Tarbat Discovery Centre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Portmahomack ( gd, Port Mo Chalmaig; 'Haven of My .e. 'Saint'Colmóc') is a small fishing village in
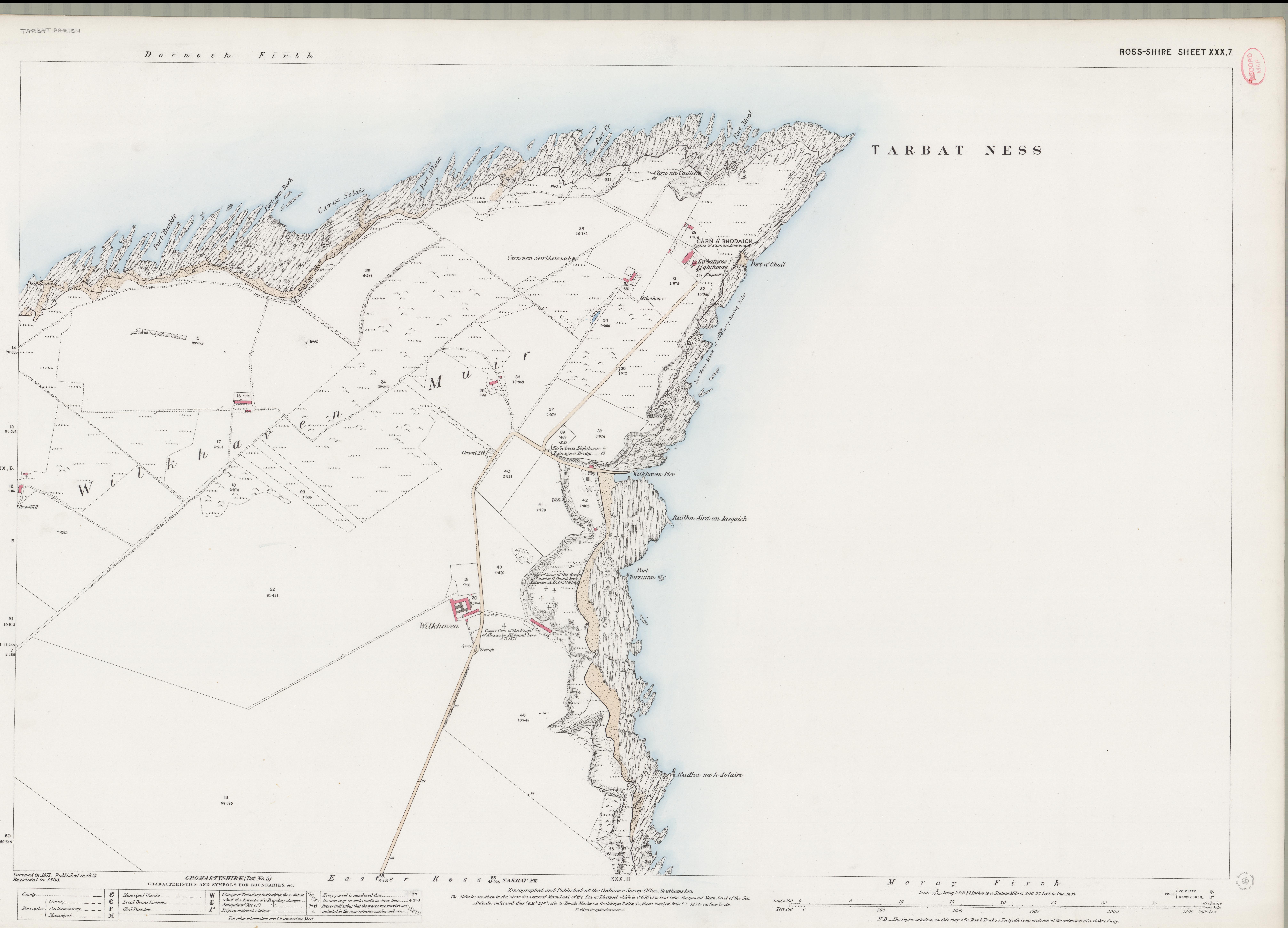
 In 1822 Rev Grant, minister of Boharn, described "a beautiful square fortification of about 100 paces of a side" near Blàr a' Chath, north of the village.
It was tentatively identified as a Roman camp in 1949 by
In 1822 Rev Grant, minister of Boharn, described "a beautiful square fortification of about 100 paces of a side" near Blàr a' Chath, north of the village.
It was tentatively identified as a Roman camp in 1949 by
 Portmahomack is the site of the first confirmed
Portmahomack is the site of the first confirmed
Fendom
road to
Montreal Gazette, Retrieved 2011-02-12
/ref> Professor
File:Portmahomack Church.jpg, Portmahomack Church
File:Portmahomack Harbour.jpg, Portmahomack Harbour
File:Portmahomack_Village.JPG, Portmahomack Village
File:Portmahomack_Village_Centre.JPG, Portmahomack Village
File:Portmahomack_War_Memorial.JPG, Portmahomack War Memorial
Portmahomack.org
Tarbat Discovery Programme
Portmahomack.net
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Highland (council area) Populated places in Ross and Cromarty Iron Age sites in Scotland
Easter Ross
Easter Ross ( gd, Ros an Ear) is a loosely defined area in the east of Ross, Highland, Scotland.
The name is used in the constituency name Caithness, Sutherland and Easter Ross, which is the name of both a British House of Commons constituenc ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
. It is situated in the Tarbat Peninsula in the parish of Tarbat
Tarbat (Gaelic , meaning 'a crossing or isthmus'Place-names of Ross and Cromarty, by W J Watson, publ. The Northern Counties Printing and Publishing Co. Ltd., Inverness 1904; p.45) is a civil parish in Highland, Scotland, in the north-east corner ...
. Tarbat Ness Lighthouse
The Tarbat Ness Lighthouse is located at the North West tip of the Tarbat Ness peninsula near the fishing village of Portmahomack on the east coast of Scotland. It was built in 1830 by Robert Stevenson and has an elevation of and 203 steps to ...
is about from the village at the end of the Tarbat Peninsula. Ballone Castle lies about from the village. There is evidence of early settlement, and the area seems to have been the site of significant activity during the time of the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
, early Christianity and the Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
. The village is situated on a sandy bay and has a small harbour designed by Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotla ...
: it shares with Hunstanton
Hunstanton () is a seaside town in Norfolk, England, which had a population of 4,229 at the 2011 Census. It faces west across The Wash, making it one of the few places on the east coast of Great Britain where the sun sets over the sea. Hunstant ...
the unusual distinction of being on the east coast but facing west. Portmahomack lies inside the Moray Firth Special Area of Conservation with the associated dolphin and whale watching activity.
The village has a primary school, golf course, hotel, a number of places to eat and a shop with a sub-post office. The nearest rail access is at Fearn railway station
, symbol_location = gb
, symbol = rail
, image = Fearn Railway Station.JPG
, borough = Hill of Fearn, Highland
, country = Scotland
, coordinates =
, grid_name = Gri ...
and the nearest commercial airport is at Inverness Airport
Inverness Airport ( gd, Port-adhair Inbhir Nis) is an international airport situated at Dalcross, north-east of the city of Inverness, Scotland. It is owned by Highlands and Islands Airports Limited (HIAL). The airport is the main gateway fo ...
. The nearest town with full services is Tain
Tain ( Gaelic: ''Baile Dhubhthaich'') is a royal burgh and parish in the County of Ross, in the Highlands of Scotland.
Etymology
The name derives from the nearby River Tain, the name of which comes from an Indo-European root meaning 'flow'. The ...
lying approximately west. Tain also has rail access. The hamlet of Rockfield is nearby and is accessed via the village of Portmahomack.
History
Situated east ofTain
Tain ( Gaelic: ''Baile Dhubhthaich'') is a royal burgh and parish in the County of Ross, in the Highlands of Scotland.
Etymology
The name derives from the nearby River Tain, the name of which comes from an Indo-European root meaning 'flow'. The ...
on the northern coast of the Tarbat Peninsula, Portmahomack has long been known to be on the site of early settlements. The earliest evidence of habitation is provided by shell middens
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofac ...
pointing to settlement as early as one or two thousand years BCE.
There are the remains of an Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
broch
A broch is an Iron Age drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland. Brochs belong to the classification "complex Atlantic roundhouse" devised by Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s. Their origin is a matter of some controversy.
Origin ...
a little to the west of the village. Finds of elaborate early Christian carved stones dating to the 8th-9th centuries (including one with an inscription), in and around the churchyard, had long suggested that Portmahomack was the site of an important early church in the sixth-seventh century.

Possible Roman camp
O. G. S. Crawford
Osbert Guy Stanhope Crawford (28 October 1886 – 28 November 1957) was a British archaeologist who specialised in the archaeology of prehistoric Britain and Sudan. A keen proponent of aerial archaeology, he spent most of his career as th ...
although he did not visit the site and no trace was found of its existence during a later visit.
It had apparently been defaced by 1872 during land reclamation, but in Crawford's opinion there may be some traces of the Roman camp still visible or to be discovered.
It has been suggested that the supposed camp was visited by emperor Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced thro ...
, based on remarks made by the Roman historian Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
: "Severus did not desist until he approached the extremity of the island".
Monastery
 Portmahomack is the site of the first confirmed
Portmahomack is the site of the first confirmed Pictish
Pictish is the extinct language, extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited num ...
monastery and the subject between 1994 and 2007 of one of the largest archaeological investigations in Scotland directed by Martin Carver
Martin Oswald Hugh Carver, FSA, Hon FSA Scot, (born 8 July 1941) is Emeritus Professor of Archaeology at the University of York, England, director of the Sutton Hoo Research Project and a leading exponent of new methods in excavation and surve ...
(b. 1941). The monastery began around 550 AD and was destroyed by fire in about 800 AD. It had a burial ground with cist and head-support burials, a stone church, at least four monumental stone crosses and workshops making church plate and early Christian books. The making of vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. Parchment is another term for this material, from which vellum is sometimes distinguished, when it is made from calfskin, as opposed to that made from other anima ...
in an early medieval site was detected for the first time here by Cecily Spall of FAS Ltd.
Over two hundred pieces of sculpture have been found, some of it broken up in a layer of burning suggesting that the monastic buildings were violently destroyed, possibly in a Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
raid, about the year 800. The tradition of holiness survived sufficiently strongly to allow the site to become that of the later medieval parish church of St Colmóc.
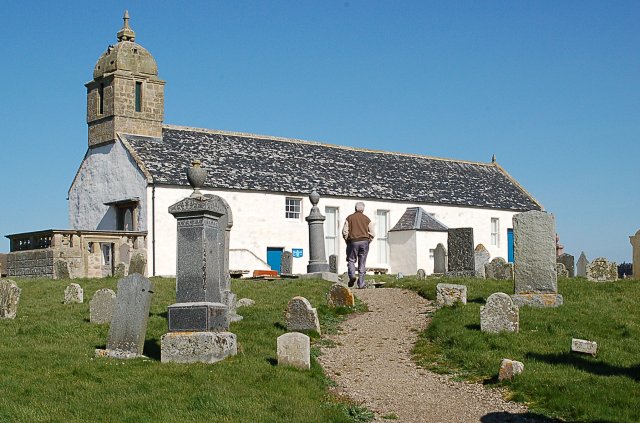
The present restored building, adapted to house a museum after lying empty for a number of years, has been shown by archaeological investigation to be itself a monument of great interest, of multi-phase construction, the oldest part (the east wall of the crypt) having been built as early as the 9th century. The museum and visitor centre in St Colmóc's Church is managed by the Tarbat Historic Trust.
The precise identity of 'Colmóc' is uncertain. The name is an 'affectionate' or hypocoristic form, and could refer either to one of the many early Irish holy men with the common name of Colmán
Colmán or Colman is both a given name and a surname. Notable people with the name include:
Medieval Irish people
* Colmán Bec (died ''c''. 585), Irish dynast
* Colmán mac Cobthaig (died ''c''. 622), Irish king
* Colmán mac Lénéni (died ''c'' ...
(e.g. Colmán of Lindisfarne
Colmán of Lindisfarne ( 605 – 18 February 675 AD) also known as Saint Colmán was Bishop of Lindisfarne from 661 until 664.
Life
Colman was a native of the west of Ireland and had received his education on Iona. He was probably a nobleman of ...
), or to St. Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is toda ...
(Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
Colm Cille
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is toda ...
).
Recent research on the ancient trench around the local monastery found organic samples in the date range from 140 AD to 590 AD. The area enclosed by the ditch may have been a "settlement, craft-working centre and/or hub of a Pictish community", connected to the possible Roman fortification in Port a Chaistell.
Battle of Tarbat Ness
TheBattle of Tarbat Ness
Tarbat Ness (Scottish Gaelic: ''Rubha Thairbeirt'') is headland that lies at the end of the Tarbat peninsula in Easter Ross, Scotland. The name is from the Gaelic ''tairbeart'' meaning "isthmus" and the Old Norse ''ness'', meaning " headland". It l ...
was a land battle fought (c 1030-1040) between Thorfinn the Mighty
Thorfinn Sigurdsson (1009?– 1065), also known as Thorfinn the Mighty (Old Norse: ''Þorfinnr inn riki''), was an 11th-century Jarl of Orkney. He was the youngest of five sons of Jarl Sigurd Hlodvirsson and the only one resulting from Sigur ...
, Earl (Jarl) of Caithness and the King of Scotland.
Middle Ages
In theBattle of Tarbat
The Battle of Tarbat was a Scottish clan battle fought in the 1480s on the Tarbat peninsula, in Easter Ross. The Clan Ross cornered a raiding party of Clan Mackay near the village of Portmahomack and put many of them to the sword. The survivor ...
in the 1480s, a raiding party from the Clan Mackay
Clan Mackay ( ; gd, Clann Mhic Aoidh ) is an ancient and once-powerful Scottish Highlands, Highland Scottish clan from the far North of the Scottish Highlands, but with roots in the old Mormaer of Moray, Kingdom of Moray. They supported Robert I ...
of Strathnaver
Strathnaver or Strath Naver ( gd, Srath Nabhair) is the fertile strath of the River Naver, a famous salmon river that flows from Loch Naver to the north coast of Scotland. The term has a broader use as the name of an ancient province also kno ...
were cornered in the Tarbat church by the Clan Ross
Clan Ross ( gd, Clann Anndrais ) is a Highland Scottish clan. The original chiefs of the clan were the original Earl of Ross, Earls of Ross.
History
Origins
The first recorded chief of the Clan Ross was Fearchar, Earl of Ross, "Fearcher Mac ...
, who killed many of them before setting fire to the church.
Agricultural Improvement
The New Statistical Account of Scotland (1840) makes reference to new and improved agricultural practices being introduced fromEast Lothian
East Lothian (; sco, East Lowden; gd, Lodainn an Ear) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area. The county was called Haddingtonshire until 1921.
In 1975, the histo ...
. The area benefited as a result and there are many newspaper accounts of grain shipments from Portmahomack to Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
and London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
during the 19th century.
White Fish Boom
Portmahomack was a centre for the white fishing boom that lasted up until the early part of the 20th century. The bay was so full of boats at time that it was said you could walk from the harbour to the rocks on the other side of the bay without getting wet.World War 2
The direcFendom
road to
Tain
Tain ( Gaelic: ''Baile Dhubhthaich'') is a royal burgh and parish in the County of Ross, in the Highlands of Scotland.
Etymology
The name derives from the nearby River Tain, the name of which comes from an Indo-European root meaning 'flow'. The ...
was closed due to the construction of the airfield at RAF Tain
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
. Parts of the area were evacuated for a period of months to allow landing exercises to be carried out in preparation for D Day
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
in 1944. The Jiri Weiss
Jiri ( ne, जिरी) is a municipality in Dolakha District in the Bagmati Province of central Nepal. At the time of the 2011 Nepal census it had a population of 13,638 people..
Jiri, which lies about 190 kilometers from Kathmandu, is the ma ...
directed propaganda film ''Before the Raid'' was filmed in Portmahomack in 1943.
Tourist site
Today, Portmahomack is a tourist destination with its traditional harbour, swimming beach, golf, dolphin watching, fishing and other watersports. It has a permanent population of between 500 and 600 residents. In the former parish church the Tarbat Discovery Centre, designed by exhibition consultants Higgins Gardner & Partners, houses displays on local history, and many of the finds from several seasons of excavation within the church itself, and in the fields surrounding the churchyard. It also houses the Peter Fraser Archive of memorabilia relating toPeter Fraser
Peter Fraser (; 28 August 1884 – 12 December 1950) was a New Zealand politician who served as the 24th prime minister of New Zealand from 27 March 1940 until 13 December 1949. Considered a major figure in the history of the New Zealand Lab ...
, wartime prime minister of New Zealand, who was born and grew up in Hill of Fearn
Hill of Fearn ( gd, Baile an Droma) is a small village near Tain in Easter Ross, in the Scottish council area of Highland.
Geography
The village is on the B9165 road, between the A9 trunk road and the smaller hamlet of Fearn to the southeast ...
, distant from Portmahomack.
Notable among these are a large collection of fragments of Pictish stone sculpture, many of them superbly carved with figures of ecclesiastics, fantastic and realistic animals, 'Celtic' interlace and key-pattern, and other motifs. The large elaborate late seventeenth- or early eighteenth-century bell-turret on the west gable of the church is an unusual and distinctive feature.
Some important Pictish carved stones from Portmahomack are on display in the Museum of Scotland
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in ...
, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
with replicas in the Tarbat Discovery Centre.
Two other important historic buildings in Portmahomack are adjoining 'girnals' (storehouses), built in the late 17th century and 1779, overlooking the harbour (restored as housing). The former is one of the oldest such buildings to survive in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
. The village also features a number of attractive 18th/early 19th century houses lining the shore.
The harbour was improved by the famous engineer Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotla ...
and was important in grain export in the 19th century.
Portmahomack was a favourite holiday location for Lord Reith (John Reith, 1st Baron Reith
John Charles Walsham Reith, 1st Baron Reith, (; 20 July 1889 – 16 June 1971), was a British broadcasting executive who established the tradition of independent public service broadcasting in the United Kingdom. In 1922, he was employed by th ...
), Director-General of the BBC, who holidayed in the Blue House, still aptly painted blue and located on the seafront, near the harbour.
The murder-mystery writer Anne Perry
Anne Perry (born Juliet Marion Hulme; 28 October 1938) was convicted of murder in New Zealand when a teenager, later moved to England and became an author. In 1954, at the age of fifteen, she and her 16-year-old friend Pauline Parker were tried ...
lived adjacent to the village for a number of years.
John Shepherd-Barron
John Adrian Shepherd-Barron OBE (23 June 1925 – 15 May 2010) was an India-born British inventor, who led the team that installed the first cash machine, sometimes referred to as the automated teller machine or ATM.
Early life
John Adrian Shep ...
, the inventor of the ATM (Auto-Teller Machine), lived in the nearby community of Geanies until his death in 2010./ref> Professor
Thomas Summers West
Thomas Summers West (18 November 1927 – 9 January 2010) was a British chemist.
Life Early years
He was born in 1927 in Peterhead, Scotland and educated at Old Tarbat Public School in Portmahomack and then Tain Royal Academy. He then studied ...
, was a famous son of the Village with an Exhibition held in his name at the Tarbat Discovery Centre in 2011
See also
*Battle of Tarbat
The Battle of Tarbat was a Scottish clan battle fought in the 1480s on the Tarbat peninsula, in Easter Ross. The Clan Ross cornered a raiding party of Clan Mackay near the village of Portmahomack and put many of them to the sword. The survivor ...
* Portmahomack sculpture fragments
* Tarbat Ness Lighthouse
The Tarbat Ness Lighthouse is located at the North West tip of the Tarbat Ness peninsula near the fishing village of Portmahomack on the east coast of Scotland. It was built in 1830 by Robert Stevenson and has an elevation of and 203 steps to ...
* Ballone Castle
Ballone Castle was built in the 16th century. It was unoccupied for a couple of centuries and fell into ruin. In the 1990s it was purchased and restored by an architect. The original castle was built on a Z-plan and is unusual in having one round ...
Gallery
Notes
References
* Carver M.O.H., 1999. ''Surviving in Symbols. A Visit to the Pictish Nation'' (Birlinn). * Carver M.O.H., 2004. ''An Iona of the East: The Early-medieval Monastery at Portmahomack, Tarbat Ness'' in ''Medieval Archaeology'' 48 (2004): 1-30. * Carver, M.O.H., 2006. "A Columban Monastery in Pictland" in ''Current Archaeology'' 205: 20-29. * Campbell George F, 2006. ''The First and Lost Iona'' (attributing the name Portmahomack to St Cormac). * Carver, Martin, 2008. ''Portmahomack: Monastery of the Picts'' (Edinburgh University Press). * Carver, M., Garner-Lahire, J. and Spall, C., 2016. ''Portmahomack on Tarbat Ness: Changing Ideologies in North-east Scotland, Sixth to Sixteenth Century AD'', Historic Scotland / FAS Heritage / University of York.External links
Portmahomack.org
Tarbat Discovery Programme
Portmahomack.net
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Highland (council area) Populated places in Ross and Cromarty Iron Age sites in Scotland