamorphism are more significant than the mineral makeup. There are threedeformation mechanism
A deformation mechanism, in geology, is a process occurring at a microscopic scale that is responsible for changes in a material's internal structure, shape and volume. The process involves planar discontinuity and/or displacement of atoms from th ...
s by which rock is mechanically deformed. These are ''cataclasis A cataclastic rock is a type of fault rock that has been wholly or partly formed by the progressive fracturing and comminution of existing rocks, a process known as ''cataclasis''. Cataclasis involves the granulation, crushing, or milling of the ori ...
'', the deformation of rock via the fracture and rotation of mineral grains; plastic deformation of individual mineral crystals; and movement of individual atoms by diffusive processes. The textures of dynamic metamorphic zones are dependent on the depth at which they were formed, as the temperature and confining pressure determine the deformation mechanisms which predominate.
At the shallowest depths, a fault zone will be filled with various kinds of unconsolidated cataclastic rock, such as '' fault gouge'' or '' fault breccia''. At greater depths, these are replaced by consolidated cataclastic rock, such as ''crush breccia'', in which the larger rock fragments are cemented together by calcite or quartz. At depths greater than about , '' cataclasites'' appear; these are quite hard rocks consist of crushed rock fragments in a flinty matrix, which forms only at elevated temperature. At still greater depths, where temperatures exceed , plastic deformation takes over, and the fault zone is composed of mylonite. Mylonite is distinguished by its strong foliation, which is absent in most cataclastic rock. It is distinguished from the surrounding rock by its finer grain size.
There is considerable evidence that cataclasites form as much through plastic deformation and recrystallization as brittle fracture of grains, and that the rock may never fully lose cohesion during the process. Different minerals become ductile at different temperatures, with quartz being among the first to become ductile, and sheared rock composed of different minerals may simultaneously show both plastic deformation and brittle fracture.
The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 10−14 sec−1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. At the highest strain rates, the rock may be so strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called '' pseudotachylite''. Pseudotachylites seem to be restricted to dry rock, such as granulite.
Classification of metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks are classified by their protolith, if this can be determined from the properties of the rock itself. For example, if examination of a metamorphic rock shows that its protolith was basalt, it will be described as a metabasalt. When the protolith cannot be determined, the rock is classified by its mineral composition or its degree of foliation.Metamorphic grades
Metamorphic grade is an informal indication of the amount or degree of metamorphism. In the Barrovian sequence (described by George Barrow in zones of progressive metamorphism in Scotland), metamorphic grades are also classified by mineral assemblage based on the appearance of key minerals in rocks ofpelitic
A pelite (Greek: ''pelos'', "clay") or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, ...
(shaly, aluminous) origin:
Low grade ------------------- Intermediate --------------------- High grade
:Greenschist ------------- Amphibolite ----------------------- Granulite
:Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
--- Phyllite ---------- Schist ---------------------- Gneiss --- Migmatite
:Chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac ...
zone
::::Biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more alumino ...
zone
::::::: Garnet zone
::::::::::Staurolite
Staurolite is a reddish brown to black, mostly opaque, nesosilicate mineral with a white streak. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and the chemical formula: Fe2+2Al9O6(SiO4)4(O,OH)2. Magnesium, zinc ...
zone
::::::::::::: Kyanite zone
:::::::::::::::: Sillimanite zone
A more complete indication of this intensity or degree is provided by the concept of metamorphic facies
A metamorphic facies is a set of mineral assemblages in metamorphic rocks formed under similar pressures and temperatures.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak The assemblage is typical of what is formed in conditions corresponding ...
.
Metamorphic facies
Metamorphic facies are recognizableterranes
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own ...
or zones with an assemblage of key minerals that were in equilibrium under specific range of temperature and pressure during a metamorphic event. The facies are named after the metamorphic rock formed under those facies conditions from basalt.
The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. However, the facies are defined such that metamorphic rock with as broad a range of compositions as is practical can be assigned to a particular facies. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. Eskola drew upon the zonal schemes, based on index minerals, that were pioneered by the British geologist, George Barrow.
The metamorphic facies is not usually considered when classifying metamorphic rock based on protolith, mineral mode, or texture. However, a few metamorphic facies produce rock of such distinctive character that the facies name is used for the rock when more precise classification is not possible. The chief examples are amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky ...
and eclogite. The British Geological Survey strongly discourages use of '' granulite'' as a classification for rock metamorphosed to the granulite facies. Instead, such rock will often be classified as a granofels. However, this is not universally accepted.
 See diagram for more detail.
See diagram for more detail.
Prograde and retrograde
Metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism. Prograde metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis) with increasing temperature and (usually) pressure conditions. These are solid state dehydration reactions, and involve the loss of volatiles such as water or carbon dioxide. Prograde metamorphism results in rock characteristic of the maximum pressure and temperature experienced. Metamorphic rocks usually do not undergo further change when they are brought back to the surface. Retrograde metamorphism involves the reconstitution of a rock via revolatisation under decreasing temperatures (and usually pressures), allowing the mineral assemblages formed in prograde metamorphism to revert to those more stable at less extreme conditions. This is a relatively uncommon process, because volatiles produced during prograde metamorphism usually migrate out of the rock and are not available to recombine with the rock during cooling. Localized retrograde metamorphism can take place when fractures in the rock provide a pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock.Equilibrium mineral assemblages

internal energy
The internal energy of a thermodynamic system is the total energy contained within it. It is the energy necessary to create or prepare the system in its given internal state, and includes the contributions of potential energy and internal kinet ...
(SI unit: joule),
* ''p'' is pressure (SI unit: pascal
Pascal, Pascal's or PASCAL may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Pascal (given name), including a list of people with the name
* Pascal (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
** Blaise Pascal, Fren ...
),
* ''V'' is volume (SI unit: m3),
* ''T'' is the temperature (SI unit: kelvin),
* ''S'' is the entropy (SI unit: joule per kelvin),
In other words, a metamorphic reaction will take place only if it lowers the total Gibbs free energy of the protolith. Recrystallization to coarser crystals lowers the Gibbs free energy by reducing surface energy, while phase changes and neocrystallization reduce the bulk Gibbs free energy. A reaction will begin at the temperature and pressure where the Gibbs free energy of the reagents becomes greater than that of the products.
A mineral phase will generally be more stable if it has a lower internal energy, reflecting tighter binding between its atoms. Phases with a higher density (expressed as a lower molar volume ''V'') are more stable at higher pressure, while minerals with a less ordered structure (expressed as a higher entropy ''S'') are favored at high temperature. Thus andalusite is stable only at low pressure, since it has the lowest density of any aluminium silicate polymorph, while sillimanite is the stable form at higher temperatures, since it has the least ordered structure.
The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. These are calibrated against experimentally measured properties and phase boundaries of mineral assemblages. The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer.
However, it is often very useful to represent equilibrium mineral assemblages using various kinds of diagrams. These include petrogenetic grids and compatibility diagrams (compositional phase diagrams.)
Petrogenetic grids
Apetrogenetic grid
A petrogenetic grid is a geological phase diagram that connects the stability ranges or metastability ranges of metamorphic minerals or mineral assemblages to the conditions of metamorphism. Experimentally determined mineral or mineral-assembla ...
is a geologic phase diagram
A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous ...
that plots experimentally derived metamorphic reactions
A metamorphic reaction is a chemical reaction that takes place during the geological process of metamorphism wherein one assemblage of minerals is transformed into a second assemblage which is stable under the new temperature/pressure conditions r ...
at their pressure and temperature conditions for a given rock composition. This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. The Al2SiO5 nesosilicate phase diagram shown is a very simple petrogenetic grid for rocks that only have a composition consisting of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. For a rock that contains multiple phases, the boundaries between many phase transformations may be plotted, though the petrogenetic grid quickly becomes complicated. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz.
Compatibility diagrams
Whereas a petrogenetic grid shows phases for a single composition over a range of temperature and pressure, a ''compatibility diagram'' shows how the mineral assemblage varies with composition at a fixed temperature and pressure. Compatibility diagrams provide an excellent way to analyze how variations in the rock's composition affect the mineral paragenesis that develops in a rock at particular pressure and temperature conditions. Because of the difficulty of depicting more than three components (as aternary diagram
A ternary plot, ternary graph, triangle plot, simplex plot, Gibbs triangle or de Finetti diagram is a barycentric plot on three variables which sum to a constant. It graphically depicts the ratios of the three variables as positions in an equ ...
), usually only the three most important components are plotted, though occasionally a compatibility diagram for four components is plotted as a projected
Projected is an American rock supergroup consisting of Sevendust members John Connolly and Vinnie Hornsby, Alter Bridge and Creed drummer Scott Phillips, and former Submersed and current Tremonti guitarist Eric Friedman. The band released thei ...
tetrahedron.
See also
* * Metamorphosis of snow *Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * Eskola P., 1920, ''The Mineral Facies of Rocks'', Norsk. Geol. Tidsskr., 6, 143–194 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Winter J.D., 2001, ''An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology'', Prentice-Hall .External links
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 1. How to Name a Metamorphic Rock
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 2. Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. Structural terms including fault rock terms
Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 4. High P/T Metamorphic Rocks
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110720035915/http://metpetdb.rpi.edu/ Metamorphic Petrology Database(
MetPetDB MetPetDB is a relational database and repository for global geochemical data on and images collected from metamorphic rocks from the earth's crust. MetPetDB is designed and built by a global community of metamorphic petrologists in collaboration ...
) – Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute () (RPI) is a private research university in Troy, New York, with an additional campus in Hartford, Connecticut. A third campus in Groton, Connecticut closed in 2018. RPI was established in 1824 by Stephen Van ...
{{Authority control
Geological processes
Metamorphic petrology