The speed of light in
vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal
physical constant
A physical constant, sometimes fundamental physical constant or universal constant, is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and have constant value in time. It is contrasted with a mathematical constant, ...
that is important in many areas of
physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the
special theory of relativity, is the upper limit for the speed at which conventional
matter or
energy (and thus any
signal carrying
information) can travel through
space.
All forms of
electromagnetic radiation, including
visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and very sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects.
Starlight
Starlight is the light emitted by stars. It typically refers to visible electromagnetic radiation from stars other than the Sun, observable from Earth at night, although a component of starlight is observable from Earth during daytime.
Sunligh ...
viewed on
Earth left the
star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s many years ago, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When
communicating with distant
space probes, it can take minutes to hours for signals to travel from Earth to the spacecraft and vice versa. In
computing, the speed of light fixes the ultimate minimum communication
delay between computers, to
computer memory, and within a
CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
. The speed of light can be used in
time of flight measurements to measure large distances to extremely high precision.
Ole Rømer
Ole Christensen Rømer (; 25 September 1644 – 19 September 1710) was a Danish astronomer who, in 1676, made the first measurement of the speed of light.
Rømer also invented the modern thermometer showing the temperature between two fix ...
first
demonstrated in 1676 that light travels at a finite speed (non-instantaneously) by studying the apparent motion of
Jupiter's moon
Io. Progressively more accurate measurements of its speed came over the following centuries. In a
paper published in 1865,
James Clerk Maxwell proposed that light was an
electromagnetic wave and, therefore, travelled at speed . In 1905,
Albert Einstein postulated that the speed of light with respect to any
inertial frame of reference is a constant and is independent of the motion of the light source.
He explored the consequences of that postulate by deriving the theory of relativity and, in doing so, showed that the parameter had relevance outside of the context of light and electromagnetism.
Massless particles and
field perturbations, such as
gravitational wave
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1 ...
s, also travel at speed in a vacuum. Such particles and waves travel at regardless of the motion of the source or the inertial reference frame of the
observer. Particles with nonzero
rest mass can be accelerated to approach but can never reach it, regardless of the frame of reference in which their speed is measured. In the
special and general theories of relativity, interrelates
space and time and also appears in the famous equation of
mass–energy equivalence
In physics, mass–energy equivalence is the relationship between mass and energy in a system's rest frame, where the two quantities differ only by a multiplicative constant and the units of measurement. The principle is described by the physicis ...
, .
In some cases, objects or waves may appear to travel
faster than light (e.g.,
phase velocities of waves,
the appearance of certain high-speed astronomical objects, and particular
quantum effects
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
). The
expansion of the universe
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not exp ...
is understood to exceed the speed of light beyond
a certain boundary.
The speed at which light propagates through
transparent materials, such as glass or air, is less than ; similarly, the speed of
electromagnetic waves
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) lig ...
in wire cables is slower than . The ratio between and the speed at which light travels in a material is called the
refractive index of the material (). For example, for visible light, the refractive index of glass is typically around 1.5, meaning that light in glass travels at ; the
refractive index of air for visible light is about 1.0003, so the speed of light in air is about slower than .
Numerical value, notation, and units
The speed of light in vacuum is usually denoted by a lowercase , for "constant" or the Latin (meaning 'swiftness, celerity'). In 1856,
Wilhelm Eduard Weber and
Rudolf Kohlrausch had used for a different constant that was later shown to equal times the speed of light in vacuum. Historically, the symbol ''V'' was used as an alternative symbol for the speed of light, introduced by
James Clerk Maxwell in 1865. In 1894,
Paul Drude redefined with its modern meaning.
Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
used ''V'' in his
original German-language papers on special relativity in 1905, but in 1907 he switched to , which by then had become the standard symbol for the speed of light.
[
"The origins of the letter c being used for the speed of light can be traced back to a paper of 1856 by Weber and Kohlrausch ..Weber apparently meant c to stand for 'constant' in his force law, but there is evidence that physicists such as Lorentz and Einstein were accustomed to a common convention that c could be used as a variable for velocity. This usage can be traced back to the classic Latin texts in which c stood for 'celeritas', meaning 'speed'."
]
Sometimes is used for the speed of waves in any material medium, and
0 for the speed of light in vacuum.
[See for example:
*
*
*
* ] This subscripted notation, which is endorsed in official SI literature,
has the same form as related electromagnetic constants: namely, ''μ''
0 for the
vacuum permeability or magnetic constant, ''ε''
0 for the
vacuum permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric consta ...
or electric constant, and ''Z''
0 for the
impedance of free space. This article uses exclusively for the speed of light in vacuum.
Use in unit systems
Since 1983, the constant has been defined in the
International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
(SI) as ''exactly'' ; this relationship is used to define the metre as exactly the distance that light travels in a vacuum in of a
second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
. By using the value of , as well as an accurate measurement of the
second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
, one can thus establish a standard for the metre.
[See, for example:
*
*
*] As a
dimensional physical constant, the numerical value of is different for different unit systems. For example, in
imperial units, the speed of light is approximately miles per second, or roughly 1
foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made ...
per nanosecond.
In branches of physics in which appears often, such as in relativity, it is common to use systems of
natural units of measurement or the
geometrized unit system where .
[
][
] Using these units, does not appear explicitly because multiplication or division by1 does not affect the result. Its unit of
light-second per second is still relevant, even if omitted.
Fundamental role in physics
The speed at which light waves propagate in vacuum is independent both of the motion of the wave source and of the
inertial frame of reference of the observer.
[However, the frequency of light can depend on the motion of the source relative to the observer, due to the ]Doppler effect
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who d ...
. This invariance of the speed of light was postulated by Einstein in 1905,
after being motivated by
Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism and the lack of evidence for the
luminiferous aether; it has since been consistently confirmed by many experiments.
[See Michelson–Morley experiment and ]Kennedy–Thorndike experiment
The Kennedy–Thorndike experiment, first conducted in 1932 by Roy J. Kennedy and Edward M. Thorndike, is a modified form of the Michelson–Morley experimental procedure, testing special relativity.
The modification is to make one arm of the class ...
, for example. It is only possible to verify experimentally that the two-way speed of light (for example, from a source to a mirror and back again) is frame-independent, because it is impossible to measure the
one-way speed of light (for example, from a source to a distant detector) without some convention as to how clocks at the source and at the detector should be synchronized. However, by adopting
Einstein synchronization for the clocks, the one-way speed of light becomes equal to the two-way speed of light by definition.
[
] The
special theory of relativity explores the consequences of this invariance of ''c'' with the assumption that the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference. One consequence is that ''c'' is the speed at which all
massless particles and waves, including light, must travel in vacuum.

Special relativity has many counterintuitive and experimentally verified implications. These include the
equivalence of mass and energy ,
length contraction (moving objects shorten), and
time dilation (moving clocks run more slowly). The factor ''γ'' by which lengths contract and times dilate is known as the
Lorentz factor and is given by , where ''v'' is the speed of the object. The difference of ''γ'' from1 is negligible for speeds much slower than ''c'', such as most everyday speedsin which case special relativity is closely approximated by
Galilean relativitybut it increases at relativistic speeds and diverges to infinity as ''v'' approaches ''c''. For example, a time dilation factor of ''γ'' = 2 occurs at a relative velocity of 86.6% of the speed of light (''v'' = 0.866 ''c''). Similarly, a time dilation factor of ''γ'' = 10 occurs at 99.5% the speed of light (''v'' = 0.995 ''c'').
The results of special relativity can be summarized by treating space and time as a unified structure known as
spacetime (with ''c'' relating the units of space and time), and requiring that physical theories satisfy a special
symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definit ...
called
Lorentz invariance, whose mathematical formulation contains the parameter ''c''. Lorentz invariance is an almost universal assumption for modern physical theories, such as
quantum electrodynamics,
quantum chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type ...
, the
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying a ...
of
particle physics, and
general relativity. As such, the parameter ''c'' is ubiquitous in modern physics, appearing in many contexts that are unrelated to light. For example, general relativity predicts that ''c'' is also the
speed of gravity and of
gravitational waves,
[
] and observations of gravitational waves have been consistent with this prediction. In
non-inertial frames of reference (gravitationally curved spacetime or
accelerated reference frames), the ''local'' speed of light is constant and equal to ''c'', but the
speed of light along a trajectory of finite length can differ from ''c'', depending on how distances and times are defined.
It is generally assumed that fundamental constants such as ''c'' have the same value throughout spacetime, meaning that they do not depend on location and do not vary with time. However, it has been suggested in various theories that the
speed of light may have changed over time.
[
] No conclusive evidence for such changes has been found, but they remain the subject of ongoing research.
[
][
]
It also is generally assumed that the speed of light is
isotropic
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence ''anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe ...
, meaning that it has the same value regardless of the direction in which it is measured. Observations of the emissions from nuclear
energy levels as a function of the orientation of the emitting
nuclei in a magnetic field (see
Hughes–Drever experiment), and of rotating
optical resonators (see
Resonator experiments) have put stringent limits on the possible two-way
anisotropy.
Upper limit on speeds
According to special relativity, the energy of an object with
rest mass ''m'' and speed ''v'' is given by , where ''γ'' is the Lorentz factor defined above. When ''v'' is zero, ''γ'' is equal to one, giving rise to the famous formula for mass–energy equivalence. The ''γ'' factor approaches infinity as ''v'' approaches ''c'', and it would take an infinite amount of energy to accelerate an object with mass to the speed of light. The speed of light is the upper limit for the speeds of objects with positive rest mass, and individual photons cannot travel faster than the speed of light. This is experimentally established in many
tests of relativistic energy and momentum
Tests of relativistic energy and momentum are aimed at measuring the relativistic expressions for energy, momentum, and mass. According to special relativity, the properties of particles moving approximately at the speed of light significantly de ...
.

More generally, it is impossible for signals or energy to travel faster than ''c''. One argument for this follows from the counter-intuitive implication of special relativity known as the
relativity of simultaneity
In physics, the relativity of simultaneity is the concept that ''distant simultaneity'' – whether two spatially separated events occur at the same time – is not absolute, but depends on the observer's reference frame. This possi ...
. If the spatial distance between two events A and B is greater than the time interval between them multiplied by ''c'' then there are frames of reference in which A precedes B, others in which B precedes A, and others in which they are simultaneous. As a result, if something were travelling faster than ''c'' relative to an inertial frame of reference, it would be travelling backwards in time relative to another frame, and
causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cau ...
would be violated.
[
] In such a frame of reference, an "effect" could be observed before its "cause". Such a violation of causality has never been recorded,
[ and would lead to paradoxes such as the tachyonic antitelephone.
]
Faster-than-light observations and experiments
There are situations in which it may seem that matter, energy, or information-carrying signal travels at speeds greater than ''c'', but they do not. For example, as is discussed in the propagation of light in a medium section below, many wave velocities can exceed ''c''. The phase velocity
The phase velocity of a wave is the rate at which the wave propagates in any medium. This is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave (for example, ...
of X-rays through most glasses can routinely exceed ''c'', but phase velocity does not determine the velocity at which waves convey information.
If a laser beam is swept quickly across a distant object, the spot of light can move faster than ''c'', although the initial movement of the spot is delayed because of the time it takes light to get to the distant object at the speed ''c''. However, the only physical entities that are moving are the laser and its emitted light, which travels at the speed ''c'' from the laser to the various positions of the spot. Similarly, a shadow projected onto a distant object can be made to move faster than ''c'', after a delay in time. In neither case does any matter, energy, or information travel faster than light.[
]
The rate of change in the distance between two objects in a frame of reference with respect to which both are moving (their closing speed
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great fo ...
) may have a value in excess of ''c''. However, this does not represent the speed of any single object as measured in a single inertial frame.Hartman effect The Hartman effect describes how the delay time for a quantum tunneling particle is independent of the thickness of the opaque barrier. It is named after Thomas Hartman, who discovered it in 1962.
Overview
The Hartman effect is the tunneling eff ...
: under certain conditions the time needed for a virtual particle to tunnel through a barrier is constant, regardless of the thickness of the barrier.[
][
] This could result in a virtual particle crossing a large gap faster than light. However, no information can be sent using this effect.
archive
/ref>
So-called superluminal motion
In astronomy, superluminal motion is the apparently faster-than-light motion seen in some
radio galaxies, BL Lac objects, quasars, blazars and recently also in some galactic sources called microquasars. Bursts of energy moving out along the rel ...
is seen in certain astronomical objects, such as the relativistic jet
An astrophysical jet is an astronomical phenomenon where outflows of ionised matter are emitted as an extended beam along the axis of rotation. When this greatly accelerated matter in the beam approaches the speed of light, astrophysical jets bec ...
s of radio galaxies and quasar
A quasar is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a m ...
s. However, these jets are not moving at speeds in excess of the speed of light: the apparent superluminal motion is a projection effect caused by objects moving near the speed of light and approaching Earth at a small angle to the line of sight: since the light which was emitted when the jet was farther away took longer to reach the Earth, the time between two successive observations corresponds to a longer time between the instants at which the light rays were emitted.
A 2011 experiment where neutrinos were observed to travel faster than light turned out to be due to experimental error.[
]
Propagation of light
In classical physics
Classical physics is a group of physics theories that predate modern, more complete, or more widely applicable theories. If a currently accepted theory is considered to be modern, and its introduction represented a major paradigm shift, then the ...
, light is described as a type of electromagnetic wave. The classical behaviour of the electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical c ...
is described by Maxwell's equations, which predict that the speed ''c'' with which electromagnetic waves (such as light) propagate in vacuum is related to the distributed capacitance and inductance of vacuum, otherwise respectively known as the electric constant ''ε''0 and the magnetic constant
The vacuum magnetic permeability (variously ''vacuum permeability'', ''permeability of free space'', ''permeability of vacuum''), also known as the magnetic constant, is the magnetic permeability in a classical vacuum. It is a physical constant, ...
''μ''0, by the equation
:
In modern quantum physics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, qua ...
, the electromagnetic field is described by the theory of quantum electrodynamics (QED). In this theory, light is described by the fundamental excitations (or quanta) of the electromagnetic field, called photons. In QED, photons are massless particles and thus, according to special relativity, they travel at the speed of light in vacuum.[
] No variation of the speed of light with frequency has been observed in rigorous testing, putting stringent limits on the mass of the photon. The limit obtained depends on the model used: if the massive photon is described by Proca theory,[
] if photon mass is generated by a Higgs mechanism, the experimental upper limit is less sharp, (roughly 2 × 10−47 g).quantum gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the vi ...
. In 2009, the observation of gamma-ray burst GRB 090510 found no evidence for a dependence of photon speed on energy, supporting tight constraints in specific models of spacetime quantization on how this speed is affected by photon energy for energies approaching the Planck scale.
In a medium
In a medium, light usually does not propagate at a speed equal to ''c''; further, different types of light wave will travel at different speeds. The speed at which the individual crests and troughs of a plane wave (a wave filling the whole space, with only one frequency) propagate is called the phase velocity
The phase velocity of a wave is the rate at which the wave propagates in any medium. This is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave (for example, ...
''v''p. A physical signal with a finite extent (a pulse of light) travels at a different speed. The overall envelope of the pulse travels at the group velocity
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall envelope shape of the wave's amplitudes—known as the ''modulation'' or ''envelope'' of the wave—propagates through space.
For example, if a stone is thrown into the middl ...
''v''g, and its earliest part travels at the front velocity
In physics, front velocity is the speed at which the first rise of a pulse above zero moves forward.
In mathematics, it is used to describe the velocity of a propagating front in the solution of hyperbolic partial differential equation.
Various ...
''v''f.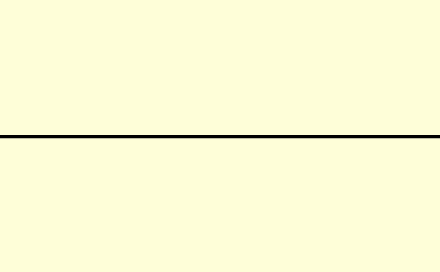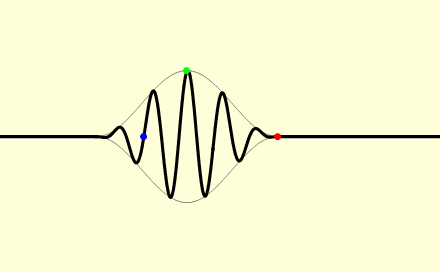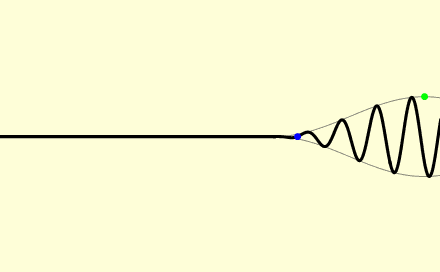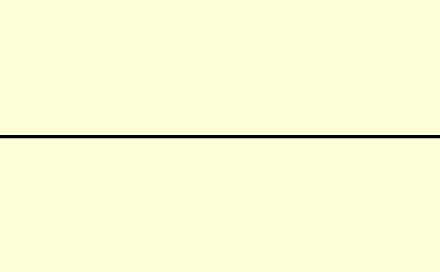 The phase velocity is important in determining how a light wave travels through a material or from one material to another. It is often represented in terms of a ''refractive index''. The refractive index of a material is defined as the ratio of ''c'' to the phase velocity ''v''p in the material: larger indices of refraction indicate lower speeds. The refractive index of a material may depend on the light's frequency, intensity,
The phase velocity is important in determining how a light wave travels through a material or from one material to another. It is often represented in terms of a ''refractive index''. The refractive index of a material is defined as the ratio of ''c'' to the phase velocity ''v''p in the material: larger indices of refraction indicate lower speeds. The refractive index of a material may depend on the light's frequency, intensity, polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:
Mathematics
*Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds
*Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by ...
, or direction of propagation; in many cases, though, it can be treated as a material-dependent constant. The refractive index of air is approximately 1.0003.rubidium
Rubidium is the chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher ...
. However, the popular description of light being "stopped" in these experiments refers only to light being stored in the excited states of atoms, then re-emitted at an arbitrarily later time, as stimulated by a second laser pulse. During the time it had "stopped", it had ceased to be light. This type of behaviour is generally microscopically true of all transparent media which "slow" the speed of light.
In transparent materials, the refractive index generally is greater than 1, meaning that the phase velocity is less than ''c''. In other materials, it is possible for the refractive index to become smaller than1 for some frequencies; in some exotic materials it is even possible for the index of refraction to become negative. The requirement that causality is not violated implies that the real and imaginary parts of the dielectric constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insulat ...
of any material, corresponding respectively to the index of refraction and to the attenuation coefficient, are linked by the Kramers–Kronig relations. In practical terms, this means that in a material with refractive index less than 1, the wave will be absorbed quickly.
A pulse with different group and phase velocities (which occurs if the phase velocity is not the same for all the frequencies of the pulse) smears out over time, a process known as dispersion. Certain materials have an exceptionally low (or even zero) group velocity for light waves, a phenomenon called slow light
Slow light is the propagation of an optical pulse or other modulation of an optical carrier at a very low group velocity. Slow light occurs when a propagating pulse is substantially slowed by the interaction with the medium in which the propagatio ...
.
The opposite, group velocities exceeding ''c'', was proposed theoretically in 1993 and achieved experimentally in 2000. It should even be possible for the group velocity to become infinite or negative, with pulses travelling instantaneously or backwards in time.
Practical effects of finiteness
The speed of light is of relevance to communications: the one-way and round-trip delay time are greater than zero. This applies from small to astronomical scales. On the other hand, some techniques depend on the finite speed of light, for example in distance measurements.
Small scales
In computers
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs ...
, the speed of light imposes a limit on how quickly data can be sent between processors. If a processor operates at 1 gigahertz, a signal can travel only a maximum of about in a single clock cycle — in practice, this distance is even shorter since the printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
itself has a refractive index and slows down signals. Processors must therefore be placed close to each other, as well as memory chips, to minimize communication latencies, and care must be exercised when routing wires between them to ensure signal integrity
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an electrical signal. In digital electronics, a stream of binary values is represented by a voltage (or current) waveform. However, digital signals are fundamentally analog in nature, ...
. If clock frequencies continue to increase, the speed of light may eventually become a limiting factor for the internal design of single chips.
Large distances on Earth
Given that the equatorial circumference of the Earth is about and that ''c'' is about , the theoretical shortest time for a piece of information to travel half the globe along the surface is about 67 milliseconds. When light is traveling in optical fibre
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
(a transparent material
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimension ...
) the actual transit time is longer, in part because the speed of light is slower by about 35% in optical fibre, depending on its refractive index ''n''. Furthermore, straight lines are rare in global communications and the travel time increases when signals pass through electronic switches or signal regenerators.
Although this distance is largely irrelevant for most applications, latency becomes important in fields such as high-frequency trading
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic financial trading characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools. While there is no ...
, where traders seek to gain minute advantages by delivering their trades to exchanges fractions of a second ahead of other traders. For example, traders have been switching to microwave communications between trading hubs, because of the advantage which radio waves travelling at near to the speed of light through air have over comparatively slower fibre optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
signals.
Spaceflight and astronomy
 Similarly, communications between the Earth and spacecraft are not instantaneous. There is a brief delay from the source to the receiver, which becomes more noticeable as distances increase. This delay was significant for communications between ground control and
Similarly, communications between the Earth and spacecraft are not instantaneous. There is a brief delay from the source to the receiver, which becomes more noticeable as distances increase. This delay was significant for communications between ground control and Apollo 8
Apollo 8 (December 21–27, 1968) was the first crewed spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit and the first human spaceflight to reach the Moon. The crew orbited the Moon ten times without landing, and then departed safely back to Earth. These ...
when it became the first crewed spacecraft to orbit the Moon: for every question, the ground control station had to wait at least three seconds for the answer to arrive. The communications delay between Earth and Mars can vary between five and twenty minutes depending upon the relative positions of the two planets. As a consequence of this, if a robot on the surface of Mars were to encounter a problem, its human controllers would not be aware of it until later. It would then take a further for commands to travel from Earth to Mars.
Receiving light and other signals from distant astronomical sources takes much longer. For example, it takes 13 billion (13) years for light to travel to Earth from the faraway galaxies viewed in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF) is a deep-field image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, containing an estimated 10,000 galaxies. The original data for the image was collected by the Hubble Space Telescope from Septemb ...
images.[ The fact that more distant objects appear to be younger, due to the finite speed of light, allows astronomers to infer the evolution of stars, of galaxies, and of the universe itself.
Astronomical distances are sometimes expressed in ]light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s, especially in popular science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, incl ...
publications and media. A light-year is the distance light travels in one Julian year, around 9461 billion kilometres, 5879 billion miles, or 0.3066 parsecs. In round figures, a light year is nearly 10 trillion kilometres or nearly 6 trillion miles. Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is a small, low-mass star located away from the Sun in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Its Latin name means the 'nearest tarof Centaurus'. It was discovered in 1915 by Robert Innes and is the nearest-kno ...
, the closest star to Earth after the Sun, is around 4.2 light-years away.[Further discussion can be found at ]
Distance measurement
Radar systems measure the distance to a target by the time it takes a radio-wave pulse to return to the radar antenna after being reflected by the target: the distance to the target is half the round-trip transit time multiplied by the speed of light. A Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
(GPS) receiver measures its distance to GPS satellites based on how long it takes for a radio signal to arrive from each satellite, and from these distances calculates the receiver's position. Because light travels about () in one second, these measurements of small fractions of a second must be very precise. The Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment, radar astronomy and the Deep Space Network determine distances to the Moon,
Measurement
There are different ways to determine the value of ''c''. One way is to measure the actual speed at which light waves propagate, which can be done in various astronomical and Earth-based setups. However, it is also possible to determine ''c'' from other physical laws where it appears, for example, by determining the values of the electromagnetic constants ''ε''0 and ''μ''0 and using their relation to ''c''. Historically, the most accurate results have been obtained by separately determining the frequency and wavelength of a light beam, with their product equalling ''c''. This is described in more detail in the "Interferometry" section below.
In 1983 the metre was defined as "the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second",[ fixing the value of the speed of light at by definition, as described below. Consequently, accurate measurements of the speed of light yield an accurate realization of the metre rather than an accurate value of ''c''.
]
Astronomical measurements
 Outer space is a convenient setting for measuring the speed of light because of its large scale and nearly perfect vacuum. Typically, one measures the time needed for light to traverse some reference distance in the Solar System, such as the radius of the Earth's orbit. Historically, such measurements could be made fairly accurately, compared to how accurately the length of the reference distance is known in Earth-based units.
Ole Christensen Rømer used an astronomical measurement to make the first quantitative estimate of the speed of light in the year 1676.
Outer space is a convenient setting for measuring the speed of light because of its large scale and nearly perfect vacuum. Typically, one measures the time needed for light to traverse some reference distance in the Solar System, such as the radius of the Earth's orbit. Historically, such measurements could be made fairly accurately, compared to how accurately the length of the reference distance is known in Earth-based units.
Ole Christensen Rømer used an astronomical measurement to make the first quantitative estimate of the speed of light in the year 1676.[
]
Translated in
Reproduced in
The account published in ''Journal des sçavans'' was based on a report that Rømer read to the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
in November 1676 (Cohen, 1940, p. 346). When measured from Earth, the periods of moons orbiting a distant planet are shorter when the Earth is approaching the planet than when the Earth is receding from it. The distance travelled by light from the planet (or its moon) to Earth is shorter when the Earth is at the point in its orbit that is closest to its planet than when the Earth is at the farthest point in its orbit, the difference in distance being the diameter of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. The observed change in the moon's orbital period is caused by the difference in the time it takes light to traverse the shorter or longer distance. Rømer observed this effect for Jupiter's innermost major moon Io and deduced that light takes 22 minutes to cross the diameter of the Earth's orbit. Another method is to use the aberration of light, discovered and explained by James Bradley in the 18th century.
Another method is to use the aberration of light, discovered and explained by James Bradley in the 18th century.arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
s) it is possible to express the speed of light in terms of the Earth's velocity around the Sun, which with the known length of a year can be converted to the time needed to travel from the Sun to the Earth. In 1729, Bradley used this method to derive that light travelled times faster than the Earth in its orbit (the modern figure is times faster) or, equivalently, that it would take light 8 minutes 12 seconds to travel from the Sun to the Earth.
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit (AU) is approximately the average distance between the Earth and Sun. It was redefined in 2012 as exactly .International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
but in terms of the gravitational force exerted by the Sun in the framework of classical mechanics. The current definition uses the recommended value in metres for the previous definition of the astronomical unit, which was determined by measurement.[
]
:light time for unit distance: ''t''au =
:''c'' = =
The relative uncertainty in these measurements is 0.02 parts per billion (), equivalent to the uncertainty in Earth-based measurements of length by interferometry. Since the metre is defined to be the length travelled by light in a certain time interval, the measurement of the light time in terms of the previous definition of the astronomical unit can also be interpreted as measuring the length of an AU (old definition) in metres.
Time of flight techniques
 A method of measuring the speed of light is to measure the time needed for light to travel to a mirror at a known distance and back. This is the working principle behind the Fizeau–Foucault apparatus developed by Hippolyte Fizeau and Léon Foucault, based on a suggestion by
A method of measuring the speed of light is to measure the time needed for light to travel to a mirror at a known distance and back. This is the working principle behind the Fizeau–Foucault apparatus developed by Hippolyte Fizeau and Léon Foucault, based on a suggestion by François Arago
Dominique François Jean Arago ( ca, Domènec Francesc Joan Aragó), known simply as François Arago (; Catalan: ''Francesc Aragó'', ; 26 February 17862 October 1853), was a French mathematician, physicist, astronomer, freemason, supporter of t ...
.
Electromagnetic constants
An option for deriving ''c'' that does not directly depend on a measurement of the propagation of electromagnetic waves is to use the relation between ''c'' and the vacuum permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric consta ...
''ε''0 and vacuum permeability ''μ''0 established by Maxwell's theory: ''c''2 = 1/(''ε''0''μ''0). The vacuum permittivity may be determined by measuring the capacitance and dimensions of a capacitor, whereas the value of the vacuum permeability was historically fixed at exactly through the definition of the ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to elect ...
. Rosa and Dorsey used this method in 1907 to find a value of . Their method depended upon having a standard unit of electrical resistance, the "international ohm", and so its accuracy was limited by how this standard was defined.
Cavity resonance
 Another way to measure the speed of light is to independently measure the frequency ''f'' and wavelength ''λ'' of an electromagnetic wave in vacuum. The value of ''c'' can then be found by using the relation ''c'' = ''fλ''. One option is to measure the resonance frequency of a cavity resonator. If the dimensions of the resonance cavity are also known, these can be used to determine the wavelength of the wave. In 1946,
Another way to measure the speed of light is to independently measure the frequency ''f'' and wavelength ''λ'' of an electromagnetic wave in vacuum. The value of ''c'' can then be found by using the relation ''c'' = ''fλ''. One option is to measure the resonance frequency of a cavity resonator. If the dimensions of the resonance cavity are also known, these can be used to determine the wavelength of the wave. In 1946, Louis Essen
Louis Essen FRS O.B.E. (6 September 1908 – 24 August 1997) was an English physicist whose most notable achievements were in the precise measurement of time and the determination of the speed of light. He was a critic of Albert Einstein's ...
and A.C. Gordon-Smith established the frequency for a variety of normal mode
A normal mode of a dynamical system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The free motion described by the normal modes takes place at fixed frequencies. ...
s of microwaves of a microwave cavity of precisely known dimensions. The dimensions were established to an accuracy of about ±0.8 μm using gauges calibrated by interferometry.[
]
A household demonstration of this technique is possible, using a microwave oven and food such as marshmallows or margarine: if the turntable is removed so that the food does not move, it will cook the fastest at the antinodes (the points at which the wave amplitude is the greatest), where it will begin to melt. The distance between two such spots is half the wavelength of the microwaves; by measuring this distance and multiplying the wavelength by the microwave frequency (usually displayed on the back of the oven, typically 2450 MHz), the value of ''c'' can be calculated, "often with less than 5% error".
Interferometry

Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
is another method to find the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation for determining the speed of light. A coherent beam of light (e.g. from a laser), with a known frequency (''f''), is split to follow two paths and then recombined. By adjusting the path length while observing the interference pattern and carefully measuring the change in path length, the wavelength of the light (''λ'') can be determined. The speed of light is then calculated using the equation ''c'' = ''λf''.
Before the advent of laser technology, coherent radio sources were used for interferometry measurements of the speed of light.[
] However interferometric determination of wavelength becomes less precise with wavelength and the experiments were thus limited in precision by the long wavelength (~) of the radiowaves. The precision can be improved by using light with a shorter wavelength, but then it becomes difficult to directly measure the frequency of the light. One way around this problem is to start with a low frequency signal of which the frequency can be precisely measured, and from this signal progressively synthesize higher frequency signals whose frequency can then be linked to the original signal. A laser can then be locked to the frequency, and its wavelength can be determined using interferometry.[
] This technique was due to a group at the National Bureau of Standards (which later became the National Institute of Standards and Technology). They used it in 1972 to measure the speed of light in vacuum with a fractional uncertainty of .[
]
History
Until the early modern period, it was not known whether light travelled instantaneously or at a very fast finite speed. The first extant recorded examination of this subject was in ancient Greece. The ancient Greeks, Arabic scholars, and classical European scientists long debated this until Rømer provided the first calculation of the speed of light. Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity concluded that the speed of light is constant regardless of one's frame of reference. Since then, scientists have provided increasingly accurate measurements.
Early history
Empedocles (c. 490–430 BCE) was the first to propose a theory of light and claimed that light has a finite speed. He maintained that light was something in motion, and therefore must take some time to travel. Aristotle argued, to the contrary, that "light is due to the presence of something, but it is not a movement".[
(click on "Historical background" in the table of contents)] Euclid and Ptolemy advanced Empedocles' emission theory of vision, where light is emitted from the eye, thus enabling sight. Based on that theory, Heron of Alexandria argued that the speed of light must be infinite because distant objects such as stars appear immediately upon opening the eyes.
Early Islamic philosophers initially agreed with the Aristotelian view that light had no speed of travel. In 1021, Alhazen
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham, Latinized as Alhazen (; full name ; ), was a medieval mathematician, astronomer, and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age from present-day Iraq.For the description of his main fields, see e.g. ("He is one of the prin ...
(Ibn al-Haytham) published the ''Book of Optics
The ''Book of Optics'' ( ar, كتاب المناظر, Kitāb al-Manāẓir; la, De Aspectibus or ''Perspectiva''; it, Deli Aspecti) is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Arab scholar Ibn al- ...
'', in which he presented a series of arguments dismissing the emission theory of vision in favour of the now accepted intromission theory, in which light moves from an object into the eye. This led Alhazen to propose that light must have a finite speed,[
][
] and that the speed of light is variable, decreasing in denser bodies.[ He argued that light is substantial matter, the propagation of which requires time, even if this is hidden from the senses. Also in the 11th century, Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī agreed that light has a finite speed, and observed that the speed of light is much faster than the speed of sound.
In the 13th century, ]Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
argued that the speed of light in air was not infinite, using philosophical arguments backed by the writing of Alhazen and Aristotle.[
] In the 1270s, Witelo considered the possibility of light travelling at infinite speed in vacuum, but slowing down in denser bodies.[
]
In the early 17th century, Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
believed that the speed of light was infinite since empty space presents no obstacle to it. René Descartes argued that if the speed of light were to be finite, the Sun, Earth, and Moon would be noticeably out of alignment during a lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth ...
. (Although this argument fails when aberration of light is taken into account, the latter was not recognized until the following century.) Since such misalignment had not been observed, Descartes concluded the speed of light was infinite. Descartes speculated that if the speed of light were found to be finite, his whole system of philosophy might be demolished.Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through ...
, Descartes assumed that some kind of motion associated with light was faster in denser media. Pierre de Fermat derived Snell's law using the opposing assumption, the denser the medium the slower light travelled. Fermat also argued in support of a finite speed of light.
First measurement attempts
In 1629, Isaac Beeckman proposed an experiment in which a person observes the flash of a cannon reflecting off a mirror about one mile (1.6 km) away. In 1638, Galileo Galilei proposed an experiment, with an apparent claim to having performed it some years earlier, to measure the speed of light by observing the delay between uncovering a lantern and its perception some distance away. He was unable to distinguish whether light travel was instantaneous or not, but concluded that if it were not, it must nevertheless be extraordinarily rapid.[
][
] In 1667, the Accademia del Cimento
The Accademia del Cimento (Academy of Experiment), an early scientific society, was founded in Florence in 1657 by students of Galileo, Giovanni Alfonso Borelli and Vincenzo Viviani and ceased to exist about a decade later. The foundation of Acade ...
of Florence reported that it had performed Galileo's experiment, with the lanterns separated by about one mile, but no delay was observed. The actual delay in this experiment would have been about 11 microseconds.
 The first quantitative estimate of the speed of light was made in 1676 by Ole Rømer.
The first quantitative estimate of the speed of light was made in 1676 by Ole Rømer.Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists of ...
combined this estimate with an estimate for the diameter of the Earth's orbit to obtain an estimate of speed of light of , which is 27% lower than the actual value.stellar aberration
In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon which produces an apparent motion of celestial objects about their true positions, dependent on the velocity of t ...
.
Connections with electromagnetism
In the 19th century Hippolyte Fizeau developed a method to determine the speed of light based on time-of-flight measurements on Earth and reported a value of .[
]
"Luminiferous aether"
 It was thought at the time that empty space was filled with a background medium called the luminiferous aether in which the electromagnetic field existed. Some physicists thought that this aether acted as a preferred frame of reference for the propagation of light and therefore it should be possible to measure the motion of the Earth with respect to this medium, by measuring the isotropy of the speed of light. Beginning in the 1880s several experiments were performed to try to detect this motion, the most famous of which is
It was thought at the time that empty space was filled with a background medium called the luminiferous aether in which the electromagnetic field existed. Some physicists thought that this aether acted as a preferred frame of reference for the propagation of light and therefore it should be possible to measure the motion of the Earth with respect to this medium, by measuring the isotropy of the speed of light. Beginning in the 1880s several experiments were performed to try to detect this motion, the most famous of which is the experiment
''The Experiment'' is a 2002 BBC documentary series in which 15 men are randomly selected to be either "prisoner" or guard, contained in a simulated prison over an eight-day period. Produced by Steve Reicher and Alex Haslam, it presents the fi ...
performed by Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley
Edward Williams Morley (January 29, 1838 – February 24, 1923) was an American scientist known for his precise and accurate measurement of the atomic weight of oxygen, and for the Michelson–Morley experiment.
Biography
Morley was born in New ...
in 1887. The detected motion was always less than the observational error. Modern experiments indicate that the two-way speed of light is isotropic
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence ''anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe ...
(the same in every direction) to within 6 nanometres per second.
Because of this experiment Hendrik Lorentz
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. He also derived the Lorentz t ...
proposed that the motion of the apparatus through the aether may cause the apparatus to contract along its length in the direction of motion, and he further assumed that the time variable for moving systems must also be changed accordingly ("local time"), which led to the formulation of the Lorentz transformation. Based on Lorentz's aether theory, Henri Poincaré
Jules Henri Poincaré ( S: stress final syllable ; 29 April 1854 – 17 July 1912) was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science. He is often described as a polymath, and in mathematics as "The ...
(1900) showed that this local time (to first order in ''v''/''c'') is indicated by clocks moving in the aether, which are synchronized under the assumption of constant light speed. In 1904, he speculated that the speed of light could be a limiting velocity in dynamics, provided that the assumptions of Lorentz's theory are all confirmed. In 1905, Poincaré brought Lorentz's aether theory into full observational agreement with the principle of relativity
In physics, the principle of relativity is the requirement that the equations describing the laws of physics have the same form in all admissible frames of reference.
For example, in the framework of special relativity the Maxwell equations have ...
.
Special relativity
In 1905 Einstein postulated from the outset that the speed of light in vacuum, measured by a non-accelerating observer, is independent of the motion of the source or observer. Using this and the principle of relativity as a basis he derived the special theory of relativity, in which the speed of light in vacuum ''c'' featured as a fundamental constant, also appearing in contexts unrelated to light. This made the concept of the stationary aether (to which Lorentz and Poincaré still adhered) useless and revolutionized the concepts of space and time.
Increased accuracy of ''c'' and redefinition of the metre and second
In the second half of the 20th century, much progress was made in increasing the accuracy of measurements of the speed of light, first by cavity resonance techniques and later by laser interferometer techniques. These were aided by new, more precise, definitions of the metre and second. In 1950, Louis Essen
Louis Essen FRS O.B.E. (6 September 1908 – 24 August 1997) was an English physicist whose most notable achievements were in the precise measurement of time and the determination of the speed of light. He was a critic of Albert Einstein's ...
determined the speed as , using cavity resonance.second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
was redefined in terms of the hyperfine transition frequency of the ground state of caesium-133
Caesium (55Cs) has 40 known isotopes, making it, along with barium and mercury, one of the elements with the most isotopes. The atomic masses of these isotopes range from 112 to 151. Only one isotope, 133Cs, is stable. The longest-lived radioisoto ...
.Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a home rule city that is the county seat and most populous municipality of Boulder County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, making it the 12th most populous city in Color ...
determined the speed of light in vacuum to be ''c'' = . This was 100 times less uncertain than the previously accepted value. The remaining uncertainty was mainly related to the definition of the metre.General Conference on Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (GCWM; french: Conférence générale des poids et mesures, CGPM) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established i ...
in 1975 recommended using the value for the speed of light.[
]
Defined as an explicit constant
In 1983 the 17th meeting of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) found that wavelengths from frequency measurements and a given value for the speed of light are more reproducible than the previous standard. They kept the 1967 definition of second, so the caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
hyperfine frequency would now determine both the second and the metre. To do this, they redefined the metre as "the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/ of a second."[
] As a result of this definition, the value of the speed of light in vacuum is exactly [
][
] and has become a defined constant in the SI system of units.[
][
]
In 2011, the CGPM stated its intention to redefine all seven SI base units using what it calls "the explicit-constant formulation", where each "unit is defined indirectly by specifying explicitly an exact value for a well-recognized fundamental constant", as was done for the speed of light. It proposed a new, but completely equivalent, wording of the metre's definition: "The metre, symbol m, is the unit of length; its magnitude is set by fixing the numerical value of the speed of light in vacuum to be equal to exactly when it is expressed in the SI unit ." This was one of the changes that was incorporated in the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units
In 2019, four of the seven SI base units specified in the International System of Quantities were redefined in terms of natural physical constants, rather than human artifacts such as the standard kilogram.
Effective 20 May 2019, the 144t ...
, also termed the ''New SI''.[See, for example:
*
*
* ]
See also
* Light-second
* Speed of electricity
* Speed of gravity
* Speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or one kilometre in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as w ...
* Velocity factor
* Warp factor (fictional)
Notes
References
Further reading
Historical references
*
** Translated as
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Modern references
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
"Test Light Speed in Mile Long Vacuum Tube."
''Popular Science Monthly'', September 1930, pp. 17–18.
(International Bureau of Weights and Measures, BIPM)
Speed of light in vacuum
(National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST)
(download data gathered by Albert A. Michelson)
Subluminal
(Java applet by Greg Egan demonstrating group velocity information limits)
Light discussion on adding velocities
(Sixty Symbols, University of Nottingham Department of Physics ideo
Speed of Light
BBC Radio4 discussion (''In Our Time'', 30 November 2006)
Speed of Light
(Live-Counter – Illustrations)
Speed of Light – animated demonstrations
*
The Velocity of Light
, Albert A. Nicholson, Scientific American, 28 September 1878, p. 193
{{DEFAULTSORT:Speed Of Light
Fundamental constants
Physical quantities
Light
Light
Velocity
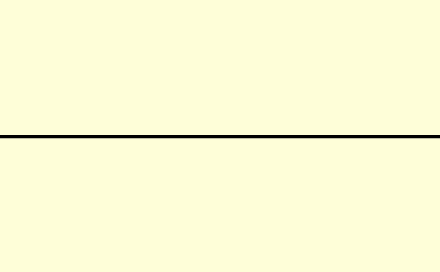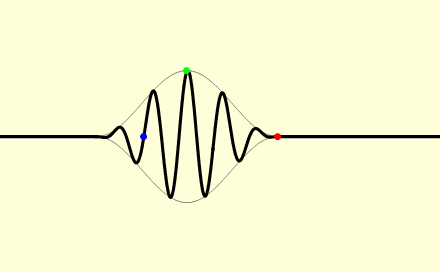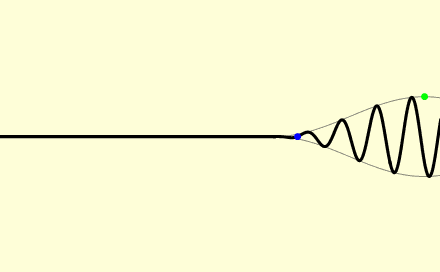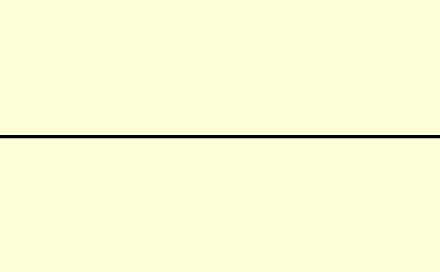 The phase velocity is important in determining how a light wave travels through a material or from one material to another. It is often represented in terms of a ''refractive index''. The refractive index of a material is defined as the ratio of ''c'' to the phase velocity ''v''p in the material: larger indices of refraction indicate lower speeds. The refractive index of a material may depend on the light's frequency, intensity,
The phase velocity is important in determining how a light wave travels through a material or from one material to another. It is often represented in terms of a ''refractive index''. The refractive index of a material is defined as the ratio of ''c'' to the phase velocity ''v''p in the material: larger indices of refraction indicate lower speeds. The refractive index of a material may depend on the light's frequency, intensity,  Similarly, communications between the Earth and spacecraft are not instantaneous. There is a brief delay from the source to the receiver, which becomes more noticeable as distances increase. This delay was significant for communications between ground control and
Similarly, communications between the Earth and spacecraft are not instantaneous. There is a brief delay from the source to the receiver, which becomes more noticeable as distances increase. This delay was significant for communications between ground control and  A method of measuring the speed of light is to measure the time needed for light to travel to a mirror at a known distance and back. This is the working principle behind the Fizeau–Foucault apparatus developed by Hippolyte Fizeau and Léon Foucault, based on a suggestion by
A method of measuring the speed of light is to measure the time needed for light to travel to a mirror at a known distance and back. This is the working principle behind the Fizeau–Foucault apparatus developed by Hippolyte Fizeau and Léon Foucault, based on a suggestion by  The first quantitative estimate of the speed of light was made in 1676 by Ole Rømer. From the observation that the periods of Jupiter's innermost moon Io appeared to be shorter when the Earth was approaching Jupiter than when receding from it, he concluded that light travels at a finite speed, and estimated that it takes light 22 minutes to cross the diameter of Earth's orbit.
The first quantitative estimate of the speed of light was made in 1676 by Ole Rømer. From the observation that the periods of Jupiter's innermost moon Io appeared to be shorter when the Earth was approaching Jupiter than when receding from it, he concluded that light travels at a finite speed, and estimated that it takes light 22 minutes to cross the diameter of Earth's orbit.  It was thought at the time that empty space was filled with a background medium called the luminiferous aether in which the electromagnetic field existed. Some physicists thought that this aether acted as a preferred frame of reference for the propagation of light and therefore it should be possible to measure the motion of the Earth with respect to this medium, by measuring the isotropy of the speed of light. Beginning in the 1880s several experiments were performed to try to detect this motion, the most famous of which is
It was thought at the time that empty space was filled with a background medium called the luminiferous aether in which the electromagnetic field existed. Some physicists thought that this aether acted as a preferred frame of reference for the propagation of light and therefore it should be possible to measure the motion of the Earth with respect to this medium, by measuring the isotropy of the speed of light. Beginning in the 1880s several experiments were performed to try to detect this motion, the most famous of which is