Tendaguru on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
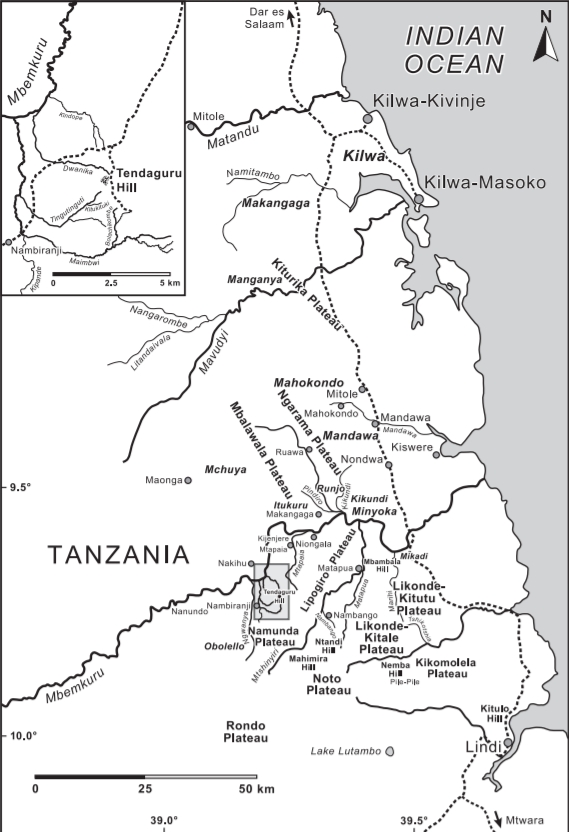 The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly
 The Tendaguru Formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit in the
The Tendaguru Formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit in the
 The Tendaguru Formation was deposited in the
The Tendaguru Formation was deposited in the
 The sedimentary rocks and fossils record a repeated shift from shallow marine to tidal flat environments indicating that the strata of the Tendaguru Formation were deposited near an oscillating strandline which was controlled by sea level changes. The three dinosaur-bearing members are continental to marginal marine and the three sandstone-dominated members are marginal marine in origin.Bussert et al., 2009, p.168
;''Nerinella'' Member
The composition of benthic molluscs and foraminifera, euhaline to mesohaline ostracods, and dinoflagellate assemblages indicate marine, shallow water conditions for the ''Nerinella'' Member, in particular for the lower part. Sedimentation occurred as tidal channel fills, subtidal and tidal
The sedimentary rocks and fossils record a repeated shift from shallow marine to tidal flat environments indicating that the strata of the Tendaguru Formation were deposited near an oscillating strandline which was controlled by sea level changes. The three dinosaur-bearing members are continental to marginal marine and the three sandstone-dominated members are marginal marine in origin.Bussert et al., 2009, p.168
;''Nerinella'' Member
The composition of benthic molluscs and foraminifera, euhaline to mesohaline ostracods, and dinoflagellate assemblages indicate marine, shallow water conditions for the ''Nerinella'' Member, in particular for the lower part. Sedimentation occurred as tidal channel fills, subtidal and tidal
 The Tendaguru Beds as a fossil deposit were first discovered in 1906, when
The Tendaguru Beds as a fossil deposit were first discovered in 1906, when
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* ;Paleontology * Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* * * * * Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* * * * * *
*
*
*  *
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*  *
*
*
*
*
*  *
*
*
*  *
*  *
*
{{National Historic Sites of Tanzania
Geologic formations of Tanzania
Jurassic System of Africa
Jurassic Tanzania
Lower Cretaceous Series of Africa
Cretaceous Tanzania
Sandstone formations
Shale formations
Siltstone formations
Conglomerate formations
Limestone formations
Shallow marine deposits
Tidal deposits
Deltaic deposits
Lacustrine deposits
Lagoonal deposits
Paleontology in Tanzania
Rufiji-Ruvuma languages
*
*
{{National Historic Sites of Tanzania
Geologic formations of Tanzania
Jurassic System of Africa
Jurassic Tanzania
Lower Cretaceous Series of Africa
Cretaceous Tanzania
Sandstone formations
Shale formations
Siltstone formations
Conglomerate formations
Limestone formations
Shallow marine deposits
Tidal deposits
Deltaic deposits
Lacustrine deposits
Lagoonal deposits
Paleontology in Tanzania
Rufiji-Ruvuma languages
 The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly fossiliferous
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ...
and Lagerstätte
A Lagerstätte (, from ''Lager'' 'storage, lair' '' Stätte'' 'place'; plural ''Lagerstätten'') is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues. These for ...
located in the Lindi Region
Lindi Region (''Mkoa wa Lindi'' in Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The region covers an area of . The region is comparable in size to the combined land area of the nation state of Sri Lanka. The regional capital is the m ...
of southeastern Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
. The formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit of the Mandawa Basin
Mandawa is a town in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is part of Shekhawati region. Mandawa is located at . It has an average elevation of 316 metres (1036 ft).
History
The town of Mandawa was a thikana of Jaipur Sta ...
, overlying Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
basement
A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, ...
, separating by a long hiatus and unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval o ...
. The formation reaches a total sedimentary thickness of more than . The formation ranges in age from the late Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations co ...
to the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
, Oxfordian to Hauterivian
The Hauterivian is, in the geologic timescale, an age in the Early Cretaceous Epoch or a stage in the Lower Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 132.9 ± 2 Ma and 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma (million years ago). The Hauterivian is preceded by the Va ...
stages, with the base of the formation possibly extending into the Callovian
In the geologic timescale, the Callovian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic, lasting between 166.1 ± 4.0 Ma (million years ago) and 163.5 ± 4.0 Ma. It is the last stage of the Middle Jurassic, following the Bathonian and preceding the ...
.
The Tendaguru Formation is subdivided into six members; from oldest to youngest Lower Dinosaur Member, the ''Nerinella'' Member, the Middle Dinosaur Member, ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member, the Upper Dinosaur Member, and the ''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Member. The succession comprises a sequence of sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
s, shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
s, siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, p ...
s, conglomerates with minor oolitic limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
s, deposited in an overall shallow marine to coastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
, characterized by tidal, fluvial
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluviog ...
and lacustrine
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
influence with a tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
deposit occurring in the ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member. The climate of the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous was semi-arid with seasonal rainfall and the eustatic sea level was rising in the Late Jurassic from low levels in the Middle Jurassic. Paleogeographical reconstructions show the Tendaguru area was located in the subtropical southern hemisphere during the Late Jurassic.
The Tendaguru Formation is considered the richest Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987.
In European lithostratigraphy, the name ...
strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum ( : strata) is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as ei ...
in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The formation has provided a wealth of fossils of different groups; early mammaliaform
Mammaliaformes ("mammalian forms") is a clade that contains the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent com ...
s, several genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
of dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s, crocodyliforms
Crocodyliformes is a clade of crurotarsan archosaurs, the group often traditionally referred to as "crocodilians". They are the first members of Crocodylomorpha to possess many of the features that define later relatives. They are the only pseudo ...
, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s and flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
. More than of material was shipped to Germany during early excavations in the early twentieth century. The faunal assemblage of the Tendaguru is similar to the Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Late Jurassic, Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandsto ...
of the central-western United States, with an additional marine interbed fauna not present in the Morrison.
The dinosaur fauna found in the formation is similar to that of other highly fossiliferous stratigraphic units of the Late Jurassic; among others the Kimmeridge
Kimmeridge () is a small village and civil parish on the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula on the English Channel coast in Dorset, England. It is situated about south of Wareham and west of Swanage. In 2013 the estimated population of the civil p ...
and Oxford Clay
The Oxford Clay (or Oxford Clay Formation) is a Jurassic marine sedimentary rock formation underlying much of southeast England, from as far west as Dorset and as far north as Yorkshire. The Oxford Clay Formation dates to the Jurassic, specifical ...
s of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, the Sables de Glos, Argiles d'Octeville
The Argiles d'Octeville (meaning Octeville-sur-Mer, Octeville Clay) is a geological Formation (geology), formation in Normandy, France. It dates back to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distr ...
, Marnes de Bléville
The Marnes de Bleville is a geological formation in France. It dates back to the Late Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Jurassic, Europe)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (ed ...
of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the Alcobaça, Guimarota and Lourinhã Formation
The Lourinhã Formation () is a fossil rich geological formation in western Portugal, named for the municipality of Lourinhã. The formation is mostly Late Jurassic in age (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian), with the top of the formation extending into the ...
s of Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, the Villar del Arzobispo Formation
The Villar del Arzobispo Formation is a Late Jurassic to possibly Early Cretaceous geologic formation in eastern Spain. It is equivalent in age to the Lourinhã Formation of Portugal. It was originally thought to date from the Late Tithonian-Middl ...
of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, the Shishugou, Kalazha and Shangshaximiao Formation
The Shaximiao Formation () is a Middle to Late Jurassic aged geological formation in Sichuan, China, most notable for the wealth of dinosaurs fossils that have been excavated from its strata. The Shaximiao Formation is exposed in and around the ...
s in China, the Toqui Formation
The Toqui Formation is a geological formation in the Aysén Region of southern Chile. It has been dated to the Tithonian stage of the Late Jurassic by uranium–lead dating of zircons, providing an age of 147 ± 0.1 Ma. It consists of an sequence ...
of Chile and Cañadón Calcáreo Formation
The Cañadón Calcáreo Formation is an Oxfordian to Kimmeridgian-aged geologic formation, from the Cañadón Asfalto Basin in Chubut Province, Argentina, a rift basin that started forming since the earliest Jurassic.Figari et al., 2015, p.142 It ...
and the Morrison Formation, with the presence of dinosaurs with similar counterparts, e.g., ''Brachiosaurus
''Brachiosaurus'' () is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic, about 154to 150million years ago. It was first described by American paleontologist Elmer S. Riggs in 1903 from fossils found in th ...
'' and ''Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been foun ...
'' in the Morrison, and ''Giraffatitan
''Giraffatitan'' (name meaning "titanic giraffe") is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the late Jurassic Period (geology), Period (Kimmeridgian–Tithonian stages) in what is now Lindi Region, Tanzania. It was originally named as an ...
'' and ''Kentrosaurus
''Kentrosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of stegosaurid dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. The type species is ''K. aethiopicus'', named and described by German palaeontologist Edwin Hennig in 1915. Often thought to be a " pri ...
'' in the Tendaguru.Mateus, 2006, pp.223–232
Description
 The Tendaguru Formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit in the
The Tendaguru Formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit in the Mandawa Basin
Mandawa is a town in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is part of Shekhawati region. Mandawa is located at . It has an average elevation of 316 metres (1036 ft).
History
The town of Mandawa was a thikana of Jaipur Sta ...
, directly overlying Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
basement
A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, ...
consisting of gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures an ...
. The contact contains a large hiatus, a missing sequence of stratigraphy, spanning the Paleozoic, Triassic and Early Jurassic. The formation is unconformably overlain by late Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
sediments of the Makonde Formation, that forms the top of several plateaus; Namunda, Rondo, Noto, and Likonde-Kitale.Bussert et al., 2009, p.154
Based on extended geological and paleontological observations the "Tendaguruschichten" (Tendaguru Beds) were defined by Werner Janensch
Werner Ernst Martin Janensch (11 November 1878 – 20 October 1969) was a German paleontologist and geologist.
Biography
Janensch was born at Herzberg (Elster).
In addition to Friedrich von Huene, Janensch was probably Germany's most imp ...
as expedition leader and Edwin Hennig
Edwin Hennig (27 April 1882 – 12 November 1977) was a German paleontologist.
Career
Edwin Hennig was one of five children of a merchant who died when Hennig was 10 years old. Starting in 1902, Hennig studied natural sciences, anthropolog ...
in 1914 to define a sequence of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous strata, exposed in the Tendaguru area, which is named after Tendaguru Hill.Bussert et al., 2009, p.142
Stratigraphy
The Tendaguru is divided into 6 members, which represent differentdepositional environment
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be ...
s, with the 'Dinosaur Beds' representing terrestrial facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formatio ...
while the beds with genus/species names represent marine interbeds with shallow marine to lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') a ...
al facies. In ascending order these are: the Lower Dinosaur Member, the ''Nerinella'' Member, the Middle Dinosaur Member, ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member, the Upper Dinosaur Member, and the ''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Member.Schwarz-Wings & Böhm, 2014, p.82
Paleogeography and depositional environment
Paleogeography
 The Tendaguru Formation was deposited in the
The Tendaguru Formation was deposited in the Mandawa Basin
Mandawa is a town in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is part of Shekhawati region. Mandawa is located at . It has an average elevation of 316 metres (1036 ft).
History
The town of Mandawa was a thikana of Jaipur Sta ...
, a post-Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ext ...
,Muhongo, 2013, p.28 Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
rift basin
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben wi ...
located between the Ruvu Basin Ruvu may refer to:
* Ruvu River, a river in Morogoro and Pwani Regions of eastern Tanzania
* River Ruvu, a source of the Pangani River or Jipe Ruvu in northeastern Tanzania
* Ruvu, Kibaha District, a town in Tanzania
* Ruvu Ward in Same District
...
and Rufiji Trough Rufiji may refer to:
* Rufiji Delta, a region in Tanzania
* Rufiji District, in the Pwani Region of Tanzania
* Rufiji River
The Rufiji River lies entirely within Tanzania. It is also the largest and longest river in the country. The river is fo ...
to the north and the Ruvuma Basin to the south.Muhongo, 2013, p.8 To the west of the basin, Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
and Early Proterozoic basement rocks crop out.Muhongo, 2013, p.33 The main rift phase in present-day southeastern Africa led to the separation of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and the then-connected Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
happened during the Early Cretaceous.Muhongo, 2013, p.3 The Songo Songo and Kiliwani gas field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence ...
s are located just offshore the basin.Muhongo, 2013, p.17Muhongo, 2013, p.22
At time of deposition was undergoing a semi-arid climate with coastal influences that maintained somewhat higher moisture levels than seen inland.Noto & Grossmann, 2010, p.7 The upper parts of the formation, the Middle Dinosaur and ''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Members in particular, showed prevailing semiarid conditions with pronounced dry seasons, based on palynologic analysis.Schrank, 1999, p.181 The Tendaguru fauna was stable through the Late Jurassic.Noto & Grossmann, 2010, p.9
During the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, the Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
paleocontinent was breaking up and the separation of the Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
n and Gondwana supercontinents resulted from the connection of the Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents ...
with the proto-Atlantic and the Pacific Ocean. In addition, the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
developed towards the end of the Late Jurassic with the separation of South America and Africa. Africa became increasingly isolated from most other continents by marine barriers from the Kimmeridgian into the Early Cretaceous, but retained a continental connection with South America. Global sea levels dropped significantly in the Early Jurassic and remained low through the Middle Jurassic but rose considerably towards the Late Jurassic, deepening the marine trenches
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from eros ...
between continents.Arratia et al., 2002, p.227
Depositional environment
 The sedimentary rocks and fossils record a repeated shift from shallow marine to tidal flat environments indicating that the strata of the Tendaguru Formation were deposited near an oscillating strandline which was controlled by sea level changes. The three dinosaur-bearing members are continental to marginal marine and the three sandstone-dominated members are marginal marine in origin.Bussert et al., 2009, p.168
;''Nerinella'' Member
The composition of benthic molluscs and foraminifera, euhaline to mesohaline ostracods, and dinoflagellate assemblages indicate marine, shallow water conditions for the ''Nerinella'' Member, in particular for the lower part. Sedimentation occurred as tidal channel fills, subtidal and tidal
The sedimentary rocks and fossils record a repeated shift from shallow marine to tidal flat environments indicating that the strata of the Tendaguru Formation were deposited near an oscillating strandline which was controlled by sea level changes. The three dinosaur-bearing members are continental to marginal marine and the three sandstone-dominated members are marginal marine in origin.Bussert et al., 2009, p.168
;''Nerinella'' Member
The composition of benthic molluscs and foraminifera, euhaline to mesohaline ostracods, and dinoflagellate assemblages indicate marine, shallow water conditions for the ''Nerinella'' Member, in particular for the lower part. Sedimentation occurred as tidal channel fills, subtidal and tidal sand bar
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It o ...
s, minor storm layers (tempestite
Tempestites are storm deposits that can be recognized throughout the geologic record. They are studied in the scientific disciplines of sedimentary geology and paleotempestology. The deposits derive their meaning from the word ''tempest'', a vi ...
s), and beach deposits. Overall, the ''Nerinella'' Member represents a variety of shallow subtidal to lower intertidal environments influenced by tides and storms.Bussert et al., 2009, p.167
;Middle Dinosaur Member
The sedimentological characteristics of the basal part of the Middle Dinosaur Member suggest deposition on tidal flat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal fl ...
s and in small tidal channels of a lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') a ...
al paleoenvironment. The ostracod '' Bythocypris sp.'' from the member indicates polyhaline to euhaline conditions. Slightly higher up, a faunal sample dominated by the bivalve '' Eomiodon'' and an ostracod assemblage composed of brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
to freshwater taxa is indicative of a brackish water paleoenvironment with distinct influx of freshwater as revealed by the nonmarine ostracod genus '' Cypridea'', charophyte
Charophyta () is a group of freshwater green algae, called charophytes (), sometimes treated as a phylum, division, yet also as a superdivision or an unranked clade. The terrestrial plants, the Embryophyta emerged within Charophyta, possibly fro ...
s, and other freshwater algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
. The paleoenvironment of the ostracod assemblages of the Middle Dinosaur Member changed upsection from a marine setting in the basal parts through alternating marine-brackish conditions to freshwater conditions in the higher parts of this member. The highly sporadic occurrence, in this part of the section, of molluscs typical of marginal marine habitats indicates only a very weak marine influence, at sabkha-like coastal plains with ephemeral brackish lakes and ponds are recorded in the upper part of the Middle Dinosaur Member. This part also contains pedogenic calcretes indicating subaerial exposure and the onset of soil formation. The calcrete intraclasts within adjacent sandstone beds testify to erosive reworking of calcrete horizons.Aberhan et al., 2002, p.32 The presence of crocodyilforms indicates freshwater to littoral environments and adjacent terrestrial areas.Aberhan et al., 2002, p.33
;''Indotrigonia africana'' Member
The coarse-grained sandstone of the lower part of the ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member that shows highly variable transport directions is interpreted as deposits of large tidal channels. Grain-size, large-scale sedimentary structures, and the lack of both trace fossil
A trace fossil, also known as an ichnofossil (; from el, ἴχνος ''ikhnos'' "trace, track"), is a fossil record of biological activity but not the preserved remains of the plant or animal itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, ...
s and epifaunal and infaunal body fossils suggest high water energy and frequent reworking. This basal succession passes upward in cross-bedded sandstone and minor siltstone and claystone with flaser or lenticular bedding that are interpreted as tidal flat and tidal channel deposits. Horizontal to low-angle cross-bedded, fine-grained sandstone with intercalated bivalve pavements indicates tidal currents that operated in small flood and ebb tidal deltas and along the coast. Stacked successions of trough cross-bedded, medium- to coarse-grained sandstone of the upper part of the ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member are interpreted as tidal channel and sand bar deposits. At some places in the surroundings of Tendaguru Hill, these sediments interfinger with oolitic limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
layers that represent high-energy ooid shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It ...
s.
In the Tingutinguti stream section, the ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member exhibits several up to thick, poorly sorted, conglomeratic sandstone beds. They contain mud clast
A MUD (; originally multi-user dungeon, with later variants multi-user dimension and multi-user domain) is a Multiplayer video game, multiplayer Time-keeping systems in games#Real-time, real-time virtual world, usually Text-based game, text-bas ...
s, reworked concretion
A concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions are often ovoid or spherical in shape, although irregular ...
s and/or accumulations of thick-shelled bivalves (mainly '' Indotrigonia africana'' and '' Seebachia janenschi''), and exhibit megaripple surfaces. These conglomeratic sandstone layers are interpreted as storm deposits. In the Dwanika and Bolachikombe stream sections, and in a small tributary of the Bolachikombe creek, a discrete, up to thick conglomerate in the lower portion of the ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member displays evidence of a tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
deposit. Overall, lithofacies and the
diverse macroinvertebrate and microfossil assemblages of the ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member suggest a shallow marine environment. Based on the diverse mesoflora and the abundance of '' Classopollis'', a nearby vegetated hinterland is postulated that was dominated by xerophytic conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
s.
;Upper Dinosaur Member
The small-scale trough and ripple cross-bedded fine-grained sandstone at the base of the Upper Dinosaur Member is interpreted as tidal flat deposits. Unfossiliferous sandstone in the upper part
was most likely deposited in small fluvial channels in a coastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
environment, whereas argillaceous
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates (e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4), sometimes with variable amounts of iron, magnesium, alkali metals, alkaline earths, and other cations found on or near some planetary surfaces.
Clay minerals ...
deposits were laid down in still water bodies such as small lakes and ponds. Rare occurrences of the ostracod ''Cypridea'' and charophytes signal the influence of freshwater, whereas the sporadic occurrence of marine invertebrates suggests a depositional environment close to the sea.
;''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Member
Fining upward sequences of the basal part of the ''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Member are interpreted as tidal channel fills, the overlying fine-grained sandstone, silt- and claystone as tidal flat deposits. From the immediate surroundings of Tendaguru Hill, invertebrates and vertebrates are poorly known and limit the palaeoenvironmental interpretation of this member. The composition of the land-derived sporomorph assemblage suggests a terrestrial vegetation which was dominated by cheirolepidiacean conifers in association with fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except t ...
s.
Excavation history
 The Tendaguru Beds as a fossil deposit were first discovered in 1906, when
The Tendaguru Beds as a fossil deposit were first discovered in 1906, when German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
pharmacist, chemical analyst and mining engineer Bernhard Wilhelm Sattler, on his way to a mine south of the Mbemkure River in German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
(today Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
), was shown by his local staff enormous bones weathering out of the path near the base of Tendaguru Hill, south of Mtapaia (close to Nambiranji village, Mipingo ward, northwest of Lindi town).Maier, 2003 Because of its morphology, the hill was locally known as "steep hill": "tendaguru" in the language of the local Wamwera people. Sattler sent a report of the discoveries that found its way to German palaeontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
Eberhard Fraas
Eberhard Fraas (26 June 1862 – 6 March 1915) was a German scientist, geologist and paleontologist. He worked as a curator at the Stuttgarter Naturaliensammlung and discovered the dinosaurs of the Tendaguru formation in then German East Afric ...
, then on a round trip through Africa, who visited the site in 1907 and with the aid of Sattler recovered two partial skeletons of enormous size.Fraas, 1908
Following the discovery in 1906, teams from the Museum für Naturkunde, Berlin (1907–1913), and the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
(Natural History), London (1924–1931) launched a series of collecting expeditions that remain unequalled in scope and ambition. Led by the vision and influence of geologist Wilhelm von Branca
Carl Wilhelm Franz von Branca Until 1895: Wilhelm Branco; 1895-1907: Wilhelm von Branco (9 September 1844 – 12 March 1928) was a German geologist and paleontologist.
Biography
Von Branca was born in Potsdam.
After having been an officer, ...
, the German expeditions were particularly successful, in large part because the project was taken up as a matter of national ambition (Germany was then a young nation, having been unified by von Bismarck less than 40 years earlier) and enjoyed the benevolence of many wealthy patrons. Eventually, nearly 250 tons of bones, representing an entirely new dinosaur fauna that remains the best understood assemblage from all of former Gondwana, was shipped to Berlin.Cifelli, 2003, p.608
From there, the material was transported to Fraas' institution, the Royal Natural History Collection in Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. Fraas described two species in the badly known genus ''"Gigantosaurus
''Gigantosaurus'' () is a dubious genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay Formation of England. The type species, ''Gigantosaurus megalonyx'', was named and described by Harry Govier Seeley in 1869. Its syntype series ...
"''; ''G. robustus'' and ''G. africanus'' (today ''Janenschia
''Janenschia'' (named after Werner Janensch) is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Lindi Region, Tanzania around 155 million years ago.
Discovery and naming
''Janenschia'' has had a convolut ...
robusta'' and ''Tornieria
''Tornieria'' ("for Tornier") is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. It has a convoluted taxonomic history.
Discovery and naming
In 1907, German paleontologist Eberhard Fraas who wa ...
africana'', respectively).
German Tendaguru Expedition
The Berlin's Natural History Museum excavated at Tendaguru hill and in the surroundings for four years. From 1909 through 1911,Werner Janensch
Werner Ernst Martin Janensch (11 November 1878 – 20 October 1969) was a German paleontologist and geologist.
Biography
Janensch was born at Herzberg (Elster).
In addition to Friedrich von Huene, Janensch was probably Germany's most imp ...
as expedition leader and Edwin Hennig
Edwin Hennig (27 April 1882 – 12 November 1977) was a German paleontologist.
Career
Edwin Hennig was one of five children of a merchant who died when Hennig was 10 years old. Starting in 1902, Hennig studied natural sciences, anthropolog ...
as assistant directed excavations, while Hans Reck
Hans Gottfried Reck (24 January 1886 – 4 August 1937) was a German volcanologist and paleontologist.
In 1913 he was the first to discover an ancient skeleton of a human in the Olduvai Gorge, in what is now Tanzania.
He collaborated with Lo ...
and his wife Ina Reck led the 1912 field season. Other European participants include Hans von Staff. In the rainy seasons the scientists explored the geology of the colony German East Africa on long safaris.
Public discussion about provenance and restitution
In the context of international discussion about theprovenance
Provenance (from the French ''provenir'', 'to come from/forth') is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art but is now used in similar senses i ...
and possible restitution
The law of restitution is the law of gains-based recovery, in which a court orders the defendant to ''give up'' their gains to the claimant. It should be contrasted with the law of compensation, the law of loss-based recovery, in which a court o ...
of colonial heritage, as discussed for example in the 2018 report on the restitution of African cultural heritage
''The Restitution of African Cultural Heritage. Toward a New Relational Ethics'' (in French: ''Rapport sur la restitution du patrimoine culturel africain. Vers une nouvelle éthique relationnelle'') is a report written by Senegalese academic and ...
, both German as well as Tanzanian commentators have called the claim to rightful ownership by the Berlin museum into question. The Tanzanian government has, however, not submitted any official demand for repatriation. German authorities have preferred to offer information on the provenance and research by increasing cooperation between Tanzanian paleontologists and museums with their German counterparts.
In popular culture
In 1998, an illustrated book in Swahili, whose title translates as Dinosaurs of Tendaguru, was published for young readers in East Africa. It presents a slightly different, fictitious story of the first discovery, which is attributed to a Tanzanian farmer, rather than to the German engineer Sattler.Paleontological significance
Possible dinosaur eggs have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al., 2004, p.552 The fauna of the Tendaguru Formation has been correlated with theMorrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Late Jurassic, Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandsto ...
of the central-western United States,Taylor, 2009, p.790 several formations in England, among which the Kimmeridge Clay
The Kimmeridge Clay is a sedimentary deposit of fossiliferous marine clay which is of Late Jurassic to lowermost Cretaceous age and occurs in southern and eastern England and in the North Sea. This rock formation is the major source rock for North ...
and Oxford Clay
The Oxford Clay (or Oxford Clay Formation) is a Jurassic marine sedimentary rock formation underlying much of southeast England, from as far west as Dorset and as far north as Yorkshire. The Oxford Clay Formation dates to the Jurassic, specifical ...
, and France ( Sables de Glos, Argiles d'Octeville
The Argiles d'Octeville (meaning Octeville-sur-Mer, Octeville Clay) is a geological Formation (geology), formation in Normandy, France. It dates back to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distr ...
, Marnes de Bléville
The Marnes de Bleville is a geological formation in France. It dates back to the Late Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Jurassic, Europe)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (ed ...
), the Alcobaça, Guimarota and Lourinhã Formation
The Lourinhã Formation () is a fossil rich geological formation in western Portugal, named for the municipality of Lourinhã. The formation is mostly Late Jurassic in age (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian), with the top of the formation extending into the ...
s of Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
,Mateus, 2006, p.1 the Villar del Arzobispo Formation
The Villar del Arzobispo Formation is a Late Jurassic to possibly Early Cretaceous geologic formation in eastern Spain. It is equivalent in age to the Lourinhã Formation of Portugal. It was originally thought to date from the Late Tithonian-Middl ...
of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, the Shishugou, Kalazha and Shangshaximiao Formation
The Shaximiao Formation () is a Middle to Late Jurassic aged geological formation in Sichuan, China, most notable for the wealth of dinosaurs fossils that have been excavated from its strata. The Shaximiao Formation is exposed in and around the ...
s of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and the Toqui Formation
The Toqui Formation is a geological formation in the Aysén Region of southern Chile. It has been dated to the Tithonian stage of the Late Jurassic by uranium–lead dating of zircons, providing an age of 147 ± 0.1 Ma. It consists of an sequence ...
of the Magallanes Basin
The Magallanes Basin or Austral Basin is a major sedimentary basin in southern Patagonia. The basin covers a surface of about and has a NNW-SSE oriented shape. The basin is bounded to the west by the Andes mountains and is separated from the Malv ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
and the Cañadón Calcáreo Formation
The Cañadón Calcáreo Formation is an Oxfordian to Kimmeridgian-aged geologic formation, from the Cañadón Asfalto Basin in Chubut Province, Argentina, a rift basin that started forming since the earliest Jurassic.Figari et al., 2015, p.142 It ...
of the Cañadón Asfalto Basin
The Cañadón Asfalto Basin ( es, Cuenca de Cañadón Asfalto) is an irregularly shaped sedimentary basin located in north-central Patagonia, Argentina. The basin stretches from and partly covers the North Patagonian Massif in the north, a high for ...
in central Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and gl ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
.Noto & Grossmann, 2010, p.3
Fossil content
Mammaliaformes
Pterosaurs
Ornithischians
Sauropods
Theropods
Crocodyliformes
Amphibians
Fish
Invertebrates
=Gastropods
==Bivalves
==Coral
==Ostracods
=Flora
See also
*List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils
This is a list of stratigraphic units from which dinosaur body fossils have been recovered. Although Dinosauria is a clade which includes modern birds, this article covers only Mesozoic stratigraphic units. Units listed are all either formation ...
* List of African dinosaurs
This is a list of dinosaurs whose remains have been recovered from Africa. Africa has a rich fossil record, but it is patchy and incomplete. It is rich in Triassic and Early Jurassic dinosaurs. African dinosaurs from these time periods include ''Co ...
* Manda Formation
The Manda Formation (also known as the Manda Beds) is a Middle Triassic (Anisian?) or possibly Late Triassic (Carnian?) geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassic, including some of the e ...
, Triassic fossiliferous formation of Tanzania
* Usili Formation
The Usili Formation is a Late Permian geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Permian, including temnospondyls, pareiasaurs, therapsids and the archosauromorph ''Aenigmastropheus''.
History ...
, Permian fossiliferous formation of Tanzania
* Mugher Mudstone, Tithonian fossiliferous formation of Ethiopia
* Ksar Metlili Formation
The Ksar Metlili Formation is a geological formation in eastern High Atlas of Morocco, it is late Tithonian to Berriasian
In the geological timescale, the Berriasian is an age/stage of the Early/Lower Cretaceous. It is the oldest subdivision ...
, Tithonian to Berriasian fossiliferous formation of Morocco
* Kirkwood Formation
The Kirkwood Formation is a geological Geological formation, formation found in the Eastern and Western Cape provinces in South Africa. It is one of the four formations found within the Uitenhage Group of the Algoa Basin – its type locality – ...
, Berriasian to Hauterivian fossiliferous formation of South Africa
* Sundays River Formation
The Sundays River Formation is a geological formation found in the Eastern and Western Cape provinces in South Africa. It is the second youngest of the four formations found within the Uitenhage Group of the Algoa Basin, its type locality, and t ...
, Valanginian to Hauterivian fossiliferous formation of South Africa
* Bajada Colorada Formation
The Bajada Colorada Formation is a geologic formation of the southern Neuquén Province in the Neuquén Basin of northern Patagonia, Argentina. The formation belongs to the Mendoza Group and is Late Berriasian to Early Valanginian in age. The f ...
, Berriasian to Valanginian fossiliferous formation of Argentina
* Dinosaurs of Tendaguru, Book for young readers in Swahili
Notes and references
Notes
References
Bibliography
;Geology *Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
*
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* ;Paleontology *
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* * * * *
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
* * * * *